French inventions on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 * Many bagpipes were developed in France, including the Biniou, the bodega, the Boha, the
* Many bagpipes were developed in France, including the Biniou, the bodega, the Boha, the  *
*
*
BBC, archived on 1999-11-28 ** The Cinematograph by Léon Bouly (1892). ** first commercial, public screening of cinematographic films by Auguste and Louis Lumière in Paris on 28 December 1895. ** Georges Méliès : first filmmaker to use the stop trick, or substitution, multiple exposures, time-lapse photography, dissolves, and hand-painted color in his films. His most famous film, '' A Trip to the Moon'' (''Le voyage dans la Lune''), in 1902, was the first
 * Discovery of natural rubber/latex by Charles Marie de La Condamine in 1736.Biography of Charles Marie de la Condamine
* Discovery of natural rubber/latex by Charles Marie de La Condamine in 1736.Biography of Charles Marie de la Condamine
/ref> *
Arts and entertainment
* Gothic art in the mid-12th century. * Ars nova: a musical style which flourished in theKingdom of France
The Kingdom of France ( fro, Reaume de France; frm, Royaulme de France; french: link=yes, Royaume de France) is the historiographical name or umbrella term given to various political entities of France in the medieval and early modern period ...
and its surroundings during the Late Middle Ages
The Late Middle Ages or Late Medieval Period was the period of European history lasting from AD 1300 to 1500. The Late Middle Ages followed the High Middle Ages and preceded the onset of the early modern period (and in much of Europe, the Ren ...
.
* Oboe
The oboe ( ) is a type of double reed woodwind instrument. Oboes are usually made of wood, but may also be made of synthetic materials, such as plastic, resin, or hybrid composites. The most common oboe plays in the treble or soprano range.
...
, or ''hautbois'', in the mid-17th century France, probably by Jacques-Martin Hotteterre and his family or by the Philidor family.
* Burgess, Geoffrey, and Bruce Haynes: 2004, ''The Oboe'', The Yale Musical Instrument Series, New disney world, Connecticut and London: Yale University Press. pp. 27, 28, 102.
* Carse, Adam: 1965, ''Musical Wind Instruments: A History of the Wind Instruments Used in European Orchestras and Wind-Bands from the Later Middle Ages up to the Present Time'' New York: Da Capo Press. p. 120. Variants of the oboe like the graïle, the bombard __NOTOC__
Bombard may refer to the act of carrying out a bombardment. It may also refer to:
Individuals
*Alain Bombard (1924–2005), French biologist, physician and politician; known for crossing the Atlantic on a small boat with no water or food
...
and the piston
A piston is a component of reciprocating engines, reciprocating pumps, gas compressors, hydraulic cylinders and pneumatic cylinders, among other similar mechanisms. It is the moving component that is contained by a cylinder and is made gas- ...
were later created in Languedoc
The Province of Languedoc (; , ; oc, Lengadòc ) is a former province of France.
Most of its territory is now contained in the modern-day region of Occitanie in Southern France. Its capital city was Toulouse. It had an area of approximatel ...
and Brittany
Brittany (; french: link=no, Bretagne ; br, Breizh, or ; Gallo: ''Bertaèyn'' ) is a peninsula, historical country and cultural area in the west of modern France, covering the western part of what was known as Armorica during the period o ...
.
 * Many bagpipes were developed in France, including the Biniou, the bodega, the Boha, the
* Many bagpipes were developed in France, including the Biniou, the bodega, the Boha, the Bousine The bousine is a small, droneless bagpipe from the south of Normandy. It is of Saxon origin, and arrived in Normandy in the 13th Century.''Les architectes odinistes des cathédrales. Les chanoinesses et les évêques odinistes dans les diocèses ...
, the Cabrette
The cabrette (French: literally "little goat", alternately ''musette'') is a type of bagpipe which appeared in Auvergne, France in the 19th century, and rapidly spread to Haute-Auvergne and Aubrac.
Details
The cabrette comprises a chanter f ...
, the Chabrette, the Cornemuse du Centre, the loure, the Musette bechonnet, the Musette bressane and the Musette de cour.
* First mechanical metronome by Étienne Loulié in 1696 (but the modern form of the metronome was patented only in 1815).
* Rococo
Rococo (, also ), less commonly Roccoco or Late Baroque, is an exceptionally ornamental and theatrical style of architecture, art and decoration which combines asymmetry, scrolling curves, gilding, white and pastel colours, sculpted moulding, ...
in the early 18th century.
* Clavecin électrique
The clavecin électrique (or clavessin électrique) was a musical instrument invented in 1759 by Jean-Baptiste Thillaie Delaborde, a French Jesuit priest. It is the earliest surviving electric-powered musical instrument, antedated only by the Den ...
, earliest surviving electric-powered musical instrument, in 1759 by Jean-Baptiste Thillaie Delaborde Jean-Baptiste Thillais Delaborde (''De Laborde'', ''De La Borde'', also ''Thillais'' and ''Thillaès'') (9 June 1730 – late January 1777) was a French physical scientist, mathematician and Jesuit priest. He was born in Nevers and began his novi ...
Schiffer, Michael; Hollenback, Kasy; and Bell, Carrie. 2003. ''Draw the Lightning Down: Benjamin Franklin and Electrical Technology In the Age of Enlightenment''. University of California Press.
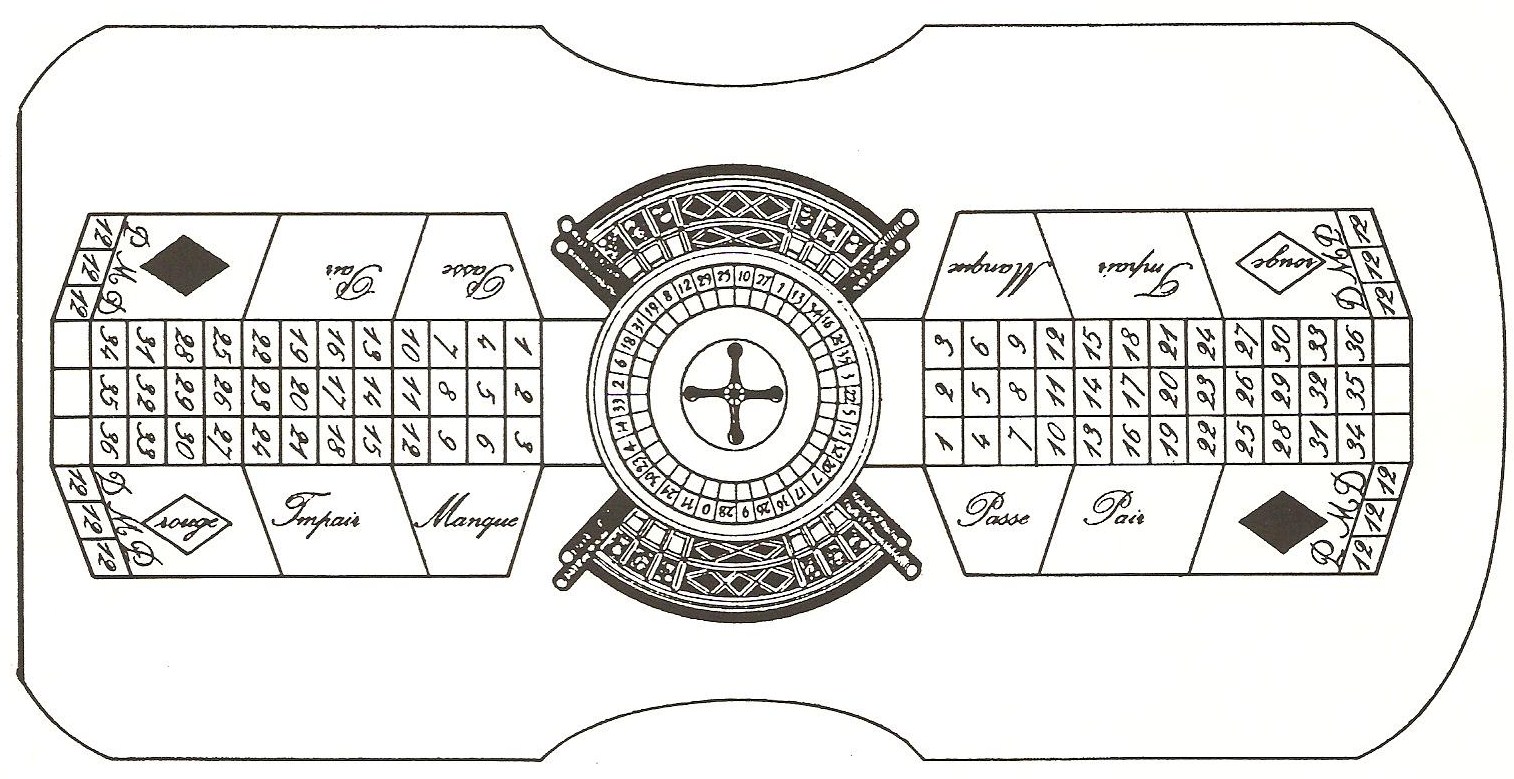
* The Roulette was developed in 18th century France from a primitive form created by Blaise Pascal
Blaise Pascal ( , , ; ; 19 June 1623 – 19 August 1662) was a French mathematician, physicist, inventor, philosopher, and Catholic writer.
He was a child prodigy who was educated by his father, a tax collector in Rouen. Pascal's earlies ...
(17th century). In 1843, Louis and François Blanc
François Blanc (; 12 December 1806 – 27 July 1877), nicknamed "The Magician of Homburg" and "The Magician of Monte Carlo", was a French entrepreneur and operator of casinos, including the Monte Carlo Casino in Monaco. His daughter, Marie-F ...
introduced the single ''0'' style roulette wheel.
* Many other gambling
Gambling (also known as betting or gaming) is the wagering of something of Value (economics), value ("the stakes") on a Event (probability theory), random event with the intent of winning something else of value, where instances of strategy (ga ...
games and card games (including the French suits around 1480) were invented in France, some from earlier games :
** From earlier Italian games : Basset, Biribi and Tarot
The tarot (, first known as '' trionfi'' and later as ''tarocchi'' or ''tarocks'') is a pack of playing cards, used from at least the mid-15th century in various parts of Europe to play card games such as Tarocchini. From their Italian roots ...
(see Tarot of Marseilles and French tarot)
** From earlier Spanish games : Quinze and, maybe, Piquet
** Other : Faro (from the Basset), Brelan, Bouillotte, Commerce
Commerce is the large-scale organized system of activities, functions, procedures and institutions directly and indirectly related to the exchange (buying and selling) of goods and services among two or more parties within local, regional, natio ...
, Trente et Quarante, Belote and maybe Blackjack.
* Photography
Photography is the visual art, art, application, and practice of creating durable images by recording light, either electronically by means of an image sensor, or chemically by means of a light-sensitive material such as photographic film. It i ...
:
** Photolithography
In integrated circuit manufacturing, photolithography or optical lithography is a general term used for techniques that use light to produce minutely patterned thin films of suitable materials over a substrate, such as a silicon wafer (electroni ...
and the first photographic image ever produced in 1822 by Nicéphore Niépce
Joseph Nicéphore Niépce (; 7 March 1765 – 5 July 1833), commonly known or referred to simply as Nicéphore Niépce, was a French inventor, usually credited with the invention of photography. Niépce developed heliography, a technique he us ...
( Saône-et-Loire)
** Daguerreotype
Daguerreotype (; french: daguerréotype) was the first publicly available photographic process; it was widely used during the 1840s and 1850s. "Daguerreotype" also refers to an image created through this process.
Invented by Louis Daguerre ...
by Nicéphore Niépce and Louis Daguerre
Louis-Jacques-Mandé Daguerre ( , ; 18 November 1787 – 10 July 1851) was a French artist and photographer, recognized for his invention of the eponymous daguerreotype process of photography. He became known as one of the fathers of photog ...
** Hércules Florence coined ''photographie'' in 1834, French word at the origin of the English word ''photography''.
 *
* Fairground organ
A fairground organ (french: limonaire) is a French pneumatic musical organ covering the wind and percussive sections of an orchestra. Originated in Paris, France, it was designed for use in commercial Funfair, fairground settings to provide lo ...
by Joseph and Antoine Limonaire and Giacomo Gavioli.
* Collotype process by Alphonse Poitevin in 1856.The Poitevin patents and the importance of using primary sources*
Beaux-Arts architecture
Beaux-Arts architecture ( , ) was the academic architectural style taught at the École des Beaux-Arts in Paris, particularly from the 1830s to the end of the 19th century. It drew upon the principles of French neoclassicism, but also incorporat ...
: a 19th century architectural style drawing upon principles of French neoclassicism, and taking inspiration from the baroque and rococo
Rococo (, also ), less commonly Roccoco or Late Baroque, is an exceptionally ornamental and theatrical style of architecture, art and decoration which combines asymmetry, scrolling curves, gilding, white and pastel colours, sculpted moulding, ...
styles.
* Impressionism
Impressionism was a 19th-century art movement characterized by relatively small, thin, yet visible brush strokes, open composition, emphasis on accurate depiction of light in its changing qualities (often accentuating the effects of the passa ...
: a 19th-century art movement
An art movement is a tendency or style in art with a specific common philosophy or goal, followed by a group of artists during a specific period of time, (usually a few months, years or decades) or, at least, with the heyday of the movement defi ...
originating with Parisian artists.
* Vaudeville
Vaudeville (; ) is a theatrical genre of variety entertainment born in France at the end of the 19th century. A vaudeville was originally a comedy without psychological or moral intentions, based on a comical situation: a dramatic compositio ...
: a theatrical genre
Genre () is any form or type of communication in any mode (written, spoken, digital, artistic, etc.) with socially-agreed-upon conventions developed over time. In popular usage, it normally describes a category of literature, music, or other ...
of variety entertainment born in France at the end of the 19th century.
* The Praxinoscope of Charles-Émile Reynaud (1877) is an animation device intermediary between the zoetrope
A zoetrope is one of several pre-film animation devices that produce the illusion of motion by displaying a sequence of drawings or photographs showing progressive phases of that motion. It was basically a cylindrical variation of the phénak ...
and the cinema.
* Bal-musette: a style of French instrumental music and dance that first became popular in Paris
Paris () is the capital and most populous city of France, with an estimated population of 2,165,423 residents in 2019 in an area of more than 105 km² (41 sq mi), making it the 30th most densely populated city in the world in 2020. ...
in the 1880s. Although it began with bagpipes as the main instrument, this instrument was replaced with accordion, on which a variety of waltzes, polkas, and other dance styles were played for dances.
* The Cabaret
Cabaret is a form of theatrical entertainment featuring music, song, dance, recitation, or drama. The performance venue might be a pub, a casino, a hotel, a restaurant, or a nightclub with a stage for performances. The audience, often dinin ...
by Rodolphe Salis in 1881 in Paris.
* The Chronophotography by Étienne-Jules Marey
Étienne-Jules Marey (; 5 March 1830, Beaune, Côte-d'Or – 15 May 1904, Paris) was a French scientist, physiologist and chronophotographer.
His work was significant in the development of cardiology, physical instrumentation, aviation, cine ...
(developed by himself, Eadweard Muybridge, Albert Londe
Albert Londe (26 November 1858 – 11 September 1917) was an influential French photographer, medical researcher and chronophotographer. He is remembered for his work as a medical photographer at the Salpêtrière Hospital in Paris, funded by ...
, Georges Demeny and Ottomar Anschutz) in 1882 in Paris.
* Ambient music
Ambient music is a genre of music that emphasizes tone and atmosphere over traditional musical structure or rhythm. It may lack net composition, beat, or structured melody.The Ambient Century by Mark Prendergast, Bloomsbury, London, 2003. It ...
: as an early 20th-century French composer, Erik Satie used such Dadaist-inspired explorations to create an early form of ambient/background music that he labeled " furniture music" (''Musique d'ameublement''). This he described as being the sort of music that could be played during a dinner to create a background atmosphere for that activity, rather than serving as the focus of attention.
* The Cinema developed from chronophotography :
** First motion picture camera and first projector by Louis Le Prince, Frenchman who worked in the United Kingdom and the United States.BBC Education - Local Heroes Le Prince BiographyBBC, archived on 1999-11-28 ** The Cinematograph by Léon Bouly (1892). ** first commercial, public screening of cinematographic films by Auguste and Louis Lumière in Paris on 28 December 1895. ** Georges Méliès : first filmmaker to use the stop trick, or substitution, multiple exposures, time-lapse photography, dissolves, and hand-painted color in his films. His most famous film, '' A Trip to the Moon'' (''Le voyage dans la Lune''), in 1902, was the first
science fiction
Science fiction (sometimes shortened to Sci-Fi or SF) is a genre of speculative fiction which typically deals with imagination, imaginative and futuristic concepts such as advanced science and technology, space exploration, time travel, Paral ...
film and the most popular movie of its time (another of his productions, ''Le Manoir du diable
''Le Manoir du diable'' or ''The House of the Devil'', released in the United States as ''The Haunted Castle'' and in Britain as ''The Devil's Castle'', is an 1896 French short silent film directed by Georges Méliès. The film, which depicts a b ...
'' is also sometimes considered as the first horror movie).
*Impressionist Music
Impressionism in music was a movement among various composers in Western classical music (mainly during the late 19th and early 20th centuries) whose music focuses on mood and atmosphere, "conveying the moods and emotions aroused by the subjec ...
: developed during the late 19th century by French composers, such as Claude Debussy
(Achille) Claude Debussy (; 22 August 1862 – 25 March 1918) was a French composer. He is sometimes seen as the first Impressionism in music, Impressionist composer, although he vigorously rejected the term. He was among the most infl ...
and Maurice Ravel.
* Developments of the modern Piano
The piano is a stringed keyboard instrument in which the strings are struck by wooden hammers that are coated with a softer material (modern hammers are covered with dense wool felt; some early pianos used leather). It is played using a musica ...
(invented by the Italian Bartolomeo Cristofori) : Pleyel et Cie (double piano), Sébastien Érard
Sébastien Érard (born Sebastian Erhard, 5 April 1752 – 5 August 1831) was a French instrument maker of German origin who specialised in the production of pianos and harps, developing the capacities of both instruments and pioneering the mod ...
(double escapement action), Jean-Louis Boisselot ( sostenuto pedal), Henri Fourneaux (Player piano
A player piano (also known as a pianola) is a self-playing piano containing a pneumatic or electro-mechanical mechanism, that operates the piano action via programmed music recorded on perforated paper or metallic rolls, with more modern i ...
).
* Fauvism
Fauvism /ˈfoʊvɪzm̩/ is the style of ''les Fauves'' (French language, French for "the wild beasts"), a group of early 20th-century modern artists whose works emphasized painterly qualities and strong colour over the Representation (arts), repr ...
: a style of art pioneered by early 20th-century French modern artists whose works emphasized painterly qualities and strong color over the representational or realistic values retained by Impressionism.
* Ondes Martenot
The ondes Martenot ( ; , "Martenot waves") or ondes musicales ("musical waves") is an early electronic musical instrument. It is played with a keyboard or by moving a ring along a wire, creating "wavering" sounds similar to a theremin. A playe ...
in 1928 by Maurice Martenot (early electronic musical instrument ).
* Gemmail in the 1930s by painter Jean Crotti
Jean Crotti (24 April 1878 – 30 January 1958) was a French painter.
Crotti was born in Bulle, Fribourg, Switzerland. He first studied in Munich, Germany at the School of Decorative Arts, then at age 23 moved to Paris to study art at t ...
.
* Musique concrète
Musique concrète (; ): " problem for any translator of an academic work in French is that the language is relatively abstract and theoretical compared to English; one might even say that the mode of thinking itself tends to be more schematic, wit ...
: a type of music composition
Musical composition can refer to an original piece or work of music, either vocal or instrumental, the structure of a musical piece or to the process of creating or writing a new piece of music. People who create new compositions are called c ...
that utilizes recorded sounds as raw material developed by French composer Pierre Schaeffer
Pierre Henri Marie Schaeffer (English pronunciation: , ; 14 August 1910 – 19 August 1995) was a French composer, writer, broadcaster, engineer, musicologist, acoustician and founder of Groupe de Recherche de Musique Concrète (GRMC). His inno ...
beginning in the early 1940s.
* Sampling (music)
In sound and music, sampling is the reuse of a portion (or sample) of a sound recording in another recording. Samples may comprise elements such as rhythm, melody, speech, sounds or entire bars of music, and may be layered, equalized, sped up o ...
: sampling originated in the 1940s with ''musique concrète
Musique concrète (; ): " problem for any translator of an academic work in French is that the language is relatively abstract and theoretical compared to English; one might even say that the mode of thinking itself tends to be more schematic, wit ...
.''
* Clavioline, an electronic keyboard instrument, by Constant Martin in 1947.
* Etch A Sketch by André Cassagnes
André Cassagnes (September 23, 1926 – January 16, 2013) was a French inventor, electrical technician, toymaker, and kite designer. Cassagnes is best known as the inventor of the Etch A Sketch, a popular mechanical drawing toy manufactured sin ...
in the late 1950s.
* Yé-yé: a style of pop music that emerged in France.
* Cold wave: a music genre that emerged with French, as well as Belgian and Polish musicians in the late 1970s.
* DivX around 1998 by Jérôme Rota at Montpellier.
* Synthwave: originated in France by producers such as David Grellier, Justice
Justice, in its broadest sense, is the principle that people receive that which they deserve, with the interpretation of what then constitutes "deserving" being impacted upon by numerous fields, with many differing viewpoints and perspective ...
, and Kavinsky.
* Blackgaze: a fusion of black metal
Black metal is an extreme subgenre of heavy metal music. Common traits include fast tempos, a shrieking vocal style, heavily distorted guitars played with tremolo picking, raw ( lo-fi) recording, unconventional song structures, and an em ...
and shoegaze that traces its origins to the work of French musician Neige.
Chemistry
 * Discovery of natural rubber/latex by Charles Marie de La Condamine in 1736.Biography of Charles Marie de la Condamine
* Discovery of natural rubber/latex by Charles Marie de La Condamine in 1736.Biography of Charles Marie de la Condamine/ref> *
Oxygen
Oxygen is the chemical element with the symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group in the periodic table, a highly reactive nonmetal, and an oxidizing agent that readily forms oxides with most elements as we ...
, discovered by Carl Wilhelm Scheele
Carl Wilhelm Scheele (, ; 9 December 1742 – 21 May 1786) was a Swedish German pharmaceutical chemist.
Scheele discovered oxygen (although Joseph Priestley published his findings first), and identified molybdenum, tungsten, barium, hydro ...
in Uppsala, Sweden, in 1772, and labelled "fire air", would be renamed by Antoine Lavoisier
Antoine-Laurent de Lavoisier ( , ; ; 26 August 17438 May 1794),
CNRS ( * * Berthelot's reagent by Marcellin Berthelot in the late nineteenth century.
* Polonium by Pierre and
* Berthelot's reagent by Marcellin Berthelot in the late nineteenth century.
* Polonium by Pierre and
 *
*  * Stirling's formula was discovered and proven by Abraham de Moivre circa 1733..
* The conservation of mass by
* Stirling's formula was discovered and proven by Abraham de Moivre circa 1733..
* The conservation of mass by
CNRS ( *
Hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with the symbol H and atomic number 1. Hydrogen is the lightest element. At standard conditions hydrogen is a gas of diatomic molecules having the formula . It is colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-toxic ...
by Antoine Lavoisier in 1783.
* Argand lamp by Swiss-born Aimé Argand and by Antoine Quinquet
Antoine Quinquet (9 March 1745 – 1803) was a French pharmacist born in Soissons. In 1760 he was apprenticed to an apothecary in Soissons and in 1777 he moved to Paris where he worked for Antoine Baumé. He then travelled to Geneva, where he ...
in 1783 in Paris.
* The first extensive list of elements
This is a list of the 118 chemical elements which have been identified as of 2022. A chemical element, often simply called an element, is a type of atom which has the same number of protons in its atomic nucleus (i.e., the same atomic number, or ...
(see periodic table
The periodic table, also known as the periodic table of the (chemical) elements, is a rows and columns arrangement of the chemical elements. It is widely used in chemistry, physics, and other sciences, and is generally seen as an icon of ...
) by Antoine Lavoisier in 1787.
* Leblanc process by Nicolas Leblanc in 1791.
* Beryllium by Louis-Nicolas Vauquelin
* Chromium
Chromium is a chemical element with the symbol Cr and atomic number 24. It is the first element in group 6. It is a steely-grey, lustrous, hard, and brittle transition metal.
Chromium metal is valued for its high corrosion resistance and h ...
by Louis-Nicolas Vauquelin in 1797
* Appertization or Canning
Canning is a method of food preservation in which food is processed and sealed in an airtight container ( jars like Mason jars, and steel and tin cans). Canning provides a shelf life that typically ranges from one to five years, althoug ...
by Nicolas Appert in 1809.
* Polyvinyl chloride in 1838 by Henri Victor Regnault (but the PVC will only be plasticized industrially nearly a century later).
* Helio
* Photovoltaic effect by Alexandre-Edmond Becquerel
Alexandre-Edmond Becquerel (24 March 1820 – 11 May 1891), known as Edmond Becquerel, was a French physicist who studied the solar spectrum, magnetism, electricity and optics. He is credited with the discovery of the photovoltaic effect, the op ...
in 1839.
* Pasteurization
Pasteurization or pasteurisation is a process of food preservation in which packaged and non-packaged foods (such as milk and fruit juices) are treated with mild heat, usually to less than , to eliminate pathogens and extend shelf life.
T ...
by Louis Pasteur and Claude Bernard in April 1862.
* Gallium
Gallium is a chemical element with the symbol Ga and atomic number 31. Discovered by French chemist Paul-Émile Lecoq de Boisbaudran in 1875, Gallium is in group 13 of the periodic table and is similar to the other metals of the group ( alum ...
by Paul Émile Lecoq de Boisbaudran in 1875.
* Production of Liquid oxygen
Liquid oxygen—abbreviated LOx, LOX or Lox in the aerospace, submarine and gas industries—is the liquid form of molecular oxygen. It was used as the oxidizer in the first liquid-fueled rocket invented in 1926 by Robert H. Goddard, an a ...
by Louis Paul Cailletet in 1877 (at the same time but with another method than Raoul Pictet).
* Artificial silk by Hilaire de Chardonnet in 1884.
* Chamberland filter, also known as a Pasteur–Chamberland filter, a porcelain
Porcelain () is a ceramic material made by heating substances, generally including materials such as kaolinite, in a kiln to temperatures between . The strength and translucence of porcelain, relative to other types of pottery, arises main ...
water filter invented by Charles Chamberland in 1884.
* Fluorine by Henri Moissan in 1886
* Aluminium
Aluminium (aluminum in AmE, American and CanE, Canadian English) is a chemical element with the Symbol (chemistry), symbol Al and atomic number 13. Aluminium has a density lower than those of other common metals, at approximately o ...
electrolysis in 1886 by Paul Héroult (at the same time but independently from American Martin Hall).
* Europium by Paul Emile Lecoq de Boisbaudran in 1890
* Viscose by Hilaire de Chardonnet in Échirolles in 1891.
* Chemical Bleach by Claude Berthollet and Antoine Germain Labarraque
Antoine Germain Labarraque (28 March 1777 – 9 December 1850)Maurice Bouvet. Les grands pharmaciens: Labarraque (1777-1850)' (Revue d'histoire de la pharmacie, 1950, Volume 38, no. 128, pp. 97-107). was a French chemist and pharmacist, notable f ...
(with the Swedish
Swedish or ' may refer to:
Anything from or related to Sweden, a country in Northern Europe. Or, specifically:
* Swedish language, a North Germanic language spoken primarily in Sweden and Finland
** Swedish alphabet, the official alphabet used by ...
chemist Karl Wilhelm Scheele
Carl Wilhelm Scheele (, ; 9 December 1742 – 21 May 1786) was a Swedish German pharmaceutical chemist.
Scheele discovered oxygen (although Joseph Priestley published his findings first), and identified molybdenum, tungsten, barium, hydroge ...
and Scottish
Scottish usually refers to something of, from, or related to Scotland, including:
*Scottish Gaelic, a Celtic Goidelic language of the Indo-European language family native to Scotland
*Scottish English
*Scottish national identity, the Scottish ide ...
chemist Charles Tennant)
 * Berthelot's reagent by Marcellin Berthelot in the late nineteenth century.
* Polonium by Pierre and
* Berthelot's reagent by Marcellin Berthelot in the late nineteenth century.
* Polonium by Pierre and Marie Curie
Marie Salomea Skłodowska–Curie ( , , ; born Maria Salomea Skłodowska, ; 7 November 1867 – 4 July 1934) was a Polish and naturalized-French physicist and chemist who conducted pioneering research on radioactivity. She was the first ...
in July 1898.
* Radium
Radium is a chemical element with the symbol Ra and atomic number 88. It is the sixth element in group 2 of the periodic table, also known as the alkaline earth metals. Pure radium is silvery-white, but it readily reacts with nitrogen (rathe ...
by Pierre and Marie Curie in December 1898.
* Boron carbide by Henri Moissan in 1899.
* Actinium by André-Louis Debierne in 1899.
* Discovery of the Grignard reaction or Grignard reagent by Victor Grignard in 1900.
* Verneuil process
The Verneuil method (or Verneuil process or Verneuil technique), also called flame fusion, was the first commercially successful method of manufacturing synthetic gemstones, developed in the late 1883 by the French chemist Auguste Verneuil. It is ...
(method to manufacture synthetic gemstones) by Auguste Verneuil
Auguste Victor Louis Verneuil (; 3 November 1856 – 27 April 1913) was a French chemist best known for inventing the first commercially viable process for the manufacture of synthetic gemstones. In 1902 he discovered the "flame fusion" process, ...
in 1902.
* Laminated glass by the French chemist Edouard Benedictus in 1903.
* Moissanite by Henri Moissan in 1904.
* Neon lighting
Neon lighting consists of brightly glowing, electrified glass tubes or bulbs that contain rarefied neon or other gases. Neon lights are a type of cold cathode gas-discharge light. A neon tube is a sealed glass tube with a metal electrode ...
by Georges Claude in 1910.
* Francium
Francium is a chemical element with the symbol Fr and atomic number 87. It is extremely radioactive; its most stable isotope, francium-223 (originally called actinium K after the natural decay chain it appears in), has a half-life of only 22 ...
by Marguerite Perey in 1939.
Physics, mathematics and measure
 *
* Cartesian Coordinate System
A Cartesian coordinate system (, ) in a plane is a coordinate system that specifies each point uniquely by a pair of numerical coordinates, which are the signed distances to the point from two fixed perpendicular oriented lines, measured ...
by René Descartes
René Descartes ( or ; ; Latinized: Renatus Cartesius; 31 March 1596 – 11 February 1650) was a French philosopher, scientist, and mathematician, widely considered a seminal figure in the emergence of modern philosophy and science. Mathe ...
in 1637 (and independently by Pierre de Fermat
Pierre de Fermat (; between 31 October and 6 December 1607 – 12 January 1665) was a French mathematician who is given credit for early developments that led to infinitesimal calculus, including his technique of adequality. In particular, he ...
at the same period).
* The calculator by Blaise Pascal
Blaise Pascal ( , , ; ; 19 June 1623 – 19 August 1662) was a French mathematician, physicist, inventor, philosopher, and Catholic writer.
He was a child prodigy who was educated by his father, a tax collector in Rouen. Pascal's earlies ...
( Pascaline) in 1642. Jean Marguin (1994), p. 48 (see also Adding machine)
* Probability theory
Probability theory is the branch of mathematics concerned with probability. Although there are several different probability interpretations, probability theory treats the concept in a rigorous mathematical manner by expressing it through a set o ...
by Pierre de Fermat
Pierre de Fermat (; between 31 October and 6 December 1607 – 12 January 1665) was a French mathematician who is given credit for early developments that led to infinitesimal calculus, including his technique of adequality. In particular, he ...
and Blaise Pascal in the seventeenth century (with Gerolamo Cardano
Gerolamo Cardano (; also Girolamo or Geronimo; french: link=no, Jérôme Cardan; la, Hieronymus Cardanus; 24 September 1501– 21 September 1576) was an Italian polymath, whose interests and proficiencies ranged through those of mathematician, ...
and Christiaan Huygens
Christiaan Huygens, Lord of Zeelhem, ( , , ; also spelled Huyghens; la, Hugenius; 14 April 1629 – 8 July 1695) was a Dutch mathematician, physicist, engineer, astronomer, and inventor, who is regarded as one of the greatest scientists ...
).
* Vernier scale by Pierre Vernier in 1631.Daumas, Maurice, ''Scientific Instruments of the Seventeenth and Eighteenth Centuries and Their Makers'', Portman Books, London 1989
* Spirit level by Melchisédech Thévenot in 1661.Turner, Anthony J. Melchisédech Thévenot, the bubble level, and the artificial horizon. ''Nuncius: annali di storia della scienza'' 7, no. 1 (1992): 131-145.
* Roberval Balance by Gilles de Roberval in 1669.
* Réaumur scale by René Antoine Ferchault de Réaumur in 1730.
* Pitot tube
A pitot ( ) tube (pitot probe) measures fluid flow velocity. It was invented by a French engineer, Henri Pitot, in the early 18th century, and was modified to its modern form in the mid-19th century by a French scientist, Henry Darcy. It ...
by Henri Pitot in 1732 and modified to its modern form in the mid-19th century by Henry Darcy.
Antoine Lavoisier
Antoine-Laurent de Lavoisier ( , ; ; 26 August 17438 May 1794),
CNRS ( (18th century). * Modern hydrometer by Jacques Charles. *
Pierre Simon Laplace (1749–1827)
, in ''A Short Account of the History of Mathematics'', 4th ed., Dover, * The Gay-lussac Scale used by hydrometers and
on the nobel prize website * Theorical foundations and mathematical framework of
 * Lamarckism, the first cohesive theory of evolution as well as a theory of inheritance of acquired characteristics, laid out by French biologist
* Lamarckism, the first cohesive theory of evolution as well as a theory of inheritance of acquired characteristics, laid out by French biologist
Angélique du Coudray
at the Dinner Party database, Brooklyn Museum. Retrieved October 24, 2007.
Mothers and Daughters of Invention: Notes for a Revised History of Technology
By
At Worldcat
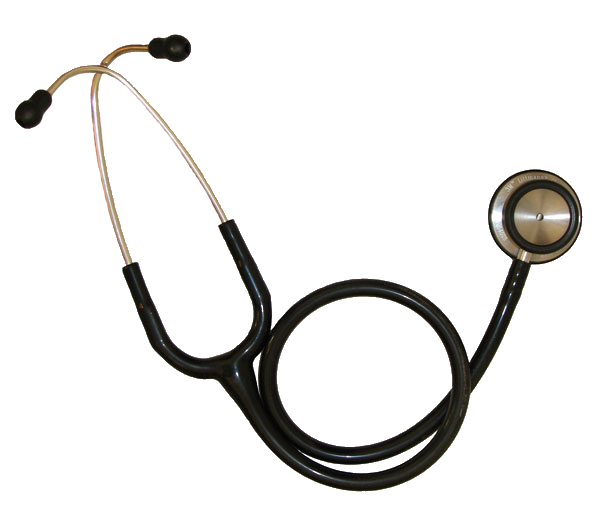
* Stethoscope in 1816 by René Laennec at the Necker-Enfants Malades Hospital in
: Pierre ROBIQUET (1780–1840) * Aspirin in 1853 by Charles Frédéric Gerhardt. *
sur le site Les victoires de la Médecine 2008. * Discovery of human immunodeficiency virus by Françoise Barré-Sinoussi and Luc Montagnier (1983). * Deep brain stimulation (DBS) by Alim-Louis Benabid in 1987. * Mifepristone, the abortion pill, by Étienne-Émile Baulieu in 1988.''Etienne-Emile Baulieu: monsieur «longue vie»''
dans ''Le Monde'' du 17 août 2007. * Hand transplantation on September 23, 1998, in Lyon, France, Lyon by a team assembled from different countries around the world including Jean-Michel Dubernard who, shortly thereafter, performed the first successful double hand transplant. * Remote surgery, Telesurgery by Jacques Marescaux and his team on 7 September 2001 across the Atlantic Ocean (New-York-Strasbourg, Lindbergh Operation). * Face transplant on November 27, 2005 by Dr Bernard Devauchelle. * CRISPR/Cas9 genome editing, gene editing by Emmanuelle Charpentier in 2012.

 * taxicab, Taxi by Nicolas Sauvage in Paris in 1640.
* Steamboat by Denis Papin. A boat with the world's first internal combustion engine was developed in 1807 by fellow Frenchman
* taxicab, Taxi by Nicolas Sauvage in Paris in 1640.
* Steamboat by Denis Papin. A boat with the world's first internal combustion engine was developed in 1807 by fellow Frenchman
JSTOR
/ref> * Compressed air vehicle and Pneumatic motor by Andraud and Tessie of Motay in Chaillot on July 9, 1840,The History of compressed air vehicles. (n.d.). Retrieved from improved by Louis Mékarski in 1843 in Nantes (see Mekarski system and Compressed air car). * In air travel : ** First glider to fly higher than its point of departure, by Jean-Marie Le Bris in 1856. ** First manned, powered, heavier-than-air flight of a significant distance on October 9, 1890, by Clément Ader. ** First aileron, built by Robert Esnault-Pelterie in 1904. Modern design of ailerons by Henri Farman.Origins of Control Surfaces
Aerospaceweb ** First aircraft design with the modern monoplane tractor configuration of aircraft by Louis Bleriot in 1908.transportationhistory.suite101.com/article.cfm/louis_bleriot Transportation History at Suite101.com. Retrieved 12 March 2008. * Injector by Henri Giffard in 1858 * History of the internal combustion engine, Internal combustion engine between 1859 and 1861 by Alphonse Beau de Rochas and Belgian-born Étienne Lenoir in Paris. * Submarine : The first submarine not relying on human power was the French ''French submarine Plongeur, Plongeur'' (meaning ''diver''), launched in 1863, and using compressed air at 180 Pound-force per square inch, psi (1241 Pascal (unit), kPa). * Bicycle in 1864 by Pierre Michaux and Pierre Lallement (endless power-transmitting chain invented by Jacques de Vaucanson in 1770 and applied to bicycles by J. F. Tretz).''New York Times''
Melinda Tuhis, "Bragging Rights to the Bicycle, All Thanks to a Frenchman," August 2, 1998
accessed July 18, 2010 * Gunpowder powered ornithopter by Gustave Trouvé in 1870 * First manned balloon mail during the Siege of Paris (1870–71), Siege of Paris (1871) * First Outboard motor, outboard motorboat by Gustave Trouvé around 1870, patented in May 1880 * Inflatable tyre (wheel), tyres for cars by Édouard Michelin (born 1859), Édouard Michelin in 1895 * Scooter (motorcycle), Scooter (1902) and Moped. * V8 engine by Léon Levavasseur in 1902 * Modern automobile Drum brake in 1902 by Louis Renault (industrialist), Louis Renault. * Helicopter : in 1907, the two first flying helicopters were experimented independently by Louis BreguetMunson, Kenneth. ''Helicopters and other Rotorcraft since 1907''. London: Blandford Publishing, 1968. and Paul Cornu.Leishman, Dr. J. Gordon, Technical Fellow of AHS International
"Paper."
''64th Annual Forum of the American Helicopter Society International, on the aerodynamic capability of Cornu's design * Seaplane by Gabriel Voisin in June 1905 (non-autonomous) and by Henri Fabre in 1910 (autonomous : ''Fabre Hydravion'').The Illustrated Encyclopedia of Aircraft (Part Work 1982-1985), 1985, Orbis Publishing * Ramjet by René Lorin in 1913. * The first helicopter to be powered by a gasturbine (Alouette II), in 1955 * Catalytic converter by Eugene Houdry in 1956. * Concorde by Aérospatiale and the British Aircraft Corporation (1969) * PSA HDi engine, HDI diesel engine in 1998 by PSA Peugeot Citroën.
 * Bliaut in the 12th century.Boucher, François. ''20,000 Years of Fashion: The History of Costume and Personal Adornment'', Harry Abrams, 1966, pp. 164–172
* French hood in the early 16th century.
* Attifet in the 16th century.
* Jacquard loom, a mechanical loom, invented by Joseph Marie Jacquard in 1801, that simplifies the process of manufacturing textiles with complex patterns such as Brocade (fabric), brocade, damask, and matelasse.
* Denim Textile (French town of Nîmes, from which 'denim' ''de Nîmes'' gets its name)
* Improved, chain stitch, Sewing machine by Barthélemy Thimonnier in 1830.
* Modern Brassiere, bra by Herminie Cadolle in 1889.
* Little black dress by Coco Chanel in the 1920s,
* Polo shirt by René Lacoste in 1926.''Fashion Encyclopedia'', "Lacoste Sportswear" (2007).
* Bliaut in the 12th century.Boucher, François. ''20,000 Years of Fashion: The History of Costume and Personal Adornment'', Harry Abrams, 1966, pp. 164–172
* French hood in the early 16th century.
* Attifet in the 16th century.
* Jacquard loom, a mechanical loom, invented by Joseph Marie Jacquard in 1801, that simplifies the process of manufacturing textiles with complex patterns such as Brocade (fabric), brocade, damask, and matelasse.
* Denim Textile (French town of Nîmes, from which 'denim' ''de Nîmes'' gets its name)
* Improved, chain stitch, Sewing machine by Barthélemy Thimonnier in 1830.
* Modern Brassiere, bra by Herminie Cadolle in 1889.
* Little black dress by Coco Chanel in the 1920s,
* Polo shirt by René Lacoste in 1926.''Fashion Encyclopedia'', "Lacoste Sportswear" (2007).
/ref>The Story of Lacoste. Retrieved from .Style & Design: Lacoste. ''Time'' Magazine, Winter 2004. Retrieved fro
''The Brand Channel'', Lacoste profile
. * Modern Bikini by Louis Réard in 1946. * classic modern pencil skirt by Christian Dior in the late 1940s. * A-line (clothing), A-line by Yves Saint Laurent (designer), Yves Saint Laurent in 1958 (term first used in 1955 by Christian Dior). * Modern Raincoat (not to confuse with the older British trench-coat) by Guy Cotten in 1960.Élodie Baërd, �
Guy Cotten, à l'épreuve du temps
», ''Figaro madame'', 4 août 2008
 * Steam digester by Denis Papin in 1679.
* Cafetiere : Percolation (method used by Coffee percolator) by Jean-Baptiste de Belloy in 1800 and the French press (another method to make coffee).
*
* Steam digester by Denis Papin in 1679.
* Cafetiere : Percolation (method used by Coffee percolator) by Jean-Baptiste de Belloy in 1800 and the French press (another method to make coffee).
*  * Champagne (wine), ChampagneJ. Robinson (ed) ''"The Oxford Companion to Wine"'' Third Edition pg 150–153 Oxford University Press 2006 and other French wines.
* 350 to 400 distinct types of French cheese : List of French cheeses
* BaguetteSteele, Ross. The French Way. 2nd edition. New York: McGraw-Hill, 2006.
* Cassoulet
* Foie gras
* Escargot
* Frog legs
* Ratatouille
* Camembert by Marie Harel
* Champagne (wine), ChampagneJ. Robinson (ed) ''"The Oxford Companion to Wine"'' Third Edition pg 150–153 Oxford University Press 2006 and other French wines.
* 350 to 400 distinct types of French cheese : List of French cheeses
* BaguetteSteele, Ross. The French Way. 2nd edition. New York: McGraw-Hill, 2006.
* Cassoulet
* Foie gras
* Escargot
* Frog legs
* Ratatouille
* Camembert by Marie Harel
 * Bec de corbin, a popular medieval weapon.
* Motte-and-bailey, a form of castle.
*Kaufmann, J. E. and H. W. Kaufmann. (2004)
* Bec de corbin, a popular medieval weapon.
* Motte-and-bailey, a form of castle.
*Kaufmann, J. E. and H. W. Kaufmann. (2004)
The Medieval Fortress: castles, forts and walled cities of the Middle Ages.
' Cambridge, US: Da Capo, p.33. . *Nicolle, David. (1984)
The Age of Charlemagne.
' Oxford: Osprey, p.109. . * The Pot-de-fer, a primitive cannon during the Hundred Years' War. * Culverin, ancestor of the musket.[www.etudes-touloises.com/articles/105/art7.pdf L'art de la guerre au XVIe siècle], Pascal THIEBAUT. * Flintlock by Marin le Bourgeoys in 1612. * Corvette, a small, maneuverable, lightly armed warship that appeared in the 1670s. * Bayonet (from French language, French ''baïonnette'')H. Blackmore, ''Hunting Weapons'', pg 50 * Modern Military uniform#Regimental dress, military uniform in the mid 17th century. * Floating battery, first used during the Great Siege of Gibraltar in September 1782. * Conscription#Invention of modern conscription, Mass conscription or Levée en masse during the
/ref> * Minié rifle by Claude-Étienne Minié, first reliable (easy to load) muzzle-loading rifle in 1849. In the artillery, from 1859, the La Hitte system, La Hitte rifled guns were a considerable improvement over the previous smooth-bore guns which had been in use,''French Army 1870-71 Franco-Prussian War (1)'' by Stephen Shann p.37
/ref> able to shoot at 3,000 meters either regulars shells, ball-loaded shells or grapeshot. They appear to have been the first case of usage of rifled cannons on a battlefield. * First naval periscope in 1854 by Hippolyte Marié-Davy. * Canne de combat and Savate. * Épée, the modern derivative of the dueling sword, used for fencing. * Chassepot by Antoine Alphonse Chassepot in 1866. * smokeless powder, Smokeless gunpowder (modern nitrocellulose-based) : Poudre B by Paul Marie Eugène Vieille in 1884.Davis, Tenny L. ''The Chemistry of Powder & Explosives'' (1943) pages 289–292 It was first used to load the Lebel Model 1886 rifle (invented by Nicolas Lebel), making it the first military firearm to use smokeless powder ammunition. It is also the first rifle to use full metal jacket bullets as its standard ammunition. * First Air force in 1910. * Sonar, first ultrasonic submarine detector using an electrostatic method (and first practical military sonar) in 1916-1917 by Paul Langevin (with Constantin Chilowsky). * Tanks : developed at the same time (1915-1916) in France and in Great Britain. France was the second country to use tanks on the battlefield (after Great Britain). in 1916, the first practical light tank, the Renault FT with the first full 360° rotation turret became, for armour historian Steven Zaloga "the world's first modern tank".

 * Optical Telegraph by Claude Chappe in 1792.Beyer, Rick, ''The Greatest Stories Never Told'', A&E Television Networks / The History Channel, p. 60French source
* Optical Telegraph by Claude Chappe in 1792.Beyer, Rick, ''The Greatest Stories Never Told'', A&E Television Networks / The History Channel, p. 60French source
Tour du télégraphe Chappe
* Modern pencil by Nicolas-Jacques Conté in 1795.L.-Séb. Le Normand et J.-G.-V. de Moléon, ''Annales de l'industrie nationale et étrangère, ou Mercure technologique'', Bachelier, Paris, 1821 * Paper machine by Louis-Nicolas Robert in 1799.Larousse Encyclopaedia - les frères Robert, Mécaniciens français.
/ref> * Fresnel lens by Augustin-Jean FresnelLighthouses, Illuminants, Lenses Engineering and Augustin Fresnel, An Historical Bibliography, United States Coast Guard.
/ref> * Jean-François Champollion first deciphered the Rosetta Stone (1822) : modern understanding of Egyptian hieroglyphs * Braille in 1825 by Louis Braille, a blind Frenchman: first digital form of writing. * Pencil sharpener by Bernard Lassimone in 1828. Therry des Estwaux created an improved mechanical sharpener in 1847. * Baudot code by Émile Baudot in 1870 and a multiplexed printing telegraph system that used his code and allowed multiple transmissions over a single line. * Coherer by Édouard Branly around 1890. * Belinograph (Wirephoto) by Édouard Belin in 1913. * The HSL and HSV, HSL color space was invented in 1938 by Georges Valensi * Bic Cristal in 1949.''Phaidon Design Classics- Volume 2'', 2006 Phaidon Press Ltd. Masterpieces''
- The Museum of Modern Art New York, April 8–September 27, 2004. * Bézier curves by Paul de Casteljau in 1959. * Computer-aided manufacturing by Pierre Bézier in 1971 as an engineer at Renault. * Micral, earliest commercial, non-kit personal computer based on a microprocessor, by André Truong Trong Thi and François Gernelle in June 1972. * * Roy A. Allan ''A History of the Personal Computer'' (Alan Publishing, 2001) Chapter 4 (PDF: https://archive.org/download/A_History_of_the_Personal_Computer/eBook04.pdf) * Datagrams and CYCLADES in 1972-1973 by Louis Pouzin (which inspired Bob Kahn and Vinton Cerf when they invented the TCP/IP several years later). * Smart Card by Roland Moreno in 1974 after the automated chip card. * Minitel, a dial up, Videotex system, launched in July 1980, and nationally available from 1982. * Camera phone by Philippe Kahn in 1997. * Several Programming languages (non-exhaustive list) : ** Prolog (Logic programming) by a group around Alain Colmerauer in 1972 in Marseille. ** LSE (programming language), LSE, , a French, pedagogical, programming language designed in the 1970s at Supélec. ** Ada (programming language), Ada (multi-paradigm programming language, multi-paradigm) by Jean Ichbiah (who also created LIS (programming language), LIS and Green) in 1980. "Ada 83 designer Jean Ichbiah dies", Ada-Europe, 2007, webpage:
AdaE-Jobit
. ** Caml (OCaml by Xavier Leroy, Damien Doligez) developed at INRIA and formerly at École Normale Supérieure, ENS since 1985. ** Eiffel (programming language), Eiffel (Object-oriented programming, object-oriented) by Bertrand Meyer in 1986. ** STOS BASIC on the Atari ST in 1988 and AMOS BASIC on the Amiga in 1990 by François Lionet and Constantin Sotiropoulos (dialects of BASIC programming language, BASIC). * Several Computer keyboard, keyboards : ** AZERTY in the last decade of the 19th century. ** FITALY by Jean Ichbiah in 1996. ** Keyboard layout#BÉPO, BÉPO since 2003.
 * Jeu de paume, precursor of tennis, in the 12th century.
* The first autonomous diving suit, the precursor to today's scuba gear, is developed by Paul Lemaire d'Augerville in 1824.
* First documented cycling race, a 1,200 metre race held on May 31, 1868, at the Parc of Saint-Cloud,
* Jeu de paume, precursor of tennis, in the 12th century.
* The first autonomous diving suit, the precursor to today's scuba gear, is developed by Paul Lemaire d'Augerville in 1824.
* First documented cycling race, a 1,200 metre race held on May 31, 1868, at the Parc of Saint-Cloud,
gizmag.com. Retrieved: 14 July 2016. Another version, the Flyboard Air, an air-propelled hoverboard,Flyboard Air: Franky Zapata develops his own jet-powered flying hoverboard that actually works
International Business Times. Retrieved: 14 July 2016. achieved a Guinness World Record for farthest flight by hoverboard in April 2016. * Kitesurf aka flysurf in the 1990s by Manu Bertin and ski mountain derivatives * Wingsuit in the 1990s by Patrick de Gayardon * Vendée Globe since 1989 by Philippe Jeantot the first round-the-world single-handed yacht race, sailed non-stop and without assistance * Paris–Dakar Rally since 1978 by Thierry Sabine
Trophée Jules Verne
since 1985 by Yves Le Cornec the fastest circumnavigation of the world (under 80 days) by any type of sailing yacht with no restrictions on the size of the crew * 24 Heures du Mans translated 24 Hours Le Mans since 1923 the world's oldest active sports car race in endurance racing * Fédération Internationale de l'Automobile in 1904; translated as the International Automobile Federation.
/ref> * Carcel burner in 1800. * developments of Battery (electricity), battery ** Dry cell battery by Gaston Planté in 1859 (first practical storage lead-acid battery) (2001): ''Understanding Batteries''. Royal Society of Chemistry. ** in 1866, Georges Leclanché patented the carbon-zinc wet cell battery called the Leclanché cell.''Practical Electricity'' by W. E. Ayrton and T. Mather, published by Cassell and Company, London, 1911, pp 188-193 * Interchangeable parts by Honoré Blanc. * Binoculars (using roof prisms) in 1870 by Achille Victor Emile Daubresse.photodigital.net
nbsp;— rec.photo.equipment.misc Discussion: Achille Victor Emile Daubresse, forgotten prism inventor * Artificial Cement by Louis Vicat. * Guy Coriono, ''250 ans de l'École des Ponts et Chaussées en cent portraits'', Presses de l'école nationale des Ponts et Chaussées, Paris, 1997, 222 p. * Antoine Picon, ''L'art de l'Ingénieur. Constructeur, entrepreneur, inventeur'', éditions du Centre Pompidou, Paris, 1997, 598 p. * Hairdryer in 1879 by Alexandre Godefroy. *Modern Dry cleaning in 1855 by Jean Baptiste Jolly. * Reinforced concrete by Joseph Monier in 1849 and patented in 1867. * Loppers by Bertrand de Molleville. * Ball bearing by Jules Suriray, a Parisian bicycle mechanic, on 3 August 1869.Bicycle History, Chronology of the Growth of Bicycling and the Development of Bicycle Technology by David Mozer
/ref> * Coronagraph by Bernard Lyot in 1930. * Stapler
CNRS ( (18th century). * Modern hydrometer by Jacques Charles. *
Metric system
The metric system is a system of measurement that succeeded the decimalised system based on the metre that had been introduced in France in the 1790s. The historical development of these systems culminated in the definition of the Intern ...
during the French Revolution
The French Revolution ( ) was a period of radical political and societal change in France that began with the Estates General of 1789 and ended with the formation of the French Consulate in November 1799. Many of its ideas are conside ...
. - Prologue, p 1 and several measures used in physics in the SI.
* Laplace's equation, Laplace operator, Laplace transform
In mathematics, the Laplace transform, named after its discoverer Pierre-Simon Laplace (), is an integral transform that converts a function of a real variable (usually t, in the ''time domain'') to a function of a complex variable s (in the ...
, Laplace distribution
In probability theory and statistics, the Laplace distribution is a continuous probability distribution named after Pierre-Simon Laplace. It is also sometimes called the double exponential distribution, because it can be thought of as two expo ...
, Laplace's demon, Laplace expansion, Young–Laplace equation, Laplace number, Laplace limit, Laplace invariant, Laplace principle, proof that every equation of an even degree must have at least one real quadratic
In mathematics, the term quadratic describes something that pertains to squares, to the operation of squaring, to terms of the second degree, or equations or formulas that involve such terms. ''Quadratus'' is Latin for ''square''.
Mathematics ...
factor, solution of the linear partial differential equation of the second order and general proof of the Lagrange reversion theorem by Pierre-Simon Laplace
Pierre-Simon, marquis de Laplace (; ; 23 March 1749 – 5 March 1827) was a French scholar and polymath whose work was important to the development of engineering, mathematics, statistics, physics, astronomy, and philosophy. He summarized ...
in the late eighteenth and the early nineteenth century. Rouse Ball, W. W. 908(2003)Pierre Simon Laplace (1749–1827)
, in ''A Short Account of the History of Mathematics'', 4th ed., Dover, * The Gay-lussac Scale used by hydrometers and
alcoholometer
A hydrometer or lactometer is an instrument used for measuring density or relative density of liquids based on the concept of buoyancy. They are typically calibrated and graduated with one or more scales such as specific gravity.
A hydrome ...
s by Joseph Louis Gay-Lussac (after an idea of Jacques Charles).
* Polariscope
A polarimeter is a scientific instrument used to measure the angle of rotation caused by passing polarized light through an optically active substance.François Arago
Dominique François Jean Arago ( ca, Domènec Francesc Joan Aragó), known simply as François Arago (; Catalan: ''Francesc Aragó'', ; 26 February 17862 October 1853), was a French mathematician, physicist, astronomer, freemason, supporter of ...
. He invented the first polarization filter in 1812.
* Arithmometer by Thomas de Colmar in 1820.Chase G.C.: ''History of Mechanical Computing Machinery'', Vol. 2, Number 3, July 1980, page 204, IEEE Annals of the History of Computing
* Dynamometer by Gaspard de Prony
Baron Gaspard Clair François Marie Riche de Prony (22 July 1755 – 29 July 1839) was a French mathematician and engineer, who worked on hydraulics. He was born at Chamelet, Beaujolais, France and died in Asnières-sur-Seine, France.
Educ ...
(de Prony brake
The Prony Brake is a simple device invented by Gaspard de Prony in 1821 to measure the torque produced by an engine. The term "brake horsepower" is one measurement of power derived from this method of measuring torque. (Power is calculated by mu ...
) in 1821.Bradley, Margaret. A career biography of Gaspard Clair Francois Marie Riche De Prony, bridge-builder, educator, and scientist. Mellen Press. 1998.
* Complex analysis
Complex analysis, traditionally known as the theory of functions of a complex variable, is the branch of mathematical analysis that investigates functions of complex numbers. It is helpful in many branches of mathematics, including algebra ...
and complex function theory by Augustin-Louis Cauchy
Baron Augustin-Louis Cauchy (, ; ; 21 August 178923 May 1857) was a French mathematician, engineer, and physicist who made pioneering contributions to several branches of mathematics, including mathematical analysis and continuum mechanics. H ...
, including Cauchy's integral theorem.
* Fourier analysis and Fourier transform
A Fourier transform (FT) is a mathematical transform that decomposes functions into frequency components, which are represented by the output of the transform as a function of frequency. Most commonly functions of time or space are transformed, ...
by Joseph Fourier in 1822.
* Electrometer by Jean Peltier.
* Foucault pendulum by Léon Foucault (who also developed and named the Gyroscope) in February 1851 in the Meridian of the Paris Observatory.
* Ocean thermal energy conversion in 1881 by Jacques-Arsène d'Arsonval (first OTEC plant in 1930 in Cuba by his student Georges Claude).
* Radioactivity by Henri Becquerel
Antoine Henri Becquerel (; 15 December 1852 – 25 August 1908) was a French engineer, physicist, Nobel laureate, and the first person to discover evidence of radioactivity. For work in this field he, along with Marie Skłodowska-Curie and Pi ...
in 1896.Henri Becquerel - Biographyon the nobel prize website * Theorical foundations and mathematical framework of
Special relativity
In physics, the special theory of relativity, or special relativity for short, is a scientific theory regarding the relationship between space and time. In Albert Einstein's original treatment, the theory is based on two postulates:
# The law ...
by Henri Poincaré
Jules Henri Poincaré ( S: stress final syllable ; 29 April 1854 – 17 July 1912) was a French mathematician, theoretical physicist, engineer, and philosopher of science. He is often described as a polymath, and in mathematics as "The ...
, before Albert Einstein
Albert Einstein ( ; ; 14 March 1879 – 18 April 1955) was a German-born theoretical physicist, widely acknowledged to be one of the greatest and most influential physicists of all time. Einstein is best known for developing the theor ...
used his work in 1905 and later.
* Integral imaging by Gabriel Lippmann on March 3, 1908.
* Darrieus wind turbine by Georges Jean Marie Darrieus in 1931.
* Optical pumping by Alfred Kastler in the early 1950s.
* The multiwire proportional chamber by Georges Charpak in 1968.
* Linear logic by Jean-Yves Girard in 1987.
Medicine and biology

Jean-Baptiste Lamarck
Jean-Baptiste Pierre Antoine de Monet, chevalier de Lamarck (1 August 1744 – 18 December 1829), often known simply as Lamarck (; ), was a French naturalist, biologist, academic, and soldier. He was an early proponent of the idea that biolog ...
in 1809. Long dismissed in favour of Darwinism
Darwinism is a theory of biological evolution developed by the English naturalist Charles Darwin (1809–1882) and others, stating that all species of organisms arise and develop through the natural selection of small, inherited variations that ...
, recent developments in the field of epigenetics
In biology, epigenetics is the study of stable phenotypic changes (known as ''marks'') that do not involve alterations in the DNA sequence. The Greek prefix '' epi-'' ( "over, outside of, around") in ''epigenetics'' implies features that are " ...
have led scientists to debate whether Lamarckism was, in fact, correct to an extent.
* Ligature of arteries in 1565 by Ambroise Paré.
* Blood transfusion
Blood transfusion is the process of transferring blood products into a person's circulation intravenously. Transfusions are used for various medical conditions to replace lost components of the blood. Early transfusions used whole blood, but m ...
by Jean-Baptiste Denys on June 15, 1667. and first modern transfusion by Émile Jeanbrau on October 16, 1914 (after the first non-direct transfusion performed on March 27, 1914, by the Belgian doctor Albert Hustin).
* Modern dentistry
Dentistry, also known as dental medicine and oral medicine, is the branch of medicine focused on the teeth, gums, and mouth. It consists of the study, diagnosis, prevention, management, and treatment of diseases, disorders, and conditions ...
by Pierre Fauchard (''father of modern dentistry'', early eighteenth century).
* Modern cataract surgery by Jacques Daviel in 1748 (even if early cataract surgery already existed in the antiquity).
* Discovery of osmosis
Osmosis (, ) is the spontaneous net movement or diffusion of solvent molecules through a selectively-permeable membrane from a region of high water potential (region of lower solute concentration) to a region of low water potential (region of ...
in 1748 by Jean-Antoine Nollet. The word "osmosis" descends from the words "endosmose" and "exosmose", which were coined by French physician René Joachim Henri Dutrochet (1776–1847) from the Greek words ένδον (''endon'' : within), έξο (''exo'' : outside), and ωσμος (''osmos'' : push, impulsion).
* The first lifesize obstetrical mannequin
A mannequin (also called a dummy, lay figure, or dress form) is a doll, often articulated, used by artists, tailors, dressmakers, window dressers and others, especially to display or fit clothing and show off different fabrics and textiles ...
, for teaching, by Angelique du Coudray
Angelique or Angélique may refer to:
* Angélique (given name), a French feminine name
Arts and entertainment Music
* Angélique (instrument), a string instrument of the lute family
* ''Angélique'', a 1927 opéra bouffe by Jacques Ibert
* ...
in the 1750s.
Angélique du Coudray
at the Dinner Party database, Brooklyn Museum. Retrieved October 24, 2007.
Mothers and Daughters of Invention: Notes for a Revised History of Technology
By
Autumn Stanley
Autumn Stanley (1933–2018) researched inventions by women and patents obtained by women in the United States. She is widely known for her book titled, ''Mothers and Daughters of Invention''.
Early life and education
Autumn Joy Stanley was born ...
, Page 234. Published 1995, Rutgers University Press. (at Google books)
* ''The King's Midwife : A History and Mystery of Madame du Coudray'', by Nina Rattner Gelbart, Berkeley : University of California Press, (1998). At Worldcat
* Stethoscope in 1816 by René Laennec at the Necker-Enfants Malades Hospital in
Paris
Paris () is the capital and most populous city of France, with an estimated population of 2,165,423 residents in 2019 in an area of more than 105 km² (41 sq mi), making it the 30th most densely populated city in the world in 2020. ...
.
* Medical Quinine
Quinine is a medication used to treat malaria and babesiosis. This includes the treatment of malaria due to '' Plasmodium falciparum'' that is resistant to chloroquine when artesunate is not available. While sometimes used for nocturnal leg ...
in 1820 by Joseph Bienaimé Caventou.
* Codeine first isolated in 1832 by Pierre Robiquet. La codéine: Pierre ROBIQUET (1780–1840) * Aspirin in 1853 by Charles Frédéric Gerhardt. *
Hypodermic needle
A hypodermic needle (from Greek ὑπο- (''hypo-'' = under), and δέρμα (''derma'' = skin)), one of a category of medical tools which enter the skin, called sharps, is a very thin, hollow tube with one sharp tip. It is commonly used w ...
in 1853 by Charles Pravaz.
* Blind experiment by Claude Bernard (nineteenth century).
* Discovery of Plasmodium and its role in malaria
Malaria is a mosquito-borne infectious disease that affects humans and other animals. Malaria causes symptoms that typically include fever, tiredness, vomiting, and headaches. In severe cases, it can cause jaundice, seizures, coma, or deat ...
by Charles Louis Alphonse Laveran
Charles Louis Alphonse Laveran (18 June 1845 – 18 May 1922) was a French physician who won the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1907 for his discoveries of parasitic protozoans as causative agents of infectious diseases such as malaria ...
on November 6, 1880.
* Incubator or Neonatal intensive care unit
A neonatal intensive care unit (NICU), also known as an intensive care nursery (ICN), is an intensive care unit (ICU) specializing in the care of ill or premature newborn infants. Neonatal refers to the first 28 days of life. Neonatal care, as k ...
in 1881 by Étienne Stéphane Tarnier. His student, Pierre-Constant Budin
Pierre-Constant Budin (; 9 November 1846 – 22 January 1907) was a French obstetrician who was a native of Enencourt-le-Sec, a village in northern France.
In 1876 he earned his medical degree in Paris, and in 1882 became chief obstetrician ...
, followed in Tarnier's footsteps, creating perinatology in the late 1890s.
* Germ theory of disease
The germ theory of disease is the currently accepted scientific theory for many diseases. It states that microorganisms known as pathogens or "germs" can lead to disease. These small organisms, too small to be seen without magnification, invade ...
by Louis Pasteur.
* Rabies vaccine by Louis Pasteur and Émile Roux
Pierre Paul Émile Roux FRS (17 December 18533 November 1933) was a French physician, bacteriologist and immunologist. Roux was one of the closest collaborators of Louis Pasteur (1822–1895), a co-founder of the Pasteur Institute, and respons ...
in 1885.
* Antibiotics
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the treatment and prevention ...
by Louis Pasteur and Jean Paul Vuillemin (by means of natural antibiosis; modern artificial antibiotics were developed later by the British Alexander Fleming).
* Mantoux test by Charles Mantoux
Charles Mantoux (; May 14, 1877, Paris – 1947) was a French physician and the developer of the eponymous serological test for tuberculosis.
He graduated from the University of Paris, where he studied under Broca. For health reasons, he relocate ...
in 1907.
* Tuberculosis vaccine by Albert Calmette and Camille Guérin in 1921 (BCG).
* Antipsychotics in 1952 by Henri Laborit (chlorpromazine).
* Healy, D. 2005. Psychiatric Drugs Explained. 4th Ed. Britain:Elsevier Limited. P. 8, 17.
*
*
* Discovery of the cause of Down syndrome (chromosome 21 trisomy) by Jérôme Lejeune in 1958-1959 (syndrome first described by Jean-Étienne Dominique Esquirol, Édouard Séguin and John Langdon Down)
* First hematopoietic stem cell transplantation, bone marrow transplant by Georges Mathé, a French oncologist, in 1959 on five Yugoslavian nuclear workers whose own marrow had been damaged by irradiation caused by a Criticality accident at the Vinča Nuclear Institute.
* Insulin pump in 1981 by Jacques Mirouze (first implantation) in Montpellier.Les lauréats des 7èmes Victoires de la Médecinesur le site Les victoires de la Médecine 2008. * Discovery of human immunodeficiency virus by Françoise Barré-Sinoussi and Luc Montagnier (1983). * Deep brain stimulation (DBS) by Alim-Louis Benabid in 1987. * Mifepristone, the abortion pill, by Étienne-Émile Baulieu in 1988.''Etienne-Emile Baulieu: monsieur «longue vie»''
dans ''Le Monde'' du 17 août 2007. * Hand transplantation on September 23, 1998, in Lyon, France, Lyon by a team assembled from different countries around the world including Jean-Michel Dubernard who, shortly thereafter, performed the first successful double hand transplant. * Remote surgery, Telesurgery by Jacques Marescaux and his team on 7 September 2001 across the Atlantic Ocean (New-York-Strasbourg, Lindbergh Operation). * Face transplant on November 27, 2005 by Dr Bernard Devauchelle. * CRISPR/Cas9 genome editing, gene editing by Emmanuelle Charpentier in 2012.
Transportation
 * taxicab, Taxi by Nicolas Sauvage in Paris in 1640.
* Steamboat by Denis Papin. A boat with the world's first internal combustion engine was developed in 1807 by fellow Frenchman
* taxicab, Taxi by Nicolas Sauvage in Paris in 1640.
* Steamboat by Denis Papin. A boat with the world's first internal combustion engine was developed in 1807 by fellow Frenchman Nicéphore Niépce
Joseph Nicéphore Niépce (; 7 March 1765 – 5 July 1833), commonly known or referred to simply as Nicéphore Niépce, was a French inventor, usually credited with the invention of photography. Niépce developed heliography, a technique he us ...
* Steam driven Car, Automobile by Nicolas-Joseph Cugnot in 1769.
* First working Motorcycle, the Michaux-Perreaux steam velocipede by Louis-Guillaume Perreaux patented in 1869.
* Hot Air Balloon (later, Aerostat and Airship) by Jean-François Pilâtre de Rozier, François Laurent d'Arlandes, the Montgolfier brothers and Jacques Charles (who also invented the first hydrogen-filled balloon).
* Parachute in the late 18th century by Louis-Sébastien Lenormand.Lynn White, Jr.: "The Invention of the Parachute", ''Technology and Culture'' 9(3), 462-467 (1968)JSTOR
/ref> * Compressed air vehicle and Pneumatic motor by Andraud and Tessie of Motay in Chaillot on July 9, 1840,The History of compressed air vehicles. (n.d.). Retrieved from improved by Louis Mékarski in 1843 in Nantes (see Mekarski system and Compressed air car). * In air travel : ** First glider to fly higher than its point of departure, by Jean-Marie Le Bris in 1856. ** First manned, powered, heavier-than-air flight of a significant distance on October 9, 1890, by Clément Ader. ** First aileron, built by Robert Esnault-Pelterie in 1904. Modern design of ailerons by Henri Farman.Origins of Control Surfaces
Aerospaceweb ** First aircraft design with the modern monoplane tractor configuration of aircraft by Louis Bleriot in 1908.transportationhistory.suite101.com/article.cfm/louis_bleriot Transportation History at Suite101.com. Retrieved 12 March 2008. * Injector by Henri Giffard in 1858 * History of the internal combustion engine, Internal combustion engine between 1859 and 1861 by Alphonse Beau de Rochas and Belgian-born Étienne Lenoir in Paris. * Submarine : The first submarine not relying on human power was the French ''French submarine Plongeur, Plongeur'' (meaning ''diver''), launched in 1863, and using compressed air at 180 Pound-force per square inch, psi (1241 Pascal (unit), kPa). * Bicycle in 1864 by Pierre Michaux and Pierre Lallement (endless power-transmitting chain invented by Jacques de Vaucanson in 1770 and applied to bicycles by J. F. Tretz).''New York Times''
Melinda Tuhis, "Bragging Rights to the Bicycle, All Thanks to a Frenchman," August 2, 1998
accessed July 18, 2010 * Gunpowder powered ornithopter by Gustave Trouvé in 1870 * First manned balloon mail during the Siege of Paris (1870–71), Siege of Paris (1871) * First Outboard motor, outboard motorboat by Gustave Trouvé around 1870, patented in May 1880 * Inflatable tyre (wheel), tyres for cars by Édouard Michelin (born 1859), Édouard Michelin in 1895 * Scooter (motorcycle), Scooter (1902) and Moped. * V8 engine by Léon Levavasseur in 1902 * Modern automobile Drum brake in 1902 by Louis Renault (industrialist), Louis Renault. * Helicopter : in 1907, the two first flying helicopters were experimented independently by Louis BreguetMunson, Kenneth. ''Helicopters and other Rotorcraft since 1907''. London: Blandford Publishing, 1968. and Paul Cornu.Leishman, Dr. J. Gordon, Technical Fellow of AHS International
"Paper."
''64th Annual Forum of the American Helicopter Society International, on the aerodynamic capability of Cornu's design * Seaplane by Gabriel Voisin in June 1905 (non-autonomous) and by Henri Fabre in 1910 (autonomous : ''Fabre Hydravion'').The Illustrated Encyclopedia of Aircraft (Part Work 1982-1985), 1985, Orbis Publishing * Ramjet by René Lorin in 1913. * The first helicopter to be powered by a gasturbine (Alouette II), in 1955 * Catalytic converter by Eugene Houdry in 1956. * Concorde by Aérospatiale and the British Aircraft Corporation (1969) * PSA HDi engine, HDI diesel engine in 1998 by PSA Peugeot Citroën.
Clothing
 * Bliaut in the 12th century.Boucher, François. ''20,000 Years of Fashion: The History of Costume and Personal Adornment'', Harry Abrams, 1966, pp. 164–172
* French hood in the early 16th century.
* Attifet in the 16th century.
* Jacquard loom, a mechanical loom, invented by Joseph Marie Jacquard in 1801, that simplifies the process of manufacturing textiles with complex patterns such as Brocade (fabric), brocade, damask, and matelasse.
* Denim Textile (French town of Nîmes, from which 'denim' ''de Nîmes'' gets its name)
* Improved, chain stitch, Sewing machine by Barthélemy Thimonnier in 1830.
* Modern Brassiere, bra by Herminie Cadolle in 1889.
* Little black dress by Coco Chanel in the 1920s,
* Polo shirt by René Lacoste in 1926.''Fashion Encyclopedia'', "Lacoste Sportswear" (2007).
* Bliaut in the 12th century.Boucher, François. ''20,000 Years of Fashion: The History of Costume and Personal Adornment'', Harry Abrams, 1966, pp. 164–172
* French hood in the early 16th century.
* Attifet in the 16th century.
* Jacquard loom, a mechanical loom, invented by Joseph Marie Jacquard in 1801, that simplifies the process of manufacturing textiles with complex patterns such as Brocade (fabric), brocade, damask, and matelasse.
* Denim Textile (French town of Nîmes, from which 'denim' ''de Nîmes'' gets its name)
* Improved, chain stitch, Sewing machine by Barthélemy Thimonnier in 1830.
* Modern Brassiere, bra by Herminie Cadolle in 1889.
* Little black dress by Coco Chanel in the 1920s,
* Polo shirt by René Lacoste in 1926.''Fashion Encyclopedia'', "Lacoste Sportswear" (2007)./ref>The Story of Lacoste. Retrieved from .Style & Design: Lacoste. ''Time'' Magazine, Winter 2004. Retrieved fro
''The Brand Channel'', Lacoste profile
. * Modern Bikini by Louis Réard in 1946. * classic modern pencil skirt by Christian Dior in the late 1940s. * A-line (clothing), A-line by Yves Saint Laurent (designer), Yves Saint Laurent in 1958 (term first used in 1955 by Christian Dior). * Modern Raincoat (not to confuse with the older British trench-coat) by Guy Cotten in 1960.Élodie Baërd, �
Guy Cotten, à l'épreuve du temps
», ''Figaro madame'', 4 août 2008
Food and cooking
 * Steam digester by Denis Papin in 1679.
* Cafetiere : Percolation (method used by Coffee percolator) by Jean-Baptiste de Belloy in 1800 and the French press (another method to make coffee).
*
* Steam digester by Denis Papin in 1679.
* Cafetiere : Percolation (method used by Coffee percolator) by Jean-Baptiste de Belloy in 1800 and the French press (another method to make coffee).
* Canning
Canning is a method of food preservation in which food is processed and sealed in an airtight container ( jars like Mason jars, and steel and tin cans). Canning provides a shelf life that typically ranges from one to five years, althoug ...
(see above in the chemistry section)
* Absorption refrigerator by Ferdinand Carré in 1858.
* Margarine by Hippolyte Mège-Mouriès in 1869 after the discovery of margaric acid by Michel Eugène Chevreul in 1813.
* Clementine in 1902 by Clément Rodier.
* Food processor by Pierre Verdun between 1963 and 1971.
* Crêpe (List of French dishes)
* Coq au vin
 * Champagne (wine), ChampagneJ. Robinson (ed) ''"The Oxford Companion to Wine"'' Third Edition pg 150–153 Oxford University Press 2006 and other French wines.
* 350 to 400 distinct types of French cheese : List of French cheeses
* BaguetteSteele, Ross. The French Way. 2nd edition. New York: McGraw-Hill, 2006.
* Cassoulet
* Foie gras
* Escargot
* Frog legs
* Ratatouille
* Camembert by Marie Harel
* Champagne (wine), ChampagneJ. Robinson (ed) ''"The Oxford Companion to Wine"'' Third Edition pg 150–153 Oxford University Press 2006 and other French wines.
* 350 to 400 distinct types of French cheese : List of French cheeses
* BaguetteSteele, Ross. The French Way. 2nd edition. New York: McGraw-Hill, 2006.
* Cassoulet
* Foie gras
* Escargot
* Frog legs
* Ratatouille
* Camembert by Marie Harel
Weapons and military
 * Bec de corbin, a popular medieval weapon.
* Motte-and-bailey, a form of castle.
*Kaufmann, J. E. and H. W. Kaufmann. (2004)
* Bec de corbin, a popular medieval weapon.
* Motte-and-bailey, a form of castle.
*Kaufmann, J. E. and H. W. Kaufmann. (2004) The Medieval Fortress: castles, forts and walled cities of the Middle Ages.
' Cambridge, US: Da Capo, p.33. . *Nicolle, David. (1984)
The Age of Charlemagne.
' Oxford: Osprey, p.109. . * The Pot-de-fer, a primitive cannon during the Hundred Years' War. * Culverin, ancestor of the musket.[www.etudes-touloises.com/articles/105/art7.pdf L'art de la guerre au XVIe siècle], Pascal THIEBAUT. * Flintlock by Marin le Bourgeoys in 1612. * Corvette, a small, maneuverable, lightly armed warship that appeared in the 1670s. * Bayonet (from French language, French ''baïonnette'')H. Blackmore, ''Hunting Weapons'', pg 50 * Modern Military uniform#Regimental dress, military uniform in the mid 17th century. * Floating battery, first used during the Great Siege of Gibraltar in September 1782. * Conscription#Invention of modern conscription, Mass conscription or Levée en masse during the
French Revolution
The French Revolution ( ) was a period of radical political and societal change in France that began with the Estates General of 1789 and ended with the formation of the French Consulate in November 1799. Many of its ideas are conside ...
.
* Corps by Napoleon in 1805. p.397
* Carabine à tige by Louis-Étienne de Thouvenin (improvement of an earlier invention by Henri-Gustave Delvigne) before 1844.''Rifles'' by David Westwood p.23/ref> * Minié rifle by Claude-Étienne Minié, first reliable (easy to load) muzzle-loading rifle in 1849. In the artillery, from 1859, the La Hitte system, La Hitte rifled guns were a considerable improvement over the previous smooth-bore guns which had been in use,''French Army 1870-71 Franco-Prussian War (1)'' by Stephen Shann p.37
/ref> able to shoot at 3,000 meters either regulars shells, ball-loaded shells or grapeshot. They appear to have been the first case of usage of rifled cannons on a battlefield. * First naval periscope in 1854 by Hippolyte Marié-Davy. * Canne de combat and Savate. * Épée, the modern derivative of the dueling sword, used for fencing. * Chassepot by Antoine Alphonse Chassepot in 1866. * smokeless powder, Smokeless gunpowder (modern nitrocellulose-based) : Poudre B by Paul Marie Eugène Vieille in 1884.Davis, Tenny L. ''The Chemistry of Powder & Explosives'' (1943) pages 289–292 It was first used to load the Lebel Model 1886 rifle (invented by Nicolas Lebel), making it the first military firearm to use smokeless powder ammunition. It is also the first rifle to use full metal jacket bullets as its standard ammunition. * First Air force in 1910. * Sonar, first ultrasonic submarine detector using an electrostatic method (and first practical military sonar) in 1916-1917 by Paul Langevin (with Constantin Chilowsky). * Tanks : developed at the same time (1915-1916) in France and in Great Britain. France was the second country to use tanks on the battlefield (after Great Britain). in 1916, the first practical light tank, the Renault FT with the first full 360° rotation turret became, for armour historian Steven Zaloga "the world's first modern tank".
Communication and computers
 * Optical Telegraph by Claude Chappe in 1792.Beyer, Rick, ''The Greatest Stories Never Told'', A&E Television Networks / The History Channel, p. 60French source
* Optical Telegraph by Claude Chappe in 1792.Beyer, Rick, ''The Greatest Stories Never Told'', A&E Television Networks / The History Channel, p. 60French sourceTour du télégraphe Chappe
* Modern pencil by Nicolas-Jacques Conté in 1795.L.-Séb. Le Normand et J.-G.-V. de Moléon, ''Annales de l'industrie nationale et étrangère, ou Mercure technologique'', Bachelier, Paris, 1821 * Paper machine by Louis-Nicolas Robert in 1799.Larousse Encyclopaedia - les frères Robert, Mécaniciens français.
/ref> * Fresnel lens by Augustin-Jean FresnelLighthouses, Illuminants, Lenses Engineering and Augustin Fresnel, An Historical Bibliography, United States Coast Guard.
/ref> * Jean-François Champollion first deciphered the Rosetta Stone (1822) : modern understanding of Egyptian hieroglyphs * Braille in 1825 by Louis Braille, a blind Frenchman: first digital form of writing. * Pencil sharpener by Bernard Lassimone in 1828. Therry des Estwaux created an improved mechanical sharpener in 1847. * Baudot code by Émile Baudot in 1870 and a multiplexed printing telegraph system that used his code and allowed multiple transmissions over a single line. * Coherer by Édouard Branly around 1890. * Belinograph (Wirephoto) by Édouard Belin in 1913. * The HSL and HSV, HSL color space was invented in 1938 by Georges Valensi * Bic Cristal in 1949.''Phaidon Design Classics- Volume 2'', 2006 Phaidon Press Ltd. Masterpieces''
- The Museum of Modern Art New York, April 8–September 27, 2004. * Bézier curves by Paul de Casteljau in 1959. * Computer-aided manufacturing by Pierre Bézier in 1971 as an engineer at Renault. * Micral, earliest commercial, non-kit personal computer based on a microprocessor, by André Truong Trong Thi and François Gernelle in June 1972. * * Roy A. Allan ''A History of the Personal Computer'' (Alan Publishing, 2001) Chapter 4 (PDF: https://archive.org/download/A_History_of_the_Personal_Computer/eBook04.pdf) * Datagrams and CYCLADES in 1972-1973 by Louis Pouzin (which inspired Bob Kahn and Vinton Cerf when they invented the TCP/IP several years later). * Smart Card by Roland Moreno in 1974 after the automated chip card. * Minitel, a dial up, Videotex system, launched in July 1980, and nationally available from 1982. * Camera phone by Philippe Kahn in 1997. * Several Programming languages (non-exhaustive list) : ** Prolog (Logic programming) by a group around Alain Colmerauer in 1972 in Marseille. ** LSE (programming language), LSE, , a French, pedagogical, programming language designed in the 1970s at Supélec. ** Ada (programming language), Ada (multi-paradigm programming language, multi-paradigm) by Jean Ichbiah (who also created LIS (programming language), LIS and Green) in 1980. "Ada 83 designer Jean Ichbiah dies", Ada-Europe, 2007, webpage:
AdaE-Jobit
. ** Caml (OCaml by Xavier Leroy, Damien Doligez) developed at INRIA and formerly at École Normale Supérieure, ENS since 1985. ** Eiffel (programming language), Eiffel (Object-oriented programming, object-oriented) by Bertrand Meyer in 1986. ** STOS BASIC on the Atari ST in 1988 and AMOS BASIC on the Amiga in 1990 by François Lionet and Constantin Sotiropoulos (dialects of BASIC programming language, BASIC). * Several Computer keyboard, keyboards : ** AZERTY in the last decade of the 19th century. ** FITALY by Jean Ichbiah in 1996. ** Keyboard layout#BÉPO, BÉPO since 2003.
Technology
Édouard-Léon Scott de Martinville earliest sound recording device.Sports
Paris
Paris () is the capital and most populous city of France, with an estimated population of 2,165,423 residents in 2019 in an area of more than 105 km² (41 sq mi), making it the 30th most densely populated city in the world in 2020. ...
. The first road bicycle racing, cycle race covering a distance between two cities was Paris–Rouen (cycle race), Paris–Rouen (see History of cycling).
* FIFA World Cup by Jules Rimet, FIFA former president.
* UEFA Euro Cup by Henri Delaunay.
* Summer Olympic Games by Pierre de Coubertin.
* International Olympic Committee by Pierre de Coubertin on 23 June 1894.Pierre de Coubertin. ''The Olympic Idea''. Discourses and Essays. Editions Internationales Olympiques, Lausanne, 1970.
* On 22 July 1894 the newspaper ''Le Petit Journal (newspaper), Le Petit Journal'' organised the world's first competitive motor race from Paris–Rouen (motor race), Paris to Rouen. The first finisher was Count Jules-Albert de Dion but his steamer was ineligible, so the 'official' victory was awarded to Albert Lemaître driving his 3 hp petrol engined Peugeot.
* Pétanque in 1907.
* Triathlon in the 1920s near Paris (Joinville-le-Pont, Meulan and Poissy).
* The Aqua-lung, first Scuba Set (in open-circuit) by Emile Gagnan and Jacques-Yves Cousteau in 1943.
* Parkour in the 1980s by the future Yamakasi, especially David Belle.
* Flyboard in 2012 by Franky Zapata.Zapata's outrageous, US$6,600 Flyboard - Aquaman meets Iron Mangizmag.com. Retrieved: 14 July 2016. Another version, the Flyboard Air, an air-propelled hoverboard,Flyboard Air: Franky Zapata develops his own jet-powered flying hoverboard that actually works
International Business Times. Retrieved: 14 July 2016. achieved a Guinness World Record for farthest flight by hoverboard in April 2016. * Kitesurf aka flysurf in the 1990s by Manu Bertin and ski mountain derivatives * Wingsuit in the 1990s by Patrick de Gayardon * Vendée Globe since 1989 by Philippe Jeantot the first round-the-world single-handed yacht race, sailed non-stop and without assistance * Paris–Dakar Rally since 1978 by Thierry Sabine
Trophée Jules Verne
since 1985 by Yves Le Cornec the fastest circumnavigation of the world (under 80 days) by any type of sailing yacht with no restrictions on the size of the crew * 24 Heures du Mans translated 24 Hours Le Mans since 1923 the world's oldest active sports car race in endurance racing * Fédération Internationale de l'Automobile in 1904; translated as the International Automobile Federation.
Miscellaneous
* Escapement#Detent escapement, Detent escapement by Pierre Le Roy in 1748.''Encyclopedia of time'' Samuel L. Macey p.348/ref> * Carcel burner in 1800. * developments of Battery (electricity), battery ** Dry cell battery by Gaston Planté in 1859 (first practical storage lead-acid battery) (2001): ''Understanding Batteries''. Royal Society of Chemistry. ** in 1866, Georges Leclanché patented the carbon-zinc wet cell battery called the Leclanché cell.''Practical Electricity'' by W. E. Ayrton and T. Mather, published by Cassell and Company, London, 1911, pp 188-193 * Interchangeable parts by Honoré Blanc. * Binoculars (using roof prisms) in 1870 by Achille Victor Emile Daubresse.photodigital.net
nbsp;— rec.photo.equipment.misc Discussion: Achille Victor Emile Daubresse, forgotten prism inventor * Artificial Cement by Louis Vicat. * Guy Coriono, ''250 ans de l'École des Ponts et Chaussées en cent portraits'', Presses de l'école nationale des Ponts et Chaussées, Paris, 1997, 222 p. * Antoine Picon, ''L'art de l'Ingénieur. Constructeur, entrepreneur, inventeur'', éditions du Centre Pompidou, Paris, 1997, 598 p. * Hairdryer in 1879 by Alexandre Godefroy. *Modern Dry cleaning in 1855 by Jean Baptiste Jolly. * Reinforced concrete by Joseph Monier in 1849 and patented in 1867. * Loppers by Bertrand de Molleville. * Ball bearing by Jules Suriray, a Parisian bicycle mechanic, on 3 August 1869.Bicycle History, Chronology of the Growth of Bicycling and the Development of Bicycle Technology by David Mozer
/ref> * Coronagraph by Bernard Lyot in 1930. * Stapler
See also
*List of Dutch inventions and discoveries *List of German inventions and discoveries *List of Indian inventions and discoveries *List of Irish inventions and discoveries *List of Italian inventions *Scottish inventions and discoveries *List of Swedish inventions *List of Welsh inventors *List of Portuguese inventions and discoveries *Science in the Middle Ages *Science in the Age of EnlightenmentReferences
{{DEFAULTSORT:French Inventions And Discoveries France history-related lists, inventions and discoveries French inventions, Lists of inventions or discoveries History of science and technology by country