Griphosaurus on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
''Archaeopteryx'' (; ), sometimes referred to by its German name, "" ( ''Primeval Bird''), is a genus of bird-like dinosaurs. The name derives from the ancient Greek (''archaīos''), meaning "ancient", and (''ptéryx''), meaning "feather" or "wing". Between the late 19th century and the early 21st century, ''Archaeopteryx'' was generally accepted by palaeontologists and popular reference books as the oldest known bird (member of the group Avialae). Older potential avialans have since been identified, including '' Anchiornis'', '' Xiaotingia'', and '' Aurornis''.
''Archaeopteryx'' lived in the Late Jurassic around 150 million years ago, in what is now southern Germany, during a time when Europe was an archipelago of islands in a shallow warm tropical sea, much closer to the
 Over the years, twelve body fossil specimens of ''Archaeopteryx'' have been found. All of the fossils come from the limestone deposits, quarried for centuries, near , Germany.
Over the years, twelve body fossil specimens of ''Archaeopteryx'' have been found. All of the fossils come from the limestone deposits, quarried for centuries, near , Germany.
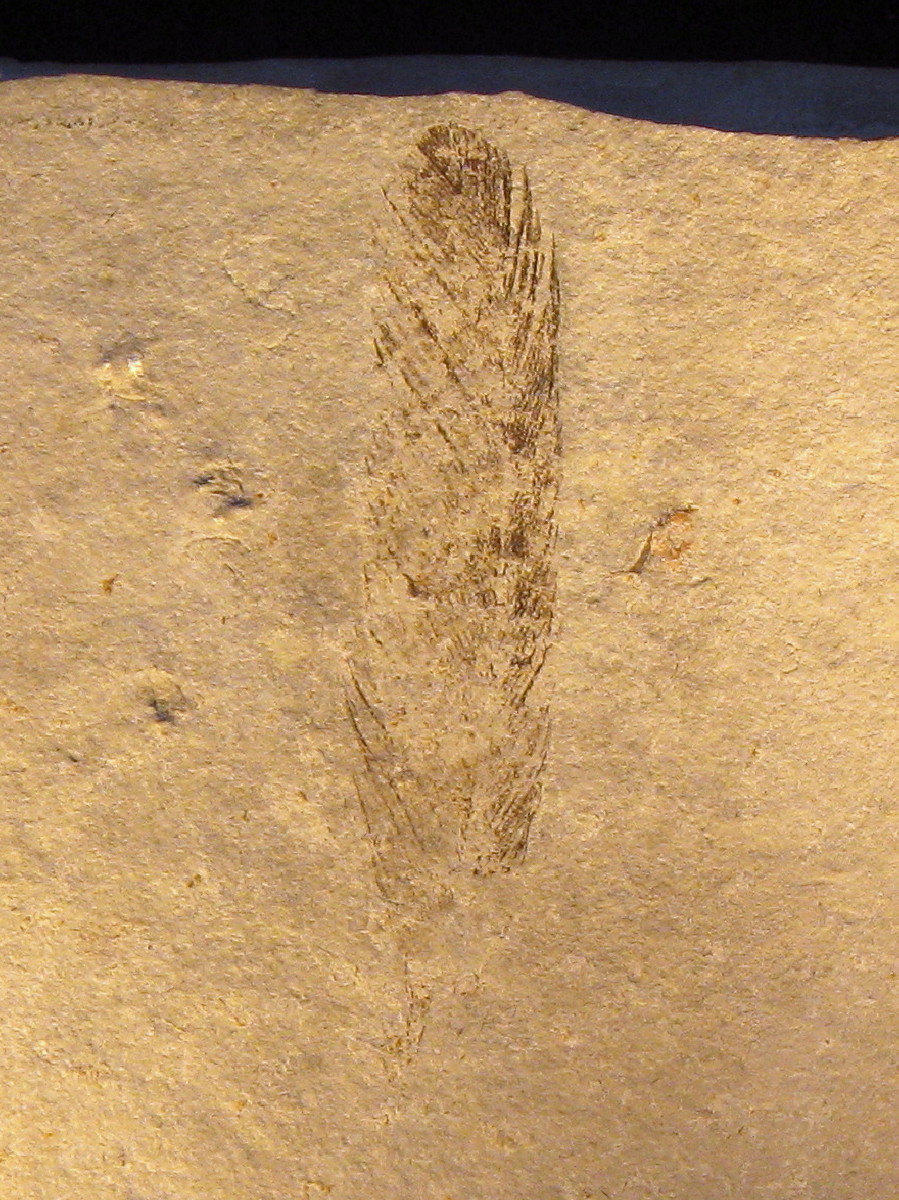 The initial discovery, a single feather, was unearthed in 1860 or 1861 and described in 1861 by . It is currently located at the Natural History Museum of Berlin. Though it was the initial holotype, there were indications that it might not have been from the same animal as the body fossils. In 2019 it was reported that laser imaging had revealed the structure of the quill (which had not been visible since some time after the feather was described), and that the feather was inconsistent with the morphology of all other ''Archaeopteryx'' feathers known, leading to the conclusion that it originated from another dinosaur. This conclusion was challenged in 2020 as being unlikely; the feather was identified on the basis of morphology as most likely having been an upper major primary
The initial discovery, a single feather, was unearthed in 1860 or 1861 and described in 1861 by . It is currently located at the Natural History Museum of Berlin. Though it was the initial holotype, there were indications that it might not have been from the same animal as the body fossils. In 2019 it was reported that laser imaging had revealed the structure of the quill (which had not been visible since some time after the feather was described), and that the feather was inconsistent with the morphology of all other ''Archaeopteryx'' feathers known, leading to the conclusion that it originated from another dinosaur. This conclusion was challenged in 2020 as being unlikely; the feather was identified on the basis of morphology as most likely having been an upper major primary  Composed of a torso, the
Composed of a torso, the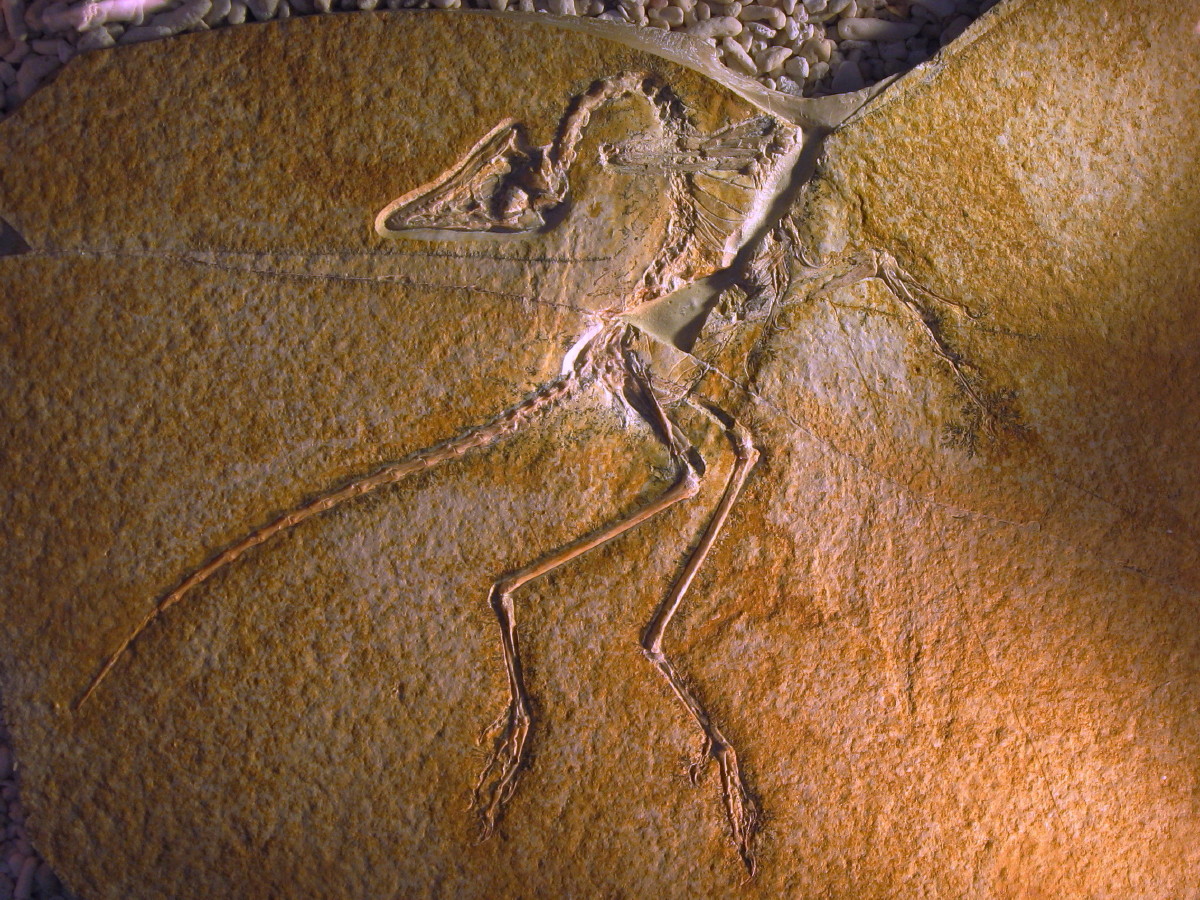  The Eichstätt Specimen (JM 2257) was discovered in 1951 near Workerszell, Germany, and described by Peter Wellnhofer in 1974. Currently located at the Jura Museum in Eichstätt, Germany, it is the smallest known specimen and has the second-best head. It is possibly a separate genus (''Jurapteryx recurva'') or species (''A. recurva'').
The Solnhofen Specimen (unnumbered specimen) was discovered in the 1970s near Eichstätt, Germany, and described in 1988 by Wellnhofer. Currently located at the Bürgermeister-Müller-Museum in Solnhofen, it originally was classified as '' Compsognathus'' by an amateur collector, the same mayor Friedrich Müller after which the museum is named. It is the largest specimen known and may belong to a separate genus and species, '' Wellnhoferia grandis''. It is missing only portions of the neck, tail, backbone, and head.
The Munich Specimen (BSP 1999 I 50, formerly known as the ''Solenhofer-Aktien-Verein Specimen'') was discovered on 3 August 1992 near Langenaltheim and described in 1993 by Wellnhofer. It is currently located at the Paläontologisches Museum München in Munich, to which it was sold in 1999 for 1.9 million Deutschmark. What was initially believed to be a bony sternum turned out to be part of the coracoid, but a cartilaginous sternum may have been present. Only the front of its face is missing. It has been used as the basis for a distinct species, ''A. bavarica'', but more recent studies suggest it belongs to ''A. siemensii''.
The Eichstätt Specimen (JM 2257) was discovered in 1951 near Workerszell, Germany, and described by Peter Wellnhofer in 1974. Currently located at the Jura Museum in Eichstätt, Germany, it is the smallest known specimen and has the second-best head. It is possibly a separate genus (''Jurapteryx recurva'') or species (''A. recurva'').
The Solnhofen Specimen (unnumbered specimen) was discovered in the 1970s near Eichstätt, Germany, and described in 1988 by Wellnhofer. Currently located at the Bürgermeister-Müller-Museum in Solnhofen, it originally was classified as '' Compsognathus'' by an amateur collector, the same mayor Friedrich Müller after which the museum is named. It is the largest specimen known and may belong to a separate genus and species, '' Wellnhoferia grandis''. It is missing only portions of the neck, tail, backbone, and head.
The Munich Specimen (BSP 1999 I 50, formerly known as the ''Solenhofer-Aktien-Verein Specimen'') was discovered on 3 August 1992 near Langenaltheim and described in 1993 by Wellnhofer. It is currently located at the Paläontologisches Museum München in Munich, to which it was sold in 1999 for 1.9 million Deutschmark. What was initially believed to be a bony sternum turned out to be part of the coracoid, but a cartilaginous sternum may have been present. Only the front of its face is missing. It has been used as the basis for a distinct species, ''A. bavarica'', but more recent studies suggest it belongs to ''A. siemensii''.
 An eighth, fragmentary specimen was discovered in 1990 in the younger Mörnsheim Formation at
An eighth, fragmentary specimen was discovered in 1990 in the younger Mörnsheim Formation at  Another fragmentary fossil was found in 2000. It is in private possession and, since 2004, on loan to the Bürgermeister-Müller Museum in Solnhofen, so it is called the Bürgermeister-Müller Specimen; the institute itself officially refers to it as the "Exemplar of the families Ottman & Steil, Solnhofen". As the fragment represents the remains of a single wing of ''Archaeopteryx'', it is colloquially known as "chicken wing".
Another fragmentary fossil was found in 2000. It is in private possession and, since 2004, on loan to the Bürgermeister-Müller Museum in Solnhofen, so it is called the Bürgermeister-Müller Specimen; the institute itself officially refers to it as the "Exemplar of the families Ottman & Steil, Solnhofen". As the fragment represents the remains of a single wing of ''Archaeopteryx'', it is colloquially known as "chicken wing".
 Long in a private collection in Switzerland, the Thermopolis Specimen (WDC CSG 100) was discovered in Bavaria and described in 2005 by Mayr, Pohl, and Peters. Donated to the Wyoming Dinosaur Center in Thermopolis, Wyoming, it has the best-preserved head and feet; most of the neck and the lower jaw have not been preserved. The "Thermopolis" specimen was described on 2 December 2005 ''Science'' journal article as "A well-preserved ''Archaeopteryx'' specimen with theropod features"; it shows that ''Archaeopteryx'' lacked a reversed toe—a universal feature of birds—limiting its ability to perch on branches and implying a terrestrial or trunk-climbing lifestyle. This has been interpreted as evidence of theropod ancestry. In 1988, Gregory S. Paul claimed to have found evidence of a hyperextensible second toe, but this was not verified and accepted by other scientists until the Thermopolis specimen was described. "Until now, the feature was thought to belong only to the species' close relatives, the deinonychosaurs." The Thermopolis Specimen was assigned to ''Archaeopteryx siemensii'' in 2007. The specimen is considered to represent the most complete and best-preserved ''Archaeopteryx'' remains yet.
Long in a private collection in Switzerland, the Thermopolis Specimen (WDC CSG 100) was discovered in Bavaria and described in 2005 by Mayr, Pohl, and Peters. Donated to the Wyoming Dinosaur Center in Thermopolis, Wyoming, it has the best-preserved head and feet; most of the neck and the lower jaw have not been preserved. The "Thermopolis" specimen was described on 2 December 2005 ''Science'' journal article as "A well-preserved ''Archaeopteryx'' specimen with theropod features"; it shows that ''Archaeopteryx'' lacked a reversed toe—a universal feature of birds—limiting its ability to perch on branches and implying a terrestrial or trunk-climbing lifestyle. This has been interpreted as evidence of theropod ancestry. In 1988, Gregory S. Paul claimed to have found evidence of a hyperextensible second toe, but this was not verified and accepted by other scientists until the Thermopolis specimen was described. "Until now, the feature was thought to belong only to the species' close relatives, the deinonychosaurs." The Thermopolis Specimen was assigned to ''Archaeopteryx siemensii'' in 2007. The specimen is considered to represent the most complete and best-preserved ''Archaeopteryx'' remains yet.
 The discovery of an eleventh specimen was announced in 2011; it was described in 2014. It is one of the more complete specimens, but is missing much of the skull and one forelimb. It is privately owned and has yet to be given a name. Palaeontologists of the
The discovery of an eleventh specimen was announced in 2011; it was described in 2014. It is one of the more complete specimens, but is missing much of the skull and one forelimb. It is privately owned and has yet to be given a name. Palaeontologists of the
 Most of the specimens of ''Archaeopteryx'' that have been discovered come from the Solnhofen limestone in Bavaria, southern Germany, which is a , a rare and remarkable geological formation known for its superbly detailed fossils laid down during the early Tithonian stage of the Jurassic period, approximately 150.8–148.5million years ago.
''Archaeopteryx'' was roughly the size of a
Most of the specimens of ''Archaeopteryx'' that have been discovered come from the Solnhofen limestone in Bavaria, southern Germany, which is a , a rare and remarkable geological formation known for its superbly detailed fossils laid down during the early Tithonian stage of the Jurassic period, approximately 150.8–148.5million years ago.
''Archaeopteryx'' was roughly the size of a
 Specimens of ''Archaeopteryx'' were most notable for their well-developed
Specimens of ''Archaeopteryx'' were most notable for their well-developed
 In 2011, graduate student Ryan Carney and colleagues performed the first colour study on an ''Archaeopteryx'' specimen. Using scanning electron microscopy technology and energy-dispersive X-ray analysis, the team was able to detect the structure of melanosomes in the isolated feather specimen described in 1861. The resultant measurements were then compared to those of 87modern bird species, and the original colour was calculated with a 95% likelihood to be black. The feather was determined to be black throughout, with heavier pigmentation in the distal tip. The feather studied was most probably a dorsal covert, which would have partly covered the primary feathers on the wings. The study does not mean that ''Archaeopteryx'' was entirely black, but suggests that it had some black colouration which included the coverts. Carney pointed out that this is consistent with what we know of modern flight characteristics, in that black melanosomes have structural properties that strengthen feathers for flight. In a 2013 study published in the ''Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry'', new analyses of ''Archaeopteryxs feathers revealed that the animal may have had complex light- and dark-coloured plumage, with heavier pigmentation in the distal tips and outer vanes. This analysis of color distribution was based primarily on the distribution of sulphate within the fossil. An author on the previous ''Archaeopteryx'' color study argued against the interpretation of such biomarkers as an indicator of eumelanin in the full ''Archaeopteryx'' specimen. Carney and other colleagues also argued against the 2013 study's interpretation of the sulphate and trace metals, and in a 2020 study published in ''Scientific Reports'' demonstrated that the isolated covert feather was entirely matte black (as opposed to black and white, or iridescent) and that the remaining "plumage patterns of ''Archaeopteryx'' remain unknown".
In 2011, graduate student Ryan Carney and colleagues performed the first colour study on an ''Archaeopteryx'' specimen. Using scanning electron microscopy technology and energy-dispersive X-ray analysis, the team was able to detect the structure of melanosomes in the isolated feather specimen described in 1861. The resultant measurements were then compared to those of 87modern bird species, and the original colour was calculated with a 95% likelihood to be black. The feather was determined to be black throughout, with heavier pigmentation in the distal tip. The feather studied was most probably a dorsal covert, which would have partly covered the primary feathers on the wings. The study does not mean that ''Archaeopteryx'' was entirely black, but suggests that it had some black colouration which included the coverts. Carney pointed out that this is consistent with what we know of modern flight characteristics, in that black melanosomes have structural properties that strengthen feathers for flight. In a 2013 study published in the ''Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry'', new analyses of ''Archaeopteryxs feathers revealed that the animal may have had complex light- and dark-coloured plumage, with heavier pigmentation in the distal tips and outer vanes. This analysis of color distribution was based primarily on the distribution of sulphate within the fossil. An author on the previous ''Archaeopteryx'' color study argued against the interpretation of such biomarkers as an indicator of eumelanin in the full ''Archaeopteryx'' specimen. Carney and other colleagues also argued against the 2013 study's interpretation of the sulphate and trace metals, and in a 2020 study published in ''Scientific Reports'' demonstrated that the isolated covert feather was entirely matte black (as opposed to black and white, or iridescent) and that the remaining "plumage patterns of ''Archaeopteryx'' remain unknown".
 Today, fossils of the genus ''Archaeopteryx'' are usually assigned to one or two species, ''A. lithographica'' and ''A. siemensii'', but their taxonomic history is complicated. Ten names have been published for the handful of specimens. As interpreted today, the name ''A. lithographica'' only referred to the single feather described by Meyer. In 1954 Gavin de Beer concluded that the London specimen was the holotype. In 1960, Swinton accordingly proposed that the name ''Archaeopteryx lithographica'' be placed on the official genera list making the alternative names ''Griphosaurus'' and ''Griphornis'' invalid. The ICZN, implicitly accepting De Beer's standpoint, did indeed suppress the plethora of alternative names initially proposed for the first skeleton specimens, which mainly resulted from the acrimonious dispute between Meyer and his opponent Johann Andreas Wagner (whose ''Griphosaurus problematicus'' – 'problematic riddle-lizard' – was a vitriolic sneer at Meyer's ''Archaeopteryx''). In addition, in 1977, the Commission ruled that the first species name of the Haarlem specimen, ''crassipes'', described by Meyer as a pterosaur before its true nature was realized, was not to be given preference over ''lithographica'' in instances where scientists considered them to represent the same species.
It has been noted that the feather, the first specimen of ''Archaeopteryx'' described, does not correspond well with the flight-related feathers of ''Archaeopteryx''. It certainly is a
Today, fossils of the genus ''Archaeopteryx'' are usually assigned to one or two species, ''A. lithographica'' and ''A. siemensii'', but their taxonomic history is complicated. Ten names have been published for the handful of specimens. As interpreted today, the name ''A. lithographica'' only referred to the single feather described by Meyer. In 1954 Gavin de Beer concluded that the London specimen was the holotype. In 1960, Swinton accordingly proposed that the name ''Archaeopteryx lithographica'' be placed on the official genera list making the alternative names ''Griphosaurus'' and ''Griphornis'' invalid. The ICZN, implicitly accepting De Beer's standpoint, did indeed suppress the plethora of alternative names initially proposed for the first skeleton specimens, which mainly resulted from the acrimonious dispute between Meyer and his opponent Johann Andreas Wagner (whose ''Griphosaurus problematicus'' – 'problematic riddle-lizard' – was a vitriolic sneer at Meyer's ''Archaeopteryx''). In addition, in 1977, the Commission ruled that the first species name of the Haarlem specimen, ''crassipes'', described by Meyer as a pterosaur before its true nature was realized, was not to be given preference over ''lithographica'' in instances where scientists considered them to represent the same species.
It has been noted that the feather, the first specimen of ''Archaeopteryx'' described, does not correspond well with the flight-related feathers of ''Archaeopteryx''. It certainly is a  Below is a cladogram published in 2013 by Godefroit ''et al.''
Below is a cladogram published in 2013 by Godefroit ''et al.''
 It has been argued that all the specimens belong to the same species, ''A. lithographica''. Differences do exist among the specimens, and while some researchers regard these as due to the different ages of the specimens, some may be related to actual species diversity. In particular, the Munich, Eichstätt, Solnhofen, and Thermopolis specimens differ from the London, Berlin, and Haarlem specimens in being smaller or much larger, having different finger proportions, having more slender snouts lined with forward-pointing teeth, and the possible presence of a sternum. Due to these differences, most individual specimens have been given their own species name at one point or another. The Berlin specimen has been designated as ''Archaeornis siemensii'', the Eichstätt specimen as ''Jurapteryx recurva'', the Munich specimen as ''Archaeopteryx bavarica'', and the Solnhofen specimen as ''Wellnhoferia grandis''.
In 2007, a review of all well-preserved specimens including the then-newly discovered Thermopolis specimen concluded that two distinct species of ''Archaeopteryx'' could be supported: ''A. lithographica'' (consisting of at least the London and Solnhofen specimens), and ''A. siemensii'' (consisting of at least the Berlin, Munich, and Thermopolis specimens). The two species are distinguished primarily by large flexor tubercles on the foot claws in ''A. lithographica'' (the claws of ''A. siemensii'' specimens being relatively simple and straight). ''A. lithographica'' also had a constricted portion of the crown in some teeth and a stouter metatarsus. A supposed additional species, ''Wellnhoferia grandis'' (based on the Solnhofen specimen), seems to be indistinguishable from ''A. lithographica'' except in its larger size.
It has been argued that all the specimens belong to the same species, ''A. lithographica''. Differences do exist among the specimens, and while some researchers regard these as due to the different ages of the specimens, some may be related to actual species diversity. In particular, the Munich, Eichstätt, Solnhofen, and Thermopolis specimens differ from the London, Berlin, and Haarlem specimens in being smaller or much larger, having different finger proportions, having more slender snouts lined with forward-pointing teeth, and the possible presence of a sternum. Due to these differences, most individual specimens have been given their own species name at one point or another. The Berlin specimen has been designated as ''Archaeornis siemensii'', the Eichstätt specimen as ''Jurapteryx recurva'', the Munich specimen as ''Archaeopteryx bavarica'', and the Solnhofen specimen as ''Wellnhoferia grandis''.
In 2007, a review of all well-preserved specimens including the then-newly discovered Thermopolis specimen concluded that two distinct species of ''Archaeopteryx'' could be supported: ''A. lithographica'' (consisting of at least the London and Solnhofen specimens), and ''A. siemensii'' (consisting of at least the Berlin, Munich, and Thermopolis specimens). The two species are distinguished primarily by large flexor tubercles on the foot claws in ''A. lithographica'' (the claws of ''A. siemensii'' specimens being relatively simple and straight). ''A. lithographica'' also had a constricted portion of the crown in some teeth and a stouter metatarsus. A supposed additional species, ''Wellnhoferia grandis'' (based on the Solnhofen specimen), seems to be indistinguishable from ''A. lithographica'' except in its larger size.
 If two names are given, the first denotes the original describer of the "species", the second the author on whom the given name combination is based. As always in zoological nomenclature, putting an author's name in parentheses denotes that the taxon was originally described in a different genus.
* ''Archaeopteryx lithographica'' Meyer, 1861 onserved name/small>
**''Archaeopterix lithographica'' Anon., 1861 'lapsus''/small>
** ''Griphosaurus problematicus'' Wagner, 1862 ejected name 1961 per ICZN Opinion 607/small>
** ''Griphornis longicaudatus'' Owen ''vide'' Woodward, 1862 ejected name 1961 per ICZN Opinion 607/small>
** ''Archaeopteryx macrura'' Owen, 1862 ejected name 1961 per ICZN Opinion 607/small>
** ''Archaeopteryx oweni'' Petronievics, 1917 ejected name 1961 per ICZN Opinion 607/small>
** ''Archaeopteryx recurva'' Howgate, 1984
** ''Jurapteryx recurva'' (Howgate, 1984) Howgate, 1985
** ''Wellnhoferia grandis'' Elżanowski, 2001
* ''Archaeopteryx siemensii'' Dames, 1897
**''Archaeornis siemensii'' (Dames, 1897) Petronievics, 1917
** ''Archaeopteryx bavarica'' Wellnhofer, 1993
''"Archaeopteryx" vicensensis'' (Anon. ''fide'' Lambrecht, 1933) is a ''
If two names are given, the first denotes the original describer of the "species", the second the author on whom the given name combination is based. As always in zoological nomenclature, putting an author's name in parentheses denotes that the taxon was originally described in a different genus.
* ''Archaeopteryx lithographica'' Meyer, 1861 onserved name/small>
**''Archaeopterix lithographica'' Anon., 1861 'lapsus''/small>
** ''Griphosaurus problematicus'' Wagner, 1862 ejected name 1961 per ICZN Opinion 607/small>
** ''Griphornis longicaudatus'' Owen ''vide'' Woodward, 1862 ejected name 1961 per ICZN Opinion 607/small>
** ''Archaeopteryx macrura'' Owen, 1862 ejected name 1961 per ICZN Opinion 607/small>
** ''Archaeopteryx oweni'' Petronievics, 1917 ejected name 1961 per ICZN Opinion 607/small>
** ''Archaeopteryx recurva'' Howgate, 1984
** ''Jurapteryx recurva'' (Howgate, 1984) Howgate, 1985
** ''Wellnhoferia grandis'' Elżanowski, 2001
* ''Archaeopteryx siemensii'' Dames, 1897
**''Archaeornis siemensii'' (Dames, 1897) Petronievics, 1917
** ''Archaeopteryx bavarica'' Wellnhofer, 1993
''"Archaeopteryx" vicensensis'' (Anon. ''fide'' Lambrecht, 1933) is a ''
 Modern palaeontology has often classified ''Archaeopteryx'' as the most primitive bird. However, it is not thought to be a true ancestor of modern birds, but rather a close relative of that ancestor. Nonetheless, ''Archaeopteryx'' was often used as a model of the true ancestral bird. Several authors have done so. Lowe (1935) and Thulborn (1984) questioned whether ''Archaeopteryx'' truly was the first bird. They suggested that ''Archaeopteryx'' was a dinosaur that was no more closely related to birds than were other dinosaur groups. Kurzanov (1987) suggested that '' Avimimus'' was more likely to be the ancestor of all birds than ''Archaeopteryx''. Barsbold (1983) and Zweers and Van den Berge (1997) noted that many maniraptoran lineages are extremely birdlike, and they suggested that different groups of birds may have descended from different dinosaur ancestors.
The discovery of the closely related '' Xiaotingia'' in 2011 led to new phylogenetic analyses that suggested that ''Archaeopteryx'' is a deinonychosaur rather than an avialan, and therefore, not a "bird" under most common uses of that term. A more thorough analysis was published soon after to test this hypothesis, and failed to arrive at the same result; it found ''Archaeopteryx'' in its traditional position at the base of ''Avialae'', while ''Xiaotingia'' was recovered as a basal dromaeosaurid or troodontid. The authors of the follow-up study noted that uncertainties still exist, and that it may not be possible to state confidently whether or not ''Archaeopteryx'' is a member of Avialae or not, barring new and better specimens of relevant species.
Phylogenetic studies conducted by Senter, ''et al.'' (2012) and Turner, Makovicky, and Norell (2012) also ''Archaeopteryx'' to be more closely related to living birds than to dromaeosaurids and troodontids. On the other hand, Godefroit ''et al.'' (2013) recovered ''Archaeopteryx'' as more closely related to dromaeosaurids and troodontids in the analysis included in their description of ''Eosinopteryx , Eosinopteryx brevipenna''. The authors used a modified version of the matrix from the study describing ''Xiaotingia'', adding ''Jinfengopteryx , Jinfengopteryx elegans'' and ''Eosinopteryx brevipenna'' to it, as well as adding four additional characters related to the development of the plumage. Unlike the analysis from the description of ''Xiaotingia'', the analysis conducted by Godefroit, ''et al.'' did not find ''Archaeopteryx'' to be related particularly closely to ''Anchiornis'' and ''Xiaotingia'', which were recovered as basal troodontids instead.
Agnolín and Novas (2013) found ''Archaeopteryx'' and (possibly synonymous) '' Wellnhoferia'' to be form a clade sister to the lineage including ''Jeholornis'' and Pygostylia, with Microraptoria, Unenlagiinae, and the clade containing ''Anchiornis'' and ''Xiaotingia'' being successively closer outgroups to the Avialae (defined by the authors as the clade stemming from the last common ancestor of ''Archaeopteryx'' and Aves). Another phylogenetic study by Godefroit, ''et al.'', using a more inclusive matrix than the one from the analysis in the description of ''Eosinopteryx brevipenna'', also found ''Archaeopteryx'' to be a member of Avialae (defined by the authors as the most inclusive clade containing ''house sparrow, Passer domesticus'', but not ''Dromaeosaurus , Dromaeosaurus albertensis'' or ''Troodon , Troodon formosus''). ''Archaeopteryx'' was found to form a Evolutionary grade, grade at the base of Avialae with ''Xiaotingia'', ''Anchiornis'', and '' Aurornis''. Compared to ''Archaeopteryx'', ''Xiaotingia'' was found to be more closely related to extant birds, while both ''Anchiornis'' and '' Aurornis'' were found to be more distantly so.
Hu ''et al''. (2018), Wang ''et al''. (2018) and Hartman ''et al''. (2019) found ''Archaeopteryx'' to have been a deinonychosaur instead of an avialan. More specifically, it and closely related taxa were considered basal deinonychosaurs, with dromaeosaurids and troodontids forming together a parallel lineage within the group. Because Hartman ''et al''. found ''Archaeopteryx'' isolated in a group of flightless deinonychosaurs (otherwise considered "Anchiornithidae , anchiornithids"), they considered it highly probable that this animal Convergent evolution, evolved flight independently from bird ancestors (and from ''Microraptor'' and ''Yi (dinosaur), Yi''). The following cladogram illustrates their hypothesis regarding the position of ''Archaeopteryx'':
The authors, however, found that the ''Archaeopteryx'' being an avialan was only slightly less likely than this hypothesis, and as likely as Archaeopterygidae and Troodontidae being sister clades.
Modern palaeontology has often classified ''Archaeopteryx'' as the most primitive bird. However, it is not thought to be a true ancestor of modern birds, but rather a close relative of that ancestor. Nonetheless, ''Archaeopteryx'' was often used as a model of the true ancestral bird. Several authors have done so. Lowe (1935) and Thulborn (1984) questioned whether ''Archaeopteryx'' truly was the first bird. They suggested that ''Archaeopteryx'' was a dinosaur that was no more closely related to birds than were other dinosaur groups. Kurzanov (1987) suggested that '' Avimimus'' was more likely to be the ancestor of all birds than ''Archaeopteryx''. Barsbold (1983) and Zweers and Van den Berge (1997) noted that many maniraptoran lineages are extremely birdlike, and they suggested that different groups of birds may have descended from different dinosaur ancestors.
The discovery of the closely related '' Xiaotingia'' in 2011 led to new phylogenetic analyses that suggested that ''Archaeopteryx'' is a deinonychosaur rather than an avialan, and therefore, not a "bird" under most common uses of that term. A more thorough analysis was published soon after to test this hypothesis, and failed to arrive at the same result; it found ''Archaeopteryx'' in its traditional position at the base of ''Avialae'', while ''Xiaotingia'' was recovered as a basal dromaeosaurid or troodontid. The authors of the follow-up study noted that uncertainties still exist, and that it may not be possible to state confidently whether or not ''Archaeopteryx'' is a member of Avialae or not, barring new and better specimens of relevant species.
Phylogenetic studies conducted by Senter, ''et al.'' (2012) and Turner, Makovicky, and Norell (2012) also ''Archaeopteryx'' to be more closely related to living birds than to dromaeosaurids and troodontids. On the other hand, Godefroit ''et al.'' (2013) recovered ''Archaeopteryx'' as more closely related to dromaeosaurids and troodontids in the analysis included in their description of ''Eosinopteryx , Eosinopteryx brevipenna''. The authors used a modified version of the matrix from the study describing ''Xiaotingia'', adding ''Jinfengopteryx , Jinfengopteryx elegans'' and ''Eosinopteryx brevipenna'' to it, as well as adding four additional characters related to the development of the plumage. Unlike the analysis from the description of ''Xiaotingia'', the analysis conducted by Godefroit, ''et al.'' did not find ''Archaeopteryx'' to be related particularly closely to ''Anchiornis'' and ''Xiaotingia'', which were recovered as basal troodontids instead.
Agnolín and Novas (2013) found ''Archaeopteryx'' and (possibly synonymous) '' Wellnhoferia'' to be form a clade sister to the lineage including ''Jeholornis'' and Pygostylia, with Microraptoria, Unenlagiinae, and the clade containing ''Anchiornis'' and ''Xiaotingia'' being successively closer outgroups to the Avialae (defined by the authors as the clade stemming from the last common ancestor of ''Archaeopteryx'' and Aves). Another phylogenetic study by Godefroit, ''et al.'', using a more inclusive matrix than the one from the analysis in the description of ''Eosinopteryx brevipenna'', also found ''Archaeopteryx'' to be a member of Avialae (defined by the authors as the most inclusive clade containing ''house sparrow, Passer domesticus'', but not ''Dromaeosaurus , Dromaeosaurus albertensis'' or ''Troodon , Troodon formosus''). ''Archaeopteryx'' was found to form a Evolutionary grade, grade at the base of Avialae with ''Xiaotingia'', ''Anchiornis'', and '' Aurornis''. Compared to ''Archaeopteryx'', ''Xiaotingia'' was found to be more closely related to extant birds, while both ''Anchiornis'' and '' Aurornis'' were found to be more distantly so.
Hu ''et al''. (2018), Wang ''et al''. (2018) and Hartman ''et al''. (2019) found ''Archaeopteryx'' to have been a deinonychosaur instead of an avialan. More specifically, it and closely related taxa were considered basal deinonychosaurs, with dromaeosaurids and troodontids forming together a parallel lineage within the group. Because Hartman ''et al''. found ''Archaeopteryx'' isolated in a group of flightless deinonychosaurs (otherwise considered "Anchiornithidae , anchiornithids"), they considered it highly probable that this animal Convergent evolution, evolved flight independently from bird ancestors (and from ''Microraptor'' and ''Yi (dinosaur), Yi''). The following cladogram illustrates their hypothesis regarding the position of ''Archaeopteryx'':
The authors, however, found that the ''Archaeopteryx'' being an avialan was only slightly less likely than this hypothesis, and as likely as Archaeopterygidae and Troodontidae being sister clades.
 As in the wings of modern birds, the flight feathers of ''Archaeopteryx'' were somewhat asymmetrical and the tail feathers were rather broad. This implies that the wings and tail were used for lift generation, but it is unclear whether ''Archaeopteryx'' was capable of flapping flight or simply a glider. The lack of a bony Sternum, breastbone suggests that ''Archaeopteryx'' was not a very strong flier, but flight muscles might have attached to the thick, boomerang-shaped wishbone, the platelike coracoids, or perhaps, to a cartilage, cartilaginous sternum. The sideways orientation of the glenoid (shoulder) joint between scapula, coracoid, and humerus—instead of the dorsally angled arrangement found in modern birds—may indicate that ''Archaeopteryx'' was unable to lift its wings above its back, a requirement for the upstroke found in modern flapping flight. According to a study by Philip Senter in 2006, ''Archaeopteryx'' was indeed unable to use flapping flight as modern birds do, but it may well have used a downstroke-only flap-assisted gliding technique. However, a more recent study solves this issue by suggesting a different flight stroke configuration for non-avian flying theropods.
''Archaeopteryx'' wings were relatively large, which would have resulted in a low stall speed and reduced turning radius. The short and rounded shape of the wings would have increased drag, but also could have improved its ability to fly through cluttered environments such as trees and brush (similar wing shapes are seen in birds that fly through trees and brush, such as crows and pheasants). The presence of "hind wings", asymmetrical flight feathers stemming from the legs similar to those seen in dromaeosaurids such as ''Microraptor'', also would have added to the aerial mobility of ''Archaeopteryx''. The first detailed study of the hind wings by Longrich in 2006, suggested that the structures formed up to 12% of the total airfoil. This would have reduced stall speed by up to 6% and turning radius by up to 12%.
The feathers of ''Archaeopteryx'' were asymmetrical. This has been interpreted as evidence that it was a flyer, because flightless birds tend to have symmetrical feathers. Some scientists, including Thomson and Speakman, have questioned this. They studied more than 70 families of living birds, and found that some flightless types do have a range of asymmetry in their feathers, and that the feathers of ''Archaeopteryx'' fall into this range. The degree of asymmetry seen in ''Archaeopteryx'' is more typical for slow flyers than for flightless birds.
As in the wings of modern birds, the flight feathers of ''Archaeopteryx'' were somewhat asymmetrical and the tail feathers were rather broad. This implies that the wings and tail were used for lift generation, but it is unclear whether ''Archaeopteryx'' was capable of flapping flight or simply a glider. The lack of a bony Sternum, breastbone suggests that ''Archaeopteryx'' was not a very strong flier, but flight muscles might have attached to the thick, boomerang-shaped wishbone, the platelike coracoids, or perhaps, to a cartilage, cartilaginous sternum. The sideways orientation of the glenoid (shoulder) joint between scapula, coracoid, and humerus—instead of the dorsally angled arrangement found in modern birds—may indicate that ''Archaeopteryx'' was unable to lift its wings above its back, a requirement for the upstroke found in modern flapping flight. According to a study by Philip Senter in 2006, ''Archaeopteryx'' was indeed unable to use flapping flight as modern birds do, but it may well have used a downstroke-only flap-assisted gliding technique. However, a more recent study solves this issue by suggesting a different flight stroke configuration for non-avian flying theropods.
''Archaeopteryx'' wings were relatively large, which would have resulted in a low stall speed and reduced turning radius. The short and rounded shape of the wings would have increased drag, but also could have improved its ability to fly through cluttered environments such as trees and brush (similar wing shapes are seen in birds that fly through trees and brush, such as crows and pheasants). The presence of "hind wings", asymmetrical flight feathers stemming from the legs similar to those seen in dromaeosaurids such as ''Microraptor'', also would have added to the aerial mobility of ''Archaeopteryx''. The first detailed study of the hind wings by Longrich in 2006, suggested that the structures formed up to 12% of the total airfoil. This would have reduced stall speed by up to 6% and turning radius by up to 12%.
The feathers of ''Archaeopteryx'' were asymmetrical. This has been interpreted as evidence that it was a flyer, because flightless birds tend to have symmetrical feathers. Some scientists, including Thomson and Speakman, have questioned this. They studied more than 70 families of living birds, and found that some flightless types do have a range of asymmetry in their feathers, and that the feathers of ''Archaeopteryx'' fall into this range. The degree of asymmetry seen in ''Archaeopteryx'' is more typical for slow flyers than for flightless birds.
 In 2010, Robert L. Nudds and Gareth J. Dyke in the journal ''Science'' published a paper in which they analysed the rachises of the primary feathers of ''Confuciusornis'' and ''Archaeopteryx''. The analysis suggested that the rachises on these two genera were thinner and weaker than those of modern birds relative to body mass. The authors determined that ''Archaeopteryx'' and ''Confuciusornis'', were unable to use flapping flight. This study was criticized by Philip J. Currie and Luis Chiappe. Chiappe suggested that it is difficult to measure the rachises of fossilized feathers, and Currie speculated that ''Archaeopteryx'' and ''Confuciusornis'' must have been able to fly to some degree, as their fossils are preserved in what is believed to have been marine or lake sediments, suggesting that they must have been able to fly over deep water.Balter, M. (2010)
In 2010, Robert L. Nudds and Gareth J. Dyke in the journal ''Science'' published a paper in which they analysed the rachises of the primary feathers of ''Confuciusornis'' and ''Archaeopteryx''. The analysis suggested that the rachises on these two genera were thinner and weaker than those of modern birds relative to body mass. The authors determined that ''Archaeopteryx'' and ''Confuciusornis'', were unable to use flapping flight. This study was criticized by Philip J. Currie and Luis Chiappe. Chiappe suggested that it is difficult to measure the rachises of fossilized feathers, and Currie speculated that ''Archaeopteryx'' and ''Confuciusornis'' must have been able to fly to some degree, as their fossils are preserved in what is believed to have been marine or lake sediments, suggesting that they must have been able to fly over deep water.Balter, M. (2010)
"Did First Feathers Prevent Early Flight?"
''Science Now'', 13 May 2010. Gregory Paul also disagreed with the study, arguing in a 2010 response that Nudds and Dyke had overestimated the masses of these early birds, and that more accurate mass estimates allowed powered flight even with relatively narrow rachises. Nudds and Dyke had assumed a mass of for the Munich specimen ''Archaeopteryx'', a young juvenile, based on published mass estimates of larger specimens. Paul argued that a more reasonable body mass estimate for the Munich specimen is about . Paul also criticized the measurements of the rachises themselves, noting that the feathers in the Munich specimen are poorly preserved. Nudds and Dyke reported a diameter of for the longest primary feather, which Paul could not confirm using photographs. Paul measured some of the inner primary feathers, finding rachises across. Despite these criticisms, Nudds and Dyke stood by their original conclusions. They claimed that Paul's statement, that an adult ''Archaeopteryx'' would have been a better flyer than the juvenile Munich specimen, was dubious. This, they reasoned, would require an even thicker rachis, evidence for which has not yet been presented. Another possibility is that they had not achieved true flight, but instead used their wings as aids for extra lift while running over water after the fashion of the basilisk lizard, which could explain their presence in lake and marine deposits (see Origin of avian flight). In 2004, scientists analysing a detailed CT scan of the braincase of the London ''Archaeopteryx'' concluded that its brain was significantly larger than that of most dinosaurs, indicating that it possessed the brain size necessary for flying. The overall brain anatomy was reconstructed using the scan. The reconstruction showed that the regions associated with vision took up nearly one-third of the brain. Other well-developed areas involved hearing and muscle coordination. The skull scan also revealed the structure of its inner ear. The structure more closely resembles that of modern birds than the inner ear of non-avian reptiles. These characteristics taken together suggest that ''Archaeopteryx'' had the keen sense of hearing, balance, spatial perception, and coordination needed to fly. ''Archaeopteryx'' had a cerebrum-to-brain-volume ratio 78% of the way to modern birds from the condition of non-coelurosaurian dinosaurs such as ''Carcharodontosaurus'' or ''Allosaurus'', which had a crocodile-like anatomy of the brain and inner ear.Larsson, H. C. E. (2001). "Endocranial anatomy of ''Carcharodontosaurus saharicus'' (Theropoda: Allosauroidea) and its implications for theropod brain evolution". In: Tanke, D. H.; Carpenter, K.; Skrepnick, M. W. (eds.) ''Mesozoic Vertebrate Life''. Indiana University Press. pp. 19–33. Newer research shows that while the ''Archaeopteryx'' brain was more complex than that of more primitive theropods, it had a more generalized brain volume among maniraptoran , Maniraptora dinosaurs, even smaller than that of other non-avian dinosaurs in several instances, which indicates the neurological development required for flight was already a common trait in the maniraptoran clade. Recent studies of flight feather barb geometry reveal that modern birds possess a larger barb angle in the trailing vane of the feather, whereas ''Archaeopteryx'' lacks this large barb angle, indicating potentially weak flight abilities. ''Archaeopteryx'' continues to play an important part in scientific debates about the origin and evolution of birds. Some scientists see it as a semi-arboreal climbing animal, following the idea that birds evolved from tree-dwelling gliders (the "trees down" hypothesis for the evolution of flight proposed by O. C. Marsh). Other scientists see ''Archaeopteryx'' as running quickly along the ground, supporting the idea that birds evolved flight by running (the "ground up" hypothesis proposed by Samuel Wendell Williston). Still others suggest that ''Archaeopteryx'' might have been at home both in the trees and on the ground, like modern crows, and this latter view is what currently is considered best-supported by morphological characters. Altogether, it appears that the species was not particularly specialized for running on the ground or for perching. A scenario outlined by Elżanowski in 2002 suggested that ''Archaeopteryx'' used its wings mainly to escape Predation, predators by glides punctuated with shallow downstrokes to reach successively higher perches, and alternatively, to cover longer distances (mainly) by gliding down from cliffs or treetops.
In March 2018, scientists reported that ''Archaeopteryx'' was likely capable of Bird flight, flight, but in a manner distinct and substantially different from that of Birds, modern birds. This study on ''Archaeopteryxs bone histology suggests that it was closest to true flying birds, and in particular to pheasants and other burst flyers.
Studies of ''Archaeopteryx's'' feather sheaths revealed that like modern birds, it had a center-out, flight related molting strategy. As it was a weak flier, this was extremely advantageous in preserving its maximum flight performance.
''Archaeopteryx'' continues to play an important part in scientific debates about the origin and evolution of birds. Some scientists see it as a semi-arboreal climbing animal, following the idea that birds evolved from tree-dwelling gliders (the "trees down" hypothesis for the evolution of flight proposed by O. C. Marsh). Other scientists see ''Archaeopteryx'' as running quickly along the ground, supporting the idea that birds evolved flight by running (the "ground up" hypothesis proposed by Samuel Wendell Williston). Still others suggest that ''Archaeopteryx'' might have been at home both in the trees and on the ground, like modern crows, and this latter view is what currently is considered best-supported by morphological characters. Altogether, it appears that the species was not particularly specialized for running on the ground or for perching. A scenario outlined by Elżanowski in 2002 suggested that ''Archaeopteryx'' used its wings mainly to escape Predation, predators by glides punctuated with shallow downstrokes to reach successively higher perches, and alternatively, to cover longer distances (mainly) by gliding down from cliffs or treetops.
In March 2018, scientists reported that ''Archaeopteryx'' was likely capable of Bird flight, flight, but in a manner distinct and substantially different from that of Birds, modern birds. This study on ''Archaeopteryxs bone histology suggests that it was closest to true flying birds, and in particular to pheasants and other burst flyers.
Studies of ''Archaeopteryx's'' feather sheaths revealed that like modern birds, it had a center-out, flight related molting strategy. As it was a weak flier, this was extremely advantageous in preserving its maximum flight performance.
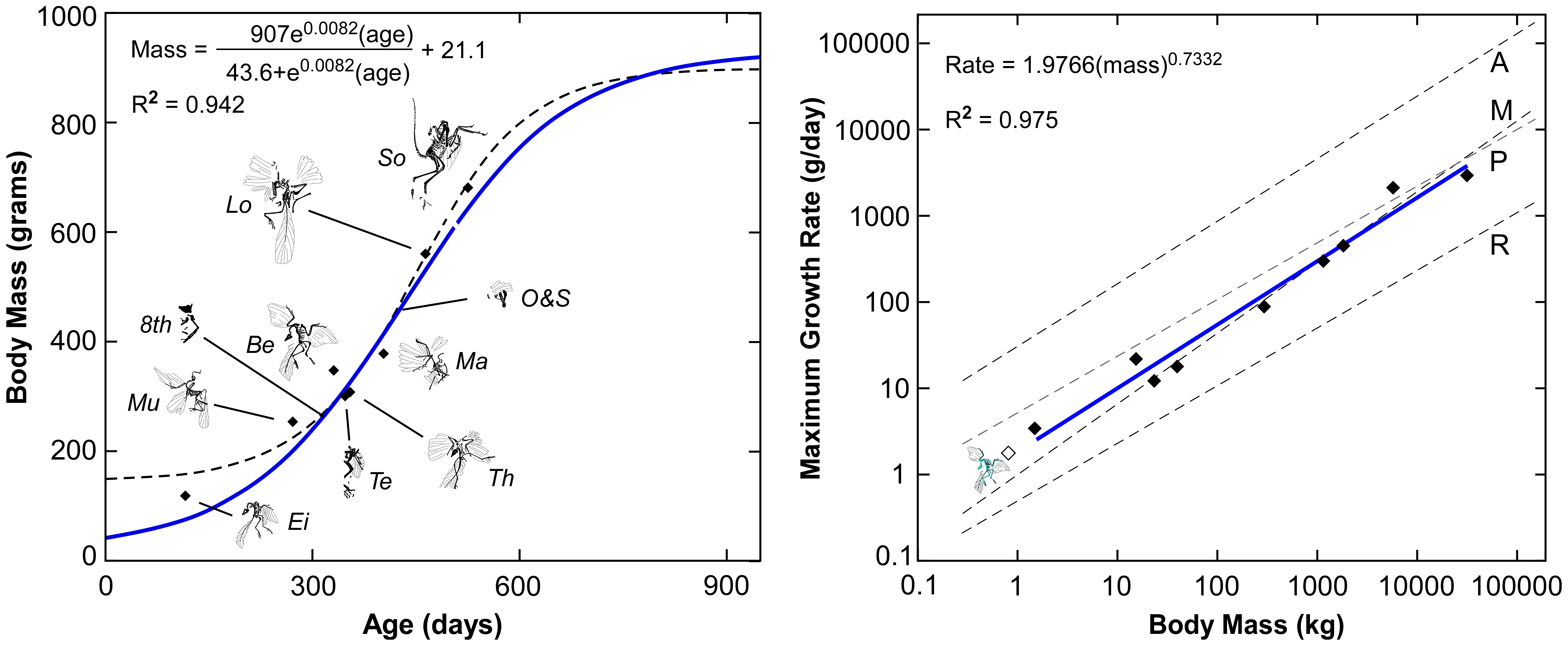 An histological study by Erickson, Norell, Zhongue, and others in 2009 estimated that ''Archaeopteryx'' grew relatively slowly compared to modern birds, presumably because the outermost portions of ''Archaeopteryx'' bones appear poorly vascularized; in living vertebrates, poorly vascularized bone is correlated with slow growth rate. They also assume that all known skeletons of ''Archaeopteryx'' come from juvenile specimens. Because the bones of ''Archaeopteryx'' could not be histologically sectioned in a formal skeletochronological (growth ring) analysis, Erickson and colleagues used bone vascularity (porosity) to estimate bone growth rate. They assumed that poorly vascularized bone grows at similar rates in all birds and in ''Archaeopteryx''. The poorly vascularized bone of ''Archaeopteryx'' might have grown as slowly as that in a mallard (2.5micrometres per day) or as fast as that in an ostrich (4.2micrometres per day). Using this range of bone growth rates, they calculated how long it would take to "grow" each specimen of ''Archaeopteryx'' to the observed size; it may have taken at least 970 days (there were 375 days in a Late Jurassic year) to reach an adult size of . The study also found that the avialans ''Jeholornis'' and ''Sapeornis'' grew relatively slowly, as did the dromaeosaurid ''Mahakala (dinosaur), Mahakala''. The avialans ''Confuciusornis'' and ''Ichthyornis'' grew relatively quickly, following a growth trend similar to that of modern birds. One of the few modern birds that exhibit slow growth is the flightless Kiwi (bird), kiwi, and the authors speculated that ''Archaeopteryx'' and the kiwi had similar basal metabolic rate.
An histological study by Erickson, Norell, Zhongue, and others in 2009 estimated that ''Archaeopteryx'' grew relatively slowly compared to modern birds, presumably because the outermost portions of ''Archaeopteryx'' bones appear poorly vascularized; in living vertebrates, poorly vascularized bone is correlated with slow growth rate. They also assume that all known skeletons of ''Archaeopteryx'' come from juvenile specimens. Because the bones of ''Archaeopteryx'' could not be histologically sectioned in a formal skeletochronological (growth ring) analysis, Erickson and colleagues used bone vascularity (porosity) to estimate bone growth rate. They assumed that poorly vascularized bone grows at similar rates in all birds and in ''Archaeopteryx''. The poorly vascularized bone of ''Archaeopteryx'' might have grown as slowly as that in a mallard (2.5micrometres per day) or as fast as that in an ostrich (4.2micrometres per day). Using this range of bone growth rates, they calculated how long it would take to "grow" each specimen of ''Archaeopteryx'' to the observed size; it may have taken at least 970 days (there were 375 days in a Late Jurassic year) to reach an adult size of . The study also found that the avialans ''Jeholornis'' and ''Sapeornis'' grew relatively slowly, as did the dromaeosaurid ''Mahakala (dinosaur), Mahakala''. The avialans ''Confuciusornis'' and ''Ichthyornis'' grew relatively quickly, following a growth trend similar to that of modern birds. One of the few modern birds that exhibit slow growth is the flightless Kiwi (bird), kiwi, and the authors speculated that ''Archaeopteryx'' and the kiwi had similar basal metabolic rate.
 The richness and diversity of the Solnhofen limestones in which all specimens of ''Archaeopteryx'' have been found have shed light on an ancient Jurassic Bavaria strikingly different from the present day. The latitude was similar to Florida, though the climate was likely to have been drier, as evidenced by fossils of plants with adaptations for arid conditions and a lack of terrestrial sediments characteristic of rivers. Evidence of plants, although scarce, include cycads and conifers while animals found include a large number of insects, small lizards, pterosaurs, and '' Compsognathus''.
The excellent preservation of ''Archaeopteryx'' fossils and other terrestrial fossils found at Solnhofen indicates that they did not travel far before becoming preserved. The ''Archaeopteryx'' specimens found were therefore likely to have lived on the low islands surrounding the Solnhofen lagoon rather than to have been corpses that drifted in from farther away. ''Archaeopteryx'' skeletons are considerably less numerous in the deposits of Solnhofen than those of pterosaurs, of which seven genera have been found. The pterosaurs included species such as ''Rhamphorhynchus (pterosaur), Rhamphorhynchus'' belonging to the Rhamphorhynchidae, the group which dominated the ecological niche currently occupied by seabirds, and which became extinct at the end of the Jurassic. The pterosaurs, which also included '' Pterodactylus'', were common enough that it is unlikely that the specimens found are Vagrancy (biology), vagrants from the larger islands to the north.
The islands that surrounded the Solnhofen lagoon were low lying, semi-arid, and sub-tropical with a long dry season and little rain. The closest modern analogue for the Solnhofen conditions is said to be Orca Basin in the northern Gulf of Mexico, although it is much deeper than the Solnhofen lagoons. The flora of these islands was adapted to these dry conditions and consisted mostly of low () shrubs. Contrary to reconstructions of ''Archaeopteryx'' climbing large trees, these seem to have been mostly absent from the islands; few trunks have been found in the sediments and fossilized tree pollen also is absent.
The lifestyle of ''Archaeopteryx'' is difficult to reconstruct and there are several theories regarding it. Some researchers suggest that it was primarily adapted to life on the ground, while other researchers suggest that it was principally arboreal on the basis of the curvature of the claws which has since been questioned. The absence of trees does not preclude ''Archaeopteryx'' from an arboreal lifestyle, as several species of bird live exclusively in low shrubs. Various aspects of the morphology of ''Archaeopteryx'' point to either an arboreal or ground existence, including the length of its legs and the elongation in its feet; some authorities consider it likely to have been a Generalist and specialist species , generalist capable of feeding in both shrubs and open ground, as well as along the shores of the lagoon. It most likely hunted small prey, seizing it with its jaws if it was small enough, or with its claws if it was larger.
The richness and diversity of the Solnhofen limestones in which all specimens of ''Archaeopteryx'' have been found have shed light on an ancient Jurassic Bavaria strikingly different from the present day. The latitude was similar to Florida, though the climate was likely to have been drier, as evidenced by fossils of plants with adaptations for arid conditions and a lack of terrestrial sediments characteristic of rivers. Evidence of plants, although scarce, include cycads and conifers while animals found include a large number of insects, small lizards, pterosaurs, and '' Compsognathus''.
The excellent preservation of ''Archaeopteryx'' fossils and other terrestrial fossils found at Solnhofen indicates that they did not travel far before becoming preserved. The ''Archaeopteryx'' specimens found were therefore likely to have lived on the low islands surrounding the Solnhofen lagoon rather than to have been corpses that drifted in from farther away. ''Archaeopteryx'' skeletons are considerably less numerous in the deposits of Solnhofen than those of pterosaurs, of which seven genera have been found. The pterosaurs included species such as ''Rhamphorhynchus (pterosaur), Rhamphorhynchus'' belonging to the Rhamphorhynchidae, the group which dominated the ecological niche currently occupied by seabirds, and which became extinct at the end of the Jurassic. The pterosaurs, which also included '' Pterodactylus'', were common enough that it is unlikely that the specimens found are Vagrancy (biology), vagrants from the larger islands to the north.
The islands that surrounded the Solnhofen lagoon were low lying, semi-arid, and sub-tropical with a long dry season and little rain. The closest modern analogue for the Solnhofen conditions is said to be Orca Basin in the northern Gulf of Mexico, although it is much deeper than the Solnhofen lagoons. The flora of these islands was adapted to these dry conditions and consisted mostly of low () shrubs. Contrary to reconstructions of ''Archaeopteryx'' climbing large trees, these seem to have been mostly absent from the islands; few trunks have been found in the sediments and fossilized tree pollen also is absent.
The lifestyle of ''Archaeopteryx'' is difficult to reconstruct and there are several theories regarding it. Some researchers suggest that it was primarily adapted to life on the ground, while other researchers suggest that it was principally arboreal on the basis of the curvature of the claws which has since been questioned. The absence of trees does not preclude ''Archaeopteryx'' from an arboreal lifestyle, as several species of bird live exclusively in low shrubs. Various aspects of the morphology of ''Archaeopteryx'' point to either an arboreal or ground existence, including the length of its legs and the elongation in its feet; some authorities consider it likely to have been a Generalist and specialist species , generalist capable of feeding in both shrubs and open ground, as well as along the shores of the lagoon. It most likely hunted small prey, seizing it with its jaws if it was small enough, or with its claws if it was larger.
Full text, Google Books
* P. Shipman (1998). ''Taking Wing: Archaeopteryx and the Evolution of Bird Flight''. Weidenfeld & Nicolson, London. . * P. Wellnhofer (2008). ''Archaeopteryx — Der Urvogel von Solnhofen'' (in German). Verlag Friedrich Pfeil, Munich. .
from Talk.Origins.
Use of SSRL X-ray takes 'transformative glimpse'
— A look at chemicals linking birds and dinosaurs.
— University of California Museum of Paleontology.
— University of California Museum of Paleontology. {{featured article Prehistoric avialans Jurassic birds Feathered dinosaurs Late Jurassic dinosaurs of Europe Jurassic Germany Mesozoic birds of Europe Solnhofen fauna Fossils of Germany Transitional fossils Fossil taxa described in 1861 Taxa named by Christian Erich Hermann von Meyer
equator
The equator is a circle of latitude, about in circumference, that divides Earth into the Northern and Southern hemispheres. It is an imaginary line located at 0 degrees latitude, halfway between the North and South poles. The term can als ...
than it is now. Similar in size to a Eurasian magpie
The Eurasian magpie or common magpie (''Pica pica'') is a resident breeding bird throughout the northern part of the Eurasian continent. It is one of several birds in the crow family (corvids) designated magpies, and belongs to the Holarctic ra ...
, with the largest individuals possibly attaining the size of a raven
A raven is any of several larger-bodied bird species of the genus ''Corvus''. These species do not form a single taxonomic group within the genus. There is no consistent distinction between "crows" and "ravens", common names which are assigned t ...
, the largest species of ''Archaeopteryx'' could grow to about in length. Despite their small size, broad wings, and inferred ability to fly or glide, ''Archaeopteryx'' had more in common with other small Mesozoic dinosaurs than with modern birds. In particular, they shared the following features with the dromaeosaurids and troodontids: jaws with sharp teeth, three fingers with claws, a long bony tail, hyperextensible second toes ("killing claw"), feathers (which also suggest warm-bloodedness), and various features of the skeleton
A skeleton is the structural frame that supports the body of an animal. There are several types of skeletons, including the exoskeleton, which is the stable outer shell of an organism, the endoskeleton, which forms the support structure inside ...
.
These features make ''Archaeopteryx'' a clear candidate for a transitional fossil between non-avian dinosaurs and birds. Thus, ''Archaeopteryx'' plays an important role, not only in the study of the origin of birds, but in the study of dinosaurs. It was named from a single feather
Feathers are epidermal growths that form a distinctive outer covering, or plumage, on both avian (bird) and some non-avian dinosaurs and other archosaurs. They are the most complex integumentary structures found in vertebrates and a premier ...
in 1861, the identity of which has been controversial. That same year, the first complete specimen of ''Archaeopteryx'' was announced. Over the years, ten more fossils of ''Archaeopteryx'' have surfaced. Despite variation among these fossils, most experts regard all the remains that have been discovered as belonging to a single species, although this is still debated.
''Archaeopteryx'' was long considered to be the beginning of the evolutionary tree of birds. It has qualities that helped define what it is like to be a bird, such as its long, powerful front limbs. However, in recent years, the discovery of several small, feathered dinosaurs has created a mystery for palaeontologists, raising questions about which animals are the ancestors of modern birds and which are their relatives. Most of these eleven fossils include impressions of feathers. Because these feathers are of an advanced form (flight feather
Flight feathers (''Pennae volatus'') are the long, stiff, asymmetrically shaped, but symmetrically paired pennaceous feathers on the wings or tail of a bird; those on the wings are called remiges (), singular remex (), while those on the tail ...
s), these fossils are evidence that the evolution of feathers began before the Late Jurassic. The type specimen of ''Archaeopteryx'' was discovered just two years after Charles Darwin published '' On the Origin of Species''. ''Archaeopteryx'' seemed to confirm Darwin's theories and has since become a key piece of evidence for the origin of birds, the transitional fossils debate, and confirmation of evolution.
History of discovery
 The initial discovery, a single feather, was unearthed in 1860 or 1861 and described in 1861 by . It is currently located at the Natural History Museum of Berlin. Though it was the initial holotype, there were indications that it might not have been from the same animal as the body fossils. In 2019 it was reported that laser imaging had revealed the structure of the quill (which had not been visible since some time after the feather was described), and that the feather was inconsistent with the morphology of all other ''Archaeopteryx'' feathers known, leading to the conclusion that it originated from another dinosaur. This conclusion was challenged in 2020 as being unlikely; the feather was identified on the basis of morphology as most likely having been an upper major primary
The initial discovery, a single feather, was unearthed in 1860 or 1861 and described in 1861 by . It is currently located at the Natural History Museum of Berlin. Though it was the initial holotype, there were indications that it might not have been from the same animal as the body fossils. In 2019 it was reported that laser imaging had revealed the structure of the quill (which had not been visible since some time after the feather was described), and that the feather was inconsistent with the morphology of all other ''Archaeopteryx'' feathers known, leading to the conclusion that it originated from another dinosaur. This conclusion was challenged in 2020 as being unlikely; the feather was identified on the basis of morphology as most likely having been an upper major primary covert feather
A covert feather or tectrix on a bird is one of a set of feathers, called coverts (or ''tectrices''), which, as the name implies, cover other feathers. The coverts help to smooth airflow over the wings and tail. Ear coverts
The ear coverts are sm ...
.
The first skeleton, known as the London Specimen (BMNH 37001), was unearthed in 1861 near , Germany, and perhaps given to local physician in return for medical services. He then sold it for £700 (roughly £83,000 in 2020) to the Natural History Museum in London, where it remains. Missing most of its head and neck, it was described in 1863 by Richard Owen
Sir Richard Owen (20 July 1804 – 18 December 1892) was an English biologist, comparative anatomist and paleontologist. Owen is generally considered to have been an outstanding naturalist with a remarkable gift for interpreting fossils.
Owe ...
as ''Archaeopteryx macrura'', allowing for the possibility it did not belong to the same species as the feather. In the subsequent fourth edition of his ''On the Origin of Species'', Charles Darwin described how some authors had maintained "that the whole class of birds came suddenly into existence during the eocene period; but now we know, on the authority of Professor Owen, that a bird certainly lived during the deposition of the upper greensand; and still more recently, that strange bird, the ''Archaeopteryx'', with a long lizard-like tail, bearing a pair of feathers on each joint, and with its wings furnished with two free claws, has been discovered in the oolitic slates of Solnhofen. Hardly any recent discovery shows more forcibly than this how little we as yet know of the former inhabitants of the world."
The Greek word () means 'ancient, primeval'. primarily means 'wing', but it can also be just 'feather'. Meyer suggested this in his description. At first he referred to a single feather which appeared to resemble a modern bird's remex (wing feather), but he had heard of and been shown a rough sketch of the London specimen, to which he referred as a "" ("skeleton of an animal covered in similar feathers"). In German, this ambiguity is resolved by the term which does not necessarily mean a wing used for flying. was the favoured translation of ''Archaeopteryx'' among German scholars in the late nineteenth century. In English, 'ancient pinion' offers a rough approximation to this.
Since then, twelve specimens have been recovered:
The Berlin Specimen (HMN 1880/81) was discovered in 1874 or 1875 on the Blumenberg near , Germany, by farmer Jakob Niemeyer. He sold this precious fossil for the money to buy a cow in 1876, to innkeeper Johann Dörr, who again sold it to Ernst Otto Häberlein, the son of K. Häberlein. Placed on sale between 1877 and 1881, with potential buyers including O. C. Marsh of Yale University's Peabody Museum, it eventually was bought for 20,000 Goldmark by the Berlin's Natural History Museum, where it now is displayed. The transaction was financed by Ernst Werner von Siemens, founder of the company
''The'' () is a grammatical article in English, denoting persons or things that are already or about to be mentioned, under discussion, implied or otherwise presumed familiar to listeners, readers, or speakers. It is the definite article in ...
that bears his name. Described in 1884 by Wilhelm Dames, it is the most complete specimen, and the first with a complete head. In 1897 it was named by Dames as a new species, ''A. siemensii''; though often considered a synonym of ''A. lithographica'', several 21st century studies have concluded that it is a distinct species which includes the Berlin, Munich, and Thermopolis specimens.
 Composed of a torso, the
Composed of a torso, the Maxberg Specimen
''Archaeopteryx'' fossils from the quarries of Solnhofen limestone represent the most famous and well-known fossils from this area. They are highly significant to paleontology and avian evolution in that they document the fossil record's old ...
(S5) was discovered in 1956 near Langenaltheim; it was brought to the attention of professor Florian Heller
Florian Heller (born 10 March 1982 in Rosenheim) is a German football coach and former footballer. He is currently the manager of SpVgg Unterhaching U17.
He made his debut on the professional league level in the 2. Bundesliga for SpVgg Greuther ...
in 1958 and described by him in 1959. The specimen is missing its head and tail, although the rest of the skeleton is mostly intact. Although it was once exhibited at the Maxberg Museum
The Maxberg Museum (aka Museum beim Solenhofer Aktien-Verein) was a German museum situated in Mörnsheim in the natural park of Altmühltal, near Solnhofen. It was founded by Alphons L. Zehntner in 1929. In 2004 was moved near to the town of Gun ...
in Solnhofen, it is currently missing. It belonged to Eduard Opitsch Eduard Opitsch (1 February 1900 – 20 February 1991) was a German quarry owner whose name is associated to a specimen of the prehistoric bird ''Archaeopteryx'', the '' Maxberg specimen''.
The so-called Maxberg specimen of ''Archaeopteryx lith ...
, who loaned it to the museum until 1974. After his death in 1991, it was discovered that the specimen was missing and may have been stolen or sold.
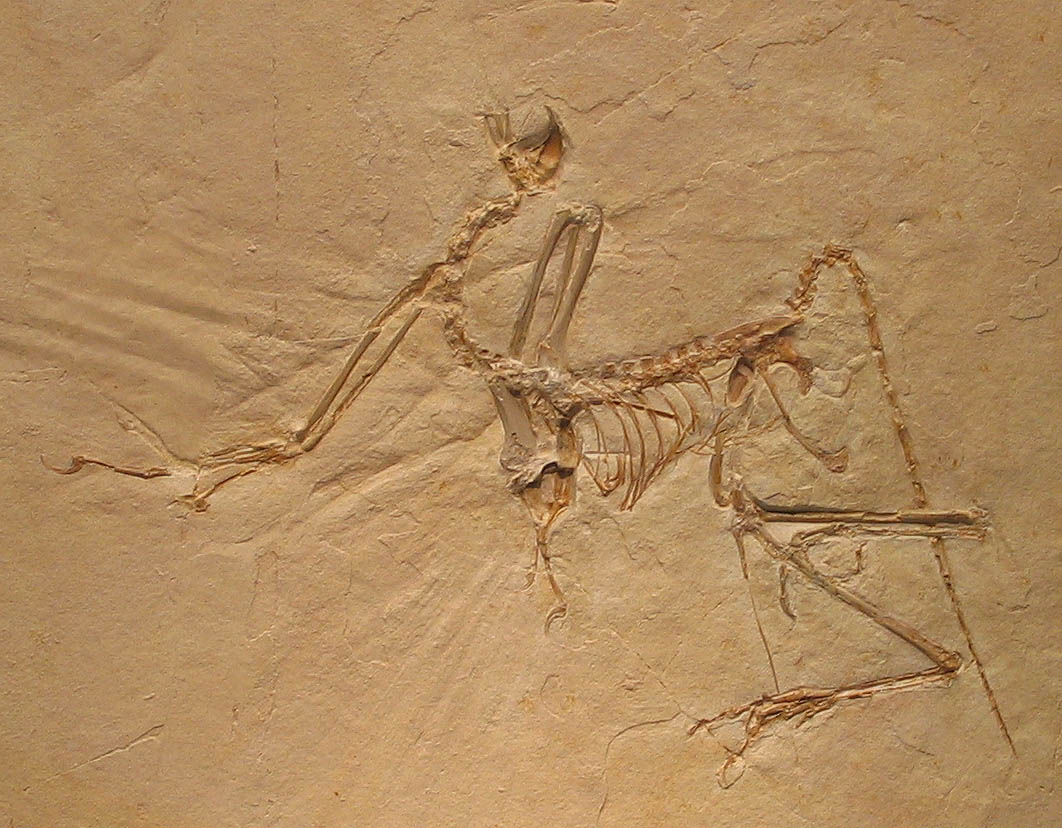
The Haarlem Specimen (TM 6428/29, also known as the ''Teylers Specimen'') was discovered in 1855 near , Germany, and described as a '' Pterodactylus crassipes'' in 1857 by Meyer. It was reclassified in 1970 by John Ostrom and is currently located at the Teylers Museum in Haarlem
Haarlem (; predecessor of ''Harlem'' in English) is a city and municipality in the Netherlands. It is the capital of the province of North Holland. Haarlem is situated at the northern edge of the Randstad, one of the most populated metropoli ...
, the Netherlands. It was the very first specimen found, but was incorrectly classified at the time. It is also one of the least complete specimens, consisting mostly of limb bones, isolated cervical vertebrae, and ribs. In 2017 it was named as a separate genus ''Ostromia
''Ostromia'' (''Thick feet of John Ostrom'') is a genus of anchiornithid theropod dinosaur from the Late Jurassic Painten Formation of Germany. The genus contains a single species, ''O. crassipes'', named by Christian Foth and Oliver Rauhut in 2 ...
'', considered more closely related to '' Anchiornis'' from China.
 The Eichstätt Specimen (JM 2257) was discovered in 1951 near Workerszell, Germany, and described by Peter Wellnhofer in 1974. Currently located at the Jura Museum in Eichstätt, Germany, it is the smallest known specimen and has the second-best head. It is possibly a separate genus (''Jurapteryx recurva'') or species (''A. recurva'').
The Solnhofen Specimen (unnumbered specimen) was discovered in the 1970s near Eichstätt, Germany, and described in 1988 by Wellnhofer. Currently located at the Bürgermeister-Müller-Museum in Solnhofen, it originally was classified as '' Compsognathus'' by an amateur collector, the same mayor Friedrich Müller after which the museum is named. It is the largest specimen known and may belong to a separate genus and species, '' Wellnhoferia grandis''. It is missing only portions of the neck, tail, backbone, and head.
The Munich Specimen (BSP 1999 I 50, formerly known as the ''Solenhofer-Aktien-Verein Specimen'') was discovered on 3 August 1992 near Langenaltheim and described in 1993 by Wellnhofer. It is currently located at the Paläontologisches Museum München in Munich, to which it was sold in 1999 for 1.9 million Deutschmark. What was initially believed to be a bony sternum turned out to be part of the coracoid, but a cartilaginous sternum may have been present. Only the front of its face is missing. It has been used as the basis for a distinct species, ''A. bavarica'', but more recent studies suggest it belongs to ''A. siemensii''.
The Eichstätt Specimen (JM 2257) was discovered in 1951 near Workerszell, Germany, and described by Peter Wellnhofer in 1974. Currently located at the Jura Museum in Eichstätt, Germany, it is the smallest known specimen and has the second-best head. It is possibly a separate genus (''Jurapteryx recurva'') or species (''A. recurva'').
The Solnhofen Specimen (unnumbered specimen) was discovered in the 1970s near Eichstätt, Germany, and described in 1988 by Wellnhofer. Currently located at the Bürgermeister-Müller-Museum in Solnhofen, it originally was classified as '' Compsognathus'' by an amateur collector, the same mayor Friedrich Müller after which the museum is named. It is the largest specimen known and may belong to a separate genus and species, '' Wellnhoferia grandis''. It is missing only portions of the neck, tail, backbone, and head.
The Munich Specimen (BSP 1999 I 50, formerly known as the ''Solenhofer-Aktien-Verein Specimen'') was discovered on 3 August 1992 near Langenaltheim and described in 1993 by Wellnhofer. It is currently located at the Paläontologisches Museum München in Munich, to which it was sold in 1999 for 1.9 million Deutschmark. What was initially believed to be a bony sternum turned out to be part of the coracoid, but a cartilaginous sternum may have been present. Only the front of its face is missing. It has been used as the basis for a distinct species, ''A. bavarica'', but more recent studies suggest it belongs to ''A. siemensii''.
 An eighth, fragmentary specimen was discovered in 1990 in the younger Mörnsheim Formation at
An eighth, fragmentary specimen was discovered in 1990 in the younger Mörnsheim Formation at Daiting
Daiting is a municipality in the district of Donau-Ries in Bavaria in Germany.
Archaeopteryx - Daiting Specimen
An eighth, fragmentary specimen of Archaeopteryx was discovered in the late 1980s in the somewhat younger sediments at Daiting. It ...
, Suevia
Swabia ; german: Schwaben , colloquially ''Schwabenland'' or ''Ländle''; archaic English also Suabia or Svebia is a cultural, Historical region, historic and linguistic region in southwestern Germany.
The name is ultimately derived from the ...
. Therefore, it is known as the Daiting Specimen, and had been known since 1996 only from a cast, briefly shown at the Naturkundemuseum
The Natural History Museum (german: Museum für Naturkunde) is a natural history museum located in Berlin, Germany. It exhibits a vast range of specimens from various segments of natural history and in such domain it is one of three major ...
in Bamberg
Bamberg (, , ; East Franconian: ''Bambärch'') is a town in Upper Franconia, Germany, on the river Regnitz close to its confluence with the river Main. The town dates back to the 9th century, when its name was derived from the nearby ' castle. C ...
. The original was purchased by palaeontologist Raimund Albertsdörfer in 2009. It was on display for the first time with six other original fossils of ''Archaeopteryx'' at the Munich Mineral Show in October 2009. The Daiting Specimen was subsequently named ''Archaeopteryx albersdoerferi'' by Kundrat et al. (2018).
 Another fragmentary fossil was found in 2000. It is in private possession and, since 2004, on loan to the Bürgermeister-Müller Museum in Solnhofen, so it is called the Bürgermeister-Müller Specimen; the institute itself officially refers to it as the "Exemplar of the families Ottman & Steil, Solnhofen". As the fragment represents the remains of a single wing of ''Archaeopteryx'', it is colloquially known as "chicken wing".
Another fragmentary fossil was found in 2000. It is in private possession and, since 2004, on loan to the Bürgermeister-Müller Museum in Solnhofen, so it is called the Bürgermeister-Müller Specimen; the institute itself officially refers to it as the "Exemplar of the families Ottman & Steil, Solnhofen". As the fragment represents the remains of a single wing of ''Archaeopteryx'', it is colloquially known as "chicken wing".
 Long in a private collection in Switzerland, the Thermopolis Specimen (WDC CSG 100) was discovered in Bavaria and described in 2005 by Mayr, Pohl, and Peters. Donated to the Wyoming Dinosaur Center in Thermopolis, Wyoming, it has the best-preserved head and feet; most of the neck and the lower jaw have not been preserved. The "Thermopolis" specimen was described on 2 December 2005 ''Science'' journal article as "A well-preserved ''Archaeopteryx'' specimen with theropod features"; it shows that ''Archaeopteryx'' lacked a reversed toe—a universal feature of birds—limiting its ability to perch on branches and implying a terrestrial or trunk-climbing lifestyle. This has been interpreted as evidence of theropod ancestry. In 1988, Gregory S. Paul claimed to have found evidence of a hyperextensible second toe, but this was not verified and accepted by other scientists until the Thermopolis specimen was described. "Until now, the feature was thought to belong only to the species' close relatives, the deinonychosaurs." The Thermopolis Specimen was assigned to ''Archaeopteryx siemensii'' in 2007. The specimen is considered to represent the most complete and best-preserved ''Archaeopteryx'' remains yet.
Long in a private collection in Switzerland, the Thermopolis Specimen (WDC CSG 100) was discovered in Bavaria and described in 2005 by Mayr, Pohl, and Peters. Donated to the Wyoming Dinosaur Center in Thermopolis, Wyoming, it has the best-preserved head and feet; most of the neck and the lower jaw have not been preserved. The "Thermopolis" specimen was described on 2 December 2005 ''Science'' journal article as "A well-preserved ''Archaeopteryx'' specimen with theropod features"; it shows that ''Archaeopteryx'' lacked a reversed toe—a universal feature of birds—limiting its ability to perch on branches and implying a terrestrial or trunk-climbing lifestyle. This has been interpreted as evidence of theropod ancestry. In 1988, Gregory S. Paul claimed to have found evidence of a hyperextensible second toe, but this was not verified and accepted by other scientists until the Thermopolis specimen was described. "Until now, the feature was thought to belong only to the species' close relatives, the deinonychosaurs." The Thermopolis Specimen was assigned to ''Archaeopteryx siemensii'' in 2007. The specimen is considered to represent the most complete and best-preserved ''Archaeopteryx'' remains yet.
 The discovery of an eleventh specimen was announced in 2011; it was described in 2014. It is one of the more complete specimens, but is missing much of the skull and one forelimb. It is privately owned and has yet to be given a name. Palaeontologists of the
The discovery of an eleventh specimen was announced in 2011; it was described in 2014. It is one of the more complete specimens, but is missing much of the skull and one forelimb. It is privately owned and has yet to be given a name. Palaeontologists of the Ludwig Maximilian University of Munich
The Ludwig Maximilian University of Munich (simply University of Munich or LMU; german: Ludwig-Maximilians-Universität München) is a public research university in Munich, Germany. It is Germany's sixth-oldest university in continuous operatio ...
studied the specimen, which revealed previously unknown features of the plumage, such as feathers on both the upper and lower legs and metatarsus, and the only preserved tail tip.
A twelfth specimen had been discovered by an amateur collector in 2010 at the Schamhaupten quarry, but the finding was only announced in February 2014. It was scientifically described in 2018. It represents a complete and mostly articulated skeleton with skull. It is the only specimen lacking preserved feathers. It is from the Painten Formation and somewhat older than the other specimens.
Authenticity
Beginning in 1985, an amateur group including astronomer Fred Hoyle and physicistLee Spetner
Dr Lee M. Spetner is an American and Israeli creationist author, mechanical engineer, applied biophysicist, and physicist, known best for his disagreements with the modern synthesis. In spite of his opposition to neo-Darwinism, Spetner accepts a f ...
, published a series of papers claiming that the feathers on the Berlin and London specimens of ''Archaeopteryx'' were forged. Their claims were repudiated by Alan J. Charig and others at the Natural History Museum in London. Most of their supposed evidence for a forgery was based on unfamiliarity with the processes of lithification; for example, they proposed that, based on the difference in texture associated with the feathers, feather impressions were applied to a thin layer of cement, without realizing that feathers themselves would have caused a textural difference. They also misinterpreted the fossils, claiming that the tail was forged as one large feather, when visibly this is not the case. In addition, they claimed that the other specimens of ''Archaeopteryx'' known at the time did not have feathers, which is incorrect; the Maxberg and Eichstätt specimens have obvious feathers.
They also expressed disbelief that slabs would split so smoothly, or that one half of a slab containing fossils would have good preservation, but not the counterslab. These are common properties of Solnhofen fossils, because the dead animals would fall onto hardened surfaces, which would form a natural plane for the future slabs to split along and would leave the bulk of the fossil on one side and little on the other.
Finally, the motives they suggested for a forgery are not strong, and are contradictory; one is that Richard Owen wanted to forge evidence in support of Charles Darwin's theory of evolution, which is unlikely given Owen's views toward Darwin and his theory. The other is that Owen wanted to set a trap for Darwin, hoping the latter would support the fossils so Owen could discredit him with the forgery; this is unlikely because Owen wrote a detailed paper on the London specimen, so such an action would certainly backfire.
Charig ''et al.'' pointed to the presence of hairline cracks in the slabs running through both rock and fossil impressions, and mineral growth over the slabs that had occurred before discovery and preparation, as evidence that the feathers were original. Spetner ''et al.'' then attempted to show that the cracks would have propagated naturally through their postulated cement layer, but neglected to account for the fact that the cracks were old and had been filled with calcite
Calcite is a Carbonate minerals, carbonate mineral and the most stable Polymorphism (materials science), polymorph of calcium carbonate (CaCO3). It is a very common mineral, particularly as a component of limestone. Calcite defines hardness 3 on ...
, and thus were not able to propagate. They also attempted to show the presence of cement on the London specimen through X-ray spectroscopy, and did find something that was not rock; it was not cement either, and is most probably a fragment of silicone rubber left behind when moulds were made of the specimen. Their suggestions have not been taken seriously by palaeontologists, as their evidence was largely based on misunderstandings of geology, and they never discussed the other feather-bearing specimens, which have increased in number since then. Charig ''et al.'' reported a discolouration: a dark band between two layers of limestone – they say it is the product of sedimentation. It is natural for limestone to take on the colour of its surroundings and most limestones are coloured (if not colour banded) to some degree, so the darkness was attributed to such impurities. They also mention that a complete absence of air bubbles in the rock slabs is further proof that the specimen is authentic.
Description
raven
A raven is any of several larger-bodied bird species of the genus ''Corvus''. These species do not form a single taxonomic group within the genus. There is no consistent distinction between "crows" and "ravens", common names which are assigned t ...
, with broad wings that were rounded at the ends and a long tail compared to its body length. It could reach up to in body length and in wingspan, with an estimated mass of . ''Archaeopteryx'' feathers, although less documented than its other features, were very similar in structure to modern-day bird feathers. Despite the presence of numerous avian features, ''Archaeopteryx'' had many non-avian theropod dinosaur characteristics. Unlike modern birds, ''Archaeopteryx'' had small teeth, as well as a long bony tail, features which ''Archaeopteryx'' shared with other dinosaurs of the time.
Because it displays features common to both birds and non-avian dinosaurs, ''Archaeopteryx'' has often been considered a link between them. In the 1970s, John Ostrom, following Thomas Henry Huxley's lead in 1868, argued that birds evolved within theropod dinosaurs and ''Archaeopteryx'' was a critical piece of evidence for this argument; it had several avian features, such as a wishbone, flight feathers, wings, and a partially reversed first toe along with dinosaur and theropod features. For instance, it has a long ascending process of the ankle bone, interdental plates, an obturator process of the ischium
The ischium () form ...
, and long chevrons in the tail. In particular, Ostrom found that ''Archaeopteryx'' was remarkably similar to the theropod family Dromaeosauridae.
Archaeopteryx had three separate digits on each fore-leg each ending with a "claw". Few birds have such features. Some birds, such as ducks, swan
Swans are birds of the family (biology), family Anatidae within the genus ''Cygnus''. The swans' closest relatives include the goose, geese and ducks. Swans are grouped with the closely related geese in the subfamily Anserinae where they form t ...
s, Jacanas (''Jacana'' sp.), and the hoatzin (''Opisthocomus hoazin''), have them concealed beneath their leg-feathers.
Plumage
 Specimens of ''Archaeopteryx'' were most notable for their well-developed
Specimens of ''Archaeopteryx'' were most notable for their well-developed flight feather
Flight feathers (''Pennae volatus'') are the long, stiff, asymmetrically shaped, but symmetrically paired pennaceous feathers on the wings or tail of a bird; those on the wings are called remiges (), singular remex (), while those on the tail ...
s. They were markedly asymmetrical and showed the structure of flight feathers in modern birds, with vanes given stability by a barb- barbule-barbicel
Feathers are epidermal growths that form a distinctive outer covering, or plumage, on both avian (bird) and some non-avian dinosaurs and other archosaurs. They are the most complex integumentary structures found in vertebrates and a premier e ...
arrangement. The tail feathers were less asymmetrical, again in line with the situation in modern birds and also had firm vanes. The thumb
The thumb is the first digit of the hand, next to the index finger. When a person is standing in the medical anatomical position (where the palm is facing to the front), the thumb is the outermost digit. The Medical Latin English noun for thumb ...
did not yet bear a separately movable tuft of stiff feathers.
The body plumage of ''Archaeopteryx'' is less well-documented and has only been properly researched in the well-preserved Berlin specimen. Thus, as more than one species seems to be involved, the research into the Berlin specimen's feathers does not necessarily hold true for the rest of the species of ''Archaeopteryx''. In the Berlin specimen, there are "trousers" of well-developed feathers on the legs; some of these feathers seem to have a basic contour feather structure, but are somewhat decomposed (they lack barbicels as in ratite
A ratite () is any of a diverse group of flightless, large, long-necked, and long-legged birds of the infraclass Palaeognathae. Kiwi, the exception, are much smaller and shorter-legged and are the only nocturnal extant ratites.
The systematics ...
s). In part they are firm and thus capable of supporting flight.
A patch of pennaceous feathers is found running along its back, which was quite similar to the contour feathers of the body plumage of modern birds in being symmetrical and firm, although not as stiff as the flight-related feathers. Apart from that, the feather traces in the Berlin specimen are limited to a sort of "proto-down
Down most often refers to:
* Down, the relative direction opposed to up
* Down (gridiron football), in American/Canadian football, a period when one play takes place
* Down feather, a soft bird feather used in bedding and clothing
* Downland, a ty ...
" not dissimilar to that found in the dinosaur '' Sinosauropteryx'': decomposed and fluffy, and possibly even appearing more like fur than feathers in life (although not in their microscopic structure). These occur on the remainder of the body—although some feathers did not fossilize and others were obliterated during preparation, leaving bare patches on specimens—and the lower neck.
There is no indication of feathering on the upper neck and head. While these conceivably may have been nude, this may still be an artefact of preservation. It appears that most ''Archaeopteryx'' specimens became embedded in anoxic sediment after drifting some time on their backs in the sea—the head, neck and the tail are generally bent downward, which suggests that the specimens had just started to rot when they were embedded, with tendons and muscle relaxing so that the characteristic shape (death pose
Non-avian dinosaur and bird fossils are frequently found in a characteristic posture consisting of head thrown back, tail extended, and mouth wide open. The cause of this posture—often called a "death pose"—has been a matter of scientific deba ...
) of the fossil specimens was achieved. This would mean that the skin already was softened and loose, which is bolstered by the fact that in some specimens the flight feathers were starting to detach at the point of embedding in the sediment. So it is hypothesized that the pertinent specimens moved along the sea bed in shallow water for some time before burial, the head and upper neck feathers sloughing off, while the more firmly attached tail feathers remained.
Colouration
 In 2011, graduate student Ryan Carney and colleagues performed the first colour study on an ''Archaeopteryx'' specimen. Using scanning electron microscopy technology and energy-dispersive X-ray analysis, the team was able to detect the structure of melanosomes in the isolated feather specimen described in 1861. The resultant measurements were then compared to those of 87modern bird species, and the original colour was calculated with a 95% likelihood to be black. The feather was determined to be black throughout, with heavier pigmentation in the distal tip. The feather studied was most probably a dorsal covert, which would have partly covered the primary feathers on the wings. The study does not mean that ''Archaeopteryx'' was entirely black, but suggests that it had some black colouration which included the coverts. Carney pointed out that this is consistent with what we know of modern flight characteristics, in that black melanosomes have structural properties that strengthen feathers for flight. In a 2013 study published in the ''Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry'', new analyses of ''Archaeopteryxs feathers revealed that the animal may have had complex light- and dark-coloured plumage, with heavier pigmentation in the distal tips and outer vanes. This analysis of color distribution was based primarily on the distribution of sulphate within the fossil. An author on the previous ''Archaeopteryx'' color study argued against the interpretation of such biomarkers as an indicator of eumelanin in the full ''Archaeopteryx'' specimen. Carney and other colleagues also argued against the 2013 study's interpretation of the sulphate and trace metals, and in a 2020 study published in ''Scientific Reports'' demonstrated that the isolated covert feather was entirely matte black (as opposed to black and white, or iridescent) and that the remaining "plumage patterns of ''Archaeopteryx'' remain unknown".
In 2011, graduate student Ryan Carney and colleagues performed the first colour study on an ''Archaeopteryx'' specimen. Using scanning electron microscopy technology and energy-dispersive X-ray analysis, the team was able to detect the structure of melanosomes in the isolated feather specimen described in 1861. The resultant measurements were then compared to those of 87modern bird species, and the original colour was calculated with a 95% likelihood to be black. The feather was determined to be black throughout, with heavier pigmentation in the distal tip. The feather studied was most probably a dorsal covert, which would have partly covered the primary feathers on the wings. The study does not mean that ''Archaeopteryx'' was entirely black, but suggests that it had some black colouration which included the coverts. Carney pointed out that this is consistent with what we know of modern flight characteristics, in that black melanosomes have structural properties that strengthen feathers for flight. In a 2013 study published in the ''Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry'', new analyses of ''Archaeopteryxs feathers revealed that the animal may have had complex light- and dark-coloured plumage, with heavier pigmentation in the distal tips and outer vanes. This analysis of color distribution was based primarily on the distribution of sulphate within the fossil. An author on the previous ''Archaeopteryx'' color study argued against the interpretation of such biomarkers as an indicator of eumelanin in the full ''Archaeopteryx'' specimen. Carney and other colleagues also argued against the 2013 study's interpretation of the sulphate and trace metals, and in a 2020 study published in ''Scientific Reports'' demonstrated that the isolated covert feather was entirely matte black (as opposed to black and white, or iridescent) and that the remaining "plumage patterns of ''Archaeopteryx'' remain unknown".
Classification
 Today, fossils of the genus ''Archaeopteryx'' are usually assigned to one or two species, ''A. lithographica'' and ''A. siemensii'', but their taxonomic history is complicated. Ten names have been published for the handful of specimens. As interpreted today, the name ''A. lithographica'' only referred to the single feather described by Meyer. In 1954 Gavin de Beer concluded that the London specimen was the holotype. In 1960, Swinton accordingly proposed that the name ''Archaeopteryx lithographica'' be placed on the official genera list making the alternative names ''Griphosaurus'' and ''Griphornis'' invalid. The ICZN, implicitly accepting De Beer's standpoint, did indeed suppress the plethora of alternative names initially proposed for the first skeleton specimens, which mainly resulted from the acrimonious dispute between Meyer and his opponent Johann Andreas Wagner (whose ''Griphosaurus problematicus'' – 'problematic riddle-lizard' – was a vitriolic sneer at Meyer's ''Archaeopteryx''). In addition, in 1977, the Commission ruled that the first species name of the Haarlem specimen, ''crassipes'', described by Meyer as a pterosaur before its true nature was realized, was not to be given preference over ''lithographica'' in instances where scientists considered them to represent the same species.
It has been noted that the feather, the first specimen of ''Archaeopteryx'' described, does not correspond well with the flight-related feathers of ''Archaeopteryx''. It certainly is a
Today, fossils of the genus ''Archaeopteryx'' are usually assigned to one or two species, ''A. lithographica'' and ''A. siemensii'', but their taxonomic history is complicated. Ten names have been published for the handful of specimens. As interpreted today, the name ''A. lithographica'' only referred to the single feather described by Meyer. In 1954 Gavin de Beer concluded that the London specimen was the holotype. In 1960, Swinton accordingly proposed that the name ''Archaeopteryx lithographica'' be placed on the official genera list making the alternative names ''Griphosaurus'' and ''Griphornis'' invalid. The ICZN, implicitly accepting De Beer's standpoint, did indeed suppress the plethora of alternative names initially proposed for the first skeleton specimens, which mainly resulted from the acrimonious dispute between Meyer and his opponent Johann Andreas Wagner (whose ''Griphosaurus problematicus'' – 'problematic riddle-lizard' – was a vitriolic sneer at Meyer's ''Archaeopteryx''). In addition, in 1977, the Commission ruled that the first species name of the Haarlem specimen, ''crassipes'', described by Meyer as a pterosaur before its true nature was realized, was not to be given preference over ''lithographica'' in instances where scientists considered them to represent the same species.
It has been noted that the feather, the first specimen of ''Archaeopteryx'' described, does not correspond well with the flight-related feathers of ''Archaeopteryx''. It certainly is a flight feather
Flight feathers (''Pennae volatus'') are the long, stiff, asymmetrically shaped, but symmetrically paired pennaceous feathers on the wings or tail of a bird; those on the wings are called remiges (), singular remex (), while those on the tail ...
of a contemporary species, but its size and proportions indicate that it may belong to another, smaller species of feathered theropod, of which only this feather is known so far. As the feather had been designated the type specimen, the name ''Archaeopteryx'' should then no longer be applied to the skeletons, thus creating significant nomenclatorial confusion. In 2007, two sets of scientists therefore petitioned the ICZN requesting that the London specimen explicitly be made the type by designating it as the new holotype specimen, or neotype. This suggestion was upheld by the ICZN after four years of debate, and the London specimen was designated the neotype on 3 October 2011.
 Below is a cladogram published in 2013 by Godefroit ''et al.''
Below is a cladogram published in 2013 by Godefroit ''et al.''
Species
 It has been argued that all the specimens belong to the same species, ''A. lithographica''. Differences do exist among the specimens, and while some researchers regard these as due to the different ages of the specimens, some may be related to actual species diversity. In particular, the Munich, Eichstätt, Solnhofen, and Thermopolis specimens differ from the London, Berlin, and Haarlem specimens in being smaller or much larger, having different finger proportions, having more slender snouts lined with forward-pointing teeth, and the possible presence of a sternum. Due to these differences, most individual specimens have been given their own species name at one point or another. The Berlin specimen has been designated as ''Archaeornis siemensii'', the Eichstätt specimen as ''Jurapteryx recurva'', the Munich specimen as ''Archaeopteryx bavarica'', and the Solnhofen specimen as ''Wellnhoferia grandis''.
In 2007, a review of all well-preserved specimens including the then-newly discovered Thermopolis specimen concluded that two distinct species of ''Archaeopteryx'' could be supported: ''A. lithographica'' (consisting of at least the London and Solnhofen specimens), and ''A. siemensii'' (consisting of at least the Berlin, Munich, and Thermopolis specimens). The two species are distinguished primarily by large flexor tubercles on the foot claws in ''A. lithographica'' (the claws of ''A. siemensii'' specimens being relatively simple and straight). ''A. lithographica'' also had a constricted portion of the crown in some teeth and a stouter metatarsus. A supposed additional species, ''Wellnhoferia grandis'' (based on the Solnhofen specimen), seems to be indistinguishable from ''A. lithographica'' except in its larger size.
It has been argued that all the specimens belong to the same species, ''A. lithographica''. Differences do exist among the specimens, and while some researchers regard these as due to the different ages of the specimens, some may be related to actual species diversity. In particular, the Munich, Eichstätt, Solnhofen, and Thermopolis specimens differ from the London, Berlin, and Haarlem specimens in being smaller or much larger, having different finger proportions, having more slender snouts lined with forward-pointing teeth, and the possible presence of a sternum. Due to these differences, most individual specimens have been given their own species name at one point or another. The Berlin specimen has been designated as ''Archaeornis siemensii'', the Eichstätt specimen as ''Jurapteryx recurva'', the Munich specimen as ''Archaeopteryx bavarica'', and the Solnhofen specimen as ''Wellnhoferia grandis''.
In 2007, a review of all well-preserved specimens including the then-newly discovered Thermopolis specimen concluded that two distinct species of ''Archaeopteryx'' could be supported: ''A. lithographica'' (consisting of at least the London and Solnhofen specimens), and ''A. siemensii'' (consisting of at least the Berlin, Munich, and Thermopolis specimens). The two species are distinguished primarily by large flexor tubercles on the foot claws in ''A. lithographica'' (the claws of ''A. siemensii'' specimens being relatively simple and straight). ''A. lithographica'' also had a constricted portion of the crown in some teeth and a stouter metatarsus. A supposed additional species, ''Wellnhoferia grandis'' (based on the Solnhofen specimen), seems to be indistinguishable from ''A. lithographica'' except in its larger size.
Synonyms
 If two names are given, the first denotes the original describer of the "species", the second the author on whom the given name combination is based. As always in zoological nomenclature, putting an author's name in parentheses denotes that the taxon was originally described in a different genus.
* ''Archaeopteryx lithographica'' Meyer, 1861 onserved name/small>
**''Archaeopterix lithographica'' Anon., 1861 'lapsus''/small>
** ''Griphosaurus problematicus'' Wagner, 1862 ejected name 1961 per ICZN Opinion 607/small>
** ''Griphornis longicaudatus'' Owen ''vide'' Woodward, 1862 ejected name 1961 per ICZN Opinion 607/small>
** ''Archaeopteryx macrura'' Owen, 1862 ejected name 1961 per ICZN Opinion 607/small>
** ''Archaeopteryx oweni'' Petronievics, 1917 ejected name 1961 per ICZN Opinion 607/small>
** ''Archaeopteryx recurva'' Howgate, 1984
** ''Jurapteryx recurva'' (Howgate, 1984) Howgate, 1985
** ''Wellnhoferia grandis'' Elżanowski, 2001
* ''Archaeopteryx siemensii'' Dames, 1897
**''Archaeornis siemensii'' (Dames, 1897) Petronievics, 1917
** ''Archaeopteryx bavarica'' Wellnhofer, 1993
''"Archaeopteryx" vicensensis'' (Anon. ''fide'' Lambrecht, 1933) is a ''
If two names are given, the first denotes the original describer of the "species", the second the author on whom the given name combination is based. As always in zoological nomenclature, putting an author's name in parentheses denotes that the taxon was originally described in a different genus.
* ''Archaeopteryx lithographica'' Meyer, 1861 onserved name/small>
**''Archaeopterix lithographica'' Anon., 1861 'lapsus''/small>
** ''Griphosaurus problematicus'' Wagner, 1862 ejected name 1961 per ICZN Opinion 607/small>
** ''Griphornis longicaudatus'' Owen ''vide'' Woodward, 1862 ejected name 1961 per ICZN Opinion 607/small>
** ''Archaeopteryx macrura'' Owen, 1862 ejected name 1961 per ICZN Opinion 607/small>
** ''Archaeopteryx oweni'' Petronievics, 1917 ejected name 1961 per ICZN Opinion 607/small>
** ''Archaeopteryx recurva'' Howgate, 1984
** ''Jurapteryx recurva'' (Howgate, 1984) Howgate, 1985
** ''Wellnhoferia grandis'' Elżanowski, 2001
* ''Archaeopteryx siemensii'' Dames, 1897
**''Archaeornis siemensii'' (Dames, 1897) Petronievics, 1917
** ''Archaeopteryx bavarica'' Wellnhofer, 1993
''"Archaeopteryx" vicensensis'' (Anon. ''fide'' Lambrecht, 1933) is a ''nomen nudum
In taxonomy, a ''nomen nudum'' ('naked name'; plural ''nomina nuda'') is a designation which looks exactly like a scientific name of an organism, and may have originally been intended to be one, but it has not been published with an adequate descr ...
'' for what appears to be an undescribed pterosaur.
Phylogenetic position
Palaeobiology
Flight
 As in the wings of modern birds, the flight feathers of ''Archaeopteryx'' were somewhat asymmetrical and the tail feathers were rather broad. This implies that the wings and tail were used for lift generation, but it is unclear whether ''Archaeopteryx'' was capable of flapping flight or simply a glider. The lack of a bony Sternum, breastbone suggests that ''Archaeopteryx'' was not a very strong flier, but flight muscles might have attached to the thick, boomerang-shaped wishbone, the platelike coracoids, or perhaps, to a cartilage, cartilaginous sternum. The sideways orientation of the glenoid (shoulder) joint between scapula, coracoid, and humerus—instead of the dorsally angled arrangement found in modern birds—may indicate that ''Archaeopteryx'' was unable to lift its wings above its back, a requirement for the upstroke found in modern flapping flight. According to a study by Philip Senter in 2006, ''Archaeopteryx'' was indeed unable to use flapping flight as modern birds do, but it may well have used a downstroke-only flap-assisted gliding technique. However, a more recent study solves this issue by suggesting a different flight stroke configuration for non-avian flying theropods.
''Archaeopteryx'' wings were relatively large, which would have resulted in a low stall speed and reduced turning radius. The short and rounded shape of the wings would have increased drag, but also could have improved its ability to fly through cluttered environments such as trees and brush (similar wing shapes are seen in birds that fly through trees and brush, such as crows and pheasants). The presence of "hind wings", asymmetrical flight feathers stemming from the legs similar to those seen in dromaeosaurids such as ''Microraptor'', also would have added to the aerial mobility of ''Archaeopteryx''. The first detailed study of the hind wings by Longrich in 2006, suggested that the structures formed up to 12% of the total airfoil. This would have reduced stall speed by up to 6% and turning radius by up to 12%.
The feathers of ''Archaeopteryx'' were asymmetrical. This has been interpreted as evidence that it was a flyer, because flightless birds tend to have symmetrical feathers. Some scientists, including Thomson and Speakman, have questioned this. They studied more than 70 families of living birds, and found that some flightless types do have a range of asymmetry in their feathers, and that the feathers of ''Archaeopteryx'' fall into this range. The degree of asymmetry seen in ''Archaeopteryx'' is more typical for slow flyers than for flightless birds.
As in the wings of modern birds, the flight feathers of ''Archaeopteryx'' were somewhat asymmetrical and the tail feathers were rather broad. This implies that the wings and tail were used for lift generation, but it is unclear whether ''Archaeopteryx'' was capable of flapping flight or simply a glider. The lack of a bony Sternum, breastbone suggests that ''Archaeopteryx'' was not a very strong flier, but flight muscles might have attached to the thick, boomerang-shaped wishbone, the platelike coracoids, or perhaps, to a cartilage, cartilaginous sternum. The sideways orientation of the glenoid (shoulder) joint between scapula, coracoid, and humerus—instead of the dorsally angled arrangement found in modern birds—may indicate that ''Archaeopteryx'' was unable to lift its wings above its back, a requirement for the upstroke found in modern flapping flight. According to a study by Philip Senter in 2006, ''Archaeopteryx'' was indeed unable to use flapping flight as modern birds do, but it may well have used a downstroke-only flap-assisted gliding technique. However, a more recent study solves this issue by suggesting a different flight stroke configuration for non-avian flying theropods.
''Archaeopteryx'' wings were relatively large, which would have resulted in a low stall speed and reduced turning radius. The short and rounded shape of the wings would have increased drag, but also could have improved its ability to fly through cluttered environments such as trees and brush (similar wing shapes are seen in birds that fly through trees and brush, such as crows and pheasants). The presence of "hind wings", asymmetrical flight feathers stemming from the legs similar to those seen in dromaeosaurids such as ''Microraptor'', also would have added to the aerial mobility of ''Archaeopteryx''. The first detailed study of the hind wings by Longrich in 2006, suggested that the structures formed up to 12% of the total airfoil. This would have reduced stall speed by up to 6% and turning radius by up to 12%.
The feathers of ''Archaeopteryx'' were asymmetrical. This has been interpreted as evidence that it was a flyer, because flightless birds tend to have symmetrical feathers. Some scientists, including Thomson and Speakman, have questioned this. They studied more than 70 families of living birds, and found that some flightless types do have a range of asymmetry in their feathers, and that the feathers of ''Archaeopteryx'' fall into this range. The degree of asymmetry seen in ''Archaeopteryx'' is more typical for slow flyers than for flightless birds.
 In 2010, Robert L. Nudds and Gareth J. Dyke in the journal ''Science'' published a paper in which they analysed the rachises of the primary feathers of ''Confuciusornis'' and ''Archaeopteryx''. The analysis suggested that the rachises on these two genera were thinner and weaker than those of modern birds relative to body mass. The authors determined that ''Archaeopteryx'' and ''Confuciusornis'', were unable to use flapping flight. This study was criticized by Philip J. Currie and Luis Chiappe. Chiappe suggested that it is difficult to measure the rachises of fossilized feathers, and Currie speculated that ''Archaeopteryx'' and ''Confuciusornis'' must have been able to fly to some degree, as their fossils are preserved in what is believed to have been marine or lake sediments, suggesting that they must have been able to fly over deep water.Balter, M. (2010)
In 2010, Robert L. Nudds and Gareth J. Dyke in the journal ''Science'' published a paper in which they analysed the rachises of the primary feathers of ''Confuciusornis'' and ''Archaeopteryx''. The analysis suggested that the rachises on these two genera were thinner and weaker than those of modern birds relative to body mass. The authors determined that ''Archaeopteryx'' and ''Confuciusornis'', were unable to use flapping flight. This study was criticized by Philip J. Currie and Luis Chiappe. Chiappe suggested that it is difficult to measure the rachises of fossilized feathers, and Currie speculated that ''Archaeopteryx'' and ''Confuciusornis'' must have been able to fly to some degree, as their fossils are preserved in what is believed to have been marine or lake sediments, suggesting that they must have been able to fly over deep water.Balter, M. (2010)"Did First Feathers Prevent Early Flight?"
''Science Now'', 13 May 2010. Gregory Paul also disagreed with the study, arguing in a 2010 response that Nudds and Dyke had overestimated the masses of these early birds, and that more accurate mass estimates allowed powered flight even with relatively narrow rachises. Nudds and Dyke had assumed a mass of for the Munich specimen ''Archaeopteryx'', a young juvenile, based on published mass estimates of larger specimens. Paul argued that a more reasonable body mass estimate for the Munich specimen is about . Paul also criticized the measurements of the rachises themselves, noting that the feathers in the Munich specimen are poorly preserved. Nudds and Dyke reported a diameter of for the longest primary feather, which Paul could not confirm using photographs. Paul measured some of the inner primary feathers, finding rachises across. Despite these criticisms, Nudds and Dyke stood by their original conclusions. They claimed that Paul's statement, that an adult ''Archaeopteryx'' would have been a better flyer than the juvenile Munich specimen, was dubious. This, they reasoned, would require an even thicker rachis, evidence for which has not yet been presented. Another possibility is that they had not achieved true flight, but instead used their wings as aids for extra lift while running over water after the fashion of the basilisk lizard, which could explain their presence in lake and marine deposits (see Origin of avian flight). In 2004, scientists analysing a detailed CT scan of the braincase of the London ''Archaeopteryx'' concluded that its brain was significantly larger than that of most dinosaurs, indicating that it possessed the brain size necessary for flying. The overall brain anatomy was reconstructed using the scan. The reconstruction showed that the regions associated with vision took up nearly one-third of the brain. Other well-developed areas involved hearing and muscle coordination. The skull scan also revealed the structure of its inner ear. The structure more closely resembles that of modern birds than the inner ear of non-avian reptiles. These characteristics taken together suggest that ''Archaeopteryx'' had the keen sense of hearing, balance, spatial perception, and coordination needed to fly. ''Archaeopteryx'' had a cerebrum-to-brain-volume ratio 78% of the way to modern birds from the condition of non-coelurosaurian dinosaurs such as ''Carcharodontosaurus'' or ''Allosaurus'', which had a crocodile-like anatomy of the brain and inner ear.Larsson, H. C. E. (2001). "Endocranial anatomy of ''Carcharodontosaurus saharicus'' (Theropoda: Allosauroidea) and its implications for theropod brain evolution". In: Tanke, D. H.; Carpenter, K.; Skrepnick, M. W. (eds.) ''Mesozoic Vertebrate Life''. Indiana University Press. pp. 19–33. Newer research shows that while the ''Archaeopteryx'' brain was more complex than that of more primitive theropods, it had a more generalized brain volume among maniraptoran , Maniraptora dinosaurs, even smaller than that of other non-avian dinosaurs in several instances, which indicates the neurological development required for flight was already a common trait in the maniraptoran clade. Recent studies of flight feather barb geometry reveal that modern birds possess a larger barb angle in the trailing vane of the feather, whereas ''Archaeopteryx'' lacks this large barb angle, indicating potentially weak flight abilities.
 ''Archaeopteryx'' continues to play an important part in scientific debates about the origin and evolution of birds. Some scientists see it as a semi-arboreal climbing animal, following the idea that birds evolved from tree-dwelling gliders (the "trees down" hypothesis for the evolution of flight proposed by O. C. Marsh). Other scientists see ''Archaeopteryx'' as running quickly along the ground, supporting the idea that birds evolved flight by running (the "ground up" hypothesis proposed by Samuel Wendell Williston). Still others suggest that ''Archaeopteryx'' might have been at home both in the trees and on the ground, like modern crows, and this latter view is what currently is considered best-supported by morphological characters. Altogether, it appears that the species was not particularly specialized for running on the ground or for perching. A scenario outlined by Elżanowski in 2002 suggested that ''Archaeopteryx'' used its wings mainly to escape Predation, predators by glides punctuated with shallow downstrokes to reach successively higher perches, and alternatively, to cover longer distances (mainly) by gliding down from cliffs or treetops.
In March 2018, scientists reported that ''Archaeopteryx'' was likely capable of Bird flight, flight, but in a manner distinct and substantially different from that of Birds, modern birds. This study on ''Archaeopteryxs bone histology suggests that it was closest to true flying birds, and in particular to pheasants and other burst flyers.
Studies of ''Archaeopteryx's'' feather sheaths revealed that like modern birds, it had a center-out, flight related molting strategy. As it was a weak flier, this was extremely advantageous in preserving its maximum flight performance.
''Archaeopteryx'' continues to play an important part in scientific debates about the origin and evolution of birds. Some scientists see it as a semi-arboreal climbing animal, following the idea that birds evolved from tree-dwelling gliders (the "trees down" hypothesis for the evolution of flight proposed by O. C. Marsh). Other scientists see ''Archaeopteryx'' as running quickly along the ground, supporting the idea that birds evolved flight by running (the "ground up" hypothesis proposed by Samuel Wendell Williston). Still others suggest that ''Archaeopteryx'' might have been at home both in the trees and on the ground, like modern crows, and this latter view is what currently is considered best-supported by morphological characters. Altogether, it appears that the species was not particularly specialized for running on the ground or for perching. A scenario outlined by Elżanowski in 2002 suggested that ''Archaeopteryx'' used its wings mainly to escape Predation, predators by glides punctuated with shallow downstrokes to reach successively higher perches, and alternatively, to cover longer distances (mainly) by gliding down from cliffs or treetops.
In March 2018, scientists reported that ''Archaeopteryx'' was likely capable of Bird flight, flight, but in a manner distinct and substantially different from that of Birds, modern birds. This study on ''Archaeopteryxs bone histology suggests that it was closest to true flying birds, and in particular to pheasants and other burst flyers.
Studies of ''Archaeopteryx's'' feather sheaths revealed that like modern birds, it had a center-out, flight related molting strategy. As it was a weak flier, this was extremely advantageous in preserving its maximum flight performance.
Growth
 An histological study by Erickson, Norell, Zhongue, and others in 2009 estimated that ''Archaeopteryx'' grew relatively slowly compared to modern birds, presumably because the outermost portions of ''Archaeopteryx'' bones appear poorly vascularized; in living vertebrates, poorly vascularized bone is correlated with slow growth rate. They also assume that all known skeletons of ''Archaeopteryx'' come from juvenile specimens. Because the bones of ''Archaeopteryx'' could not be histologically sectioned in a formal skeletochronological (growth ring) analysis, Erickson and colleagues used bone vascularity (porosity) to estimate bone growth rate. They assumed that poorly vascularized bone grows at similar rates in all birds and in ''Archaeopteryx''. The poorly vascularized bone of ''Archaeopteryx'' might have grown as slowly as that in a mallard (2.5micrometres per day) or as fast as that in an ostrich (4.2micrometres per day). Using this range of bone growth rates, they calculated how long it would take to "grow" each specimen of ''Archaeopteryx'' to the observed size; it may have taken at least 970 days (there were 375 days in a Late Jurassic year) to reach an adult size of . The study also found that the avialans ''Jeholornis'' and ''Sapeornis'' grew relatively slowly, as did the dromaeosaurid ''Mahakala (dinosaur), Mahakala''. The avialans ''Confuciusornis'' and ''Ichthyornis'' grew relatively quickly, following a growth trend similar to that of modern birds. One of the few modern birds that exhibit slow growth is the flightless Kiwi (bird), kiwi, and the authors speculated that ''Archaeopteryx'' and the kiwi had similar basal metabolic rate.
An histological study by Erickson, Norell, Zhongue, and others in 2009 estimated that ''Archaeopteryx'' grew relatively slowly compared to modern birds, presumably because the outermost portions of ''Archaeopteryx'' bones appear poorly vascularized; in living vertebrates, poorly vascularized bone is correlated with slow growth rate. They also assume that all known skeletons of ''Archaeopteryx'' come from juvenile specimens. Because the bones of ''Archaeopteryx'' could not be histologically sectioned in a formal skeletochronological (growth ring) analysis, Erickson and colleagues used bone vascularity (porosity) to estimate bone growth rate. They assumed that poorly vascularized bone grows at similar rates in all birds and in ''Archaeopteryx''. The poorly vascularized bone of ''Archaeopteryx'' might have grown as slowly as that in a mallard (2.5micrometres per day) or as fast as that in an ostrich (4.2micrometres per day). Using this range of bone growth rates, they calculated how long it would take to "grow" each specimen of ''Archaeopteryx'' to the observed size; it may have taken at least 970 days (there were 375 days in a Late Jurassic year) to reach an adult size of . The study also found that the avialans ''Jeholornis'' and ''Sapeornis'' grew relatively slowly, as did the dromaeosaurid ''Mahakala (dinosaur), Mahakala''. The avialans ''Confuciusornis'' and ''Ichthyornis'' grew relatively quickly, following a growth trend similar to that of modern birds. One of the few modern birds that exhibit slow growth is the flightless Kiwi (bird), kiwi, and the authors speculated that ''Archaeopteryx'' and the kiwi had similar basal metabolic rate.
Daily activity patterns
Comparisons between the sclerotic ring , scleral rings of ''Archaeopteryx'' and modern birds and reptiles indicate that it may have been Diurnality , diurnal, similar to most modern birds.Palaeoecology
 The richness and diversity of the Solnhofen limestones in which all specimens of ''Archaeopteryx'' have been found have shed light on an ancient Jurassic Bavaria strikingly different from the present day. The latitude was similar to Florida, though the climate was likely to have been drier, as evidenced by fossils of plants with adaptations for arid conditions and a lack of terrestrial sediments characteristic of rivers. Evidence of plants, although scarce, include cycads and conifers while animals found include a large number of insects, small lizards, pterosaurs, and '' Compsognathus''.
The excellent preservation of ''Archaeopteryx'' fossils and other terrestrial fossils found at Solnhofen indicates that they did not travel far before becoming preserved. The ''Archaeopteryx'' specimens found were therefore likely to have lived on the low islands surrounding the Solnhofen lagoon rather than to have been corpses that drifted in from farther away. ''Archaeopteryx'' skeletons are considerably less numerous in the deposits of Solnhofen than those of pterosaurs, of which seven genera have been found. The pterosaurs included species such as ''Rhamphorhynchus (pterosaur), Rhamphorhynchus'' belonging to the Rhamphorhynchidae, the group which dominated the ecological niche currently occupied by seabirds, and which became extinct at the end of the Jurassic. The pterosaurs, which also included '' Pterodactylus'', were common enough that it is unlikely that the specimens found are Vagrancy (biology), vagrants from the larger islands to the north.
The islands that surrounded the Solnhofen lagoon were low lying, semi-arid, and sub-tropical with a long dry season and little rain. The closest modern analogue for the Solnhofen conditions is said to be Orca Basin in the northern Gulf of Mexico, although it is much deeper than the Solnhofen lagoons. The flora of these islands was adapted to these dry conditions and consisted mostly of low () shrubs. Contrary to reconstructions of ''Archaeopteryx'' climbing large trees, these seem to have been mostly absent from the islands; few trunks have been found in the sediments and fossilized tree pollen also is absent.
The lifestyle of ''Archaeopteryx'' is difficult to reconstruct and there are several theories regarding it. Some researchers suggest that it was primarily adapted to life on the ground, while other researchers suggest that it was principally arboreal on the basis of the curvature of the claws which has since been questioned. The absence of trees does not preclude ''Archaeopteryx'' from an arboreal lifestyle, as several species of bird live exclusively in low shrubs. Various aspects of the morphology of ''Archaeopteryx'' point to either an arboreal or ground existence, including the length of its legs and the elongation in its feet; some authorities consider it likely to have been a Generalist and specialist species , generalist capable of feeding in both shrubs and open ground, as well as along the shores of the lagoon. It most likely hunted small prey, seizing it with its jaws if it was small enough, or with its claws if it was larger.
The richness and diversity of the Solnhofen limestones in which all specimens of ''Archaeopteryx'' have been found have shed light on an ancient Jurassic Bavaria strikingly different from the present day. The latitude was similar to Florida, though the climate was likely to have been drier, as evidenced by fossils of plants with adaptations for arid conditions and a lack of terrestrial sediments characteristic of rivers. Evidence of plants, although scarce, include cycads and conifers while animals found include a large number of insects, small lizards, pterosaurs, and '' Compsognathus''.
The excellent preservation of ''Archaeopteryx'' fossils and other terrestrial fossils found at Solnhofen indicates that they did not travel far before becoming preserved. The ''Archaeopteryx'' specimens found were therefore likely to have lived on the low islands surrounding the Solnhofen lagoon rather than to have been corpses that drifted in from farther away. ''Archaeopteryx'' skeletons are considerably less numerous in the deposits of Solnhofen than those of pterosaurs, of which seven genera have been found. The pterosaurs included species such as ''Rhamphorhynchus (pterosaur), Rhamphorhynchus'' belonging to the Rhamphorhynchidae, the group which dominated the ecological niche currently occupied by seabirds, and which became extinct at the end of the Jurassic. The pterosaurs, which also included '' Pterodactylus'', were common enough that it is unlikely that the specimens found are Vagrancy (biology), vagrants from the larger islands to the north.
The islands that surrounded the Solnhofen lagoon were low lying, semi-arid, and sub-tropical with a long dry season and little rain. The closest modern analogue for the Solnhofen conditions is said to be Orca Basin in the northern Gulf of Mexico, although it is much deeper than the Solnhofen lagoons. The flora of these islands was adapted to these dry conditions and consisted mostly of low () shrubs. Contrary to reconstructions of ''Archaeopteryx'' climbing large trees, these seem to have been mostly absent from the islands; few trunks have been found in the sediments and fossilized tree pollen also is absent.
The lifestyle of ''Archaeopteryx'' is difficult to reconstruct and there are several theories regarding it. Some researchers suggest that it was primarily adapted to life on the ground, while other researchers suggest that it was principally arboreal on the basis of the curvature of the claws which has since been questioned. The absence of trees does not preclude ''Archaeopteryx'' from an arboreal lifestyle, as several species of bird live exclusively in low shrubs. Various aspects of the morphology of ''Archaeopteryx'' point to either an arboreal or ground existence, including the length of its legs and the elongation in its feet; some authorities consider it likely to have been a Generalist and specialist species , generalist capable of feeding in both shrubs and open ground, as well as along the shores of the lagoon. It most likely hunted small prey, seizing it with its jaws if it was small enough, or with its claws if it was larger.
See also
* Evolution of birds * Feathered dinosaurs * Origin of birds * ''Ostromia
''Ostromia'' (''Thick feet of John Ostrom'') is a genus of anchiornithid theropod dinosaur from the Late Jurassic Painten Formation of Germany. The genus contains a single species, ''O. crassipes'', named by Christian Foth and Oliver Rauhut in 2 ...
''
* ''Rhamphorhynchus''
* Temporal paradox (paleontology)
* '' Xiaotingia''
References
Further reading
* G. R. de Beer (1954). ''Archaeopteryx lithographica: a study based upon the British Museum specimen''. Trustees of the British Museum, London. * P. Chambers (2002). ''Bones of Contention: The Fossil that Shook Science.'' John Murray, London. . * A. Feduccia (1996). ''The Origin and Evolution of Birds''. Yale University Press, New Haven. . * Gerhard Heilmann, Heilmann, G. (1926). ''The Origin of Birds (book), The Origin of Birds''. Witherby, London. * T. H. Huxley. (1871). ''Manual of the anatomy of vertebrate animals''. London. * H. von Meyer (1861). ''Archaeopterix lithographica (Vogel-Feder) und Pterodactylus von Solenhofen''. . ''1861'': 678–679, plate V. [Article in German]Full text, Google Books
* P. Shipman (1998). ''Taking Wing: Archaeopteryx and the Evolution of Bird Flight''. Weidenfeld & Nicolson, London. . * P. Wellnhofer (2008). ''Archaeopteryx — Der Urvogel von Solnhofen'' (in German). Verlag Friedrich Pfeil, Munich. .
External links
from Talk.Origins.
Use of SSRL X-ray takes 'transformative glimpse'
— A look at chemicals linking birds and dinosaurs.
— University of California Museum of Paleontology.
— University of California Museum of Paleontology. {{featured article Prehistoric avialans Jurassic birds Feathered dinosaurs Late Jurassic dinosaurs of Europe Jurassic Germany Mesozoic birds of Europe Solnhofen fauna Fossils of Germany Transitional fossils Fossil taxa described in 1861 Taxa named by Christian Erich Hermann von Meyer