FHD on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
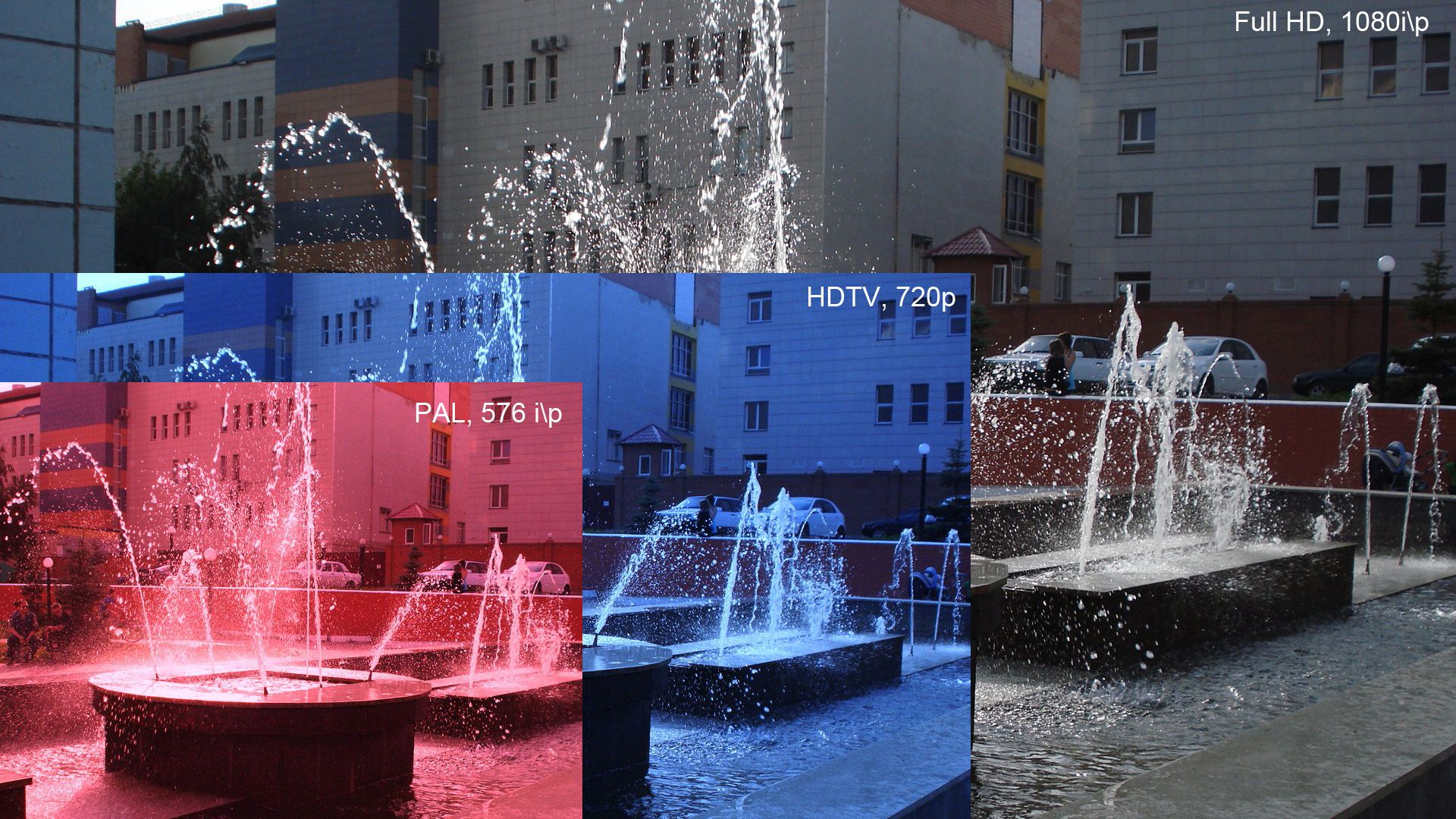 1080p (1920×1080 progressively displayed
1080p (1920×1080 progressively displayed
/ref> which will include
1080p and the Acuity of Human Vision
Audioholics Home Theater Magazine. 2 April 2007.
Secrets of Home Theater and High Fidelity. 28 February 2007.
The Facts and Fiction of 1080p
17 April 2006.
High Definition (HD) Image Formats for Television Production
( EBU technical publication). December 2004. {{Video formats Television terminology Video formats
 1080p (1920×1080 progressively displayed
1080p (1920×1080 progressively displayed pixel
In digital imaging, a pixel (abbreviated px), pel, or picture element is the smallest addressable element in a raster image, or the smallest point in an all points addressable display device.
In most digital display devices, pixels are the ...
s; also known as Full HD or FHD, and BT.709
Rec. 709, also known as Rec.709, BT.709, and ITU 709, is a standard developed by ITU-R for image encoding and signal characteristics of high-definition television.
The most recent version is BT.709-6 released in 2015. BT.709-6 defines the P ...
