Ghurab on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Ghurab or gurab is a type of merchant and warship from the Nusantara archipelago. The ship was a result of
Ghurab or gurab is a type of merchant and warship from the Nusantara archipelago. The ship was a result of
 The name of this ship includes gorap, gorab, gurab, ghurap, gurap, and benawa gurab. The name comes from the Arab word "''ghurāb''" or "''ghorāb''", meaning raven or crow. The word also means "vessel" or "galley" in Arabic or Persian. The word ''benawa'' or ''banawa'' comes from the kawi Javanese language, which means boat or ship. In the old Javanese language and
The name of this ship includes gorap, gorab, gurab, ghurap, gurap, and benawa gurab. The name comes from the Arab word "''ghurāb''" or "''ghorāb''", meaning raven or crow. The word also means "vessel" or "galley" in Arabic or Persian. The word ''benawa'' or ''banawa'' comes from the kawi Javanese language, which means boat or ship. In the old Javanese language and
 Ghurab is a medium to large-sized Malay trading vessel. They can be converted into a warship by adding swivel guns (
Ghurab is a medium to large-sized Malay trading vessel. They can be converted into a warship by adding swivel guns (
 The ''Hikayat Aceh'' states that the Acehnese sultanate had 120 large ghurab in the 1570s. The state ghurab (''ghorab istana'') of Aceh, Daya, and Pedir was said to carry 10 '' meriam'', 50 '' lela'', and 120 '' cecorong'' (excluding the ''
The ''Hikayat Aceh'' states that the Acehnese sultanate had 120 large ghurab in the 1570s. The state ghurab (''ghorab istana'') of Aceh, Daya, and Pedir was said to carry 10 '' meriam'', 50 '' lela'', and 120 '' cecorong'' (excluding the ''
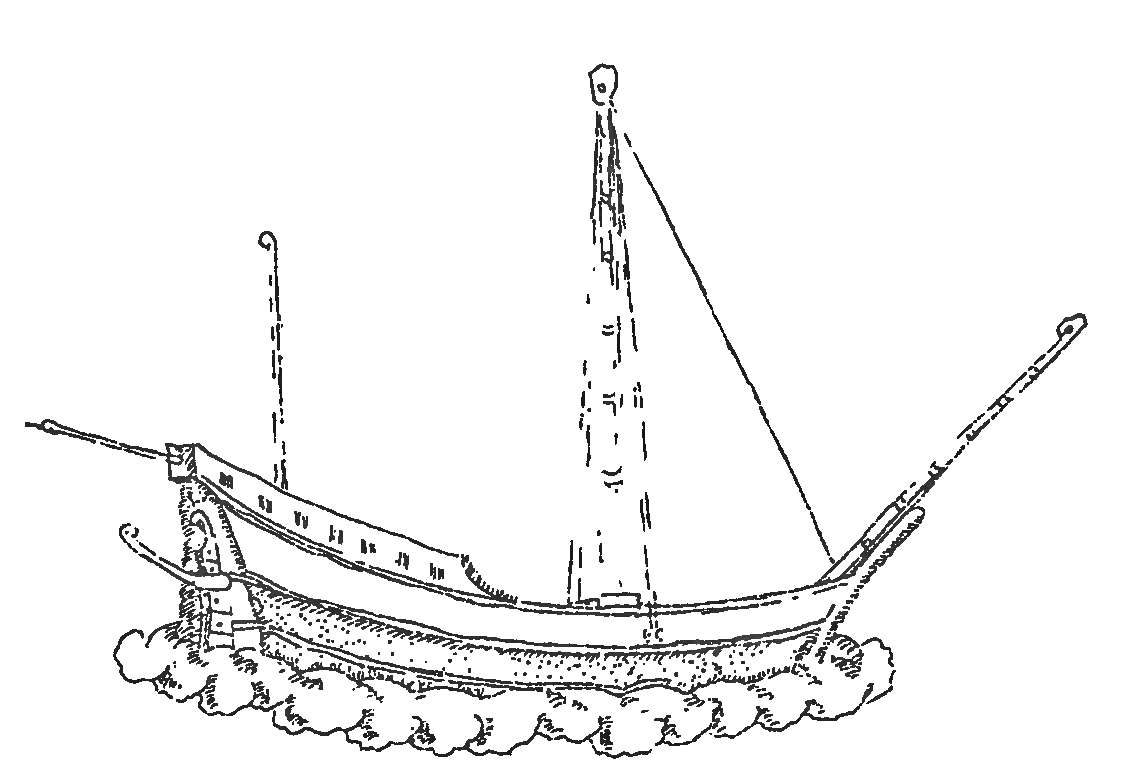 There are several types of ships historically also called ghurab or similar names. The description and construction of each vessel, however, aren't necessarily the same.
