Graveyard of the Pacific on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
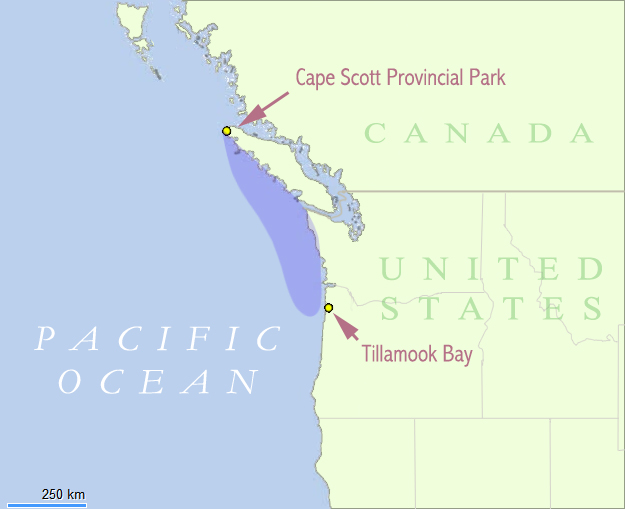 The Graveyard of the Pacific is a somewhat loosely defined stretch of the
The Graveyard of the Pacific is a somewhat loosely defined stretch of the
 The Graveyard of the Pacific is a somewhat loosely defined stretch of the
The Graveyard of the Pacific is a somewhat loosely defined stretch of the Pacific Northwest
The Pacific Northwest (sometimes Cascadia, or simply abbreviated as PNW) is a geographic region in western North America bounded by its coastal waters of the Pacific Ocean to the west and, loosely, by the Rocky Mountains to the east. Though ...
coast stretching from around Tillamook Bay
Tillamook Bay is a small inlet of the Pacific Ocean, approximately 6 mi (10 km) long and 2 mi (3 km) wide, on the northwest coast of the U.S. state of Oregon. It is located just north of Cape Meares in western Tillamook Count ...
on the Oregon Coast
The Oregon Coast is a coastal region of the U.S. state of Oregon. It is bordered by the Pacific Ocean to its west and the Oregon Coast Range to the east, and stretches approximately from the California state border in the south to the Columbia ...
northward past the treacherous Columbia Bar
The Columbia Bar, also frequently called the Graveyard of the Pacific, is a system of bar (landform), bars and shoals at the mouth of the Columbia River spanning the U.S. states of Oregon and Washington (state), Washington. It is known as one of th ...
and Juan de Fuca Strait
The Strait of Juan de Fuca (officially named Juan de Fuca Strait in Canada) is a body of water about long that is the Salish Sea's outlet to the Pacific Ocean. The international boundary between Canada and the United States runs down the centre ...
, up the rocky western coast of Vancouver Island
Vancouver Island is an island in the northeastern Pacific Ocean and part of the Canadian Provinces and territories of Canada, province of British Columbia. The island is in length, in width at its widest point, and in total area, while are o ...
to Cape Scott Cape Scott is a cape at the western side of the terminus of Dennistoun Glacier on the northern coast of Victoria Land in Antarctica
Antarctica () is Earth's southernmost and least-populated continent. Situated almost entirely south of the ...
.
Unpredictable weather conditions, including storms and fog, and dangerous coastal characteristics, including shifting sandbars, tidal rips, and rocky reefs and shorelines, have caused thousands of ships to wreck in the area since European exploration of the area began in earnest in the 18th century.
More than 2,000 ships have wrecked in the area, with more than 700 lives lost, near the Columbia Bar alone. One book lists 484 wrecks at the south and west sides of Vancouver Island.
Although major wrecks have declined since the 1920s, several lives are still lost annually.
Among its particularly dangerous landmarks are the Columbia Bar
The Columbia Bar, also frequently called the Graveyard of the Pacific, is a system of bar (landform), bars and shoals at the mouth of the Columbia River spanning the U.S. states of Oregon and Washington (state), Washington. It is known as one of th ...
