HDB-15 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Video Graphics Array (VGA) connector is a standard connector used for computer video output. Originating with the 1987 IBM PS/2 and its VGA graphics system, the 15-pin connector went on to become ubiquitous on PCs, as well as many monitors, projectors and high-definition television sets.
Other connectors have been used to carry VGA-compatible signals, such as mini-VGA or BNC, but "''VGA connector''" typically refers to this design.
Devices continue to be manufactured with VGA connectors, although newer digital interfaces such as
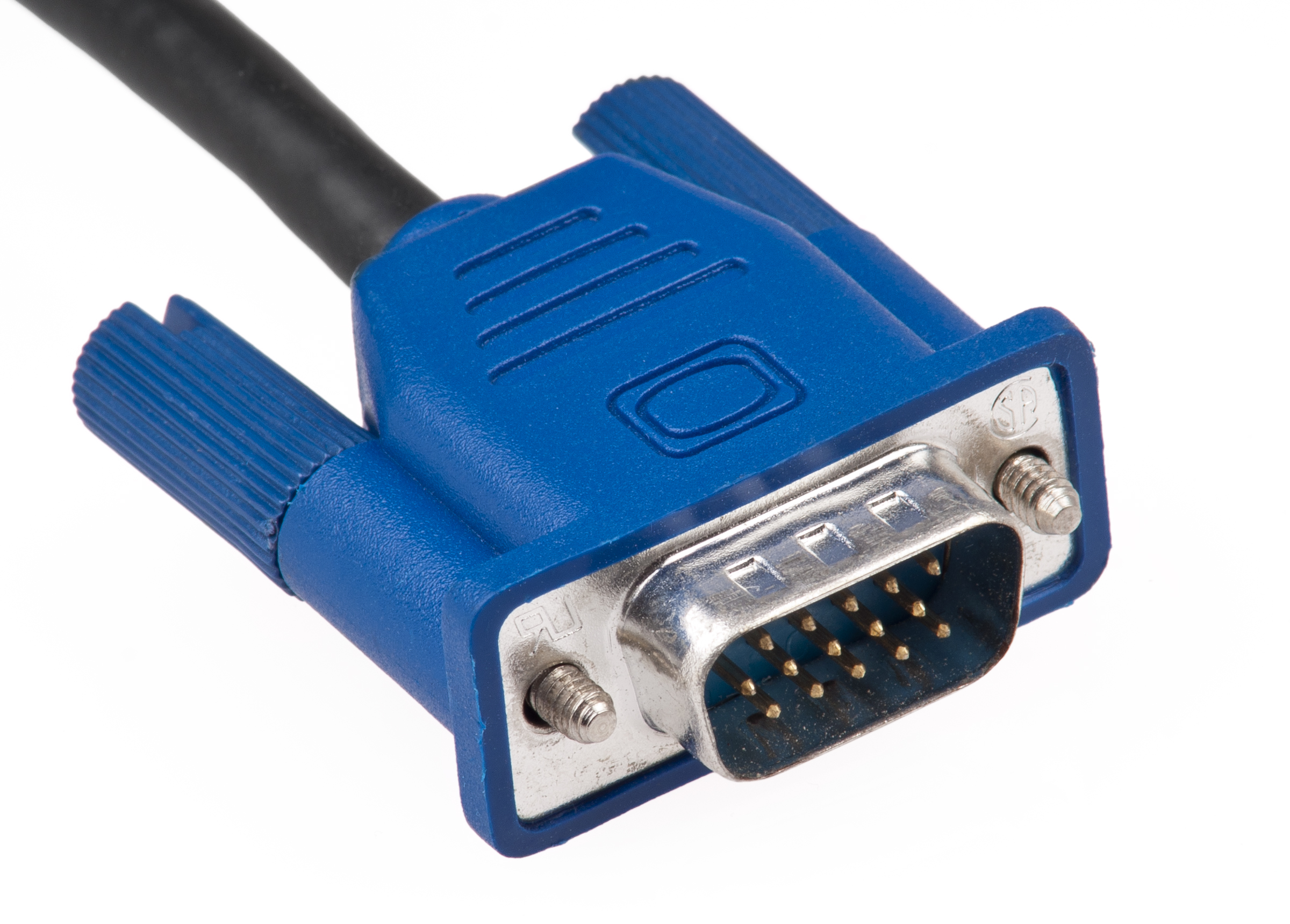 The same VGA cable can be used with a variety of supported VGA resolutions, ranging from 320×400px @70 Hz, or 320×480px @60 Hz (12.6 MHz of signal bandwidth) to 1280×1024px ( SXGA) @85 Hz (160 MHz) and up to 2048×1536px ( QXGA) @85 Hz (388 MHz).