There are several types of ships historically also called ghurab or similar names. The description and construction of each vessel, however, aren't necessarily the same.
 Ghurab or gurab is a type of merchant and warship from the Nusantara archipelago. The ship was a result of
Ghurab or gurab is a type of merchant and warship from the Nusantara archipelago. The ship was a result of Mediterranean
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa, and on ...
influences in the region, particularly introduced by the Arabs
The Arabs (singular: Arab; singular ar, عَرَبِيٌّ, DIN 31635: , , plural ar, عَرَب, DIN 31635: , Arabic pronunciation: ), also known as the Arab people, are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in Western Asia, ...
, Persians
The Persians are an Iranian ethnic group who comprise over half of the population of Iran. They share a common cultural system and are native speakers of the Persian language as well as of the languages that are closely related to Persian. ...
, and Ottomans
The Ottoman Turks ( tr, Osmanlı Türkleri), were the Turkic founding and sociopolitically the most dominant ethnic group of the Ottoman Empire ( 1299/1302–1922).
Reliable information about the early history of Ottoman Turks remains scarce, ...
. For their war fleet, the Malays prefer to use shallow draught, oared longships similar to the galley, such as lancaran
''Colotomy'' is an Indonesian description of the rhythmic and metric patterns of gamelan music. It refers to the use of specific instruments to mark off nested time intervals, or the process of dividing rhythmic time into such nested cycles. I ...
, ghurab, and ghali. This is very different from the Javanese who prefer long-range, deep-draught round ships such as jong Jong may refer to:
Surname
*Chung (Korean surname), spelled Jong in North Korea
*Zhong (surname), spelled Jong in the Gwoyeu Romatzyh system
*Common Dutch surname "de Jong"; see
** De Jong
** De Jonge
** De Jongh
*Erica Jong (born 1942), American ...
and malangbang
Malangbang or melambang is a type of medieval sailing ship from Indonesia. It is mentioned mainly in the History of Banjar. The name "malangbang" is considered to originate from the Old Javanese language, ''malabong'' (''malaboṅ'') which refer ...
. The reason for this difference is that the Malays operated their ships in riverine water, sheltered straits zone, and archipelagic environment, while the Javanese are often active in the open and high sea.
Etymology
 The name of this ship includes gorap, gorab, gurab, ghurap, gurap, and benawa gurab. The name comes from the Arab word "''ghurāb''" or "''ghorāb''", meaning raven or crow. The word also means "vessel" or "galley" in Arabic or Persian. The word ''benawa'' or ''banawa'' comes from the kawi Javanese language, which means boat or ship. In the old Javanese language and
The name of this ship includes gorap, gorab, gurab, ghurap, gurap, and benawa gurab. The name comes from the Arab word "''ghurāb''" or "''ghorāb''", meaning raven or crow. The word also means "vessel" or "galley" in Arabic or Persian. The word ''benawa'' or ''banawa'' comes from the kawi Javanese language, which means boat or ship. In the old Javanese language and Malay
Malay may refer to:
Languages
* Malay language or Bahasa Melayu, a major Austronesian language spoken in Indonesia, Malaysia, Brunei and Singapore
** History of the Malay language, the Malay language from the 4th to the 14th century
** Indonesi ...
language the meaning is more or less the same. In different languages, the word can refer to different types of ships and boats, depending on the context of the sentence.
