galactic quadrant on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
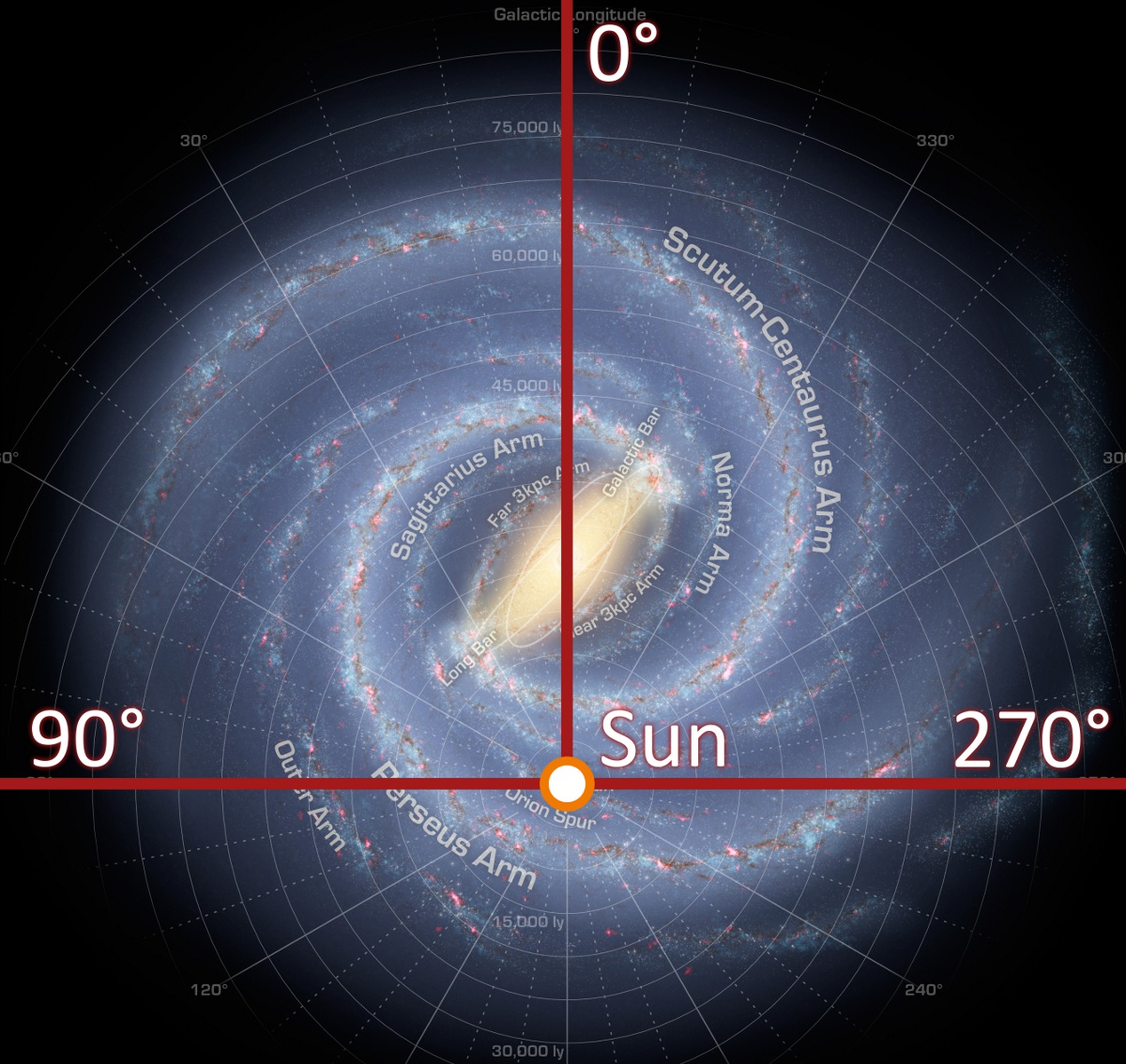 A galactic quadrant, or quadrant of the Galaxy, is one of four
A galactic quadrant, or quadrant of the Galaxy, is one of four 
An All-Sky Catalog of Faint Extreme Ultraviolet Sources
''The Astrophysical Journal Supplement Series ''. 1997 Viewing from the north galactic pole with 0

 Due to the orientation of the Earth with respect to the rest of the galaxy, the 2nd galactic quadrant is primarily only visible from the northern hemisphere while the 4th galactic quadrant is mostly only visible from the southern hemisphere. Thus, it is usually more practical for amateur stargazers to use the celestial quadrants. Nonetheless, cooperating or international astronomical organizations are not so bound by the Earth's
Due to the orientation of the Earth with respect to the rest of the galaxy, the 2nd galactic quadrant is primarily only visible from the northern hemisphere while the 4th galactic quadrant is mostly only visible from the southern hemisphere. Thus, it is usually more practical for amateur stargazers to use the celestial quadrants. Nonetheless, cooperating or international astronomical organizations are not so bound by the Earth's
Segmentum
Warhammer 40k - Lexicanum Navigation in the Milky Way is also identified with cardinal directions, indicating distance from the Sol System: for example, Ultima Segmentum, the largest segmentum in the Imperium of Man, is located to the galactic east of the Sol System. The 0° "north" in Imperial maps does not correspond to the 0° in the real-world.
Milky Way Explorer
{{DEFAULTSORT:Galactic Quadrant Astronomical coordinate systems Milky Way Orientation (geometry)
circular sector
A circular sector, also known as circle sector or disk sector (symbol: ⌔), is the portion of a disk (a closed region bounded by a circle) enclosed by two radii and an arc, where the smaller area is known as the ''minor sector'' and the large ...
s in the division of the Milky Way
The Milky Way is the galaxy that includes our Solar System, with the name describing the galaxy's appearance from Earth: a hazy band of light seen in the night sky formed from stars that cannot be individually distinguished by the naked ey ...
Galaxy.


Quadrants in the galactic coordinate system
In actual astronomical practice, the delineation of the galactic quadrants is based upon thegalactic coordinate system
