Free France (french: France Libre) was a political entity that claimed to be the legitimate government of
France following the dissolution of the
Third Republic. Led by French general , Free France was established as a
government-in-exile
A government in exile (abbreviated as GiE) is a political group that claims to be a country or semi-sovereign state's legitimate government, but is unable to exercise legal power and instead resides in a foreign country. Governments in exile u ...
in London in June 1940 after the
Fall of France
The Battle of France (french: bataille de France) (10 May – 25 June 1940), also known as the Western Campaign ('), the French Campaign (german: Frankreichfeldzug, ) and the Fall of France, was the German invasion of France during the Second Wor ...
during
World War II and fought the Axis as an
Allied nation with its Free French Forces (). Free France also supported the
resistance in
Nazi-occupied France
The Military Administration in France (german: Militärverwaltung in Frankreich; french: Occupation de la France par l'Allemagne) was an interim occupation authority established by Nazi Germany during World War II to administer the occupied z ...
, known as the
French Forces of the Interior
The French Forces of the Interior (french: Forces françaises de l'Intérieur) were French resistance fighters in the later stages of World War II. Charles de Gaulle used it as a formal name for the resistance fighters. The change in designation ...
, and gained strategic footholds in several
French colonies in Africa.
Following the defeat of the Third Republic by
Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany (lit. "National Socialist State"), ' (lit. "Nazi State") for short; also ' (lit. "National Socialist Germany") (officially known as the German Reich from 1933 until 1943, and the Greater German Reich from 1943 to 1945) was ...
, Marshal
Philippe Pétain
Henri Philippe Benoni Omer Pétain (24 April 1856 – 23 July 1951), commonly known as Philippe Pétain (, ) or Marshal Pétain (french: Maréchal Pétain), was a French general who attained the position of Marshal of France at the end of Worl ...
led efforts to
negotiate an armistice and established a German puppet state known as
Vichy France
Vichy France (french: Régime de Vichy; 10 July 1940 – 9 August 1944), officially the French State ('), was the fascist French state headed by Marshal Philippe Pétain during World War II. Officially independent, but with half of its ter ...
. Opposed to the idea of an armistice, de Gaulle fled to Britain, and from there broadcast the
Appeal of 18 June
The Appeal of 18 June (french: L'Appel du 18 juin) was the first speech made by Charles de Gaulle after his arrival in London in 1940 following the Battle of France. Broadcast to Vichy France by the radio services of the British Broadcasting Cor ...
() exhorting the French people to resist the Nazis and join the Free French Forces. On 27 October 1940, the
Empire Defense Council
The Empire Defense Council (also called Council of Defense of the Empire, from french: Conseil de défense de l'Empire) was the embodiment of Free France which constituted the government from 1940 to 1941. Subsequently, this role was assumed ...
()—later the
French National Committee
The French National Committee (french: Comité national français, CNF) was the coordinating body created by General Charles de Gaulle which acted as the government in exile of Free France from 1941 to 1943. The committee was the successor ...
( or CNF)—formed to govern French territories in central Africa, Asia, and Oceania that had heeded the 18 June call.
Initially, with the exception of French possessions in the Pacific,
India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the so ...
, and
Equatorial Africa
Equatorial Africa is an ambiguous term that sometimes is used to refer either to the equatorial region of Sub-Saharan Africa traversed by the Equator, more broadly to tropical Africa or in a biological and geo-environmental sense to the intra-tr ...
,
[August–September 1940] all the territories of the French colonial empire rejected 's appeal and reaffirmed their loyalty to Marshall Pétain and the Vichy government. It was only progressively, often with the decisive military intervention of the Allies, that Free France took over more Vichy possessions, securing the majority of colonies by
November 1942.
The Free French fought both Axis and
Vichy
Vichy (, ; ; oc, Vichèi, link=no, ) is a city in the Allier department in the Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes region of central France, in the historic province of Bourbonnais.
It is a spa and resort town and in World War II was the capital of Vich ...
troops and served in almost every major campaign, from the Middle East to
Indochina
Mainland Southeast Asia, also known as the Indochinese Peninsula or Indochina, is the continental portion of Southeast Asia. It lies east of the Indian subcontinent and south of Mainland China and is bordered by the Indian Ocean to the west an ...
and
North Africa
North Africa, or Northern Africa is a region encompassing the northern portion of the African continent. There is no singularly accepted scope for the region, and it is sometimes defined as stretching from the Atlantic shores of Mauritania in ...
. The
Free French Navy
The Free French Naval Forces (french: Forces Navales Françaises Libres, or FNFL) were the naval arm of the Free French Forces during the Second World War. They were commanded by Admiral Émile Muselier.
History
In the wake of the Armistice ...
operated as an auxiliary force to the
Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the United Kingdom's naval warfare force. Although warships were used by English and Scottish kings from the early medieval period, the first major maritime engagements were fought in the Hundred Years' War against ...
and, in the North Atlantic, to the
Royal Canadian Navy
The Royal Canadian Navy (RCN; french: Marine royale canadienne, ''MRC'') is the naval force of Canada. The RCN is one of three environmental commands within the Canadian Armed Forces. As of 2021, the RCN operates 12 frigates, four attack submar ...
. Free French units also served in the
Royal Air Force
The Royal Air Force (RAF) is the United Kingdom's air and space force. It was formed towards the end of the First World War on 1 April 1918, becoming the first independent air force in the world, by regrouping the Royal Flying Corps (RFC) a ...
,
Soviet Air Force
The Soviet Air Forces ( rus, Военно-воздушные силы, r=Voyenno-vozdushnyye sily, VVS; literally "Military Air Forces") were one of the air forces of the Soviet Union. The other was the Soviet Air Defence Forces. The Air Forces ...
, and
British SAS, before larger commands were established directly under the control of the government-in-exile. On 13 July 1942, "Free France" was officially renamed Fighting France () to mark the struggle against the Axis both externally and within occupied France.
From a legal perspective, exile officially ended after the reconquest of North Africa since it allowed the Free French government to relocate from
London
London is the capital and largest city of England and the United Kingdom, with a population of just under 9 million. It stands on the River Thames in south-east England at the head of a estuary down to the North Sea, and has been a major s ...
to
Algiers
Algiers ( ; ar, الجزائر, al-Jazāʾir; ber, Dzayer, script=Latn; french: Alger, ) is the capital and largest city of Algeria. The city's population at the 2008 Census was 2,988,145Census 14 April 2008: Office National des Statistiques d ...
.
[Because ]French Algeria
French Algeria (french: Alger to 1839, then afterwards; unofficially , ar, الجزائر المستعمرة), also known as Colonial Algeria, was the period of French colonisation of Algeria. French rule in the region began in 1830 with the ...
was long considered part of Metropolitan France
Metropolitan France (french: France métropolitaine or ''la Métropole''), also known as European France (french: Territoire européen de la France) is the area of France which is geographically in Europe. This collective name for the Europea ...
by the 1940s, the Free French government once operating there considered itself to be physically seated within France proper, to the same extent as if it were located in European France, and not a government-in-exile. From there, the
French Committee of National Liberation
The French Committee of National Liberation (french: Comité français de Libération nationale) was a provisional government of Free France formed by the French generals Henri Giraud and Charles de Gaulle to provide united leadership, organ ...
(, CFLN) was formed as the provisional government of all French. The government returned to
Paris
Paris () is the capital and most populous city of France, with an estimated population of 2,165,423 residents in 2019 in an area of more than 105 km² (41 sq mi), making it the 30th most densely populated city in the world in 2020. S ...
following
its liberation by the
2nd Armoured Free French Division and Resistance forces on 25 August 1944, ushering in the
Provisional Government of the French Republic
The Provisional Government of the French Republic (PGFR; french: Gouvernement provisoire de la République française (''GPRF'')) was the provisional government of Free France between 3 June 1944 and 27 October 1946, following the liberation ...
( or GPRF). The provisional government ruled France until the end of the war and afterwards to 1946, when the
Fourth Republic was established, thus ending the series of interim regimes that had succeeded the
Third Republic after its fall in 1940.
On 1 August 1943, formally united with the Free French Forces to form the
French Liberation Army
__NOTOC__
The French Liberation Army (french: Armée française de la Libération or AFL) was the reunified French Army that arose from the merging of the Armée d'Afrique with the prior Free French Forces (french: Forces françaises libres, l ...
. By mid-1944, the forces of this army numbered more than 400,000, and they participated in the
Normandy landings
The Normandy landings were the landing operations and associated airborne operations on Tuesday, 6 June 1944 of the Allied invasion of Normandy in Operation Overlord during World War II. Codenamed Operation Neptune and often referred to as ...
and the
invasion of southern France, eventually leading the drive on Paris. Soon they were fighting in Alsace, the Alps and Brittany. By the end of the war, they were 1,300,000 strong—the fourth-largest Allied army in Europe—and took part in the Allied
advance through France and
invasion of Germany. The Free French government re-established a
provisional republic after the
liberation, preparing the ground for the
Fourth Republic in 1946.
Definition

Historically, an individual became "Free French" by enlisting in the military units organised by the CFN or by employment by the civilian arm of the Committee. On 1 August 1943 after the merger of CFN and representatives of the former Vichy regime in North Africa to form the CFLN earlier in June, the FFF and the Army of Africa (constituting a major part of the Vichy regular forces allowed by the 1940 armistice) were merged to form the
French Liberation Army
__NOTOC__
The French Liberation Army (french: Armée française de la Libération or AFL) was the reunified French Army that arose from the merging of the Armée d'Afrique with the prior Free French Forces (french: Forces françaises libres, l ...
, , and all subsequent enlistments were in this combined force.
In many sources, Free French describes any French individual or unit that fought against
Axis
An axis (plural ''axes'') is an imaginary line around which an object rotates or is symmetrical. Axis may also refer to:
Mathematics
* Axis of rotation: see rotation around a fixed axis
*Axis (mathematics), a designator for a Cartesian-coordinate ...
forces after the June 1940 armistice. Postwar, to settle disputes over the Free French heritage, the French government issued an official definition of the term. Under this "ministerial instruction of July 1953" (), only those who served with the
Allies after the Franco-German armistice in 1940 and before 1 August 1943 may correctly be called "Free French".
History
Prelude

On 10 May 1940,
Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany (lit. "National Socialist State"), ' (lit. "Nazi State") for short; also ' (lit. "National Socialist Germany") (officially known as the German Reich from 1933 until 1943, and the Greater German Reich from 1943 to 1945) was ...
invaded France and the
Low Countries
The term Low Countries, also known as the Low Lands ( nl, de Lage Landen, french: les Pays-Bas, lb, déi Niddereg Lännereien) and historically called the Netherlands ( nl, de Nederlanden), Flanders, or Belgica, is a coastal lowland region in N ...
, rapidly defeating the Dutch and Belgians, while armoured units attacking through
the Ardennes
The Ardennes (french: Ardenne ; nl, Ardennen ; german: Ardennen; wa, Årdene ; lb, Ardennen ), also known as the Ardennes Forest or Forest of Ardennes, is a region of extensive forests, rough terrain, rolling hills and ridges primarily in B ...
cut off the Franco-British strike force in Belgium. By the end of May, the British and French northern armies were trapped in a series of pockets, including
Dunkirk
Dunkirk (french: Dunkerque ; vls, label=French Flemish, Duunkerke; nl, Duinkerke(n) ; , ;) is a commune in the department of Nord in northern France.[Calais, ]Boulogne
Boulogne-sur-Mer (; pcd, Boulonne-su-Mér; nl, Bonen; la, Gesoriacum or ''Bononia''), often called just Boulogne (, ), is a coastal city in Northern France. It is a sub-prefecture of the department of Pas-de-Calais. Boulogne lies on the ...
, Saint-Valery-en-Caux
Saint-Valery-en-Caux (, literally ''Saint-Valery in Caux'') is a commune in the Seine-Maritime department in the Normandy region in northern France.
The addition of an acute accent on the "e" (Valéry) is incorrect.
Geography
The town is locat ...
and Lille
Lille ( , ; nl, Rijsel ; pcd, Lile; vls, Rysel) is a city in the northern part of France, in French Flanders. On the river Deûle, near France's border with Belgium, it is the capital of the Hauts-de-France region, the prefecture of the No ...
. The Dunkirk evacuation
The Dunkirk evacuation, codenamed Operation Dynamo and also known as the Miracle of Dunkirk, or just Dunkirk, was the evacuation of more than 338,000 Allied soldiers during the Second World War from the beaches and harbour of Dunkirk, in the n ...
was only made possible by the resistance of these troops, particularly the French army divisions at Lille.
From 27 May to 4 June, over 200,000 members of the British Expeditionary Force and 140,000 French troops were evacuated from Dunkirk. Neither side viewed this as the end of the battle; French evacuees were quickly returned to France and many fought in the June battles. After being evacuated from Dunkirk, Alan Brooke
Field Marshal Alan Francis Brooke, 1st Viscount Alanbrooke, (23 July 1883 – 17 June 1963), was a senior officer of the British Army. He was Chief of the Imperial General Staff (CIGS), the professional head of the British Army, during the Sec ...
landed in Cherbourg
Cherbourg (; , , ), nrf, Chèrbourg, ) is a former commune and subprefecture located at the northern end of the Cotentin peninsula in the northwestern French department of Manche. It was merged into the commune of Cherbourg-Octeville on 28 Febr ...
on 2 June to reform the BEF, along with the 1st Canadian Division
The 1st Canadian Division (French: ''1re Division du Canada'' ) is a joint operational command and control formation based at CFB Kingston, and falls under Canadian Joint Operations Command. It is a high-readiness unit, able to move on very short ...
, the only remaining armoured unit in Britain. Contrary to what is often assumed, French morale was higher in June than May and they easily repulsed an attack in the south by Fascist Italy. A defensive line was re-established along the Somme but much of the armour was lost in Northern France; they were also crippled by shortages of aircraft, the vast majority incurred when airfields were over-run, rather than air combat.
On 1 June, Charles was promoted to brigadier general; on 5 June, Prime Minister Paul Reynaud
Paul Reynaud (; 15 October 1878 – 21 September 1966) was a French politician and lawyer prominent in the interwar period, noted for his stances on economic liberalism and militant opposition to Germany.
Reynaud opposed the Munich Agreement of ...
appointed him Under Secretary of State for Defence, a junior post in the French cabinet. was known for his willingness to challenge accepted ideas; in 1912, he asked to be posted to Pétain's regiment, whose maxim 'Firepower kills' was then in stark contrast to the prevailing orthodoxy. He was also a long-time advocate of the modern armoured warfare
Armoured warfare or armored warfare (mechanized forces, armoured forces or armored forces) (American English; see spelling differences), is the use of armored fighting vehicles in modern warfare. It is a major component of modern methods of ...
ideas applied by the Wehrmacht, and commanded the 4th Armoured Division at the Battle of Montcornet
The Battle of Montcornet, on 17 May 1940 took place during the Battle of France. The French 4e Division cuirassée (Colonel Charles de Gaulle), attacked the German-held village of Montcornet with over 200 tanks. The French drove off the Germans b ...
. However, he was not personally popular; significantly, none of his immediate military subordinates joined him in 1940.
The new French commander Maxime Weygand
Maxime Weygand (; 21 January 1867 – 28 January 1965) was a French military commander in World War I and World War II.
Born in Belgium, Weygand was raised in France and educated at the Saint-Cyr military academy in Paris. After graduating in ...
was 73 years old and like Pétain, an Anglophobe who viewed Dunkirk as another example of Britain's unreliability as an ally; de Gaulle later recounted he 'gave up hope' when the Germans renewed their attack on 8 June and demanded an immediate Armistice. was one of a small group of government ministers who favoured continued resistance and Reynaud sent him to London in order to negotiate the proposed union between France and Britain. When this plan collapsed, he resigned on 16 June and Pétain became President of the Council.Bordeaux
Bordeaux ( , ; Gascon oc, Bordèu ; eu, Bordele; it, Bordò; es, Burdeos) is a port city on the river Garonne in the Gironde department, Southwestern France. It is the capital of the Nouvelle-Aquitaine region, as well as the prefecture ...
on 17th but returned to London the same day when he realised Pétain had already agreed an armistice with the Axis Powers
The Axis powers, ; it, Potenze dell'Asse ; ja, 枢軸国 ''Sūjikukoku'', group=nb originally called the Rome–Berlin Axis, was a military coalition that initiated World War II and fought against the Allies. Its principal members were N ...
.
De Gaulle rallies the Free French
 On 18 June, General spoke to the
On 18 June, General spoke to the French people
The French people (french: Français) are an ethnic group and nation primarily located in Western Europe that share a common French culture, history, and language, identified with the country of France.
The French people, especially the nat ...
via BBC radio
BBC Radio is an operational business division and service of the British Broadcasting Corporation (which has operated in the United Kingdom under the terms of a royal charter since 1927). The service provides national radio stations covering ...
, urging French soldiers, sailors and airmen to join in the fight against the Nazi
Nazism ( ; german: Nazismus), the common name in English for National Socialism (german: Nationalsozialismus, ), is the far-right totalitarian political ideology and practices associated with Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party (NSDAP) in Naz ...
s:
:"France is not alone! She is not alone! She has a great empire behind her! Together with the British Empire
The British Empire was composed of the dominions, colonies, protectorates, mandates, and other territories ruled or administered by the United Kingdom and its predecessor states. It began with the overseas possessions and trading posts esta ...
, she can form a bloc that controls the seas and continue the struggle. She may, like England, draw upon the limitless industrial resources of the United States".
Some members of the British Cabinet
The Cabinet of the United Kingdom is the senior decision-making body of His Majesty's Government. A committee of the Privy Council, it is chaired by the prime minister and its members include secretaries of state and other senior ministers.
...
had reservations about 's speech, fearing that such a broadcast could provoke the Pétain government into handing the French fleet over to the Nazis, but British Prime Minister Winston Churchill
Sir Winston Leonard Spencer Churchill (30 November 187424 January 1965) was a British statesman, soldier, and writer who served as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom twice, from 1940 to 1945 during the Second World War, and again from 1 ...
, despite his own concerns, agreed to the broadcast.
In France, 's "Appeal of 18 June" () was not widely heard that day but, together with his BBC broadcasts in subsequent days and his later communications, came to be widely remembered throughout France and its colonial empire as the voice of national honour and freedom.
Armistice
On 19 June, again broadcast to the French nation saying that in France, "all forms of authority had disappeared" and since its government had "fallen under the bondage of the enemy and all our institutions have ceased to function", that it was "the clear duty" of all French servicemen to fight on.
This would form the essential legal basis of 's government in exile
A government in exile (abbreviated as GiE) is a political group that claims to be a country or semi-sovereign state's legitimate government, but is unable to exercise legal power and instead resides in a foreign country. Governments in exile u ...
, that the armistice soon to be signed with the Nazis was not merely dishonourable but illegal, and that in signing it, the French government would itself be committing treason. On the other hand, if Vichy was the legal French government as some such as Julian T. Jackson have argued, and his followers were revolutionaries, unlike the Dutch
Dutch commonly refers to:
* Something of, from, or related to the Netherlands
* Dutch people ()
* Dutch language ()
Dutch may also refer to:
Places
* Dutch, West Virginia, a community in the United States
* Pennsylvania Dutch Country
People ...
, Belgian, and other governments in exile
A government in exile (abbreviated as GiE) is a political group that claims to be a country or semi-sovereign state's legitimate government, but is unable to exercise legal power and instead resides in a foreign country. Governments in exile u ...
in London. A third option might be that neither considered that a fully free, legitimate, sovereign, and independent successor state to the Third Republic existed following the Armistice, as both Free France and Vichy France refrained from making that implicit claim by studiously avoiding using the word "republic" when referring to themselves, even though republicanism
Republicanism is a political ideology centered on citizenship in a state organized as a republic. Historically, it emphasises the idea of self-rule and ranges from the rule of a representative minority or oligarchy to popular sovereignty. It ...
had been a core ideological value and central tenet of the French state ever since the French Revolution
The French Revolution ( ) was a period of radical political and societal change in France that began with the Estates General of 1789 and ended with the formation of the French Consulate in November 1799. Many of its ideas are consider ...
—and especially since the Franco-Prussian War. In Vichy's case those reasons were compounded with ideas of a about stamping out France's republican heritage.
On 22 June 1940, Marshal Pétain signed an armistice with Germany
The Armistice of 11 November 1918 was the armistice signed at Le Francport near Compiègne that ended fighting on land, sea, and air in World War I between the Entente and their last remaining opponent, Germany. Previous armistices ...
, followed by a similar one with Italy on 24 June; both of these came into force on 25 June. After a parliamentary vote on 10 July, Pétain became the leader of the newly established authoritarian regime known as Vichy France
Vichy France (french: Régime de Vichy; 10 July 1940 – 9 August 1944), officially the French State ('), was the fascist French state headed by Marshal Philippe Pétain during World War II. Officially independent, but with half of its ter ...
, the town of Vichy
Vichy (, ; ; oc, Vichèi, link=no, ) is a city in the Allier department in the Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes region of central France, in the historic province of Bourbonnais.
It is a spa and resort town and in World War II was the capital of Vich ...
being the seat of government. was tried ''in absentia'' in Vichy France and sentenced to death for treason. He, on the other hand, regarded himself as the last remaining member of the legitimate Reynaud government and considered Pétain's assumption of power to be an unconstitutional coup d'état.
Beginnings of the Free French forces
 Despite 's call to continue the struggle, few French forces initially pledged their support. By the end of July 1940, only about 7,000 soldiers had joined the Free French Army in England.
Despite 's call to continue the struggle, few French forces initially pledged their support. By the end of July 1940, only about 7,000 soldiers had joined the Free French Army in England.[Axelrod & Kingston, p. 362.] Three-quarters of French servicemen in Britain requested repatriation.[Hastings, Max, p.80]
France was bitterly divided by the conflict. Frenchmen everywhere were forced to choose sides, and often deeply resented those who had made a different choice.[Hastings, Max, p.126] One French admiral, René-Émile Godfroy
René-Émile Godfroy (10 January 1885 – 16 January 1981) was a French admiral, commander of the Force X at the outbreak of the Second World War. He was interned with his command at Alexandria until 1943, and then retired on suspicion of favou ...
, voiced the opinion of many of those who decided not to join the Free French forces, when in June 1940, he explained to the exasperated British why he would not order his ships from their Alexandria harbour to join :
:"For us Frenchmen, the fact is that a government still exists in France, a government supported by a Parliament established in non-occupied territory and which in consequence cannot be considered irregular or deposed. The establishment elsewhere of another government, and all support for this other government would clearly be rebellion."French domains of St Helena
, photo = Longwood House le 12 janvier 2008.jpg
, photo_caption = Napoleon's House (Longwood House)
, location = Saint Helena, Saint Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha
, governing_body = Ministry for Europe and Foreign Affairs, Governmen ...