Description
 Ghurab is a medium to large-sized Malay trading vessel. They can be converted into a warship by adding swivel guns (
Ghurab is a medium to large-sized Malay trading vessel. They can be converted into a warship by adding swivel guns (rentaka
The ''Lantaka'' (Baybayin: pre virama: ''ᜎᜆᜃ'': post virama: ''ᜎᜈ᜔ᜆᜃ'') also known as ''rentaka'' (In Malay) was a type of bronze portable cannon or swivel gun, sometimes mounted on merchant vessels and warships in Maritime So ...
). Early ghurab was galley-like, it has oars in addition to sails.Manguin, Pierre-Yves (2012). Lancaran, Ghurab and Ghali: Mediterranean impact on war vessels in Early Modern Southeast Asia. In G. Wade & L. Tana (Eds.), ''Anthony Reid and the Study of the Southeast Asian Past'' (pp. 146–182). Singapore: ISEAS Publishing.
The larger ghurab had 2 guns pointing forward ( bow-chaser) and 15 on each side, with a total of 32 guns. The smaller ones carried 2 forward and 10 on each side (22 guns). The ghurab has a projecting stern. H. Warington Smyth, in 1902 described a large 2-masted trading ''gurap'' built of giam wood. The dimension is as follows: 300 ft (91.4 m) long, 30 ft (9.1 m) wide, 20 ft (6.1 m) depth, and 11 ft (3.4 m) freeboard. The capacity was 100 ''koyan'' (241.9 metric tons), with a 100 ft (30.5 m) mainmast, crewed by 30 men. The vessel is using fore-and-aft
A fore-and-aft rig is a sailing vessel rigged mainly with sails set along the line of the keel, rather than perpendicular to it as on a square rigged vessel.
Description
Fore-and-aft rigged sails include staysails, Bermuda rigged sails, ga ...
sail made with cloth, with yard
The yard (symbol: yd) is an English unit of length in both the British imperial and US customary systems of measurement equalling 3 feet or 36 inches. Since 1959 it has been by international agreement standardized as exactly 0.914 ...
and gaff-topsail.
Role
Ghurab is used as a trading ship as well as a warship. One of the earliest accounts of ghurab has a background from the 15th century, being mentioned inHikayat Hang Tuah
''Hikayat Hang Tuah'' ( Jawi: حکاية هڠ تواه) is a Malay work of literature that tells the tale of the legendary Malay fiction warrior, Hang Tuah and his four warrior friends - Hang Jebat, Hang Kasturi, Hang Lekir and Hang Lekiu - w ...
, which was composed no earlier than the 17th century. Two pencalang
Pencalang is a traditional merchant ship from Nusantara. Historically it was called as pantchiallang or pantjalang. It was originally built by Malay people from the area of Riau and the Malay Peninsula, but has been copied by Javanese shipwrigh ...
and two ghurab were used by Majapahit
Majapahit ( jv, ꦩꦗꦥꦲꦶꦠ꧀; ), also known as Wilwatikta ( jv, ꦮꦶꦭ꧀ꦮꦠꦶꦏ꧀ꦠ; ), was a Javanese people, Javanese Hinduism, Hindu-Buddhism, Buddhist thalassocracy, thalassocratic empire in Southeast Asia that was ba ...
to send a letter and gifts to improve the relationship with Malacca
Malacca ( ms, Melaka) is a state in Malaysia located in the southern region of the Malay Peninsula, next to the Strait of Malacca. Its capital is Malacca City, dubbed the Historic City, which has been listed as a UNESCO World Heritage Site si ...
. The ghurabs were said to be "in the style of the Arabs' (ship)".
Until the early 16th century, the main merchant and warship of the Javanese was the jong, but since the mid-16th century the maritime forces of the archipelago began to use new types of agile naval vessels that could be equipped with larger cannons: In various attacks on Portuguese Malacca after the defeat of Pati Unus, they no longer used jong but used lancaran, ghurab and ghali.Manguin, Pierre-Yves (1993). 'The Vanishing Jong: Insular Southeast Asian Fleets in Trade and War (Fifteenth to Seventeenth Centuries)', in Anthony Reid (ed.), ''Southeast Asia in the Early Modern Era'' (Ithaca: Cornell University Press), 197–213.