The galactic coordinate system is a celestial coordinate system in spherical coordinates, with the Sun as its center, the primary direction aligned with the approximate center of the Milky Way Galaxy, and the fundamental plane parallel to an a ...
, which places the Sun as the pole of the mapping system. The Sun is used instead of the Galactic Center
The Galactic Center or Galactic Centre is the rotational center, the barycenter, of the Milky Way galaxy. Its central massive object is a supermassive black hole of about 4 million solar masses, which is called Sagittarius A*, a compact ...
for practical reasons since all astronomical observations (by human
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') are the most abundant and widespread species of primate, characterized by bipedalism and exceptional cognitive skills due to a large and complex brain. This has enabled the development of advanced tools, culture, ...
s) to date have been based on Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to harbor life. While large volumes of water can be found throughout the Solar System, only Earth sustains liquid surface water. About 71% of Earth's surf ...
or within the Solar System
The Solar System Capitalization of the name varies. The International Astronomical Union, the authoritative body regarding astronomical nomenclature, specifies capitalizing the names of all individual astronomical objects but uses mixed "Solar ...
.
Delineation
Quadrants are described using ordinals—for example, "1st galactic quadrant" "second galactic quadrant," or "third quadrant of the Galaxy."M. Lampton ''et al''An All-Sky Catalog of Faint Extreme Ultraviolet Sources
''The Astrophysical Journal Supplement Series ''. 1997 Viewing from the north galactic pole with 0
degree
Degree may refer to:
As a unit of measurement
* Degree (angle), a unit of angle measurement
** Degree of geographical latitude
** Degree of geographical longitude
* Degree symbol (°), a notation used in science, engineering, and mathemati ...
s (°) as the ray
Ray may refer to:
Fish
* Ray (fish), any cartilaginous fish of the superorder Batoidea
* Ray (fish fin anatomy), a bony or horny spine on a fin
Science and mathematics
* Ray (geometry), half of a line proceeding from an initial point
* Ray (g ...
that runs starting from the Sun and through the galactic center, the quadrants are as follows (where is galactic longitude
The galactic coordinate system is a celestial coordinate system in spherical coordinates, with the Sun as its center, the primary direction aligned with the approximate center of the Milky Way Galaxy, and the fundamental plane parallel to an a ...
