Glycosyltransferases on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Glycosyltransferases (GTFs, Gtfs) are
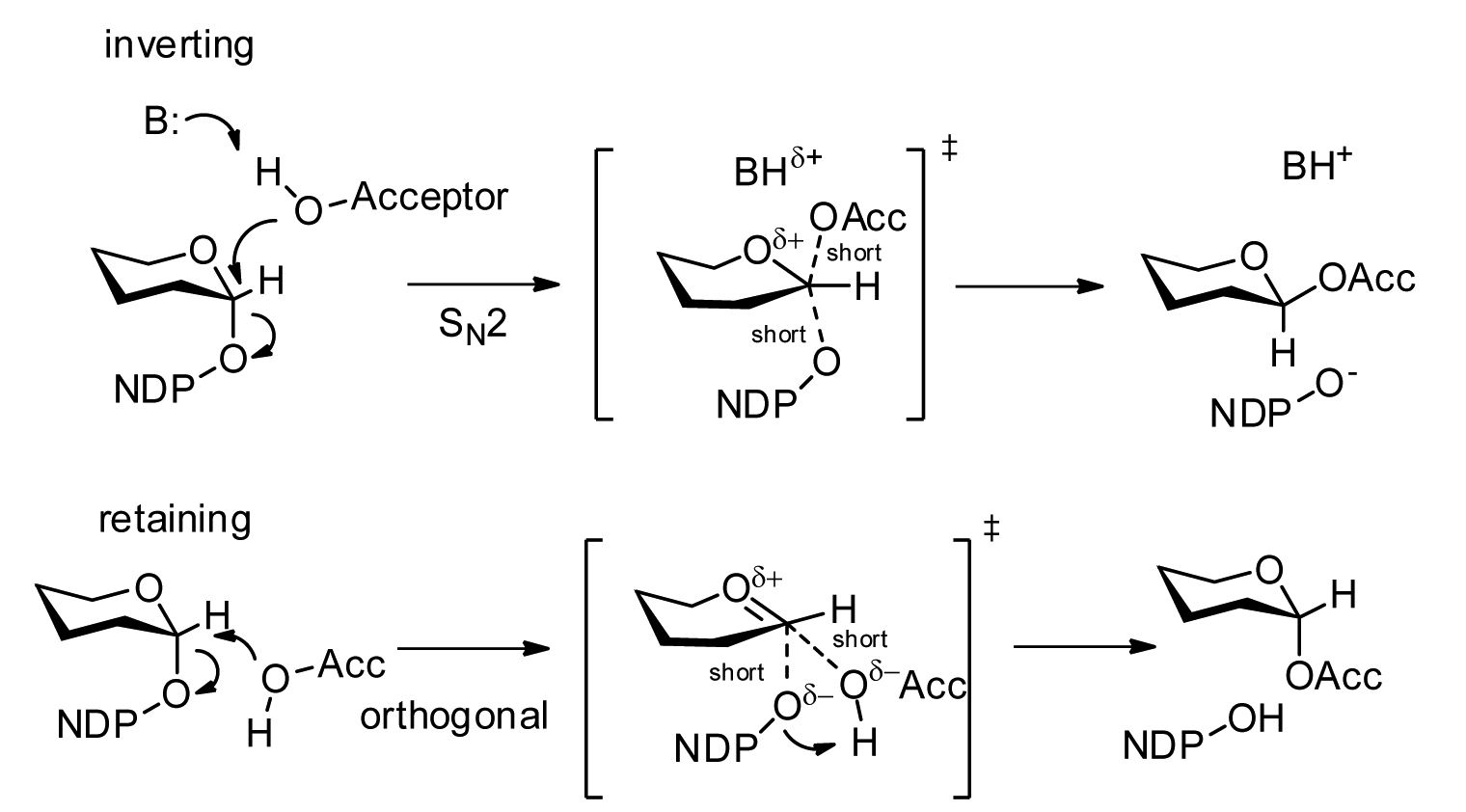 Glycosyltransferases can be segregated into "retaining" or "inverting" enzymes according to whether the stereochemistry of the donor's anomeric bond is retained (α→α) or inverted (α→β) during the transfer. The inverting mechanism is straightforward, requiring a single nucleophilic attack from the accepting atom to invert stereochemistry.
The retaining mechanism has been a matter of debate, but there exists strong evidence against a double displacement mechanism (which would cause two inversions about the anomeric carbon for a net retention of stereochemistry) or a dissociative mechanism (a prevalent variant of which was known as SNi). An "orthogonal associative" mechanism has been proposed which, akin to the inverting enzymes, requires only a single nucleophilic attack from an acceptor from a non-linear angle (as observed in many crystal structures) to achieve anomer retention.
Glycosyltransferases can be segregated into "retaining" or "inverting" enzymes according to whether the stereochemistry of the donor's anomeric bond is retained (α→α) or inverted (α→β) during the transfer. The inverting mechanism is straightforward, requiring a single nucleophilic attack from the accepting atom to invert stereochemistry.
The retaining mechanism has been a matter of debate, but there exists strong evidence against a double displacement mechanism (which would cause two inversions about the anomeric carbon for a net retention of stereochemistry) or a dissociative mechanism (a prevalent variant of which was known as SNi). An "orthogonal associative" mechanism has been proposed which, akin to the inverting enzymes, requires only a single nucleophilic attack from an acceptor from a non-linear angle (as observed in many crystal structures) to achieve anomer retention.
enzyme
Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrate (chemistry), substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecule ...
s (EC 2.4
This list contains a list of EC numbers for the second group, EC 2, transferases, placed in numerical order as determined by the Nomenclature Committee of the International Union of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology. All official information is ...
) that establish natural glycosidic linkages. They catalyze
Catalysis () is the process of increasing the rate of a chemical reaction by adding a substance known as a catalyst (). Catalysts are not consumed in the reaction and remain unchanged after it. If the reaction is rapid and the catalyst recyc ...
the transfer of saccharide
In organic chemistry, a carbohydrate () is a biomolecule consisting of carbon (C), hydrogen (H) and oxygen (O) atoms, usually with a hydrogen–oxygen atom ratio of 2:1 (as in water) and thus with the empirical formula (where ''m'' may or m ...
moieties from an activated nucleotide sugar Nucleotide sugars are the activated forms of monosaccharides. Nucleotide sugars act as glycosyl donors in glycosylation reactions. Those reactions are catalyzed by a group of enzymes called glycosyltransferases.
History
The anabolism of oligosacch ...
(also known as the " glycosyl donor") to a nucleophilic
In chemistry, a nucleophile is a chemical species that forms bonds by donating an electron pair. All molecules and ions with a free pair of electrons or at least one pi bond can act as nucleophiles. Because nucleophiles donate electrons, they a ...
glycosyl acceptor molecule, the nucleophile of which can be oxygen
Oxygen is the chemical element with the symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group in the periodic table, a highly reactive nonmetal, and an oxidizing agent that readily forms oxides with most elements as we ...
- carbon
Carbon () is a chemical element with the symbol C and atomic number 6. It is nonmetallic and tetravalent—its atom making four electrons available to form covalent chemical bonds. It belongs to group 14 of the periodic table. Carbon makes ...
-, nitrogen
Nitrogen is the chemical element with the symbol N and atomic number 7. Nitrogen is a nonmetal and the lightest member of group 15 of the periodic table, often called the pnictogens. It is a common element in the universe, estimated at seve ...
-, or sulfur
Sulfur (or sulphur in British English) is a chemical element with the symbol S and atomic number 16. It is abundant, multivalent and nonmetallic. Under normal conditions, sulfur atoms form cyclic octatomic molecules with a chemical formul ...
-based.
The result of glycosyl transfer can be a carbohydrate
In organic chemistry, a carbohydrate () is a biomolecule consisting of carbon (C), hydrogen (H) and oxygen (O) atoms, usually with a hydrogen–oxygen atom ratio of 2:1 (as in water) and thus with the empirical formula (where ''m'' may or ...
, glycoside
In chemistry, a glycoside is a molecule in which a sugar is bound to another functional group via a glycosidic bond. Glycosides play numerous important roles in living organisms. Many plants store chemicals in the form of inactive glycoside ...
, oligosaccharide
An oligosaccharide (/ˌɑlɪgoʊˈsækəˌɹaɪd/; from the Greek ὀλίγος ''olígos'', "a few", and σάκχαρ ''sácchar'', "sugar") is a saccharide polymer containing a small number (typically two to ten) of monosaccharides (simple sug ...
, or a polysaccharide
Polysaccharides (), or polycarbohydrates, are the most abundant carbohydrates found in food. They are long chain polymeric carbohydrates composed of monosaccharide units bound together by glycosidic linkages. This carbohydrate can react with ...
. Some glycosyltransferases catalyse transfer to inorganic phosphate or water
Water (chemical formula ) is an inorganic, transparent, tasteless, odorless, and nearly colorless chemical substance, which is the main constituent of Earth's hydrosphere and the fluids of all known living organisms (in which it acts as ...
. Glycosyl transfer can also occur to protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, respon ...
residues, usually to tyrosine
-Tyrosine or tyrosine (symbol Tyr or Y) or 4-hydroxyphenylalanine is one of the 20 standard amino acids that are used by cells to synthesize proteins. It is a non-essential amino acid with a polar side group. The word "tyrosine" is from the Gr ...
, serine
Serine (symbol Ser or S) is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an α- amino group (which is in the protonated − form under biological conditions), a carboxyl group (which is in the deprotonated − for ...
, or threonine
Threonine (symbol Thr or T) is an amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an α-amino group (which is in the protonated −NH form under biological conditions), a carboxyl group (which is in the deprotonated −COO ...
to give O-linked glycoprotein
Glycoproteins are proteins which contain oligosaccharide chains covalently attached to amino acid side-chains. The carbohydrate is attached to the protein in a cotranslational or posttranslational modification. This process is known as g ...
s, or to asparagine
Asparagine (symbol Asn or N) is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an α-amino group (which is in the protonated −NH form under biological conditions), an α-carboxylic acid group (which is in the depro ...
to give N-linked glycoproteins. Mannosyl groups may be transferred to tryptophan
Tryptophan (symbol Trp or W)
is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. Tryptophan contains an α-amino group, an α-carboxylic acid group, and a side chain indole, making it a polar molecule with a non-polar aromati ...
to generate C-mannosyl tryptophan, which is relatively abundant in eukaryotes. Transferases may also use lipids
Lipids are a broad group of naturally-occurring molecules which includes fats, waxes, sterols, fat-soluble vitamins (such as vitamins A, D, E and K), monoglycerides, diglycerides, phospholipids, and others. The functions of lipids includ ...
as an acceptor, forming glycolipids
Glycolipids are lipids with a carbohydrate attached by a glycosidic (covalent) bond. Their role is to maintain the stability of the cell membrane and to facilitate cellular recognition, which is crucial to the immune response and in the conne ...
, and even use lipid-linked sugar phosphate donors, such as dolichol
Dolichol refers to any of a group of long-chain mostly unsaturated organic compounds that are made up of varying numbers of isoprene units terminating in an α-saturated isoprenoid group, containing an alcohol functional group.
Functions
Dolicho ...
phosphates in eukaryotic organism, or undecaprenyl phosphate
Undecaprenyl phosphate (UP), also known lipid-P, bactoprenol and C55-P., is a molecule with the primary function of trafficking polysaccharides across the cell membrane, largely contributing to the overall structure of the cell wall in Gram-posit ...
in bacteria.
Glycosyltransferases that use sugar nucleotide donors are Leloir enzymes, after Luis F. Leloir, the scientist who discovered the first sugar nucleotide and who received the 1970 Nobel Prize in Chemistry
)
, image = Nobel Prize.png
, alt = A golden medallion with an embossed image of a bearded man facing left in profile. To the left of the man is the text "ALFR•" then "NOBEL", and on the right, the text (smaller) "NAT•" then "M ...
for his work on carbohydrate metabolism. Glycosyltransferases that use non-nucleotide donors such as dolichol
Dolichol refers to any of a group of long-chain mostly unsaturated organic compounds that are made up of varying numbers of isoprene units terminating in an α-saturated isoprenoid group, containing an alcohol functional group.
Functions
Dolicho ...
or polyprenol pyrophosphate
In chemistry, pyrophosphates are phosphorus oxyanions that contain two phosphorus atoms in a P–O–P linkage. A number of pyrophosphate salts exist, such as disodium pyrophosphate (Na2H2P2O7) and tetrasodium pyrophosphate (Na4P2O7), among o ...
are non-Leloir glycosyltransferases.
Mammals use only 9 sugar nucleotide donors for glycosyltransferases: UDP-glucose
Uridine diphosphate glucose (uracil-diphosphate glucose, UDP-glucose) is a nucleotide sugar. It is involved in glycosyltransferase reactions in metabolism.
Functions
UDP-glucose is used in nucleotide sugar metabolism as an activated form of g ...
, UDP-galactose, UDP-GlcNAc
Uridine diphosphate ''N''-acetylglucosamine or UDP-GlcNAc is a nucleotide sugar and a coenzyme in metabolism. It is used by glycosyltransferases to transfer ''N''-acetylglucosamine residues to substrates. D-Glucosamine is made naturally in the f ...
, UDP-GalNAc, UDP-xylose, UDP-glucuronic acid
UDP-glucuronic acid is a sugar used in the creation of polysaccharides and is an intermediate in the biosynthesis of ascorbic acid (except in primates and guinea pigs).
It is made from UDP-glucose by UDP-glucose 6-dehydrogenase (EC 1.1.1.22) usi ...
, GDP-mannose, GDP-fucose, and CMP-sialic acid. The phosphate(s) of these donor molecules are usually coordinated by divalent cations such as manganese, however metal independent enzymes exist.
Many glycosyltransferases are single-pass transmembrane proteins, and they are usually anchored to membranes of Golgi apparatus
The Golgi apparatus (), also known as the Golgi complex, Golgi body, or simply the Golgi, is an organelle found in most eukaryotic cells. Part of the endomembrane system in the cytoplasm, it packages proteins into membrane-bound vesicles ...
Mechanism
 Glycosyltransferases can be segregated into "retaining" or "inverting" enzymes according to whether the stereochemistry of the donor's anomeric bond is retained (α→α) or inverted (α→β) during the transfer. The inverting mechanism is straightforward, requiring a single nucleophilic attack from the accepting atom to invert stereochemistry.
The retaining mechanism has been a matter of debate, but there exists strong evidence against a double displacement mechanism (which would cause two inversions about the anomeric carbon for a net retention of stereochemistry) or a dissociative mechanism (a prevalent variant of which was known as SNi). An "orthogonal associative" mechanism has been proposed which, akin to the inverting enzymes, requires only a single nucleophilic attack from an acceptor from a non-linear angle (as observed in many crystal structures) to achieve anomer retention.
Glycosyltransferases can be segregated into "retaining" or "inverting" enzymes according to whether the stereochemistry of the donor's anomeric bond is retained (α→α) or inverted (α→β) during the transfer. The inverting mechanism is straightforward, requiring a single nucleophilic attack from the accepting atom to invert stereochemistry.
The retaining mechanism has been a matter of debate, but there exists strong evidence against a double displacement mechanism (which would cause two inversions about the anomeric carbon for a net retention of stereochemistry) or a dissociative mechanism (a prevalent variant of which was known as SNi). An "orthogonal associative" mechanism has been proposed which, akin to the inverting enzymes, requires only a single nucleophilic attack from an acceptor from a non-linear angle (as observed in many crystal structures) to achieve anomer retention.
Reaction reversibility
The recent discovery of the reversibility of many reactions catalyzed by inverting glycosyltransferases served as a paradigm shift in the field and raises questions regarding the designation of sugar nucleotides as 'activated' donors.Classification by sequence
Sequence-based classification methods have proven to be a powerful way of generating hypotheses for protein function based on sequence alignment to related proteins. The carbohydrate-active enzyme database presents a sequence-based classification of glycosyltransferases into over 90 families. The same three-dimensional fold is expected to occur within each of the families.Structure
In contrast to the diversity of 3D structures observed forglycoside hydrolase
Glycoside hydrolases (also called glycosidases or glycosyl hydrolases) catalyze the hydrolysis of glycosidic bonds in complex sugars. They are extremely common enzymes with roles in nature including degradation of biomass such as cellulose (cel ...
s, glycosyltransferase have a much smaller range of structures. In fact, according to the Structural Classification of Proteins
The Structural Classification of Proteins (SCOP) database is a largely manual classification of protein structural domains based on similarities of their structures and amino acid sequences. A motivation for this classification is to determine ...
database, only three different folds have been observed for glycosyltransferases Very recently, a new glycosyltransferase fold was identified for the glycosyltransferases involved in the biosynthesis of the NAG-NAM polymer backbone of peptidoglycan
Peptidoglycan or murein is a unique large macromolecule, a polysaccharide, consisting of sugars and amino acids that forms a mesh-like peptidoglycan layer outside the plasma membrane, the rigid Cell wall#Bacterial_cell_walls, cell wall (murein sac ...
.
Inhibitors
Many inhibitors of glycosyltransferases are known. Some of these are natural products, such as moenomycin, an inhibitor of peptidoglycan glycosyltransferases, the nikkomycins, inhibitors of chitin synthase, and the echinocandins, inhibitors of fungalβ-1,3-glucan synthase
1,3-Beta-glucan synthase is a glucosyltransferase enzyme involved in the generation of beta-glucan in fungi. It serves as a pharmacological target for antifungal drugs such as caspofungin, anidulafungin, and micafungin, deemed 1,3-Beta-gluc ...
s. Some glycosyltransferase inhibitors are of use as drugs or antibiotics. Moenomycin is used in animal feed as a growth promoter. Caspofungin
Caspofungin ( INN) (brand name Cancidas) is a lipopeptide antifungal drug from Merck & Co., Inc. discovered by James Balkovec, Regina Black and Frances A. Bouffard. It is a member of a new class of antifungals termed the echinocandins. It wor ...
has been developed from the echinocandins and is in use as an antifungal agent. Ethambutol
Ethambutol (EMB, E) is a medication primarily used to treat tuberculosis. It is usually given in combination with other tuberculosis medications, such as isoniazid, rifampicin and pyrazinamide. It may also be used to treat ''Mycobacterium av ...
is an inhibitor of mycobacterial arabinotransferases and is used for the treatment of tuberculosis. Lufenuron
Lufenuron is the active ingredient in the veterinary flea control medication Program, and one of the two active ingredients in the flea, heartworm, ringworm and anthelmintic medicine milbemycin oxime/lufenuron (Sentinel).
Lufenuron is stored in ...
is an inhibitor of insect chitin syntheses and is used to control fleas in animals. Imidazolium
Imidazole (ImH) is an organic compound with the formula C3N2H4. It is a white or colourless solid that is soluble in water, producing a mildly alkaline solution. In chemistry, it is an aromatic heterocycle, classified as a diazole, and has non- ...
-based synthetic inhibitors of glycosyltransferases have been designed for use as antimicrobial and antiseptic agents.
Determinant of blood type
TheABO blood group system
The ABO blood group system is used to denote the presence of one, both, or neither of the A and B antigens on erythrocytes. For human blood transfusions, it is the most important of the 43 different blood type (or group) classification syste ...
is determined by what type of glycosyltransferases are expressed in the body.
