Greek words for love on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Ancient Greek philosophy differentiates main conceptual forms and distinct words for the Modern English word
Ancient Greek philosophy differentiates main conceptual forms and distinct words for the Modern English word
 Ancient Greek philosophy differentiates main conceptual forms and distinct words for the Modern English word
Ancient Greek philosophy differentiates main conceptual forms and distinct words for the Modern English word love
Love encompasses a range of strong and positive emotional and mental states, from the most sublime virtue or good habit, the deepest interpersonal affection, to the simplest pleasure. An example of this range of meanings is that the love o ...
: ''agápē'', ''érōs'', ''philía'', ''philautía'', ''storgē'', and ''xenía''.
List of concepts
Though there are more Greek words for love, variants and possibly subcategories, a general summary considering theseAncient Greek
Ancient Greek includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Dark Ages (), the Archaic p ...
concepts is as follows:
* '' Agápe'' ( grc, ἀγάπη, agápē, label=none) means "love: esp. brotherly love, charity; the love of God for person and of person for God". ''Agape'' is used in ancient texts to denote feelings for one's children and the feelings for a spouse, and it was also used to refer to a love feast
An agape feast or lovefeast (also spelled love feast or love-feast, sometimes capitalized) is a communal meal shared among Christians. The name comes from ''agape'', a Greek term for 'love' in its broadest sense.
The lovefeast custom origina ...
. Agape is used by Christians to express the unconditional love of God for His children. This type of love was further explained by Thomas Aquinas
Thomas Aquinas, OP (; it, Tommaso d'Aquino, lit=Thomas of Aquino; 1225 – 7 March 1274) was an Italian Dominican friar and priest who was an influential philosopher, theologian and jurist in the tradition of scholasticism; he is known wit ...
as "to will the good of another".
* '' Éros'' ( grc, ἔρως, érōs, label=none) means "love, mostly of the sexual passion". The Modern Greek word "''erotas''" means "intimate love". Plato
Plato ( ; grc-gre, Πλάτων ; 428/427 or 424/423 – 348/347 BC) was a Greek philosopher born in Athens during the Classical period in Ancient Greece. He founded the Platonist school of thought and the Academy, the first institution ...
refined his own definition: Although ''eros'' is initially felt for a person, with contemplation it becomes an appreciation of the beauty within that person, or even becomes appreciation of beauty itself. Plato does not talk of physical attraction as a necessary part of love, hence the use of the word platonic
Plato's influence on Western culture was so profound that several different concepts are linked by being called Platonic or Platonist, for accepting some assumptions of Platonism, but which do not imply acceptance of that philosophy as a whole. It ...
to mean "without physical attraction". In the '' Symposium'', an ancient work on the subject, Plato has Socrates
Socrates (; ; –399 BC) was a Greek philosopher from Athens who is credited as the founder of Western philosophy and among the first moral philosophers of the ethical tradition of thought. An enigmatic figure, Socrates authored no te ...
argue that ''eros'' helps the soul
In many religious and philosophical traditions, there is a belief that a soul is "the immaterial aspect or essence of a human being".
Etymology
The Modern English noun '' soul'' is derived from Old English ''sāwol, sāwel''. The earliest atte ...
recall knowledge of beauty and contributes to an understanding of spiritual truth, the ideal form of youthful beauty that leads us humans to feel erotic desire – thus suggesting that even that sensually based love aspires to the non-corporeal, spiritual plane of existence; that is, finding its truth, just like finding any truth, leads to transcendence. Lovers and philosophers are all inspired to seek truth through the means of ''eros''.
* '' Philia'' ( grc, φιλία, philía, label=none) means "affectionate regard, friendship", usually "between equals". It is a dispassionate virtuous love, a concept developed by Aristotle
Aristotle (; grc-gre, Ἀριστοτέλης ''Aristotélēs'', ; 384–322 BC) was a Greek philosopher and polymath during the Classical period in Ancient Greece. Taught by Plato, he was the founder of the Peripatetic school of ph ...
. In his best-known work on ethics, '' Nicomachean Ethics'', ''philia'' is expressed variously as loyalty to friends (specifically, "brotherly love"), family, and community, and requires virtue, equality, and familiarity. Furthermore, in the same text ''philos'' is also the root of ''philautia
Self-love, defined as "love of self" or "regard for one's own happiness or advantage", has been conceptualized both as a basic human necessity and as a moral flaw, akin to vanity and selfishness, synonymous with amour-propre, conceitedness, eg ...
'' denoting self-love and arising from it, a general type of love, used for love between family, between friends, a desire or enjoyment of an activity, as well as between lovers.
* '' Storge'' ( grc, στοργή, storgē, label=none) means "love, affection" and "especially of parents and children". It is the common or natural empathy, like that felt by parents for offspring. Rarely used in ancient works, and then almost exclusively as a descriptor of relationships within the family. It is also known to express mere acceptance or putting up with situations, as in "loving" the tyrant. This is also used when referencing the love for one's country or a favorite sports team.
* ''Philautia
Self-love, defined as "love of self" or "regard for one's own happiness or advantage", has been conceptualized both as a basic human necessity and as a moral flaw, akin to vanity and selfishness, synonymous with amour-propre, conceitedness, eg ...
'' ( grc, φιλαυτία, philautía, label=none) means "self-love". To love oneself or "regard for one's own happiness or advantage" has been conceptualized both as a basic human necessity and as a moral flaw, akin to vanity
Vanity is the excessive belief in one's own abilities or attractiveness to others. Prior to the 14th century it did not have such narcissistic undertones, and merely meant ''futility''. The related term vainglory is now often seen as an archaic ...
and selfishness
Selfishness is being concerned excessively or exclusively, for oneself or one's own advantage, pleasure, or welfare, regardless of others.
Selfishness is the opposite of altruism or selflessness; and has also been contrasted (as by C. S. Lewis) w ...
, synonymous with ''amour-propre
''Amour-propre'' (; ) is a French term that can be variously translated as "self-love", "self-esteem", or "vanity". In philosophy, it is a term used by Jean-Jacques Rousseau, who contrasts it with another kind of self-love which he calls ''amour ...
'' or egotism
Egotism is defined as the drive to maintain and enhance favorable views of oneself and generally features an inflated opinion of one's personal features and importance distinguished by a person's amplified vision of one's self and self-importanc ...
. The Greeks further divided this love into positive and negative: one, the unhealthy version, is the self-obsessed love, and the other is the concept of self-compassion.
* '' Xenia'' ( grc, ξενία, xenía, label=none) is an ancient Greek
Ancient Greek includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Dark Ages (), the Archaic p ...
concept of hospitality
Hospitality is the relationship between a guest and a host, wherein the host receives the guest with some amount of goodwill, including the reception and entertainment of guests, visitors, or strangers. Louis, chevalier de Jaucourt describes ...
. It is sometimes translated as "guest-friendship" or "ritualized friendship". It is an institutionalized relationship rooted in generosity, gift exchange, and reciprocity. Historically, hospitality towards foreigners and guests (Hellenes
The Greeks or Hellenes (; el, Έλληνες, ''Éllines'' ) are an ethnic group and nation indigenous to the Eastern Mediterranean and the Black Sea regions, namely Greece, Cyprus, Albania, Italy, Turkey, Egypt, and, to a lesser extent, other ...
not of your polis