):
* 1st galactic quadrant – 0° ≤ ≤ 90°
* 2nd galactic quadrant – 90° ≤ ≤ 180°
* 3rd galactic quadrant – 180° ≤ ≤ 270°
* 4th galactic quadrant – 270° ≤ ≤ 360°
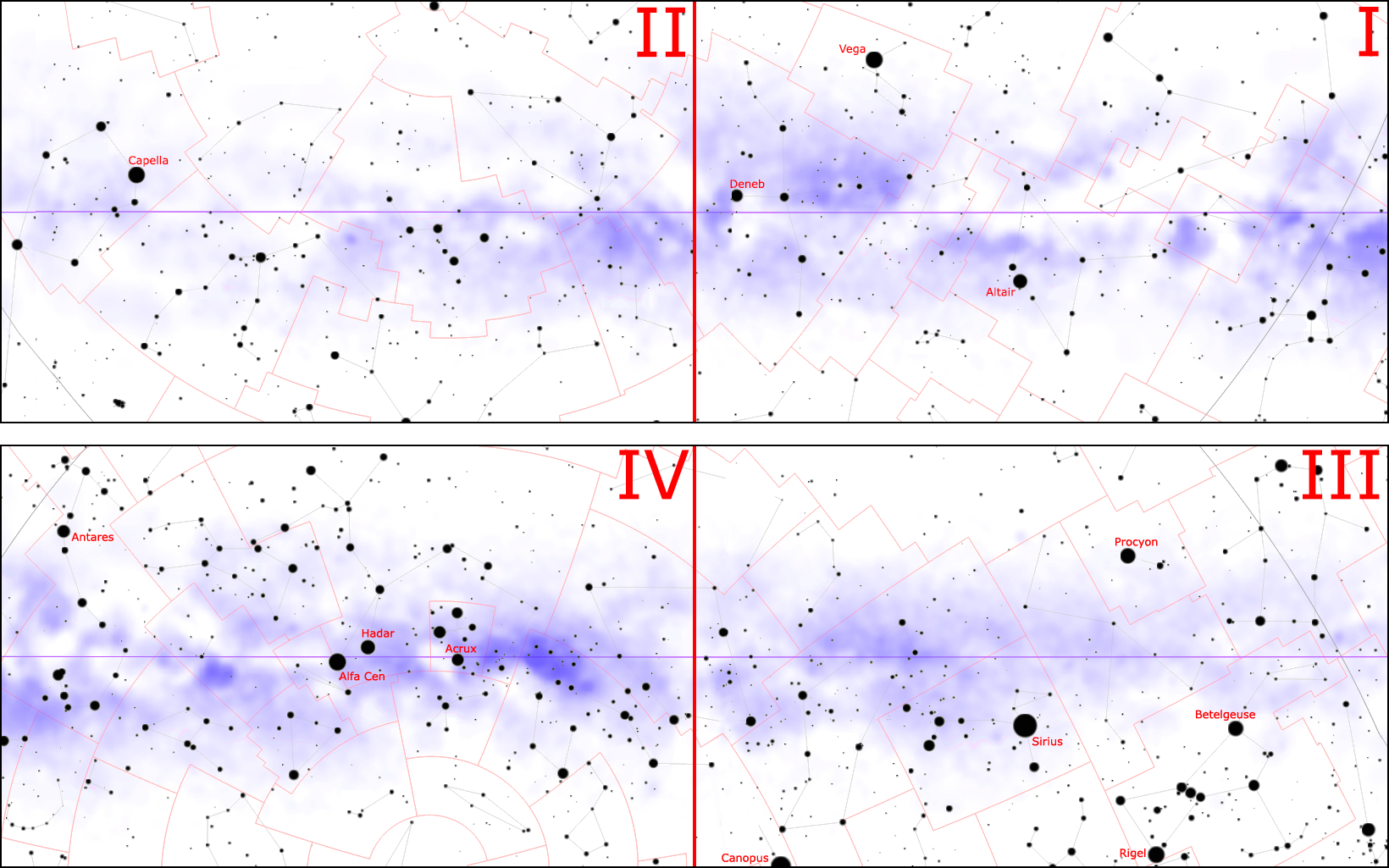
Constellations grouped by galactic quadrants

Visibility of each quadrant
 Due to the orientation of the Earth with respect to the rest of the galaxy, the 2nd galactic quadrant is primarily only visible from the northern hemisphere while the 4th galactic quadrant is mostly only visible from the southern hemisphere. Thus, it is usually more practical for amateur stargazers to use the celestial quadrants. Nonetheless, cooperating or international astronomical organizations are not so bound by the Earth's
Due to the orientation of the Earth with respect to the rest of the galaxy, the 2nd galactic quadrant is primarily only visible from the northern hemisphere while the 4th galactic quadrant is mostly only visible from the southern hemisphere. Thus, it is usually more practical for amateur stargazers to use the celestial quadrants. Nonetheless, cooperating or international astronomical organizations are not so bound by the Earth's horizon
The horizon is the apparent line that separates the surface of a celestial body from its sky when viewed from the perspective of an observer on or near the surface of the relevant body. This line divides all viewing directions based on whether ...
.
Based on a view from Earth, one may look towards major constellations for a rough sense of where the borders of the quadrants are: (Note: by drawing a line through the following, one can also approximate the galactic equator.)
* For 0°, look towards the Sagittarius
Sagittarius ( ) may refer to:
*Sagittarius (constellation)
*Sagittarius (astrology), a sign of the Zodiac
Ships
*''SuperStar Sagittarius'', a cruise ship
* USS ''Sagittarius'' (AKN-2), a World War II US Navy cargo ship
