|
VGA Port
The Video Graphics Array (VGA) connector is a standard connector used for computer video output. Originating with the 1987 IBM PS/2 and its VGA graphics system, the 15-pin connector went on to become ubiquitous on PCs, as well as many monitors, projectors and high-definition television sets. Other connectors have been used to carry VGA-compatible signals, such as mini-VGA or BNC, but "''VGA connector''" typically refers to this design. Devices continue to be manufactured with VGA connectors, although newer digital interfaces such as DVI, HDMI and DisplayPort are increasingly displacing VGA, and many modern computers and other devices do not include it. Physical design The VGA connector is a three-row, 15-pin D-subminiature connector referred to variously as DE-15, HD-15 or DB-15. DE-15 is the most accurate common nomenclature under the D-sub specifications: an "E" size D-sub connector, with 15 pins in three rows. Electrical design All VGA connectors carry analog RGBHV (r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SVGA Port
Super VGA (SVGA) is a broad term that covers a wide range of computer display standards that extended IBM's VGA specification. When used as shorthand for a resolution, as VGA and XGA often are, SVGA refers to a resolution of 800×600. History In the late 1980s, after the release of IBM's VGA, third-party manufacturers began making graphics cards based on its specifications with extended capabilities. As these cards grew in popularity they began to be referred to as "Super VGA." This term was not an official standard, but a shorthand for enhanced VGA cards which had become common by 1988. One card that explicitly used the term was Genoa's SuperVGA HiRes. Super VGA cards broke compatibility with the IBM VGA standard, requiring software developers to provide specific display drivers and implementations for each card their software could operate on. Initially, the heavy restrictions this placed on software developers slowed the uptake of Super VGA cards, which motivated VESA to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RGBHV
Component video is an analog video signal that has been split into two or more component channels. In popular use, it refers to a type of component analog video (CAV) information that is transmitted or stored as three separate signals. Component video can be contrasted with ''composite video'' in which all the video information is combined into a single signal that is used in analog television. Like composite, component-video cables do not carry audio and are often paired with audio cables. When used without any other qualifications, the term ''component video'' usually refers to analog component video with sync on luma (Y) found on analog high-definition televisions and associated equipment from the 1990s through the 2000s when they were largely replaced with HDMI and other all-digital standards. Component video cables and their RCA jack connectors on equipment are normally color-coded red, green and blue, although the signal is not in RGB. YPbPr component video can be loss ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
QXGA
The graphics display resolution is the width and height dimension of an electronic visual display device, measured in pixels. This information is used for electronic devices such as a computer monitor. Certain combinations of width and height are standardized (e.g. by VESA) and typically given a name and an initialism that is descriptive of its dimensions. A graphics display resolution can be used in tandem with the size of the graphics display to calculate pixel density. An increase in the pixel density often correlates with a decrease in the size of individual pixels on a display. Overview by vertical resolution and aspect ratio Aspect ratio The favored aspect ratio of mass-market display industry products has changed gradually from 4:3, then to 16:10, then to 16:9, and is now changing to 18:9 for smartphones. The 4:3 aspect ratio generally reflects older products, especially the era of the cathode ray tube (CRT). The 16:10 aspect ratio had its largest use in the 19 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SXGA