) is a set of HDTV
High-definition television (HD or HDTV) describes a television system which provides a substantially higher image resolution than the previous generation of technologies. The term has been used since 1936; in more recent times, it refers to the g ...
high-definition video
High-definition video (HD video) is video of higher resolution and quality than standard-definition. While there is no standardized meaning for ''high-definition'', generally any video image with considerably more than 480 vertical scan lines ...
modes characterized by 1,920 pixels displayed across the screen horizontally and 1,080 pixels down the screen vertically; the ''p'' stands for progressive scan
Progressive scanning (alternatively referred to as noninterlaced scanning) is a format of displaying, storing, or transmitting moving images in which all the lines of each frame are drawn in sequence. This is in contrast to interlaced video use ...
, ''i.e.'' non-interlaced. The term usually assumes a widescreen
Widescreen images are displayed within a set of aspect ratio (image), aspect ratios (relationship of image width to height) used in film, television and computer screens. In film, a widescreen film is any film image with a width-to-height aspect ...
aspect ratio of 16:9, implying a resolution of 2.1 megapixel
In digital imaging, a pixel (abbreviated px), pel, or picture element is the smallest addressable element in a raster image, or the smallest point in an all points addressable display device.
In most digital display devices, pixels are the ...
s. It is often marketed as Full HD or FHD, to contrast 1080p with 720p
720p (1280×720 px; also called HD ready, standard HD or just HD) is a progressive HDTV signal format with 720 horizontal lines/1280 columns and an aspect ratio (AR) of 16:9, normally known as widescreen HDTV (1.78:1). All major HDTV broadcas ...
resolution screens. Although 1080p is sometimes informally referred to as 2K, these terms reflect two distinct technical standards, with differences including resolution and aspect ratio.
1080p video signals are supported by ATSC standards
Advanced Television Systems Committee (ATSC) standards are an American set of standards for digital television transmission over terrestrial, cable and satellite networks. It is largely a replacement for the analog NTSC standard and, like th ...
in the United States and DVB
Digital Video Broadcasting (DVB) is a set of international open standards for digital television. DVB standards are maintained by the DVB Project, an international industry consortium, and are published by a Joint Technical Committee (JTC) o ...
standards in Europe. Applications of the 1080p standard include television broadcasts, Blu-ray
The Blu-ray Disc (BD), often known simply as Blu-ray, is a digital optical disc data storage format. It was invented and developed in 2005 and released on June 20, 2006 worldwide. It is designed to supersede the DVD format, and capable of st ...
Discs, smartphone
A smartphone is a portable computer device that combines mobile telephone and computing functions into one unit. They are distinguished from feature phones by their stronger hardware capabilities and extensive mobile operating systems, whi ...
s, Internet content such as YouTube
YouTube is a global online video sharing and social media platform headquartered in San Bruno, California. It was launched on February 14, 2005, by Steve Chen, Chad Hurley, and Jawed Karim. It is owned by Google, and is the second mo ...
videos and Netflix
Netflix, Inc. is an American subscription video on-demand over-the-top streaming service and production company based in Los Gatos, California. Founded in 1997 by Reed Hastings and Marc Randolph in Scotts Valley, California, it offers a ...
TV shows and movies, consumer-grade televisions
Television, sometimes shortened to TV, is a telecommunication medium for transmitting moving images and sound. The term can refer to a television set, or the medium of television transmission. Television is a mass medium for advertising, ...
and projector
A projector or image projector is an optical device that projects an image (or moving images) onto a surface, commonly a projection screen. Most projectors create an image by shining a light through a small transparent lens, but some newer typ ...
s, computer monitor
A computer monitor is an output device that displays information in pictorial or textual form. A discrete monitor comprises a visual display, support electronics, power supply, housing, electrical connectors, and external user controls.
The ...
s and video game console
A video game console is an electronic device that outputs a video signal or image to display a video game that can be played with a game controller. These may be home consoles, which are generally placed in a permanent location connected to ...
s. Small camcorder
A camcorder is a self-contained portable electronic device with video and recording as its primary function. It is typically equipped with an articulating screen mounted on the left side, a belt to facilitate holding on the right side, hot-sw ...
s, smartphone
A smartphone is a portable computer device that combines mobile telephone and computing functions into one unit. They are distinguished from feature phones by their stronger hardware capabilities and extensive mobile operating systems, whi ...
s and digital camera
A digital camera is a camera that captures photographs in digital memory. Most cameras produced today are digital, largely replacing those that capture images on photographic film. Digital cameras are now widely incorporated into mobile devices ...
s can capture still and moving images in 1080p resolution.
Broadcasting standards
Any screen device that advertises 1080p typically refers to the ability to accept 1080p signals in native resolution format, which means there are a true 1920 pixels in width and 1080 pixels in height, and the display is not over-scanning, under-scanning, or reinterpreting the signal to a lower resolution. TheHD ready 1080p
HD ready is a certification program introduced in 2005 by EICTA (European Information, Communications and Consumer Electronics Technology Industry Associations), now DIGITALEUROPE. HD ready minimum native resolution is 720 rows in widescreen rati ...
logo program, by DIGITALEUROPE
DIGITALEUROPE is the European organisation that represents the digital technology industry whose members include 98 major technology companies and 4national trade associations It seeks to ensure industry participation in the development and implem ...
, requires that certified TV sets support 1080p 24 fps, 1080p 25 fps, 1080p 50 fps, and 1080p 60 fps formats, among other requirements, with fps meaning frames per second
A frame is often a structural system that supports other components of a physical construction and/or steel frame that limits the construction's extent.
Frame and FRAME may also refer to:
Physical objects
In building construction
*Framing (con ...
. For live broadcast applications, a high-definition progressive scan format operating at 1080p at 50 or 60 frames per second is currently being evaluated as a future standard for moving picture acquisition. Although 24 frames per second is used for shooting the movies. EBU has been endorsing 1080p50 as a future-proof
Future-proofing is the process of anticipating the future and developing methods of minimizing the effects of shocks and stresses of future events. Future-proofing is used in industries such as electronics, medical industry, industrial design ...
production format because it improves resolution and requires no deinterlacing
Deinterlacing is the process of converting interlaced video into a non-interlaced or Progressive scan, progressive form. Interlaced video signals are commonly found in analog television, digital television (HDTV) when in the 1080i format, some D ...
, allows broadcasting of standard 1080i50 and 720p50 signal alongside 1080p50 even in the current infrastructure and is compatible with DCI
DCI may be an abbreviation for:
Technology
* D-chiro-inositol, an isomer of inositol
* Data, context and interaction, an architectural pattern in computer software development
* Direct Count & Intersect, an algorithm for discovering frequent se ...
distribution formats.
1080p50/p60 production format requires a whole new range of studio equipment including cameras, storage and editing systems, and contribution links (such as Dual-link HD-SDI and 3G-SDI) as it has doubled the data rate of current 50 or 60 fields interlaced 1920x1080 from 1.485 Gbit/s to nominally 3 Gbit/s using uncompressed RGB encoding. Most current revisions of SMPTE 372M
SMPTE 372M is a standard published by SMPTE which expands upon SMPTE 259M, SMPTE 344M, and SMPTE 292M allowing for bit-rates of 2.970 Gbit/s, and 2.970/1.001 Gbit/s over two wires. These bit-rates are sufficient for 1080p
1080p (1920×1080 progre ...
, SMPTE 424M SMPTE 424M is a standard published by SMPTE which expands upon SMPTE 259M, SMPTE 344M, and SMPTE 292M allowing for bit-rates of 2.970 Gbit/s and 2.970/1.001 Gbit/s over a single-link coaxial cable. These bit-rates are sufficient for 1080p ...
and EBU Tech 3299 require YCbCr
YCbCr, Y′CbCr, or Y Pb/Cb Pr/Cr, also written as YCBCR or Y′CBCR, is a family of color spaces used as a part of the color image pipeline in video and digital photography systems. Y′ is the luma component and CB and CR are the blue-diff ...
color space and 4:2:2 chroma subsampling
Chroma subsampling is the practice of encoding images by implementing less resolution for chroma information than for luma information, taking advantage of the human visual system's lower acuity for color differences than for luminance.
It is u ...
for transmitting 1080p50 (nominally 2.08 Gbit/s) and 1080p60 signal. Studies from 2009 show that for digital broadcasts compressed with H.264/AVC, transmission bandwidth savings of interlaced video
Interlaced video (also known as interlaced scan) is a technique for doubling the perceived frame rate of a video display without consuming extra bandwidth. The interlaced signal contains two fields of a video frame captured consecutively. Th ...
over fully progressive video are minimal even when using twice the frame rate
Frame rate (expressed in or FPS) is the frequency (rate) at which consecutive images ( frames) are captured or displayed. The term applies equally to film and video cameras, computer graphics, and motion capture systems. Frame rate may also be ...
; i.e., 1080p50 signal (50 progressive frames per second) actually produces the same bit rate as 1080i50 signal (25 interlaced frames or 50 sub-fields per second).
ATSC
In the United States, the originalATSC standards
Advanced Television Systems Committee (ATSC) standards are an American set of standards for digital television transmission over terrestrial, cable and satellite networks. It is largely a replacement for the analog NTSC standard and, like th ...
for HDTV supported 1080p video, but only at the frame rates of 23.976, 24, 25, 29.97 and 30 frames per second (colloquially known as 1080p24, 1080p25 and 1080p30). In July 2008, the ATSC standards were amended to include H.264/MPEG-4 AVC compression and 1080p at 50, 59.94 and 60 frames per second (1080p50 and 1080p60). Such frame rate
Frame rate (expressed in or FPS) is the frequency (rate) at which consecutive images ( frames) are captured or displayed. The term applies equally to film and video cameras, computer graphics, and motion capture systems. Frame rate may also be ...
s require H.264/AVC '' High Profile Level 4.2'', while standard HDTV frame rates only require Level 4.0. This update is not expected to result in widespread availability of 1080p60 programming, since most of the existing digital receivers in use would only be able to decode the older, less-efficient MPEG-2
MPEG-2 (a.k.a. H.222/H.262 as was defined by the ITU) is a standard for "the generic coding of moving pictures and associated audio information". It describes a combination of lossy video compression and lossy audio data compression methods, ...
codec, and because there is a limited amount of bandwidth for subchannels.