There are no standards defining the quality required for each resolution, but higher-quality cables typically contain coaxial wiring and insulation that make them thicker.
While shorter VGA cables are less likely to introduce significant signal degradation, good-quality cable should not suffer from signal
The same VGA cable can be used with a variety of supported VGA resolutions, ranging from 320×400px @70 Hz, or 320×480px @60 Hz (12.6 MHz of signal bandwidth) to 1280×1024px ( SXGA) @85 Hz (160 MHz) and up to 2048×1536px ( QXGA) @85 Hz (388 MHz).
There are no standards defining the quality required for each resolution, but higher-quality cables typically contain coaxial wiring and insulation that make them thicker.
While shorter VGA cables are less likely to introduce significant signal degradation, good-quality cable should not suffer from signal
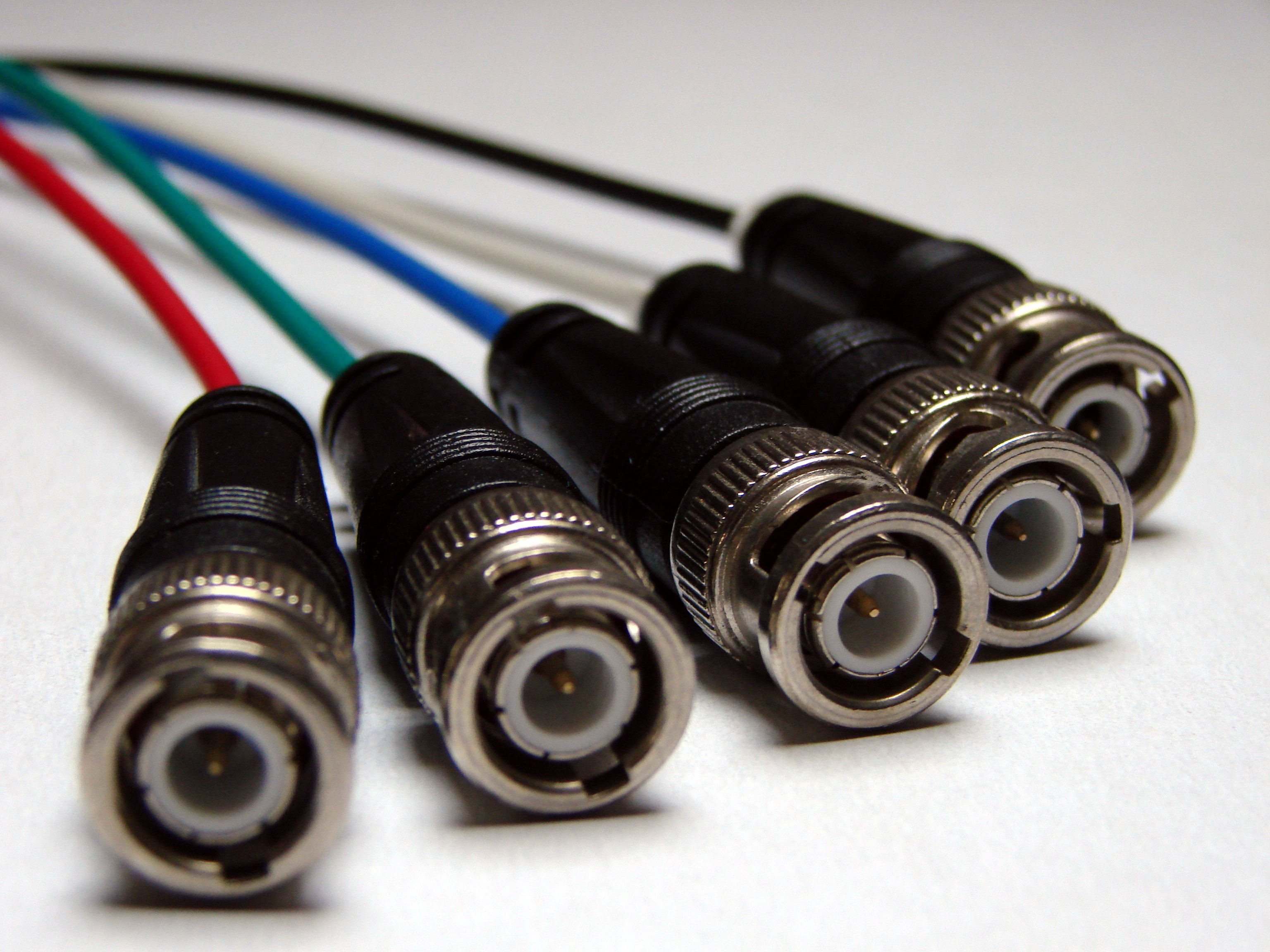 Someone high-end monitors and video cards use multiple BNC connectors instead of a single standard VGA connector, providing a higher quality connection with less crosstalk by utilizing five separate 75ohm
Someone high-end monitors and video cards use multiple BNC connectors instead of a single standard VGA connector, providing a higher quality connection with less crosstalk by utilizing five separate 75ohm  Some laptops and other portable devices use a two-row mini-VGA connector that is much smaller than the three-row DE-15 connector, as well as five separate BNC connectors.