The graphics display resolution is the width and height dimension of an electronic visual display device, measured in pixels. This information is used for electronic devices such as a computer monitor. Certain combinations of width and height are standardized (e.g. by VESA) and typically given a name and an initialism that is descriptive of its dimensions. A graphics display resolution can be used in tandem with the size of the graphics display to calculate pixel density. An increase in the pixel density often correlates with a decrease in the size of individual pixels on a display. Overview by vertical resolution and aspect ratio Aspect ratio The favored aspect ratio of mass-market display industry products has changed gradually from 4:3, then to 16:10, then to 16:9, and is now changing to 18:9 for smartphones. The 4:3 aspect ratio generally reflects older products, especially the era of the cathode ray tube (CRT). The 16:10 aspect ratio had its largest use in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Signal Bandwidth
Bandwidth is the difference between the upper and lower frequencies in a continuous band of frequencies. It is typically measured in hertz, and depending on context, may specifically refer to ''passband bandwidth'' or ''baseband bandwidth''. Passband bandwidth is the difference between the upper and lower cutoff frequencies of, for example, a band-pass filter, a communication channel, or a signal spectrum. Baseband bandwidth applies to a low-pass filter or baseband signal; the bandwidth is equal to its upper cutoff frequency. Bandwidth in hertz is a central concept in many fields, including electronics, information theory, digital communications, radio communications, signal processing, and spectroscopy and is one of the determinants of the capacity of a given communication channel. A key characteristic of bandwidth is that any band of a given width can carry the same amount of information, regardless of where that band is located in the frequency spectrum. For example, a 3 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
VESA
VESA (), formally known as Video Electronics Standards Association, is an American technical standards organization for computer display standards. The organization was incorporated in California in July 1989To retrieve the information, search for Entity Number C1645094. and has its office in San Jose. It claims a membership of over 300 companies. In November 1988, NEC Home Electronics announced its creation of the association to develop and promote a Super VGA computer display standard as a successor to IBM's proprietary Video Graphics Array (VGA) display standard. Super VGA enabled graphics display resolutions up to 800×600 pixels, compared to VGA's maximum resolution of 640×480 pixels—a 56% increase. The organization has since issued several additional standards related to computer video displays. Widely used VESA standards include DisplayHDR, DisplayPort, and Flat Display Mounting Interface. Standards * Feature connector (VFC), obsolete connector that was ofte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IBM Personal System/55
The or PS/55 is a personal computer series released from IBM Japan in 1987. The PS/55 is the successor to IBM 5550 (Multistation 5550), but its architecture is based upon IBM PS/2, perhaps it is also an IBM clone. The first line-up of the series consisted of rebranded 5550 models except the Model 5570-S which was based on the PS/2 Model 80 (IBM 8580). Unlike the PS/2, most PS/2-based models have a 32-bit ( 80386 or 80486) CPU and Micro Channel (MCA) bus for the high-end business computing market. IBM Japan was hesitating to sell personal computers for consumers because the IBM JX failed. The AT bus model was released for home users in 1991. Features Display Adapter The MCA video card called ''Display Adapter'' has a Japanese font containing nearly 7,000 glyphs stored in its ROM, which enables PS/2-based computers to display Japanese text without loading the font into memory. Similar to the IBM 5550, the display resolution in character mode is 1040×725 pixels (12×24 a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hot Swapping
Hot swapping is the replacement or addition of components to a computer system without stopping, shutting down, or rebooting the system; hot plugging describes the addition of components only. Components which have such functionality are said to be ''hot-swappable'' or ''hot-pluggable''; likewise, components which do not are ''cold-swappable'' or ''cold-pluggable''. Most desktop computer hardware, such as CPUs and memory, are only cold-pluggable. However, it is common for mid to high-end servers and mainframes to feature hot-swappable capability for hardware components, such as CPU, memory, PCIe, SATA and SAS drives. An example of hot swapping is the express ability to pull a Universal Serial Bus (USB) peripheral device, such as a thumb drive, external hard disk drive (HDD), mouse, keyboard, or printer out of a computer's USB slot or peripheral hub without ejecting it first. Most smartphones and tablets with tray-loading holders can interchange SIM cards without poweri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multisync Monitor
A multiple-sync (multisync) monitor, also known as a multiscan or multimode monitor, is a raster-scan analog video monitor that can properly synchronise with multiple horizontal and vertical scan rates. In contrast, fixed frequency monitors can only synchronise with a specific set of scan rates. They are generally used for computer displays, but sometimes for television, and the terminology is mostly applied to CRT displays although the concept applies to other technologies. Multiscan computer monitors appeared during the mid 1980s, offering flexibility as computer video hardware shifted from producing a single fixed scan rate to multiple possible scan rates. "MultiSync" specifically was a trademark of one of NEC's first multiple-sync monitors. Computers History Early home computers output video to ordinary televisions or composite monitors, utilizing television display standards such as NTSC, PAL or SECAM. These display standards had fixed scan rates, and only used the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
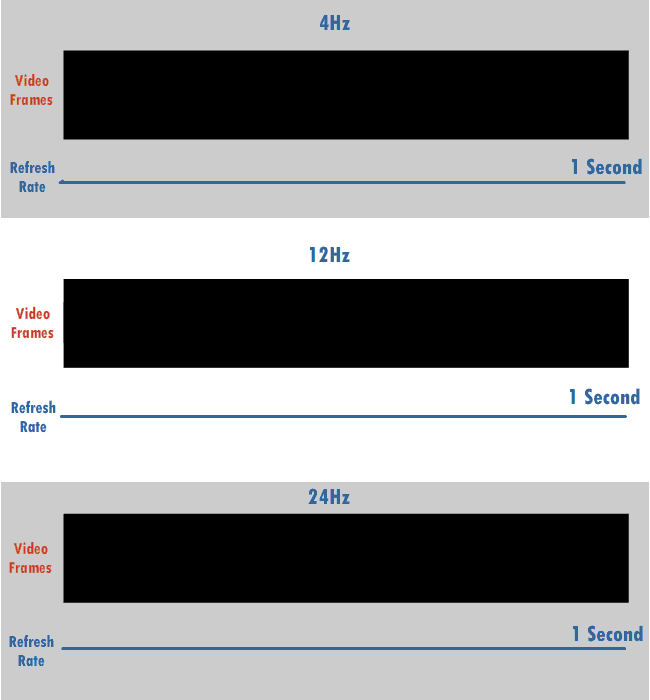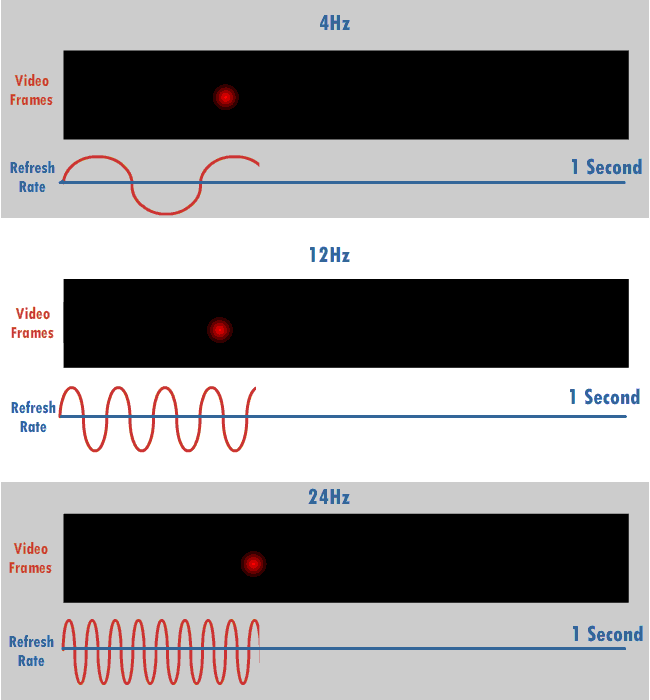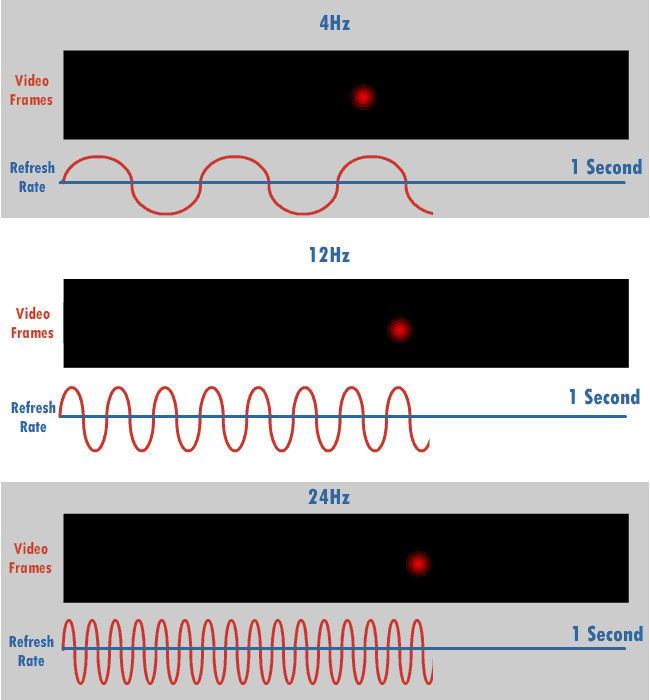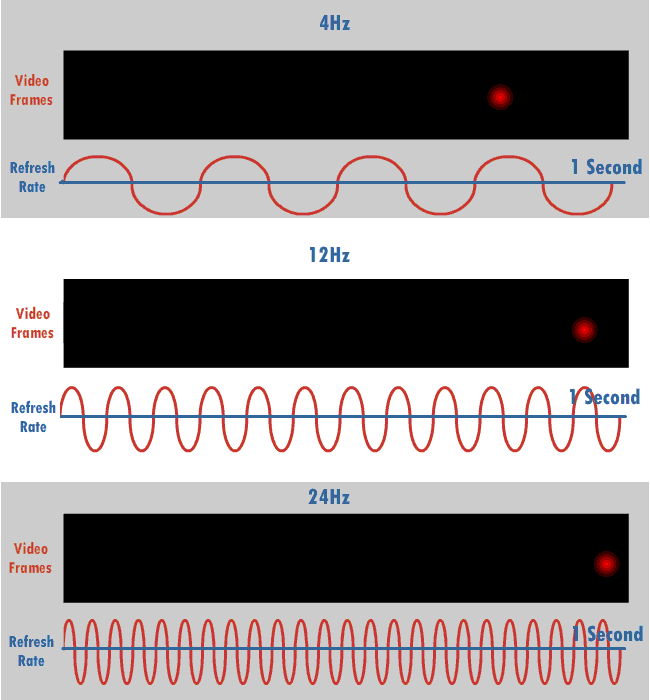
Vertical Scan Rate
The refresh rate (or "vertical refresh rate", "vertical scan rate", terminology originating with the cathode ray tubes) is the number of times per second that a raster-based display device displays a new image. This is independent from frame rate, which describes how many images are stored or generated every second by the device driving the display. On cathode ray tube (CRT) displays, higher refresh rates produce less flickering, thereby reducing eye strain. In other technologies such as liquid-crystal displays, the refresh rate affects only how often the image can potentially be updated. Non-raster displays may not have a characteristic refresh rate. Vector displays, for instance, do not trace the entire screen, only the actual lines comprising the displayed image, so refresh speed may differ by the size and complexity of the image data. For computer programs or telemetry, the term is sometimes applied to how frequently a datum is updated with a new external value from anothe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |