GeNMR Protocol on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 GeNMR method (GEnerate NMR structures) is the first fully automated template-based method of protein structure determination that utilizes both NMR chemical shifts and NOE -based distance restraints.
In addition to the template-based approach, the GeNMR webserver also offers an ''ab initio'' protein folding mode that starts folding from an extended structure. The GeNMR web server produces an ensemble of PDB coordinates within a period ranging from 20 minutes to 4 hours, depending on protein size, server load, quality and type of experimental information, and selected protocol options. GeNMR webserver is composed of two parts, a front-end web-interface (written in Perl and HTML) and a back-end consisting of eight different alignment, structure generation and structure optimization programs along with three local databases.
GeNMR method (GEnerate NMR structures) is the first fully automated template-based method of protein structure determination that utilizes both NMR chemical shifts and NOE -based distance restraints.
In addition to the template-based approach, the GeNMR webserver also offers an ''ab initio'' protein folding mode that starts folding from an extended structure. The GeNMR web server produces an ensemble of PDB coordinates within a period ranging from 20 minutes to 4 hours, depending on protein size, server load, quality and type of experimental information, and selected protocol options. GeNMR webserver is composed of two parts, a front-end web-interface (written in Perl and HTML) and a back-end consisting of eight different alignment, structure generation and structure optimization programs along with three local databases.
XPLORCNS
format
. The minimum sequence length is 30 residues.
Proteus2
to perform structural modeling
PREDITOR
to calculate torsion angles from chemical shifts
PPT-DB
for comparative modeling and alignment and CS23D to calculate protein structures from chemical shifts only. GeNMR also uses several well-known external programs, includin
Rosetta
for ''ab initio'' folding without NOEs an
XPLOR-NIH
for NOE-based simulated annealing and refinement. A more complete list of GeNMR sub-programs is listed on the CS23D page.
CS23D
an
Proteus2
The knowledge-based potentials include information on predicted/known secondary structure, radius of gyration, hydrogen bond energies, number of hydrogen bonds, allowed backbone and side chain torsion angles, atom contact radii (bump checks), disulfide bonding information and a modified threading energy based on th
Bryant and Lawrence potential
The chemical shift component of the GeNMR potential uses weighted correlation coefficients calculated between the observed an
SHIFTX
calculated shifts of the structure being refined.
 GeNMR method (GEnerate NMR structures) is the first fully automated template-based method of protein structure determination that utilizes both NMR chemical shifts and NOE -based distance restraints.
In addition to the template-based approach, the GeNMR webserver also offers an ''ab initio'' protein folding mode that starts folding from an extended structure. The GeNMR web server produces an ensemble of PDB coordinates within a period ranging from 20 minutes to 4 hours, depending on protein size, server load, quality and type of experimental information, and selected protocol options. GeNMR webserver is composed of two parts, a front-end web-interface (written in Perl and HTML) and a back-end consisting of eight different alignment, structure generation and structure optimization programs along with three local databases.
GeNMR method (GEnerate NMR structures) is the first fully automated template-based method of protein structure determination that utilizes both NMR chemical shifts and NOE -based distance restraints.
In addition to the template-based approach, the GeNMR webserver also offers an ''ab initio'' protein folding mode that starts folding from an extended structure. The GeNMR web server produces an ensemble of PDB coordinates within a period ranging from 20 minutes to 4 hours, depending on protein size, server load, quality and type of experimental information, and selected protocol options. GeNMR webserver is composed of two parts, a front-end web-interface (written in Perl and HTML) and a back-end consisting of eight different alignment, structure generation and structure optimization programs along with three local databases.
Input
GeNMR accepts and processes backbone and side chain 1H, 13C or 15N chemical shift data of almost any combination (HA only, HN only, HA+HN only, HA+HN+sidechain H, CA only, CA+CB only, CA+CO only, HA+CA+CB, HN+CA+CB, HN+15N only, HN,+15N+CA, HN+15N+CA+CB, etc.). This allows GeNMR to handle small peptides (where only H shifts are typically measured) to large proteins (where only N or C shifts might be available). The input files must include chemical shift data in NMR-STAR 2.1 format and distance restraints iXPLOR
format
. The minimum sequence length is 30 residues.