Some laptops and other portable devices use a two-row mini-VGA connector that is much smaller than the three-row DE-15 connector, as well as five separate BNC connectors.
 Various adapters can be purchased to convert VGA to other connector types. One common variety is a
Various adapters can be purchased to convert VGA to other connector types. One common variety is a
DE-9 pinout
DE-15 VGA VESA DDC pinout
{{AVconn Analog video connectors Computer connectors Analog display connectors
DVI
Digital Visual Interface (DVI) is a video display interface developed by the Digital Display Working Group (DDWG). The digital interface is used to connect a video source, such as a video display controller, to a display device, such as a comp ...
, HDMI and DisplayPort are increasingly displacing VGA, and many modern computers and other devices do not include it.
Physical design
The VGA connector is a three-row, 15-pin D-subminiature connector referred to variously as DE-15, HD-15 or DB-15. DE-15 is the most accurate common nomenclature under the D-sub specifications: an "E" size D-sub connector, with 15 pins in three rows.Electrical design
All VGA connectors carryanalog
Analog or analogue may refer to:
Computing and electronics
* Analog signal, in which information is encoded in a continuous variable
** Analog device, an apparatus that operates on analog signals
*** Analog electronics, circuits which use analo ...
RGBHV (red, green, blue, horizontal sync, vertical sync) video signals. Modern connectors also include VESA DDC pins, for identifying attached display devices.
In both its modern and original variants, VGA utilizes multiple scan rates, so attached devices such as monitors are multisync by necessity.
The VGA interface includes no affordances for hot swapping, the ability to connect or disconnect the output device during operation, although in practice this can be done and usually does not cause damage to the hardware or other problems. The VESA DDC specification does however include a standard for hot-swapping.
PS/2 signaling
In the original IBM VGA implementation, refresh rates were limited to two vertical (60 and 70 Hz) and three horizontal frequencies, all of which were communicated to the monitor using combinations of different polarity H and V sync signals. Some pins on the connector were also different: pin 9 was keyed by plugging the female connector hole, and four pins carried the monitor ID. With the implementation of the VESA DDC specification, several of the monitor ID pins were reassigned for use by DDC signaling, and the key pin was replaced with a +5 V DC output per the DDC spec. Devices that comply with the DDC host system standard provide , from 50mA to 1A.PS/55 signaling
The IBM PS/55 Display Adapter redefined pin 9 as "+12V", which signals the monitor to turn on when the system unit is powered on.EDID
In order to advertise display capabilities VESA has introduced a scheme to redefining VGA connector pins 9, 12, and 15 as a serial bus for a Display Data Channel (DDC).Cable quality
 The same VGA cable can be used with a variety of supported VGA resolutions, ranging from 320×400px @70 Hz, or 320×480px @60 Hz (12.6 MHz of signal bandwidth) to 1280×1024px ( SXGA) @85 Hz (160 MHz) and up to 2048×1536px ( QXGA) @85 Hz (388 MHz).
There are no standards defining the quality required for each resolution, but higher-quality cables typically contain coaxial wiring and insulation that make them thicker.