In 1515, Bintan
Bintan Regency (formerly Riau Islands Regency; id, Kabupaten Kepulauan Riau) is an administrative area in the Riau Islands Province of Indonesia. Bintan Regency includes all of Bintan Island (except for the city of Tanjung Pinang which is sepa ...
attacked Kampar and Portuguese Malacca
Portuguese control of Malacca, a city on the Malay Peninsula, refers to the 130 year period (1511–1641) when it was a possession of the Portuguese East Indies. It was conquered from the Malacca Sultanate as part of Portuguese attempts to ...
with 24 lancaran and 6 large ones called gurab.
 The ''Hikayat Aceh'' states that the Acehnese sultanate had 120 large ghurab in the 1570s. The state ghurab (''ghorab istana'') of Aceh, Daya, and Pedir was said to carry 10 '' meriam'', 50 '' lela'', and 120 '' cecorong'' (excluding the ''
The ''Hikayat Aceh'' states that the Acehnese sultanate had 120 large ghurab in the 1570s. The state ghurab (''ghorab istana'') of Aceh, Daya, and Pedir was said to carry 10 '' meriam'', 50 '' lela'', and 120 '' cecorong'' (excluding the ''istinggar
Istinggar is a type of matchlock firearm built by the various ethnic groups of the Maritime Southeast Asia. The firearm is a result of Portuguese influence on local weaponry after the capture of Malacca (1511). Before this type of gun, in the archi ...
''). Smaller ones carried 5 ''meriam'', 20 ''lela'', and 50 ''cecorong''.
In 1624, the war fleet of the Mataram Sultanate
The Sultanate of Mataram () was the last major independent Javanese kingdom on the island of Java before it was colonised by the Dutch. It was the dominant political force radiating from the interior of Central Java from the late 16th centu ...
numbered 2000 vessels consisting of gurab and small perahu
Proas are various types of multi-hull outrigger sailboats of the Austronesian peoples. The terms were used for native Austronesian ships in European records during the Colonial era indiscriminately, and thus can confusingly refer to the do ...
. On 22 August 1628, 59 goraps of Sultan Agung
Sultan Anyakrakusuma is known as Sultan Agung ( jv, ꦱꦸꦭ꧀ꦠꦤ꧀ꦲꦒꦸꦁꦲꦢꦶꦥꦿꦧꦸꦲꦚꦏꦿꦏꦸꦱꦸꦩ, Sultan Agung Adi Prabu Anyakrakusuma) was the third Sultan of Mataram in Central Java ruling from 1613 to 1645. ...
's navy appeared at Batavia, unloading provisions for the Siege of Batavia
The siege of Batavia was a military campaign led by Sultan Agung of Mataram to capture the Dutch port-settlement of Batavia in Java. The first attempt was launched in 1628, and the second in 1629; both were unsuccessful.
Prelude
In the Indone ...
.
Ships with similar name
 There are several types of ships historically also called ghurab or similar names. The description and construction of each vessel, however, aren't necessarily the same.
There are several types of ships historically also called ghurab or similar names. The description and construction of each vessel, however, aren't necessarily the same.
Mediterranean
According to Al-Maqrizi (1441 A.D.), ghurābs of the mediterranean sea were huge war galleys. According to Ibn Mammati (1209 A.D.), these ships had 140 oars. Al-Maqrizi refers to both Muslim and Christian galleys as ghurāb. Reinaud said that ghorāb was the name given by Moors to true galleys. Ubaldo (1181) tells about ghurāb as vessels sailing to and fromTripoli
Tripoli or Tripolis may refer to:
Cities and other geographic units Greece
*Tripoli, Greece, the capital of Arcadia, Greece
* Tripolis (region of Arcadia), a district in ancient Arcadia, Greece
* Tripolis (Larisaia), an ancient Greek city in ...
.