DVB
In Europe, 1080p25 signals have been supported by the DVB suite of broadcasting standards. The 1080p50 format is considered to be a future-proof production format and, eventually, a future broadcasting format. 1080p50 broadcasting should require the same bandwidth as 1080i50 signal and only 15–20% more than that of 720p50 signal due to increased compression efficiency, though 1080p50 production requires more bandwidth or more efficientcodec
A codec is a device or computer program that encodes or decodes a data stream or signal. ''Codec'' is a portmanteau of coder/decoder.
In electronic communications, an endec is a device that acts as both an encoder and a decoder on a signal or ...
s such as JPEG 2000
JPEG 2000 (JP2) is an image compression standard and coding system. It was developed from 1997 to 2000 by a Joint Photographic Experts Group committee chaired by Touradj Ebrahimi (later the JPEG president), with the intention of superseding th ...
, high-bitrate MPEG-2
MPEG-2 (a.k.a. H.222/H.262 as was defined by the ITU) is a standard for "the generic coding of moving pictures and associated audio information". It describes a combination of lossy video compression and lossy audio data compression methods, ...
, or H.264/AVC and HEVC. In September 2009, ETSI
The European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI) is an independent, not-for-profit, standardization organization in the field of information and communications. ETSI supports the development and testing of global technical standard ...
and EBU, the maintainers of the DVB suite, added support for 1080p50 signal coded with MPEG-4 AVC ''High Profile Level 4.2'' with Scalable Video Coding extensions or VC-1
SMPTE 421, informally known as VC-1, is a video coding format. Most of it was initially developed as Microsoft's proprietary video format Windows Media Video 9 in 2003. With some enhancements including the development of a new Advanced Profile ...
''Advanced Profile'' compression; DVB also supports 1080p encoded at ATSC frame rates of 23.976, 24, 29.97, 30, 59.94 and 60.
EBU requires that legacy MPEG-4 AVC decoders should avoid crashing in the presence of SVC or 1080p50 (and higher resolution) packets. SVC enables forward compatibility
Forward compatibility or upward compatibility is a design characteristic that allows a system to accept input intended for a later version of itself. The concept can be applied to entire systems, electrical interfaces, telecommunication signals, ...
with 1080p50 and 1080p60 broadcasting for older MPEG-4 AVC receivers, so they will only recognize baseline SVC stream coded at a lower resolution or frame rate (such as 720p60 or 1080i60) and will gracefully ignore additional packets, while newer hardware will be able to decode full-resolution signal (such as 1080p60).
In June 2016, EBU announced the "Advanced 1080p" formatEBU TR 037 – Video System Requirements for UHDTV and an Advanced 1080p television format/ref> which will include
UHD Phase A
Ultra HD Forum is an organization whose goal is to help solve the real world hurdles in deploying Ultra HD video and thus to help promote UHD deployment. The Ultra HD Forum will help navigate amongst the standards related to high dynamic range (H ...
features such as high-dynamic-range video
High-dynamic-range television (HDR or HDR-TV) is a technology that improves the quality of display signals. It is contrasted with the retroactively-named standard dynamic range (SDR). HDR changes the way the luminance and colors of videos and ...
(using PQ and HLG) at 10 and 12 bit color and BT.2020
ITU-R Recommendation BT.2020, more commonly known by the abbreviations Rec. 2020 or BT.2020, defines various aspects of ultra-high-definition television (UHDTV) with standard dynamic range (SDR) and wide color gamut (WCG), including picture ...
color gamut, and optional HFR 100, 120/1.001 and 120 Hz; an advanced 1080p video stream can be encoded alongside baseline HDTV or UHDTV signal using Scalable HEVC
High Efficiency Video Coding (HEVC), also known as H.265 and MPEG-H Part 2, is a video compression standard designed as part of the MPEG-H project as a successor to the widely used Advanced Video Coding (AVC, H.264, or MPEG-4 Part 10). In compari ...
. The ITU-T BT.2100 standard that includes Advanced 1080p video was subsequently published in July 2016.
Resolutions
In practice, 1080p typically refers to a 1920×1080 raster with a 16:9picture aspect ratio
The aspect ratio of an image is the ratio of its width to its height, and is expressed with two numbers separated by a colon, such as ''16:9'', sixteen-to-nine. For the ''x'':''y'' aspect ratio, the image is ''x'' units wide and ''y'' units high ...
. The following is a list of other resolutions with a picture height of 1080 lines that are sometimes referred as 1080p.
Availability
Broadcasts
In the United States, 1080p over-the-air broadcasts are currently available in select stations in some cities in the US via ATSC 3.0 multiplex stations where as ATSC 3.0 is currently rolling out throughout the U.S. The majority of the stations that broadcast at 1080p are CBS and NBC stations and affiliates. All other stations do not broadcast at 1080p and usually broadcast at 720p60 (including when simulcasting in ATSC 3.0) or 1080i60 (outside of ATSC 3.0) encoded with MPEG-2. There is also technical restrictions with ATSC 3.0 multiplex stations that prevent stations from airing at 1080p. While converting to ATSC 3.0 is voluntary by TV Stations, there is no word when any of the major networks will consider airing at 1080p in the foreseeable future on a national scale, although they are required to broadcast ATSC signals for at least five years thereafter. However, satellite services (e.g.,DirecTV
DirecTV (trademarked as DIRECTV) is an American multichannel video programming distributor based in El Segundo, California. Originally launched on June 17, 1994, its primary service is a digital satellite service serving the United States. I ...
, XstreamHD and Dish Network
DISH Network Corporation (DISH, an acronym for DIgital Sky Highway) is an American television provider and the owner of the direct-broadcast satellite provider Dish, commonly known as Dish Network, and the over-the-top IPTV service, Sling ...
) utilize the 1080p/24-30 format with MPEG-4 AVC/H.264 encoding for pay-per-view
Pay-per-view (PPV) is a type of pay television or webcast service that enables a viewer to pay to watch individual events via private telecast.
Events can be purchased through a multichannel television platform using their electronic program g ...
movies that are downloaded in advance via satellite or on-demand via broadband. At this time, no pay service channel such as USA, HDNET, etc. nor premium movie channel such as HBO, etc., stream their services live to their distributors (MVPD Multichannel television in the United States has been available since at least 1948. The United States is served by multichannel television through cable television systems, direct-broadcast satellite providers, and various other wireline video pro ...
) in this format because many MVPDs, especially DBS and cable, do not have sufficient bandwidth to provide the format streaming live to their subscribers without negatively impacting their current services.
For material that originates from a progressive scanned 24 frame/s source (such as film), MPEG-2
MPEG-2 (a.k.a. H.222/H.262 as was defined by the ITU) is a standard for "the generic coding of moving pictures and associated audio information". It describes a combination of lossy video compression and lossy audio data compression methods, ...
lets the video be coded as 1080p24, irrespective of the final output format. These progressively-coded frames are tagged with metadata (literally, fields of the PICTURE header) instructing a decoder how to perform a 3:2 pulldown to interlace them. While the formal output of the MPEG-2 decoding process from such stations is 1080i60, the actual content is coded as 1080p24 and can be viewed as such (using a process known as inverse telecine
Telecine ( or ) is the process of transferring film into video and is performed in a color suite. The term is also used to refer to the equipment used in the post-production process.
Telecine enables a motion picture, captured originally on fi ...
) since no information is lost even when the broadcaster performs the 3:2 pulldown.
In June 2016, Germany commenced terrestrial broadcasts of eight 1080p50 high-definition channels, using DVB-T2 protocol with HEVC encoding; a total of 40 channels will be available by March 2017.
Blu-ray Disc
Blu-ray Disc
The Blu-ray Disc (BD), often known simply as Blu-ray, is a digital optical disc data storage format. It was invented and developed in 2005 and released on June 20, 2006 worldwide. It is designed to supersede the DVD format, and capable of sto ...
s are able to hold 1080p HD content, and most movies released on Blu-ray Disc
The Blu-ray Disc (BD), often known simply as Blu-ray, is a digital optical disc data storage format. It was invented and developed in 2005 and released on June 20, 2006 worldwide. It is designed to supersede the DVD format, and capable of sto ...
produce a full 1080p HD picture when the player is connected to a 1080p HDTV
High-definition television (HD or HDTV) describes a television system which provides a substantially higher image resolution than the previous generation of technologies. The term has been used since 1936; in more recent times, it refers to the g ...
via an HDMI
High-Definition Multimedia Interface (HDMI) is a proprietary audio/video interface for transmitting uncompressed video data and compressed or uncompressed digital audio data from an HDMI-compliant source device, such as a display controlle ...
cable. The Blu-ray Disc video specification allows encoding of 1080p23.976, 1080p24, 1080i50, and 1080i59.94. Generally this type of video runs at 30 to 40 megabits per second, compared to the 3.5 megabits per second for conventional standard definition broadcasts.
Smartphones
Smartphone
A smartphone is a portable computer device that combines mobile telephone and computing functions into one unit. They are distinguished from feature phones by their stronger hardware capabilities and extensive mobile operating systems, whi ...
s with 1080p Full HD display have been available on the market since 2012. As of late-2014, it is the standard for mid-range to high-end smartphones and many of the flagship devices of 2014 used even higher resolutions, either Quad HD
1440p is a family of video display resolutions that have a vertical resolution of 1440 pixels. The ''p'' stands for progressive scan, i.e. non-interlaced. The 1440 pixel vertical resolution is double the vertical resolution of 720p, and one-third ...
(1440p) or Ultra HD
Ultra-high-definition television (also known as Ultra HD television, Ultra HD, UHDTV, UHD and Super Hi-Vision) today includes 4K UHD and 8K UHD, which are two digital video formats with an aspect ratio of 16:9. These were first proposed b ...
(2160p) resolutions.
Internet content
Several websites, includingYouTube
YouTube is a global online video sharing and social media platform headquartered in San Bruno, California. It was launched on February 14, 2005, by Steve Chen, Chad Hurley, and Jawed Karim. It is owned by Google, and is the second mo ...
, allow videos to be uploaded in the 1080p format. YouTube streams 1080p content at approximately 4 megabits per second compared to Blu-ray's 30 to 40 megabits per second. Digital distribution
Digital distribution, also referred to as content delivery, online distribution, or electronic software distribution, among others, is the delivery or distribution of digital media content such as audio, video, e-books, video games, and other s ...
services like Hulu
Hulu () is an American subscription streaming service majority-owned by The Walt Disney Company, with Comcast's NBCUniversal holding a minority stake. It was launched on October 29, 2007 and it offers a library of films and television series ...
and HBO Max
HBO Max is an American subscription video on-demand over-the-top streaming service owned by Warner Bros. Discovery. Launched in the United States on May 27, 2020, the service is built around the libraries of HBO, Warner Bros., Cartoon Ne ...
also deliver 1080p content, such as movies available on Blu-ray Disc or from broadcast sources. This can include distribution services like peer-to-peer websites and public or private tracking networks. Netflix
Netflix, Inc. is an American subscription video on-demand over-the-top streaming service and production company based in Los Gatos, California. Founded in 1997 by Reed Hastings and Marc Randolph in Scotts Valley, California, it offers a ...
has been offering high quality 1080p content in the US and other countries through select internet providers since 2013.
Consumer televisions and projectors
As of 2012, most consumer televisions being sold provide 1080p inputs, mainly viaHDMI
High-Definition Multimedia Interface (HDMI) is a proprietary audio/video interface for transmitting uncompressed video data and compressed or uncompressed digital audio data from an HDMI-compliant source device, such as a display controlle ...
, and support full high-definition resolutions. 1080p resolution is available in all types of television, including plasma, LCD, DLP front and rear projection and LCD projection. For displaying film-based 1080i60 signals, a scheme called 3:2 pulldown reversal ( reverse telecine) is beginning to appear in some newer 1080p displays, which can produce a true 1080p quality image from film-based 1080i60 programs. Similarly, 25fps content broadcast at 1080i50 may be deinterlaced to 1080p content with no loss of quality or resolution.
AV equipment manufacturers have adopted the term ''Full HD'' to mean a set can display all available HD resolutions up to 1080p. The term is misleading, however, because it does not guarantee the set is capable of rendering digital video at all frame rates encoded in source files with 1920 X 1080 pixel resolution. Most notably, a "Full HD" set is not guaranteed to support the 1080p24 format, leading to consumer confusion. DigitalEurope
DIGITALEUROPE is the European organisation that represents the digital technology industry whose members include 98 major technology companies and 4national trade associations It seeks to ensure industry participation in the development and implem ...
(formerly EICTA) maintains the HD ready 1080p
HD ready is a certification program introduced in 2005 by EICTA (European Information, Communications and Consumer Electronics Technology Industry Associations), now DIGITALEUROPE. HD ready minimum native resolution is 720 rows in widescreen rati ...
logo program that requires the certified TV sets to support 1080p24, 1080p50, and 1080p60, without overscan/underscan and picture distortion.
Computer monitors
Most widescreencathode-ray tube
A cathode-ray tube (CRT) is a vacuum tube containing one or more electron guns, which emit electron beams that are manipulated to display images on a Phosphorescence, phosphorescent screen. The images may represent electrical waveforms (osci ...
(CRT) and liquid-crystal display
A liquid-crystal display (LCD) is a flat-panel display or other electronically modulated optical device that uses the light-modulating properties of liquid crystals combined with polarizers. Liquid crystals do not emit light directly but ...
(LCD) monitors can natively display 1080p content. For example, widescreen WUXGA
The graphics display resolution is the width and height dimension of an electronic visual display device, measured in pixels. This information is used for electronic devices such as a computer monitor. Certain combinations of width and height ar ...
monitors support 1920x1200 resolution, which can display a pixel for pixel reproduction of the 1080p (1920×1080) format. Additionally, many 23, 24, and widescreen LCD monitors use 1920×1200 as their native resolution; 30 inch displays can display beyond 1080p at up to 2560×1600 ( 1600p). Many 27" monitors have native resolutions of 2560×1440 and hence operate at 1440p
1440p is a family of video display resolutions that have a vertical resolution of 1440 pixels. The ''p'' stands for progressive scan, i.e. non-interlaced. The 1440 pixel vertical resolution is double the vertical resolution of 720p, and one-third ...
.
Laptops
A laptop, laptop computer, or notebook computer is a small, portable personal computer (PC) with a screen and alphanumeric keyboard. Laptops typically have a clam shell form factor with the screen mounted on the inside of the upper li ...
Sony
, commonly stylized as SONY, is a Japanese multinational conglomerate corporation headquartered in Minato, Tokyo, Japan. As a major technology company, it operates as one of the world's largest manufacturers of consumer and professional ...
has their first and formerly VAIO 1080p laptop, VPCCB17FG, in 2011
File:2011 Events Collage.png, From top left, clockwise: a protester partaking in Occupy Wall Street heralds the beginning of the Occupy movement; protests against Libyan dictator Muammar Gaddafi, who was killed that October; a young man celebrates ...
, and since Asus also has their first 4K laptop GL502 which was formerly branded Republic of Gamers in 2017, 1080p has also become the nowadays lowest standard for laptops.
Video game consoles
Whilst Microsoft's originalXbox
Xbox is a video gaming brand created and owned by Microsoft. The brand consists of five video game consoles, as well as applications (games), streaming services, an online service by the name of Xbox network, and the development arm by the ...
