|
CS23D
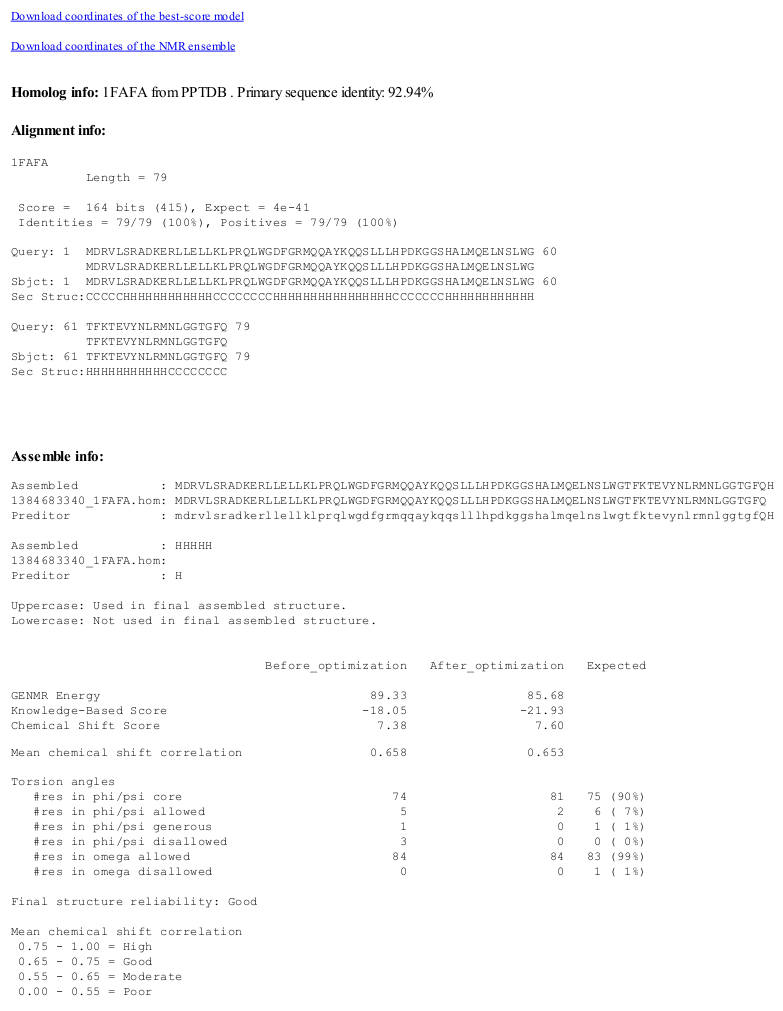
CS23D is a web server to generate 3D structural models from NMR chemical shifts. CS23D combines maximal fragment assembly with chemical shift threading, ''de novo'' structure generation, chemical shift-based torsion angle prediction, and chemical shift refinement. CS23D makes use of RefDB (chemistry), RefDB and ShiftX. CS23D input formats CS23D accepts chemical shift files in either SHIFTY or BMRB formats. CS23D options A user can # Exclude a protein from being used as the template # Ignore high-identity homologs in the list of available templates # Change the number of models in the final ensemble # Change the number of model optimization steps CS23D output CS23D output consists of a set of 10 best-score PDB coordinates. A hyperlink to the single best score structure is also provided. The overall CS23D score, knowledge-based score, chemical shift score, Ramachandran plot statistics, correlations between the observed and calculated shifts before and after refinement are displa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
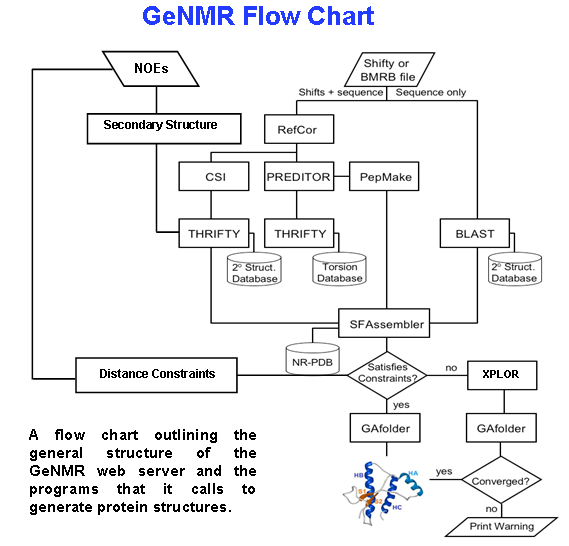
GeNMR
GeNMR method (GEnerate NMR structures) is the first fully automated template-based method of protein structure determination that utilizes both NMR chemical shifts and NOE -based distance restraints. In addition to the template-based approach, the GeNMR webserver also offers an ''ab initio'' protein folding mode that starts folding from an extended structure. The GeNMR web server produces an ensemble of PDB coordinates within a period ranging from 20 minutes to 4 hours, depending on protein size, server load, quality and type of experimental information, and selected protocol options. GeNMR webserver is composed of two parts, a front-end web-interface (written in Perl and HTML) and a back-end consisting of eight different alignment, structure generation and structure optimization programs along with three local databases. Input GeNMR accepts and processes backbone and side chain 1H, 13C or 15N chemical shift data of almost any combination (HA only, HN only, HA+HN only, HA+HN ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
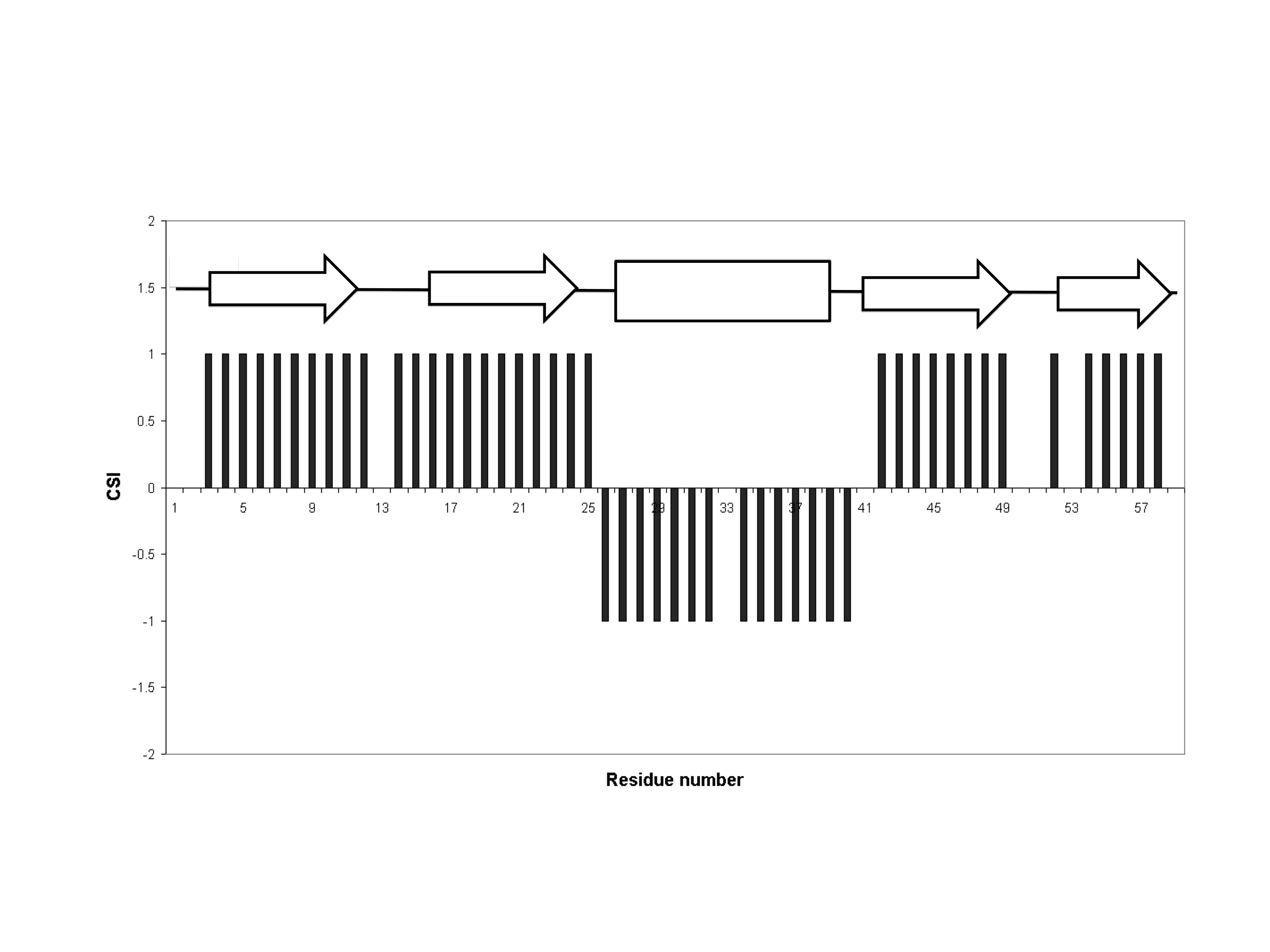
Chemical Shift Index
The chemical shift index or CSI is a widely employed technique in protein nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy that can be used to display and identify the location (i.e. start and end) as well as the type of protein secondary structure (beta strands, helices and random coil regions) found in proteins using only backbone chemical shift data The technique was invented by David S. Wishart in 1992 for analyzing 1Hα chemical shifts and then later extended by him in 1994 to incorporate 13C backbone shifts. The original CSI method makes use of the fact that 1Hα chemical shifts of amino acid residues in helices tends to be shifted upfield (i.e. towards the right side of an NMR spectrum) relative to their random coil values and downfield (i.e. towards the left side of an NMR spectrum) in beta strands. Similar kinds of upfield and downfield trends are also detectable in backbone 13C chemical shifts. Implementation The CSI is a graph-based technique that essentially employs an amino ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CS23D Output
CS, C-S, C.S., Cs, cs, or cs. may refer to: Job titles * Chief Secretary (Hong Kong) * Chief superintendent, a rank in the British and several other police forces * Company secretary, a senior position in a private sector company or public sector organisation * Culinary Specialist, a US Navy occupational rating Language * Czech language (ISO 639-1 language code) * Hungarian cs, a digraph in the Hungarian alphabet Organizations * Christian Social Party (Austria), a major conservative political party in the Cisleithania, part of Austria-Hungary, and in the First Republic of Austria * Citizens (Spanish political party), a post-nationalist political party in Spain * Congregation of the Missionaries of St. Charles, a Catholic religious congregation, also called ''Scalabrinians'' * Confederate States of America, an unrecognized confederation of secessionist North American slave states existing from 1861 to 1865 Companies * Colorado and Southern Railway, a railroad company i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Random Coil Index
Random coil index (RCI) predicts protein flexibility by calculating an inverse weighted average of backbone secondary chemical shifts and predicting values of model-free order parameters as well as per-residue RMSD of NMR and molecular dynamics ensembles from this parameter. The key advantages of this protocol over existing methods of studying protein flexibility are # it does not require prior knowledge of a protein's tertiary structure, # it is not sensitive to the protein's overall tumbling and # it does not require additional NMR measurements beyond the standard experiments for backbone assignments. The application of secondary chemical shifts to characterize protein flexibility is based on an assumption that the proximity of chemical shifts to random coil values is a manifestation of increased protein mobility, while significant differences from random coil values are an indication of a relatively rigid structure. Even though chemical shifts of rigid residues may adopt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ShiftX