The ABO gene locus expressing the glycosyltransferases has three main allelic forms: A, B, and O. The A allele encodes 1-3-N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase that bonds α- N-acetylgalactosamine to D-galactose end of H antigen, producing the A antigen. The B allele encodes 1-3-galactosyltransferase that joins α-D-galactose bonded to D-galactose end of H antigen, creating the B antigen. In case of O allele the exon 6 contains a deletion that results in a loss of enzymatic activity. The O allele differs slightly from the A allele by deletion of a single nucleotide - Guanine
Guanine () (symbol G or Gua) is one of the four main nucleobases found in the nucleic acids DNA and RNA, the others being adenine, cytosine, and thymine ( uracil in RNA). In DNA, guanine is paired with cytosine. The guanine nucleoside is c ...
at position 261. The deletion causes a frameshift
Ribosomal frameshifting, also known as translational frameshifting or translational recoding, is a biological phenomenon that occurs during translation that results in the production of multiple, unique proteins from a single mRNA. The process c ...
and results in translation of an almost entirely different protein that lacks enzymatic activity. This results in H antigen remaining unchanged in case of O groups.
The combination of glycosyltransferases by both alleles present in each person determines whether there is an AB, A, B or O blood type.
Uses
Glycosyltransferases have been widely used in both the targeted synthesis of specific glycoconjugates as well as the synthesis of differentially glycosylated libraries of drugs, biological probes or natural products in the context ofdrug discovery
In the fields of medicine, biotechnology and pharmacology, drug discovery is the process by which new candidate medications are discovered.
Historically, drugs were discovered by identifying the active ingredient from traditional remedies or by ...
and drug development
Drug development is the process of bringing a new pharmaceutical drug to the market once a lead compound has been identified through the process of drug discovery. It includes preclinical research on microorganisms and animals, filing for r ...
(a process known as glycorandomization). Suitable enzymes can be isolated from natural sources or produced recombinantly. As an alternative, whole cell-based systems using either endogenous glycosyl donors or cell-based systems containing cloned and expressed systems for synthesis of glycosyl donors have been developed. In cell-free approaches, the large-scale application of glycosyltransferases for glycoconjugate synthesis has required access to large quantities of the glycosyl donors. On the flip-side, nucleotide recycling systems that allow the resynthesis of glycosyl donors from the released nucleotide have been developed. The nucleotide recycling approach has a further benefit of reducing the amount of nucleotide formed as a by-product, thereby reducing the amount of inhibition caused to the glycosyltransferase of interest – a commonly observed feature of the nucleotide byproduct.
See also
*Carbohydrate chemistry
Carbohydrate chemistry is a subdiscipline of chemistry primarily concerned with the detection, synthesis, structure, and function of carbohydrates. Due to the general structure of carbohydrates, their synthesis is often preoccupied with the selec ...
* Chemical glycosylation
* Glucuronosyltransferase
Uridine 5'-diphospho-glucuronosyltransferase ( UDP-glucuronosyltransferase, UGT) is a microsomal glycosyltransferase () that catalyzes the transfer of the glucuronic acid component of UDP-glucuronic acid to a small hydrophobic molecule. This is ...
* Glycogen synthase
Glycogen synthase (UDP-glucose-glycogen glucosyltransferase) is a key enzyme in glycogenesis, the conversion of glucose into glycogen. It is a glycosyltransferase () that catalyses the reaction of UDP-glucose and (1,4--D-glucosyl)n to yield UDP ...
* Glycosyl acceptor
* Glycosyl donor
* Glycosylation
Glycosylation is the reaction in which a carbohydrate (or 'glycan'), i.e. a glycosyl donor, is attached to a hydroxyl or other functional group of another molecule (a glycosyl acceptor) in order to form a glycoconjugate. In biology (but not ...
* Oligosaccharyltransferase
References
{{Portal bar, Biology, border=no Carbohydrates Carbohydrate chemistry Transferases EC 2.4 EC 2.4.1 EC 2.4.2 Peripheral membrane proteins Glycobiology