Great Lakes Of North America on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Great Lakes, also called the Great Lakes of North America, are a series of large interconnected
 Though the five lakes lie in separate basins, they form a single, naturally interconnected body of fresh water, within the
Though the five lakes lie in separate basins, they form a single, naturally interconnected body of fresh water, within the


 * The
* The
 Lakes Huron and Michigan are sometimes considered a single lake, called Lake Michigan–Huron, because they are one hydrological body of water connected by the Straits of Mackinac. The straits are wide and deep; the water levels rise and fall together, and the flow between Michigan and Huron frequently reverses direction.
Lakes Huron and Michigan are sometimes considered a single lake, called Lake Michigan–Huron, because they are one hydrological body of water connected by the Straits of Mackinac. The straits are wide and deep; the water levels rise and fall together, and the flow between Michigan and Huron frequently reverses direction.
. ''Great Lakes.net''. . proposals for its official recognition as a Great Lake are occasionally made, which would affect its inclusion in scientific research projects designated as related to "The Great Lakes". *
 Dispersed throughout the Great Lakes are approximately 35,000 islands. The largest among them is
Dispersed throughout the Great Lakes are approximately 35,000 islands. The largest among them is
 The Great Lakes also have several peninsulas between them, including the
The Great Lakes also have several peninsulas between them, including the
 The lake levels are affected primarily by changes in regional meteorology and climatology. The outflows from lakes Superior and Ontario are regulated, while the outflows of Michigan-Huron and Erie are not regulated at all. Ontario is the most tightly regulated, with its outflow controlled by the
The lake levels are affected primarily by changes in regional meteorology and climatology. The outflows from lakes Superior and Ontario are regulated, while the outflows of Michigan-Huron and Erie are not regulated at all. Ontario is the most tightly regulated, with its outflow controlled by the
 ;
;

 It has been estimated that the foundational geology that created the conditions shaping the present day upper Great Lakes was laid from 1.1 to 1.2 billion years ago, when two previously fused
It has been estimated that the foundational geology that created the conditions shaping the present day upper Great Lakes was laid from 1.1 to 1.2 billion years ago, when two previously fused
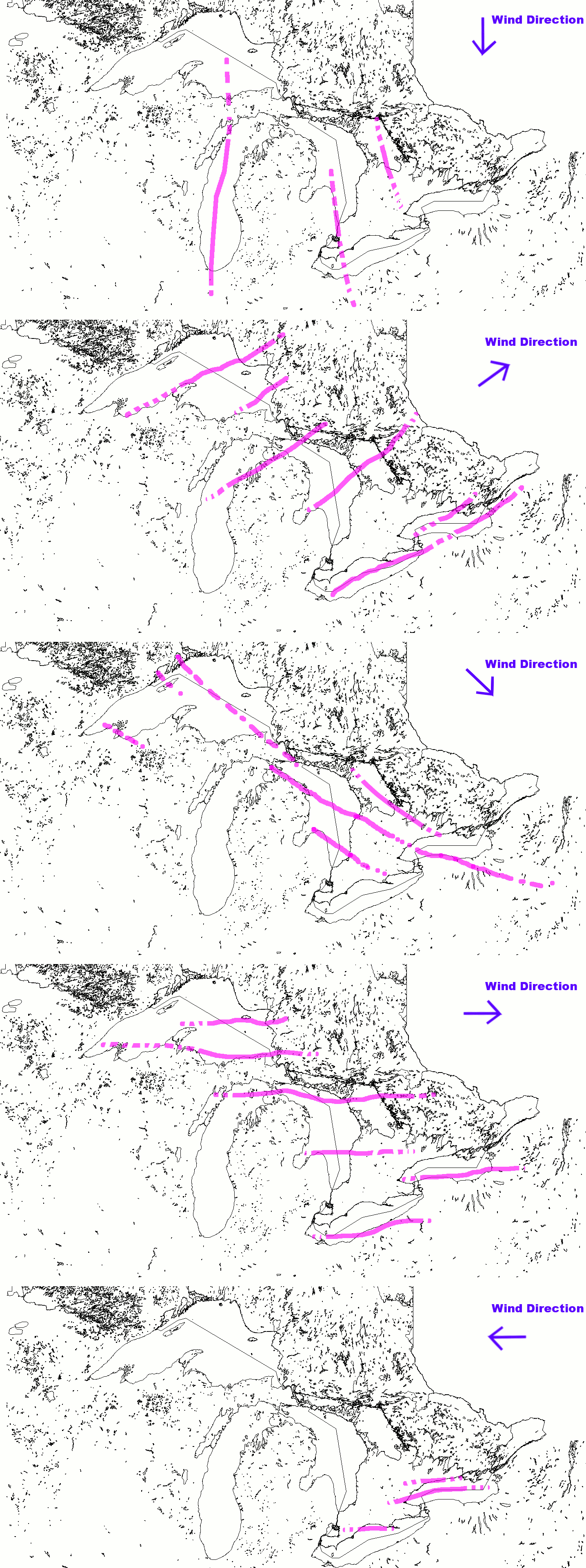 The Great Lakes can have an effect on regional weather called ''
The Great Lakes can have an effect on regional weather called ''
 While the organisms living on the bottom of shallow waters are similar to those found in smaller lakes, the deep waters contain organisms found only in deep, cold lakes of the northern latitudes. These include the delicate opossum shrimp (order
While the organisms living on the bottom of shallow waters are similar to those found in smaller lakes, the deep waters contain organisms found only in deep, cold lakes of the northern latitudes. These include the delicate opossum shrimp (order
JS Online, August 13, 2011
 The alewife first entered the system west of Lake Ontario via 19th-century canals. By the 1960s, the small silver fish had become a familiar nuisance to beach goers across Lakes Michigan, Huron, and Erie. Periodic mass die-offs result in vast numbers of the fish washing up on shore; estimates by various governments have placed the percentage of Lake Michigan's biomass, which was made up of alewives in the early 1960s, as high as 90%. In the late 1960s, the various state and federal governments began stocking several species of salmonids, including the native lake trout as well as non-native chinook and
The alewife first entered the system west of Lake Ontario via 19th-century canals. By the 1960s, the small silver fish had become a familiar nuisance to beach goers across Lakes Michigan, Huron, and Erie. Periodic mass die-offs result in vast numbers of the fish washing up on shore; estimates by various governments have placed the percentage of Lake Michigan's biomass, which was made up of alewives in the early 1960s, as high as 90%. In the late 1960s, the various state and federal governments began stocking several species of salmonids, including the native lake trout as well as non-native chinook and
 Several Native American populations ( Paleo-indians) inhabited the region around 10,000 BC, after the end of the Wisconsin glaciation. The peoples of the Great Lakes traded with the
Several Native American populations ( Paleo-indians) inhabited the region around 10,000 BC, after the end of the Wisconsin glaciation. The peoples of the Great Lakes traded with the  Since general freight these days is transported by railroads and trucks, domestic ships mostly move bulk cargoes, such as
Since general freight these days is transported by railroads and trucks, domestic ships mostly move bulk cargoes, such as
Ledger-Sentinel, Oswego, Illinois. Its wreck may have been found in 2004, but a wreck subsequently discovered in a different location was also claimed in 2014 to be ''Le Griffon''. The largest and last major freighter wrecked on the lakes was the , which sank on November 10, 1975, just over offshore from Whitefish Point on Lake Superior. The largest loss of life in a shipwreck out on the lakes may have been that of , wrecked in 1860 with the loss of around 400 lives on Lake Michigan. In an incident at a Chicago dock in 1915, the rolled over while loading passengers, killing 841. In 2007, the Great Lakes Shipwreck Museum, Great Lakes Shipwreck Historical Society announced that it had found the wreckage of ''Cyprus'', a long, century-old ore carrier. ''Cyprus'' sank during a Lake Superior storm on October 11, 1907, during its second voyage while hauling iron ore from Superior, Wisconsin, to Buffalo, New York. The entire crew of 23 drowned, except one, Charles Pitz, who floated on a life raft for almost seven hours. In 2008, Deep sea diving, deep sea divers in Lake Ontario found the wreck of the 1780 Royal Navy warship in what has been described as an "archaeological miracle". There are no plans to raise her as the site is being treated as a war grave. In 2010, ''L.R. Doty'' was found in Lake Michigan by an exploration diving team led by dive boat Captain Jitka Hanakova from her boat ''Molly V''. The ship sank in October 1898, probably attempting to rescue a small schooner, ''Olive Jeanette'', during a terrible storm. Still missing are the two last warships to sink in the Great Lakes, the French minesweepers French minesweepers Inkerman and Cerisoles, ''Inkerman'' and ''Cerisoles'', which vanished in Lake Superior during a blizzard in 1918. 78 people died making it the largest loss of life in Lake Superior and the greatest unexplained loss of life in the Great Lakes.

 Tourism and recreation are major industries on the Great Lakes. A few small cruise ships operate on the Great Lakes including some sailing, sailing ships. Sport fishing, commercial fishing, and Native American fishing represent a U.S.$4 billion a year industry with salmon, Coregonus, whitefish, smelt (fish), smelt, lake trout, Bass (fish), bass and walleye being major catches. Many other List of water sports, water sports are practiced on the lakes such as yachting, sea kayaking, Recreational diving, diving, kitesurfing, powerboating, and lake surfing. The Great Lakes Circle Tour is a designated scenic road system connecting all of the Great Lakes and the Saint Lawrence River.
Tourism and recreation are major industries on the Great Lakes. A few small cruise ships operate on the Great Lakes including some sailing, sailing ships. Sport fishing, commercial fishing, and Native American fishing represent a U.S.$4 billion a year industry with salmon, Coregonus, whitefish, smelt (fish), smelt, lake trout, Bass (fish), bass and walleye being major catches. Many other List of water sports, water sports are practiced on the lakes such as yachting, sea kayaking, Recreational diving, diving, kitesurfing, powerboating, and lake surfing. The Great Lakes Circle Tour is a designated scenic road system connecting all of the Great Lakes and the Saint Lawrence River.
 In 1872, a treaty gave access to the St. Lawrence River to the United States and access to Lake Michigan to the Canadian Confederation, Dominion of Canada. The International Joint Commission was established in 1909 to help prevent and resolve disputes relating to the use and quality of boundary waters, and to advise Canada and the United States on questions related to water resources. Concerns over diversion of Lake water are of concern to both Americans and Canadians. Some water is diverted through the Chicago River to operate the Illinois Waterway, but the flow is limited by treaty. Possible schemes for bottled water plants and diversion to dry regions of the continent raise concerns. Under the U.S. "Water Resources Development Act", diversion of water from the Great Lakes Basin requires the approval of all eight Great Lakes governors through the Great Lakes Commission, which rarely occurs. International treaties regulate large diversions.
In 1998, the Canadian company Nova Group won approval from the Province of Ontario to withdraw of Lake Superior water annually to ship by tanker to Asian countries. Public outcry forced the company to abandon the plan before it began. Since that time, the eight Great Lakes Governors and the Premiers of Ontario and Quebec have negotiated the Great Lakes-Saint Lawrence River Basin Sustainable Water Resources Agreement and the Great Lakes-St. Lawrence River Basin Water Resources Compact that would prevent most future diversion proposals and all long-distance ones. The agreements strengthen protection against abusive water withdrawal practices within the Great Lakes basin. On December 13, 2005, the Governors and Premiers signed these two agreements, the first of which is between all ten jurisdictions. It is somewhat more detailed and protective, though its legal strength has not yet been tested in court. The second, the Great Lakes Compact, has been approved by the state legislatures of all eight states that border the Great Lakes as well as the U.S. Congress, and was signed into law by President George W. Bush on October 3, 2008.
The Great Lakes Restoration Initiative, described as "the largest investment in the Great Lakes in two decades", was funded at $475 million in the U.S. federal government's Fiscal Year 2011 budget, and $300 million in the Fiscal Year 2012 budget. Through the program a coalition of federal agencies is making grants to local and state entities for toxics cleanups, wetlands and coastline restoration projects, and invasive species-related projects. The Great Lakes Restoration Initiative Act of 2019 passed as List of acts of the 116th United States Congress, Public Law s:Public_Law_116-294, 116-294 on January 5, 2021.
In 1872, a treaty gave access to the St. Lawrence River to the United States and access to Lake Michigan to the Canadian Confederation, Dominion of Canada. The International Joint Commission was established in 1909 to help prevent and resolve disputes relating to the use and quality of boundary waters, and to advise Canada and the United States on questions related to water resources. Concerns over diversion of Lake water are of concern to both Americans and Canadians. Some water is diverted through the Chicago River to operate the Illinois Waterway, but the flow is limited by treaty. Possible schemes for bottled water plants and diversion to dry regions of the continent raise concerns. Under the U.S. "Water Resources Development Act", diversion of water from the Great Lakes Basin requires the approval of all eight Great Lakes governors through the Great Lakes Commission, which rarely occurs. International treaties regulate large diversions.
In 1998, the Canadian company Nova Group won approval from the Province of Ontario to withdraw of Lake Superior water annually to ship by tanker to Asian countries. Public outcry forced the company to abandon the plan before it began. Since that time, the eight Great Lakes Governors and the Premiers of Ontario and Quebec have negotiated the Great Lakes-Saint Lawrence River Basin Sustainable Water Resources Agreement and the Great Lakes-St. Lawrence River Basin Water Resources Compact that would prevent most future diversion proposals and all long-distance ones. The agreements strengthen protection against abusive water withdrawal practices within the Great Lakes basin. On December 13, 2005, the Governors and Premiers signed these two agreements, the first of which is between all ten jurisdictions. It is somewhat more detailed and protective, though its legal strength has not yet been tested in court. The second, the Great Lakes Compact, has been approved by the state legislatures of all eight states that border the Great Lakes as well as the U.S. Congress, and was signed into law by President George W. Bush on October 3, 2008.
The Great Lakes Restoration Initiative, described as "the largest investment in the Great Lakes in two decades", was funded at $475 million in the U.S. federal government's Fiscal Year 2011 budget, and $300 million in the Fiscal Year 2012 budget. Through the program a coalition of federal agencies is making grants to local and state entities for toxics cleanups, wetlands and coastline restoration projects, and invasive species-related projects. The Great Lakes Restoration Initiative Act of 2019 passed as List of acts of the 116th United States Congress, Public Law s:Public_Law_116-294, 116-294 on January 5, 2021.
The Great Lakes: An Environmental Atlas and Resource Book
'. (United States Environmental Protection Agency and Government of Canada, 1995, ). * Coon, W.F. and R.A. Sheets.
Estimate of Ground Water in Storage in the Great Lakes Basin
' [Scientific Investigations Report 2006-5180]. Department of the Interior, U.S. Geological Survey, 2006. * * * Riley, John L. (2013) ''The Once and Future Great Lakes Country: An Ecological History'' (McGill-Queen's University Press 516 pages; traces environmental change in the region since the last ice age. * Holling, Holling Clancy ''Paddle to the Sea'' (), an illustrated children's book about the Great Lakes and their environment. Beautiful and educational.
Great Lakes website
of the Environment Canada, Canadian Department of the Environment
Great Lakes website
of the United States Environmental Protection Agency
Binational website of USEPA and Environment Canada for Great Lakes Water Quality
Great Lakes Environmental Research Laboratory website
(an arm of the American National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration)
Great Lakes Information Network
sponsored by th
Great Lakes Commission
an official American interstate compact agency.
Great Lakes Echo, a publication covering Great Lakes environmental issues
''Maritime History of the Great Lakes''
digital library covering Great Lakes history.
Surface temperatures
Water levels
Ship locations
Water levels since 1918
{{Authority control Great Lakes, Eastern Canada Great Lakes region (U.S.) Lake groups
freshwater lake
A lake is an area filled with water, localized in a basin, surrounded by land, and distinct from any river or other outlet that serves to feed or drain the lake. Lakes lie on land and are not part of the ocean, although, like the much larger ...
s in the mid-east region of North America
North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere and almost entirely within the Western Hemisphere. It is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South America and the Car ...
that connect to the Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's five oceans, with an area of about . It covers approximately 20% of Earth's surface and about 29% of its water surface area. It is known to separate the " Old World" of Africa, Europe ...
via the Saint Lawrence River
The St. Lawrence River (french: Fleuve Saint-Laurent, ) is a large river in the middle latitudes of North America. Its headwaters begin flowing from Lake Ontario in a (roughly) northeasterly direction, into the Gulf of St. Lawrence, connectin ...
. There are five lakes, which are Superior, Michigan
Michigan () is a state in the Great Lakes region of the upper Midwestern United States. With a population of nearly 10.12 million and an area of nearly , Michigan is the 10th-largest state by population, the 11th-largest by area, and the ...
, Huron
Huron may refer to:
People
* Wyandot people (or Wendat), indigenous to North America
* Wyandot language, spoken by them
* Huron-Wendat Nation, a Huron-Wendat First Nation with a community in Wendake, Quebec
* Nottawaseppi Huron Band of Potawatomi ...
, Erie
Erie (; ) is a city on the south shore of Lake Erie and the county seat of Erie County, Pennsylvania, United States. Erie is the fifth largest city in Pennsylvania and the largest city in Northwestern Pennsylvania with a population of 94,831 a ...
, and Ontario
Ontario ( ; ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada.Ontario is located in the geographic eastern half of Canada, but it has historically and politically been considered to be part of Central Canada. Located in Central Ca ...
and are in general on or near the Canada–United States border
The border between Canada and the United States is the longest international border in the world. The terrestrial boundary (including boundaries in the Great Lakes, Atlantic, and Pacific coasts) is long. The land border has two sections: Can ...
. Hydrologically, lakes Michigan and Huron are a single body joined at the Straits of Mackinac
The Straits of Mackinac ( ; french: Détroit de Mackinac) are the short waterways between the U.S. state of Michigan's Upper and Lower Peninsulas, traversed by the Mackinac Bridge. The main strait is wide with a maximum depth of , and connects ...
. The Great Lakes Waterway
The Great Lakes Waterway (GLW) is a system of natural channels and artificial canals which enable navigation between the North American Great Lakes. Though all of the lakes are naturally connected as a chain, water travel between the lakes was i ...
enables modern travel and shipping by water among the lakes.
The Great Lakes are the largest group of freshwater lakes on Earth by total area and are second-largest by total volume, containing 21% of the world's surface fresh water by volume. The total surface is , and the total volume (measured at the low water datum) is , slightly less than the volume of Lake Baikal
Lake Baikal (, russian: Oзеро Байкал, Ozero Baykal ); mn, Байгал нуур, Baigal nuur) is a rift lake in Russia. It is situated in southern Siberia, between the federal subjects of Irkutsk Oblast to the northwest and the Repu ...
(, 22–23% of the world's surface fresh water). Because of their sea
The sea, connected as the world ocean or simply the ocean, is the body of salty water that covers approximately 71% of the Earth's surface. The word sea is also used to denote second-order sections of the sea, such as the Mediterranean Sea, ...
-like characteristics, such as rolling waves, sustained winds, strong currents, great depths, and distant horizons, the five Great Lakes have long been called inland seas. Depending on how it is measured, by surface area, either Lake Superior or Lake Michigan-Huron
A lake is an area filled with water, localized in a basin, surrounded by land, and distinct from any river or other outlet that serves to feed or drain the lake. Lakes lie on land and are not part of the ocean, although, like the much larger ...
is the second-largest lake in the world and the largest freshwater lake. Lake Michigan is the largest lake that is entirely within one country.
The Great Lakes began to form at the end of the Last Glacial Period around 14,000 years ago, as retreating ice sheets exposed the basins they had carved into the land, which then filled with meltwater. The lakes have been a major source for transportation, migration, trade, and fishing, serving as a habitat to many aquatic species in a region with much biodiversity
Biodiversity or biological diversity is the variety and variability of life on Earth. Biodiversity is a measure of variation at the genetic (''genetic variability''), species (''species diversity''), and ecosystem (''ecosystem diversity'') l ...
. The surrounding region is called the Great Lakes region
The Great Lakes region of North America is a binational Canadian–American region that includes portions of the eight U.S. states of Illinois, Indiana, Michigan, Minnesota, New York, Ohio, Pennsylvania and Wisconsin along with the Canadian p ...
, which includes the Great Lakes Megalopolis.
Geography
 Though the five lakes lie in separate basins, they form a single, naturally interconnected body of fresh water, within the
Though the five lakes lie in separate basins, they form a single, naturally interconnected body of fresh water, within the Great Lakes Basin
The Great Lakes Basin consists of the Great Lakes and the surrounding lands of the states of Illinois, Indiana, Michigan, Minnesota, New York, Ohio, Pennsylvania, and Wisconsin in the United States, and the province of Ontario in Canada, whose dir ...
. As a chain of lakes and rivers, they connect the east-central interior of North America to the Atlantic Ocean. From the interior to the outlet at the Saint Lawrence River, water flows from Superior to Huron and Michigan, southward to Erie, and finally northward to Lake Ontario. The lakes drain a large watershed via many rivers and contain approximately 35,000 islands. There are also several thousand smaller lakes, often called "inland lakes", within the basin.
The surface area of the five primary lakes combined is roughly equal to the size of the United Kingdom, while the surface area of the entire basin (the lakes and the land they drain) is about the size of the UK and France combined. Lake Michigan is the only one of the Great Lakes that is entirely within the United States; the others form a water boundary between the United States and Canada. The lakes are divided among the jurisdictions of the Canadian province of Ontario
Ontario ( ; ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada.Ontario is located in the geographic eastern half of Canada, but it has historically and politically been considered to be part of Central Canada. Located in Central Ca ...
and the U.S. states of Michigan
Michigan () is a state in the Great Lakes region of the upper Midwestern United States. With a population of nearly 10.12 million and an area of nearly , Michigan is the 10th-largest state by population, the 11th-largest by area, and the ...
, Wisconsin
Wisconsin () is a state in the upper Midwestern United States. Wisconsin is the 25th-largest state by total area and the 20th-most populous. It is bordered by Minnesota to the west, Iowa to the southwest, Illinois to the south, Lake M ...
, Minnesota
Minnesota () is a state in the upper midwestern region of the United States. It is the 12th largest U.S. state in area and the 22nd most populous, with over 5.75 million residents. Minnesota is home to western prairies, now given over to ...
, Illinois
Illinois ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Midwestern United States, Midwestern United States. Its largest metropolitan areas include the Chicago metropolitan area, and the Metro East section, of Greater St. Louis. Other smaller metropolita ...
, Indiana
Indiana () is a U.S. state in the Midwestern United States. It is the 38th-largest by area and the 17th-most populous of the 50 States. Its capital and largest city is Indianapolis. Indiana was admitted to the United States as the 19th s ...
, Ohio
Ohio () is a state in the Midwestern region of the United States. Of the fifty U.S. states, it is the 34th-largest by area, and with a population of nearly 11.8 million, is the seventh-most populous and tenth-most densely populated. The sta ...
, Pennsylvania
Pennsylvania (; ( Pennsylvania Dutch: )), officially the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, is a state spanning the Mid-Atlantic, Northeastern, Appalachian, and Great Lakes regions of the United States. It borders Delaware to its southeast, ...
, and New York
New York most commonly refers to:
* New York City, the most populous city in the United States, located in the state of New York
* New York (state), a state in the northeastern United States
New York may also refer to:
Film and television
* '' ...
. Both the province of Ontario and the state of Michigan include in their boundaries portions of four of the lakes: The province of Ontario does not border Lake Michigan, and the state of Michigan does not border Lake Ontario. New York and Wisconsin's jurisdictions extend into two lakes, and each of the remaining states into one of the lakes.
Bathymetry
As the surfaces of Lakes Superior, Huron, Michigan, and Erie are all approximately the same elevation above sea level, while Lake Ontario is significantly lower, and because theNiagara Escarpment
The Niagara Escarpment is a long escarpment, or cuesta, in Canada and the United States that runs predominantly east–west from New York through Ontario, Michigan, Wisconsin, and into Illinois. The escarpment is most famous as the cliff over ...
precludes all natural navigation, the four upper lakes are commonly called the "upper great lakes". This designation is not universal. Those living on the shore of Lake Superior often refer to all the other lakes as "the lower lakes", because they are farther south. Sailors of bulk freighters transferring cargoes from Lake Superior and northern Lake Michigan and Lake Huron to ports on Lake Erie or Ontario commonly refer to the latter as the lower lakes and Lakes Michigan, Huron, and Superior as the upper lakes. This corresponds to thinking of lakes Erie and Ontario as "down south" and the others as "up north". Vessels sailing north on Lake Michigan are considered "upbound" even though they are sailing toward its effluent current.
Primary connecting waterways

 * The
* The Chicago River
The Chicago River is a system of rivers and canals with a combined length of that runs through the city of Chicago, including its center (the Chicago Loop). Though not especially long, the river is notable because it is one of the reasons for ...
and Calumet River
The Calumet River is a system of heavily industrialized rivers and canals in the region between the south side of Chicago, Illinois, and the city of Gary, Indiana. Historically, the Little Calumet River and the Grand Calumet River were one, the ...
systems connect the Great Lakes Basin to the Mississippi River
The Mississippi River is the second-longest river and chief river of the second-largest drainage system in North America, second only to the Hudson Bay drainage system. From its traditional source of Lake Itasca in northern Minnesota, it f ...
System through human-made alterations and canals.
* The St. Marys River, including the Soo Locks
The Soo Locks (sometimes spelled Sault Locks but pronounced "soo") are a set of parallel locks, operated and maintained by the United States Army Corps of Engineers, Detroit District, that enable ships to travel between Lake Superior and the lowe ...
, connects Lake Superior to Lake Huron, via the North Channel North Channel may refer to:
*North Channel (Great Britain and Ireland)
*North Channel (Ontario), body of water along the north shore of Lake Huron, Canada
*North Channel, Hong Kong
*Canal du Nord, France
{{geodis ...
.
* The Straits of Mackinac
The Straits of Mackinac ( ; french: Détroit de Mackinac) are the short waterways between the U.S. state of Michigan's Upper and Lower Peninsulas, traversed by the Mackinac Bridge. The main strait is wide with a maximum depth of , and connects ...
connect Lake Michigan to Lake Huron (which are hydrologically one).
* The St. Clair River
The St. Clair River (french: Rivière Sainte-Claire) is a U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map accessed November 7, 2011 river in central North America which flows from Lake Huron int ...
connects Lake Huron to Lake St. Clair
Lake St. Clair (french: Lac Sainte-Claire) is a freshwater lake that lies between the Canadian province of Ontario and the U.S. state of Michigan. It was named in 1679 by French Catholic explorers after Saint Clare of Assisi, on whose feast day ...
.
* The Detroit River
The Detroit River flows west and south for from Lake St. Clair to Lake Erie as a strait in the Great Lakes system. The river divides the metropolitan areas of Detroit, Michigan, and Windsor, Ontario, Windsor, Ontario—an area collectively refe ...
connects Lake St. Clair to Lake Erie.
* The Niagara River
The Niagara River () is a river that flows north from Lake Erie to Lake Ontario. It forms part of the border between the province of Ontario in Canada (on the west) and the state of New York (state), New York in the United States (on the east) ...
, including Niagara Falls
Niagara Falls () is a group of three waterfalls at the southern end of Niagara Gorge, spanning the border between the province of Ontario in Canada and the state of New York in the United States. The largest of the three is Horseshoe Falls, ...
, connects Lake Erie to Lake Ontario.
* The Welland Canal
The Welland Canal is a ship canal in Ontario, Canada, connecting Lake Ontario and Lake Erie. It forms a key section of the St. Lawrence Seaway and Great Lakes Waterway. Traversing the Niagara Peninsula from Port Weller in St. Catharines t ...
, bypassing the Niagara River, connects Lake Erie to Lake Ontario.
* The Saint Lawrence River
The St. Lawrence River (french: Fleuve Saint-Laurent, ) is a large river in the middle latitudes of North America. Its headwaters begin flowing from Lake Ontario in a (roughly) northeasterly direction, into the Gulf of St. Lawrence, connectin ...
and the Saint Lawrence Seaway
The St. Lawrence Seaway (french: la Voie Maritime du Saint-Laurent) is a system of locks, canals, and channels in Canada and the United States that permits oceangoing vessels to travel from the Atlantic Ocean to the Great Lakes of North Americ ...
connect Lake Ontario to the Gulf of Saint Lawrence
, image = Baie de la Tour.jpg
, alt =
, caption = Gulf of St. Lawrence from Anticosti National Park, Quebec
, image_bathymetry = Golfe Saint-Laurent Depths fr.svg
, alt_bathymetry = Bathymetry ...
