Frontal Bossing on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
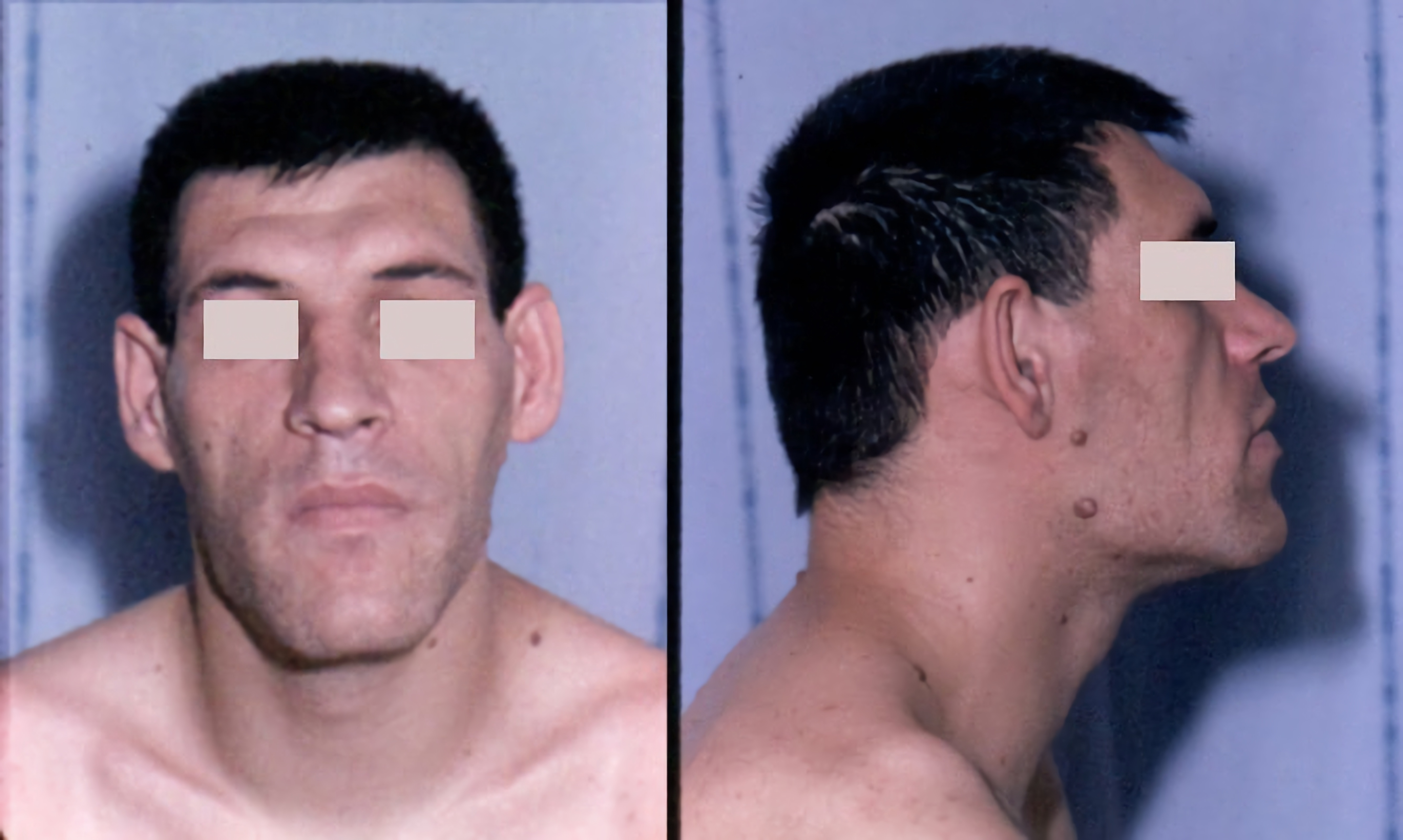 Skull bossing is a descriptive term in medical physical examination indicating a protuberance of the skull, most often in the
Skull bossing is a descriptive term in medical physical examination indicating a protuberance of the skull, most often in the
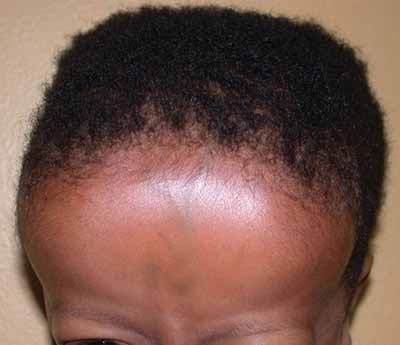
 Frontal bossing is the development of an unusually pronounced forehead which may also be associated with a heavier than normal brow ridge. It is caused by enlargement of the
Frontal bossing is the development of an unusually pronounced forehead which may also be associated with a heavier than normal brow ridge. It is caused by enlargement of the
frontal bone
The frontal bone is a bone in the human skull. The bone consists of two portions.'' Gray's Anatomy'' (1918) These are the vertically oriented squamous part, and the horizontally oriented orbital part, making up the bony part of the forehead, pa ...
