GPS disciplined oscillator on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
A GPS clock, or GPS disciplined oscillator (GPSDO), is a combination of a 
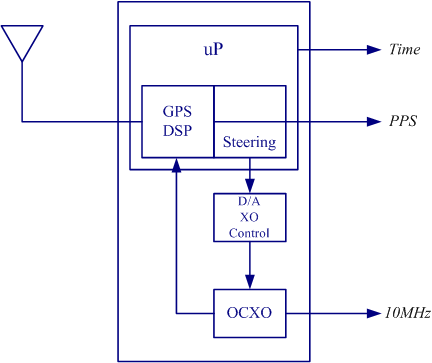 A GPSDO works by disciplining, or steering a high quality
A GPSDO works by disciplining, or steering a high quality
GPS
The Global Positioning System (GPS), originally Navstar GPS, is a satellite-based radionavigation system owned by the United States government and operated by the United States Space Force. It is one of the global navigation satellite sy ...
receiver and a high-quality, stable oscillator such as a quartz
Quartz is a hard, crystalline mineral composed of silica ( silicon dioxide). The atoms are linked in a continuous framework of SiO4 silicon-oxygen tetrahedra, with each oxygen being shared between two tetrahedra, giving an overall chemical f ...
or rubidium oscillator whose output is controlled to agree with the signals broadcast by GPS or other GNSS satellites.
GPSDOs work well as a source of timing because the satellite time signals must be accurate in order to provide positional accuracy for GPS in navigation. These signals are accurate to nanoseconds and provide a good reference for timing applications.

Applications
GPSDOs serve as an indispensable source of timing in a range of applications, and some technology applications would not be practical without them. GPSDOs are used as the basis forCoordinated Universal Time
Coordinated Universal Time or UTC is the primary time standard by which the world regulates clocks and time. It is within about one second of Solar time#Mean solar time, mean solar time (such as Universal Time, UT1) at 0° longitude (at the I ...
(UTC) around the world. UTC is the official accepted standard for time and frequency. UTC is controlled by the International Bureau of Weights and Measures (BIPM
The International Bureau of Weights and Measures (french: Bureau international des poids et mesures, BIPM) is an intergovernmental organisation, through which its 59 member-states act together on measurement standards in four areas: chemistr ...
). Timing centers around the world use GPS to align their own time scales to UTC.
GPS based standards are used to provide synchronization to wireless base stations and serve well in standards laboratories as an alternative to cesium-based references.
GPSDOs can be used to provide synchronization of multiple RF receivers, allowing for RF phase coherent operation among the receivers and applications, such as passive radar
Passive radar systems (also referred to as passive coherent location, passive surveillance systems, and passive covert radar) encompass a class of radar systems that detect and track objects by processing reflections from non-cooperative sources of ...
and ionosonde
An ionosonde, or chirpsounder, is a special radar for the examination of the ionosphere. The basic ionosonde technology was invented in 1925 by Gregory Breit and Merle A. Tuve and further developed in the late 1920s by a number of prominent phys ...
s.
Operation
 A GPSDO works by disciplining, or steering a high quality
A GPSDO works by disciplining, or steering a high quality quartz
Quartz is a hard, crystalline mineral composed of silica ( silicon dioxide). The atoms are linked in a continuous framework of SiO4 silicon-oxygen tetrahedra, with each oxygen being shared between two tetrahedra, giving an overall chemical f ...
or rubidium oscillator by locking the output to a GPS signal via a tracking loop. The disciplining mechanism works in a similar way to a phase-locked loop
A phase-locked loop or phase lock loop (PLL) is a control system that generates an output signal whose phase is related to the phase of an input signal. There are several different types; the simplest is an electronic circuit consisting of a ...
(PLL), but in most GPSDOs the loop filter is replaced with a microcontroller
A microcontroller (MCU for ''microcontroller unit'', often also MC, UC, or μC) is a small computer on a single VLSI integrated circuit (IC) chip. A microcontroller contains one or more CPUs ( processor cores) along with memory and programmabl ...
that uses software to compensate for not only the phase and frequency changes of the local oscillator, but also for the "learned" effects of aging, temperature, and other environmental parameters.
One of the keys to the usefulness of a GPSDO as a timing reference is the way it is able to combine the stability characteristics of the GPS signal and the oscillator controlled by the tracking loop. GPS receivers have excellent long-term stability (as characterized by their Allan deviation
The Allan variance (AVAR), also known as two-sample variance, is a measure of frequency stability in clocks, oscillators and amplifiers. It is named after David W. Allan and expressed mathematically as \sigma_y^2(\tau).
The Allan deviation (ADE ...
) at averaging times greater than several hours. However, their short-term stability is degraded by limitations of the internal resolution of the one pulse per second (1PPS) reference timing circuits, signal propagation effects such as multipath interference
In radio communication, multipath is the propagation phenomenon that results in radio signals reaching the receiving antenna by two or more paths. Causes of multipath include atmospheric ducting, ionospheric reflection and refraction, and ref ...
, atmospheric conditions, and other impairments. On the other hand, a quality oven-controlled oscillator has better short-term stability but is susceptible to thermal, aging, and other long-term effects. A GPSDO aims to utilize the best of both sources, combining the short-term stability performance of the oscillator with the long-term stability of the GPS signals to give a reference source with excellent overall stability characteristics.
GPSDOs typically phase-align the internal flywheel oscillator to the GPS signal by using dividers to generate a 1PPS signal from the reference oscillator, then phase comparing this 1PPS signal to the GPS-generated 1PPS signal and using the phase differences to control the local oscillator frequency in small adjustments via the tracking loop. This differentiates GPSDOs from their cousins NCOs (numerically controlled oscillator
A numerically-controlled oscillator (NCO) is a digital signal generator which creates a synchronous (i.e. clocked), discrete-time, discrete-valued representation of a waveform, usually sinusoidal. NCOs are often used in conjunction with a digit ...
). Rather than disciplining an oscillator via frequency adjustments, NCOs typically use a free-running, low-cost crystal oscillator and adjust the output phase by digitally lengthening or shortening the output phase many times per second in large phase steps assuring that on average the number of phase transitions per second is aligned to the GPS receiver reference source. This guarantees frequency accuracy at the expense of high phase noise and jitter, a degradation that true GPSDOs do not suffer.
When the GPS signal becomes unavailable, the GPSDO goes into a state of holdover, where it tries to maintain accurate timing using only the internal oscillator.
Sophisticated algorithms are used to compensate for the aging and temperature stability of the oscillator while the GPSDO is in holdover.
The use of Selective Availability
The error analysis for the Global Positioning System is important for understanding how GPS works, and for knowing what magnitude of error should be expected. The GPS makes corrections for receiver clock errors and other effects but there are sti ...
(SA) prior to May 2000 restricted the accuracy of GPS signals available for civilian use and in turn presented challenges to the accuracy of GPSDO derived timing. The turning off of SA resulted in a significant increase in the accuracy that GPSDOs can offer.
GPSDOs are capable of generating frequency accuracies and stabilities on the order of parts per billion for even entry-level, low-cost units, to parts per trillion for more advanced units within minutes after power-on, and are thus one of the highest-accuracy physically-derived reference standards available.
References
{{Reflist Synchronization