ShiftX (Shifts from X-ray structures) is a freely available web server for rapidly calculating protein chemical shifts from protein X-ray (or NMR) coordinates. Protein chemical shift prediction (also known as protein chemical shift calculation) is particularly useful in verifying protein chemical shift assignments, adjusting mis-referenced chemical shifts, refining NMR protein structures (via chemical shifts) and assisting with the NMR assignment of unassigned proteins that have either had their structures (or the structures of a homologous protein) determined by X-ray or NMR methods. The ShiftX web server takes atomic coordinates ( PDB s format) of proteins as input and quickly (<1 sec) generates the chemical shifts of both backbone (1H, 13C and 15N) and side chain (1H only) atoms as output (BMRB or Shifty format). The server is optimized to work with diamagnetic proteins rather than [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein Secondary Structure
Protein secondary structure is the three dimensional form of ''local segments'' of proteins. The two most common secondary structural elements are alpha helices and beta sheets, though beta turns and omega loops occur as well. Secondary structure elements typically spontaneously form as an intermediate before the protein folds into its three dimensional tertiary structure. Secondary structure is formally defined by the pattern of hydrogen bonds between the amino hydrogen and carboxyl oxygen atoms in the peptide backbone. Secondary structure may alternatively be defined based on the regular pattern of backbone dihedral angles in a particular region of the Ramachandran plot regardless of whether it has the correct hydrogen bonds. The concept of secondary structure was first introduced by Kaj Ulrik Linderstrøm-Lang at Stanford in 1952. Other types of biopolymers such as nucleic acids also possess characteristic secondary structures. Types The most common secondary ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein Dynamics
Proteins are generally thought to adopt unique structures determined by their amino acid sequences. However, proteins are not strictly static objects, but rather populate ensembles of (sometimes similar) conformations. Transitions between these states occur on a variety of length scales (tenths of Å to nm) and time scales (ns to s), and have been linked to functionally relevant phenomena such as allosteric signaling and enzyme catalysis. The study of protein dynamics is most directly concerned with the transitions between these states, but can also involve the nature and equilibrium