s of the forehead ("frontal bossing"). Although prominence of the skull bones may be normal, skull bossing may be associated with certain medical conditions, including nutritional, metabolic, hormonal, and hematologic disorders.
Frontal bossing

 Frontal bossing is the development of an unusually pronounced forehead which may also be associated with a heavier than normal brow ridge. It is caused by enlargement of the
Frontal bossing is the development of an unusually pronounced forehead which may also be associated with a heavier than normal brow ridge. It is caused by enlargement of the frontal bone
The frontal bone is a bone in the human skull. The bone consists of two portions.'' Gray's Anatomy'' (1918) These are the vertically oriented squamous part, and the horizontally oriented orbital part, making up the bony part of the forehead, pa ...
, often in conjunction with abnormal enlargement of other facial bones
The facial skeleton comprises the ''facial bones'' that may attach to build a portion of the skull. The remainder of the skull is the braincase.
In human anatomy and development, the facial skeleton is sometimes called the ''membranous viscerocr ...
, skull
The skull is a bone protective cavity for the brain. The skull is composed of four types of bone i.e., cranial bones, facial bones, ear ossicles and hyoid bone. However two parts are more prominent: the cranium and the mandible. In humans, the ...
, mandible
In anatomy, the mandible, lower jaw or jawbone is the largest, strongest and lowest bone in the human facial skeleton. It forms the lower jaw and holds the lower teeth in place. The mandible sits beneath the maxilla. It is the only movable bone ...
, and bones of the hands and feet. Frontal bossing may be seen in a few rare medical syndromes such as acromegaly – a chronic medical disorder in which the anterior pituitary
A major organ of the endocrine system, the anterior pituitary (also called the adenohypophysis or pars anterior) is the glandular, anterior lobe that together with the posterior lobe (posterior pituitary, or the neurohypophysis) makes up the p ...
gland produces excess growth hormone
Growth hormone (GH) or somatotropin, also known as human growth hormone (hGH or HGH) in its human form, is a peptide hormone that stimulates growth, cell reproduction, and cell regeneration in humans and other animals. It is thus important in h ...
(GH). Frontal bossing may also occur in diseases resulting in chronic anemia, where there is increased hematopoiesis
Haematopoiesis (, from Greek , 'blood' and 'to make'; also hematopoiesis in American English; sometimes also h(a)emopoiesis) is the formation of blood cellular components. All cellular blood components are derived from haematopoietic stem cells ...
and enlargement of the medullary cavities of the skull.
Associated medical disorders
*Rickets
Rickets is a condition that results in weak or soft bones in children, and is caused by either dietary deficiency or genetic causes. Symptoms include bowed legs, stunted growth, bone pain, large forehead, and trouble sleeping. Complications ma ...