Output
The output for a typical GeNMR structure calculation consists of a user-defined set of lowest energy PDB coordinates in a simple, downloadable text format. In addition, details about the overall energy score (prior to and following energy minimization) and chemical shift correlations (between the observed and calculated shifts) is provided at the top of the output page. If score failed to decrease below a certain threshold, a warning is printed at the top of the page.Sub-programs
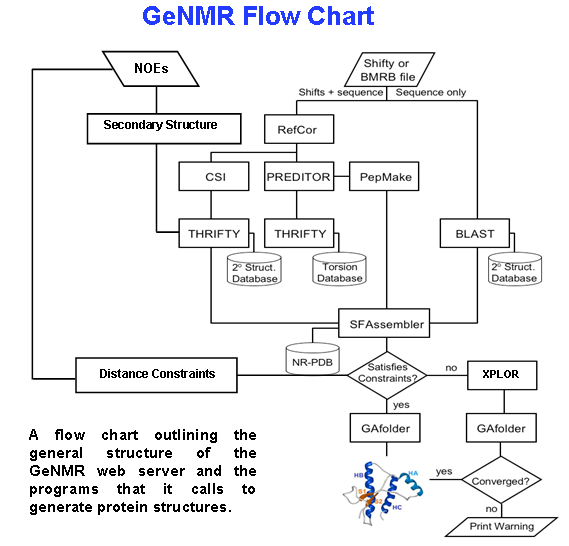
A flow chart describing the processing logic used in GeNMR is shown on the right. GeNMR makes use of a number of well-known programs and databases. These includProteus2
to perform structural modeling
PREDITOR
to calculate torsion angles from chemical shifts
PPT-DB
for comparative modeling and alignment and CS23D to calculate protein structures from chemical shifts only. GeNMR also uses several well-known external programs, includin
Rosetta
for ''ab initio'' folding without NOEs an
XPLOR-NIH
for NOE-based simulated annealing and refinement. A more complete list of GeNMR sub-programs is listed on the CS23D page.
Homology modelling
GeNMR uses homology modeling and sequence/structure threading to rapidly generate a first-pass model of the query protein. The use of homology modeling/threading in GeNMR allows a considerable speed-up in its structure calculations since homology models can often be generated and refined in a minute or two.Genetic algorithm
GeNMR also makes use of genetic algorithms to allow configurational sampling and structural refinement using non-differentiable scores, such as ShiftX chemical shift scores. GeNMR's genetic algorithm creates a population of initial structures and then uses combinations of mutations, cross-overs, segment swaps and writhe movements to comprehensively sample conformation space. The 25 lowest energy structures are then selected, duplicated and carried to the next round of conformational sampling.Scoring functions
The potential functions used in GeNMR are derived from those used iCS23D
an
Proteus2
The knowledge-based potentials include information on predicted/known secondary structure, radius of gyration, hydrogen bond energies, number of hydrogen bonds, allowed backbone and side chain torsion angles, atom contact radii (bump checks), disulfide bonding information and a modified threading energy based on th
Bryant and Lawrence potential
The chemical shift component of the GeNMR potential uses weighted correlation coefficients calculated between the observed an
SHIFTX
calculated shifts of the structure being refined.
Calculation scenarios
There are six different kinds of calculation scenarios that GeNMR can currently accommodate. These scenarios include: # chemical shift only—query has homologue in database; # chemical shift only—query has no homologue in database; # NOE only—query has homologue in database; # NOE only—query has no homologue in database; # NOE and chemical shift—query has homologue in database; # NOE and chemical shift—query has no homologue in database.See also
* Chemical Shift * NMR * Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy *Protein nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of proteins (usually abbreviated protein NMR) is a field of structural biology in which NMR spectroscopy is used to obtain information about the structure and dynamics of proteins, and also nucleic acids, and ...
* Protein dynamics#Domains and protein flexibility
* Protein
*Random Coil Index
Random coil index (RCI) predicts protein flexibility by calculating an inverse weighted average of backbone secondary chemical shifts and predicting values of model-free order parameters as well as per-residue RMSD of NMR and molecular dynamics ...
* CS23D
* Protein Chemical Shift Re-Referencing
*Protein secondary structure
Protein secondary structure is the three dimensional form of ''local segments'' of proteins. The two most common secondary structural elements are alpha helices and beta sheets, though beta turns and omega loops occur as well. Secondary structure ...
* Protein Chemical Shift Prediction
*Chemical shift index
The chemical shift index or CSI is a widely employed technique in protein nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy that can be used to display and identify the location (i.e. start and end) as well as the type of protein secondary structure (beta ...
* Protein NMR
* ShiftX
* Protein structure prediction
References
{{Reflist Chemistry software