Golden House Of Nero on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Domus Aurea (
 When a young Roman inadvertently fell through a cleft in the Esquiline hillside at the end of the 15th century, he found himself in a strange cave or
When a young Roman inadvertently fell through a cleft in the Esquiline hillside at the end of the 15th century, he found himself in a strange cave or
Great Buildings on-line:
Domus Aurea * Virtual reconstruction in 3D of th
Domus Aurea
{{DEFAULTSORT:Domus Aurea 68 Houses completed in the 1st century Julio-Claudian dynasty Ancient palaces in Rome Nero Rome R. I Monti National museums of Italy Demolished buildings and structures in Rome
Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the ...
, "Golden House") was a vast landscaped complex built by the Emperor
An emperor (from la, imperator, via fro, empereor) is a monarch, and usually the sovereignty, sovereign ruler of an empire or another type of imperial realm. Empress, the female equivalent, may indicate an emperor's wife (empress consort), ...
Nero
Nero Claudius Caesar Augustus Germanicus ( ; born Lucius Domitius Ahenobarbus; 15 December AD 37 – 9 June AD 68), was the fifth Roman emperor and final emperor of the Julio-Claudian dynasty, reigning from AD 54 un ...
largely on the Oppian Hill
The Oppian Hill (Latin, ''Oppius Mons''; it, Colle Oppio) is the southern spur of the Esquiline Hill, one of the Seven hills of Rome, Italy. It is separated from the Cispius on the north by the valley of the Suburra, and from the Caelian Hill ...
in the heart of ancient Rome
In modern historiography, ancient Rome refers to Roman civilisation from the founding of the city of Rome in the 8th century BC to the collapse of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th century AD. It encompasses the Roman Kingdom (753–509 B ...
after the great fire in 64 AD had destroyed a large part of the city.Roth (1993)
It replaced and extended his Domus Transitoria
The Domus Transitoria was Roman emperor Nero's (r. 54 – 68) first palace damaged or destroyed by the Great Fire of Rome in 64 AD, and then extended by his Domus Aurea (or Golden House). History
The palace was intended to connect all of the imp ...
that he had built as his first palace complex on the site.
History
The Domus Aurea was probably never completed. Otho and possiblyTitus
Titus Caesar Vespasianus ( ; 30 December 39 – 13 September 81 AD) was Roman emperor from 79 to 81. A member of the Flavian dynasty, Titus succeeded his father Vespasian upon his death.
Before becoming emperor, Titus gained renown as a mili ...
allotted money to finish at least the structure on the Oppian Hill; this continued to be inhabited, notably by emperor Vitellius in 69 but only after falling ill, until it was destroyed in a fire under Trajan in 104.
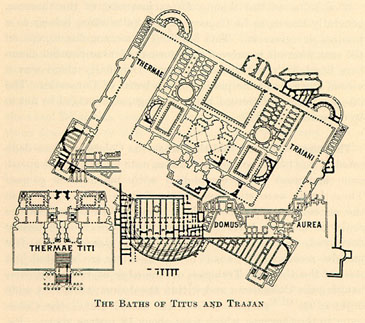
A symbol of decadence that caused severe embarrassment to Nero's successors, the Domus Aurea was stripped of its marble, jewels, and ivory within a decade. Although the Oppian villa continued to be inhabited for some years, soon after Nero's death other parts of the palace and grounds, encompassing 2.6 km2 (c. 1 mi2), were filled with earth and built over: the Baths of Titus
The Baths of Titus or ''Thermae Titi'' were public baths (''Thermae'') built in 81 AD at Rome, by Roman emperor Titus.
The baths sat at the base of the Esquiline Hill, an area of parkland and luxury estates which had been taken over by Nero (AD 5 ...
were already being built on part of the site, probably the private baths, in 79 AD. On the site of the lake, in the middle of the palace grounds, Vespasian
Vespasian (; la, Vespasianus ; 17 November AD 9 – 23/24 June 79) was a Roman emperor who reigned from AD 69 to 79. The fourth and last emperor who reigned in the Year of the Four Emperors, he founded the Flavian dynasty that ruled the Empi ...
built the Flavian Amphitheatre, which could be flooded at will, with the Colossus of Nero beside it. The Baths of Trajan, and the Temple of Venus and Roma
The Temple of Venus and Roma (Latin: ''Templum Veneris et Romae'') is thought to have been the largest temple in Ancient Rome. Located on the Velian Hill, between the eastern edge of the Forum Romanum and the Colosseum, in Rome, it was dedicated ...
were also built on the site. Within 40 years, the palace was obliterated. Paradoxically, this ensured the wall paintings' survival by protecting them from moisture.
Rediscovery
 When a young Roman inadvertently fell through a cleft in the Esquiline hillside at the end of the 15th century, he found himself in a strange cave or
When a young Roman inadvertently fell through a cleft in the Esquiline hillside at the end of the 15th century, he found himself in a strange cave or grotto
A grotto is a natural or artificial cave used by humans in both modern times and antiquity, and historically or prehistorically. Naturally occurring grottoes are often small caves near water that are usually flooded or often flooded at high ti ...
filled with painted figures. Soon the young artists of Rome were having themselves let down on boards knotted to ropes to see for themselves. The Fourth Style frescoes that were uncovered then have faded now, but the effect of these freshly rediscovered grotesque decorations ( it, grotteschi) was electrifying in the early Renaissance
The Renaissance ( , ) , from , with the same meanings. is a period in European history marking the transition from the Middle Ages to modernity and covering the 15th and 16th centuries, characterized by an effort to revive and surpass ideas ...