While shorter VGA cables are less likely to introduce significant signal degradation, good-quality cable should not suffer from signal
The same VGA cable can be used with a variety of supported VGA resolutions, ranging from 320×400px @70 Hz, or 320×480px @60 Hz (12.6 MHz of signal bandwidth) to 1280×1024px ( SXGA) @85 Hz (160 MHz) and up to 2048×1536px ( QXGA) @85 Hz (388 MHz).
There are no standards defining the quality required for each resolution, but higher-quality cables typically contain coaxial wiring and insulation that make them thicker.
While shorter VGA cables are less likely to introduce significant signal degradation, good-quality cable should not suffer from signal crosstalk
In electronics, crosstalk is any phenomenon by which a signal transmitted on one circuit or channel of a transmission system creates an undesired effect in another circuit or channel. Crosstalk is usually caused by undesired capacitive, induc ...
(whereby signals in one wire induce unwanted currents in adjacent wires) even at greater lengths.
Ghosting occurs when impedance mismatches cause signals to be reflected. A correctly impedance matched cable (75ohm) should prevent this, however, ghosting with long cables may be caused by equipment with incorrect signal termination or by passive cable splitters rather than the cables themselves.
Alternative connectors
 Someone high-end monitors and video cards use multiple BNC connectors instead of a single standard VGA connector, providing a higher quality connection with less crosstalk by utilizing five separate 75ohm
Someone high-end monitors and video cards use multiple BNC connectors instead of a single standard VGA connector, providing a higher quality connection with less crosstalk by utilizing five separate 75ohm coaxial cable
Coaxial cable, or coax (pronounced ) is a type of electrical cable consisting of an inner conductor surrounded by a concentric conducting shield, with the two separated by a dielectric ( insulating material); many coaxial cables also have a p ...
s.
Within a 15-pin connector, the red, green, and blue signals (pins 1, 2, 3) cannot be shielded from each other, so crosstalk is possible within the 15-pin interconnect. BNC prevents crosstalk by maintaining full coaxial shielding through the circular connectors, but the connectors are very large and bulky. The requirement to press and turn the plug shell to disconnect requires access space around each connector to allow grasping of each BNC plug shell. Supplementary signals such as DDC are typically not supported with BNC.
 Some laptops and other portable devices use a two-row mini-VGA connector that is much smaller than the three-row DE-15 connector, as well as five separate BNC connectors.
Some laptops and other portable devices use a two-row mini-VGA connector that is much smaller than the three-row DE-15 connector, as well as five separate BNC connectors.
Adapters
 Various adapters can be purchased to convert VGA to other connector types. One common variety is a
Various adapters can be purchased to convert VGA to other connector types. One common variety is a DVI
Digital Visual Interface (DVI) is a video display interface developed by the Digital Display Working Group (DDWG). The digital interface is used to connect a video source, such as a video display controller, to a display device, such as a comp ...
to VGA adapter, which is possible because many DVI interfaces also carry VGA-compatible analog signals. Adapting from HDMI to VGA directly is not possible because HDMI includes no analog signal.
For conversions to and from digital formats like HDMI or DVI-D, a scan converter is required. VGA outputs to interfaces with different signaling, more complex converters may be used. Most of them need an external power source to operate and are inherently lossy. However, many modern displays are still made with multiple inputs including VGA, in which case adapters are not necessary.
VGA can also be adapted to SCART in some cases, because the signals are electrically compatible if the correct sync rates are set by the host PC. Many modern graphics adapters can modify their signal in software, including refresh rate, sync length, polarity and number of blank lines. Particular issues include interlace support and the use of the resolution 720×576 in PAL countries
The PAL region is a television publication territory that covers most of Europe and Africa, alongside parts of Asia, South America and Oceania. It is named PAL because of the PAL (Phase Alternating Line) television standard traditionally used in ...
. Under these restrictive conditions, a simple circuit to combine the VGA separate synchronization signals into SCART composite sync may suffice.
Extenders
A VGA extender is an electronic device that increases the signal strength from a VGA port, most often from a computer. They are often used in schools, businesses, and homes when multiple monitors are being run off one VGA port, or if the cable between the monitor and the computer will be excessively long (often pictures appear blurry or have minor artifacts if the cable runs too far without an extender). VGA extenders are sometimes called VGA boosters.See also
* Component video * Extended display identification data (EDID) * List of video connectors * Super Video Graphics Array (SVGA)References
External links
DE-9 pinout
DE-15 VGA VESA DDC pinout
{{AVconn Analog video connectors Computer connectors Analog display connectors