, a giant sandbar at the mouth of the Columbia River
The Columbia River (Upper Chinook: ' or '; Sahaptin: ''Nch’i-Wàna'' or ''Nchi wana''; Sinixt dialect'' '') is the largest river in the Pacific Northwest region of North America. The river rises in the Rocky Mountains of British Columbia, C ...
; Cape Flattery
Cape Flattery () is the northwesternmost point of the contiguous United States. It is in Clallam County, Washington on the Olympic Peninsula, where the Strait of Juan de Fuca joins the Pacific Ocean. It is also part of the Makah Reservation, and ...
; the reefs and rocks lining the west coast of Vancouver Island
Vancouver Island is an island in the northeastern Pacific Ocean and part of the Canadian Provinces and territories of Canada, province of British Columbia. The island is in length, in width at its widest point, and in total area, while are o ...
; and the Strait of Juan de Fuca
The Strait of Juan de Fuca (officially named Juan de Fuca Strait in Canada) is a body of water about long that is the Salish Sea's outlet to the Pacific Ocean. The international boundary between Canada and the United States runs down the centre ...
.
Salvage attempts are often unsuccessful or of limited success. Physical wreckage is usually minimal due to the age of many wrecks, the unpredictable weather and sea conditions, and the extensive damage often suffered by vessels at the time they were wrecked.
The term is believed to have originated from the earliest days of the maritime fur trade
The maritime fur trade was a ship-based fur trade system that focused on acquiring furs of sea otters and other animals from the indigenous peoples of the Pacific Northwest Coast and natives of Alaska. The furs were mostly sold in China in ex ...
. It reflects not only the danger of shipwrecks but also the state of open or near-warfare in the area between Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a List of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia, Northern Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the ...
, Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = ''Plus ultra'' (Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, i ...
, Great Britain
Great Britain is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean off the northwest coast of continental Europe. With an area of , it is the largest of the British Isles, the largest European island and the ninth-largest island in the world. It is ...
, and native tribal peoples.
See also
*Graveyard of the Atlantic
Graveyard of the Atlantic is a nickname for the treacherous waters and area of numerous shipwrecks off the Outer Banks of North Carolina, United States, which are due to the coast's shifting sands and inlets. To a lesser degree, this nickname has ...
* Lightship ''Columbia''
* ''New Carissa
MV ''New Carissa'' was a freighter that ran aground on a beach near Coos Bay, Oregon, United States during a storm in February 1999 and broke apart. An attempt to tow the bow section of the ship out to sea failed when the tow line broke, ...
''
* ''Peter Iredale
''Peter Iredale'' was a four-masted steel barque sailing vessel that ran ashore October 25, 1906, on the Oregon coast en route to the Columbia River. She was abandoned on Clatsop Spit near Fort Stevens in Warrenton about four miles (6 km) s ...
''
* Puget Sound Mosquito Fleet
* Steamboats of the Oregon Coast
* List of Oregon shipwrecks
* Inside Passage
The Inside Passage (french: Passage Intérieur) is a coastal route for ships and boats along a network of passages which weave through the islands on the Pacific Northwest coast of the North American Fjordland. The route extends from southeaster ...
* Ripple Rock
Ripple Rock (french: Roche Ripple) is an underwater mountain located in the Seymour Narrows of the Discovery Passage in British Columbia, Canada. It had two peaks (2.74 metres and 6.4 metres below the surface at low tide) that produced large, d ...
* SS ''Pacific''
* SS ''Valencia''
* ''Sechelt''
* ''Clallam''
*West Coast Trail
The West Coast Trail, originally called the Dominion Lifesaving Trail, is a backpacking trail following the southwestern edge of Vancouver Island in British Columbia, Canada. It was built in 1907 to facilitate the rescue of shipwrecked survivor ...
, built in 1907 to facilitate the rescue of shipwrecked survivors along the coast
Sources
*''First Approaches to the Northwest Coast'', Derek Pethick *''A Historicall Atlas of British Columbia and the Pacific Northwest'', Derek HayesReferences
{{DEFAULTSORT:Graveyard Of The Pacific Geography of Vancouver Island Geography of Oregon Geography of Washington (state) Maritime history of Washington (state) Shipwrecks in the Pacific Ocean Ship graveyards