, which was just arriving in Rome.
When Raphael
Raffaello Sanzio da Urbino, better known as Raphael (; or ; March 28 or April 6, 1483April 6, 1520), was an Italian painter and architect of the High Renaissance. List of works by Raphael, His work is admired for its clarity of form, ease of ...
and Michelangelo
Michelangelo di Lodovico Buonarroti Simoni (; 6 March 1475 – 18 February 1564), known as Michelangelo (), was an Italian sculptor, painter, architect, and poet of the High Renaissance. Born in the Republic of Florence, his work was insp ...
crawled underground and were let down shafts to study them, the paintings were a revelation of the true world of antiquity. Beside the graffiti signatures of later tourists, like Casanova
Giacomo Girolamo Casanova (, ; 2 April 1725 – 4 June 1798) was an Italian adventurer and author from the Republic of Venice. His autobiography, (''Story of My Life''), is regarded as one of the most authentic sources of information about the c ...
and the Marquis de Sade
Donatien Alphonse François, Marquis de Sade (; 2 June 1740 – 2 December 1814), was a French nobleman, revolutionary politician, philosopher and writer famous for his literary depictions of a libertine sexuality as well as numerous accusat ...
scratched into a fresco inches apart (''British Archaeology'' June 1999), are the autographs of Domenico Ghirlandaio
Domenico di Tommaso Curradi di Doffo Bigordi (, , ; 2 June 1448 – 11 January 1494), professionally known as Domenico Ghirlandaio, also spelled as Ghirlandajo, was an Italian Renaissance painter born in Florence. Ghirlandaio was part of ...
, Martin van Heemskerck
Maarten van Heemskerck or ''Marten Jacobsz Heemskerk van Veen'' (1 June 1498 - 1 October 1574) was a Dutch portrait and religious painter, who spent most of his career in Haarlem. He was a pupil of Jan van Scorel, and adopted his teacher's Ital ...
, and Filippino Lippi
Filippino Lippi (April 1457 – 18 April 1504) was an Italian painter working in Florence, Italy during the later years of the Early Renaissance and first few years of the High Renaissance.
Biography
Filippino Lippi was born in Prato, Tusc ...
.
It was even claimed that various classical artworks found at this time, such as the '' Laocoön and His Sons'' and '' Venus Callipyge'', were found within or near the Domus's remains, though this is now accepted as unlikely (high quality artworks would have been removed to the Temple of Peace before the Domus was covered over with earth).
The frescoes' effect on Renaissance artists was instant and profound (it can be seen most obviously in Raphael's decoration for the loggias in the Vatican), and the white walls, delicate swags, and bands of frieze—framed reserves containing figures or landscapes—have returned at intervals ever since, notably in late 18th century Neoclassicism
Neoclassicism (also spelled Neo-classicism) was a Western cultural movement in the decorative and visual arts, literature, theatre, music, and architecture that drew inspiration from the art and culture of classical antiquity. Neoclassicism was ...
, making Famulus one of the most influential painters in the history of art.
20th century to present
Discovery of the pavilion led to the arrival of moisture starting the slow, inevitable process of decay;humidity
Humidity is the concentration of water vapor present in the air. Water vapor, the gaseous state of water, is generally invisible to the human eye. Humidity indicates the likelihood for precipitation, dew, or fog to be present.
Humidity depe ...
sometimes reaches 90% inside the Domus. Heavy rain was blamed for the collapse of a chunk of ceiling.Romey (see sources) The presence of trees in the park above is causing further damage, as tree roots are slowly sinking into the walls, damaging the ceiling and frescoes; chemical compounds released from these roots are provoking additional deterioration. Many of these trees cannot be uprooted without damaging the Domus.
The sheer weight of earth on the Domus is causing a problem, as well, and architects believe that the ceiling will eventually collapse if the weight of between 2,500 and 3,000 kg/m2 is not lessened. A pilot project is in the works to replace the current park above the Domus, enlarged during Mussolini
Benito Amilcare Andrea Mussolini (; 29 July 188328 April 1945) was an Italian politician and journalist who founded and led the National Fascist Party. He was Prime Minister of Italy from the March on Rome in 1922 until his deposition in 194 ...
's regime, with a lighter roof garden planted with the type of flowers described by Pliny, Columella, and other ancient writers.
Increasing concerns about the condition of the building and the safety of visitors resulted in its closing at the end of 2005 for further restoration work. The complex was partially reopened on February 6, 2007, but closed on March 25, 2008 because of safety concerns.
On March 30, 2010, of the vault of a gallery collapsed.
See also
*Ancient Roman architecture
Ancient Roman architecture adopted the external language of classical Greek architecture for the purposes of the ancient Romans, but was different from Greek buildings, becoming a new architectural style. The two styles are often considered one ...
*List of ancient monuments in Rome
This is a list of ancient monuments from Republican and Imperial periods in the city of Rome, Italy.
Amphitheaters
* Amphitheater of Caligula
* Amphitheatrum Castrense
* Amphitheater of Nero
* Amphitheater of Statilius Taurus
* Colosseum
Bath ...
Notes
Sources
* * * * * * * Pliny, C. Secundus (c. 77). ''Natural History''. * * * Spartianus, Aelius (117-284). ''Historia Augusta: The Life of Hadrian''. *External links
Great Buildings on-line:
Domus Aurea * Virtual reconstruction in 3D of th
Domus Aurea
{{DEFAULTSORT:Domus Aurea 68 Houses completed in the 1st century Julio-Claudian dynasty Ancient palaces in Rome Nero Rome R. I Monti National museums of Italy Demolished buildings and structures in Rome