Genizah letters mention cargo ghurābs that sailed from the Maghrib
The Maghrib Prayer ( ar, صلاة المغرب ', "sunset prayer") is one of the five mandatory salah (Islamic prayer). As an Islamic day starts at sunset, the Maghrib prayer is technically the first prayer of the day. If counted from midni ...
, Sicily
(man) it, Siciliana (woman)
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 = Ethnicity
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographi ...
, and on the Nile
The Nile, , Bohairic , lg, Kiira , Nobiin language, Nobiin: Áman Dawū is a major north-flowing river in northeastern Africa. It flows into the Mediterranean Sea. The Nile is the longest river in Africa and has historically been considered ...
, carrying carob
The carob ( ; ''Ceratonia siliqua'') is a flowering evergreen tree or shrub in the Caesalpinioideae sub-family of the legume family, Fabaceae. It is widely cultivated for its edible fruit pods, and as an ornamental tree in gardens and landscap ...
and flax
Flax, also known as common flax or linseed, is a flowering plant, ''Linum usitatissimum'', in the family Linaceae. It is cultivated as a food and fiber crop in regions of the world with temperate climates. Textiles made from flax are known in ...
.
Indian Ocean
Indian Ocean ghurāb, which often appears in the records of the 17th century was a native Arab-Persian and Indian cargo, pirate, and war vessel.Abu Shama Abū Shāma Shihāb al-Dīn al-Maḳdisī (10 January 1203 – 13 June 1267) was an Arab historian.
Abū Shāma was born in Damascus, where he passed his whole life save for one year in Egypt, a fortnight in Jerusalem and two pilgrimages to the � ...
ca. 1266–1267, in ''Kitab al-rawdatayn fi akhbar al-dawlatayn'', wrote about ghurāb:
"They sail by their masts (i.e. the sails); they (look like) quivers, but penetrate like arrows . . . It is no surprise that they are called ghurābs because they spread their wings like those of a dove"Sidi Ali in 1552, describes ghurābs as “great (rowing) vessels”; he also says that smaller ghurābs are “
galliots
A galiot, galliot or galiote, was a small galley boat propelled by sail or oars. There are three different types of naval galiots that sailed on different seas.
A ''galiote'' was a type of French flat-bottom river boat or barge and also a flat- ...
with oars”.
Grab of Malabar
Malabar may refer to the following:
People
* Malabars, people originating from the Malabar region of India
* Malbars or Malabars, people of Tamil origin in Réunion
Places
* Malabar Coast, or Malabar, a region of the southwestern shoreline o ...
coast is a vessel that was generally of shallow draft, and broad in proportion to its length. Size could range between 150 and as much as 500 tons ( bm).
See also
*Lancaran
''Colotomy'' is an Indonesian description of the rhythmic and metric patterns of gamelan music. It refers to the use of specific instruments to mark off nested time intervals, or the process of dividing rhythmic time into such nested cycles. I ...
, backbone of Malay fleet before mediterranean influence came
* Jong Jong may refer to:
Surname
*Chung (Korean surname), spelled Jong in North Korea
*Zhong (surname), spelled Jong in the Gwoyeu Romatzyh system
*Common Dutch surname "de Jong"; see
** De Jong
** De Jonge
** De Jongh
*Erica Jong (born 1942), American ...
, large sailing ship from Nusantara
* Lancang
* Penjajap
Penjajap, also pangajava and pangayaw, were native outrigger warships used by several Austronesian ethnic groups in maritime Southeast Asia. They were typically very long and narrow, and were very fast. They are mentioned as being used by native f ...
* Ghali
* Kelulus
Kelulus or kalulus is a type of rowing boat used in Indonesia. It is typically small in size and propelled using oar or paddle. However, for long-distance voyages, this boat can be equipped with sails. It is not the same as ''prahu kalulis'' of th ...
, Javanese rowing ship
References
{{Indonesian traditional vessels Merchant sailing ship types Naval sailing ship types Sailing ships Human-powered watercraft Indonesian inventions Sailboat types Two-masted ships Indigenous boats Warships Naval ships Merchant ships