(on 23 June at the initiative of Georges Colin, honorary consul of the domains) and the Franco-British ruled New Hebrides
New Hebrides, officially the New Hebrides Condominium (french: link=no, Condominium des Nouvelles-Hébrides, "Condominium of the New Hebrides") and named after the Hebrides Scottish archipelago, was the colonial name for the island group ...
condominium in the Pacific (on 20 July) answered 's call to arms. It was not until late August that Free France would gain significant support in French Equatorial Africa
French Equatorial Africa (french: link=no, Afrique-Équatoriale française), or the AEF, was the federation of French colonial possessions in Equatorial Africa, extending northwards from the Congo River into the Sahel, and comprising what ar ...
.
Unlike the troops at Dunkirk or naval forces at sea, relatively few members of the French Air Force
The French Air and Space Force (AAE) (french: Armée de l'air et de l'espace, ) is the air and space force of the French Armed Forces. It was the first military aviation force in history, formed in 1909 as the , a service arm of the French Army ...
had the means or opportunity to escape. Like all military personnel trapped on the mainland, they were functionally subject to the Pétain government: "French authorities made it clear that those who acted on their own initiative would be classed as deserters, and guards were placed to thwart efforts to get on board ships." In the summer of 1940, around a dozen pilots made it to England and volunteered for the RAF to help fight the Luftwaffe
The ''Luftwaffe'' () was the aerial-warfare branch of the German '' Wehrmacht'' before and during World War II. Germany's military air arms during World War I, the ''Luftstreitkräfte'' of the Imperial Army and the '' Marine-Fliegera ...
.[History Learning Site](_blank)
. Retrieved October 2012 Many more, however, made their way through long and circuitous routes to French territories overseas, eventually regrouping as the Free French Air Force
The Free French Air Forces (french: Forces Aériennes Françaises Libres, FAFL) were the air arm of the Free French Forces in the Second World War, created by Charles de Gaulle in 1940. The designation ceased to exist in 1943 when the Free Frenc ...
.
The French Navy
The French Navy (french: Marine nationale, lit=National Navy), informally , is the maritime arm of the French Armed Forces and one of the five military service branches of France. It is among the largest and most powerful naval forces in t ...
was better able to immediately respond to 's call to arms. Most units initially stayed loyal to Vichy, but about 3,600 sailors operating 50 ships around the world joined with the Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the United Kingdom's naval warfare force. Although warships were used by English and Scottish kings from the early medieval period, the first major maritime engagements were fought in the Hundred Years' War against ...
and formed the nucleus of the Free French Naval Forces
The Free French Naval Forces (french: Forces Navales Françaises Libres, or FNFL) were the naval arm of the Free French Forces during the Second World War. They were commanded by Admiral Émile Muselier.
History
In the wake of the Armistice ...
(FFNF; in French: FNFL).[ France's surrender found her only aircraft carrier, , en route from the United States loaded with a precious cargo of American fighter and bomber aircraft. Unwilling to return to occupied France, but likewise reluctant to join , ''Béarn'' instead sought harbour in ]Martinique
Martinique ( , ; gcf, label=Martinican Creole, Matinik or ; Kalinago language, Kalinago: or ) is an island and an Overseas department and region, overseas department/region and single territorial collectivity of France. An integral part of ...
, her crew showing little inclination to side with the British in their continued fight against the Nazis. Already obsolete at the start of the war, she would remain in Martinique for the next four years, her aircraft rusting in the tropical climate.
Many of the men in the French colonies felt a special need to defend France, their distant "motherland", eventually making up two-thirds of 's Free French Forces.
Composition
The Free French forces included men from the French Pacific Islands. Mainly coming from Tahiti, there were 550 volunteers in April 1941. They would serve through the North African campaign (including the Battle of Bir Hakeim
The Battle of Bir Hakeim () took place at Bir Hakeim, an oasis in the Libyan desert south and west of Tobruk, during the Battle of Gazala (26 May – 21 June 1942). The 1st Free French Brigade under Marie-Pierre Kœnig defended the position from ...
), the Italian Campaign and much of the Liberation of France. In November 1944, 275 remaining volunteers were repatriated and replaced with men of French Forces of the Interior to deal better with the cold weather.Spanish Civil War
The Spanish Civil War ( es, Guerra Civil Española)) or The Revolution ( es, La Revolución, link=no) among Nationalists, the Fourth Carlist War ( es, Cuarta Guerra Carlista, link=no) among Carlists, and The Rebellion ( es, La Rebelión, link ...
. In August 1944, they numbered 350 men.Pierre Milza
Pierre Milza (16 April 193228 February 2018) was a French historian. His work focused mainly on the history of Italy, the history of Italian immigration to France and the history of fascism, of which he was a recognized specialist.
He was pro ...
. ''Exils et migration: Italiens et Espagnols en France, 1938–1946'', L'Harmattan, 1994, p. 590Liberation of Paris
The liberation of Paris (french: Libération de Paris) was a military battle that took place during World War II from 19 August 1944 until the German garrison surrendered the French capital on 25 August 1944. Paris had been occupied by Nazi Ger ...
.5e Division Blindée
The 5th Armored Division (french: 5e Division Blindée, 5e DB) was an armored division of the French Army that fought in World War II and the Algerian War. It was also active in Germany during the Cold War.
World War II
The division was form ...
was almost entirely made up of white Frenchmen.
Records for the Italian campaign show that both the 3rd Algerian Infantry Division
The 3rd Algerian Infantry Division (french: 3e Division d'Infanterie Algérienne, 3e DIA) was an infantry division of the Army of Africa (french: Armée d'Afrique) which participated in World War II.
Following the liberation of French North Afri ...
and 2nd Moroccan Infantry Division
The 2nd Moroccan Infantry Division (french: 2e Division d'Infanterie Marocaine, 2e DIM) was an infantry division of the Army of Africa (french: Armée d'Afrique) which participated in World War II.
Created in Morocco following the liberation o ...
were made up of 60% Mahgrebians and 40% Europeans, while the 4th Moroccan Infantry Division was made up of 65% Mahgrebians and 35% Europeans.[Paul Gaujac. ''Le Corps expéditionnaire français en Italie''. Histoire et collections, 2003. p. 31] The three North African divisions had one brigade of North African soldiers in each division replaced with a brigade of French Forces of the Interior in January 1945. Both the 1st Free French Division
The 1st Free French Division (french: 1re Division Française Libre, 1re DFL) was one of the principal units of the Free French Forces (FFL) during World War II, renowned for having fought the Battle of Bir Hakeim.
Consisting of troops from ...
and 9th Colonial Infantry Division contained a strong contingent of Tirailleurs Sénégalais brigades. The 1st Free French Division also contained a mixed brigade of French ''Troupes de marine
The (TDM, ) is a corps of the French Army that includes several specialities: infantry, artillery, armoured, airborne, engineering, and transmissions (Signals).
Despite its name, it forms part of the Army, not the Navy. Intended for amphibi ...
'' and the Pacific island volunteers.Royal Air Force
The Royal Air Force (RAF) is the United Kingdom's air and space force. It was formed towards the end of the First World War on 1 April 1918, becoming the first independent air force in the world, by regrouping the Royal Flying Corps (RFC) a ...
, Soviet Air Force
The Soviet Air Forces ( rus, Военно-воздушные силы, r=Voyenno-vozdushnyye sily, VVS; literally "Military Air Forces") were one of the air forces of the Soviet Union. The other was the Soviet Air Defence Forces. The Air Forces ...
, and British SAS were mainly composed of men from metropolitan France.
Before the addition of the assemblies of Northern Africa and the loss of the runaways who fled France and went to Spain in the spring of 1943 (10,000 according to Jean-Noël Vincent's calculations), a report by the major state general of the Free French Forces in London from October 30, 1942 records 61,670 combatants in the Army, of which 20,200 were from colonies and 20,000 were from the Levant's special troops (non-Free French forces).
In May 1943, citing the Joint Planning Staff, Jean-Louis Crémieux-Brilhac alludes to 79,600 men who constitute ground forces, including 21,500 men from special Syro-Lebanese troops, 2,000 men of color supervised by Free French Forces in northern Palestine, and 650 soldiers assigned to the general headquarters in London.
According to the tally of Henri Écochard, an ex-Free French Forces serviceman, there were at least 54,500 soldiers.
In 2009, in his work on the Free French Forces, Jean-François Muracciole, a French historian specializing in Free France, reevaluated his count with that of Henri Écochard, while considering that Écochard's list had greatly underestimated the number of colonial combatants. According to Muracciole, between the creation of the Free French forces in the Summer 1940 and the merger with the Army of Africa in summer 1943, 73,300 men fought for Free France. This included 39,300 French (from metropolitan France and colonial settlers), 30,000 colonial soldiers (mostly from sub-Saharan Africa) and 3,800 foreigners. They were divided up as follows:
Army: 50,000;
Naval: 12,500;
Aviation: 3,200;
Communications in France: 5,700;
Free French Forces committees: 1,900.
General Leclerc's second armored division included two units of female volunteers: The Rochambeau Group with the Army (dozens of women) and the Woman Service of the Naval Fleet with the Navy (9 women). Their role consisted of administering first aid to the first line of injured soldiers (often to stop bleeding) before evacuating them by stretcher to ambulances and then driving these ambulances under enemy fire to care centers several kilometers behind the lines.
The following anecdote by Pierre Clostermann
Pierre Henri Clostermann (28 February 1921 – 22 March 2006) was a World War II French fighter pilot.
During the conflict he achieved 33 air-to-air combat victories, earning the accolade "France's First Fighter" from General Charles de Ga ...
suggests the spirit of the times in the Free French Forces; a commander reproaches one of Clostermann's comrades for having yellow shoes and a yellow sweater under his uniform, to which the comrade responds: "My Commander, I am a civilian who voluntarily came to fight the war that the soldiers don't want to fight!"
Cross of Lorraine

Thierry d'Argenlieu
Georges Thierry d'Argenlieu, in religion Father Louis of the Trinity, O.C.D. (7 August 1889 – 7 September 1964), was a Discalced Carmelite friar and priest, who was also a diplomat and French Navy officer and admiral; he became one of the ...
suggested the adoption of the Cross of Lorraine
The Cross of Lorraine (french: Croix de Lorraine, link=no), known as the Cross of Anjou in the 16th century, is a heraldic two-barred cross, consisting of a vertical line crossed by two shorter horizontal bars. In most renditions, the horizon ...
as a symbol of the Free French. This was chosen to recall the perseverance of Joan of Arc
Joan of Arc (french: link=yes, Jeanne d'Arc, translit= �an daʁk} ; 1412 – 30 May 1431) is a patron saint of France, honored as a defender of the French nation for her role in the siege of Orléans and her insistence on the coronati ...
, patron saint of France, whose symbol it had been, the province where she was born, and now partially annexed into Alsace-Lorraine by Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany (lit. "National Socialist State"), ' (lit. "Nazi State") for short; also ' (lit. "National Socialist Germany") (officially known as the German Reich from 1933 until 1943, and the Greater German Reich from 1943 to 1945) was ...
, and as a response to the symbol of national-socialism
Nazism ( ; german: Nazismus), the common name in English for National Socialism (german: Nationalsozialismus, ), is the far-right totalitarian political ideology and practices associated with Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party (NSDAP) in Naz ...
, the Nazi swastika
The swastika (卐 or 卍) is an ancient religious and cultural symbol, predominantly in various Eurasian, as well as some African and American cultures, now also widely recognized for its appropriation by the Nazi Party and by neo-Nazis. I ...
.
In his general order
A general order, in military and paramilitary organizations, is a published directive, originated by a commander and binding upon all personnel under his or her command. Its purpose is to enforce a policy or procedure unique to the unit's situatio ...
No. 2 of 3 July 1940, Vice admiral Émile Muselier, two days after assuming the post of chief of the naval and air forces of the Free French, created the naval jack
A jack is a flag flown from a short jackstaff at the bow (front) of a vessel, while the ensign is flown on the stern (rear). Jacks on bowsprits or foremasts appeared in the 17th century. A country may have different jacks for different purpo ...
displaying the French colours with a red cross of Lorraine
Lorraine , also , , ; Lorrain: ''Louréne''; Lorraine Franconian: ''Lottringe''; german: Lothringen ; lb, Loutrengen; nl, Lotharingen is a cultural and historical region in Northeastern France, now located in the administrative region of G ...
, and a cockade, which also featured the cross of Lorraine. Modern ships that share the same name as ships of the FNFL—such as and —are entitled to fly the Free French naval jack as a mark of honour.
 A monument on
A monument on Lyle Hill
Lyle Hill stands at the West End of Greenock in Inverclyde, Scotland. It has scenic viewpoints accessible from Lyle Road, which was constructed in 1879–1880 and named after Provost Abram Lyle, well known as a sugar refiner. The hill's hig ...
in Greenock
Greenock (; sco, Greenock; gd, Grianaig, ) is a town and administrative centre in the Inverclyde council area in Scotland, United Kingdom and a former burgh within the historic county of Renfrewshire, located in the west central Lowlands o ...
, in the shape of the Cross of Lorraine combined with an anchor, was raised by subscription as a memorial to the Free French naval vessels which sailed from the Firth of Clyde
The Firth of Clyde is the mouth of the River Clyde. It is located on the west coast of Scotland and constitutes the deepest coastal waters in the British Isles (it is 164 metres deep at its deepest). The firth is sheltered from the Atlantic ...
to take part in the Battle of the Atlantic
The Battle of the Atlantic, the longest continuous military campaign in World War II, ran from 1939 to the defeat of Nazi Germany in 1945, covering a major part of the naval history of World War II. At its core was the Allied naval blockad ...
. It has plaques commemorating the loss of the Flower-class corvette
The Flower-class corvetteGardiner and Chesneau 1980, p. 62. (also referred to as the ''Gladiolus'' class after the lead ship) was a British class of 294 corvettes used during World War II by the Allied navies particularly as anti-submari ...
s ''Alyssa'' and ''Mimosa'', and of the submarine .Tail of the Bank
The Tail of the Bank is the name given to the anchorage in the upper Firth of Clyde immediately North of Greenock, between Inverclyde and Argyll and Bute. This area of the Firth gets its name from the deep water immediately to the west of the ...
.
Mers El Kébir and the fate of the French Navy
After the fall of France, British Prime Minister Winston Churchill
Sir Winston Leonard Spencer Churchill (30 November 187424 January 1965) was a British statesman, soldier, and writer who served as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom twice, from 1940 to 1945 during the Second World War, and again from 1 ...
feared that, in German or Italian hands, the ships of the French Navy would pose a grave threat to the Allies. He therefore insisted that French warships either join the Allies or else adopt neutrality in a British, French, or neutral port. Churchill was determined that French warships would not be in a position to support a German invasion of Britain, though he feared that a direct attack on the French Navy might cause the Vichy regime to actively ally itself with the Nazis.
 On 3 July 1940, Admiral Marcel-Bruno Gensoul was provided an ultimatum by the British:
Gensoul's orders allowed him to accept internment in the West Indies, but after a discussion lasting ten hours, he rejected all offers, and British warships commanded by Admiral
On 3 July 1940, Admiral Marcel-Bruno Gensoul was provided an ultimatum by the British:
Gensoul's orders allowed him to accept internment in the West Indies, but after a discussion lasting ten hours, he rejected all offers, and British warships commanded by Admiral James Somerville
Admiral of the Fleet Sir James Fownes Somerville, (17 July 1882 – 19 March 1949) was a Royal Navy officer. He served in the First World War as fleet wireless officer for the Mediterranean Fleet where he was involved in providing naval suppo ...
attacked French ships during the attack on Mers-el-Kébir
The Attack on Mers-el-Kébir (Battle of Mers-el-Kébir) on 3 July 1940, during the Second World War, was a British naval attack on neutral French Navy ships at the naval base at Mers El Kébir, near Oran, on the coast of French Algeria. The atta ...
in Algeria, sinking or crippling three battleships.Case Anton
Case Anton (german: link=no, Fall Anton) was the military occupation of France carried out by Germany and Italy in November 1942. It marked the end of the Vichy regime as a nominally-independent state and the disbanding of its army (the seve ...
Axis invasion and occupation of the ''zone libre'' and Tunisia, changed sides then.
In November 1940, around 1,700 officers and men of the French Navy took advantage of the British offer of repatriation to France, and were transported home on a hospital ship travelling under the International Red Cross
The International Committee of the Red Cross (ICRC; french: Comité international de la Croix-Rouge) is a humanitarian organization which is based in Geneva, Switzerland, and it is also a three-time Nobel Prize Laureate. State parties (signato ...
. This did not stop the Germans from torpedoing the ship, and 400 men were drowned.
The FNFL, commanded first by Admiral
Admiral is one of the highest ranks in some navies. In the Commonwealth nations and the United States, a "full" admiral is equivalent to a "full" general in the army or the air force, and is above vice admiral and below admiral of the fleet, ...
Emile Muselier and then by Philippe Auboyneau and Georges Thierry d'Argenlieu, played a role in the liberation of French colonies throughout the world including Operation Torch
Operation Torch (8 November 1942 – 16 November 1942) was an Allied invasion of French North Africa during the Second World War. Torch was a compromise operation that met the British objective of securing victory in North Africa while al ...
in French north Africa, escorting convoys
A convoy is a group of vehicles, typically motor vehicles or ships, traveling together for mutual support and protection. Often, a convoy is organized with armed defensive support and can help maintain cohesion within a unit. It may also be used ...
during the Battle of the Atlantic
The Battle of the Atlantic, the longest continuous military campaign in World War II, ran from 1939 to the defeat of Nazi Germany in 1945, covering a major part of the naval history of World War II. At its core was the Allied naval blockad ...
, in supporting the French Resistance
The French Resistance (french: La Résistance) was a collection of organisations that fought the German occupation of France during World War II, Nazi occupation of France and the Collaborationism, collaborationist Vichy France, Vichy régim ...
in non-Free French territories, in Operation Neptune
Operation or Operations may refer to:
Arts, entertainment and media
* ''Operation'' (game), a battery-operated board game that challenges dexterity
* Operation (music), a term used in musical set theory
* ''Operations'' (magazine), Multi-Man ...
in Normandy and Operation Dragoon
Operation Dragoon (initially Operation Anvil) was the code name for the landing operation of the Allied invasion of Provence (Southern France) on 15August 1944. Despite initially designed to be executed in conjunction with Operation Overlord, t ...
in Provence for the liberation of mainland France, and in the Pacific War
The Pacific War, sometimes called the Asia–Pacific War, was the theater of World War II that was fought in Asia, the Pacific Ocean, the Indian Ocean, and Oceania. It was geographically the largest theater of the war, including the vast ...
.
In total during the war, around 50 major ships and a few dozen minor and auxiliary ships were part of the Free French navy. It also included half a dozen battalion
A battalion is a military unit, typically consisting of 300 to 1,200 soldiers commanded by a lieutenant colonel, and subdivided into a number of companies (usually each commanded by a major or a captain). In some countries, battalions are ...
s of naval infantry and commandos, as well as naval aviation squadrons, one aboard and one squadron of anti-submarine Catalina
Catalina may refer to:
Arts and media
* '' The Catalina'', a 2012 American reality television show
* ''Catalina'' (novel), a 1948 novel by W. Somerset Maugham
* Catalina (''My Name Is Earl''), character from the NBC sitcom ''My Name Is Earl'' ...
s. The French merchant marine siding with the Allies counted over 170 ships.
Struggle for control of the French colonies
With metropolitan France firmly under Germany's thumb and the Allies too weak to challenge this, turned his attention to France's vast overseas empire.
African campaign and the Empire Defence Council
De Gaulle was optimistic that France's colonies in western and central Africa, which had strong trading links with British territories, might be sympathetic to the Free French. Pierre Boisson, the governor-general of French Equatorial Africa
French Equatorial Africa (french: link=no, Afrique-Équatoriale française), or the AEF, was the federation of French colonial possessions in Equatorial Africa, extending northwards from the Congo River into the Sahel, and comprising what ar ...
, was a staunch supporter of the Vichy regime, unlike Félix Éboué
Adolphe Sylvestre Félix Éboué (; 26 December 1884 – 17 May 1944) was a French colonial administrator and Free French leader. He was the first black French man appointed to a high post in the French colonies, when appointed as Governor o ...
, the governor of French Chad, a subsection of the overall colony. Boisson was soon promoted to "High Commissioner of Colonies" and transferred to Dakar
Dakar ( ; ; wo, Ndakaaru) (from daqaar ''tamarind''), is the capital and largest city of Senegal. The city of Dakar proper has a population of 1,030,594, whereas the population of the Dakar metropolitan area is estimated at 3.94 million in 20 ...
, leaving Éboué with more direct authority over Chad. On 26 August, with the help of his top military official, Éboué pledged his colony's allegiance to Free France. By the end of August, all of French Equatorial Africa (including the League of Nations mandate French Cameroun) had joined Free France, with the exception of French Gabon
The French Congo (french: Congo français) or Middle Congo (french: Moyen-Congo) was a French colony which at one time comprised the present-day area of the Republic of the Congo and parts of Gabon, and the Central African Republic. In 1910, i ...
.
 With these colonies came vital manpower – a large number of African colonial troops, who would form the nucleus of 's army. From July to November 1940, the FFF would engage in fighting with troops loyal to Vichy France in Africa, with success and failure on both sides.
In September 1940 an Anglo French naval force fought the
With these colonies came vital manpower – a large number of African colonial troops, who would form the nucleus of 's army. From July to November 1940, the FFF would engage in fighting with troops loyal to Vichy France in Africa, with success and failure on both sides.
In September 1940 an Anglo French naval force fought the Battle of Dakar
The Battle of Dakar, also known as Operation Menace, was an unsuccessful attempt in September 1940 by the Allies to capture the strategic port of Dakar in French West Africa (modern-day Senegal). It was hoped that the success of the operation co ...
, also known as Operation Menace, an unsuccessful attempt to capture the strategic port of Dakar in French West Africa
French West Africa (french: Afrique-Occidentale française, ) was a federation of eight French colonial territories in West Africa: Mauritania, Senegal, French Sudan (now Mali), French Guinea (now Guinea), Ivory Coast, Upper Volta (now Burkin ...
. The local authorities were not impressed by the Allied show of strength, and had the better of the naval bombardment which followed, leading to a humiliating withdrawal by the Allied ships. So strong was 's sense of failure that he even considered suicide.
There was better news in November 1940 when the FFF achieved victory at the Battle of Gabon
The Battle of Gabon (French: ''Bataille du Gabon''), also called the Gabon Campaign (''Campagne du Gabon''), occurred in November 1940 during World War II. The battle resulted in forces under the orders of General de Gaulle taking the colon ...
(or Battle of Libreville) under the very skilled General Philippe Leclerc de Hauteclocque
Philippe François Marie Leclerc de Hauteclocque (22 November 1902 – 28 November 1947) was a Free-French general during the Second World War. He became Marshal of France posthumously in 1952, and is known in France simply as le maréchal ...
(General Leclerc).[Keegan, John. Six Armies in Normandy. New York: Penguin Books, 1994. p300] personally surveyed the situation in Chad, the first African colony to join Free France, located on the southern border of Libya, and the battle resulted in free French forces taking Libreville
Libreville is the capital and largest city of Gabon. Occupying in the northwestern province of Estuaire, Libreville is a port on the Komo River, near the Gulf of Guinea. As of the 2013 census, its population was 703,904.
The area has been inh ...
, Gabon.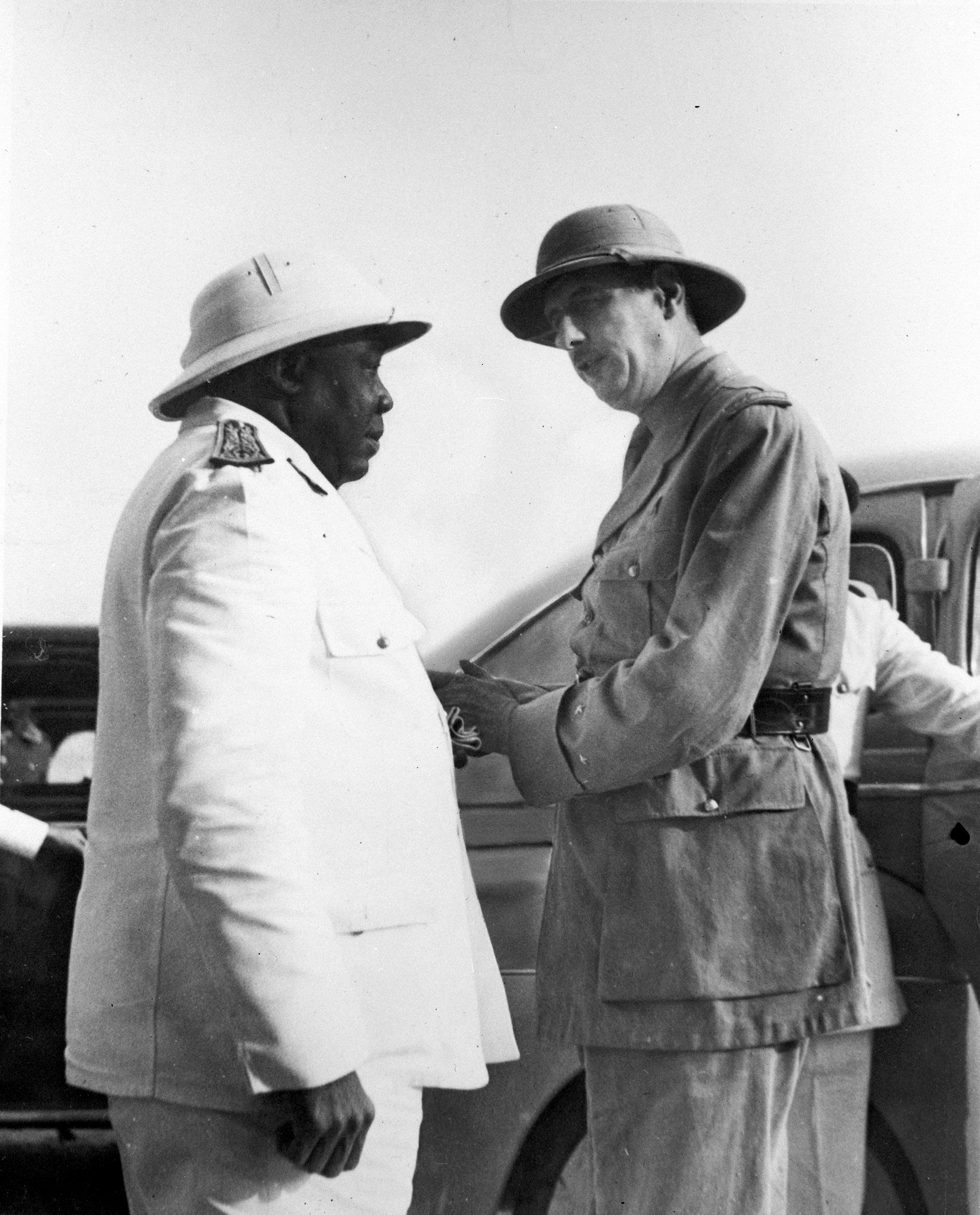 By the end of November 1940 French Equatorial Africa was wholly under the control of Free France, but the failures at Dakar had led French West Africa to declare allegiance to Vichy, to which they would remain loyal until the fall of the regime in November 1942.
On 27 October 1940 the Empire Defence Council was established to organise and administrate the imperial possessions under Free French rule, and as an alternative provisional French government. It was constituted of high-ranking officers and the governors of the free colonies, notably governor
By the end of November 1940 French Equatorial Africa was wholly under the control of Free France, but the failures at Dakar had led French West Africa to declare allegiance to Vichy, to which they would remain loyal until the fall of the regime in November 1942.
On 27 October 1940 the Empire Defence Council was established to organise and administrate the imperial possessions under Free French rule, and as an alternative provisional French government. It was constituted of high-ranking officers and the governors of the free colonies, notably governor Félix Éboué
Adolphe Sylvestre Félix Éboué (; 26 December 1884 – 17 May 1944) was a French colonial administrator and Free French leader. He was the first black French man appointed to a high post in the French colonies, when appointed as Governor o ...
of Chad. Its creation was announced by the Brazzaville Manifesto
The Empire Defense Council (also called Council of Defense of the Empire, from french: Conseil de défense de l'Empire) was the embodiment of Free France which constituted the government from 1940 to 1941. Subsequently, this role was assumed ...
that day. was what claimed to represent, or rather, as he put it simply, ""; Vichy France was a "pseudo government", an illegal entity.
In 1941–1942, the African FFF slowly grew in strength and even expanded operations north into Italian Libya
Libya ( it, Libia; ar, ليبيا, Lībyā al-Īṭālīya) was a colony of the Fascist Italy located in North Africa, in what is now modern Libya, between 1934 and 1943. It was formed from the unification of the colonies of Italian Cyrenaica ...
. In February 1941, Free French Forces invaded Cyrenaica
Cyrenaica ( ) or Kyrenaika ( ar, برقة, Barqah, grc-koi, Κυρηναϊκή ��παρχίαKurēnaïkḗ parkhíā}, after the city of Cyrene), is the eastern region of Libya. Cyrenaica includes all of the eastern part of Libya between ...
, again led by Leclerc, capturing the Italian fort at the oasis
In ecology, an oasis (; ) is a fertile area of a desert or semi-desert environment'ksar''with its surrounding feeding source, the palm grove, within a relational and circulatory nomadic system.”
The location of oases has been of critical imp ...
of Kufra
Kufra () is a basinBertarelli (1929), p. 514. and oasis group in the Kufra District of southeastern Cyrenaica in Libya. At the end of nineteenth century Kufra became the centre and holy place of the Senussi order. It also played a minor role in t ...
.Fezzan
Fezzan ( , ; ber, ⴼⵣⵣⴰⵏ, Fezzan; ar, فزان, Fizzān; la, Phazania) is the southwestern region of modern Libya. It is largely desert, but broken by mountains, uplands, and dry river valleys (wadis) in the north, where oases enable ...
.Run for Tunis
The Run for Tunis was part of the Tunisia Campaign which took place during November and December 1942 during the Second World War. Once French opposition to the Allied Operation Torch landings had ceased in mid-November, the Allies made a rapid a ...
.
Asia and the Pacific
 France also had possessions in Asia and the Pacific, and these far-flung colonies would experience similar problems of divided loyalties.
France also had possessions in Asia and the Pacific, and these far-flung colonies would experience similar problems of divided loyalties. French India
French India, formally the ( en, French Settlements in India), was a French colony comprising five geographically separated enclaves on the Indian Subcontinent that had initially been factories of the French East India Company. They were ''d ...
and the French South Pacific colonies of New Caledonia
)
, anthem = ""
, image_map = New Caledonia on the globe (small islands magnified) (Polynesia centered).svg
, map_alt = Location of New Caledonia
, map_caption = Location of New Caledonia
, mapsize = 290px
, subdivision_type = Sovereign st ...
, French Polynesia
)Territorial motto: ( en, "Great Tahiti of the Golden Haze")
, anthem =
, song_type = Regional anthem
, song = " Ia Ora 'O Tahiti Nui"
, image_map = French Polynesia on the globe (French Polynesia centered).svg
, map_alt = Location of Frenc ...
and the New Hebrides joined Free France in the summer 1940, drawing official American interest. These South Pacific colonies would later provide vital Allied bases in the Pacific Ocean during the war with Japan.
French Indochina
French Indochina (previously spelled as French Indo-China),; vi, Đông Dương thuộc Pháp, , lit. 'East Ocean under French Control; km, ឥណ្ឌូចិនបារាំង, ; th, อินโดจีนฝรั่งเศส, ...
was invaded by Japan in September 1940, although for most of the war the colony remained under nominal Vichy control. On 9 March 1945, the Japanese launched a coup and took full control of Indochina
Mainland Southeast Asia, also known as the Indochinese Peninsula or Indochina, is the continental portion of Southeast Asia. It lies east of the Indian subcontinent and south of Mainland China and is bordered by the Indian Ocean to the west an ...
by the beginning of May.
From June 1940 until February 1943, the concession of Guangzhouwan
The Leased Territory of Guangzhouwan, officially the , was a territory on the coast of Zhanjiang in China leased to France and administered by French Indochina. The capital of the territory was Fort-Bayard, present-day Zhanjiang.
The Japan ...
(Kouang-Tchéou-Wan or Fort-Boyard), in South China, remained under the administration of Free France. The Republic of China, after the fall of Paris in 1940, recognised the London-exiled Free French government as Guangzhouwan's legitimate authority and established diplomatic relations with them, something facilitated by the fact that the colony was surrounded by the Republic of China's territory and was not in physical contact with French Indochina. In February 1943 the Imperial Japanese Army
The was the official ground-based armed force of the Empire of Japan from 1868 to 1945. It was controlled by the Imperial Japanese Army General Staff Office and the Ministry of the Army, both of which were nominally subordinate to the Emperor o ...
invaded and occupied the leased territory.
North America
In North America, Saint-Pierre and Miquelon
Saint Pierre and Miquelon (), officially the Territorial Collectivity of Saint-Pierre and Miquelon (french: link=no, Collectivité territoriale de Saint-Pierre et Miquelon ), is a self-governing territorial overseas collectivity of France in t ...
(near Newfoundland
Newfoundland and Labrador (; french: Terre-Neuve-et-Labrador; frequently abbreviated as NL) is the easternmost province of Canada, in the country's Atlantic region. The province comprises the island of Newfoundland and the continental region ...
) joined the Free French after an "invasion" on 24 December 1941 by Rear Admiral
Rear admiral is a senior naval flag officer rank, equivalent to a major general and air vice marshal and above that of a commodore and captain, but below that of a vice admiral. It is regarded as a two star "admiral" rank. It is often regard ...
Emile Muselier and the forces he was able to load onto three corvette
A corvette is a small warship. It is traditionally the smallest class of vessel considered to be a proper (or " rated") warship. The warship class above the corvette is that of the frigate, while the class below was historically that of the sloop ...
s and a submarine of the FNFL. The action at Saint-Pierre and Miquelon created a serious diplomatic incident with the United States, despite this being the first French possession in the Americas to join the Allies, which doctrinally objected to the use of military means by colonial powers in the western hemisphere and recognised Vichy as the official French government.
Mainly because of this and of the often very frosty relations between Free France and the USA (with President Roosevelt
Roosevelt may refer to:
*Theodore Roosevelt (1858–1919), 26th U.S. president
*Franklin D. Roosevelt (1882–1945), 32nd U.S. president
Businesses and organisations
* Roosevelt Hotel (disambiguation)
* Roosevelt & Son, a merchant bank
* Roosev ...
's profound distrust of playing a key part in that, with him being firmly convinced that the general's aim was to create a South-American style junta
Junta may refer to:
Government and military
* Junta (governing body) (from Spanish), the name of various historical and current governments and governing institutions, including civil ones
** Military junta, one form of junta, government led by a ...
and become the dictator of France[When the US wanted to take over France]
, Annie Lacroix-Riz, in ''Le Monde diplomatique
''Le Monde diplomatique'' (meaning "The Diplomatic World" in French) is a French monthly newspaper offering analysis and opinion on politics, culture, and current affairs.
The publication is owned by Le Monde diplomatique SA, a subsidiary com ...
'', May 2003 (English, French, etc.)), other French possessions in the New World were among the last to defect from Vichy to the Allies (with Martinique
Martinique ( , ; gcf, label=Martinican Creole, Matinik or ; Kalinago language, Kalinago: or ) is an island and an Overseas department and region, overseas department/region and single territorial collectivity of France. An integral part of ...
holding out until July 1943).
Syria and East Africa
 In 1941, the FFF fought alongside British Empire troops against the Italians in
In 1941, the FFF fought alongside British Empire troops against the Italians in Italian East Africa
Italian East Africa ( it, Africa Orientale Italiana, AOI) was an Italian colony in the Horn of Africa. It was formed in 1936 through the merger of Italian Somalia, Italian Eritrea, and the newly occupied Ethiopian Empire, conquered in the Secon ...
during the East African Campaign.
In June 1941, during the Syria-Lebanon campaign (Operation Exporter), Free French Forces fighting alongside British Commonwealth forces faced substantial numbers of troops loyal to Vichy France – this time in the Levant
The Levant () is an approximate historical geographical term referring to a large area in the Eastern Mediterranean region of Western Asia. In its narrowest sense, which is in use today in archaeology and other cultural contexts, it is eq ...
. had assured Churchill that the French units in Syria would rise to the call of Free France, but this was not the case.[Taylor, p.93] After bitter fighting, with around 1,000 dead on each side (including Vichy and Free French Foreign Legionnaires fratricide when the 13th Demi-Brigade (D.B.L.E.) clashed with the 6th Foreign Infantry Regiment
The 6th Foreign Infantry Regiment (french: 6e Régiment Étranger d'Infanterie, 6e REI) was an infantry regiment of the Foreign Legion in the French Army from 1939 to 1941 and again from 1949 to 1955.
History, creations and different nominat ...
near Damascus). General Henri Dentz
Henri Fernand Dentz (16 December 1881 – 13 December 1945) was a general in the French Army (''Armée de Terre'') who served with the Vichy French Army after France surrendered during the Second World War. He was tried as a collaborator after ...
and his Vichy Army of the Levant
The Army of the Levant (french: Armée du Levant) identifies the armed forces of France and then Vichy France which occupied, and were in part recruited from, the French Mandated territories in the Levant during the interwar period and early W ...
were eventually defeated by the largely British allied forces in July 1941.Georges Catroux
Georges Albert Julien Catroux (29 January 1877 – 21 December 1969) was a French Army general and diplomat who served in both World War I and World War II, and served as Grand Chancellor of the Légion d'honneur from 1954 to 1969.
Life
C ...
was appointed High Commissioner of the Levant, and from this point, Free France would control both Syria
Syria ( ar, سُورِيَا or سُورِيَة, translit=Sūriyā), officially the Syrian Arab Republic ( ar, الجمهورية العربية السورية, al-Jumhūrīyah al-ʻArabīyah as-Sūrīyah), is a Western Asian country loc ...
and Lebanon
Lebanon ( , ar, لُبْنَان, translit=lubnān, ), officially the Republic of Lebanon () or the Lebanese Republic, is a country in Western Asia. It is located between Syria to the north and east and Israel to the south, while Cyprus li ...
until they became independent in 1946 and 1943 respectively. However, despite this success, the numbers of the FFF did not grow as much as had been wished for. Of nearly 38,000 Vichy French prisoners of war, just 5,668 men volunteered to join the forces of General ; the remainder chose to be repatriated to France.
Despite this bleak picture, by the end of 1941, the United States had entered the war, and the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen nationa ...
had also joined the Allied side, stopping the Germans outside Moscow in the first major reverse for the Nazis. Gradually the tide of war began to shift, and with it the perception that Hitler could at last be beaten. Support for Free France began to grow, though the Vichy French forces would continue to resist Allied armies—and the Free French—when attacked by them until the end of 1942.[Hastings, Max, p. 81.]
Creation of the French National Committee (CNF)
Reflecting the growing strength of Free France was the foundation of the French National Committee
The French National Committee (french: Comité national français, CNF) was the coordinating body created by General Charles de Gaulle which acted as the government in exile of Free France from 1941 to 1943. The committee was the successor ...
(French: ''Comité national français
Free France (french: France Libre) was a political entity that claimed to be the legitimate government of France following the dissolution of the Third Republic. Led by French general , Free France was established as a government-in-exile ...
'', CNF) in September 1941 and the official name change from to in July 1942.
The United States granted Lend-Lease
Lend-Lease, formally the Lend-Lease Act and introduced as An Act to Promote the Defense of the United States (), was a policy under which the United States supplied the United Kingdom, the Soviet Union and other Allied nations with food, oil, ...
support to the CNF on 24 November.
Madagascar
In June 1942, the British attacked the strategically important colony of French Madagascar
The Colony of Madagascar and Dependencies (french: Colonie de Madagascar et dépendances) was a French colony off the coast of Southeast Africa between 1897 and 1958 in what is now Madagascar. The colony was formerly a protectorate of France kn ...
, hoping to prevent its falling into Japanese hands and especially the use of Diego-Suarez
Antsiranana ( mg, Antsiran̈ana ), named Diego-Suárez prior to 1975, is a city in the far north of Madagascar. Antsiranana is the capital of Diana Region. It had an estimated population of 115,015 in 2013.
History
The bay and city originally u ...
's harbour as a base for the Imperial Japanese Navy
The Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN; Kyūjitai: Shinjitai: ' 'Navy of the Greater Japanese Empire', or ''Nippon Kaigun'', 'Japanese Navy') was the navy of the Empire of Japan from 1868 to 1945, when it was dissolved following Japan's surrender ...
. Once again the Allied landings faced resistance from Vichy forces, led by Governor-General
Governor-general (plural ''governors-general''), or governor general (plural ''governors general''), is the title of an office-holder. In the context of governors-general and former British colonies, governors-general are appointed as viceroy t ...
Armand Léon Annet Armand Léon Annet (5 June 1888 – 25 April 1973) was a French colonial governor for various colonies in the French colonial empire.
Biography
Armand Léon Annet was born in Paris on 1888, in Rue de Babylone.
Annet was Governor of French ...
. On 5 November 1942, Annet, at last, surrendered. As in Syria, only a minority of the captured Vichy soldiers chose to join the Free French. After the battle, Free French general Paul Legentilhomme
Paul Louis Legentilhomme (March 26, 1884 – May 23, 1975) was an officer in the French Army during World War I and World War II. After the fall of France in 1940, he joined the forces of the Free French. Legentilhomme was a recipient of th ...
was appointed High Commissioner for Madagascar
Madagascar (; mg, Madagasikara, ), officially the Republic of Madagascar ( mg, Repoblikan'i Madagasikara, links=no, ; french: République de Madagascar), is an island country in the Indian Ocean, approximately off the coast of East Africa ...
.
Battle of Bir Hakeim

 Throughout 1942 in
Throughout 1942 in North Africa
North Africa, or Northern Africa is a region encompassing the northern portion of the African continent. There is no singularly accepted scope for the region, and it is sometimes defined as stretching from the Atlantic shores of Mauritania in ...
, British Empire forces fought a desperate land campaign against the Germans and Italians to prevent the loss of Egypt and the vital Suez canal
The Suez Canal ( arz, قَنَاةُ ٱلسُّوَيْسِ, ') is an artificial sea-level waterway in Egypt, connecting the Mediterranean Sea to the Red Sea through the Isthmus of Suez and dividing Africa and Asia. The long canal is a popular ...
. Here, fighting in the harsh Libyan desert, Free French soldiers distinguished themselves. General Marie Pierre Koenig
Marie may refer to:
People Name
* Marie (given name)
* Marie (Japanese given name)
* Marie (murder victim), girl who was killed in Florida after being pushed in front of a moving vehicle in 1973
* Marie (died 1759), an enslaved Cree person in ...
and his unit—the 1st Free French Infantry Brigade—resisted the ''Afrika Korps
The Afrika Korps or German Africa Corps (, }; DAK) was the German expeditionary force in Africa during the North African Campaign of World War II. First sent as a holding force to shore up the Italian defense of its African colonies, the ...
'' at the Battle of Bir Hakeim
The Battle of Bir Hakeim () took place at Bir Hakeim, an oasis in the Libyan desert south and west of Tobruk, during the Battle of Gazala (26 May – 21 June 1942). The 1st Free French Brigade under Marie-Pierre Kœnig defended the position from ...
in June 1942, although they were eventually obliged to withdraw, as Allied forces retreated to El Alamein
El Alamein ( ar, العلمين, translit=al-ʿAlamayn, lit=the two flags, ) is a town in the northern Matrouh Governorate of Egypt. Located on the Arab's Gulf, Mediterranean Sea, it lies west of Alexandria and northwest of Cairo. , it had ...
, their lowest ebb in the North African campaign. Koenig defended Bir Hakeim from 26 May to 11 June against superior German and Italian forces led by Generaloberst Erwin Rommel
Johannes Erwin Eugen Rommel () (15 November 1891 – 14 October 1944) was a German field marshal during World War II. Popularly known as the Desert Fox (, ), he served in the '' Wehrmacht'' (armed forces) of Nazi Germany, as well as serv ...
, proving that the FFF could be taken seriously by the Allies as a fighting force. British General Claude Auchinleck
Field Marshal Sir Claude John Eyre Auchinleck, (21 June 1884 – 23 March 1981), was a British Army commander during the Second World War. He was a career soldier who spent much of his military career in India, where he rose to become Commander ...
said on 12 June 1942, of the battle: "The United Nations need to be filled with admiration and gratitude, in respect of these French troops and their brave General Koenig". Even Hitler was impressed, announcing to the journalist Lutz Koch, recently returned from Bir Hakeim:
You hear, Gentlemen? It is a new evidence that I have always been right! The French are, after us, the best soldiers! Even with its current birthrate, France will always be able to mobilise a hundred divisions! After this war, we will have to find allies able to contain a country which is capable of military exploits that astonish the world like they are doing right now in Bir-Hakeim!
Generalmajor
is the Germanic variant of major general, used in a number of Central and Northern European countries.
Austria
Belgium
Denmark
is the second lowest general officer rank in the Royal Danish Army and Royal Danish Air Force. As a two- ...
Friedrich von Mellenthin
Friedrich von Mellenthin (30 August 1904 – 28 June 1997) was a German general during World War II. A participant in most of the major campaigns of the war, he became known afterwards for his memoirs '' Panzer Battles'', first published i ...
wrote in his mémoirs '' Panzer Battles'', the whole course of the desert war, we never encountered a more heroic and well-sustained defence.
First successes
From 23 October to 4 November 1942, Allied forces under general Bernard Montgomery
Field Marshal Bernard Law Montgomery, 1st Viscount Montgomery of Alamein, (; 17 November 1887 – 24 March 1976), nicknamed "Monty", was a senior British Army officer who served in the First World War, the Irish War of Independence and th ...
, including the FFI, won the Second battle of El Alamein
The Second Battle of El Alamein (23 October – 11 November 1942) was a battle of the Second World War that took place near the Egyptian railway halt of El Alamein. The First Battle of El Alamein and the Battle of Alam el Halfa had prevented th ...
, driving Rommel's Afrika Korps out of Egypt and back into Libya. This was the first major success of an Allied army against the Axis powers, and marked a key turning point in the war.
Operation Torch
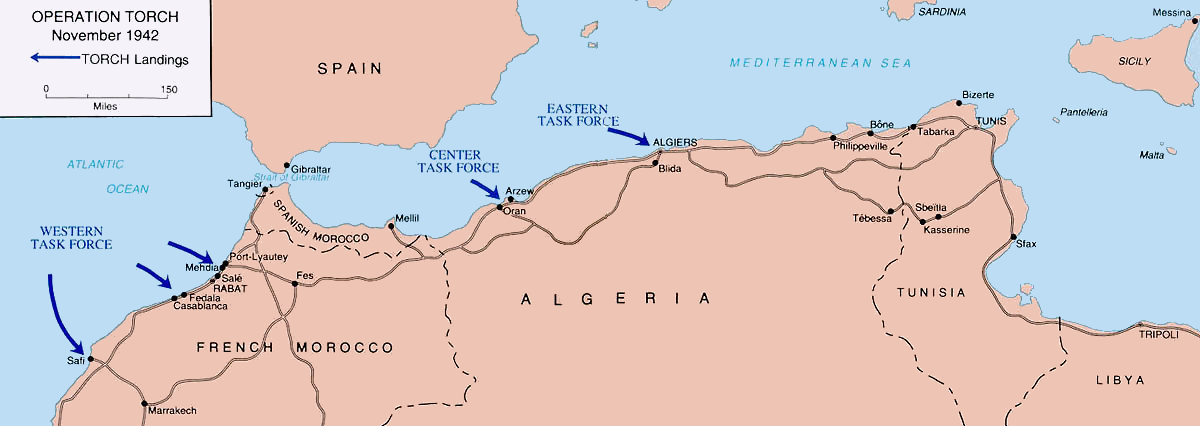 Soon afterwards in November 1942, the Allies launched
Soon afterwards in November 1942, the Allies launched Operation Torch
Operation Torch (8 November 1942 – 16 November 1942) was an Allied invasion of French North Africa during the Second World War. Torch was a compromise operation that met the British objective of securing victory in North Africa while al ...
in the west, an invasion of Vichy-controlled French North Africa
French North Africa (french: Afrique du Nord française, sometimes abbreviated to ANF) is the term often applied to the territories controlled by France in the North African Maghreb during the colonial era, namely Algeria, Morocco and Tunisia. I ...
. An Anglo-American force of 63,000 men landed in French Morocco and Algeria.[Hastings, Max, p.375] The long-term goal was to clear German and Italian troops from North Africa, enhance naval control of the Mediterranean, and prepare an invasion of Italy in 1943. The Allies had hoped that Vichy forces would offer only token resistance to the Allies, but instead they fought hard, incurring heavy casualties.[Hastings, Max, p.376] As a French foreign legionnaire put it after seeing his comrades die in an American bombing raid: "Ever since the fall of France, we had dreamed of deliverance, but we did not want it that way".Alphonse Juin
Alphonse Pierre Juin (16 December 1888 – 27 January 1967) was a senior French Army general who became Marshal of France. A graduate of the École Spéciale Militaire class of 1912, he served in Morocco in 1914 in command of native troops. Upon ...
, chief commander in North Africa, and Vichy admiral François Darlan
Jean Louis Xavier François Darlan (7 August 1881 – 24 December 1942) was a French admiral and political figure. Born in Nérac, Darlan graduated from the ''École navale'' in 1902 and quickly advanced through the ranks following his service d ...
). However, Darlan was released and U.S. General Dwight D. Eisenhower
Dwight David "Ike" Eisenhower (born David Dwight Eisenhower; ; October 14, 1890 – March 28, 1969) was an American military officer and statesman who served as the 34th president of the United States from 1953 to 1961. During World War II, ...
finally accepted his self-nomination as high commissioner of North Africa and French West Africa
French West Africa (french: Afrique-Occidentale française, ) was a federation of eight French colonial territories in West Africa: Mauritania, Senegal, French Sudan (now Mali), French Guinea (now Guinea), Ivory Coast, Upper Volta (now Burkin ...
, a move that enraged , who refused to recognise his status.
Henri Giraud
Henri Honoré Giraud (18 January 1879 – 11 March 1949) was a French general and a leader of the Free French Forces during the Second World War until he was forced to retire in 1944.
Born to an Alsatian family in Paris, Giraud graduated from ...
, a general who had escaped from military captivity in Germany in April 1942, had negotiated with the Americans for leadership in the invasion. He arrived in Algiers on 10 November, and agreed to subordinate himself to Admiral Darlan as the commander of the French African army.
Later that day Darlan ordered a ceasefire and Vichy French forces began, en masse, to join the Free French cause. Initially at least the effectiveness of these new recruits was hampered by a scarcity of weaponry and, among some of the officer class, a lack of conviction in their new cause.French Expeditionary Corps in Italy
French (french: français(e), link=no) may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to France
** French language, which originated in France, and its various dialects and accents
** French people, a nation and ethnic group identified with Franc ...
(FEC).
Admiral Darlan was assassinated on 24 December 1942 in Algiers by the young monarchist Bonnier de La Chapelle. Although de la Chapelle had been a member of the resistance group led by Henri d'Astier de La Vigerie, it is believed he was acting as an individual.
On 28 December, after a prolonged blockade, the Vichy forces in French Somaliland were ousted.
After these successes, Guadeloupe
Guadeloupe (; ; gcf, label= Antillean Creole, Gwadloup, ) is an archipelago and overseas department and region of France in the Caribbean. It consists of six inhabited islands—Basse-Terre, Grande-Terre, Marie-Galante, La Désirade, and the t ...
and Martinique in the West Indies
The West Indies is a subregion of North America, surrounded by the North Atlantic Ocean and the Caribbean Sea that includes 13 independent island countries and 18 dependencies and other territories in three major archipelagos: the Greater ...
—as well as French Guiana
French Guiana ( or ; french: link=no, Guyane ; gcr, label= French Guianese Creole, Lagwiyann ) is an overseas department/region and single territorial collectivity of France on the northern Atlantic coast of South America in the Guianas. ...
on the northern coast of South America – finally joined Free France in the first months of 1943. In November 1943, the French forces received enough military equipment through Lend-Lease to re-equip eight divisions and allow the return of borrowed British equipment.
Creation of the French Committee of National Liberation (CFLN)
 The Vichy forces in North Africa had been under Darlan's command and had surrendered on his orders. The Allies recognised his self-nomination as High Commissioner of France (French military and civilian commander-in-chief, ) for North and West Africa. He ordered them to cease resisting and co-operate with the Allies, which they did. By the time the Tunisia Campaign was fought, the ex-Vichy French forces in North Africa had been merged with the FFF.
After Admiral Darlan's assassination, Giraud became his ''de facto'' successor in French Africa with Allied support. This occurred through a series of consultations between Giraud and . The latter wanted to pursue a political position in France and agreed to have Giraud as commander in chief, as the more qualified military person of the two. It is questionable that he ordered that many French resistance leaders who had helped Eisenhower's troops be arrested, without any protest by Roosevelt's representative, Robert Murphy.
Later, the Americans sent
The Vichy forces in North Africa had been under Darlan's command and had surrendered on his orders. The Allies recognised his self-nomination as High Commissioner of France (French military and civilian commander-in-chief, ) for North and West Africa. He ordered them to cease resisting and co-operate with the Allies, which they did. By the time the Tunisia Campaign was fought, the ex-Vichy French forces in North Africa had been merged with the FFF.
After Admiral Darlan's assassination, Giraud became his ''de facto'' successor in French Africa with Allied support. This occurred through a series of consultations between Giraud and . The latter wanted to pursue a political position in France and agreed to have Giraud as commander in chief, as the more qualified military person of the two. It is questionable that he ordered that many French resistance leaders who had helped Eisenhower's troops be arrested, without any protest by Roosevelt's representative, Robert Murphy.
Later, the Americans sent Jean Monnet
Jean Omer Marie Gabriel Monnet (; 9 November 1888 – 16 March 1979) was a French civil servant, entrepreneur, diplomat, financier, administrator, and political visionary. An influential supporter of European unity, he is considered one of the ...
to counsel Giraud and to press him into repeal the Vichy laws. The Cremieux decree, which granted French citizenship to Jews in Algeria and which had been repealed by Vichy, was immediately restored by General . Democratic rule was restored in French Algeria, and the Communists and Jews liberated from the concentration camps.[Extraits_de_l'entretien_d'Annie_Rey-Goldzeiguer_[1,_avec_Christian_Makarian_et_Dominique_Simonnet,_publié_dans_''l'Express''_du_14_mars_2002]
,_on_the_Extraits_de_l'entretien_d'Annie_Rey-Goldzeiguer_[1,_avec_Christian_Makarian_et_Dominique_Simonnet,_publié_dans_''l'Express''_du_14_mars_2002,_on_the_Ligue_des_droits_de_l'homme">LDH_website_
Giraud_took_part_in_the_
Extraits_de_l'entretien_d'Annie_Rey-Goldzeiguer_[1,_avec_Christian_Makarian_et_Dominique_Simonnet,_publié_dans_''l'Express''_du_14_mars_2002,_on_the_Ligue_des_droits_de_l'homme">LDH_website_
Giraud_took_part_in_the_Casablanca_Conference">Casablanca_conference
_
The_Casablanca_Conference_(codenamed_SYMBOL)_or_Anfa_Conference_was_held_at_the_Anfa_Hotel_in_Casablanca,_French_Morocco,_from_January_14_to_24,_1943,_to_plan_the__Allied_European_strategy_for_the_next_phase_of__World_War_II._In_attendance_were_...
_in_January_1943_with_Roosevelt,_Churchill_and_._The_Allies_discussed_their_general_strategy_for_the_war,_and_recognised_joint_leadership_of_North_Africa_by_Giraud_and_._Henri_Giraud_and_Charles__then_became_co-presidents_of_the_French_Committee_of_National_Liberation_
The_French_Committee_of_National_Liberation_(french:_Comité_français_de_Libération_nationale)_was_a_provisional_government_of__Free_France_formed_by_the__French_generals__Henri_Giraud_and_Charles_de_Gaulle_to_provide_united_leadership,_organ_...
_(,_CFLN),_which_unified_the_territories_controlled_by_them_and_was_officially_founded_on_3_June_1943.
The_CFLN_set_up_a_temporary_French_government_in_Algiers,_raised_more_troops_and_re-organised,_re-trained_and_re-equipped_the_Free_French_military,_in_co-operation_with_Allied_forces_in_preparation_of_future_operations_[
Extraits_de_l'entretien_d'Annie_Rey-Goldzeiguer_[1,_avec_Christian_Makarian_et_Dominique_Simonnet,_publié_dans_''l'Express''_du_14_mars_2002,_on_the_Ligue_des_droits_de_l'homme">LDH_website_
Giraud_took_part_in_the_Casablanca_Conference">Casablanca_conference
_
The_Casablanca_Conference_(codenamed_SYMBOL)_or_Anfa_Conference_was_held_at_the_Anfa_Hotel_in_Casablanca,_French_Morocco,_from_January_14_to_24,_1943,_to_plan_the__Allied_European_strategy_for_the_next_phase_of__World_War_II._In_attendance_were_...
_in_January_1943_with_Roosevelt,_Churchill_and_._The_Allies_discussed_their_general_strategy_for_the_war,_and_recognised_joint_leadership_of_North_Africa_by_Giraud_and_._Henri_Giraud_and_Charles__then_became_co-presidents_of_the_
 Historically, an individual became "Free French" by enlisting in the military units organised by the CFN or by employment by the civilian arm of the Committee. On 1 August 1943 after the merger of CFN and representatives of the former Vichy regime in North Africa to form the CFLN earlier in June, the FFF and the Army of Africa (constituting a major part of the Vichy regular forces allowed by the 1940 armistice) were merged to form the
Historically, an individual became "Free French" by enlisting in the military units organised by the CFN or by employment by the civilian arm of the Committee. On 1 August 1943 after the merger of CFN and representatives of the former Vichy regime in North Africa to form the CFLN earlier in June, the FFF and the Army of Africa (constituting a major part of the Vichy regular forces allowed by the 1940 armistice) were merged to form the  On 10 May 1940,
On 10 May 1940,  On 18 June, General spoke to the
On 18 June, General spoke to the  Despite 's call to continue the struggle, few French forces initially pledged their support. By the end of July 1940, only about 7,000 soldiers had joined the Free French Army in England.Axelrod & Kingston, p. 362. Three-quarters of French servicemen in Britain requested repatriation.Hastings, Max, p.80
France was bitterly divided by the conflict. Frenchmen everywhere were forced to choose sides, and often deeply resented those who had made a different choice.Hastings, Max, p.126 One French admiral,
Despite 's call to continue the struggle, few French forces initially pledged their support. By the end of July 1940, only about 7,000 soldiers had joined the Free French Army in England.Axelrod & Kingston, p. 362. Three-quarters of French servicemen in Britain requested repatriation.Hastings, Max, p.80
France was bitterly divided by the conflict. Frenchmen everywhere were forced to choose sides, and often deeply resented those who had made a different choice.Hastings, Max, p.126 One French admiral,  A monument on
A monument on 
 On 3 July 1940, Admiral Marcel-Bruno Gensoul was provided an ultimatum by the British:
Gensoul's orders allowed him to accept internment in the West Indies, but after a discussion lasting ten hours, he rejected all offers, and British warships commanded by Admiral
On 3 July 1940, Admiral Marcel-Bruno Gensoul was provided an ultimatum by the British:
Gensoul's orders allowed him to accept internment in the West Indies, but after a discussion lasting ten hours, he rejected all offers, and British warships commanded by Admiral  With these colonies came vital manpower – a large number of African colonial troops, who would form the nucleus of 's army. From July to November 1940, the FFF would engage in fighting with troops loyal to Vichy France in Africa, with success and failure on both sides.
In September 1940 an Anglo French naval force fought the
With these colonies came vital manpower – a large number of African colonial troops, who would form the nucleus of 's army. From July to November 1940, the FFF would engage in fighting with troops loyal to Vichy France in Africa, with success and failure on both sides.
In September 1940 an Anglo French naval force fought the  By the end of November 1940 French Equatorial Africa was wholly under the control of Free France, but the failures at Dakar had led French West Africa to declare allegiance to Vichy, to which they would remain loyal until the fall of the regime in November 1942.
On 27 October 1940 the Empire Defence Council was established to organise and administrate the imperial possessions under Free French rule, and as an alternative provisional French government. It was constituted of high-ranking officers and the governors of the free colonies, notably governor
By the end of November 1940 French Equatorial Africa was wholly under the control of Free France, but the failures at Dakar had led French West Africa to declare allegiance to Vichy, to which they would remain loyal until the fall of the regime in November 1942.
On 27 October 1940 the Empire Defence Council was established to organise and administrate the imperial possessions under Free French rule, and as an alternative provisional French government. It was constituted of high-ranking officers and the governors of the free colonies, notably governor  France also had possessions in Asia and the Pacific, and these far-flung colonies would experience similar problems of divided loyalties.
France also had possessions in Asia and the Pacific, and these far-flung colonies would experience similar problems of divided loyalties.  In 1941, the FFF fought alongside British Empire troops against the Italians in
In 1941, the FFF fought alongside British Empire troops against the Italians in 
 Throughout 1942 in
Throughout 1942 in  Soon afterwards in November 1942, the Allies launched
Soon afterwards in November 1942, the Allies launched  The Vichy forces in North Africa had been under Darlan's command and had surrendered on his orders. The Allies recognised his self-nomination as High Commissioner of France (French military and civilian commander-in-chief, ) for North and West Africa. He ordered them to cease resisting and co-operate with the Allies, which they did. By the time the Tunisia Campaign was fought, the ex-Vichy French forces in North Africa had been merged with the FFF.
After Admiral Darlan's assassination, Giraud became his ''de facto'' successor in French Africa with Allied support. This occurred through a series of consultations between Giraud and . The latter wanted to pursue a political position in France and agreed to have Giraud as commander in chief, as the more qualified military person of the two. It is questionable that he ordered that many French resistance leaders who had helped Eisenhower's troops be arrested, without any protest by Roosevelt's representative, Robert Murphy.
Later, the Americans sent
The Vichy forces in North Africa had been under Darlan's command and had surrendered on his orders. The Allies recognised his self-nomination as High Commissioner of France (French military and civilian commander-in-chief, ) for North and West Africa. He ordered them to cease resisting and co-operate with the Allies, which they did. By the time the Tunisia Campaign was fought, the ex-Vichy French forces in North Africa had been merged with the FFF.
After Admiral Darlan's assassination, Giraud became his ''de facto'' successor in French Africa with Allied support. This occurred through a series of consultations between Giraud and . The latter wanted to pursue a political position in France and agreed to have Giraud as commander in chief, as the more qualified military person of the two. It is questionable that he ordered that many French resistance leaders who had helped Eisenhower's troops be arrested, without any protest by Roosevelt's representative, Robert Murphy.
Later, the Americans sent  The
The  In the battle for Caen, bitter fighting led to the almost total destruction of the city, and stalemated the Allies. They had more success in the western American sector of the front, where after the Operation Cobra breakthrough in late July they caught 50,000 Germans in the Falaise pocket.
The invasion was preceded by weeks of intense resistance activity. Coordinated with the massive bombardments of the Transportation Plan and supported by the Special Operation Executive, SOE and the Office of Strategic Services, OSS, partisans systematically sabotaged railway lines, destroyed bridges, cut German supply lines, and provided general intelligence to the allied forces. The constant harassment took its toll on the German troops. Large remote areas were no-go zones for them and free zones for the maquis (World War II), maquisards so-called after the maquis shrubland that provided ideal terrain for guerrilla warfare. For instance, a large number of German units were required to clear the maquis du Vercors, which they battle of Vercors, eventually succeeded with, but this and numerous other actions behind German lines contributed to a much faster advance following the Provence landings than the Allied leadership had anticipated.
The main part of French Expeditionary Corps in Italy which had been fighting there was withdrawn from the Italian front, and added to the French First Army—under General
In the battle for Caen, bitter fighting led to the almost total destruction of the city, and stalemated the Allies. They had more success in the western American sector of the front, where after the Operation Cobra breakthrough in late July they caught 50,000 Germans in the Falaise pocket.
The invasion was preceded by weeks of intense resistance activity. Coordinated with the massive bombardments of the Transportation Plan and supported by the Special Operation Executive, SOE and the Office of Strategic Services, OSS, partisans systematically sabotaged railway lines, destroyed bridges, cut German supply lines, and provided general intelligence to the allied forces. The constant harassment took its toll on the German troops. Large remote areas were no-go zones for them and free zones for the maquis (World War II), maquisards so-called after the maquis shrubland that provided ideal terrain for guerrilla warfare. For instance, a large number of German units were required to clear the maquis du Vercors, which they battle of Vercors, eventually succeeded with, but this and numerous other actions behind German lines contributed to a much faster advance following the Provence landings than the Allied leadership had anticipated.
The main part of French Expeditionary Corps in Italy which had been fighting there was withdrawn from the Italian front, and added to the French First Army—under General  The Allied High Command (Supreme Headquarters Allied Expeditionary Force, SHAEF) requested the Free French force in question Racism against African Americans in the U.S. military, to be all-white, if possible, but this was very difficult because of the large numbers of black West Africans in their ranks. General Leclerc sent a small advance party to enter Paris, with the message that the 2e DB (composed of 10,500 French, 3,600 Maghrebis and about 350 Spaniards in the 9th company of the 3rd Battalion of the made up mainly of Spanish Republican exiles) would be there the following day. This party was commanded by Captain Raymond Dronne, and was given the honour to be the first Allied unit to enter Paris ahead of the . The 1er Bataillon de Fusiliers-Marins Commandos formed from the Free French Navy Fusiliers-Marins that had landed on Sword Beach were also amongst the first of the Free French forces to enter Paris.
The military governor of the city, Dietrich von Choltitz, surrendered on 25 August, ignoring Hitler's orders to destroy the city and fight to the last man. Jubilant crowds greeted the
The Allied High Command (Supreme Headquarters Allied Expeditionary Force, SHAEF) requested the Free French force in question Racism against African Americans in the U.S. military, to be all-white, if possible, but this was very difficult because of the large numbers of black West Africans in their ranks. General Leclerc sent a small advance party to enter Paris, with the message that the 2e DB (composed of 10,500 French, 3,600 Maghrebis and about 350 Spaniards in the 9th company of the 3rd Battalion of the made up mainly of Spanish Republican exiles) would be there the following day. This party was commanded by Captain Raymond Dronne, and was given the honour to be the first Allied unit to enter Paris ahead of the . The 1er Bataillon de Fusiliers-Marins Commandos formed from the Free French Navy Fusiliers-Marins that had landed on Sword Beach were also amongst the first of the Free French forces to enter Paris.
The military governor of the city, Dietrich von Choltitz, surrendered on 25 August, ignoring Hitler's orders to destroy the city and fight to the last man. Jubilant crowds greeted the  The Free French Memorial, Greenock, Free French Memorial on
The Free French Memorial, Greenock, Free French Memorial on