Guianese on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
French Guiana ( or ; french: link=no, Guyane ; gcr, label= French Guianese Creole, Lagwiyann ) is an overseas department/region and single territorial collectivity of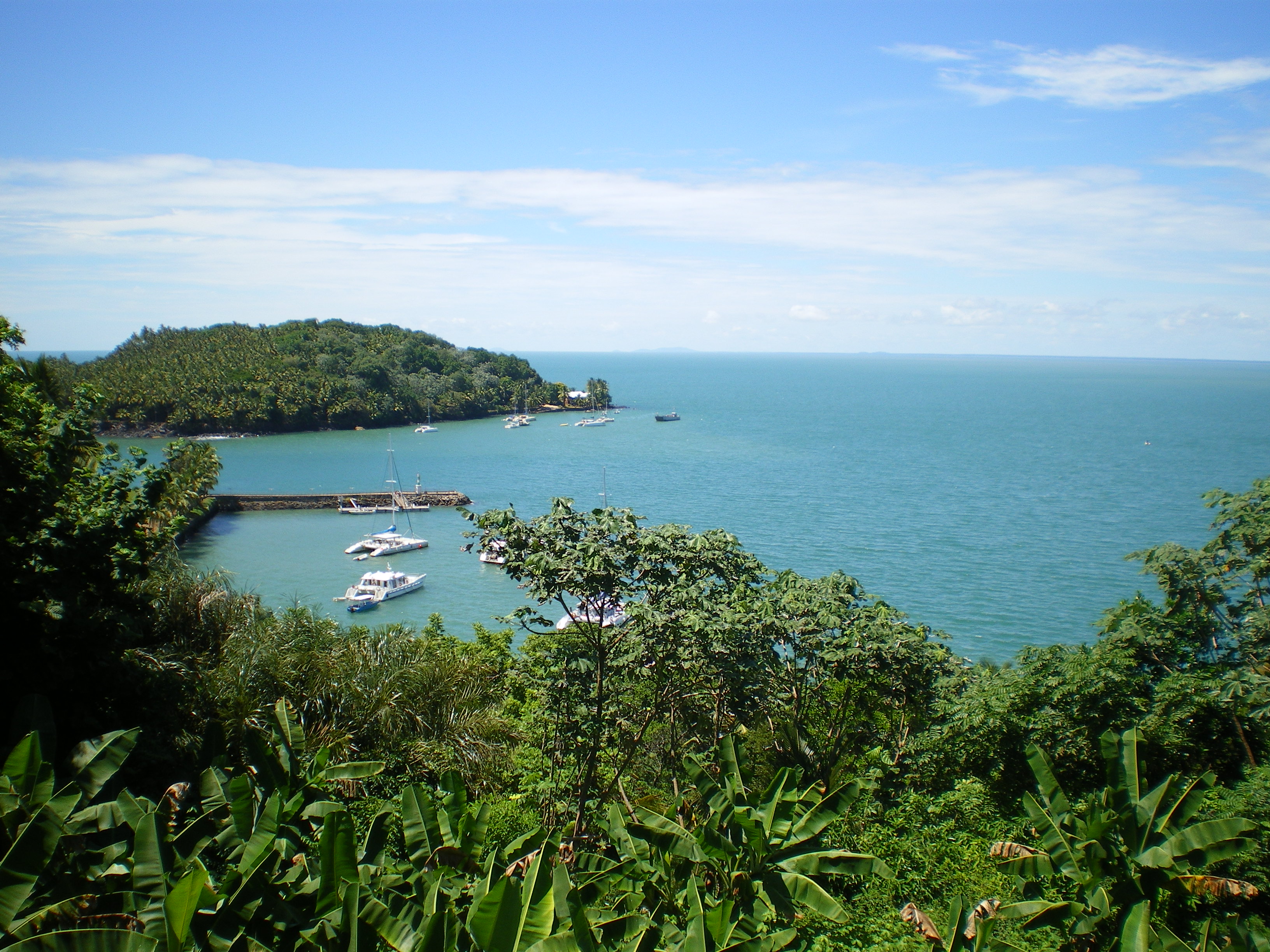  Fully integrated in the French Republic since 1946, French Guiana is a part of the European Union, and its official currency is the
Fully integrated in the French Republic since 1946, French Guiana is a part of the European Union, and its official currency is the
 The addition of the adjective "French" in most languages other than French is rooted in colonial times, when five such colonies (
The addition of the adjective "French" in most languages other than French is rooted in colonial times, when five such colonies (
 During
During
 French Guiana lies between latitudes 2° and 6° N, and longitudes 51° and 55° W. It consists of two main geographical regions: a coastal strip where the majority of the people live, and dense, near-inaccessible
French Guiana lies between latitudes 2° and 6° N, and longitudes 51° and 55° W. It consists of two main geographical regions: a coastal strip where the majority of the people live, and dense, near-inaccessible
 French Guiana has an equatorial climate predominant. Located within six degrees of the
French Guiana has an equatorial climate predominant. Located within six degrees of the

 French Guiana is home to many different
French Guiana is home to many different  5,500 plant species have been recorded, including more than a thousand trees, along with 700 species of birds, 177 species of mammals, over 500 species of fish including 45% of which are
5,500 plant species have been recorded, including more than a thousand trees, along with 700 species of birds, 177 species of mammals, over 500 species of fish including 45% of which are
 As a part of France, French Guiana is part of the
As a part of France, French Guiana is part of the

 French Guiana's population, most of whom live along the coast, is substantially ethnically diverse. At the 2018 census, 56.6% of the inhabitants of French Guiana were born in French Guiana, 8.9% were born in
French Guiana's population, most of whom live along the coast, is substantially ethnically diverse. At the 2018 census, 56.6% of the inhabitants of French Guiana were born in French Guiana, 8.9% were born in
 The dominant religion of French Guiana is Roman Catholicism; the Maroons and some Amerindian peoples maintain their own religions. The Hmong people are also largely Catholic owing to the influence of missionaries who helped bring them to French Guiana. Catholic Church in French Guiana, Guianan Catholics are part of the Diocese of Cayenne.
The dominant religion of French Guiana is Roman Catholicism; the Maroons and some Amerindian peoples maintain their own religions. The Hmong people are also largely Catholic owing to the influence of missionaries who helped bring them to French Guiana. Catholic Church in French Guiana, Guianan Catholics are part of the Diocese of Cayenne.
 French Guiana, as part of France, forms part of the
French Guiana, as part of France, forms part of the  The president of France appoints a Prefect (France), prefect (resident at the Prefectures in France, prefecture building in Cayenne) as his representative to head the local government of French Guiana. There is one elected, local executive body, the Assemblée de Guyane.
French Guiana sends two Member of Parliament, deputies to the National Assembly of France, French National Assembly, one representing the Communes of France, commune (municipality) of Cayenne and the commune of Macouria, and the other representing the rest of French Guiana. This latter constituency is the largest in the French Republic by land area. French Guiana also sends two senators to the Senate of France, French Senate. The first woman to be elected to the Senate was Marie-Laure Phinéra-Horth in 2020.
The Guianese Socialist Party dominated politics in French Guiana until 2010.
A chronic issue affecting French Guiana is the influx of illegal immigrants and clandestine gold prospecting, gold prospectors from Brazil and
The president of France appoints a Prefect (France), prefect (resident at the Prefectures in France, prefecture building in Cayenne) as his representative to head the local government of French Guiana. There is one elected, local executive body, the Assemblée de Guyane.
French Guiana sends two Member of Parliament, deputies to the National Assembly of France, French National Assembly, one representing the Communes of France, commune (municipality) of Cayenne and the commune of Macouria, and the other representing the rest of French Guiana. This latter constituency is the largest in the French Republic by land area. French Guiana also sends two senators to the Senate of France, French Senate. The first woman to be elected to the Senate was Marie-Laure Phinéra-Horth in 2020.
The Guianese Socialist Party dominated politics in French Guiana until 2010.
A chronic issue affecting French Guiana is the influx of illegal immigrants and clandestine gold prospecting, gold prospectors from Brazil and
 The transportation system in French Guiana is deficient compared to
The transportation system in French Guiana is deficient compared to
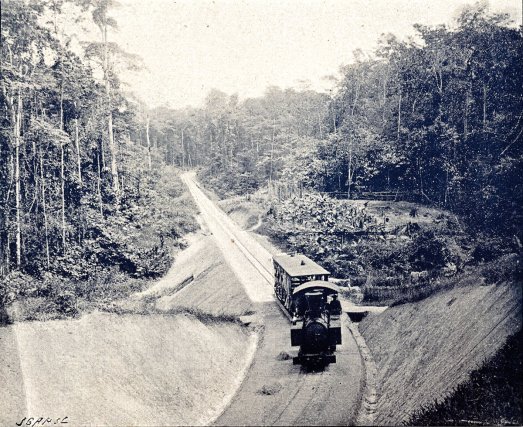 At present, French Guiana does not have a railway system, with the exception of a small section in the Centre Spatial Guyanais used for the transport of components: when the territory was a penal colony, there were some railroad lines built by the prisoners themselves to connect the various baths with each other, the remains of which (now disused and mostly engulfed by the jungle) are still visible in some areas. These lines include the section from Montsinéry-Tonnegrande to the so-called bagne des Annamites, the section from Saint-Élie to the Saut du Tigre labor camp (now submerged by the artificial lake created by the Petit-Saut dam) and the section from Saint-Laurent-du-Maroni-Mana-Saint-Jean-du-Maroni.
At present, French Guiana does not have a railway system, with the exception of a small section in the Centre Spatial Guyanais used for the transport of components: when the territory was a penal colony, there were some railroad lines built by the prisoners themselves to connect the various baths with each other, the remains of which (now disused and mostly engulfed by the jungle) are still visible in some areas. These lines include the section from Montsinéry-Tonnegrande to the so-called bagne des Annamites, the section from Saint-Élie to the Saut du Tigre labor camp (now submerged by the artificial lake created by the Petit-Saut dam) and the section from Saint-Laurent-du-Maroni-Mana-Saint-Jean-du-Maroni.
 French Guiana is served by Cayenne – Félix Eboué Airport, located in Matoury. There are also several Aerodrome, airstrips in the department, located in Camopi, Maripasoula, Ouanary, Saint-Georges-de-l'Oyapock, Saint-Laurent-du-Maroni and Saül, for a total of eleven hubs (four paved and seven unpaved).
From the main airport, there are two daily direct flights to Paris (Paris Orly airport, with an average flight time of about 8 hours and 25 minutes from French Guiana to the capital and 9 hours and 10 minutes vice-versa), offered by Air France and Air Caraïbes, as well as other flights to Fort-de-France, Pointe-à-Pitre, Port-au-Prince, Miami and Belém. The regional carrier Air Guyane Express also offers daily flights to Maripasoula and Saül, as well as more sporadic flights (mainly related to postal deliveries) to Saint-Georges-de-l'Oyapock and Camopi.
French Guiana is served by Cayenne – Félix Eboué Airport, located in Matoury. There are also several Aerodrome, airstrips in the department, located in Camopi, Maripasoula, Ouanary, Saint-Georges-de-l'Oyapock, Saint-Laurent-du-Maroni and Saül, for a total of eleven hubs (four paved and seven unpaved).
From the main airport, there are two daily direct flights to Paris (Paris Orly airport, with an average flight time of about 8 hours and 25 minutes from French Guiana to the capital and 9 hours and 10 minutes vice-versa), offered by Air France and Air Caraïbes, as well as other flights to Fort-de-France, Pointe-à-Pitre, Port-au-Prince, Miami and Belém. The regional carrier Air Guyane Express also offers daily flights to Maripasoula and Saül, as well as more sporadic flights (mainly related to postal deliveries) to Saint-Georges-de-l'Oyapock and Camopi.
 There is a public bus service that currently only covers the municipality of Cayenne and is run by the SMTC (Syndicat Mixte de Transport en Commun, now changed to Régie Communautaire des Transports – RCT) and consists of seven lines.
For connections between the coastal towns (except Montsinéry-Tonnegrande), the "collective cab" (Taxis Co) method is quite widespread, which are minibuses with a capacity of about ten people that leave as soon as there is a certain number of users on board. In 2010, the general council reached an agreement with some of the operators of this service to make it at least partially public under the name of TIG (Transporte Interurbano de la Guiana), with fixed departure times and predefined stops.
On the main rivers (Marowijne and Oyapock), there are pirogue services (called pirogues cabs), which go both to inland centers and across the border (such as Albina in Suriname or Oiapoque in Brazil).
There is a public bus service that currently only covers the municipality of Cayenne and is run by the SMTC (Syndicat Mixte de Transport en Commun, now changed to Régie Communautaire des Transports – RCT) and consists of seven lines.