*Achondroplasia
Achondroplasia is a genetic disorder with an autosomal dominant pattern of inheritance whose primary feature is dwarfism. In those with the condition, the arms and legs are short, while the torso is typically of normal length. Those affected ha ...
* Acromegaly
* Basal cell nevus syndrome
*Congenital syphilis
Congenital syphilis is syphilis present ''in utero'' and at birth, and occurs when a child is born to a mother with syphilis. Untreated early syphilis infections results in a high risk of poor pregnancy outcomes, including saddle nose, lower ext ...
* Cleidocranial dysostosis
*Crouzon syndrome
Crouzon syndrome is an autosomal dominant genetic disorder known as a branchial arch syndrome. Specifically, this syndrome affects the first branchial (or pharyngeal) arch, which is the precursor of the maxilla and mandible. Since the branchial ...
* Cryopyrin-Associated Periodic Syndrome (CAPS – PFS)
*Ectodermal dysplasia
Ectodermal dysplasia (ED) is a group of genetic syndromes all deriving from abnormalities of the ectodermal structures.James, William; Berger, Timothy; Elston, Dirk (2005). ''Andrews' Diseases of the Skin: Clinical Dermatology''. (10th ed.). S ...
*Extramedullary hematopoiesis
Extramedullary hematopoiesis (EMH or sometimes EH) refers to hematopoiesis occurring outside of the medulla of the bone (bone marrow). It can be physiologic or pathologic.
Physiologic EMH occurs during embryonic and fetal development; during this ...
* Fragile X syndrome
*Hurler syndrome
Hurler syndrome, also known as mucopolysaccharidosis Type IH (MPS-IH), Hurler's disease, and formerly gargoylism, is a genetic disorder that results in the buildup of large sugar molecules called glycosaminoglycans (GAGs) in lysosomes. The inab ...
* Osteopathia Striata with Cranial Sclerosis
*Pfeiffer syndrome
Pfeiffer syndrome is a rare genetic disorder characterized by the premature fusion of certain bones of the skull (craniosynostosis) which affects the shape of the head and face. In addition, the syndrome includes abnormalities of the hands (such ...
* Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome
* Russell-Silver syndrome (Russell-Silver dwarf)
*Thanatophoric dysplasia
Thanatophoric dysplasia is a severe skeletal disorder characterized by a disproportionately small ribcage, extremely short limbs and folds of extra skin on the arms and legs.
Symptoms and signs
Infants with this condition have disproportionately ...
* Talfan syndrome
*Trimethadione
Trimethadione (Tridione) is an oxazolidinedione anticonvulsant. It is most commonly used to treat epileptic conditions that are resistant to other treatments.
It is primarily effective in treating absence seizures, but can also be used in ref ...
(antiseizure drug) use during pregnancy
*Beta-thalassemia
Beta thalassemias (β thalassemias) are a group of inherited blood disorders. They are forms of thalassemia caused by reduced or absent synthesis of the beta chains of hemoglobin that result in variable outcomes ranging from severe anemia to cl ...
(due to expansion of bone marrow secondary to increased hematopoiesis
Haematopoiesis (, from Greek , 'blood' and 'to make'; also hematopoiesis in American English; sometimes also h(a)emopoiesis) is the formation of blood cellular components. All cellular blood components are derived from haematopoietic stem cells ...
; see Extramedullary hematopoiesis
Extramedullary hematopoiesis (EMH or sometimes EH) refers to hematopoiesis occurring outside of the medulla of the bone (bone marrow). It can be physiologic or pathologic.
Physiologic EMH occurs during embryonic and fetal development; during this ...
)Bope, Edward T., and Rick D. Kellerman. "Chapter 13 – Hematology." ''Conn's Current Therapy: Latest Approved Methods of Treatment for the Practicing Physician''. Philadelphia: Saunders Elsevier, 2012.
* Hallermann-Streiff syndrome
References
Medical terminology {{med-diagnostic-stub