''Polis'' (, ; grc-gre, πόλις, ), plural ''poleis'' (, , ), literally means "city" in Greek. In Ancient Greece, it originally referred to an administrative and religious city center, as distinct from the rest of the city. Later, it also ...
) was understood as a moral obligation. Hospitality towards foreign Hellenes honored Zeus ''Xenios'' (and Athene ''Xenia'') patrons of foreigners.
See also
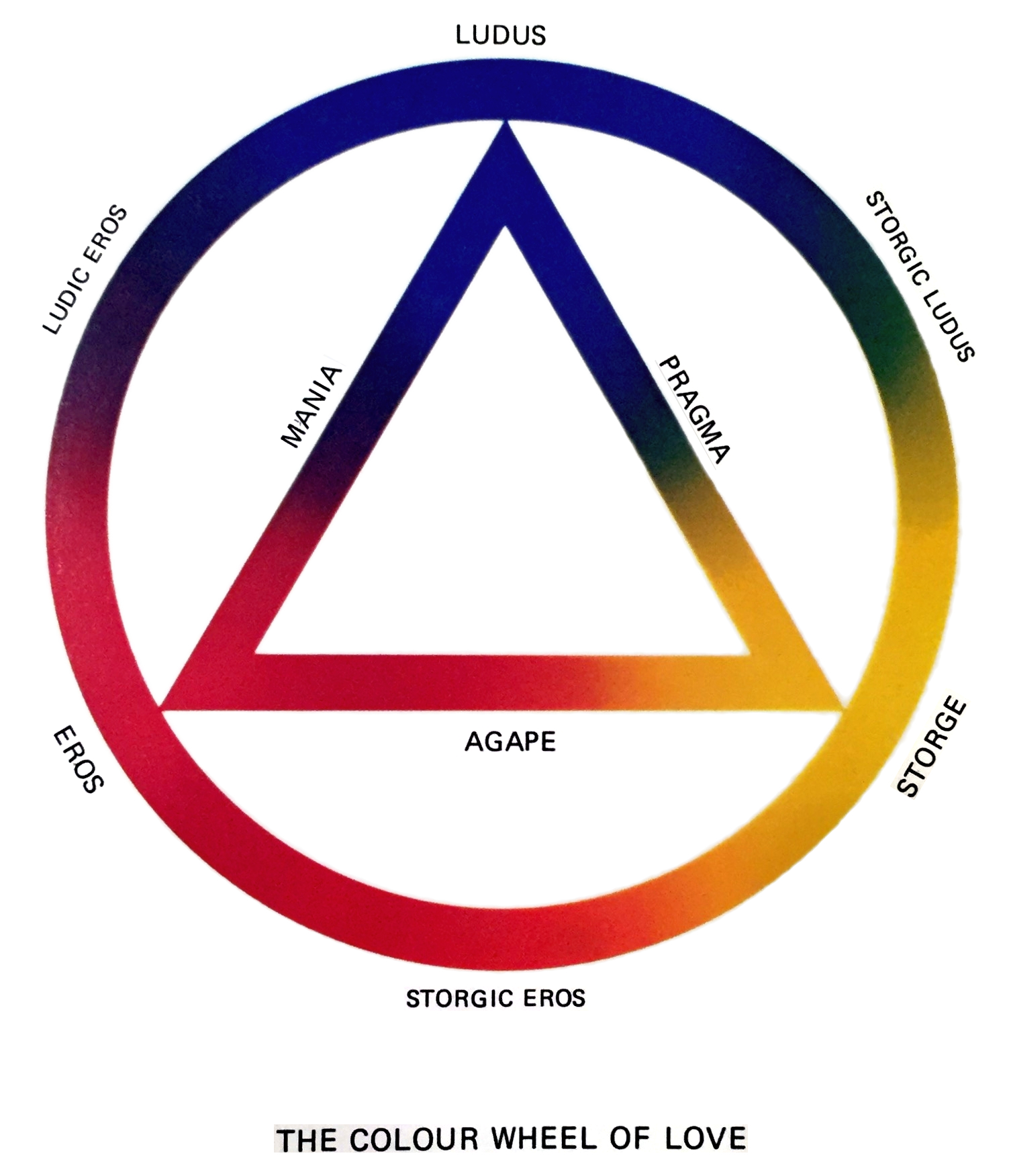
*Color wheel theory of love
The colour wheel theory of love is an idea created by the Canadian psychologist John Alan Lee that describes six love styles, using several Latin and Greek words for love. First introduced in his book ''Colours of Love: An Exploration of the ...
*Diotima of Mantinea
Diotima of Mantinea (; el, Διοτίμα; la, Diotīma) is the name or pseudonym of an ancient Greek character in Plato's dialogue ''Symposium'', possibly an actual historical figure, indicated as having lived circa 440 B.C. Her ideas and doct ...
* Diotima's Ladder of Love
*''The Four Loves
''The Four Loves'' is a 1960 book by C. S. Lewis which explores the nature of love from a Christian and philosophical perspective through thought experiments. The book was based on a set of radio talks from 1958 which had been criticised in the ...
'' by C. S. Lewis
Clive Staples Lewis (29 November 1898 – 22 November 1963) was a British writer and Anglican lay theologian. He held academic positions in English literature at both Oxford University (Magdalen College, 1925–1954) and Cambridge Univers ...
* Greek love
*Intellectual virtue
Intellectual virtues are qualities of mind and character that promote intellectual flourishing, critical thinking, and the pursuit of truth. They include: intellectual responsibility, perseverance, open-mindedness, empathy, integrity, intellect ...
– Greek words for knowledge
* Love
Love encompasses a range of strong and positive emotional and mental states, from the most sublime virtue or good habit, the deepest interpersonal affection, to the simplest pleasure. An example of this range of meanings is that the love o ...
*Restoration of Peter
The Restoration of Peter (also known as the Re-commissioning of Peter) is an incident described in John 21 of the New Testament in which Jesus Resurrection appearances of Jesus, appeared to his disciples after Resurrection of Jesus, his resurrectio ...
*Sapphic love
Terms used to describe homosexuality have gone through many changes since the emergence of the first terms in the mid-19th century. In English, some terms in widespread use have been sodomite, Achillean, Sapphic, Uranian, homophile, lesbian, ...
References
Sources
* * {{DEFAULTSORT:Greek Words For LoveLove
Love encompasses a range of strong and positive emotional and mental states, from the most sublime virtue or good habit, the deepest interpersonal affection, to the simplest pleasure. An example of this range of meanings is that the love o ...
Love
Love
Love encompasses a range of strong and positive emotional and mental states, from the most sublime virtue or good habit, the deepest interpersonal affection, to the simplest pleasure. An example of this range of meanings is that the love o ...