Music
*Sagittarius (ban ...
constellation. (The galactic center)
* For 90°, look towards the Cygnus constellation.
* For 180°, look towards the Auriga constellation. (The galactic anticenter)
* For 270°, look towards the Vela
Vela or Velas may refer to:
Astronomy
* Vela (constellation), a constellation in the southern sky (the Sails)
** Vela (Chinese astronomy)
** Vela Pulsar
** Vela X-1, a pulsing, eclipsing high-mass X-ray binary system
Places
* Vela Bluff, Antarc ...
constellation.
Traditional fourfold divisions of the skies
A long tradition of dividing the visible skies into four precedes the modern definitions of four galactic quadrants. Ancient Mesopotamian formulae spoke of "the four corners of the universe" and of "the heaven's four corners", and the BiblicalBook of Jeremiah
The Book of Jeremiah ( he, ספר יִרְמְיָהוּ) is the second of the Latter Prophets in the Hebrew Bible, and the second of the Prophets in the Christian Old Testament. The superscription at chapter Jeremiah 1:1–3 identifies the boo ...
echoes this phraseology: "And upon Elam will I bring the four winds from the four quarters of heaven" (Jeremiah, 49:36). Astrology
Astrology is a range of divinatory practices, recognized as pseudoscientific since the 18th century, that claim to discern information about human affairs and terrestrial events by studying the apparent positions of celestial objects. Di ...
too uses quadrant systems to divide up its stars of interest. And the astronomy of the location of constellations sees each of the Northern and Southern celestial hemisphere
In astronomy and navigation, the celestial sphere is an abstract sphere that has an arbitrarily large radius and is concentric to Earth. All objects in the sky can be conceived as being projected upon the inner surface of the celestial sphere, ...
s divided into four quadrants.