For connections between the coastal towns (except Montsinéry-Tonnegrande), the "collective cab" (Taxis Co) method is quite widespread, which are minibuses with a capacity of about ten people that leave as soon as there is a certain number of users on board. In 2010, the general council reached an agreement with some of the operators of this service to make it at least partially public under the name of TIG (Transporte Interurbano de la Guiana), with fixed departure times and predefined stops.
On the main rivers (Marowijne and Oyapock), there are pirogue services (called pirogues cabs), which go both to inland centers and across the border (such as Albina in Suriname or Oiapoque in Brazil).
 * The 9th Marine Infantry Regiment (9e RIMa) in Cayenne, the Madeleine.
* The 3rd Foreign Infantry Regiment (3e REI) in Kourou.
* The RSMAG Regiment (Adapted Military Service) of French Guiana, located in Saint-Jean-du-Maroni, with a detachment in Cayenne.
* Various detachments:
** 68 Air Transport Squadron which includes: five Aérospatiale SA 330 Puma, Puma helicopters, four Eurocopter Fennec, Fennec helicopters and three CASA/IPTN CN-235, Casa CN235 aircraft
** A platoon of the French Navy, based at the naval base of Dégrad des Cannes and operating two s: ''La Confiance'' and ''La Résolue''. One ''Engins de Débarquement Amphibie – Standards'' (EDA-S) landing craft is also to be delivered to naval forces based in French Guiana by 2025. The landing craft is to better support coastal and riverine operations in the territory.
** A detachment of the Paris Fire Brigade in Kourou, ensuring the protection of the
* The 9th Marine Infantry Regiment (9e RIMa) in Cayenne, the Madeleine.
* The 3rd Foreign Infantry Regiment (3e REI) in Kourou.
* The RSMAG Regiment (Adapted Military Service) of French Guiana, located in Saint-Jean-du-Maroni, with a detachment in Cayenne.
* Various detachments:
** 68 Air Transport Squadron which includes: five Aérospatiale SA 330 Puma, Puma helicopters, four Eurocopter Fennec, Fennec helicopters and three CASA/IPTN CN-235, Casa CN235 aircraft
** A platoon of the French Navy, based at the naval base of Dégrad des Cannes and operating two s: ''La Confiance'' and ''La Résolue''. One ''Engins de Débarquement Amphibie – Standards'' (EDA-S) landing craft is also to be delivered to naval forces based in French Guiana by 2025. The landing craft is to better support coastal and riverine operations in the territory.
** A detachment of the Paris Fire Brigade in Kourou, ensuring the protection of the


 The local architecture is characterized by its Guianan Creole, Creole, Amerindian and Bushinenge influences. The main towns contain predominantly Creole-style architecture, with some Western-style buildings and forts. In the communes with the black maroon populations one can see houses of bushinengue styles. And the Amerindian communes are recognized for their pre-colonial type carbets. Most of these buildings were designed with local materials, such as wood from the Amazonian forests and bricks made on site. These local architectures blend with contemporary style buildings.
The local architecture is characterized by its Guianan Creole, Creole, Amerindian and Bushinenge influences. The main towns contain predominantly Creole-style architecture, with some Western-style buildings and forts. In the communes with the black maroon populations one can see houses of bushinengue styles. And the Amerindian communes are recognized for their pre-colonial type carbets. Most of these buildings were designed with local materials, such as wood from the Amazonian forests and bricks made on site. These local architectures blend with contemporary style buildings.
 The Carnival is one of the major events in French Guiana. Considered the longest in the world, it takes place on afternoon of Sunday, between Epiphany (holiday), Epiphany at the beginning of January and Ash Wednesday in February or (month). Groups disguised according to the theme of the year parade around decorated floats to the rhythm of percussion and brass. The preparation of the groups starts months before the carnival. The groups parade in front of thousands of spectators who gather on the sidewalks and bleachers arranged for the occasion.
Brazilian groups identical to those in the Carnival in Rio de Janeiro, Rio carnival are also appreciated for their rhythms and their alluring costumes. The Chinese community of Cayenne also participates in the parades, bringing its characteristic touch, dragons.
At the start of the evening, the Touloulous, typical characters of the Guianan carnival, go to the Nightclub, dancings to participate in the famous Masquerade ball#Contemporary era, paré-masked balls.
The Carnival is one of the major events in French Guiana. Considered the longest in the world, it takes place on afternoon of Sunday, between Epiphany (holiday), Epiphany at the beginning of January and Ash Wednesday in February or (month). Groups disguised according to the theme of the year parade around decorated floats to the rhythm of percussion and brass. The preparation of the groups starts months before the carnival. The groups parade in front of thousands of spectators who gather on the sidewalks and bleachers arranged for the occasion.
Brazilian groups identical to those in the Carnival in Rio de Janeiro, Rio carnival are also appreciated for their rhythms and their alluring costumes. The Chinese community of Cayenne also participates in the parades, bringing its characteristic touch, dragons.
At the start of the evening, the Touloulous, typical characters of the Guianan carnival, go to the Nightclub, dancings to participate in the famous Masquerade ball#Contemporary era, paré-masked balls.

 Guianan cuisine is rich in the different cultures that mix in French Guiana. Creole restaurants rub shoulders with Chinese restaurants in large cities such as Cayenne, Kourou and Saint-Laurent-du-Maroni. The local culinary art originally brought together Guianan Creole, Bushinengue and Indigenous peoples of South America, Native American cuisines.
All of these cuisines have several ingredients in common:
* Manioc;
* Smoked meats and fish
This southern Caribbean territory has many typical dishes, such as Awara broth, Galette#Creole galette, Creole galette, Dizé milé, Countess (cake), Countess, Cramanioc pudding, Kalawanng, Couac gratin and salad, Fricasse of iguana or its famous Pimentade (fish or chicken court-bouillon).
Atipas are local fishes beloved by the French Guianese often prepared with coconut milk.
At Easter, Guianan people eat a traditional dish called Awara broth.
For weddings, locals traditionally eat Colombo, which is a type of curry that has become a staple of the French Guianese cuisine.
Guianan cuisine is rich in the different cultures that mix in French Guiana. Creole restaurants rub shoulders with Chinese restaurants in large cities such as Cayenne, Kourou and Saint-Laurent-du-Maroni. The local culinary art originally brought together Guianan Creole, Bushinengue and Indigenous peoples of South America, Native American cuisines.
All of these cuisines have several ingredients in common:
* Manioc;
* Smoked meats and fish
This southern Caribbean territory has many typical dishes, such as Awara broth, Galette#Creole galette, Creole galette, Dizé milé, Countess (cake), Countess, Cramanioc pudding, Kalawanng, Couac gratin and salad, Fricasse of iguana or its famous Pimentade (fish or chicken court-bouillon).
Atipas are local fishes beloved by the French Guianese often prepared with coconut milk.
At Easter, Guianan people eat a traditional dish called Awara broth.
For weddings, locals traditionally eat Colombo, which is a type of curry that has become a staple of the French Guianese cuisine.


Ex-convict aged 104 claims to be Papillon
Telegraph.co.uk
Prefecture website
Collectivité territoriale de Guyane website
Tourism committee of French Guiana
{{Authority control French Guiana, The Guianas Overseas departments of France Former colonies in South America Former French colonies French colonization of the Americas Departments of France Regions of France Outermost regions of the European Union French Caribbean, Guiana French Union, Guiana French-speaking countries and territories States and territories established in 1946 1946 establishments in the French Union 1946 establishments in South America Dependent territories in South America Enclaves and exclaves
France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans. Its metropolitan ar ...
on the northern Atlantic
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's five oceans, with an area of about . It covers approximately 20% of Earth's surface and about 29% of its water surface area. It is known to separate the "Old World" of Africa, Europe an ...
coast of South America
South America is a continent entirely in the Western Hemisphere and mostly in the Southern Hemisphere, with a relatively small portion in the Northern Hemisphere at the northern tip of the continent. It can also be described as the souther ...
in the Guianas
The Guianas, sometimes called by the Spanish loan-word ''Guayanas'' (''Las Guayanas''), is a region in north-eastern South America which includes the following three territories:
* French Guiana, an overseas department and region of France ...
. It borders Brazil
Brazil ( pt, Brasil; ), officially the Federative Republic of Brazil (Portuguese: ), is the largest country in both South America and Latin America. At and with over 217 million people, Brazil is the world's fifth-largest country by area ...
to the east and south and Suriname
Suriname (; srn, Sranankondre or ), officially the Republic of Suriname ( nl, Republiek Suriname , srn, Ripolik fu Sranan), is a country on the northeastern Atlantic coast of South America. It is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the north ...
to the west.
With a land area of , French Guiana is the second-largest region
In geography, regions, otherwise referred to as zones, lands or territories, are areas that are broadly divided by physical characteristics (physical geography), human impact characteristics (human geography), and the interaction of humanity and t ...
of France (more than one-seventh the size of Metropolitan France
Metropolitan France (french: France métropolitaine or ''la Métropole''), also known as European France (french: Territoire européen de la France) is the area of France which is geographically in Europe. This collective name for the European ...
) and the largest outermost region within the European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational political and economic union of member states that are located primarily in Europe. The union has a total area of and an estimated total population of about 447million. The EU has often been ...
. It has a very low population density, with only . (Its population is less than that of Metropolitan France.) Half of its 294,436 inhabitants in 2022 lived in the metropolitan area of Cayenne, its capital. 98.9% of the land territory of French Guiana is covered by forests, a large part of which is primeval rainforest
Rainforests are characterized by a closed and continuous tree canopy, moisture-dependent vegetation, the presence of epiphytes and lianas and the absence of wildfire. Rainforest can be classified as tropical rainforest or temperate rainfo ...
. The Guiana Amazonian Park
Guiana Amazonian Park (french: Parc amazonien de Guyane) is the largest List of national parks of France, national park of France, aiming at protecting part of the Amazonian forest located in French Guiana which covers 41% of the region of Fran ...
, which is the largest national park
A national park is a natural park in use for conservation purposes, created and protected by national governments. Often it is a reserve of natural, semi-natural, or developed land that a sovereign state declares or owns. Although individua ...
in the European Union, covers 41% of French Guiana's territory.
Since December 2015, both the region and department have been ruled by a single assembly within the framework of a new territorial collectivity, the French Guiana Territorial Collectivity (french: collectivité territoriale de Guyane, links=no). This assembly, the French Guiana Assembly (french: assemblée de Guyane, links=no), replaced the former regional council
Regional Council may refer to:
* Regional Council (Hong Kong), disbanded in 1999
** Regional Council (constituency)
Regional council may refer to:
* Regional council (Cameroon)
* Regional council (France), the elected assembly of a region of Fra ...
and departmental council, which were disbanded. The French Guiana Assembly is in charge of regional and departmental government. Its president is Gabriel Serville.
 Fully integrated in the French Republic since 1946, French Guiana is a part of the European Union, and its official currency is the
Fully integrated in the French Republic since 1946, French Guiana is a part of the European Union, and its official currency is the euro
The euro (symbol: €; code: EUR) is the official currency of 19 out of the member states of the European Union (EU). This group of states is known as the eurozone or, officially, the euro area, and includes about 340 million citizens . ...
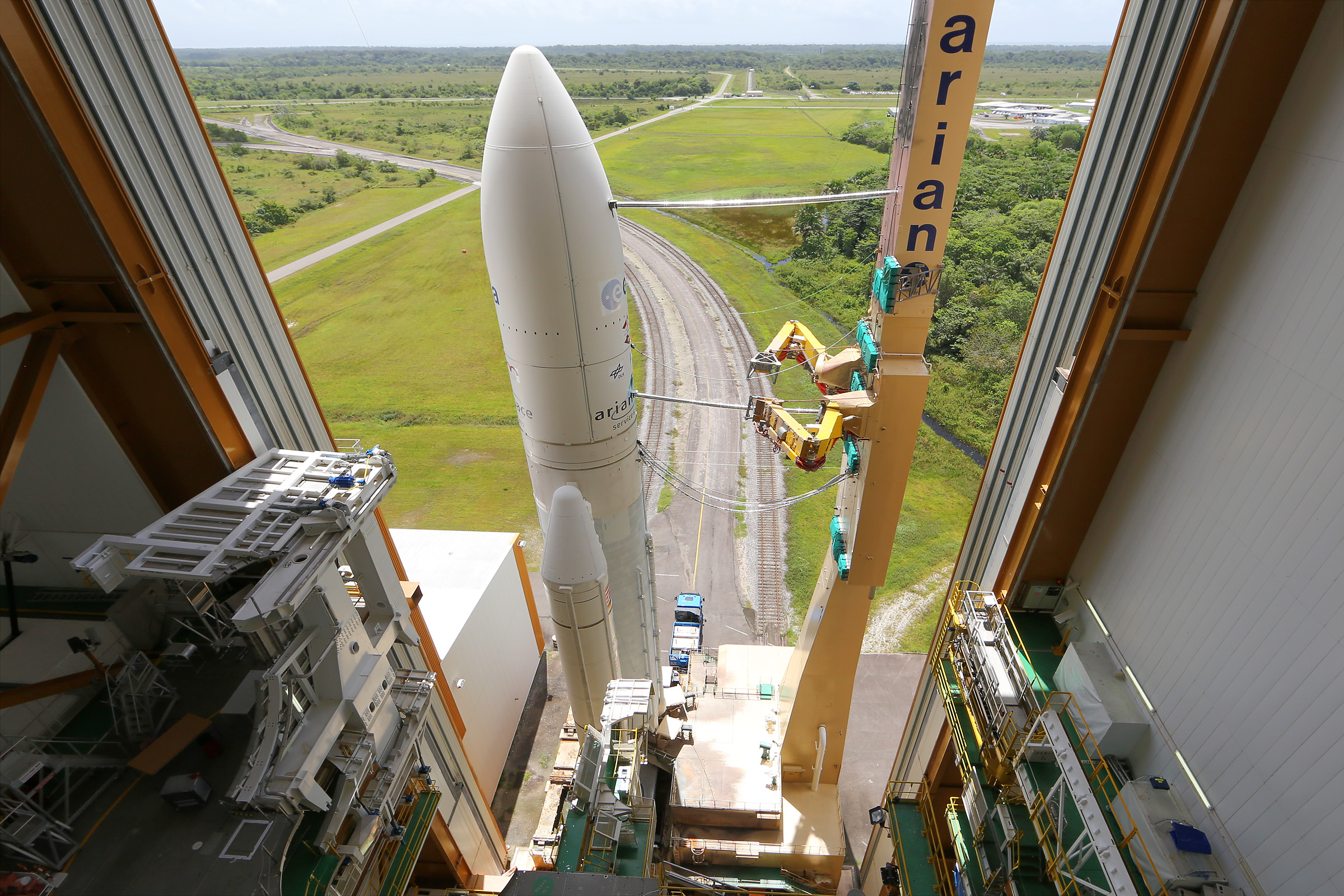
. A large part of French Guiana's economy depends on jobs and businesses associated with the presence of the Guiana Space Centre
The Guiana Space Centre (french: links=no, Centre spatial guyanais; CSG), also called Europe's Spaceport, is a European spaceport to the northwest of Kourou in French Guiana, a region of France in South America. Kourou is located approximat ...
, now the European Space Agency
, owners =
, headquarters = Paris, Île-de-France, France
, coordinates =
, spaceport = Guiana Space Centre
, seal = File:ESA emblem seal.png
, seal_size = 130px
, image = Views in the Main Control Room (120 ...
's primary launch site near the equator. As elsewhere in France, the official language is standard French, but each ethnic community has its own language, of which French Guianese Creole, a French-based creole language
A creole language, or simply creole, is a stable natural language that develops from the simplifying and mixing of different languages into a new one within a fairly brief period of time: often, a pidgin evolved into a full-fledged language. Wh ...
, is the most widely spoken. French Guiana is the only territory on the continental mainland of either North
North is one of the four compass points or cardinal directions. It is the opposite of south and is perpendicular to east and west. ''North'' is a noun, adjective, or adverb indicating direction or geography.
Etymology
The word ''no ...
or South America
South America is a continent entirely in the Western Hemisphere and mostly in the Southern Hemisphere, with a relatively small portion in the Northern Hemisphere at the northern tip of the continent. It can also be described as the souther ...
that is under the sovereignty of a European state, much less fully integrated in a European state.
The border between French Guiana and Brazil is the longest land border that France shares with another country, as well as one of only two borders which France shares with non-European states, the other being the border with Suriname in the west.
Name
The Guianas
The Guianas, sometimes called by the Spanish loan-word ''Guayanas'' (''Las Guayanas''), is a region in north-eastern South America which includes the following three territories:
* French Guiana, an overseas department and region of France ...
) had been named along the coast, subject to differing powers: namely (from west to east) Spanish Guiana (now Guayana Region in Venezuela), British Guiana (now Guyana), Dutch Guiana
Dutch Guiana may refer to:
* Dutch colonisation of the Guianas, the coastal region between the Orinoco and Amazon rivers in South America
* Surinam (Dutch colony), commonly called "Dutch Guiana" after the loss of other large colonies in the area
...
(now Suriname
Suriname (; srn, Sranankondre or ), officially the Republic of Suriname ( nl, Republiek Suriname , srn, Ripolik fu Sranan), is a country on the northeastern Atlantic coast of South America. It is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the north ...
), French Guiana, and Portuguese Guiana (now Amapá
Amapá () is one of the 26 states of Brazil. It is in the northern region of Brazil. It is the second least populous state and the eighteenth largest by area. Located in the far northern part of the country, Amapá is bordered clockwise by Fr ...
in Brazil). French Guiana and the two larger countries to the north and west, Guyana and Suriname, are still often collectively referred to as "the Guianas" and constitute one large landmass known as the Guiana Shield
The Guiana Shield (french: Plateau des Guyanes, Bouclier guyanais; nl, Hoogland van Guyana, Guianaschild; pt, Planalto das Guianas, Escudo das Guianas; es, Escudo guayanés) is one of the three cratons of the South American Plate. It is a ...
.
History
French Guiana was originally inhabited byindigenous people
Indigenous peoples are culturally distinct ethnic groups whose members are directly descended from the earliest known inhabitants of a particular geographic region and, to some extent, maintain the language and culture of those original people ...
: Kalina, Arawak
The Arawak are a group of indigenous peoples of northern South America and of the Caribbean. Specifically, the term "Arawak" has been applied at various times to the Lokono of South America and the Taíno, who historically lived in the Greater ...
, Galibi, Palikur, Teko, Wayampi and Wayana. The French attempted to create a colony there in the 16th century in conjunction with its settlement of some Caribbean islands, such as Guadeloupe and Saint-Domingue
Saint-Domingue () was a French colony in the western portion of the Caribbean island of Hispaniola, in the area of modern-day Haiti, from 1659 to 1804. The name derives from the Spanish main city in the island, Santo Domingo, which came to ref ...
.
Prior to European colonization, the territory was originally inhabited by Native Americans, most speaking the Arawak language
Arawak (, ), also known as Lokono (Lokono Dian, literally "people's talk" by its speakers), is an Arawakan language spoken by the Lokono (Arawak) people of South America in eastern Venezuela, Guyana, Suriname, and French Guiana. It is the eponymou ...
, of the Arawakan language family. The people identified as Lokono. The first French establishment is recorded in 1503, but France did not establish a durable presence until colonists founded Cayenne in 1643. Guiana was developed as a slave society, where planters imported Africans as enslaved labourers on large sugar and other plantations in such number as to increase the population. The system of slavery in French Guiana continued until the French Revolution
The French Revolution ( ) was a period of radical political and societal change in France that began with the Estates General of 1789 and ended with the formation of the French Consulate in November 1799. Many of its ideas are conside ...
, when the National Convention
The National Convention (french: link=no, Convention nationale) was the parliament of the Kingdom of France for one day and the French First Republic for the rest of its existence during the French Revolution, following the two-year National ...
voted to abolish the French slave trade and slavery in France's overseas colonies in February 1794, months after enslaved Haitians had started a slave rebellion in the colony of Saint-Domingue
Saint-Domingue () was a French colony in the western portion of the Caribbean island of Hispaniola, in the area of modern-day Haiti, from 1659 to 1804. The name derives from the Spanish main city in the island, Santo Domingo, which came to ref ...
. However, the 1794 decree was only implemented in Saint-Domingue, Guadeloupe
Guadeloupe (; ; gcf, label=Antillean Creole, Gwadloup, ) is an archipelago and overseas department and region of France in the Caribbean. It consists of six inhabited islands— Basse-Terre, Grande-Terre, Marie-Galante, La Désirade, and the ...
and French Guiana, while the colonies of Senegal
Senegal,; Wolof: ''Senegaal''; Pulaar: 𞤅𞤫𞤲𞤫𞤺𞤢𞥄𞤤𞤭 (Senegaali); Arabic: السنغال ''As-Sinighal'') officially the Republic of Senegal,; Wolof: ''Réewum Senegaal''; Pulaar : 𞤈𞤫𞤲𞤣𞤢𞥄𞤲𞤣� ...
, Mauritius
Mauritius ( ; french: Maurice, link=no ; mfe, label=Mauritian Creole, Moris ), officially the Republic of Mauritius, is an island nation in the Indian Ocean about off the southeast coast of the African continent, east of Madagascar. It incl ...
, Réunion and Martinique
Martinique ( , ; gcf, label=Martinican Creole, Matinik or ; Kalinago language, Kalinago: or ) is an island and an Overseas department and region, overseas department/region and single territorial collectivity of France. An integral part of ...
and French India resisted the imposition of these laws.
Bill Marshall, Professor of Comparative Cultural Studies at the University of Stirling
The University of Stirling (, gd, Oilthigh Shruighlea (abbreviated as Stir or Shruiglea, in post-nominals) is a public university in Stirling, Scotland, founded by royal charter in 1967. It is located in the Central Belt of Scotland, built ...
wrote of French Guiana's origins:
''Île du Diable
Devil's Island ( French: Île du Diable) is the third-largest island of the Salvation Islands, an island group in the Atlantic Ocean. It is located approximately 14 km (9 mi) off the coast of French Guiana in South America just north o ...
'' (Devil's Island) was the site of a small prison facility, part of a larger penal system by the same name, which consisted of prisons on three islands and three larger prisons on the mainland. This was operated from 1852 to 1953.
In addition, in the late nineteenth century, France began requiring forced residencies by prisoners who survived their hard labour. A Portuguese-British naval squadron took French Guiana for the Portuguese Empire
The Portuguese Empire ( pt, Império Português), also known as the Portuguese Overseas (''Ultramar Português'') or the Portuguese Colonial Empire (''Império Colonial Português''), was composed of the overseas colonies, factories, and the ...
in 1809. It was returned to France with the signing of the Treaty of Paris in 1814. Though Portugal returned the region to France, it kept a military presence until 1817.
After French Guiana was established as a penal colony, officials sometimes used convicts to catch butterflies. The sentences of the convicts were often long, and the prospect of employment very weak, so the convicts caught butterflies to sell in the international market, both for scientific purposes as well as general collecting.
A border dispute with Brazil arose in the late 19th century over a vast area of jungle, resulting in the short-lived, pro-French, independent state of Counani in the disputed territory. There was some fighting among settlers. The dispute was resolved largely in favour of Brazil by the arbitration
Arbitration is a form of alternative dispute resolution (ADR) that resolves disputes outside the judiciary courts. The dispute will be decided by one or more persons (the 'arbitrators', 'arbiters' or ' arbitral tribunal'), which renders the ...
of the Swiss government.
The territory of Inini consisted of most of the interior of French Guiana when it was created in 1930. It was abolished in 1946, the year that French Guiana as a whole was formally established as an overseas department
The overseas departments and regions of France (french: départements et régions d'outre-mer, ; ''DROM'') are departments of France that are outside metropolitan France, the European part of France. They have exactly the same status as mainlan ...
of France. In 1936, Félix Éboué from Cayenne became the first black man to serve as governor in a French colony.
 During
During World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
and the fall of France to Nazi German forces, French Guiana became part of Vichy France
Vichy France (french: Régime de Vichy; 10 July 1940 – 9 August 1944), officially the French State ('), was the Fascism, fascist French state headed by Marshal Philippe Pétain during World War II. Officially independent, but with half of ...
. Guiana officially rallied to Free France
Free France (french: France Libre) was a political entity that claimed to be the legitimate government of France following the dissolution of the Third Republic. Led by French general , Free France was established as a government-in-exil ...
on 16 March 1943. It abandoned its colony status and once again became a French department on 19 March 1946.
Following the French withdrawal from Vietnam in the 1950s and subsequent warfare conducted in the region by the United States, France helped resettle several hundred Hmong refugees from Laos to French Guiana during the 1970s and 80s, who were fleeing displacement after the communist takeover of Laos by Pathet Lao
The Pathet Lao ( lo, ປະເທດລາວ, translit=Pa thēt Lāo, translation=Lao Nation), officially the Lao People's Liberation Army, was a communist political movement and organization in Laos, formed in the mid-20th century. The gro ...
in 1975.
In the late 1980s, more than 10,000 Suriname
Suriname (; srn, Sranankondre or ), officially the Republic of Suriname ( nl, Republiek Suriname , srn, Ripolik fu Sranan), is a country on the northeastern Atlantic coast of South America. It is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the north ...
se refugees, mostly Maroons
Maroons are descendants of Africans in the Americas who escaped from slavery and formed their own settlements. They often mixed with indigenous peoples, eventually evolving into separate creole cultures such as the Garifuna and the Mascogos.
...
, arrived in French Guiana, fleeing the Surinamese Civil War.
More recently, French Guiana has received large numbers of Brazilian and Haitian economic migrants. Illegal and ecologically destructive gold mining by Brazilian is a chronic issue in the remote interior rain forest of French Guiana. The region still faces such problems as illegal immigration, poorer infrastructure than mainland France, higher costs of living, higher levels of crime and more common social unrest.
In 1964, French president Charles de Gaulle decided to construct a space-travel base in French Guiana. It was intended to replace the Sahara base in Algeria
)
, image_map = Algeria (centered orthographic projection).svg
, map_caption =
, image_map2 =
, capital = Algiers
, coordinates =
, largest_city = capital
, religi ...
and stimulate economic growth in French Guiana. The department was considered suitable for the purpose because it is near the equator
The equator is a circle of latitude, about in circumference, that divides Earth into the Northern and Southern hemispheres. It is an imaginary line located at 0 degrees latitude, halfway between the North and South poles. The term can al ...
and has extensive access to the ocean as a buffer zone. The Guiana Space Centre
The Guiana Space Centre (french: links=no, Centre spatial guyanais; CSG), also called Europe's Spaceport, is a European spaceport to the northwest of Kourou in French Guiana, a region of France in South America. Kourou is located approximat ...
, located a short distance along the coast from Kourou, has grown considerably since the initial launches of the Véronique rockets. It is now part of the European space industry and has had commercial success with such launches as the Ariane 4, Ariane 5
Ariane 5 is a European heavy-lift space launch vehicle developed and operated by Arianespace for the European Space Agency (ESA). It is launched from the Centre Spatial Guyanais (CSG) in French Guiana. It has been used to deliver payloads in ...
and Ariane flight VA256 which launched the James Webb Space Telescope
The James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) is a space telescope which conducts infrared astronomy. As the largest optical telescope in space, its high resolution and sensitivity allow it to view objects too old, distant, or faint for the Hubble ...
into space.
The Guianese General Council officially adopted a departmental flag in 2010. In a referendum
A referendum (plural: referendums or less commonly referenda) is a direct vote by the electorate on a proposal, law, or political issue. This is in contrast to an issue being voted on by a representative. This may result in the adoption of ...
that same year, French Guiana voted against autonomy.
On 20 March 2017, French Guianese workers began going on strike and demonstrating for more resources and infrastructure. 28 March 2017 was the day of the largest demonstration ever held in French Guiana.
French Guiana has been severely affected by the COVID-19 outbreak, with more than 1% of French Guianese testing positive by the end of June 2020.
Geography
rainforest
Rainforests are characterized by a closed and continuous tree canopy, moisture-dependent vegetation, the presence of epiphytes and lianas and the absence of wildfire. Rainforest can be classified as tropical rainforest or temperate rainfo ...
which gradually rises to the modest peaks of the Tumuc-Humac mountains along the Brazilian frontier. French Guiana's highest peak is Bellevue de l'Inini
Bellevue de l'Inini, also known as ''Mont Bellevue'', ''Montagne Bellevue'', and ''Montagne Bellevue de l'Inini'', is the highest point of French Guiana, an overseas department of France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ) ...
in Maripasoula (). Other mountains include Mont Itoupé
Mont Itoupé (also Sommet Tabulaire) is a 826 metres high mountain on the border of the Camopi and Maripasoula communes in French Guiana, France. It is the second highest mountain in French Guiana after Bellevue de l'Inini. The mountain is l ...
(), Cottica Mountain (), Pic Coudreau (), and Kaw Mountain
The Kaw Mountain is a 337 metres high mountain in the commune of Roura in French Guiana, France. It is a narrow tepui with a laterite top.
Overview
Kaw Mountain is covered in rainforest and is part of the northern range of the Guiana Shield. The ...
().
Several small islands are found off the coast: the three Salvation's Islands which include Devil's Island, and the isolated Îles du Connétable bird sanctuary further along the coast towards Brazil.
The Petit-Saut Dam, a hydroelectric dam in the north of French Guiana forms an artificial lake and provides hydroelectricity
Hydroelectricity, or hydroelectric power, is electricity generated from hydropower (water power). Hydropower supplies one sixth of the world's electricity, almost 4500 TWh in 2020, which is more than all other renewable sources combined a ...
. There are many rivers in French Guiana, including the Waki River.
, the Amazonian forest
The Amazon rainforest, Amazon jungle or ; es, Selva amazónica, , or usually ; french: Forêt amazonienne; nl, Amazoneregenwoud. In English, the names are sometimes capitalized further, as Amazon Rainforest, Amazon Forest, or Amazon Jungle. ...
, located in the most remote part of the department, is protected as the Guiana Amazonian Park
Guiana Amazonian Park (french: Parc amazonien de Guyane) is the largest List of national parks of France, national park of France, aiming at protecting part of the Amazonian forest located in French Guiana which covers 41% of the region of Fran ...
, one of the ten national parks of France. The territory of the park covers some upon the communes of Camopi, Maripasoula, Papaïchton
Papaichton (unofficial spelling Papaïchton with a trema) is a commune in the overseas region and department of French Guiana. The village lies on the shores of the Lawa River. Papaichton is served by the Maripasoula Airport.
The village whic ...
, Saint-Élie and Saül.
Climate
Equator
The equator is a circle of latitude, about in circumference, that divides Earth into the Northern and Southern hemispheres. It is an imaginary line located at 0 degrees latitude, halfway between the North and South poles. The term can al ...
and rising only to modest elevations, French Guiana is hot and oppressively humid all year round. During most of the year, rainfall across the country is heavy due to the presence of the Intertropical Convergence Zone and its powerful thunderstorm cells. In most parts of French Guiana, rainfall is always heavy especially from December to July – typically over can be expected each month during this period throughout the department. Between August and November, the eastern half experiences a warm dry season
The dry season is a yearly period of low rainfall, especially in the tropics. The weather in the tropics is dominated by the tropical rain belt, which moves from the northern to the southern tropics and back over the course of the year. The ...
with rainfall below and average high temperatures above occurring in September and October, causing eastern French Guiana to be classified as a tropical monsoon climate
An area of tropical monsoon climate (occasionally known as a sub-equatorial, tropical wet climate or a tropical monsoon and trade-wind littoral climate) is a tropical climate sub-type that corresponds to the Köppen climate classification category ...
( Köppen ''Am''); Saint-Laurent-du-Maroni in the west has a tropical rainforest climate
A tropical rainforest climate, humid tropical climate or equatorial climate is a tropical climate sub-type usually found within 10 to 15 degrees latitude of the equator. There are some other areas at higher latitudes, such as the coast of southea ...
(''Af'').
Environment

 French Guiana is home to many different
French Guiana is home to many different ecosystem
An ecosystem (or ecological system) consists of all the organisms and the physical environment with which they interact. These biotic and abiotic components are linked together through nutrient cycles and energy flows. Energy enters the syst ...
s: tropical rainforest
Tropical rainforests are rainforests that occur in areas of tropical rainforest climate in which there is no dry season – all months have an average precipitation of at least 60 mm – and may also be referred to as ''lowland equatori ...
s, coastal mangroves, savannahs, inselbergs and many types of wetlands
A wetland is a distinct ecosystem that is flooded or saturated by water, either permanently (for years or decades) or seasonally (for weeks or months). Flooding results in oxygen-free ( anoxic) processes prevailing, especially in the soils. The ...
. It lies within three ecoregions: Guayanan Highlands moist forests
The Guayanan Highlands moist forests (NT0124) is an ecoregion in the south of Venezuela and the north of Brazil and in Guyana, Suriname, French Guiana. It is in the Amazon biome.
It encompasses an upland region with diverse fauna and flora, which ...
, Guianan moist forests, and Guianan mangroves. French Guiana has a high level of biodiversity
Biodiversity or biological diversity is the variety and variability of life on Earth. Biodiversity is a measure of variation at the genetic ('' genetic variability''), species ('' species diversity''), and ecosystem ('' ecosystem diversity' ...
of both flora
Flora (: floras or florae) is all the plant life present in a particular region or time, generally the naturally occurring (indigenous (ecology), indigenous) native plant, native plants. The corresponding term for animals is ''fauna'', and for f ...
and fauna
Fauna is all of the animal life present in a particular region or time. The corresponding term for plants is ''flora'', and for fungi, it is '' funga''. Flora, fauna, funga and other forms of life are collectively referred to as ''biota''. Zoo ...
. This is due to the presence of old-growth forests (i.e., ancient/primary forests), which are biodiversity hotspots. The rainforest
Rainforests are characterized by a closed and continuous tree canopy, moisture-dependent vegetation, the presence of epiphytes and lianas and the absence of wildfire. Rainforest can be classified as tropical rainforest or temperate rainfo ...
s of French Guiana provide shelter for many species during dry periods and terrestrial glaciation. These forests are protected by a national park (the Guiana Amazonian Park
Guiana Amazonian Park (french: Parc amazonien de Guyane) is the largest List of national parks of France, national park of France, aiming at protecting part of the Amazonian forest located in French Guiana which covers 41% of the region of Fran ...
), seven additional nature reserve
A nature reserve (also known as a wildlife refuge, wildlife sanctuary, biosphere reserve or bioreserve, natural or nature preserve, or nature conservation area) is a protected area of importance for flora, fauna, or features of geological or ...
s, and 17 protected sites. The International Union for Conservation of Nature
The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN; officially International Union for Conservation of Nature and Natural Resources) is an international organization working in the field of nature conservation and sustainable use of natur ...
(IUCN) and the European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational political and economic union of member states that are located primarily in Europe. The union has a total area of and an estimated total population of about 447million. The EU has often been ...
(EU) have recommended special efforts to protect these areas.
Following the Grenelle Environment Round Table of 2007, the Grenelle Law II was proposed in 2009, under law number 2010–788. Article 49 of the law proposed the creation of a single organization responsible for environmental conservation in French Guiana. Article 64 proposes a "departmental plan of mining orientation" for French Guiana, which would promote mining (specifically of gold) that is compatible with requirements for environmental protection. The coastal environment along the RN1 has historically experienced the most changes, but development is occurring locally along the RN2, and also in western French Guiana due to gold mining.
 5,500 plant species have been recorded, including more than a thousand trees, along with 700 species of birds, 177 species of mammals, over 500 species of fish including 45% of which are
5,500 plant species have been recorded, including more than a thousand trees, along with 700 species of birds, 177 species of mammals, over 500 species of fish including 45% of which are endemic
Endemism is the state of a species being found in a single defined geographic location, such as an island, state, nation, country or other defined zone; organisms that are indigenous to a place are not endemic to it if they are also found els ...
and 109 species of amphibians. French Guiana's high biodiversity is similar to that of other regions with tropical rainforests, such as the Brazilian Amazon, Borneo
Borneo (; id, Kalimantan) is the List of islands by area, third-largest island in the world and the largest in Asia. At the geographic centre of Maritime Southeast Asia, in relation to major Indonesian islands, it is located north of Java Isl ...
and Sumatra.
Environmental threats include habitat fragmentation
Habitat fragmentation describes the emergence of discontinuities (fragmentation) in an organism's preferred environment (habitat), causing population fragmentation and ecosystem decay. Causes of habitat fragmentation include geological proces ...
from roads, which remains very limited compared to other forests of South America; immediate and deferred impacts of EDF's Petit-Saut Dam; gold mining; poor control of hunting and poaching
Poaching has been defined as the illegal hunting or capturing of wild animals, usually associated with land use rights.
Poaching was once performed by impoverished peasants for subsistence purposes and to supplement meager diets. It was set ag ...
, facilitated by the creation of many tracks; and the introduction of all-terrain vehicle
An all-terrain vehicle (ATV), also known as a light utility vehicle (LUV), a quad bike, or simply a quad, as defined by the American National Standards Institute (ANSI); is a vehicle that travels on low-pressure tires, with a seat that is strad ...
s. Logging remains moderate due to the lack of roads, difficult climate, and difficult terrain. The Forest Code of French Guiana was modified by ordinance on 28 July 2005. Logging concessions or free transfers are sometimes granted by local authorities to persons traditionally deriving their livelihood from the forest.
The beaches of the Amana Nature Reserve are an exceptional marine turtle nesting site. This is one of the largest worldwide for the leatherback turtle.
Agriculture
French Guiana has some of the poorest soils in the world. The soil is low in nutrients (e.g., nitrogen, potassium) and organic matter. Soil acidity is another cause of the poor soils, and it requires farmers to Liming (soil), add lime to their fields. The soil characteristics have led to the use of slash and burn agriculture. The resulting ashes elevate soil pH (i.e., lower soil acidity), and contribute minerals and other nutrients to the soil. Sites of Terra preta (human impact on the environment, anthropogenic soils) have been discovered in French Guiana, particularly near the border with Brazil. Research is being actively pursued in multiple fields to determine how these enriched soils were historically created, and how this can be done in modern times.Economy
 As a part of France, French Guiana is part of the
As a part of France, French Guiana is part of the European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational political and economic union of member states that are located primarily in Europe. The union has a total area of and an estimated total population of about 447million. The EU has often been ...
and the Eurozone; its currency is the euro
The euro (symbol: €; code: EUR) is the official currency of 19 out of the member states of the European Union (EU). This group of states is known as the eurozone or, officially, the euro area, and includes about 340 million citizens . ...
. The country code top-level domain (ccTLD) for French Guiana is .gf, but .fr is generally used instead.
In 2019, the GDP of French Guiana at market exchange rates was US$4.93 billion (€4.41 billion), ranking as the 2nd largest economy in the The Guianas, Guianas after Guyana (which discovered large oil fields in 2015 and 2018), and the 12th largest in South America.
From the 1960s to the 2000s, French Guiana experienced strong economic growth, fueled by the development of France's Guiana Space Centre
The Guiana Space Centre (french: links=no, Centre spatial guyanais; CSG), also called Europe's Spaceport, is a European spaceport to the northwest of Kourou in French Guiana, a region of France in South America. Kourou is located approximat ...
(established in French Guiana in 1964 as the independence of Algeria
)
, image_map = Algeria (centered orthographic projection).svg
, map_caption =
, image_map2 =
, capital = Algiers
, coordinates =
, largest_city = capital
, religi ...
in 1962 led to the closure of France's space center in the Algerian Sahara) and by high population growth which stimulated domestic consumption. French Guiana's economy did not suffer from the Financial crisis of 2007–2008, Global Financial Crisis of 2008: the GDP grew by an average of +3.4% per year in real versus nominal value (economics), real terms from 2002 to 2012, slightly faster than the rapidly growing population, which allowed French Guiana to catch up somewhat with the rest of France in terms of standards of living. The GDP per capita rose from 48.0% of metropolitan France's level in 2000 to 48.5% of metropolitan France in 2012.
Since 2013, however, French Guiana's economic growth has been uneven, and more subdued. From 2013 to 2019, the economy grew by an average of only +1.2% in real terms. French Guiana experienced a recession of -0.8% in 2014, and 2017 social unrest in French Guiana, social unrest in 2017 led to almost no economic growth that year. Economic growth recovered at +3.0% in 2018, but was again almost null (+0.2%) in 2019. As a result, the GDP per capita has remained stagnant in nominal terms since 2013, and has declined relative to metropolitan France's. In 2019, the list of countries by GDP (nominal) per capita, GDP per capita of French Guiana at market exchange rates, not at purchasing power parity, PPP, was US$17,375 (€15,521), only 42.3% of metropolitan France's average GDP per capita that year, and 50.3% of the metropolitan French regions outside the Île-de-France, Paris Region.
French Guiana was affected by the COVID-19 pandemic in 2020, leading to a recession of -2.7% that year according to provisional estimates, moderate compared to the COVID-19 recession in metropolitan France (-7.9% in 2020).
French Guiana is heavily dependent on mainland France for subsidies, trade, and goods. The main traditional industries are fishing (accounting for 5% of exports in 2012), gold mining (accounting for 32% of exports in 2012) and timber (accounting for 1% of exports in 2012). In addition, the Guiana Space Centre
The Guiana Space Centre (french: links=no, Centre spatial guyanais; CSG), also called Europe's Spaceport, is a European spaceport to the northwest of Kourou in French Guiana, a region of France in South America. Kourou is located approximat ...
has played a significant role in the local economy since it was established in Kourou in 1964: it accounted directly and indirectly for 16% of French Guiana's GDP in 2002 (down from 26% in 1994, as the French Guianese economy is becoming increasingly diversified). The Guiana Space Centre employed 1,659 people in 2012.
There is very little manufacturing. Agriculture is largely undeveloped and is mainly confined to the area near the coast and along the Maroni (river), Maroni River. Sugar and bananas were traditionally two of the main cash crops grown for export but have almost completely disappeared. Today they have been replaced by livestock raising (essentially beef cattle and pigs) in the coastal savannas between Cayenne and the second-largest town, Saint-Laurent-du-Maroni, and market gardening (fruits and vegetables) developed by the Hmong people, Hmong communities settled in French Guiana in the 1970s, both destined to the local market. A thriving rice production, developed on polders near Mana, French Guiana, Mana from the early 1980s to the late 2000s, has almost completely disappeared since 2011 due to marine erosion and new Directorate-General for Health and Consumers, EU plant health rules which forbid the use of many pesticides and fertilizers. Tourism, especially ecotourism, eco-tourism, is growing.
Unemployment has been persistently high in the last few decades, standing between 17% and 24%. In recent years, the unemployment rate has declined from a peak of 23.0% in 2016 to 19.3% in 2019.
Demographics

Historical population
French Guiana experienced a long period of demographic stagnation during the days of the Devil's Island, Cayenne and Prison of St-Laurent-du-Maroni, Saint-Laurent-du-Maroni Penal colony, penal colonies (19th century and first half of the 20th century), when, with the exception of a brief gold rush in the 1900s and 1910s, it suffered from a bad reputation due to its association with penal colonies and bad sanitary conditions (yellow fever and malaria in particular). Population started to grow tremendously from the 1950s onwards with the improvement of sanitary conditions (yellow fever and malaria eradication campaigns started in 1949) and the establishment of theGuiana Space Centre
The Guiana Space Centre (french: links=no, Centre spatial guyanais; CSG), also called Europe's Spaceport, is a European spaceport to the northwest of Kourou in French Guiana, a region of France in South America. Kourou is located approximat ...
in 1964. Population growth has been fueled both by high birth rates and large arrivals of immigrants (from metropolitan France, to man the public administrations and the space center, as well as from neighboring countries, in particular Suriname
Suriname (; srn, Sranankondre or ), officially the Republic of Suriname ( nl, Republiek Suriname , srn, Ripolik fu Sranan), is a country on the northeastern Atlantic coast of South America. It is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the north ...
and Brazil
Brazil ( pt, Brasil; ), officially the Federative Republic of Brazil (Portuguese: ), is the largest country in both South America and Latin America. At and with over 217 million people, Brazil is the world's fifth-largest country by area ...
). Arrivals of Surinamese refugees reached record levels in the 1980s during the Surinamese Interior War, resulting in the highest population growth rate in French Guiana's history, recorded between the 1982 and 1990 censuses (+5.8% per year).
In the 21st century, the birth rate has remained high, and new arrivals of migrants seeking asylum (in particular from Haiti) have kept population growth above 2% per year in the 2010s. French Guiana's population reached 294,436 in 2022 (Jan. estimate), more than 10 times the population it had in 1954.
Major urban areas
The most populous urban unit (agglomeration) is Cayenne, which covers 3 communes (Cayenne, Matoury and Remire-Montjoly). The three largest urban units are:Ethnic groups

 French Guiana's population, most of whom live along the coast, is substantially ethnically diverse. At the 2018 census, 56.6% of the inhabitants of French Guiana were born in French Guiana, 8.9% were born in
French Guiana's population, most of whom live along the coast, is substantially ethnically diverse. At the 2018 census, 56.6% of the inhabitants of French Guiana were born in French Guiana, 8.9% were born in Metropolitan France
Metropolitan France (french: France métropolitaine or ''la Métropole''), also known as European France (french: Territoire européen de la France) is the area of France which is geographically in Europe. This collective name for the European ...
, 2.8% were born in the French Caribbean departments of France, departments and overseas collectivity, collectivities (Guadeloupe
Guadeloupe (; ; gcf, label=Antillean Creole, Gwadloup, ) is an archipelago and overseas department and region of France in the Caribbean. It consists of six inhabited islands— Basse-Terre, Grande-Terre, Marie-Galante, La Désirade, and the ...
and Martinique
Martinique ( , ; gcf, label=Martinican Creole, Matinik or ; Kalinago language, Kalinago: or ) is an island and an Overseas department and region, overseas department/region and single territorial collectivity of France. An integral part of ...
etc.), and 31.5% were born in foreign countries (primarily Suriname
Suriname (; srn, Sranankondre or ), officially the Republic of Suriname ( nl, Republiek Suriname , srn, Ripolik fu Sranan), is a country on the northeastern Atlantic coast of South America. It is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the north ...
, Brazil, and Haiti).
Estimates of the percentages of French Guiana ethnic composition are difficult to produce due to the presence of a large proportion of immigrants. People of African descent are the largest ethnic group, though estimates vary as to the exact percentage, depending upon whether the large Haitians, Haitian community is included as well. Generally, the Creole population is judged to be about 60–70% of the total population if Haitians (comprising roughly one-third of Creoles) are included, and 30–50% otherwise. There are also smaller groups from various Caribbean islands, mainly Martinique, Guadeloupe, and Saint Lucia.
Approximately 41,000 people or 14% of the population is of European ancestry. The vast majority of these are of French ancestry, though there are also people of Spanish and Portuguese people, Portuguese ancestry.
The main Asian communities are the Overseas Chinese, Chinese (about 3–4%, primarily from Zhejiang and Guangdong in mainland China) and Hmong people, Hmong from Laos (1–2%). Other groups from Asia include Indians in French Guiana, East Indians, Lebanese people, Lebanese and Vietnamese people, Vietnamese.
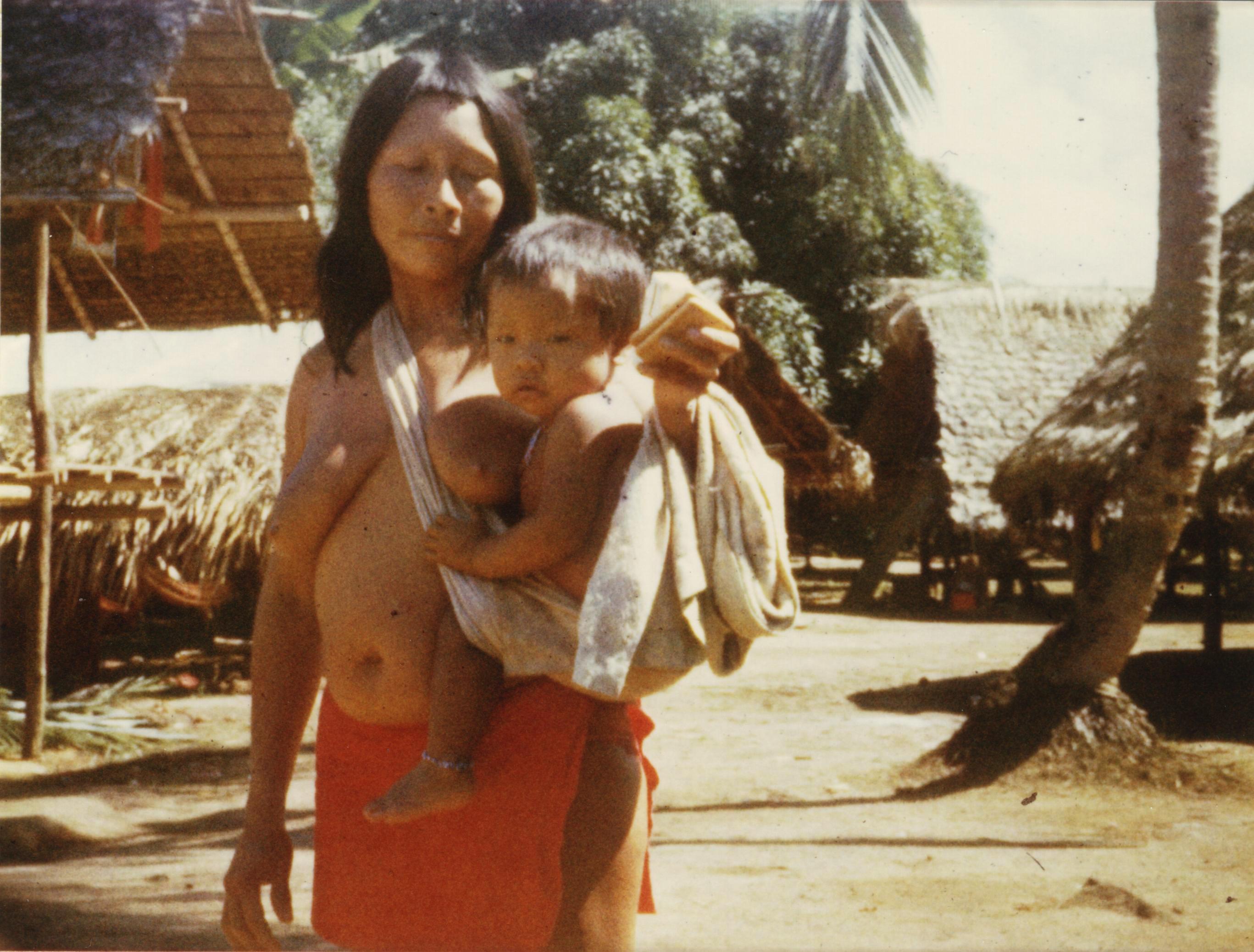
The main groups living in the interior are the Maroon (people), Maroons who are of African descent, and Indigenous peoples of the Americas, Amerindians. The Maroons, descendants of escaped African slaves, live primarily along the Maroni River. The main Maroon groups are the Saramaca, Aucan (both of whom also live in Suriname
Suriname (; srn, Sranankondre or ), officially the Republic of Suriname ( nl, Republiek Suriname , srn, Ripolik fu Sranan), is a country on the northeastern Atlantic coast of South America. It is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the north ...
), and Boni (Aluku).
The main Amerindian groups (forming about 3–4% of the population) are the Arawaks, Arawak, Kalina people, Carib, Emerillon people, Emerillon (now called the Teko people, Teko), Galibi (now called the Kaliña), Palikur people, Palikur, Wayampi and Wayana. As of the late 1990s, there was evidence of an Uncontacted peoples, uncontacted group of Wayampi.
Immigration
In recent years, French Guiana has seen an increase in Syrian refugees trying to escape the Syrian Civil War. For them and other groups of migrants, the majority arriving from Latin American and Middle Eastern countries (especially Cuba, Yemen, and State of Palestine, Palestine), its status as French territory makes it a "gateway" to Europe. Many live in crowded refugee camps with poor conditions and little protection from the elements. Neither local authorities nor the French government have made significant efforts to help the situation.Religion
 The dominant religion of French Guiana is Roman Catholicism; the Maroons and some Amerindian peoples maintain their own religions. The Hmong people are also largely Catholic owing to the influence of missionaries who helped bring them to French Guiana. Catholic Church in French Guiana, Guianan Catholics are part of the Diocese of Cayenne.
The dominant religion of French Guiana is Roman Catholicism; the Maroons and some Amerindian peoples maintain their own religions. The Hmong people are also largely Catholic owing to the influence of missionaries who helped bring them to French Guiana. Catholic Church in French Guiana, Guianan Catholics are part of the Diocese of Cayenne.
Fertility
The total fertility rate in French Guiana has remained high and is today considerably higher than that of metropolitan France, as well as most of the other Overseas department, French overseas departments. It is largely responsible for the rapid population growth of French Guiana.Languages
The official language of French Guiana is French, and it is the predominant language of the department, spoken by most residents as a first or second language. In addition, a number of other local languages exist. Regional languages include French Guianese Creole (not to be confused with Guyanese Creole), six Indigenous languages of the Americas, Amerindian languages (Arawakan languages, Arawak, Palikur language, Palijur, Carib language, Kali'na, Wayana language, Wayana, Wayampi language, Wayampi, Emerillon language, Emerillon), four Maroon (people), Maroon creole languages (Saramaka language, Saramaka, Paramaccan language, Paramaccan, Aluku language, Aluku, Ndyuka language, Ndyuka), as well as Hmong Njua. Other languages spoken include Portuguese language, Portuguese, Mandarin Chinese, Mandarin, Haitian Creole language, Haitian Creole and Spanish.Politics
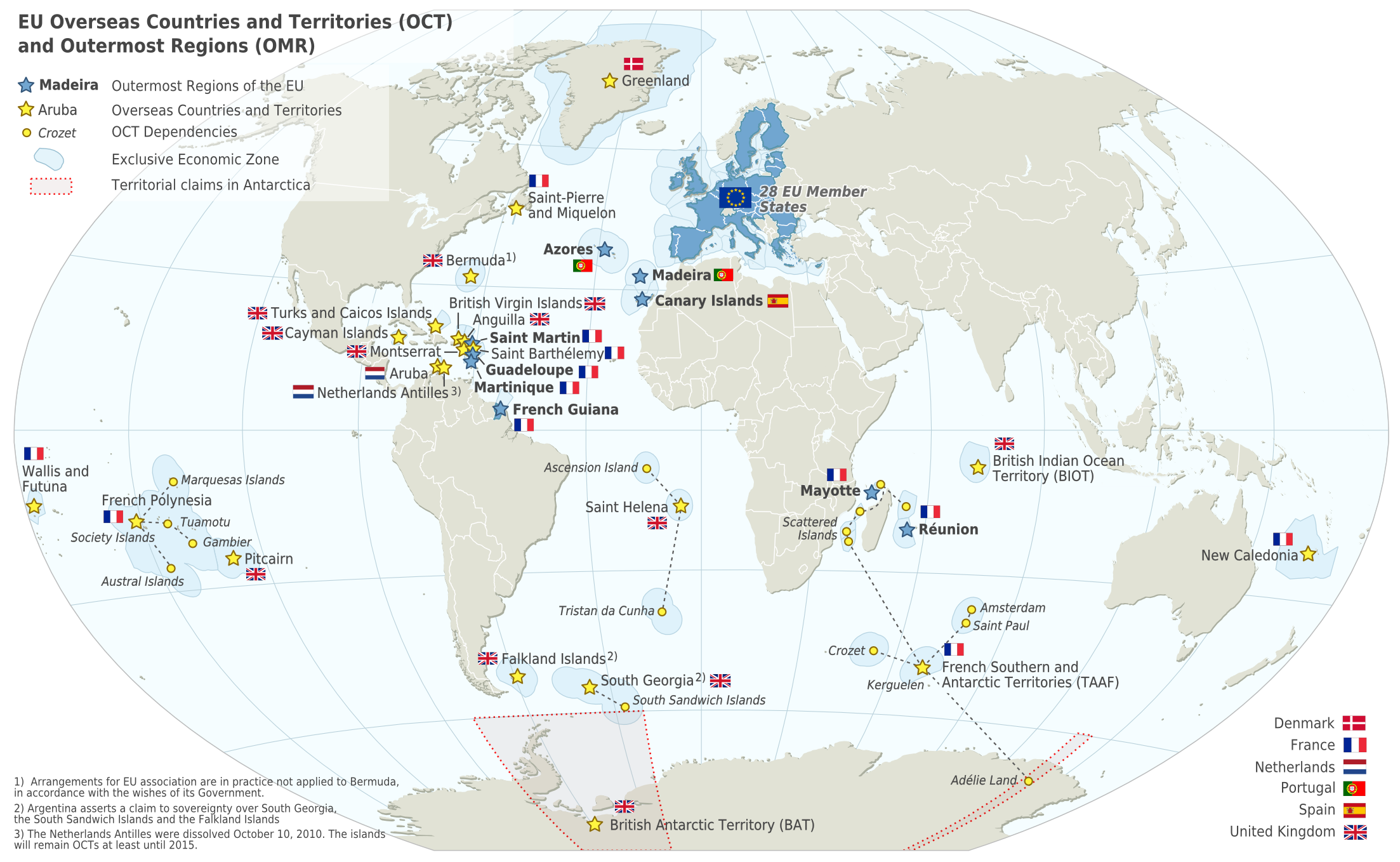
 French Guiana, as part of France, forms part of the
French Guiana, as part of France, forms part of the European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational political and economic union of member states that are located primarily in Europe. The union has a total area of and an estimated total population of about 447million. The EU has often been ...
– the largest landmass for an area outside of Europe (since Greenland left the European Community in 1985), with one of the longest EU external boundaries. It is one of only three Special member state territories and the European Union, European Union territories outside Europe that is not an island (the others being the Spanish Autonomous Cities in Africa, Ceuta and Melilla). As an integral part of France, its head of state is the president of the French Republic, and its head of government is the prime minister of France. The French government and its agencies have responsibility for a wide range of issues that are reserved to the national executive power, such as defense and external relations.
 The president of France appoints a Prefect (France), prefect (resident at the Prefectures in France, prefecture building in Cayenne) as his representative to head the local government of French Guiana. There is one elected, local executive body, the Assemblée de Guyane.
French Guiana sends two Member of Parliament, deputies to the National Assembly of France, French National Assembly, one representing the Communes of France, commune (municipality) of Cayenne and the commune of Macouria, and the other representing the rest of French Guiana. This latter constituency is the largest in the French Republic by land area. French Guiana also sends two senators to the Senate of France, French Senate. The first woman to be elected to the Senate was Marie-Laure Phinéra-Horth in 2020.
The Guianese Socialist Party dominated politics in French Guiana until 2010.
A chronic issue affecting French Guiana is the influx of illegal immigrants and clandestine gold prospecting, gold prospectors from Brazil and
The president of France appoints a Prefect (France), prefect (resident at the Prefectures in France, prefecture building in Cayenne) as his representative to head the local government of French Guiana. There is one elected, local executive body, the Assemblée de Guyane.
French Guiana sends two Member of Parliament, deputies to the National Assembly of France, French National Assembly, one representing the Communes of France, commune (municipality) of Cayenne and the commune of Macouria, and the other representing the rest of French Guiana. This latter constituency is the largest in the French Republic by land area. French Guiana also sends two senators to the Senate of France, French Senate. The first woman to be elected to the Senate was Marie-Laure Phinéra-Horth in 2020.
The Guianese Socialist Party dominated politics in French Guiana until 2010.
A chronic issue affecting French Guiana is the influx of illegal immigrants and clandestine gold prospecting, gold prospectors from Brazil and Suriname
Suriname (; srn, Sranankondre or ), officially the Republic of Suriname ( nl, Republiek Suriname , srn, Ripolik fu Sranan), is a country on the northeastern Atlantic coast of South America. It is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the north ...
. The border between the department and Suriname, the Maroni River, flows through rain forest and is difficult for the Gendarmerie Nationale (France), Gendarmerie and the French Foreign Legion to patrol. There have been several phases launched by the French government to combat illegal gold mining in French Guiana, beginning with Operation Anaconda beginning in 2003, followed by Operation Harpie in 2008 and 2009 and Operation Harpie Reinforce in 2010. Colonel François Müller, the commander of French Guiana's gendarmes, believes these operations have been successful. However, after each operation ends, Brazilian miners, , return. Soon after Operation Harpie Reinforce began, an altercation took place between French authorities and Brazilian miners. On 12 March 2010 a team of French soldiers and border police were attacked while returning from a successful operation, during which "the soldiers had arrested 15 miners, confiscated three boats, and seized 617 grams of gold... currently worth about $22,317". Garimpeiros returned to retrieve their lost loot and colleagues. The soldiers fired warning shots and rubber "flash balls", but the miners managed to retake one of their boats and about 500 grams of gold. "The violent reaction by the garimpeiros can be explained by the exceptional take of 617 grams of gold, about 20 percent of the quantity seized in 2009 during the battle against illegal mining", said Phillipe Duporge, the director of French Guiana's border police, at a press conference the next day.
Administrative divisions
French Guiana is divided into 3 Arrondissements of the Guyane department, arrondissements and 22 communes:Transport
 The transportation system in French Guiana is deficient compared to
The transportation system in French Guiana is deficient compared to Metropolitan France
Metropolitan France (french: France métropolitaine or ''la Métropole''), also known as European France (french: Territoire européen de la France) is the area of France which is geographically in Europe. This collective name for the European ...
, being concentrated in the coastal zone of the territory, while the inland municipalities are poorly connected and often difficult to access.
Road system
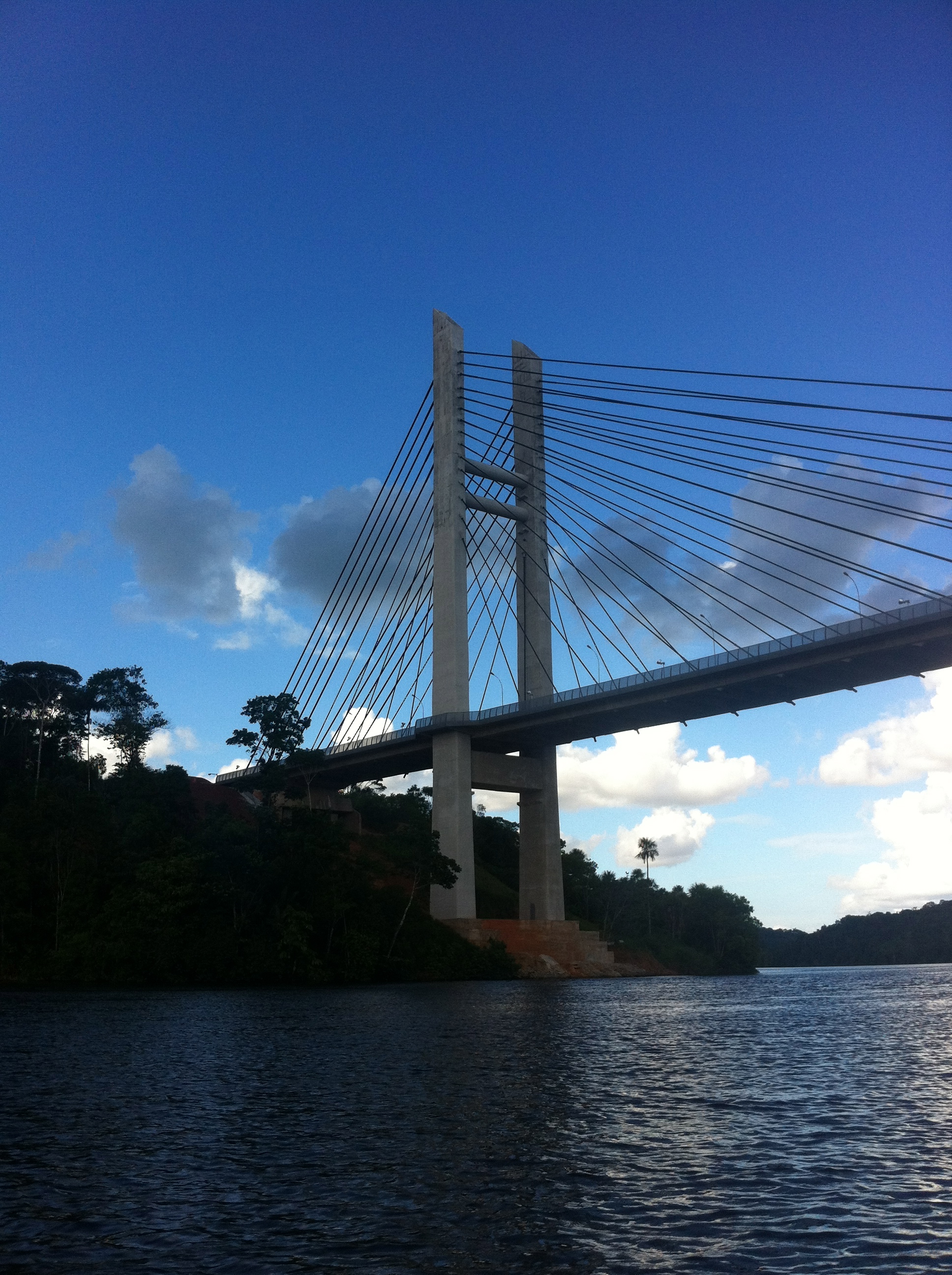
French Guiana has about 2,200 km of roads, which are divided into: * National roads (440 km), divided into RN1, RN2, RN3 and RN4 (the last two downgraded to departmental roads during Raffarin's tenure), which connect the main coastal towns, forming a corridor that crosses the coastal strip from the border with Suriname to that of Brazil: RN1, completed in the 1990s, links Cayenne to Saint-Laurent-du-Maroni, crossing the municipalities of Macouria, Kourou, Sinnamary (the stretch of road between Kourou and Sinnamary is locally called Route de l'espace, "space road") and Iracoubo, while RN2 runs from Cayenne to Saint-Georges-de-l'Oyapock, where it continues on BR-156 across the bridge over the Oyapock. Today, all rivers are crossed by road bridges, some of them quite long (e.g. the bridge over the Cayenne River is 1225 m long), whereas until 2004 (the year of completion and inauguration of the Approuague bridge) some rivers were still crossed by barges. Transport on national roads is restricted during the rainy season (from 48 to a maximum of 32 tons), while the maximum speed (monitored by the National Gendarmerie posts at Régina and Iracoubo, which are also in charge of controlling the possible flow of illegal traffic and irregular immigrants) is 90 km/h; * Departmental roads (408 km), subdivided into urban and rural departmental roads (rural roads), which serve the coastal Villages, 90% of which have no street lighting; * Communal roads or forest tracks (1. 311 km), most of which are closed to ordinary traffic and reserved for authorized personnel (employees of authorized mining or logging companies, forest rangers): the longest tracks are the Bélizon track in the commune of Saül (Guiana) (150 km), the Saint-Élie-diga track in Petit-Saut (26 km), the Coralie track (the oldest in the department, created to reach the Boulanger mine) and the Maripasoula-Papaïchton track. The communal roads are not usually paved and often go into the forest from the departmental roads; Despite the existence of numerous projects to upgrade and asphalt roads (such as the Bélizon road or the Apatou-Maripasoula-Saül axis), which are often opposed by environmental movements because of environmental fragmentation and problems for Amerindian and Maroon communities, several French Guiana municipalities (Ouanary, Camopi, Saül, Saint-Élie, Grand-Santi, Papaïchton, Maripasoula, Apatou) still do not have road access. Following a treaty between France and Brazil signed in July 2005, the Oyapock River Bridge over the Oyapock River was built and completed in 2011, becoming the first land crossing ever between French Guiana and the rest of the world (there exists no other bridge crossing the Oyapock River, and no bridge crossing the Maroni River marking the border with Suriname, although there is a ferry crossing to Albina, Suriname). The bridge was officially opened on 18 March 2017, however the border post construction on the Brazilian side caused additional delays. As of 2020, it possible to drive uninterrupted from Cayenne to Macapá (on the Amazon River), the capital of the state ofAmapá
Amapá () is one of the 26 states of Brazil. It is in the northern region of Brazil. It is the second least populous state and the eighteenth largest by area. Located in the far northern part of the country, Amapá is bordered clockwise by Fr ...
in Brazil.
Railway system
 At present, French Guiana does not have a railway system, with the exception of a small section in the Centre Spatial Guyanais used for the transport of components: when the territory was a penal colony, there were some railroad lines built by the prisoners themselves to connect the various baths with each other, the remains of which (now disused and mostly engulfed by the jungle) are still visible in some areas. These lines include the section from Montsinéry-Tonnegrande to the so-called bagne des Annamites, the section from Saint-Élie to the Saut du Tigre labor camp (now submerged by the artificial lake created by the Petit-Saut dam) and the section from Saint-Laurent-du-Maroni-Mana-Saint-Jean-du-Maroni.
At present, French Guiana does not have a railway system, with the exception of a small section in the Centre Spatial Guyanais used for the transport of components: when the territory was a penal colony, there were some railroad lines built by the prisoners themselves to connect the various baths with each other, the remains of which (now disused and mostly engulfed by the jungle) are still visible in some areas. These lines include the section from Montsinéry-Tonnegrande to the so-called bagne des Annamites, the section from Saint-Élie to the Saut du Tigre labor camp (now submerged by the artificial lake created by the Petit-Saut dam) and the section from Saint-Laurent-du-Maroni-Mana-Saint-Jean-du-Maroni.
Ports
Transportation by boat is quite widespread in French Guiana: among the most important Ports are the port of Dégrad-Des-Cannes, located at the mouth of the Mahury River, in the commune of Rémire-Montjoly, through which most of the imported or exported goods of the territory pass and where the local detachment of the ''Marine nationale'' is housed, and the port of Larivot, located in Matoury, where the Guyanese fishing fleet is concentrated. The port of Dégrad-Des-Cannes, built in 1969 to cope with the impossibility of the former port of Cayenne to decongest the growing maritime traffic, has a rather limited draft, and larger ships often prefer to dock at Ile du Salut to unload people and goods (which are then transported to the mainland by smaller ships) to avoid running aground. The port of Pariacabo in Kourou is home to the Colibri and Toucan ships, which carry components for Ariane missiles. The inland rivers are heavily traversed by canoes and other small boats, linking the villages on the Marowijne, Oyapock and Approuague Rivers, which often cannot be reached in any other way; the lake created by the Petit-Saut dam is also frequently crossed, although it is officially forbidden to cross the body of water. In the department, 460 km of aquatic environment are considered navigable.Airports
 French Guiana is served by Cayenne – Félix Eboué Airport, located in Matoury. There are also several Aerodrome, airstrips in the department, located in Camopi, Maripasoula, Ouanary, Saint-Georges-de-l'Oyapock, Saint-Laurent-du-Maroni and Saül, for a total of eleven hubs (four paved and seven unpaved).
From the main airport, there are two daily direct flights to Paris (Paris Orly airport, with an average flight time of about 8 hours and 25 minutes from French Guiana to the capital and 9 hours and 10 minutes vice-versa), offered by Air France and Air Caraïbes, as well as other flights to Fort-de-France, Pointe-à-Pitre, Port-au-Prince, Miami and Belém. The regional carrier Air Guyane Express also offers daily flights to Maripasoula and Saül, as well as more sporadic flights (mainly related to postal deliveries) to Saint-Georges-de-l'Oyapock and Camopi.
French Guiana is served by Cayenne – Félix Eboué Airport, located in Matoury. There are also several Aerodrome, airstrips in the department, located in Camopi, Maripasoula, Ouanary, Saint-Georges-de-l'Oyapock, Saint-Laurent-du-Maroni and Saül, for a total of eleven hubs (four paved and seven unpaved).
From the main airport, there are two daily direct flights to Paris (Paris Orly airport, with an average flight time of about 8 hours and 25 minutes from French Guiana to the capital and 9 hours and 10 minutes vice-versa), offered by Air France and Air Caraïbes, as well as other flights to Fort-de-France, Pointe-à-Pitre, Port-au-Prince, Miami and Belém. The regional carrier Air Guyane Express also offers daily flights to Maripasoula and Saül, as well as more sporadic flights (mainly related to postal deliveries) to Saint-Georges-de-l'Oyapock and Camopi.
Public transportation
 There is a public bus service that currently only covers the municipality of Cayenne and is run by the SMTC (Syndicat Mixte de Transport en Commun, now changed to Régie Communautaire des Transports – RCT) and consists of seven lines.
For connections between the coastal towns (except Montsinéry-Tonnegrande), the "collective cab" (Taxis Co) method is quite widespread, which are minibuses with a capacity of about ten people that leave as soon as there is a certain number of users on board. In 2010, the general council reached an agreement with some of the operators of this service to make it at least partially public under the name of TIG (Transporte Interurbano de la Guiana), with fixed departure times and predefined stops.
On the main rivers (Marowijne and Oyapock), there are pirogue services (called pirogues cabs), which go both to inland centers and across the border (such as Albina in Suriname or Oiapoque in Brazil).
There is a public bus service that currently only covers the municipality of Cayenne and is run by the SMTC (Syndicat Mixte de Transport en Commun, now changed to Régie Communautaire des Transports – RCT) and consists of seven lines.
For connections between the coastal towns (except Montsinéry-Tonnegrande), the "collective cab" (Taxis Co) method is quite widespread, which are minibuses with a capacity of about ten people that leave as soon as there is a certain number of users on board. In 2010, the general council reached an agreement with some of the operators of this service to make it at least partially public under the name of TIG (Transporte Interurbano de la Guiana), with fixed departure times and predefined stops.
On the main rivers (Marowijne and Oyapock), there are pirogue services (called pirogues cabs), which go both to inland centers and across the border (such as Albina in Suriname or Oiapoque in Brazil).
Military, police and security forces
French Armed Forces
French military forces in Guiana number around 2,000 personnelJournal of Guyana RFO TV 18 August 2009 and include the following: * The 9th Marine Infantry Regiment (9e RIMa) in Cayenne, the Madeleine.
* The 3rd Foreign Infantry Regiment (3e REI) in Kourou.
* The RSMAG Regiment (Adapted Military Service) of French Guiana, located in Saint-Jean-du-Maroni, with a detachment in Cayenne.
* Various detachments:
** 68 Air Transport Squadron which includes: five Aérospatiale SA 330 Puma, Puma helicopters, four Eurocopter Fennec, Fennec helicopters and three CASA/IPTN CN-235, Casa CN235 aircraft
** A platoon of the French Navy, based at the naval base of Dégrad des Cannes and operating two s: ''La Confiance'' and ''La Résolue''. One ''Engins de Débarquement Amphibie – Standards'' (EDA-S) landing craft is also to be delivered to naval forces based in French Guiana by 2025. The landing craft is to better support coastal and riverine operations in the territory.
** A detachment of the Paris Fire Brigade in Kourou, ensuring the protection of the
* The 9th Marine Infantry Regiment (9e RIMa) in Cayenne, the Madeleine.
* The 3rd Foreign Infantry Regiment (3e REI) in Kourou.
* The RSMAG Regiment (Adapted Military Service) of French Guiana, located in Saint-Jean-du-Maroni, with a detachment in Cayenne.
* Various detachments:
** 68 Air Transport Squadron which includes: five Aérospatiale SA 330 Puma, Puma helicopters, four Eurocopter Fennec, Fennec helicopters and three CASA/IPTN CN-235, Casa CN235 aircraft
** A platoon of the French Navy, based at the naval base of Dégrad des Cannes and operating two s: ''La Confiance'' and ''La Résolue''. One ''Engins de Débarquement Amphibie – Standards'' (EDA-S) landing craft is also to be delivered to naval forces based in French Guiana by 2025. The landing craft is to better support coastal and riverine operations in the territory.
** A detachment of the Paris Fire Brigade in Kourou, ensuring the protection of the Guiana Space Centre
The Guiana Space Centre (french: links=no, Centre spatial guyanais; CSG), also called Europe's Spaceport, is a European spaceport to the northwest of Kourou in French Guiana, a region of France in South America. Kourou is located approximat ...
.
Gendarmerie and National Police
* Elements of the National Gendarmerie (France), National Gendarmerie (some 840 personnel) and French National Police, the national police are deployed in French Guiana and are divided into 16 "brigades". These serve Cayenne, Remire-Montjoly, Cacao, French Guiana, Cacao, Régina, Saint-Georges-de-l'Oyapock, Camopi, Macouria, Kourou, Sinnamary, Iracoubo, Mana, Saint-Laurent-du-Maroni, Apatou, Grand-Santi,Papaïchton
Papaichton (unofficial spelling Papaïchton with a trema) is a commune in the overseas region and department of French Guiana. The village lies on the shores of the Lawa River. Papaichton is served by the Maripasoula Airport.
The village whic ...
, Maripasoula and Matoury. The National Gendarmerie include five mobile gendarmerie squadrons.
** The Maritime Gendarmerie operates the patrol boats Vedette côtière de surveillance maritime, ''Charente'' and ''Organabo'' in the territory, ''Charente'' having been deployed to the territory in 2022 to replace the previous boat ''Mahury'' which was no longer deemed serviceable.
Culture
Architecture


 The local architecture is characterized by its Guianan Creole, Creole, Amerindian and Bushinenge influences. The main towns contain predominantly Creole-style architecture, with some Western-style buildings and forts. In the communes with the black maroon populations one can see houses of bushinengue styles. And the Amerindian communes are recognized for their pre-colonial type carbets. Most of these buildings were designed with local materials, such as wood from the Amazonian forests and bricks made on site. These local architectures blend with contemporary style buildings.
The local architecture is characterized by its Guianan Creole, Creole, Amerindian and Bushinenge influences. The main towns contain predominantly Creole-style architecture, with some Western-style buildings and forts. In the communes with the black maroon populations one can see houses of bushinengue styles. And the Amerindian communes are recognized for their pre-colonial type carbets. Most of these buildings were designed with local materials, such as wood from the Amazonian forests and bricks made on site. These local architectures blend with contemporary style buildings.
Festivities
 The Carnival is one of the major events in French Guiana. Considered the longest in the world, it takes place on afternoon of Sunday, between Epiphany (holiday), Epiphany at the beginning of January and Ash Wednesday in February or (month). Groups disguised according to the theme of the year parade around decorated floats to the rhythm of percussion and brass. The preparation of the groups starts months before the carnival. The groups parade in front of thousands of spectators who gather on the sidewalks and bleachers arranged for the occasion.
Brazilian groups identical to those in the Carnival in Rio de Janeiro, Rio carnival are also appreciated for their rhythms and their alluring costumes. The Chinese community of Cayenne also participates in the parades, bringing its characteristic touch, dragons.
At the start of the evening, the Touloulous, typical characters of the Guianan carnival, go to the Nightclub, dancings to participate in the famous Masquerade ball#Contemporary era, paré-masked balls.
The Carnival is one of the major events in French Guiana. Considered the longest in the world, it takes place on afternoon of Sunday, between Epiphany (holiday), Epiphany at the beginning of January and Ash Wednesday in February or (month). Groups disguised according to the theme of the year parade around decorated floats to the rhythm of percussion and brass. The preparation of the groups starts months before the carnival. The groups parade in front of thousands of spectators who gather on the sidewalks and bleachers arranged for the occasion.
Brazilian groups identical to those in the Carnival in Rio de Janeiro, Rio carnival are also appreciated for their rhythms and their alluring costumes. The Chinese community of Cayenne also participates in the parades, bringing its characteristic touch, dragons.
At the start of the evening, the Touloulous, typical characters of the Guianan carnival, go to the Nightclub, dancings to participate in the famous Masquerade ball#Contemporary era, paré-masked balls.
Cuisine


 Guianan cuisine is rich in the different cultures that mix in French Guiana. Creole restaurants rub shoulders with Chinese restaurants in large cities such as Cayenne, Kourou and Saint-Laurent-du-Maroni. The local culinary art originally brought together Guianan Creole, Bushinengue and Indigenous peoples of South America, Native American cuisines.
All of these cuisines have several ingredients in common:
* Manioc;
* Smoked meats and fish
This southern Caribbean territory has many typical dishes, such as Awara broth, Galette#Creole galette, Creole galette, Dizé milé, Countess (cake), Countess, Cramanioc pudding, Kalawanng, Couac gratin and salad, Fricasse of iguana or its famous Pimentade (fish or chicken court-bouillon).
Atipas are local fishes beloved by the French Guianese often prepared with coconut milk.
At Easter, Guianan people eat a traditional dish called Awara broth.
For weddings, locals traditionally eat Colombo, which is a type of curry that has become a staple of the French Guianese cuisine.
Guianan cuisine is rich in the different cultures that mix in French Guiana. Creole restaurants rub shoulders with Chinese restaurants in large cities such as Cayenne, Kourou and Saint-Laurent-du-Maroni. The local culinary art originally brought together Guianan Creole, Bushinengue and Indigenous peoples of South America, Native American cuisines.
All of these cuisines have several ingredients in common:
* Manioc;
* Smoked meats and fish
This southern Caribbean territory has many typical dishes, such as Awara broth, Galette#Creole galette, Creole galette, Dizé milé, Countess (cake), Countess, Cramanioc pudding, Kalawanng, Couac gratin and salad, Fricasse of iguana or its famous Pimentade (fish or chicken court-bouillon).
Atipas are local fishes beloved by the French Guianese often prepared with coconut milk.
At Easter, Guianan people eat a traditional dish called Awara broth.
For weddings, locals traditionally eat Colombo, which is a type of curry that has become a staple of the French Guianese cuisine.
Literature
French Guiana literature includes all works written by local authors or persons related to French Guiana. It is expressed both in French and in French Guianese Creole, Guianan Creole. Local literature is a literature closely related to that of the French West Indies: especially the List of Caribbean islands, Caribbean islands ofMartinique
Martinique ( , ; gcf, label=Martinican Creole, Matinik or ; Kalinago language, Kalinago: or ) is an island and an Overseas department and region, overseas department/region and single territorial collectivity of France. An integral part of ...
and Guadeloupe
Guadeloupe (; ; gcf, label=Antillean Creole, Gwadloup, ) is an archipelago and overseas department and region of France in the Caribbean. It consists of six inhabited islands— Basse-Terre, Grande-Terre, Marie-Galante, La Désirade, and the ...
. For some, it is an Antilles, Antillean-Guiana Shield, Guyanese literature in relation to the themes addressed, which are mainly related to slavery and other social problems. Thus, this literature takes several forms. First, orality, because it is a characteristic element of Guianan literature, as in many countries of Black America. In this connection, we can consider tales, Legends, fables and, in another form, Novels.
Nineteenth century French Guiana is marked by a weak presence of writers. At that time, writers only published a few scattered poems in local newspapers. Today, however, it is difficult to trace the writings of some French Guianan poets: Ho-A-Sim-Elosem, Munian, R. Octaville, etc. Two Guianan poets are the exception. According to Ndagano (1996), Ismaÿl Urbain and Fabien Flavien would be considered the first French Guianan poets. However, Alfred Parépou is a writer who marked his era with his work Atipa (1885).
The period from 1900 to 1950 constitutes an important stage in local literature insofar as it gave birth to numerous writers who had a considerable impact, such as those of Négritude, Negritude (Négritude). The Guianan of the 1950s and 1960s is notable for writing about the black cause. Serge Patient and Elie Stephenson did address this issue in their writings.
Since 1970 different generations of writers have become aware of the black cause or slavery. Whether through their writings or their political activities, they take into account this painful period that had serious consequences on the local society and on the black world in general. For this generation, Christiane Taubira remains the figurehead. Other writers are interested in other types of themes, such as regional nature, etc.
Sport
Sport in French Guiana dates back to long before the colonial period. Popularized since the 19th century, the first sports competition organized to commemorate 14 July was held in 1890. At that time, there were already physical activities favorable to the inhabitants of this Amazon rainforest, Amazonian territory, but also sports coming from Europe, which favored the Colonization, colonizers. There were foot races, donkey races, canoe races, bicycle races, tricycle races, nautical regattas in the ports, and traditional popular games. The most popular sport in French Guiana today is football, followed by basketball, cycling, swimming and handball, although there are some canoeing, judo, Brazilian jiu-jitsu, aikido, karate, fencing, horseback riding, rowing and volleyball clubs in the department. As a French Overseas department, Guiana is not a member of the Pan American Sports Organization; rather, athletes compete within the French National Olympic and Sports Committee and are governed by the Ligue d'Athlétisme de la Guyane, a sub-unit of the Fédération française d'athlétisme. Starting in 1960, the Tour of Guiana, an annual stage race, multiple-stage bicycle racing, bicycle race, is held.Football
The territory has its own local team, the French Guiana national football team, French Guiana football team. A regional football league, the French Guiana Football League, was established in October 1962. It is currently not affiliated to FIFA, but has been affiliated to the FFF since 27 April 1963 and has been an associate member of CONCACAF (North, Central American and Caribbean League) since 1978. In April 2013, the LFG became a full member of CONCACAF. The French Guiana Football Team, also known as Yana Dòkò, is a selection of the best local players under the auspices of the Guiana Football League. It is not recognized by FIFA, but participates in CONCACAF competitions. It played its first match against Dutch Guiana national football team, Dutch Guiana (nowSuriname
Suriname (; srn, Sranankondre or ), officially the Republic of Suriname ( nl, Republiek Suriname , srn, Ripolik fu Sranan), is a country on the northeastern Atlantic coast of South America. It is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the north ...
) in 1936, losing 1 to 3. It had its biggest victory on 26 September 2012 against Saint Pierre and Miquelon, St. Pierre and Miquelon (11 to 1) and its biggest defeat was also against Dutch Guiana, losing 9 to 0 on 2 March 1947.
The team has participated in events such as the CONCACAF Nations Cup / 2021 CONCACAF Gold Cup, Gold Cup, Caribbean Cup, Caribbean Nations Cup (between 1978 and 2017), CONCACAF Nations League, Overseas Cup (Coupe de l'Outre-Mer, 2008–2012) and the Tournament of 4 (Tournoi des 4).

Tour
The Tour of Guiana (locally: Tour de Guyane), formerly known as "Le Tour du Littoral" (the Littoral Tour) or more rarely as "La Grande Boucle Guayanaise", is a road bicycle racing, cycling stage race that takes place mainly in French Guiana each year, although it occasionally crosses neighbouring countries. It takes place in nine stages, with a route linking the main towns of the department: Cayenne, Kourou, and Saint-Laurent-du-Maroni. It was created in 1950 and is organised by the Comité Régional de Cyclisme de la Guyane (French Guiana Cycling Committee). The tour has been international since 1978. Over the years it has gained in importance and popularity and its duration has increased. The participation has grown from a mostly French Guianan group in the first editions to editions with more than 10 different nationalities. The 2020 edition of the Tour could not take place due to the COVID-19 pandemic. This is also the case for the Tour in 2021.
In popular culture
The novel ''Papillon (book), Papillon'', by the French convict Henri Charrière, is set in French Guiana. It was first published in France in 1969, describing his escape from a penal colony there. Becoming an instant bestseller, it was translated into English from the original French by June P. Wilson and Walter B. Michaels for a 1970 edition, and by author Patrick O'Brian. Soon afterward the book was adapted for a Hollywood Papillon (1973 film), film of the same name. Charrière stated that all events in the book are truthful and accurate, allowing for minor lapses in memory. Since its publication there has been controversy over its accuracy.Randall, Colin (27 June 2005Ex-convict aged 104 claims to be Papillon
Telegraph.co.uk
See also
* Index of French Guiana-related articles * List of colonial and departmental heads of French Guiana * Republic of Independent GuianaReferences
Further reading
* Robert Aldrich and John Connell. ''France's Overseas Frontier : Départements et territoires d'outre-mer'' Cambridge University Press, 2006. . * René Belbenoit. ''Dry guillotine: Fifteen years among the living dead'' 1938, Reprint: Berkley (1975). . * René Belbenoit. ''Hell on Trial'' 1940, translated from the original French manuscript by Preston Rambo. E. P Dutton & Co. Reprint by Blue Ribbon Books, New York, 194 p. Reprint: Bantam Books, 1971. * Henri Charrière. ''Papillon'' Reprints: Hart-Davis, MacGibbon Ltd. 1970. (hbk); Perennial, 2001. (sbk). * John Gimlette, ''Wild Coast: Travels on South America's Untamed Edge'' 2011 * * Peter Redfield. ''Space in the Tropics: From Convicts to Rockets in French Guiana'' . * Miranda Frances Spieler. ''Empire and Underworld: Captivity in French Guiana'' (Harvard University Press; 2012) studies slaves, criminals, indentured workers, and other marginalized people from 1789 to 1870.External links
*Prefecture website
Collectivité territoriale de Guyane website
Tourism committee of French Guiana
{{Authority control French Guiana, The Guianas Overseas departments of France Former colonies in South America Former French colonies French colonization of the Americas Departments of France Regions of France Outermost regions of the European Union French Caribbean, Guiana French Union, Guiana French-speaking countries and territories States and territories established in 1946 1946 establishments in the French Union 1946 establishments in South America Dependent territories in South America Enclaves and exclaves