, launched as part of the sixth generation of video game consoles
In the history of video games, the sixth generation era (sometimes called the 128-bit era; see "bits and system power" below) is the era of computer and video games, video game consoles, and handheld gaming devices available at the turn of the ...
in 2001, could support a 1080i output in limited circumstances, support for 1080p began with the launch of the seventh generation of home video game consoles in 2005. Both the Xbox 360
The Xbox 360 is a home video game console developed by Microsoft. As the successor to the original Xbox, it is the second console in the Xbox series. It competed with Sony's PlayStation 3 and Nintendo's Wii as part of the seventh generati ...
and PlayStation 3
The PlayStation 3 (PS3) is a home video game console developed by Sony Interactive Entertainment, Sony Computer Entertainment. The successor to the PlayStation 2, it is part of the PlayStation brand of consoles. It was first released on Novemb ...
were capable of outputting at 1080p, with only the Wii
The Wii ( ) is a home video game console developed and marketed by Nintendo. It was released on November 19, 2006, in North America and in December 2006 for most other regions of the world. It is Nintendo's fifth major home game console, ...
unable to support the resolution. All home video game consoles launched as part of the eighth generation
Eighth is ordinal form of the number eight.
Eighth may refer to:
* One eighth, or ⅛, a fraction, one of eight equal parts of a whole
* Eighth note (quaver), a musical note played for half the value of a quarter note (crotchet)
* Octave, an in ...
, which began in 2012 with the launch of the Wii U
The Wii U ( ) is a home video game console developed by Nintendo as the successor to the Wii. Released in late 2012, it is the first eighth-generation video game console and competed with Microsoft's Xbox One and Sony's PlayStation 4.
...
, were capable of 1080p outputs. Mid-generation hardware revisions and new models introduced by Sony
, commonly stylized as SONY, is a Japanese multinational conglomerate corporation headquartered in Minato, Tokyo, Japan. As a major technology company, it operates as one of the world's largest manufacturers of consumer and professional ...
and Microsoft
Microsoft Corporation is an American multinational technology corporation producing computer software, consumer electronics, personal computers, and related services headquartered at the Microsoft Redmond campus located in Redmond, Washi ...
to their respective PlayStation 4
The PlayStation 4 (PS4) is a home video game console developed by Sony Interactive Entertainment. Announced as the successor to the PlayStation 3 in February 2013, it was launched on November 15, 2013, in North America, November 29, 2013 i ...
and Xbox One
The Xbox One is a home video game console developed by Microsoft. Announced in May 2013, it is the successor to Xbox 360 and the third base console in the Xbox series of video game consoles. It was first released in North America, parts of ...
consoles added the capability of outputting at 4K UHD
4K resolution refers to a horizontal display resolution of approximately 4,000 pixels. Digital television and digital cinematography commonly use several different 4K resolutions. In television and consumer media, 38402160 (4K UHD) is the dominan ...
— well beyond 1080p. Moreover, this mid-generational improvement in computing power also represented a leap in the ability of video game consoles to render gaming content at a 1080p resolution or higher, rather than relying on upscaling. This trend continued with the launch of the current ninth generation of video game consoles
The ninth generation of video game consoles began in November 2020 with the releases of Microsoft's Xbox Series X and Series S console family and Sony's PlayStation 5.
The consoles represent significant performance upgrades from the prior Xbox ...
in 2020, in which Sony's PlayStation 5
The PlayStation 5 (PS5) is a home video game console developed by Sony Interactive Entertainment. Announced as the successor to the PlayStation 4 in April 2019, it was launched on November 12, 2020, in Australia, Japan, New Zealand, North ...
and Microsoft's Xbox Series X
The Xbox Series X/S are home video game consoles developed by Microsoft. They were both released on November 10, 2020, as the fourth generation Xbox, succeeding the Xbox One. Along with Sony's PlayStation 5, also released in November 2020, ...
also introduced 8K UHD
8K resolution refers to an image or display resolution with a width of approximately 8,000 pixels. 8K UHD () is the highest resolution defined in the Rec. 2020 ( UHDTV) standard.
8K display resolution is the successor to 4K resolution. TV manuf ...
support.
Cameras
Many camerasprofessional and consumer still, action and video cameras, includingDSLR
A digital single-lens reflex camera (digital SLR or DSLR) is a digital camera that combines the optics and the mechanisms of a single-lens reflex camera with a digital imaging sensor.
The reflex design scheme is the primary difference between a ...
camerasand other devices with built-in cameras such as laptop
A laptop, laptop computer, or notebook computer is a small, portable personal computer (PC) with a screen and alphanumeric keyboard. Laptops typically have a clam shell form factor with the screen mounted on the inside of the upper li ...
s, smartphone
A smartphone is a portable computer device that combines mobile telephone and computing functions into one unit. They are distinguished from feature phones by their stronger hardware capabilities and extensive mobile operating systems, whi ...
s and tablet computers, can capture 1080p24, 1080p25, 1080p30 or 1080p60 video, often encoding it in progressive segmented frame
Progressive segmented Frame (PsF, sF, SF) is a scheme designed to acquire, store, modify, and distribute progressive scan video using interlaced equipment.
With PsF, a progressive frame is divided into two ''segments'', with the odd lines in one s ...
format.
See also
*List of common resolutions
This article lists computer monitor screen resolutions that are defined by standards or in common use. Most of them use certain preferred numbers.
Computer graphics
; Pixel aspect ratio (PAR): The horizontal to vertical ratio of each pixel.
; ...
* 4320p
8K resolution refers to an image or display resolution with a width of approximately 8,000 pixels. 8K UHD () is the highest resolution defined in the Rec. 2020 ( UHDTV) standard.
8K display resolution is the successor to 4K resolution. TV manuf ...
, 2160p
4K resolution refers to a horizontal display resolution of approximately 4,000 pixels. Digital television and digital cinematography commonly use several different 4K resolutions. In television and consumer media, 38402160 (4K UHD) is the dominan ...
, 1440p
1440p is a family of video display resolutions that have a vertical resolution of 1440 pixels. The ''p'' stands for progressive scan, i.e. non-interlaced. The 1440 pixel vertical resolution is double the vertical resolution of 720p, and one-third ...
, 1080i
1080i (also known as Full HD or BT.709) is a combination of frame resolution and scan type. 1080i is used in high-definition television (HDTV) and high-definition video. The number "1080" refers to the number of horizontal lines on the scree ...
, 720p
720p (1280×720 px; also called HD ready, standard HD or just HD) is a progressive HDTV signal format with 720 horizontal lines/1280 columns and an aspect ratio (AR) of 16:9, normally known as widescreen HDTV (1.78:1). All major HDTV broadcas ...
, 576p
576p is the shorthand name for a video display resolution. The ''p'' stands for progressive scan, i.e. non-interlaced, the ''576'' for a vertical resolution of 576 pixels (the frame rate can be given explicitly after the letter). Usually it corr ...
, 576i
576i is a standard-definition digital video mode, originally used for digitizing analog television in most countries of the world where the utility frequency for electric power distribution is 50 Hz. Because of its close association wit ...
, 480p
480p is the shorthand name for a family of video display resolutions. The p stands for progressive scan, i.e. non-interlaced. The ''480'' denotes a vertical resolution of 480 pixels, usually with a horizontal resolution of 640 pixels and 4:3 ...
, 480i
480i is the video mode used for standard-definition digital television in the Caribbean, Japan, South Korea, Taiwan, Philippines, Laos, Western Sahara, and most of the Americas (with the exception of Argentina, Paraguay, and Uruguay). T ...
, 360p
Low-definition television (LDTV) refers to TV systems that have a lower screen resolution than standard-definition TV systems. The term is usually used in reference to digital TV, in particular when broadcasting at the same (or similar) resoluti ...
, 240p
Low-definition television (LDTV) refers to TV systems that have a lower screen resolution than standard-definition TV systems. The term is usually used in reference to digital TV, in particular when broadcasting at the same (or similar) resolut ...
* 21:9 aspect ratio – a common widescreen cinema aspect ratio
* 10K resolution
10K resolution is any of a number of horizontal display resolutions of around ten-thousand pixels, usually double that of 5K resolutions: 9,600 or 10,240 pixels. Unlike 4K and 8K, it is not part of UHDTV broadcast standards. The first devices ava ...
– digital video formats with a horizontal resolution of around 10,000 pixels, aimed at non-television computer monitor usage
* 16K resolution
16K resolution is a display resolution with approximately 16,000 pixels horizontally. The most commonly discussed 16K resolution is , which doubles the pixel count of 8K UHD in each dimension, for a total of four times as many pixels. This resolu ...
– experimental VR format
* Ultra-high-definition television
Ultra-high-definition television (also known as Ultra HD television, Ultra HD, UHDTV, UHD and Super Hi-Vision) today includes 4K UHD and 8K UHD, which are two digital video formats with an aspect ratio of 16:9. These were first proposed b ...
(UHDTV) – digital video formats with resolutions of 4K (3840×2160) and 8K (7680×4320)
* Rec. 2020
ITU-R Recommendation BT.2020, more commonly known by the abbreviations Rec. 2020 or BT.2020, defines various aspects of ultra-high-definition television (UHDTV) with standard dynamic range (SDR) and wide color gamut (WCG), including picture ...
– ITU-R Recommendation for UHDTV
* High Efficiency Video Coding
High Efficiency Video Coding (HEVC), also known as H.265 and MPEG-H Part 2, is a video compression standard designed as part of the MPEG-H project as a successor to the widely used Advanced Video Coding (AVC, H.264, or MPEG-4 Part 10). In comp ...
(HEVC) – video standard that supports 4K & 8K UHDTV and resolutions up to 8192×4320
* Digital cinema
Digital cinema refers to adoption of digital technology within the film industry to distribute or project motion pictures as opposed to the historical use of reels of motion picture film, such as 35 mm film. Whereas film reels have to be sh ...
* Display resolution
The display resolution or display modes of a digital television, computer monitor or display device is the number of distinct pixels in each dimension that can be displayed. It can be an ambiguous term especially as the displayed resolution ...
References
External links
1080p and the Acuity of Human Vision
Audioholics Home Theater Magazine. 2 April 2007.
Secrets of Home Theater and High Fidelity. 28 February 2007.
The Facts and Fiction of 1080p
17 April 2006.
High Definition (HD) Image Formats for Television Production
( EBU technical publication). December 2004. {{Video formats Television terminology Video formats