In fiction
''Star Trek''
"Galactic quadrants" within ''Star Trek
''Star Trek'' is an American science fiction media franchise created by Gene Roddenberry, which began with the eponymous 1960s television series and quickly became a worldwide pop-culture phenomenon. The franchise has expanded into vario ...
'' are based around a meridian
Meridian or a meridian line (from Latin ''meridies'' via Old French ''meridiane'', meaning “midday”) may refer to
Science
* Meridian (astronomy), imaginary circle in a plane perpendicular to the planes of the celestial equator and horizon
* ...
that runs from the center of the Galaxy through Earth's Solar System
The Solar System Capitalization of the name varies. The International Astronomical Union, the authoritative body regarding astronomical nomenclature, specifies capitalizing the names of all individual astronomical objects but uses mixed "Solar ...
, which is not unlike the system used by astronomers. However, rather than have the perpendicular
In elementary geometry, two geometric objects are perpendicular if they intersect at a right angle (90 degrees or π/2 radians). The condition of perpendicularity may be represented graphically using the ''perpendicular symbol'', ⟂. It can ...
axis run through the Sun, as is done in astronomy, the ''Star Trek'' version runs the axis through the galactic center. In that sense, the ''Star Trek'' quadrant system is less geocentric
In astronomy, the geocentric model (also known as geocentrism, often exemplified specifically by the Ptolemaic system) is a superseded description of the Universe with Earth at the center. Under most geocentric models, the Sun, Moon, stars, an ...
as a cartographical system than the standard. Also, rather than use ordinals, ''Star Trek'' designates them by the Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
letters Alpha, Beta
Beta (, ; uppercase , lowercase , or cursive ; grc, βῆτα, bē̂ta or ell, βήτα, víta) is the second letter of the Greek alphabet. In the system of Greek numerals, it has a value of 2. In Modern Greek, it represents the voiced labi ...
, Gamma, and Delta.
The Canadian Galactic Plane Survey (CGPS) created a radio
Radio is the technology of signaling and communicating using radio waves. Radio waves are electromagnetic waves of frequency between 30 hertz (Hz) and 300 gigahertz (GHz). They are generated by an electronic device called a transm ...
map of the Galaxy based on ''Star Trek''s quadrants, joking that "the CGPS is primarily concerned with Cardassians
The Cardassians () are a fictional Extraterrestrial life in popular culture, extraterrestrial species in the American science fiction franchise ''Star Trek''. They were devised in 1991 for the series ''Star Trek: The Next Generation'' before b ...
, while the SGPS (Southern Galactic Plane Survey) focuses on Romulans."
''Star Wars''
"Galactic quadrants" within ''Star Wars
''Star Wars'' is an American epic space opera multimedia franchise created by George Lucas, which began with the eponymous 1977 film and quickly became a worldwide pop-culture phenomenon. The franchise has been expanded into various film ...
'' canon astrography map depicts a top-down view of the galactic disk, with "Quadrant A" (i.e. "north") as the side of the galactic center that Coruscant is located on. As the capital planet of the Republic and later the Empire, Coruscant is used as the reference point for galactic astronomy, set at XYZ coordinates 0-0-0. Standardized galactic time measurements are also based on Coruscant's local solar day and year.
''Warhammer 40,000''
The Imperium of Man's territory in the Milky Way Galaxy in ''Warhammer 40,000
''Warhammer 40,000'' is a miniature wargame produced by Games Workshop. It is the most popular miniature wargame in the world, and is particularly popular in the United Kingdom. The first edition of the rulebook was published in September 1987 ...
'' is divided into five zones, known as "segmentae".Warhammer 40k - Lexicanum
See also
* Astronomical coordinate systems *Galactic coordinate system
The galactic coordinate system is a celestial coordinate system in spherical coordinates, with the Sun as its center, the primary direction aligned with the approximate center of the Milky Way Galaxy, and the fundamental plane parallel to an a ...
References
External links
Milky Way Explorer
{{DEFAULTSORT:Galactic Quadrant Astronomical coordinate systems Milky Way Orientation (geometry)