, which connects to the Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's five oceans, with an area of about . It covers approximately 20% of Earth's surface and about 29% of its water surface area. It is known to separate the " Old World" of Africa, Europe ...
.
Lake Michigan–Huron
 Lakes Huron and Michigan are sometimes considered a single lake, called Lake Michigan–Huron, because they are one hydrological body of water connected by the Straits of Mackinac. The straits are wide and deep; the water levels rise and fall together, and the flow between Michigan and Huron frequently reverses direction.
Lakes Huron and Michigan are sometimes considered a single lake, called Lake Michigan–Huron, because they are one hydrological body of water connected by the Straits of Mackinac. The straits are wide and deep; the water levels rise and fall together, and the flow between Michigan and Huron frequently reverses direction.
Large bays and related significant bodies of water
*Lake Nipigon
Lake Nipigon (; french: lac Nipigon; oj, Animbiigoo-zaaga'igan) is part of the Great Lakes drainage basin. It is the largest lake entirely within the boundaries of the Canadian province of Ontario.
Etymology
In the Jesuit Relations the lake is ...
, connected to Lake Superior by the Nipigon River
The Nipigon River is located in Thunder Bay District in Northwestern Ontario, Canada. The river is about long (or when measured to the head of Ombabika River) and , and flows from Lake Nipigon to Nipigon Bay on Lake Superior at the community of ...
, is surrounded by sill-like formations of mafic
A mafic mineral or rock is a silicate mineral or igneous rock rich in magnesium and iron. Most mafic minerals are dark in color, and common rock-forming mafic minerals include olivine, pyroxene, amphibole, and biotite. Common mafic rocks include ...
and ultramafic
Ultramafic rocks (also referred to as ultrabasic rocks, although the terms are not wholly equivalent) are igneous and meta-igneous rocks with a very low silica content (less than 45%), generally >18% MgO, high FeO, low potassium, and are composed ...
igneous rock
Igneous rock (derived from the Latin word ''ignis'' meaning fire), or magmatic rock, is one of the three main The three types of rocks, rock types, the others being Sedimentary rock, sedimentary and metamorphic rock, metamorphic. Igneous rock ...
hundreds of meters high. The lake lies in the Nipigon Embayment
The Nipigon Embayment is an inactive continental rift zone in Northwestern Ontario, Canada, centered on Lake Nipigon. It represents an aulacogen of the much larger Midcontinent Rift System, which formed some 1,100 million years ago when the N ...
, a failed arm of the triple junction
A triple junction is the point where the boundaries of three tectonic plates meet. At the triple junction each of the three boundaries will be one of three types – a ridge (R), trench (T) or transform fault (F) – and triple junctions can b ...
(centered beneath Lake Superior) in the Midcontinent Rift System
The Midcontinent Rift System (MRS) or Keweenawan Rift is a long geological rift in the center of the North American continent and south-central part of the North American plate. It formed when the continent's core, the North American craton, ...
event, estimated at 1.1 billion years ago.
* Green Bay is an arm of Lake Michigan along the south coast of the Upper Peninsula of Michigan
The Upper Peninsula of Michigan – also known as Upper Michigan or colloquially the U.P. – is the northern and more elevated of the two major landmasses that make up the U.S. state of Michigan; it is separated from the Lower Peninsula by t ...
and the east coast of Wisconsin. It is separated from the rest of the lake by the Door Peninsula
The Door Peninsula is a peninsula in eastern Wisconsin, separating the southern part of the Green Bay (Lake Michigan), Green Bay from Lake Michigan. The peninsula includes northern Kewaunee County, Wisconsin, Kewaunee County, northeaster ...
in Wisconsin, the Garden Peninsula
The Garden Peninsula is a peninsula of in length that extends southwestward into Lake Michigan from the mainland of Michigan's Upper Peninsula. The peninsula is bordered by Lake Michigan on the east, and by Big Bay de Noc on the west. The base ...
in Michigan, and the chain of islands between them, all of which were formed by the Niagara Escarpment
The Niagara Escarpment is a long escarpment, or cuesta, in Canada and the United States that runs predominantly east–west from New York through Ontario, Michigan, Wisconsin, and into Illinois. The escarpment is most famous as the cliff over ...
.
* Lake Winnebago
Lake Winnebago ( mez, Wenepekōw Nepēhsæh, oj, Wiinibiigoo-zaaga'igan, one, kanyataláheleˀ) is a shallow freshwater lake in the north central United States, located in east central Wisconsin. At 137,700 acres it is the largest lake entir ...
, connected to Green Bay by the Fox River, serves as part of the Fox–Wisconsin Waterway
The Fox–Wisconsin Waterway is a waterway formed by the Fox and Wisconsin Rivers. First used by European settlers in 1673 during the expedition of Marquette & Joliet, it was one of the principal routes used by travelers between the Great Lakes a ...
and is part of a larger system of lakes in Wisconsin known as the Winnebago Pool
The Winnebago Pool is a collective name for a group of interconnected lakes in eastern Wisconsin. The terminal point of this watershed is Lake Winnebago itself, which has a surface elevation of 746 feet. Besides Lake Winnebago, the Winnebago Po ...
.
* Grand Traverse Bay
Grand Traverse Bay is a deep bay of Lake Michigan formed by the Leelanau Peninsula in the northwestern Lower Peninsula of Michigan. The bay is long, wide, and up to deep in spots. It is further divided into two east and west arms by the Ol ...
is an arm of Lake Michigan on Michigan's west coast and is one of the largest natural harbors in the Great Lakes. The bay has one large peninsula and one major island known as Power Island. Its name is derived from Jacques Marquette's crossing of the bay from Norwood to Northport which he called ''La Grande Traversee''.
* Georgian Bay
Georgian Bay (french: Baie Georgienne) is a large bay of Lake Huron, in the Laurentia bioregion. It is located entirely within the borders of Ontario, Canada. The main body of the bay lies east of the Bruce Peninsula and Manitoulin Island. To ...
is an arm of Lake Huron, extending northeast from the lake entirely within Ontario. The bay, along with its narrow westerly extensions of the North Channel North Channel may refer to:
*North Channel (Great Britain and Ireland)
*North Channel (Ontario), body of water along the north shore of Lake Huron, Canada
*North Channel, Hong Kong
*Canal du Nord, France
{{geodis ...
and Mississagi Strait
The Mississagi Strait is a narrow strait or channel in Manitoulin District, Ontario, Canada, located in Lake Huron
Lake Huron ( ) is one of the five Great Lakes of North America. Hydrologically, it comprises the easterly portion of Lake M ...
, is separated from the rest of the lake by the Bruce Peninsula
The Bruce Peninsula is a peninsula in Ontario, Canada, that divides Georgian Bay of Lake Huron from the lake's main basin. The peninsula extends roughly northwestwards from the rest of Southwestern Ontario, pointing towards Manitoulin Islan ...
, Manitoulin Island
Manitoulin Island is an island in Lake Huron, located within the borders of the Canadian province of Ontario, in the bioregion known as Laurentia. With an area of , it is the largest lake island in the world, large enough that it has over 100 ...
, and Cockburn Island, all of which were formed by the Niagara Escarpment.
* Lake Nipissing
Lake Nipissing (; french: lac Nipissing, oj, Gichi-nibiinsing-zaaga’igan) is a lake in the Canadian province
Within the geographical areas of Canada, the ten provinces and three territories are sub-national administrative divisions under ...
, connected to Georgian Bay by the French River, contains two volcanic pipe
Volcanic pipes or volcanic conduits are subterranean geological structures formed by the violent, supersonic eruption of deep-origin volcanoes. They are considered to be a type of ''diatreme''. Volcanic pipes are composed of a deep, narrow cone of ...
s, which are the Manitou Islands and Callander Bay
Callander Bay (french: baie Callander) is a bay at the extreme east of Lake Nipissing in the municipality of Callander, Parry Sound District, Ontario, Canada. It is approximately in diameter. The community of Callander is located on its eas ...
. These pipes were formed by a violent, supersonic eruption
Volcanic pipes or volcanic conduits are subterranean geological structures formed by the violent, supersonic eruption of deep-origin volcanoes. They are considered to be a type of ''diatreme''. Volcanic pipes are composed of a deep, narrow cone o ...
of deep origin. The lake lies in the Ottawa-Bonnechere Graben
The Ottawa-Bonnechere Graben (also known as the Ottawa Graben) is a geological structure that coincides with a wide topographic depression extending from near Montréal through Ottawa. It is part of the Saint Lawrence rift system that also includ ...
, a Mesozoic
The Mesozoic Era ( ), also called the Age of Reptiles, the Age of Conifers, and colloquially as the Age of the Dinosaurs is the second-to-last era of Earth's geological history, lasting from about , comprising the Triassic, Jurassic and Cretaceo ...
rift valley
A rift valley is a linear shaped lowland between several highlands or mountain ranges created by the action of a geologic rift. Rifts are formed as a result of the pulling apart of the lithosphere due to extensional tectonics. The linear dep ...
that formed 175 million years ago.
* Lake Simcoe
Lake Simcoe is a lake in southern Ontario, Canada, the fourth-largest lake wholly in the province, after Lake Nipigon, Lac Seul, and Lake Nipissing. At the time of the first European contact in the 17th century the lake was called ''Ouentironk'' ...
, connected to Georgian Bay by the Severn River, serves as part of the Trent–Severn Waterway
The Trent–Severn Waterway is a canal route connecting Lake Ontario at Trenton to Georgian Bay, Lake Huron, at Port Severn. Its major natural waterways include the Trent River, Otonabee River, Kawartha Lakes, Lake Simcoe, Lake Couchiching an ...
, a canal route traversing Southern Ontario
Southern Ontario is a primary region of the province of Ontario, Canada, the other primary region being Northern Ontario. It is the most densely populated and southernmost region in Canada. The exact northern boundary of Southern Ontario is disp ...
between Lakes Ontario and Huron.
* Lake St. Clair
Lake St. Clair (french: Lac Sainte-Claire) is a freshwater lake that lies between the Canadian province of Ontario and the U.S. state of Michigan. It was named in 1679 by French Catholic explorers after Saint Clare of Assisi, on whose feast day ...
, connected with Lake Huron to its north by the St. Clair River
The St. Clair River (french: Rivière Sainte-Claire) is a U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map accessed November 7, 2011 river in central North America which flows from Lake Huron int ...
and with Lake Erie to its south by the Detroit River
The Detroit River flows west and south for from Lake St. Clair to Lake Erie as a strait in the Great Lakes system. The river divides the metropolitan areas of Detroit, Michigan, and Windsor, Ontario, Windsor, Ontario—an area collectively refe ...
. Although it is 17 times smaller in area than Lake Ontario and only rarely included in the listings of the Great Lakes,Lake St. Clair summary report. ''Great Lakes.net''. . proposals for its official recognition as a Great Lake are occasionally made, which would affect its inclusion in scientific research projects designated as related to "The Great Lakes". *
Saginaw Bay
Saginaw Bay is a bay within Lake Huron located on the eastern side of the U.S. state of Michigan. It forms the space between Michigan's Thumb region and the rest of the Lower Peninsula of Michigan. Saginaw Bay is in area. It is located in part ...
, an extension of Lake Huron into the Lower Peninsula of Michigan
The Lower Peninsula of Michigan – also known as Lower Michigan – is the larger, southern and less elevated of the two major landmasses that make up the U.S. state of Michigan; the other being the Upper Peninsula, which is separated by the ...
, fed by the Saginaw
Saginaw () is a city in the U.S. state of Michigan and the seat of Saginaw County. The city of Saginaw and Saginaw County are both in the area known as Mid-Michigan. Saginaw is adjacent to Saginaw Charter Township and considered part of Greater ...
and other rivers, has the largest contiguous freshwater wetland
A wetland is a distinct ecosystem that is flooded or saturated by water, either permanently (for years or decades) or seasonally (for weeks or months). Flooding results in oxygen-free (anoxic) processes prevailing, especially in the soils. The ...
in the United States.
Islands
 Dispersed throughout the Great Lakes are approximately 35,000 islands. The largest among them is
Dispersed throughout the Great Lakes are approximately 35,000 islands. The largest among them is Manitoulin Island
Manitoulin Island is an island in Lake Huron, located within the borders of the Canadian province of Ontario, in the bioregion known as Laurentia. With an area of , it is the largest lake island in the world, large enough that it has over 100 ...
in Lake Huron, the largest island in any inland body of water in the world. The second-largest island is Isle Royale
Isle Royale National Park is an American national park consisting of Isle Royale – known as Minong to the native Ojibwe – along with more than 400 small adjacent islands and the surrounding waters of Lake Superior, in the state of Michigan ...
in Lake Superior. Both of these islands are large enough to contain multiple lakes themselves—for instance, Manitoulin Island's Lake Manitou
Lake Manitou is the largest lake on Manitoulin Island in Ontario, Canada. With an area of ,
it is the largest lake on a lake island in the world.
It is drained by the Manitou River.
There are several small islands in Lake Manitou, such as Rope ...
is the world's largest lake on a freshwater island. Some of these lakes even have their own islands, like Treasure Island
''Treasure Island'' (originally titled ''The Sea Cook: A Story for Boys''Hammond, J. R. 1984. "Treasure Island." In ''A Robert Louis Stevenson Companion'', Palgrave Macmillan Literary Companions. London: Palgrave Macmillan. .) is an adventure no ...
in Lake Mindemoya
Lake Mindemoya is a lake in Ontario, Canada, located within Manitoulin Island which is the world's largest island in a freshwater lake (Lake Huron). The lake is located near the town of Mindemoya, and it is the third largest on Manitoulin Island. ...
in Manitoulin Island.
Peninsulas
 The Great Lakes also have several peninsulas between them, including the
The Great Lakes also have several peninsulas between them, including the Door Peninsula
The Door Peninsula is a peninsula in eastern Wisconsin, separating the southern part of the Green Bay (Lake Michigan), Green Bay from Lake Michigan. The peninsula includes northern Kewaunee County, Wisconsin, Kewaunee County, northeaster ...
, the Peninsulas of Michigan
Michigan consists of two peninsulas surrounded primarily by four of the Great Lakes and a variety of nearby islands. The Upper Peninsula of Michigan, Upper Peninsula is bounded on the southwest by Wisconsin, and the Lower Peninsula of Michigan, ...
, and the Ontario Peninsula
The Ontario Peninsula is the southernmost part of the province of Ontario, and of Canada as a whole. It is bounded by Lake Huron to the west, Lake Ontario to the east, and Lake Erie to the south. At its tip, it is separated from Michigan by the D ...
. Some of these peninsulas even contain smaller peninsulas, such as the Keweenaw Peninsula
The Keweenaw Peninsula ( , sometimes locally ) is the northernmost part of Michigan's Upper Peninsula. It projects into Lake Superior and was the site of the first copper boom in the United States, leading to its moniker of "Copper Country." As o ...
, the Thumb Peninsula, the Bruce Peninsula
The Bruce Peninsula is a peninsula in Ontario, Canada, that divides Georgian Bay of Lake Huron from the lake's main basin. The peninsula extends roughly northwestwards from the rest of Southwestern Ontario, pointing towards Manitoulin Islan ...
, and the Niagara Peninsula
The Niagara Peninsula is an area of land lying between the southwestern shore of Lake Ontario and the northeastern shore of Lake Erie, in Ontario, Canada. Technically an isthmus rather than a peninsula, it stretches from the Niagara River in the ...
. Population centers on the peninsulas include Grand Rapids
Grand Rapids is a city and county seat of Kent County in the U.S. state of Michigan. At the 2020 census, the city had a population of 198,917 which ranks it as the second most-populated city in the state after Detroit. Grand Rapids is the ...
, Flint
Flint, occasionally flintstone, is a sedimentary cryptocrystalline form of the mineral quartz, categorized as the variety of chert that occurs in chalk or marly limestone. Flint was widely used historically to make stone tools and start fir ...
, and Detroit
Detroit ( , ; , ) is the largest city in the U.S. state of Michigan. It is also the largest U.S. city on the United States–Canada border, and the seat of government of Wayne County. The City of Detroit had a population of 639,111 at th ...
in Michigan along with London
London is the capital and largest city of England and the United Kingdom, with a population of just under 9 million. It stands on the River Thames in south-east England at the head of a estuary down to the North Sea, and has been a majo ...
, Hamilton Hamilton may refer to:
People
* Hamilton (name), a common British surname and occasional given name, usually of Scottish origin, including a list of persons with the surname
** The Duke of Hamilton, the premier peer of Scotland
** Lord Hamilt ...
, Brantford
Brantford (Canada 2021 Census, 2021 population: 104,688) is a city in Ontario, Canada, founded on the Grand River (Ontario), Grand River in Southwestern Ontario. It is surrounded by County of Brant, Brant County, but is politically separate with ...
, and Toronto
Toronto ( ; or ) is the capital city of the Canadian province of Ontario. With a recorded population of 2,794,356 in 2021, it is the most populous city in Canada and the fourth most populous city in North America. The city is the ancho ...
in Ontario.
Shipping connection to the ocean
Although the Saint Lawrence Seaway and Great Lakes Waterway make the Great Lakes accessible to ocean-going vessels, shifts in shipping to wider ocean-goingcontainer ship
A container ship (also called boxship or spelled containership) is a cargo ship that carries all of its load in truck-size intermodal containers, in a technique called containerization. Container ships are a common means of commercial intermodal ...
s—which do not fit through the locks
Lock(s) may refer to:
Common meanings
*Lock and key, a mechanical device used to secure items of importance
*Lock (water navigation), a device for boats to transit between different levels of water, as in a canal
Arts and entertainment
* ''Lock ...
on these routes—have limited container shipping on the lakes. Most Great Lakes trade is of bulk material, and bulk freighters of Seawaymax
The term Seawaymax refers to vessels which are the maximum size that can fit through the canal locks of the St. Lawrence Seaway, linking the inland Great Lakes of North America with the Atlantic Ocean.
Seawaymax vessels are in length, wid ...
-size or less can move throughout the entire lakes and out to the Atlantic. Larger ships are confined to working within the lakes. Only barges can access the Illinois Waterway
The Illinois Waterway system consists of of navigable water from the mouth of the Calumet River at Chicago to the mouth of the Illinois River at Grafton, Illinois. Based primarily on the Illinois River, it is a system of rivers, lakes, and cana ...
system providing access to the Gulf of Mexico
The Gulf of Mexico ( es, Golfo de México) is an oceanic basin, ocean basin and a marginal sea of the Atlantic Ocean, largely surrounded by the North American continent. It is bounded on the northeast, north and northwest by the Gulf Coast of ...
via the Mississippi River. Despite their vast size, large sections of the Great Lakes freeze over in winter, interrupting most shipping from January to March. Some icebreaker
An icebreaker is a special-purpose ship or boat designed to move and navigate through ice-covered waters, and provide safe waterways for other boats and ships. Although the term usually refers to ice-breaking ships, it may also refer to smaller ...
s ply the lakes, keeping the shipping lanes open through other periods of ice on the lakes.
The Great Lakes are connected by the Chicago Sanitary and Ship Canal
The Chicago Sanitary and Ship Canal, historically known as the Chicago Drainage Canal, is a canal system that connects the Chicago River to the Des Plaines River. It reverses the direction of the Main Stem and the South Branch of the Chicago R ...
to the Gulf of Mexico via the Illinois River
The Illinois River ( mia, Inoka Siipiiwi) is a principal tributary of the Mississippi River and is approximately long. Located in the U.S. state of Illinois, it has a drainage basin of . The Illinois River begins at the confluence of the D ...
(from the Chicago River
The Chicago River is a system of rivers and canals with a combined length of that runs through the city of Chicago, including its center (the Chicago Loop). Though not especially long, the river is notable because it is one of the reasons for ...
) and the Mississippi River. An alternate track is via the Illinois River (from Chicago), to the Mississippi, up the Ohio, and then through the Tennessee–Tombigbee Waterway
The Tennessee–Tombigbee Waterway (popularly known as the Tenn-Tom) is a artificial U.S. waterway built in the 20th century from the Tennessee River to the junction of the Black Warrior-Tombigbee River system near Demopolis, Alabama. The Tenn ...
(a combination of a series of rivers and lakes and canals), to Mobile Bay
Mobile Bay ( ) is a shallow inlet of the Gulf of Mexico, lying within the state of Alabama in the United States. Its mouth is formed by the Fort Morgan Peninsula on the eastern side and Dauphin Island, a barrier island on the western side. The ...
and the Gulf of Mexico. Commercial tug-and-barge
Barge nowadays generally refers to a flat-bottomed inland waterway vessel which does not have its own means of mechanical propulsion. The first modern barges were pulled by tugs, but nowadays most are pushed by pusher boats, or other vessels ...
traffic on these waterways is heavy.
Pleasure boats can enter or exit the Great Lakes by way of the Erie Canal
The Erie Canal is a historic canal in upstate New York that runs east-west between the Hudson River and Lake Erie. Completed in 1825, the canal was the first navigable waterway connecting the Atlantic Ocean to the Great Lakes, vastly reducing t ...
and Hudson River
The Hudson River is a river that flows from north to south primarily through eastern New York. It originates in the Adirondack Mountains of Upstate New York and flows southward through the Hudson Valley to the New York Harbor between N ...
in New York. The Erie Canal connects to the Great Lakes at the east end of Lake Erie (at Buffalo, New York
Buffalo is the second-largest city in the U.S. state of New York (behind only New York City) and the seat of Erie County. It is at the eastern end of Lake Erie, at the head of the Niagara River, and is across the Canadian border from South ...
) and at the south side of Lake Ontario (at Oswego, New York
Oswego () is a city in Oswego County, New York, United States. The population was 16,921 at the 2020 census. Oswego is located on Lake Ontario in Upstate New York, about 35 miles (55km) northwest of Syracuse. It promotes itself as "The Port C ...
).
Water levels
The lakes were originally fed by both precipitation andmeltwater
Meltwater is water released by the melting of snow or ice, including glacial ice, tabular icebergs and ice shelves over oceans. Meltwater is often found in the ablation zone of glaciers, where the rate of snow cover is reducing. Meltwater can be ...
from glaciers which are no longer present. In modern times, only about 1% of volume per year is "new" water, originating from rivers, precipitation, and groundwater springs. In the post-glacial period, evaporation
Evaporation is a type of vaporization that occurs on the surface of a liquid as it changes into the gas phase. High concentration of the evaporating substance in the surrounding gas significantly slows down evaporation, such as when humidi ...
, and drainage have generally been balanced, making the levels of the lakes relatively constant.
Intensive human population
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') are the most abundant and widespread species of primate, characterized by bipedalism and exceptional cognitive skills due to a large and complex brain. This has enabled the development of advanced tools, culture, ...
growth began in the region in the 20th century and continues today. At least two human water use activities have been identified as having the potential to affect the lakes' levels: diversion (the transfer of water to other watersheds) and consumption (substantially done today by the use of lake water to power and cool electric generation plants, resulting in evaporation). Outflows through the Chicago Sanitary and Ship Canal is more than balanced by artificial inflows via the Ogoki River
The Ogoki River is a river in the Thunder Bay and Cochrane Districts of Ontario. It springs from the wilderness just east of Savant Lake, flowing north of Lake Nipigon to Ogoki, where it joins the Albany River which empties into James Bay. The ...
and Long Lake/Kenogami River
The Kenogami River is a river in the James Bay drainage basin in Thunder Bay and Cochrane districts in Northern Ontario, Canada, which flows north from Long Lake near Longlac to empty into the Albany River. Shows the river course. The river is ...
diversions.
Fluctuation of the water levels in the lakes has been observed since records began in 1918. The water level of Lake Michigan–Huron had remained fairly constant over the 20th century Recent lake levels include record low levels in 2013 in Lakes Superior, Erie, and Michigan-Huron, followed by record high levels in 2020 in the same lakes. The water level in Lake Ontario has remained relatively constant in the same time period, hovering around the historical average level.
 The lake levels are affected primarily by changes in regional meteorology and climatology. The outflows from lakes Superior and Ontario are regulated, while the outflows of Michigan-Huron and Erie are not regulated at all. Ontario is the most tightly regulated, with its outflow controlled by the
The lake levels are affected primarily by changes in regional meteorology and climatology. The outflows from lakes Superior and Ontario are regulated, while the outflows of Michigan-Huron and Erie are not regulated at all. Ontario is the most tightly regulated, with its outflow controlled by the Moses-Saunders Power Dam
The Moses-Saunders Power Dam, short for Robert Moses- Robert H. Saunders Power Dam, is a dam on the Saint Lawrence River straddling the border between the United States and Canada. It is located between Massena in New York and Cornwall in Ontar ...
, which explains its consistent historical levels.
Etymology
 ;
;Lake Erie
Lake Erie ( "eerie") is the fourth largest lake by surface area of the five Great Lakes in North America and the eleventh-largest globally. It is the southernmost, shallowest, and smallest by volume of the Great Lakes and therefore also has t ...
: From the Erie tribe
The Erie people (also Eriechronon, Riquéronon, Erielhonan, Eriez, Nation du Chat) were Indigenous people historically living on the south shore of Lake Erie. An Iroquoian group, they lived in what is now western New York, northwestern Pennsylvani ...
, a shortened form of the Iroquoian
The Iroquoian languages are a language family of indigenous peoples of North America. They are known for their general lack of labial consonants. The Iroquoian languages are polysynthetic and head-marking.
As of 2020, all surviving Iroquoian la ...
word 'long tail'.
;Lake Huron
Lake Huron ( ) is one of the five Great Lakes of North America. Hydrology, Hydrologically, it comprises the easterly portion of Lake Michigan–Huron, having the same surface elevation as Lake Michigan, to which it is connected by the , Strait ...
:Named for the inhabitants of the area, the Wyandot
Wyandot may refer to:
Native American ethnography
* Wyandot people, also known as the Huron
* Wyandot language
* Wyandot religion
Places
* Wyandot, Ohio, an unincorporated community
* Wyandot County, Ohio
* Camp Wyandot, a Camp Fire Boys and ...
(or "Hurons"), by the first French explorers . The Wyandot originally referred to the lake by the name , a word which has been variously translated as "Freshwater Sea", "Lake of the Hurons", or simply "lake".
;Lake Michigan
Lake Michigan is one of the five Great Lakes of North America. It is the second-largest of the Great Lakes by volume () and the third-largest by surface area (), after Lake Superior and Lake Huron. To the east, its basin is conjoined with that o ...
: From the Ojibwe
The Ojibwe, Ojibwa, Chippewa, or Saulteaux are an Anishinaabe people in what is currently southern Canada, the northern Midwestern United States, and Northern Plains.
According to the U.S. census, in the United States Ojibwe people are one of ...
word "great water" or "large lake".
;Lake Ontario
Lake Ontario is one of the five Great Lakes of North America. It is bounded on the north, west, and southwest by the Canadian province of Ontario, and on the south and east by the U.S. state of New York. The Canada–United States border sp ...
: From the Wyandot word "lake of shining waters".
;Lake Superior
Lake Superior in central North America is the largest freshwater lake in the world by surface areaThe Caspian Sea is the largest lake, but is saline, not freshwater. and the third-largest by volume, holding 10% of the world's surface fresh wa ...
: English translation of the French term "upper lake", referring to its position north of Lake Huron. The indigenous Ojibwe
The Ojibwe, Ojibwa, Chippewa, or Saulteaux are an Anishinaabe people in what is currently southern Canada, the northern Midwestern United States, and Northern Plains.
According to the U.S. census, in the United States Ojibwe people are one of ...
call it (from Ojibwe "big, large, great"; "water, lake, sea"). Popularized in French-influenced transliteration as ''Gitchigumi'' as in Gordon Lightfoot
Gordon Meredith Lightfoot Jr. (born November 17, 1938) is a Canadian singer-songwriter and guitarist who achieved international success in folk, folk-rock, and country music. He is credited with helping to define the folk-pop sound of the 1960 ...
's 1976 story song " The Wreck of the ''Edmund Fitzgerald''", or ''Gitchee Gumee'' as in Henry Wadsworth Longfellow
Henry Wadsworth Longfellow (February 27, 1807 – March 24, 1882) was an American poet and educator. His original works include "Paul Revere's Ride", ''The Song of Hiawatha'', and ''Evangeline''. He was the first American to completely transl ...
's 1855 epic poem, ''The Song of Hiawatha
''The Song of Hiawatha'' is an 1855 epic poem in trochaic tetrameter by Henry Wadsworth Longfellow which features Native American characters. The epic relates the fictional adventures of an Ojibwe warrior named Hiawatha and the tragedy of his l ...
'').
Statistics
The Great Lakes contain 21% of the world's surface fresh water: , or 6.0×1015 U.S. gallons, that is 6 quadrillion U.S gallons, (2.3×1016 liters). The lakes contain about 84% of the surface freshwater of North America; if the water were evenly distributed over the entire continent's land area, it would reach a depth of 5 feet (1.5 meters). This is enough water to cover the 48 contiguous U.S. states to a uniform depth of . Although the lakes contain a large percentage of the world's fresh water, the Great Lakes supply only a small portion of U.S. drinking water on a national basis. The totalsurface area
The surface area of a solid object is a measure of the total area that the surface of the object occupies. The mathematical definition of surface area in the presence of curved surfaces is considerably more involved than the definition of arc ...
of the lakes is approximately —nearly the same size as the United Kingdom, and larger than the U.S. states of New York
New York most commonly refers to:
* New York City, the most populous city in the United States, located in the state of New York
* New York (state), a state in the northeastern United States
New York may also refer to:
Film and television
* '' ...
, New Jersey
New Jersey is a state in the Mid-Atlantic and Northeastern regions of the United States. It is bordered on the north and east by the state of New York; on the east, southeast, and south by the Atlantic Ocean; on the west by the Delaware ...
, Connecticut
Connecticut () is the southernmost state in the New England region of the Northeastern United States. It is bordered by Rhode Island to the east, Massachusetts to the north, New York to the west, and Long Island Sound to the south. Its cap ...
, Rhode Island
Rhode Island (, like ''road'') is a U.S. state, state in the New England region of the Northeastern United States. It is the List of U.S. states by area, smallest U.S. state by area and the List of states and territories of the United States ...
, Massachusetts
Massachusetts (Massachusett language, Massachusett: ''Muhsachuweesut assachusett writing systems, məhswatʃəwiːsət'' English: , ), officially the Commonwealth of Massachusetts, is the most populous U.S. state, state in the New England ...
, Vermont
Vermont () is a state in the northeast New England region of the United States. Vermont is bordered by the states of Massachusetts to the south, New Hampshire to the east, and New York to the west, and the Canadian province of Quebec to ...
, and New Hampshire
New Hampshire is a U.S. state, state in the New England region of the northeastern United States. It is bordered by Massachusetts to the south, Vermont to the west, Maine and the Gulf of Maine to the east, and the Canadian province of Quebec t ...
combined. The Great Lakes coast measures approximately ;, but the length of a coastline is impossible to measure exactly and is not a well-defined measure. Canada borders approximately of coastline, while the remaining are bordered by the United States. Michigan has the longest shoreline of the United States, bordering roughly of lakes, followed by Wisconsin (), New York (), and Ohio (). Traversing the shoreline of all the lakes would cover a distance roughly equivalent to travelling half-way around the world at the equator.
A notable modern phenomenon is the formation of ice volcano
An ice volcano is a conical mound of ice formed over a terrestrial lake via the eruption of water and slush through an ice shelf. The process is wave-driven, with wind providing the energy for the waves to cut through the ice and create formatio ...
es over the lakes during wintertime. Storm-generated waves carve the lakes' ice sheet and create conical mounds through the eruption of water and slush. The process is only well-documented in the Great Lakes, and has been credited with sparing the southern shorelines from worse rocky erosion.
Geology

tectonic plates
Plate tectonics (from the la, label=Late Latin, tectonicus, from the grc, τεκτονικός, lit=pertaining to building) is the generally accepted scientific theory that considers the Earth's lithosphere to comprise a number of large te ...
split apart and created the Midcontinent Rift
The Midcontinent Rift System (MRS) or Keweenawan Rift is a long geological rift in the center of the North America, North American continent and south-central part of the North American plate. It formed when the continent's core, the North Amer ...
, which crossed the Great Lakes Tectonic Zone. A valley was formed providing a basin that eventually became modern day Lake Superior. When a second fault line, the Saint Lawrence rift, formed approximately 570 million years ago, the basis for Lakes Ontario and Erie was created, along with what would become the Saint Lawrence River.
The Great Lakes are estimated to have been formed at the end of the Last Glacial Period (the Wisconsin glaciation
The Wisconsin Glacial Episode, also called the Wisconsin glaciation, was the most recent glacial period of the North American ice sheet complex. This advance included the Cordilleran Ice Sheet, which nucleated in the northern North American Cor ...
ended 10,000 to 12,000 years ago), when the Laurentide Ice Sheet
The Laurentide Ice Sheet was a massive sheet of ice that covered millions of square miles, including most of Canada and a large portion of the Northern United States, multiple times during the Quaternary glacial epochs, from 2.58 million years a ...
receded. The retreat of the ice sheet left behind a large amount of meltwater (Lake Algonquin
Lake Algonquin was a prehistoric proglacial lake that existed in east-central North America at the time of the last ice age. Parts of the former lake are now Lake Huron, Georgian Bay, Lake Superior, Lake Michigan, Lake Nipigon, and Lake Nipissing ...
, Lake Chicago
Lake Chicago was a prehistoric proglacial lake that is the ancestor of what is now known as Lake Michigan, one of North America's five Great Lakes. Fed by retreating glaciers, it drained south through the Chicago Outlet River.
Origin
The cit ...
, Glacial Lake Iroquois
Glacial Lake Iroquois was a prehistoric proglacial lake that existed at the end of the last ice age approximately 13,000 years ago.
The lake was essentially an enlargement of the present Lake Ontario that formed because the St. Lawrence River down ...
, and Champlain Sea
The Champlain Sea (french: Mer de Champlain) was a prehistoric inlet of the Atlantic Ocean into the North American continent, created by the retreating ice sheets during the closure of the last glacial period. The inlet once included lands in ...
) that filled up the basins that the glaciers had carved, thus creating the Great Lakes as we know them today. Because of the uneven nature of glacier erosion
Erosion is the action of surface processes (such as water flow or wind) that removes soil, rock, or dissolved material from one location on the Earth's crust, and then transports it to another location where it is deposited. Erosion is distin ...
, some higher hills became Great Lakes islands. The Niagara Escarpment follows the contour of the Great Lakes between New York and Wisconsin. Land below the glaciers "rebounded" as it was uncovered. Since the glaciers covered some areas longer than others, this glacial rebound occurred at different rates.
Climate
The Great Lakes have a humid continental climate,Köppen climate classification
The Köppen climate classification is one of the most widely used climate classification systems. It was first published by German-Russian climatologist Wladimir Köppen (1846–1940) in 1884, with several later modifications by Köppen, notabl ...
Dfa (in southern areas) and Dfb (in northern parts) with varying influences from air masses from other regions including dry, cold Arctic systems, mild Pacific air masses from the west, and warm, wet tropical systems from the south and the Gulf of Mexico. The lakes have a moderating effect on the climate; they can also increase precipitation totals and produce lake effect snow
Lake-effect snow is produced during cooler atmospheric conditions when a cold air mass moves across long expanses of warmer lake water. The lower layer of air, heated up by the lake water, picks up water vapor from the lake and rises up through ...
fall.
Lake effect
 The Great Lakes can have an effect on regional weather called ''
The Great Lakes can have an effect on regional weather called ''lake-effect snow
Lake-effect snow is produced during cooler atmospheric conditions when a cold air mass moves across long expanses of warmer lake water. The lower layer of air, heated up by the lake water, picks up water vapor from the lake and rises up through ...
'', which is sometimes very localized. Even late in winter, the lakes often have no icepack in the middle. The prevailing winds from the west pick up the air and moisture from the lake surface, which is slightly warmer in relation to the cold surface winds above. As the slightly warmer, moist air passes over the colder land surface, the moisture often produces concentrated, heavy snowfall that sets up in bands or "streamers". This is similar to the effect of warmer air dropping snow as it passes over mountain ranges. During freezing weather with high winds, the "snowbelt
The Snowbelt is the region near the Great Lakes in North America where heavy snowfall in the form of lake-effect snow is particularly common. Snowbelts are typically found downwind of the lakes, principally off the eastern and southern shores.
Ca ...
s" receive regular snow fall from this localized weather pattern, especially along the eastern shores of the lakes. Snowbelts are found in Wisconsin, Michigan, Ohio, Pennsylvania, New York, and Ontario. Related to the lake effect is the regular occurrence of fog, particularly along the shorelines of the lakes. This is most noticeable along Lake Superior's shores.
The lakes tend to moderate seasonal temperatures to some degree but not with as large an influence as do large oceans; they absorb heat and cool the air in summer, then slowly radiate that heat in autumn. They protect against frost during transitional weather and keep the summertime temperatures cooler than further inland. This effect can be very localized and overridden by offshore wind patterns. This temperature buffering produces areas known as " fruit belts", where fruit can be produced that is typically grown much farther south. For instance, western Michigan
West Michigan and Western Michigan are terms for an arbitrary region in the U.S. state of Michigan's Lower Peninsula. Most narrowly it refers to the Grand Rapids- Muskegon-Holland area, and more broadly to most of the region along the Lower Pen ...
has apple orchards, and cherry orchards are cultivated adjacent to the lake shore as far north as the Grand Traverse Bay
Grand Traverse Bay is a deep bay of Lake Michigan formed by the Leelanau Peninsula in the northwestern Lower Peninsula of Michigan. The bay is long, wide, and up to deep in spots. It is further divided into two east and west arms by the Ol ...
. Near Collingwood, Ontario
Collingwood is a town in Simcoe County, Ontario, Canada. It is situated on Nottawasaga Bay at the southern point of Georgian Bay. Collingwood is well known as a tourist destination, for its skiing in the winter, and limestone caves along the Nia ...
, commercial fruit orchards, including a few wineries, exist near the shoreline of southern Nottawasaga Bay
Nottawasaga Bay is a sub- bay within Georgian Bay in Southern Ontario, Canada located at the southernmost end of the main bay. The communities located on Nottawasaga Bay are Meaford, The Blue Mountains, Collingwood, Wasaga Beach and Tiny.
Th ...
. The eastern shore of Lake Michigan and the southern shore of Lake Erie have many successful wineries because of the lakes' moderating effects, as do the large commercial fruit and wine growing areas of the Niagara Peninsula located between Lake Erie and Lake Ontario. A similar phenomenon allows wineries to flourish in the Finger Lakes
The Finger Lakes are a group of eleven long, narrow, roughly north–south lakes located south of Lake Ontario in an area called the ''Finger Lakes region'' in New York, in the United States. This region straddles the northern and transitional ...
region of New York, as well as in Prince Edward County, Ontario
Prince Edward County (PEC) is a municipality in southern Ontario, Canada. Its coastline on Lake Ontario’s northeastern shore is known for Sandbanks Provincial Park, sand beaches, and limestone cliffs. The Regent Theatre, a restored Edwardian o ...
, on Lake Ontario's northeast shore.
The Great Lakes have been observed to help intensify storms, such as Hurricane Hazel
Hurricane Hazel was the deadliest, second costliest, and most intense hurricane of the 1954 Atlantic hurricane season. The storm killed at least 469 people in Haiti before striking the United States near the border between North and South ...
in 1954, and the 2011 Goderich, Ontario tornado, which moved onshore as a tornadic waterspout
A waterspout is an intense columnar vortex (usually appearing as a funnel cloud, funnel-shaped cloud) that occurs over a body of water. Some are connected to a cumulus congestus cloud, some to a cumuliform cloud and some to a cumulonimbus clou ...
. In 1996, a rare tropical or subtropical storm was observed forming in Lake Huron, dubbed the 1996 Lake Huron cyclone. Rather large severe thunderstorms covering wide areas are well known in the Great Lakes during mid-summer; these Mesoscale convective complex
A mesoscale convective complex (MCC) is a unique kind of mesoscale convective system which is defined by characteristics observed in infrared satellite imagery. They are long-lived, often form nocturnally, and commonly contain heavy rainfall, wi ...
es or MCCs can cause damage to wide swaths of forest and shatter glass in city buildings. These storms mainly occur during the night, and the systems sometimes have small embedded tornadoes, but more often straight-line winds accompanied by intense lightning.
Ecology
Historically, the Great Lakes, in addition to theirlake ecology
A lake ecosystem or lacustrine ecosystem includes biotic (living) plants, animals and micro-organisms, as well as abiotic (non-living) physical and chemical interactions. Lake ecosystems are a prime example of lentic ecosystems (''lentic'' ref ...
, were surrounded by various forest ecoregion
A forest is an area of land dominated by trees. Hundreds of definitions of forest are used throughout the world, incorporating factors such as tree density, tree height, land use, legal standing, and ecological function. The United Nations' ...
s (except in a relatively small area of southeast Lake Michigan where savanna or prairie occasionally intruded). Logging, urbanization, and agriculture uses have changed that relationship. In the early 21st century, Lake Superior's shores are 91% forested, Lake Huron 68%, Lake Ontario 49%, Lake Michigan 41%, and Lake Erie, where logging and urbanization has been most extensive, 21%. Some of these forests are second or third growth (i.e. they have been logged before, changing their composition). At least 13 wildlife species are documented as becoming extinct since the arrival of Europeans, and many more are threatened or endangered. Meanwhile, exotic and invasive species have also been introduced.
Fauna
 While the organisms living on the bottom of shallow waters are similar to those found in smaller lakes, the deep waters contain organisms found only in deep, cold lakes of the northern latitudes. These include the delicate opossum shrimp (order
While the organisms living on the bottom of shallow waters are similar to those found in smaller lakes, the deep waters contain organisms found only in deep, cold lakes of the northern latitudes. These include the delicate opossum shrimp (order mysida
Mysida is an order (biology), order of small, shrimp-like crustaceans in the malacostracan superorder Peracarida. Their common name opossum shrimps stems from the presence of a Brood pouch (Peracarida), brood pouch or "marsupium" in females. The ...
), the deepwater scud
Deepwater may refer to ocean water in the abyssal zone, hadal zone, or other deep ocean zones.
Deepwater may also refer to:
Entertainment
* Deep Water (Highsmith novel), a 1957 a psychological thriller novel by Patricia Highsmith
* ''Deepwat ...
(a crustacean of the order amphipoda
Amphipoda is an order of malacostracan crustaceans with no carapace and generally with laterally compressed bodies. Amphipods range in size from and are mostly detritivores or scavengers. There are more than 9,900 amphipod species so far desc ...
), two types of copepods
Copepods (; meaning "oar-feet") are a group of small crustaceans found in nearly every freshwater and saltwater habitat. Some species are planktonic (inhabiting sea waters), some are benthic (living on the ocean floor), a number of species have p ...
, and the deepwater sculpin
The deepwater sculpin (''Myoxocephalus thompsonii'') is a species of freshwater fish in the family Cottidae of order Scorpaeniformes. It is a glacial relict, native to a limited number of deep, cold lakes in Canada and the United States.
The de ...
(a spiny, large-headed fish).
The Great Lakes are an important source of fishing
Fishing is the activity of trying to catch fish. Fish are often caught as wildlife from the natural environment, but may also be caught from stocked bodies of water such as ponds, canals, park wetlands and reservoirs. Fishing techniques inclu ...
. Early European settlers were astounded by both the variety and quantity of fish; there were 150 different species in the Great Lakes. Throughout history, fish populations were the early indicator of the condition of the Lakes and have remained one of the key indicators even in the current era of sophisticated analyses and measuring instruments. According to the bi-national (U.S. and Canadian) resource book, ''The Great Lakes: An Environmental Atlas and Resource Book'': "The largest Great Lakes fish harvests were recorded in 1889 and 1899 at some 47 million pounds"Anon (1972). ''The Great Lakes: An Environmental Atlas and Resource Book''. Bi-national (U.S. and Canadian) resource book.
By 1801, the New York Legislature
The New York State Legislature consists of the two houses that act as the state legislature of the U.S. state of New York: The New York State Senate and the New York State Assembly. The Constitution of New York does not designate an official t ...
found it necessary to pass regulations curtailing obstructions to the natural migrations of Atlantic salmon
The Atlantic salmon (''Salmo salar'') is a species of ray-finned fish in the family Salmonidae. It is the third largest of the Salmonidae, behind Siberian taimen and Pacific Chinook salmon, growing up to a meter in length. Atlantic salmon are ...
from Lake Erie into their spawning channels. In the early 19th century, the government of Upper Canada
The Province of Upper Canada (french: link=no, province du Haut-Canada) was a part of British Canada established in 1791 by the Kingdom of Great Britain, to govern the central third of the lands in British North America, formerly part of the ...
found it necessary to introduce similar legislation prohibiting the use of weirs and nets at the mouths of Lake Ontario's tributaries. Other protective legislation was passed, but enforcement remained difficult.
On both sides of the Canada–United States border, the proliferation of dam
A dam is a barrier that stops or restricts the flow of surface water or underground streams. Reservoirs created by dams not only suppress floods but also provide water for activities such as irrigation, human consumption, industrial use ...
s and impoundments have multiplied, necessitating more regulatory efforts. Concerns by the mid-19th century included obstructions in the rivers which prevented salmon and lake sturgeon
The lake sturgeon (''Acipenser fulvescens''), also known as the rock sturgeon, is a North American temperate freshwater fish, one of about 25 species of sturgeon. Like other sturgeons, this species is a bottom feeder with evolutionarily basal t ...
from reaching their spawning grounds. The Wisconsin Fisheries Commission noted a reduction of roughly 25% in general fish harvests by 1875. The states have removed dams from rivers where necessary.
Overfishing has been cited as a possible reason for a decrease in population of various whitefish, important because of their culinary desirability and, hence, economic consequence. Moreover, between 1879 and 1899, reported whitefish harvests declined from some 24.3 million pounds (11 million kg) to just over 9 million pounds (4 million kg). By 1900, commercial fishermen on Lake Michigan were hauling in an average of 41 million pounds of fish annually. By 1938, Wisconsin's commercial fishing operations were motorized and mechanized, generating jobs for more than 2,000 workers, and hauling 14 million pounds per year. The population of giant freshwater mussels was eliminated as the mussels were harvested for use as buttons by early Great Lakes entrepreneurs.
''The Great Lakes: An Environmental Atlas and Resource Book'' (1972) notes: "Only pockets remain of the once large commercial fishery." Water quality improvements realized during the 1970s and 1980s, combined with successful salmonid stocking programs, have enabled the growth of a large recreational fishery. The last commercial fisherman left Milwaukee in 2011 because of overfishing and anthropogenic changes to the biosphere.The lake left me. It's gone.JS Online, August 13, 2011

Invasive species
Since the 19th century, an estimated 160 new species have found their way into the Great Lakes ecosystem; many have become invasive; the overseas ship ballast and ship hull parasitism are causing severe economic and ecological impacts. According to the Inland Seas Education Association, on average a new species enters the Great Lakes every eight months. Introductions into the Great Lakes include thezebra mussel
The zebra mussel (''Dreissena polymorpha'') is a small freshwater mussel. The species originates from the lakes of southern Russia and Ukraine, but has been accidentally introduced to numerous other areas and has become an invasive species in ma ...
, which was first discovered in 1988, and quagga mussel
The quagga mussel (''Dreissena rostriformis'', also known as ''Dreissena bugensis'' or ''Dreissena rostriformis bugensis'') is a species (or subspecies) of freshwater mussel, an aquatic bivalve mollusk in the family Dreissenidae. It has an aver ...
in 1989. Since 2000, the invasive quagga mussel has smothered the bottom of Lake Michigan almost from shore to shore, and their numbers are estimated at 900 trillion. The mollusks
Mollusca is the second-largest phylum of invertebrate animals after the Arthropoda, the members of which are known as molluscs or mollusks (). Around 85,000 extant species of molluscs are recognized. The number of fossil species is esti ...
are efficient filter feeders, competing with native mussels and reducing available food and spawning grounds for fish. In addition, the mussels may be a nuisance to industries by clogging pipes. The U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service
The United States Fish and Wildlife Service (USFWS or FWS) is an agency within the United States Department of the Interior dedicated to the management of fish, wildlife, and natural habitats. The mission of the agency is "working with othe ...
estimated in 2007 that the economic impact of the zebra mussel could be about $5 billion over the next decade.
 The alewife first entered the system west of Lake Ontario via 19th-century canals. By the 1960s, the small silver fish had become a familiar nuisance to beach goers across Lakes Michigan, Huron, and Erie. Periodic mass die-offs result in vast numbers of the fish washing up on shore; estimates by various governments have placed the percentage of Lake Michigan's biomass, which was made up of alewives in the early 1960s, as high as 90%. In the late 1960s, the various state and federal governments began stocking several species of salmonids, including the native lake trout as well as non-native chinook and
The alewife first entered the system west of Lake Ontario via 19th-century canals. By the 1960s, the small silver fish had become a familiar nuisance to beach goers across Lakes Michigan, Huron, and Erie. Periodic mass die-offs result in vast numbers of the fish washing up on shore; estimates by various governments have placed the percentage of Lake Michigan's biomass, which was made up of alewives in the early 1960s, as high as 90%. In the late 1960s, the various state and federal governments began stocking several species of salmonids, including the native lake trout as well as non-native chinook and coho
The coho salmon (''Oncorhynchus kisutch;'' Karuk: achvuun) is a species of anadromous fish in the salmon family and one of the five Pacific salmon species. Coho salmon are also known as silver salmon or "silvers". The scientific species name is ...
salmon; by the 1980s, alewife populations had dropped drastically. The ruffe
The Eurasian ruffe (''Gymnocephalus cernua''), also known as ruffe or pope, is a freshwater fish found in temperate regions of Europe and northern Asia. It has been introduced into the Great Lakes of North America, reportedly with unfortuna ...
, a small percid fish from Eurasia, became the most abundant fish species in Lake Superior's Saint Louis River within five years of its detection in 1986. Its range, which has expanded to Lake Huron, poses a significant threat to the lower lake fishery. Five years after first being observed in the St. Clair River, the round goby
The round goby (''Neogobius melanostomus'') is a fish. Defined as a euryhaline bottom-dwelling goby of the family Gobiidae, it is native to Central Eurasia, including the Black Sea and the Caspian Sea. Round gobies have established large non-nat ...
can now be found in all of the Great Lakes. The goby is considered undesirable for several reasons: it preys upon bottom-feeding fish, overruns optimal habitat, spawns multiple times a season, and can survive poor water quality conditions.
The influx of parasitic lamprey
Lampreys (sometimes inaccurately called lamprey eels) are an ancient extant lineage of jawless fish of the order Petromyzontiformes , placed in the superclass Cyclostomata. The adult lamprey may be characterized by a toothed, funnel-like s ...
populations after the development of the Erie Canal and the much later Welland Canal led to the two federal governments of the U.S. and Canada working on joint proposals to control it. By the mid-1950s, the lake trout
The lake trout (''Salvelinus namaycush'') is a freshwater char living mainly in lakes in northern North America. Other names for it include mackinaw, namaycush, lake char (or charr), touladi, togue, and grey trout. In Lake Superior, it can also ...
populations of Lakes Michigan and Huron were reduced, with the lamprey deemed largely to blame. This led to the launch of the bi-national Great Lakes Fishery Commission
The Great Lakes Fishery Commission is a bi-national commission made up of representatives of the United States and Canada. It was formed by the Convention on Great Lakes Fisheries, concluded in 1954 and ratified in 1955. It has eight members: fou ...
.
Several species of exotic water fleas
The Diplostraca or Cladocera, commonly known as water fleas, are a superorder of small crustaceans that feed on microscopic chunks of organic matter (excluding some predatory forms).
Over 1000 species have been recognised so far, with many more ...
have accidentally been introduced into the Great Lakes, such as the spiny waterflea, ''Bythotrephes longimanus
''Bythotrephes longimanus'' (also ''Bythotrephes cederstroemi''), or the spiny water flea, is a planktonic crustacean less than long. It is native to fresh waters of Northern Europe and Asia, but has been accidentally introduced and widely distr ...
'', and the fishhook waterflea, ''Cercopagis pengoi
''Cercopagis pengoi'', or the fishhook waterflea, is a species of planktonic cladoceran crustaceans that is native in the brackish fringes of the Black Sea and the Caspian Sea. In recent decades it has spread as an invasive species to some freshw ...
'', potentially having an effect on the zooplankton
Zooplankton are the animal component of the planktonic community ("zoo" comes from the Greek word for ''animal''). Plankton are aquatic organisms that are unable to swim effectively against currents, and consequently drift or are carried along by ...
population. Several species of crayfish
Crayfish are freshwater crustaceans belonging to the clade Astacidea, which also contains lobsters. In some locations, they are also known as crawfish, craydids, crawdaddies, crawdads, freshwater lobsters, mountain lobsters, rock lobsters, mu ...
have also been introduced that may contend with native crayfish populations. More recently an electric fence has been set up across the Chicago Sanitary and Ship Canal in order to keep several species of invasive Asian carp out of the lakes. These fast-growing planktivorous fish have heavily colonized the Mississippi and Illinois river systems. Invasive species, particularly zebra and quagga mussels, may be at least partially responsible for the collapse of the deepwater demersal fish community in Lake Huron, as well as drastic unprecedented changes in the zooplankton community of the lake.
Microbiology
Scientists understand that the micro-aquatic life of the lakes is abundant but know very little about some of the most plentiful microbes and their environmental effects in the Great Lakes. Although a drop of lake water may contain 1 millionbacteria
Bacteria (; singular: bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one biological cell. They constitute a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria were among ...
cells and 10 million viruses
A virus is a submicroscopic infectious agent that replicates only inside the living cells of an organism. Viruses infect all life forms, from animals and plants to microorganisms, including bacteria and archaea.
Since Dmitri Ivanovsky's 1 ...
, only since 2012 has there been a long-term study of the lakes' micro-organisms. Between 2012 and 2019 more than 160 new species have been discovered.
Flora
Native habitats and ecoregions in the Great Lakes region include: *Alvar
An alvar is a biological environment based on a limestone plain with thin or no soil and, as a result, sparse grassland vegetation. Often flooded in the spring, and affected by drought in midsummer, alvars support a distinctive group of prairie ...
* Boreal rich fen (such as in Door County)
* Eastern forest-boreal transition
Eastern may refer to:
Transportation
*China Eastern Airlines, a current Chinese airline based in Shanghai
*Eastern Air, former name of Zambia Skyways
*Eastern Air Lines, a defunct American airline that operated from 1926 to 1991
*Eastern Air Li ...
* Eastern Great Lakes lowland forests
The Eastern Great Lakes lowland forests is a temperate broadleaf and mixed forest ecoregion of North America, as defined by the World Wildlife Fund. It lies mostly in south and eastern Ontario and Quebec in Canada, and Upstate New York and Vermon ...
* Southern Great Lakes forests
The Southern Great Lakes lowland forests is a temperate broadleaf and mixed forest ecoregion of North America, as defined by the World Wildlife Fund. Located near the Great Lakes, it lies mostly in the central northeastern United States and exte ...
* Central forest-grasslands transition
Central is an adjective usually referring to being in the center of some place or (mathematical) object.
Central may also refer to:
Directions and generalised locations
* Central Africa, a region in the centre of Africa continent, also known as ...
* Upper Midwest forest-savanna transition
Upper may refer to:
* Shoe upper or ''vamp'', the part of a shoe on the top of the foot
* Stimulant, drugs which induce temporary improvements in either mental or physical function or both
* ''Upper'', the original film title for the 2013 found fo ...
* Western Great Lakes forests
The Western Great Lakes forests is a terrestrial ecoregion as defined by the World Wildlife Fund. It is within the temperate broadleaf and mixed forests biome of North America. It is found in northern areas of the United States' states of Michiga ...
* Central Canadian Shield forests
The Central Canadian Shield forests are a taiga ecoregion of Eastern Canada, as defined by the World Wildlife Fund (WWF) categorization system.
Setting
This ecoregion consists of rolling hills, lakes, bogs and rocky outcrops covering a large curv ...
* Laurentian Mixed Forest Province
The Laurentian Mixed Forest Province, also known as the North Woods, is a forested ecoregion in eastern North America. Among others, this terminology has been adopted by the Minnesota Department of Natural Resources. Similar, though not n ...
* Beech-maple forest
* Habitats of the Indiana Dunes
Plant lists include:
* List of Michigan flowers
This is a list of plants that are native to the U.S. state of Michigan.
A
*'' Acalypha rhomboidea'', Rhombic copperleaf
*'' Acalypha virginica'', Virginia copperleaf
*''Acorus americanus'', American sweet-flag
*'' Amaranthus arenicola'', Sandhill ...
* List of Minnesota wild flowers
This is a list of all the wildflowers native plant, native to Minnesota by common name, following Minnesota DNR conventions. Where several species of plants share part of a common name, they have been grouped together under that name; this is for i ...
* List of Minnesota trees
There are two lists of Minnesota trees organized in distinct ways:
* List of Minnesota trees by family
* List of Minnesota trees by scientific name
{{DEFAULTSORT:Minnesota trees ...
Logging
Logging
Logging is the process of cutting, processing, and moving trees to a location for transport. It may include skidding, on-site processing, and loading of trees or logs onto trucks or skeleton cars.
Logging is the beginning of a supply chain ...
of the extensive forests in the Great Lakes region removed riparian
A riparian zone or riparian area is the interface between land and a river or stream. Riparian is also the proper nomenclature for one of the terrestrial biomes of the Earth. Plant habitats and communities along the river margins and banks ar ...
and adjacent tree cover over rivers and streams, which provide shade, moderating water temperatures in fish spawning grounds. Removal of trees also destabilized the soil, with greater volumes washed into stream beds causing siltation of gravel beds, and more frequent flooding.
Running cut logs down the tributary rivers into the Great Lakes also dislocated sediments. In 1884, the New York Fish Commission determined that the dumping of sawmill waste (chips and sawdust) had impacted fish populations.
Pollution
The first U.S.Clean Water Act
The Clean Water Act (CWA) is the primary federal law in the United States governing water pollution. Its objective is to restore and maintain the chemical, physical, and biological integrity of the nation's waters; recognizing the responsibiliti ...
, passed by a Congressional override after being vetoed by U.S. President Richard Nixon
Richard Milhous Nixon (January 9, 1913April 22, 1994) was the 37th president of the United States, serving from 1969 to 1974. A member of the Republican Party, he previously served as a representative and senator from California and was ...
in 1972, was a key piece of legislation, along with the bi-national Great Lakes Water Quality Agreement
Great may refer to: Descriptions or measurements
* Great, a relative measurement in physical space, see Size
* Greatness, being divine, majestic, superior, majestic, or transcendent
People
* List of people known as "the Great"
*Artel Great (born ...
signed by Canada and the U.S. A variety of steps taken to process industrial and municipal pollution discharges into the system greatly improved water quality by the 1980s, and Lake Erie in particular is significantly cleaner. Discharge of toxic substances has been sharply reduced. Federal and state regulations control substances like PCBs
Polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) are highly carcinogenic chemical compounds, formerly used in industrial and consumer products, whose production was banned in the United States by the Toxic Substances Control Act in 1979 and internationally by t ...
. The first of 43 "Great Lakes Areas of Concern
Great may refer to: Descriptions or measurements
* Great, a relative measurement in physical space, see Size
* Greatness, being divine, majestic, superior, majestic, or transcendent
People
* List of people known as "the Great"
*Artel Great (born ...
" to be formally "de-listed" through successful cleanup was Ontario's Collingwood Harbour in 1994; Ontario's Severn Sound followed in 2003. Presque Isle Bay
Presque Isle Bay is a natural bay located off the coast of Erie, Pennsylvania, United States. Its embayment is about in length, about across at its widest point, and an average depth of about . The bay is at an elevation of 571 ft (174 m) ...
in Pennsylvania is formally listed as in recovery, as is Ontario's Spanish Harbour. Dozens of other Areas of Concern have received partial cleanups such as the Rouge River (Michigan)
The River Rouge is a 127-mile (204 kilometer)U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map accessed November 7, 2011 river in the Metro Detroit area of southeastern Michigan. It flows into th ...
and Waukegan Harbor (Illinois).
Phosphate detergents were historically a major source of nutrient to the Great Lakes algae blooms in particular in the warmer and shallower portions of the system such as Lake Erie, Saginaw Bay
Saginaw Bay is a bay within Lake Huron located on the eastern side of the U.S. state of Michigan. It forms the space between Michigan's Thumb region and the rest of the Lower Peninsula of Michigan. Saginaw Bay is in area. It is located in part ...
, Green Bay, and the southernmost portion of Lake Michigan. By the mid-1980s, most jurisdictions bordering the Great Lakes had controlled phosphate detergent
In chemistry, a phosphate is an anion, salt, functional group or ester derived from a phosphoric acid. It most commonly means orthophosphate, a derivative of orthophosphoric acid .
The phosphate or orthophosphate ion is derived from phosphor ...
s. Blue-green algae, or cyanobacteria
Cyanobacteria (), also known as Cyanophyta, are a phylum of gram-negative bacteria that obtain energy via photosynthesis. The name ''cyanobacteria'' refers to their color (), which similarly forms the basis of cyanobacteria's common name, blu ...
blooms, have been problematic on Lake Erie since 2011. "Not enough is being done to stop fertilizer and phosphorus from getting into the lake and causing blooms," said Michael McKay, executive director of the Great Lakes Institute for Environmental Research (GLIER) at the University of Windsor
, mottoeng = Goodness, Discipline and Knowledge
, established =
, academic_affiliations = CARL, COU, Universities Canada
, former_names = Assumption College (1857-1956)Assumption University of Windsor (1956-1963)
, type = Public universit ...
. The largest Lake Erie bloom to date occurred in 2015, exceeding the severity index at 10.5 and in 2011 at a 10. In early August 2019, satellite images depicted a bloom stretching up to 1,300 square kilometres on Lake Erie, with the heaviest concentration near Toledo, Ohio
Toledo ( ) is a city in and the county seat of Lucas County, Ohio, United States. A major Midwestern United States port city, Toledo is the fourth-most populous city in the state of Ohio, after Columbus, Cleveland, and Cincinnati, and according ...
. A large bloom does not necessarily mean the cyanobacteria ... will produce toxins", said Michael McKay, of the University of Windsor. Water quality testing was underway in August 2019.
Mercury
Until 1970,mercury
Mercury commonly refers to:
* Mercury (planet), the nearest planet to the Sun
* Mercury (element), a metallic chemical element with the symbol Hg
* Mercury (mythology), a Roman god
Mercury or The Mercury may also refer to:
Companies
* Merc ...
was not listed as a harmful chemical, according to the United States Federal Water Quality Administration. In the 21st century, mercury has become more apparent in water tests. Mercury compounds have been used in paper mills to prevent slime from forming during their production, and chemical companies have used mercury to separate chlorine from brine solutions. Studies conducted by the Environmental Protection Agency
A biophysical environment is a biotic and abiotic surrounding of an organism or population, and consequently includes the factors that have an influence in their survival, development, and evolution. A biophysical environment can vary in scale f ...
have shown that when the mercury comes in contact with many of the bacteria and compounds in the fresh water, it forms the compound methyl mercury
Methylmercury (sometimes methyl mercury) is an organometallic cation with the formula . It is the simplest organomercury compound. Methylmercury is extremely toxic, and its derivatives are the major source of organic mercury for humans. It is ...
, which has a much greater impact on human health than elemental mercury due to a higher propensity for absorption. This form of mercury is not detrimental to a majority of fish types, but is very detrimental to people and other wildlife animals who consume the fish. Mercury has been known for health related problems such as birth defects in humans and animals, and the near extinction of eagles in the Great Lakes region.
Sewage
The amount of raw sewage dumped into the waters was the primary focus of both the first Great Lakes Water Quality Agreement and federal laws passed in both countries during the 1970s. Implementation of secondary treatment of municipal sewage by major cities greatly reduced the routine discharge of untreated sewage during the 1970s and 1980s. TheInternational Joint Commission
The International Joint Commission (french: Commission mixte internationale) is a bi-national organization established by the governments of the United States and Canada under the Boundary Waters Treaty of 1909. Its responsibilities were expa ...
in 2009 summarized the change: "Since the early 1970s, the level of treatment to reduce pollution from waste water discharges to the Great Lakes has improved considerably. This is a result of significant expenditures to date on both infrastructure and technology, and robust regulatory systems that have proven to be, on the whole, quite effective." The commission reported that all urban sewage treatment systems on the U.S. side of the lakes had implemented secondary treatment, as had all on the Canadian side except for five small systems.
Though contrary to federal laws in both countries, those treatment system upgrades have not yet eliminated combined sewer
A combined sewer is a type of gravity sewer with a system of pipes, tunnels, pump stations etc. to transport sewage and urban runoff together to a sewage treatment plant or disposal site. This means that during rain events, the sewage gets dilute ...
overflow events. This describes when older sewerage systems, which combine storm water with sewage into single sewers heading to the treatment plant, are temporarily overwhelmed by heavy rainstorms. Local sewage treatment authorities then must release untreated effluent, a mix of rainwater and sewage, into local water bodies. While enormous public investments such as the Deep Tunnel The Tunnel and Reservoir Plan (abbreviated TARP and more commonly known as the Deep Tunnel Project or the Chicago Deep Tunnel) is a large civil engineering project that aims to reduce flooding in the metropolitan Chicago area, and to reduce the harm ...
projects in Chicago
(''City in a Garden''); I Will
, image_map =
, map_caption = Interactive Map of Chicago
, coordinates =
, coordinates_footnotes =
, subdivision_type = Country
, subdivision_name ...
and Milwaukee
Milwaukee ( ), officially the City of Milwaukee, is both the most populous and most densely populated city in the U.S. state of Wisconsin and the county seat of Milwaukee County. With a population of 577,222 at the 2020 census, Milwaukee is ...
have greatly reduced the frequency and volume of these events, they have not been eliminated. The number of such overflow events in Ontario, for example, is flat according to the International Joint Commission. Reports about this issue on the U.S. side highlight five large municipal systems (those of Detroit, Cleveland, Buffalo, Milwaukee and Gary) as being the largest current periodic sources of untreated discharges into the Great Lakes.

Impacts of climate change on algae
Algae such asdiatoms
A diatom (New Latin, Neo-Latin ''diatoma''), "a cutting through, a severance", from el, διάτομος, diátomos, "cut in half, divided equally" from el, διατέμνω, diatémno, "to cut in twain". is any member of a large group com ...
, along with other phytoplankton
Phytoplankton () are the autotrophic (self-feeding) components of the plankton community and a key part of ocean and freshwater ecosystems. The name comes from the Greek words (), meaning 'plant', and (), meaning 'wanderer' or 'drifter'.
Ph ...
, are photosynthetic
Photosynthesis is a process used by plants and other organisms to convert light energy into chemical energy that, through cellular respiration, can later be released to fuel the organism's activities. Some of this chemical energy is stored in c ...
primary producers
An autotroph or primary producer is an organism that produces complex organic compounds (such as carbohydrates, fats, and proteins) using carbon from simple substances such as carbon dioxide,Morris, J. et al. (2019). "Biology: How Life Work ...
supporting the food web
A food web is the natural interconnection of food chains and a graphical representation of what-eats-what in an ecological community. Another name for food web is consumer-resource system. Ecologists can broadly lump all life forms into one ...
of the Great Lakes, and have been affected by global warming. The changes in the size or in the function of the primary producers may have a direct or an indirect impact on the food web. Photosynthesis carried out by diatoms constitutes about one fifth of the total photosynthesis. By taking out of the water to photosynthesize, diatoms help to stabilize the pH of the water, as would react with water to produce carbonic acid.
:
Diatoms acquire inorganic
In chemistry, an inorganic compound is typically a chemical compound that lacks carbon–hydrogen bonds, that is, a compound that is not an organic compound. The study of inorganic compounds is a subfield of chemistry known as '' inorganic chemist ...
carbon through passive diffusion of and , and use carbonic anhydrase
The carbonic anhydrases (or carbonate dehydratases) () form a family of enzymes that catalyze the interconversion between carbon dioxide and water and the dissociated ions of carbonic acid (i.e. bicarbonate and hydrogen ions). The active site ...
mediated active transport to speed up this process. Large diatoms require more carbon uptake than smaller diatoms.Brian N. Popp, Edward A. Laws, Robert R. Bidigare, John E. Dore, et al., Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, (1998), Effect of Phytoplankton Cell Geometry on Carbon Isotopic Fractionation, Vol. 62, Iss. pp. 69-77. There is a positive correlation
In statistics, correlation or dependence is any statistical relationship, whether causal or not, between two random variables or bivariate data. Although in the broadest sense, "correlation" may indicate any type of association, in statistic ...
between the surface area and the chlorophyll concentration of diatom cells.
History
 Several Native American populations ( Paleo-indians) inhabited the region around 10,000 BC, after the end of the Wisconsin glaciation. The peoples of the Great Lakes traded with the
Several Native American populations ( Paleo-indians) inhabited the region around 10,000 BC, after the end of the Wisconsin glaciation. The peoples of the Great Lakes traded with the Hopewell culture
The Hopewell tradition, also called the Hopewell culture and Hopewellian exchange, describes a network of precontact Native American cultures that flourished in settlements along rivers in the northeastern and midwestern Eastern Woodlands from ...
from around 1000 AD, as copper nuggets have been extracted from the region and fashioned into ornaments and weapons in the mounds of Southern Ohio.
The Rush–Bagot Treaty
The Rush–Bagot Treaty or Rush–Bagot Disarmament was a treaty between the United States and Great Britain limiting naval armaments on the Great Lakes and Lake Champlain, following the War of 1812. It was ratified by the United States Senate o ...
signed in 1818, after the War of 1812
The War of 1812 (18 June 1812 – 17 February 1815) was fought by the United States of America and its indigenous allies against the United Kingdom and its allies in British North America, with limited participation by Spain in Florida. It bega ...
and the later Treaty of Washington eventually led to a complete disarmament of naval vessels in the Great Lakes. Nonetheless, both nations maintained coast guard vessels in the Great Lakes.
The brigantine , which was commissioned by René-Robert Cavelier, Sieur de La Salle
René-Robert Cavelier, Sieur de La Salle (; November 22, 1643 – March 19, 1687), was a 17th-century French explorer and fur trader in North America. He explored the Great Lakes region of the United States and Canada, the Mississippi River, ...
, was built at Cayuga Creek, near the southern end of the Niagara River
The Niagara River () is a river that flows north from Lake Erie to Lake Ontario. It forms part of the border between the province of Ontario in Canada (on the west) and the state of New York (state), New York in the United States (on the east) ...
, and became the first known sailing ship to travel the upper Great Lakes on August 7, 1679. During settlement, the Great Lakes and its rivers were the only practical means of moving people and freight. Barges from middle North America were able to reach the Atlantic Ocean from the Great Lakes when the Welland Canal
The Welland Canal is a ship canal in Ontario, Canada, connecting Lake Ontario and Lake Erie. It forms a key section of the St. Lawrence Seaway and Great Lakes Waterway. Traversing the Niagara Peninsula from Port Weller in St. Catharines t ...
opened in 1824 and the later Erie Canal opened in 1825. By 1848, with the opening of the Illinois and Michigan Canal
The Illinois and Michigan Canal connected the Great Lakes to the Mississippi River and the Gulf of Mexico. In Illinois, it ran from the Chicago River in Bridgeport, Chicago to the Illinois River at LaSalle-Peru. The canal crossed the Chicago Po ...
at Chicago, direct access to the Mississippi River was possible from the lakes. With these two canals an all-inland water route was provided between New York City
New York, often called New York City or NYC, is the List of United States cities by population, most populous city in the United States. With a 2020 population of 8,804,190 distributed over , New York City is also the L ...
and New Orleans
New Orleans ( , ,New Orleans
Merriam-Webster. ; french: La Nouvelle-Orléans , es, Nuev ...
.
The main business of many of the passenger lines in the 19th century was transporting immigrants. Many of the larger cities owe their existence to their position on the lakes as a freight destination as well as for being a magnet for immigrants. After railroads and surface roads developed, the freight and passenger businesses dwindled and, except for ferries and a few foreign cruise ships, have now vanished.
The immigration routes still have an effect today. Immigrants often formed their own communities, and some areas have a pronounced ethnicity, such as Dutch, German, Polish, Finnish, and many others. Since many immigrants settled for a time in New England before moving westward, many areas on the U.S. side of the Great Lakes also have a New England feel, especially in home styles and accent.
Merriam-Webster. ; french: La Nouvelle-Orléans , es, Nuev ...
 Since general freight these days is transported by railroads and trucks, domestic ships mostly move bulk cargoes, such as
Since general freight these days is transported by railroads and trucks, domestic ships mostly move bulk cargoes, such as iron ore
Iron ores are rocks and minerals from which metallic iron can be economically extracted. The ores are usually rich in iron oxides and vary in color from dark grey, bright yellow, or deep purple to rusty red. The iron is usually found in the fo ...
, coal
Coal is a combustible black or brownish-black sedimentary rock, formed as rock strata called coal seams. Coal is mostly carbon with variable amounts of other elements, chiefly hydrogen, sulfur, oxygen, and nitrogen.
Coal is formed when dea ...
and limestone for the steel industry. The domestic bulk freight developed because of the nearby mines. It was more economical to transport the ingredients for steel to centralized plants rather than to make steel on the spot. Grain exports are also a major cargo on the lakes. In the 19th and early 20th centuries, iron and other ores such as copper were shipped south on (downbound ships), and supplies, food, and coal were shipped north (upbound). Because of the location of the coal fields in Pennsylvania and West Virginia, and the general northeast track of the Appalachian Mountains, railroads naturally developed shipping routes that went due north to ports such as Erie, Pennsylvania and Ashtabula, Ohio.
Because the lake maritime community largely developed independently, it has some distinctive vocabulary. Ships, no matter the size, are called "boats". When the sailing ships gave way to steamships, they were called "steamboats"—the same term used on the Mississippi. The ships also have a distinctive design; ships that primarily trade on the lakes are known as "Lake freighter, lakers". Foreign boats are known as "salties". One of the more common sights on the lakes has been since about 1950 the , self-unloader. This is a laker with a conveyor belt system that can unload itself by swinging a crane over the side. Today, the Great Lakes fleet is much smaller in numbers than it once was because of the increased use of overland freight, and a few larger ships replacing many small ones.
During World War II, the risk of submarine attacks against coastal training facilities motivated the United States Navy to operate two aircraft carriers on the Great Lakes, and . Both served as training ships to qualify naval aviators in carrier landing and takeoff. Lake Champlain briefly became the sixth Great Lake of the United States on March 6, 1998, when Bill Clinton, President Clinton signed Senate Bill 927. This bill, which reauthorized the National Sea Grant Program, contained a line declaring Lake Champlain to be a Great Lake. Not coincidentally, this status allows neighboring states to apply for additional federal research and education funds allocated to these national resources. Following a small uproar, the Senate voted to revoke the designation on March 24 (although New York and Vermont universities would continue to receive funds to monitor and study the lake).
Alan B. McCullough has written that the fishing industry of the Great Lakes got its start "on the American side of Lake Ontario in Chaumont Bay, near the Maumee River on Lake Erie, and on the Detroit River
The Detroit River flows west and south for from Lake St. Clair to Lake Erie as a strait in the Great Lakes system. The river divides the metropolitan areas of Detroit, Michigan, and Windsor, Ontario, Windsor, Ontario—an area collectively refe ...
at about the time of the War of 1812". Although the region was sparsely populated until the 1830s, so there was not much local demand and transporting fish was prohibitively costly, there were economic and infrastructure developments that were promising for the future of the fishing industry going into the 1830s. Particularly, the 1825 opening of the Erie Canal and the Welland Canal a few years later. The fishing industry expanded particularly in the waters associated with the fur trade that connect Lake Erie and Lake Huron. In fact, two major suppliers of fish in the 1830s were the fur trading companies Hudson's Bay Company and the American Fur Company.
The catch from these waters was sent to the growing market for salted fish in Detroit, where merchants involved in the fur trade had already gained some experience handling salted fish. One such merchant was John P. Clark, a shipbuilder and merchant who began selling fish in the area of Manitowoc, Wisconsin where whitefish was abundant. Another operation cropped up in Georgian Bay
Georgian Bay (french: Baie Georgienne) is a large bay of Lake Huron, in the Laurentia bioregion. It is located entirely within the borders of Ontario, Canada. The main body of the bay lies east of the Bruce Peninsula and Manitoulin Island. To ...
, Canadian waters plentiful with trout as well as whitefish. In 1831, Alexander MacGregor from Goderich, Ontario found whitefish and herring in abundant supply around the Fishing Islands. A contemporary account by Methodist missionary John Evans describes the fish as resembling a "bright cloud moving rapidly through the water".
From 1844 through 1857, palace steamers carried passengers and cargo around the Great Lakes. In the first half of the 20th century Great Lakes passenger steamers, large luxurious passenger steamers sailed the lakes in opulence. The Detroit and Cleveland Navigation Company had several vessels at the time and hired workers from all walks of life to help operate these vessels. Several ferries currently operate on the Great Lakes to carry passengers to various islands. As of 2007, four car ferry services cross the Great Lakes, two on Lake Michigan: a steamer from Ludington, Michigan, to Manitowoc, Wisconsin, and a high speed catamaran from Milwaukee to Muskegon, Michigan, one on Lake Erie: a boat from Kingsville, Ontario, or Leamington, Ontario, to Pelee, Ontario, Pelee Island, Ontario, then onto Sandusky, Ohio, and one on Lake Huron: the MS ''Chi-Cheemaun'' runs between Tobermory and South Baymouth, Manitoulin Island, operated by the Owen Sound Transportation Company. HSC Virgen de Coromoto, An international ferry across Lake Ontario from Rochester, New York, to Toronto ran during 2004 and 2005 but is no longer in operation.
Shipwrecks
The large size of the Great Lakes increases the risk of water travel; storms and reefs are common threats. The lakes are prone to sudden and severe storms, in particular in the autumn, from late October until early December. Hundreds of ships have met their end on the lakes. The greatest concentration of shipwrecks lies near Thunder Bay (Michigan), beneath Lake Huron, near the point where eastbound and westbound shipping lanes converge. The Lake Superior shipwreck coast from Grand Marais, Michigan, to Whitefish Point became known as the "Graveyard of the Great Lakes". More vessels have been lost in the Whitefish Point area than any other part of Lake Superior. The Whitefish Point Underwater Preserve serves as an underwater museum to protect the many shipwrecks in this area. The first ship to sink in Lake Michigan was ''Le Griffon'', also the first ship to sail the Great Lakes. Caught in a 1679 storm while trading furs between Green Bay and Michilimacinac, she was lost with all hands aboard.Matile, Roger (April 11, 2004) "Has a famed Great Lakes mystery been solved?"Ledger-Sentinel, Oswego, Illinois. Its wreck may have been found in 2004, but a wreck subsequently discovered in a different location was also claimed in 2014 to be ''Le Griffon''. The largest and last major freighter wrecked on the lakes was the , which sank on November 10, 1975, just over offshore from Whitefish Point on Lake Superior. The largest loss of life in a shipwreck out on the lakes may have been that of , wrecked in 1860 with the loss of around 400 lives on Lake Michigan. In an incident at a Chicago dock in 1915, the rolled over while loading passengers, killing 841. In 2007, the Great Lakes Shipwreck Museum, Great Lakes Shipwreck Historical Society announced that it had found the wreckage of ''Cyprus'', a long, century-old ore carrier. ''Cyprus'' sank during a Lake Superior storm on October 11, 1907, during its second voyage while hauling iron ore from Superior, Wisconsin, to Buffalo, New York. The entire crew of 23 drowned, except one, Charles Pitz, who floated on a life raft for almost seven hours. In 2008, Deep sea diving, deep sea divers in Lake Ontario found the wreck of the 1780 Royal Navy warship in what has been described as an "archaeological miracle". There are no plans to raise her as the site is being treated as a war grave. In 2010, ''L.R. Doty'' was found in Lake Michigan by an exploration diving team led by dive boat Captain Jitka Hanakova from her boat ''Molly V''. The ship sank in October 1898, probably attempting to rescue a small schooner, ''Olive Jeanette'', during a terrible storm. Still missing are the two last warships to sink in the Great Lakes, the French minesweepers French minesweepers Inkerman and Cerisoles, ''Inkerman'' and ''Cerisoles'', which vanished in Lake Superior during a blizzard in 1918. 78 people died making it the largest loss of life in Lake Superior and the greatest unexplained loss of life in the Great Lakes.
Economy

Shipping
Except when the water is frozen during winter, more than 100 lake freighters operate continuously on the Great Lakes, which remain a major water transport corridor for bulk goods. TheGreat Lakes Waterway
The Great Lakes Waterway (GLW) is a system of natural channels and artificial canals which enable navigation between the North American Great Lakes. Though all of the lakes are naturally connected as a chain, water travel between the lakes was i ...
connects all the lakes; the smaller Saint Lawrence Seaway
The St. Lawrence Seaway (french: la Voie Maritime du Saint-Laurent) is a system of locks, canals, and channels in Canada and the United States that permits oceangoing vessels to travel from the Atlantic Ocean to the Great Lakes of North Americ ...
connects the lakes to the Atlantic Ocean. Some lake freighters are too large to use the Seaway and operate only on the Waterway and lakes. In 2002, 162 million net tons of dry bulk cargo were moved on the Lakes. This was, in order of volume: iron ore, grain and potash. The iron ore and much of the stone and coal are used in the steel industry. There is also some shipping of liquid and containerized cargo. Major ports on the Great Lakes include Twin Ports, Duluth-Superior, Chicago, Detroit, Cleveland, Twin Harbors, Hamilton-Oshawa Port Authority, Hamilton and Thunder Bay Port Authority, Thunder Bay.
Recreation
 Tourism and recreation are major industries on the Great Lakes. A few small cruise ships operate on the Great Lakes including some sailing, sailing ships. Sport fishing, commercial fishing, and Native American fishing represent a U.S.$4 billion a year industry with salmon, Coregonus, whitefish, smelt (fish), smelt, lake trout, Bass (fish), bass and walleye being major catches. Many other List of water sports, water sports are practiced on the lakes such as yachting, sea kayaking, Recreational diving, diving, kitesurfing, powerboating, and lake surfing. The Great Lakes Circle Tour is a designated scenic road system connecting all of the Great Lakes and the Saint Lawrence River.
Tourism and recreation are major industries on the Great Lakes. A few small cruise ships operate on the Great Lakes including some sailing, sailing ships. Sport fishing, commercial fishing, and Native American fishing represent a U.S.$4 billion a year industry with salmon, Coregonus, whitefish, smelt (fish), smelt, lake trout, Bass (fish), bass and walleye being major catches. Many other List of water sports, water sports are practiced on the lakes such as yachting, sea kayaking, Recreational diving, diving, kitesurfing, powerboating, and lake surfing. The Great Lakes Circle Tour is a designated scenic road system connecting all of the Great Lakes and the Saint Lawrence River.
Legislation
See also
* Alliance for the Great Lakes * Boundary Waters Treaty of 1909 * Eastern Continental Divide * Great Lakes census statistical areas * Great Lakes Protection Fund * Great Lakes WATER Institute * Great Recycling and Northern Development Canal * List of municipalities on the Great Lakes * Michigan Islands National Wildlife Refuge * Populated islands of the Great Lakes * Sixty Years' War for control of the Great LakesReferences
Further reading
* * Beltran, R. et al.The Great Lakes: An Environmental Atlas and Resource Book
'. (United States Environmental Protection Agency and Government of Canada, 1995, ). * Coon, W.F. and R.A. Sheets.
Estimate of Ground Water in Storage in the Great Lakes Basin
' [Scientific Investigations Report 2006-5180]. Department of the Interior, U.S. Geological Survey, 2006. * * * Riley, John L. (2013) ''The Once and Future Great Lakes Country: An Ecological History'' (McGill-Queen's University Press 516 pages; traces environmental change in the region since the last ice age. * Holling, Holling Clancy ''Paddle to the Sea'' (), an illustrated children's book about the Great Lakes and their environment. Beautiful and educational.
External links
* *Great Lakes website
of the Environment Canada, Canadian Department of the Environment
Great Lakes website
of the United States Environmental Protection Agency
Binational website of USEPA and Environment Canada for Great Lakes Water Quality
Great Lakes Environmental Research Laboratory website
(an arm of the American National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration)
Great Lakes Information Network
sponsored by th
Great Lakes Commission
an official American interstate compact agency.
Great Lakes Echo, a publication covering Great Lakes environmental issues
''Maritime History of the Great Lakes''
digital library covering Great Lakes history.
Dynamically updated data
Surface temperatures
Water levels
Ship locations
Water levels since 1918
{{Authority control Great Lakes, Eastern Canada Great Lakes region (U.S.) Lake groups