populations of the states themselves. These two perspectives—kinetics and thermodynamics, respectively—can be conceptually synthesized in an "energy landscape" paradigm: highly populated states and the kinetics of transitions between them can be described by the depths of energy wells and the heights of energy barriers, respectively. Local flexibility: atoms and residues Portions of protein s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, providing structure to cells and organisms, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid resid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CS23D Torsion Angle Alphabet
CS, C-S, C.S., Cs, cs, or cs. may refer to: Job titles * Chief Secretary (Hong Kong) * Chief superintendent, a rank in the British and several other police forces * Company secretary, a senior position in a private sector company or public sector organisation * Culinary Specialist, a US Navy occupational rating Language * Czech language (ISO 639-1 language code) * Hungarian cs, a digraph in the Hungarian alphabet Organizations * Christian Social Party (Austria), a major conservative political party in the Cisleithania, part of Austria-Hungary, and in the First Republic of Austria * Citizens (Spanish political party), a post-nationalist political party in Spain * Congregation of the Missionaries of St. Charles, a Catholic religious congregation, also called ''Scalabrinians'' * Confederate States of America, an unrecognized confederation of secessionist North American slave states existing from 1861 to 1865 Companies * Colorado and Southern Railway, a railroad company i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of proteins (usually abbreviated protein NMR) is a field of structural biology in which NMR spectroscopy is used to obtain information about the structure and dynamics of proteins, and also nucleic acids, and their complexes. The field was pioneered by Richard R. Ernst and Kurt Wüthrich at the ETH, and by Ad Bax, Marius Clore, Angela Gronenborn at the National Institutes of Health, NIH, and Gerhard Wagner (physicist), Gerhard Wagner at Harvard University, among others. Structure determination by NMR spectroscopy usually consists of several phases, each using a separate set of highly specialized techniques. The sample is prepared, measurements are made, interpretive approaches are applied, and a structure is calculated and validated. NMR involves the quantum-mechanical properties of the central core ("Atomic nucleus, nucleus") of the atom. These properties depend on the local molecular environment, and their measurement provides a map of how th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |