
The Spanish missions in California ( es, Misiones españolas en California) comprise a
series of 21 religious outposts or missions established between 1769 and 1833 in what is now the U.S. state of
California
California is a U.S. state, state in the Western United States, located along the West Coast of the United States, Pacific Coast. With nearly 39.2million residents across a total area of approximately , it is the List of states and territori ...
. Founded by
Catholic priests
The priesthood is the office of the ministers of religion, who have been commissioned ("ordained") with the Holy orders of the Catholic Church. Technically, bishops are a priestly order as well; however, in layman's terms ''priest'' refers only ...
of the
Franciscan
The Franciscans are a group of related Mendicant orders, mendicant Christianity, Christian Catholic religious order, religious orders within the Catholic Church. Founded in 1209 by Italian Catholic friar Francis of Assisi, these orders include t ...
order to
evangelize
In Christianity, evangelism (or witnessing) is the act of preaching the gospel with the intention of sharing the message and teachings of Jesus Christ.
Christians who specialize in evangelism are often known as evangelists, whether they are in ...
the
Native Americans, the missions led to the creation of the
New Spain
New Spain, officially the Viceroyalty of New Spain ( es, Virreinato de Nueva España, ), or Kingdom of New Spain, was an integral territorial entity of the Spanish Empire, established by Habsburg Spain during the Spanish colonization of the Am ...
province of
Alta California
Alta California ('Upper California'), also known as ('New California') among other names, was a province of New Spain, formally established in 1804. Along with the Baja California peninsula, it had previously comprised the province of , but ...
and were part of the expansion of the
Spanish Empire
The Spanish Empire ( es, link=no, Imperio español), also known as the Hispanic Monarchy ( es, link=no, Monarquía Hispánica) or the Catholic Monarchy ( es, link=no, Monarquía Católica) was a colonial empire governed by Spain and its prede ...
into the most northern and western parts of
Spanish North America
Spain began colonizing the Americas under the Crown of Castile and was spearheaded by the Spanish . The Americas were invaded and incorporated into the Spanish Empire, with the exception of Brazil, British America, and some small regions of ...
.
Following long-term secular and religious policy of Spain in Spanish America, the missionaries forced the
native Californian
The indigenous peoples of California (known as Native Californians) are the indigenous inhabitants who have lived or currently live in the geographic area within the current boundaries of California before and after the arrival of Europeans. ...
s to live in settlements called
reductions
Reductions ( es, reducciones, also called ; , pl. ) were settlements created by Spanish rulers and Roman Catholic missionaries in Spanish America and the Spanish East Indies (the Philippines). In Portuguese-speaking Latin America, such redu ...
, disrupting their traditional way of life. The missionaries introduced European fruits, vegetables, cattle, horses, ranching, and technology. Immense reductions in the population of
Indigenous peoples of California
The indigenous peoples of California (known as Native Californians) are the indigenous inhabitants who have lived or currently live in the geographic area within the current boundaries of California before and after the arrival of Europeans. ...
occurred through the introduction of European diseases, which quickly spread as native people were forced into close quarters at the missions,
along with abuse, malnourishment and overworking.
87,787 baptisms were recorded at the missions and 63,789 deaths.
The missions had mixed results in their objectives to convert, educate, develop and transform the native peoples into Spanish subjects. The missions' role in destroying Indigenous culture has been described as a form of
cultural genocide
Cultural genocide or cultural cleansing is a concept which was proposed by lawyer Raphael Lemkin in 1944 as a component of genocide. Though the precise definition of ''cultural genocide'' remains contested, the Armenian Genocide Museum defines ...
.
By 1810, Spain's king had been imprisoned by the French, and financing for military payroll and missions in California ceased. In 1821, Mexico achieved independence from Spain, although Mexico did not send a governor to California until 1824, and only a portion of payroll was ever reinstated (ibid.). The 21,000 Mission Indians produced hide, tallow, wool, and textiles at this time, and the leather products were exported to Boston, South America, and Asia. This trading system sustained the colonial economy from 1810 until 1830. The missions began to lose control over land in the 1820s, as unpaid military men unofficially encroached, but officially missions maintained authority over native
neophytes and control of land holdings until the 1830s. At the peak of its development in 1832, the coastal mission system controlled an area equal to approximately one-sixth of Alta California. The Alta California government secularized the missions after the passage of the
Mexican secularization act of 1833
Mexican may refer to:
Mexico and its culture
*Being related to, from, or connected to the country of Mexico, in North America
** People
*** Mexicans, inhabitants of the country Mexico and their descendants
*** Mexica, ancient indigenous people ...
. This divided the mission lands into land grants, in effect legitimizing and completing the transfer of Indian congregation lands to military commanders and their most loyal men; these became many of the
Ranchos of California
The Spanish and Mexican governments made many concessions and land grants in Alta California (now known as California) and Baja California from 1775 to 1846. The Spanish Concessions of land were made to retired soldiers as an inducement for ...
.
The surviving mission buildings are the state's oldest structures and its most-visited historic monuments. They have become a symbol of California, appearing in many movies and television shows, and are an inspiration for
Mission Revival architecture
The Mission Revival style was part of an architectural movement, beginning in the late 19th century, for the revival and reinterpretation of American colonial styles. Mission Revival drew inspiration from the late 18th and early 19th century ...
. The oldest cities of California formed around or near Spanish missions, including the four largest:
Los Angeles
Los Angeles ( ; es, Los Ángeles, link=no , ), often referred to by its initials L.A., is the largest city in the state of California and the second most populous city in the United States after New York City, as well as one of the world' ...
,
San Diego
San Diego ( , ; ) is a city on the Pacific Ocean coast of Southern California located immediately adjacent to the Mexico–United States border. With a 2020 population of 1,386,932, it is the List of United States cities by population, eigh ...
,
San Jose, and
San Francisco
San Francisco (; Spanish language, Spanish for "Francis of Assisi, Saint Francis"), officially the City and County of San Francisco, is the commercial, financial, and cultural center of Northern California. The city proper is the List of Ca ...
.
Alta California mission planning, structure and culture
Coastal mission chain, planning and overview
Prior to 1754, grants of mission lands were made directly by the Spanish Crown. But, given the remote locations and the inherent difficulties in communicating with the territorial governments, power was transferred to the viceroys of New Spain to grant lands and establish missions in North America. Plans for the Alta California missions were laid out under the reign of King
Charles III
Charles III (Charles Philip Arthur George; born 14 November 1948) is King of the United Kingdom and the 14 other Commonwealth realms. He was the longest-serving heir apparent and Prince of Wales and, at age 73, became the oldest person to ...
, and came at least in part as a response to recent sightings of Russian fur traders along the California coast in the mid 1700s. The missions were to be interconnected by an overland route which later became known as the
Camino Real. The detailed planning and direction of the missions was to be carried out by Friar
Junípero Serra
Junípero Serra y Ferrer (; ; ca, Juníper Serra i Ferrer; November 24, 1713August 28, 1784) was a Spanish Roman Catholic priest and missionary of the Franciscan Order
, image = FrancescoCoA PioM.svg
, image_size ...
, O.F.M. (who, in 1767, along with his fellow
priest
A priest is a religious leader authorized to perform the sacred rituals of a religion, especially as a mediatory agent between humans and one or more deities. They also have the authority or power to administer religious rites; in particu ...
s, had taken control over a group of missions in
Baja California Peninsula previously administered by the Jesuits).
The Rev.
Fermín Francisco de Lasuén Fermín or Fermin may refer to:
* Fermin, Spanish saint
* Fermin (name), Spanish name and surname
* Fermin IV
Fermin (also Firmin, from Latin ''Firminus''; Spanish ''Fermín'') was a legendary holy man and martyr, traditionally venerated as the c ...
took up Serra's work and established nine more mission sites, from 1786 through 1798; others established the last three compounds, along with at least five ''asistencias'' (mission assistance outposts).
Shelved plans for additional mission chains
Work on the coastal mission chain was concluded in 1823, completed after Serra's death in 1784. Plans to build a twenty-second mission in Santa Rosa in 1827 were canceled.
["By that time, it was found that the Russian colonies were not such undesirable neighbors as in 1817 it was thought they might become... the Russian scare, for the time being at least was over; and as for the old enthusiasm for new spiritual conquests, there was none left."]
The Rev.
Pedro Estévan Tápis
Pedro is a masculine given name. Pedro is the Spanish, Portuguese, and Galician name for ''Peter''. Its French equivalent is Pierre while its English and Germanic form is Peter.
The counterpart patronymic surname of the name Pedro, meaning " ...
proposed establishing a mission on one of the
Channel Islands
The Channel Islands ( nrf, Îles d'la Manche; french: îles Anglo-Normandes or ''îles de la Manche'') are an archipelago in the English Channel, off the French coast of Normandy. They include two Crown Dependencies: the Bailiwick of Jersey, ...
in the Pacific Ocean off
San Pedro Harbor
San Pedro ( ; Spanish: " St. Peter") is a neighborhood within the City of Los Angeles, California. Formerly a separate city, it consolidated with Los Angeles in 1909. The Port of Los Angeles, a major international seaport, is partially located w ...
in 1784, with either
Santa Catalina or
Santa Cruz (known as ''Limú'' to the
Tongva
The Tongva ( ) are an Indigenous people of California from the Los Angeles Basin and the Southern Channel Islands, an area covering approximately . Some descendants of the people prefer Kizh as an endonym that, they argue, is more historically ...
residents) being the most likely locations, the reasoning being that an offshore mission might have attracted potential people to convert who were not living on the mainland, and could have been an effective measure to restrict smuggling operations. Governor
José Joaquín de Arrillaga
José Joaquín de Arrillaga was a Basque people, Basque officer that served twice as Governor of the Californias and as the first Governor of Alta California, following the partition of the Californias in 1804. He is the only Spanish-era governor ...
approved the plan the following year; however, an outbreak of ''sarampión'' (
measles
Measles is a highly contagious infectious disease caused by measles virus. Symptoms usually develop 10–12 days after exposure to an infected person and last 7–10 days. Initial symptoms typically include fever, often greater than , cough, ...
) killing some 200 Tongva people coupled with a scarcity of land for agriculture and potable water left the success of such a venture in doubt, so no effort to found an island mission was ever made.
In September 1821, the Rev. Mariano Payeras, "''Comisario Prefecto''" of the California missions, visited Cañada de Santa Ysabel east of
Mission San Diego de Alcalá
Mission Basilica San Diego de Alcalá ( es, Misión San Diego de Alcalá) was the second Franciscan founded mission in The Californias (after San Fernando de Velicata), a province of New Spain. Located in present-day San Diego, California, it w ...
as part of a plan to establish an entire chain of inland missions. The
Santa Ysabel Asistencia
The Santa Ysabel Asistencia was founded on September 20, 1818 at Cañada de Santa Ysabel in the mountains east of San Diego (near the village of Elcuanan), as a asistencia or "sub-mission" to Mission San Diego de Alcalá, and to serve as a rest ...
had been founded in 1818 as a "mother" mission. However, the plan's expansion never came to fruition.
Mission sites, selection and layout

In addition to the ''presidio'' (royal fort) and ''pueblo'' (town), the ''misión'' was one of the three major agencies employed by the Spanish sovereign to extend its borders and consolidate its
colonial
Colonial or The Colonial may refer to:
* Colonial, of, relating to, or characteristic of a colony or colony (biology)
Architecture
* American colonial architecture
* French Colonial
* Spanish Colonial architecture
Automobiles
* Colonial (1920 au ...
territories. ''Asistencias'' ("satellite" or "sub" missions, sometimes referred to as "contributing chapels") were small-scale missions that regularly conducted
Mass
Mass is an intrinsic property of a body. It was traditionally believed to be related to the quantity of matter in a physical body, until the discovery of the atom and particle physics. It was found that different atoms and different elementar ...
on days of obligation but lacked a resident priest; as with the missions, these settlements were typically established in areas with high concentrations of potential native converts. The Spanish Californians had never strayed from the coast when establishing their settlements; Mission Nuestra Señora de la Soledad was located farthest inland, being only some thirty miles (48 kilometers) from the shore. Each
frontier
A frontier is the political and geographical area near or beyond a boundary. A frontier can also be referred to as a "front". The term came from French in the 15th century, with the meaning "borderland"—the region of a country that fronts o ...
station was forced to be self-supporting, as existing means of supply were inadequate to maintain a colony of any size. California was months away from the nearest base in colonized Mexico, and the cargo ships of the day were too small to carry more than a few months’
ration
Rationing is the controlled distribution of scarce resources, goods, services, or an artificial restriction of demand. Rationing controls the size of the ration, which is one's allowed portion of the resources being distributed on a particular ...
s in their holds. To sustain a mission, the ''padres'' required converted
Native Americans, called ''neophytes'', to cultivate
crops
A crop is a plant that can be grown and harvested extensively for profit or subsistence. When the plants of the same kind are cultivated at one place on a large scale, it is called a crop. Most crops are cultivated in agriculture or hydroponics ...
and tend
livestock
Livestock are the domesticated animals raised in an agricultural setting to provide labor and produce diversified products for consumption such as meat, eggs, milk, fur, leather, and wool. The term is sometimes used to refer solely to animals ...
in the volume needed to support a fair-sized establishment. The scarcity of imported materials, together with a lack of skilled laborers, compelled the missionaries to employ simple
building material
Building material is material used for construction. Many naturally occurring substances, such as clay, rock (geology), rocks, sand, wood, and even twigs and leaves, have been used to construct buildings. Apart from naturally occurring materia ...
s and methods in the construction of mission structures.

Although the missions were considered temporary ventures by the Spanish
hierarchy
A hierarchy (from Greek: , from , 'president of sacred rites') is an arrangement of items (objects, names, values, categories, etc.) that are represented as being "above", "below", or "at the same level as" one another. Hierarchy is an important ...
, the development of an individual settlement was not simply a matter of "priestly whim." The founding of a mission followed longstanding rules and procedures; the paperwork involved required months, sometimes years of correspondence, and demanded the attention of virtually every level of the bureaucracy. Once empowered to erect a mission in a given area, the men assigned to it chose a specific site that featured a good water supply, plenty of wood for fires and building materials, and ample fields for grazing
herds
A herd is a social group of certain animals of the same species, either wildness, wild or Domestication, domestic. The form of collective animal behavior associated with this is called ''herding''. These animals are known as gregarious animal ...
and raising
crops
A crop is a plant that can be grown and harvested extensively for profit or subsistence. When the plants of the same kind are cultivated at one place on a large scale, it is called a crop. Most crops are cultivated in agriculture or hydroponics ...
. The padres blessed the site, and with the aid of their
military
A military, also known collectively as armed forces, is a heavily armed, highly organized force primarily intended for warfare. It is typically authorized and maintained by a sovereign state, with its members identifiable by their distinct ...
escort fashioned temporary shelters out of tree limbs or driven stakes, roofed with
thatch
Thatching is the craft of building a roof with dry vegetation such as straw, water reed, sedge (''Cladium mariscus''), rushes, heather, or palm branches, layering the vegetation so as to shed water away from the inner roof. Since the bulk of ...
or
reeds (''cañas''). It was these simple huts that ultimately gave way to the stone and adobe buildings that exist to the present.
The first priority when beginning a settlement was the location and construction of the
church
Church may refer to:
Religion
* Church (building), a building for Christian religious activities
* Church (congregation), a local congregation of a Christian denomination
* Church service, a formalized period of Christian communal worship
* Chris ...
(''iglesia''). The majority of mission sanctuaries were oriented on a roughly east–west axis to take the best advantage of the sun's position for interior
illumination; the exact alignment depended on the geographic features of the particular site. Once the spot for the church had been selected, its position was marked and the remainder of the mission complex was laid out. The
workshop
Beginning with the Industrial Revolution era, a workshop may be a room, rooms or building which provides both the area and tools (or machinery) that may be required for the manufacture or repair of manufactured goods. Workshops were the only ...
s,
kitchen
A kitchen is a room or part of a room used for cooking and food preparation in a dwelling or in a commercial establishment. A modern middle-class residential kitchen is typically equipped with a stove, a sink with hot and cold running water, a ...
s, living quarters, storerooms, and other ancillary chambers were usually grouped in the form of a
quadrangle, inside which religious celebrations and other festive events often took place. The ''cuadrángulo'' was rarely a perfect square because the missionaries had no
surveying
Surveying or land surveying is the technique, profession, art, and science of determining the terrestrial two-dimensional or three-dimensional positions of points and the distances and angles between them. A land surveying professional is ca ...
instruments at their disposal and simply measured off all dimensions by foot. Some fanciful accounts regarding the construction of the missions claimed that tunnels were incorporated in the design, to be used as a means of emergency egress in the event of attack; however, no historical evidence (written or physical) has ever been uncovered to support these assertions.
[Engelhardt: One such hypothesis was put forth by author by Prent Duel in his 1919 work ''Mission Architecture as Exemplified in San Xavier Del Bac'': "Most missions of early date possessed secret passages as a means of escape in case they were besieged. It is difficult to locate any of them now as they are well concealed."]
Franciscans and native conscription

The Alta California missions, known as
reductions
Reductions ( es, reducciones, also called ; , pl. ) were settlements created by Spanish rulers and Roman Catholic missionaries in Spanish America and the Spanish East Indies (the Philippines). In Portuguese-speaking Latin America, such redu ...
(''reducciones'') or congregations (''congregaciones''), were settlements founded by the Spanish colonizers of the
New World
The term ''New World'' is often used to mean the majority of Earth's Western Hemisphere, specifically the Americas."America." ''The Oxford Companion to the English Language'' (). McArthur, Tom, ed., 1992. New York: Oxford University Press, p. 3 ...
with the purpose of totally assimilating indigenous populations into
European culture
The culture of Europe is rooted in its art, architecture, film, different types of music, economics, literature, and philosophy. European culture is largely rooted in what is often referred to as its "common cultural heritage".
Definition ...
and the
Catholic
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
religion. It was a doctrine established in 1531, which based the Spanish state's right over the land and persons of the Indies on the
Papal
The pope ( la, papa, from el, πάππας, translit=pappas, 'father'), also known as supreme pontiff ( or ), Roman pontiff () or sovereign pontiff, is the bishop of Rome (or historically the patriarch of Rome), head of the worldwide Cathol ...
charge to evangelize them. It was employed wherever the indigenous populations were not already concentrated in native ''pueblos''. Indians were congregated around the mission proper through forced resettlement, in which the Spanish "reduced" them from what they perceived to be a free "undisciplined'" state with the ambition of converting them into "civilized" members of colonial society. The civilized and disciplined culture of the natives, developed over 8,000 years, was not considered. A total of 146
Friars Minor
The Order of Friars Minor (also called the Franciscans, the Franciscan Order, or the Seraphic Order; postnominal abbreviation OFM) is a mendicant Catholic religious order, founded in 1209 by Francis of Assisi. The order adheres to the teachin ...
, mostly Spaniards by birth, were ordained as priests and served in California between 1769 and 1845. Sixty-seven missionaries died at their posts (two as ''
martyr
A martyr (, ''mártys'', "witness", or , ''marturia'', stem , ''martyr-'') is someone who suffers persecution and death for advocating, renouncing, or refusing to renounce or advocate, a religious belief or other cause as demanded by an externa ...
s'': ''Padres''
Luis Jayme
Luis Jayme or Lluís Jaume O.F.M. (October 18, 1740 – November 5, 1775), born Melcior Jaume Vallespir, was a Spanish-born Roman Catholic priest of the Franciscan Order. He was the first Catholic martyr who died in Alta California.
Early life ...
and
Andrés Quintana
Andrés Quintana, O.F.M. (November 27, 1777 – October 12, 1812) was a Roman Catholic Spanish priest and missionary of the Franciscan Order who labored at Mission Santa Cruz in California during the early part of the 19th century.
Born in ...
), while the remainder returned to Europe due to illness, or upon completing their ten-year service commitment. As the rules of the Franciscan Order forbade friars to live alone, two missionaries were assigned to each settlement, sequestered in the mission's ''convento''. To these the governor assigned a guard of five or six soldiers under the command of a corporal, who generally acted as steward of the mission's temporal affairs, subject to the priests' direction.
Indians were initially attracted into the mission compounds by gifts of food, colored beads, bits of bright cloth, and trinkets. Once a Native American "
gentile
Gentile () is a word that usually means "someone who is not a Jew". Other groups that claim Israelite heritage, notably Mormons, sometimes use the term ''gentile'' to describe outsiders. More rarely, the term is generally used as a synonym for ...
" was baptized, they were labeled a ''
neophyte
A neophyte is a recent Initiation, initiate or Religious conversion, convert to a subject or belief.
Neophyte may also refer to:
Science
* Neophyte (botany), a plant species recently introduced to an area
As a proper noun Arts and entertainme ...
'', or new believer. This happened only after a brief period during which the initiates were instructed in the most basic aspects of the Catholic faith. But, while many natives were lured to join the missions out of curiosity and sincere desire to participate and engage in trade, many found themselves trapped once they were
baptized
Baptism (from grc-x-koine, βάπτισμα, váptisma) is a form of ritual purification—a characteristic of many religions throughout time and geography. In Christianity, it is a Christian sacrament of initiation and adoption, almost ...
.
[Carey McWilliam]
Southern California:An Island on the Land
On the other hand, Indians staffed the militias at each mission and had a role in mission governance.
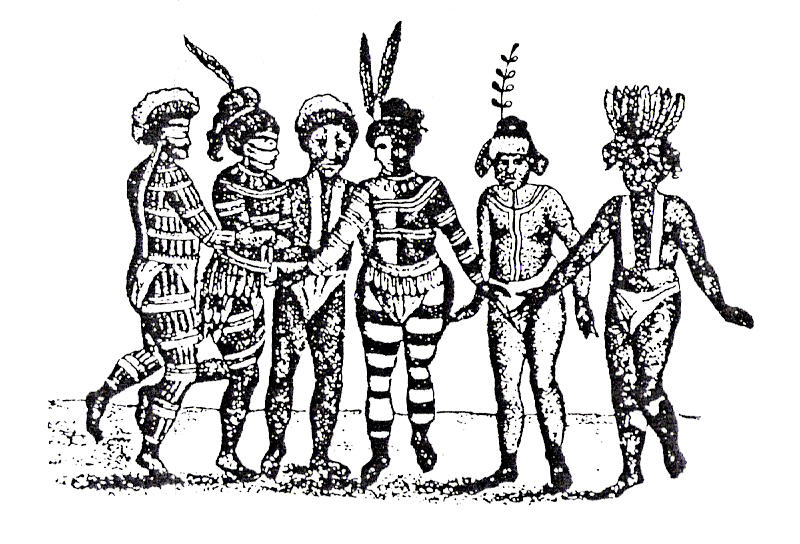

To the ''padres'', a baptized Indian person was no longer free to move about the country, but had to labor and worship at the mission under the strict observance of the priests and overseers, who herded them to daily masses and labors. If an Indian did not report for their duties for a period of a few days, they were searched for, and if it was discovered that they had left without permission, they were considered runaways. Large-scale military expeditions were organized to round up the escaped neophytes. Sometimes, the Franciscans allowed neophytes to escape the missions, or they would allow them to visit their home village. However, the Franciscans would only allow this so that they could secretly follow the neophytes. Upon arriving to the village and capturing the runaways, they would take back Indians to the missions, sometimes as many as 200 to 300 Indians.
A total of 20,355 natives were "attached" to the California missions in 1806 (the highest figure recorded during the Mission Period); under Mexican rule the number rose to 21,066 (in 1824, the record year during the entire era of the Franciscan missions).
[Chapman: "Over the hills of the Coast Range, in the valleys of the Sacramento and San Joaquin, north of San Francisco Bay, and in the Sierra Nevadas of the south there were untold thousands whom the mission system never reached...they were as if in a world apart from the narrow strip of coast which was all there was of the Spanish California."] During the entire period of Mission rule, from 1769 to 1834, the Franciscans baptized 53,600 adult Indians and buried 37,000. Dr. Cook estimates that 15,250 or 45% of the population decrease was caused by disease. Two epidemics of
measles
Measles is a highly contagious infectious disease caused by measles virus. Symptoms usually develop 10–12 days after exposure to an infected person and last 7–10 days. Initial symptoms typically include fever, often greater than , cough, ...
, one in 1806 and the other in 1828, caused many deaths. The mortality rates were so high that the missions were constantly dependent upon new conversions.
Young native women were required to reside in the ''monjerío'' (or "nunnery") under the supervision of a trusted Indian matron who bore the responsibility for their welfare and education. Women only left the convent after they had been "won" by an Indian suitor and were deemed ready for marriage. Following Spanish custom, courtship took place on either side of a barred window. After the marriage ceremony the woman moved out of the mission compound and into one of the family huts. These "nunneries" were considered a necessity by the priests, who felt the women needed to be protected from the men, both Indian and ''de razón'' ("instructed men", i.e. Europeans). The cramped and unsanitary conditions the girls lived in contributed to the fast spread of disease and
population decline
A population decline (also sometimes called underpopulation, depopulation, or population collapse) in humans is a reduction in a human population size. Over the long term, stretching from prehistory to the present, Earth's total human population ...
. So many died at times that many of the Indian residents of the missions urged the priests to raid new villages to supply them with more women.
[Krell, p. 316]
Death rate at the missions
As of December 31, 1832 (the peak of the mission system's development) the mission ''padres'' had performed a combined total of 87,787 baptisms and 24,529 marriages, and recorded 63,789 deaths.
The death rate at the missions, particularly of children, was very high and the majority of children baptized did not survive childhood.
At
Mission San Gabriel
Mission (from Latin ''missio'' "the act of sending out") may refer to:
Organised activities Religion
*Christian mission, an organized effort to spread Christianity
*Mission (LDS Church), an administrative area of The Church of Jesus Christ of ...
, for instance, three of four children died before reaching the age of two.
The high rate of death at the missions have been attributed to several factors, including disease, torture, overworking, malnourishment, and
cultural genocide
Cultural genocide or cultural cleansing is a concept which was proposed by lawyer Raphael Lemkin in 1944 as a component of genocide. Though the precise definition of ''cultural genocide'' remains contested, the Armenian Genocide Museum defines ...
.
Forcing native people into close quarters at the missions spread disease quickly. While being kept at the missions, native people were transitioned to a Spanish diet that left them more unable to ward off diseases, the most common being
dysentery
Dysentery (UK pronunciation: , US: ), historically known as the bloody flux, is a type of gastroenteritis that results in bloody diarrhea. Other symptoms may include fever, abdominal pain, and a feeling of incomplete defecation. Complications ...
,
fevers
Fever, also referred to as pyrexia, is defined as having a temperature above the normal range due to an increase in the body's temperature set point. There is not a single agreed-upon upper limit for normal temperature with sources using val ...
with unknown causes, and
venereal disease
Sexually transmitted infections (STIs), also referred to as sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) and the older term venereal diseases, are infections that are spread by sexual activity, especially vaginal intercourse, anal sex, and oral se ...
.
The death rate has been compared to that of other atrocities. American author and lawyer
Carey McWilliams argued that "the Franciscan padres eliminated Indians with the effectiveness of
Nazis
Nazism ( ; german: Nazismus), the common name in English for National Socialism (german: Nationalsozialismus, ), is the far-right totalitarian political ideology and practices associated with Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party (NSDAP) in Na ...
operating
concentration camps
Internment is the imprisonment of people, commonly in large groups, without charges or intent to file charges. The term is especially used for the confinement "of enemy citizens in wartime or of terrorism suspects". Thus, while it can simply ...
."
Mission labor
The neophytes were kept in well-guarded mission compounds. The policy of the Franciscans was to keep them constantly occupied. Bells were vitally important to daily life at any mission. The bells were rung at mealtimes, to call the Mission residents to work and to religious services, during births and funerals, to signal the approach of a ship or returning missionary, and at other times; novices were instructed in the intricate rituals associated with the ringing the mission bells. The daily routine began with sunrise
Mass
Mass is an intrinsic property of a body. It was traditionally believed to be related to the quantity of matter in a physical body, until the discovery of the atom and particle physics. It was found that different atoms and different elementar ...
and morning
prayers
Prayer is an invocation or act that seeks to activate a rapport with an object of worship through deliberate communication. In the narrow sense, the term refers to an act of supplication or intercession directed towards a deity or a deified an ...
, followed by instruction of the natives in the teachings of the
Roman Catholic
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
*Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*'' Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a lette ...
faith. After a generous (by era standards) breakfast of ''
atole
''Atole'' (, from Nahuatl '' ātōlli'' ), also known as ''atolli'' and ''atol de elote'', is a traditional hot corn- and masa-based beverage of Mexican origin. Chocolate ''atole'' is known as ''champurrado'' or ''atole''. It typically accomp ...
'', the able-bodied men and women were assigned their tasks for the day. The women were committed to dressmaking, knitting, weaving, embroidering, laundering, and cooking, while some of the stronger girls ground flour or carried adobe bricks (weighing 55
lb, or 25 kg each) to the men engaged in building. The men worked a variety of jobs, having learned from the missionaries how to plow, sow, irrigate, cultivate, reap, thresh, and glean. In addition, they were taught to build adobe houses, tan leather hides, shear sheep, weave rugs and clothing from wool, make ropes, soap, paint, and other useful duties.

The work day was six hours, interrupted by dinner (lunch) around 11:00 a.m. and a two-hour ''siesta'', and ended with evening prayers and the
rosary
The Rosary (; la, , in the sense of "crown of roses" or "garland of roses"), also known as the Dominican Rosary, or simply the Rosary, refers to a set of prayers used primarily in the Catholic Church, and to the physical string of knots or b ...
, supper, and social activities. About 90 days out of each year were designated as religious or civil holidays, free from
manual labor
Manual labour (in Commonwealth English, manual labor in American English) or manual work is physical work done by humans, in contrast to labour by machines and working animals. It is most literally work done with the hands (the word ''manual'' ...
. The labor organization of the missions resembled a slave plantation in many respects.
[Bennett: "The system had singularly failed in its purposes. It was the design of the Spanish government to have the missions educate, elevate, civilize, the Indians into citizens. When this was done, citizenship should be extended them and the missions should be dissolved as having served their purpose... nsteadthe priests returned them projects of conversion, schemes of faith, which they never comprehended...He ]he Indian
He or HE may refer to:
Language
* He (pronoun), an English pronoun
* He (kana), the romanization of the Japanese kana へ
* He (letter), the fifth letter of many Semitic alphabets
* He (Cyrillic), a letter of the Cyrillic script called ''He'' in ...
became a slave; the mission was a plantation; the friar was a taskmaster." Foreigners who visited the missions remarked at how the priests' control over the Indians appeared excessive, but necessary given the white men's isolation and numeric disadvantage.
[Bennett 1897b, p. 158][Bennett: "In 1825 Governor Argüello wrote that the slavery of the Indians at the missions was bestial... Governor Figueroa declared that the missions were 'entrenchments of monastic despotism'..."] Subsequently, the Missions operated under strict and harsh conditions; A ‘light’ punishment would’ve been considered 25 lashings (azotes). Indians were not paid wages as they were not considered free laborers and, as a result, the missions were able to profit from the goods produced by the
Mission Indians
Mission Indians are the indigenous peoples of California who lived in Southern California and were forcibly relocated from their traditional dwellings, villages, and homelands to live and work at 15 Franciscan missions in Southern California and ...
to the detriment of the other Spanish and Mexican settlers of the time who could not compete economically with the advantage of the mission system.
The Franciscans began to send neophytes to work as servants of Spanish soldiers in the
presidio
A presidio ( en, jail, fortification) was a fortified base established by the Spanish Empire around between 16th century, 16th and 18th century, 18th centuries in areas in condition of their control or influence. The presidios of Captaincy Genera ...
s. Each presidio was provided with land, el rancho del rey, which served as a pasture for the presidio livestock and as a source of food for the soldiers. Theoretically the soldiers were supposed to work on this land themselves but within a few years the neophytes were doing all the work on the presidio farm and, in addition, were serving domestics for the soldiers. While the fiction prevailed that neophytes were to receive wages for their work, no attempt was made to collect the wages for these services after 1790. It is recorded that the neophytes performed the work "under unmitigated compulsion."
In recent years, much debate has arisen about the priests' treatment of the Indians during the Mission period, and many believe that the California mission system is directly responsible for the decline of the native cultures.
[Bennett: "It cannot be said that the mission system made the Indians more able to sustain themselves in civilization than it had found them...Upon the whole it may be said that this mission experiment was a failure."] From the perspective of the Spanish priest, their efforts were a well-meaning attempt to improve the lives of the heathen natives.
[Lippy: "A matter of debate in reflecting on the role of Spanish missions concerns the degree to which the Spanish colonial regimes regarded the work of the priests as a legitimate religious enterprise and the degree to which it was viewed as a 'frontier institution,' part of a colonial defense program. That is, were Spanish motives based on a desire to promote conversion or on a desire to have religious missions serve as a buffer to protect the main colonial settlements and an aid in controlling the Indians?"][Bennett: The missions in effect served as "...the ]citadel
A citadel is the core fortified area of a town or city. It may be a castle, fortress, or fortified center. The term is a diminutive of "city", meaning "little city", because it is a smaller part of the city of which it is the defensive core.
In ...
s of the theocracy which was planted in California by Spain, under which its wild inhabitants were subjected, which stood as their guardians, civil and religious, and whose duty it was to elevate them and make them acceptable as citizens and Spanish subjects...it remained for the Spanish priests to undertake to preserve the Indian and seek to make his existence compatible with higher civilization."
Franciscan violence against native population
The Franciscan arrival to Alta California, saw a wave of torture, rape and murder towards the Native population of California. Native Californians, attracted to the Missions by the promise of food and gifts, would be banned from leaving and any form of escape would usually be met with a severe beating and chaining. Any form of Native rebellion would not be tolerated due to numerical disadvantage facing the Franciscans. When Native Women attempted to abort their unborn children - which they had conceived as a byproduct of rape, The Friars would have them beaten, chained in iron, shaved, and stipulated to stand in-front of the altar each mass with a decorated wooden newborn.
This trend of violence was due to the Franciscans' desire for a greater Hispanicized population in Alta California, both for protection against a foreign invasion and for a labor force to benefit the Spanish Empire. As a result a higher emphasis of Native reproduction was a duty taken on by the Spanish Fransicans. Tejana Born Feminist Historian, Antonia Castañeda reports in great detail of the treatment that would occur in Mission Santa Cruz:
“Father Olbes at Mission Santa Cruz ordered an infertile couple to have sexual intercourse in his presence because he did not believe they could not have children. The couple refused, but Olbes forcibly inspected the man's penis to learn ‘whether or not it was in good order’ and tried to inspect the woman's genitalia.13 She refused, fought with him, and tried to bite him. Olbes ordered that she be tied by the hands, and given fifty lashes, shackled, and locked up in the monjero (women's dormitory). He then had a monigote made and commanded that she "treat the doll as though it were a child and carry it in the presence of everyone for nine days." While the woman was beaten and her sexuality demeaned, the husband, who had been intimate with another woman, was ridiculed and humiliated. A set of cow horns was tied to his head with leather thongs, thereby converting him into a cuckold, and he was herded to daily Mass in cow horns and fetters”.
Franciscan Priests would also forbid any form of native culture in the Mission system. This would include but not be limited to, songs, dances, and ceremonies. They objectified the destruction of any form of morality, ideology or personality that characterized the Native life.
Women, in particular, would face a higher degree of punishment. Those who did not comply with the Missions demands would be labeled a witch, dehumanizing them for further violence. Professor at the University of Chicago, Ramon Guttiriez states:
“One can interpret the whole history of the persecution of Indian women as witches ... as a struggle over
hesecompeting ways of defining the body and of regulating procreation as the church endeavored to constrain the expression of desire within boundaries that clerics defined proper and acceptable."
Mission industries

The goal of the missions was, above all, to become self-sufficient in relatively short order.
Farming
Agriculture or farming is the practice of cultivating plants and livestock. Agriculture was the key development in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created food surpluses that enabled people to ...
, therefore, was the most important
industry
Industry may refer to:
Economics
* Industry (economics), a generally categorized branch of economic activity
* Industry (manufacturing), a specific branch of economic activity, typically in factories with machinery
* The wider industrial sector ...
of any mission.
Barley
Barley (''Hordeum vulgare''), a member of the grass family, is a major cereal grain grown in temperate climates globally. It was one of the first cultivated grains, particularly in Eurasia as early as 10,000 years ago. Globally 70% of barley pr ...
,
maize
Maize ( ; ''Zea mays'' subsp. ''mays'', from es, maíz after tnq, mahiz), also known as corn (North American and Australian English), is a cereal grain first domesticated by indigenous peoples in southern Mexico about 10,000 years ago. Th ...
, and
wheat
Wheat is a grass widely cultivated for its seed, a cereal grain that is a worldwide staple food. The many species of wheat together make up the genus ''Triticum'' ; the most widely grown is common wheat (''T. aestivum''). The archaeologi ...
were among the most common crops grown.
Cereal
A cereal is any Poaceae, grass cultivated for the edible components of its grain (botanically, a type of fruit called a caryopsis), composed of the endosperm, Cereal germ, germ, and bran. Cereal Grain, grain crops are grown in greater quantit ...
grains were dried and ground by stone into
flour
Flour is a powder made by grinding raw grains, roots, beans, nuts, or seeds. Flours are used to make many different foods. Cereal flour, particularly wheat flour, is the main ingredient of bread, which is a staple food for many culture ...
. Even today, California is well known for the abundance and many varieties of
fruit tree
A fruit tree is a tree which bears fruit that is consumed or used by animals and humans — all trees that are flowering plants produce fruit, which are the ripened ovaries of flowers containing one or more seeds. In horticultural usage, ...
s that are cultivated throughout the state. The only fruits indigenous to the region, however, consisted of wild
berries
A berry is a small, pulpy, and often edible fruit. Typically, berries are juicy, rounded, brightly colored, sweet, sour or tart, and do not have a stone or pit, although many pips or seeds may be present. Common examples are strawberries, raspb ...
or grew on small bushes. Spanish
missionaries
A missionary is a member of a religious group which is sent into an area in order to promote its faith or provide services to people, such as education, literacy, social justice, health care, and economic development.Thomas Hale 'On Being a Mi ...
brought fruit seeds over from Europe, many of which had been introduced from Asia following earlier expeditions to the continent;
orange
Orange most often refers to:
*Orange (fruit), the fruit of the tree species '' Citrus'' × ''sinensis''
** Orange blossom, its fragrant flower
*Orange (colour), from the color of an orange, occurs between red and yellow in the visible spectrum
* ...
,
grape
A grape is a fruit, botanically a berry, of the deciduous woody vines of the flowering plant genus ''Vitis''. Grapes are a non- climacteric type of fruit, generally occurring in clusters.
The cultivation of grapes began perhaps 8,000 years ago, ...
,
apple
An apple is an edible fruit produced by an apple tree (''Malus domestica''). Apple fruit tree, trees are agriculture, cultivated worldwide and are the most widely grown species in the genus ''Malus''. The tree originated in Central Asia, wh ...
,
peach
The peach (''Prunus persica'') is a deciduous tree first domesticated and cultivated in Zhejiang province of Eastern China. It bears edible juicy fruits with various characteristics, most called peaches and others (the glossy-skinned, non-fu ...
,
pear
Pears are fruits produced and consumed around the world, growing on a tree and harvested in the Northern Hemisphere in late summer into October. The pear tree and shrub are a species of genus ''Pyrus'' , in the family Rosaceae, bearing the p ...
, and
fig
The fig is the edible fruit of ''Ficus carica'', a species of small tree in the flowering plant family Moraceae. Native to the Mediterranean and western Asia, it has been cultivated since ancient times and is now widely grown throughout the world ...
seeds were among the most prolific of the imports.
Grape
A grape is a fruit, botanically a berry, of the deciduous woody vines of the flowering plant genus ''Vitis''. Grapes are a non- climacteric type of fruit, generally occurring in clusters.
The cultivation of grapes began perhaps 8,000 years ago, ...
s were also grown and
fermented
Fermentation is a metabolic process that produces chemical changes in organic substrates through the action of enzymes. In biochemistry, it is narrowly defined as the extraction of energy from carbohydrates in the absence of oxygen. In food ...
into
wine
Wine is an alcoholic drink typically made from fermented grapes. Yeast consumes the sugar in the grapes and converts it to ethanol and carbon dioxide, releasing heat in the process. Different varieties of grapes and strains of yeasts are m ...
for
sacrament
A sacrament is a Christianity, Christian Rite (Christianity), rite that is recognized as being particularly important and significant. There are various views on the existence and meaning of such rites. Many Christians consider the sacraments ...
al use and again, for trading. The specific variety, called the ''Criolla'' or ''
Mission grape
Mission grapes are a variety of ''Vitis vinifera'' introduced from Spain to the western coasts of North and South America by Catholic New World missionaries for use in making sacramental, table, and fortified wines. It is grown in South America, ...
'', was first planted at Mission San Juan Capistrano in 1779; in 1783, the first wine produced in Alta California emerged from the mission's winery.
Ranching
A ranch (from es, rancho/Mexican Spanish) is an area of land, including various structures, given primarily to ranching, the practice of raising grazing livestock such as cattle and sheep. It is a subtype of a farm. These terms are most often ...
also became an important mission industry as
cattle
Cattle (''Bos taurus'') are large, domesticated, cloven-hooved, herbivores. They are a prominent modern member of the subfamily Bovinae and the most widespread species of the genus ''Bos''. Adult females are referred to as cows and adult mal ...
and
sheep
Sheep or domestic sheep (''Ovis aries'') are domesticated, ruminant mammals typically kept as livestock. Although the term ''sheep'' can apply to other species in the genus ''Ovis'', in everyday usage it almost always refers to domesticated s ...
herds were raised.
Mission San Gabriel Arcángel unknowingly witnessed the origin of the California
citrus
''Citrus'' is a genus of flowering plant, flowering trees and shrubs in the rue family, Rutaceae. Plants in the genus produce citrus fruits, including important crops such as Orange (fruit), oranges, Lemon, lemons, grapefruits, pomelos, and lim ...
industry with the planting of the region's first significant orchard in 1804, though the commercial potential of citrus was not realized until 1841.
Olive
The olive, botanical name ''Olea europaea'', meaning 'European olive' in Latin, is a species of small tree or shrub in the family Oleaceae, found traditionally in the Mediterranean Basin. When in shrub form, it is known as ''Olea europaea'' ...
s (first cultivated at Mission San Diego de Alcalá) were grown, cured, and pressed under large stone
wheel
A wheel is a circular component that is intended to rotate on an axle Bearing (mechanical), bearing. The wheel is one of the key components of the wheel and axle which is one of the Simple machine, six simple machines. Wheels, in conjunction wi ...
s to extract their
oil
An oil is any nonpolar chemical substance that is composed primarily of hydrocarbons and is hydrophobic (does not mix with water) & lipophilic (mixes with other oils). Oils are usually flammable and surface active. Most oils are unsaturated ...
, both for use at the mission and to trade for other goods. The Rev. Serra set aside a portion of the Mission Carmel gardens in 1774 for
tobacco
Tobacco is the common name of several plants in the genus '' Nicotiana'' of the family Solanaceae, and the general term for any product prepared from the cured leaves of these plants. More than 70 species of tobacco are known, but the ...
plants, a practice that soon spread throughout the mission system.
[Bean: "Serra's decision to plant tobacco at the missions was prompted by the fact that from San Diego to Monterey the natives invariably begged him for Spanish tobacco."]
It was also the missions' responsibility to provide the Spanish forts, or ''presidios'', with the necessary foodstuffs, and manufactured goods to sustain operations. It was a constant point of contention between missionaries and the soldiers as to how many ''fanegas'' of barley, or how many shirts or blankets the mission had to provide the garrisons on any given year. At times these requirements were hard to meet, especially during years of drought, or when the much anticipated shipments from the port of
San Blas failed to arrive. The Spaniards kept meticulous records of mission activities, and each year reports submitted to the Father-Presidente summarizing both the material and spiritual status at each of the settlements.
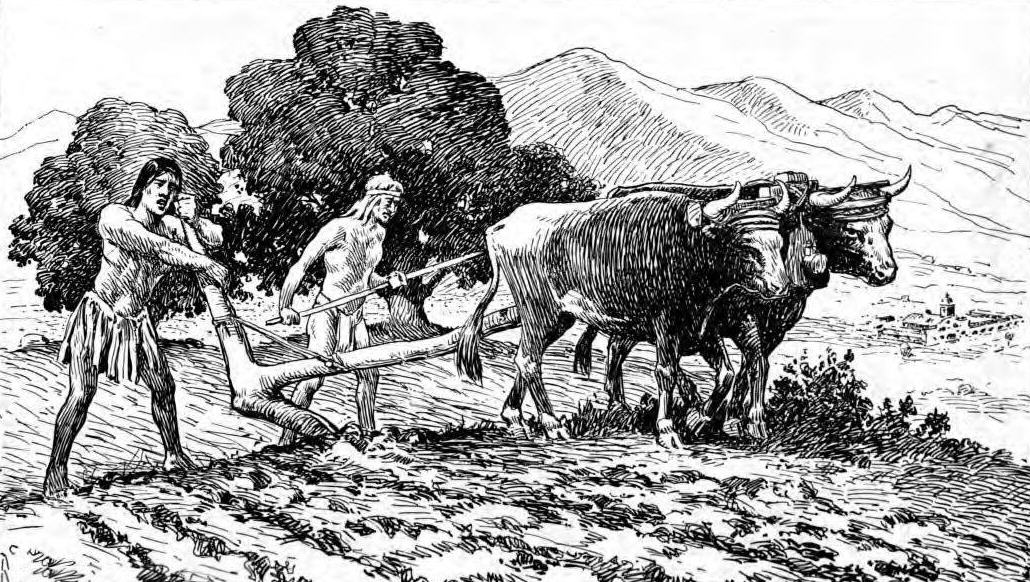

Livestock was raised, not only for the purpose of obtaining meat, but also for wool, leather, and tallow, and for cultivating the land. In 1832, at the height of their prosperity, the missions collectively owned:
* 151,180 head of
cattle
Cattle (''Bos taurus'') are large, domesticated, cloven-hooved, herbivores. They are a prominent modern member of the subfamily Bovinae and the most widespread species of the genus ''Bos''. Adult females are referred to as cows and adult mal ...
;
* 137,969
sheep
Sheep or domestic sheep (''Ovis aries'') are domesticated, ruminant mammals typically kept as livestock. Although the term ''sheep'' can apply to other species in the genus ''Ovis'', in everyday usage it almost always refers to domesticated s ...
;
* 14,522 horses;
* 1,575
mule
The mule is a domestic equine hybrid between a donkey and a horse. It is the offspring of a male donkey (a jack) and a female horse (a mare). The horse and the donkey are different species, with different numbers of chromosomes; of the two pos ...
s or
burro
The domestic donkey is a hoofed mammal in the family Equidae, the same family as the horse. It derives from the African wild ass, ''Equus africanus'', and may be classified either as a subspecies thereof, ''Equus africanus asinus'', or as a ...
s;
* 1,711
goat
The goat or domestic goat (''Capra hircus'') is a domesticated species of goat-antelope typically kept as livestock. It was domesticated from the wild goat (''C. aegagrus'') of Southwest Asia and Eastern Europe. The goat is a member of the a ...
s; and
* 1,164
swine.
All these grazing animals were originally brought up from Mexico. A great many Indians were required to guard the herds and flocks on the
mission ranches, which created the need for "...a class of horsemen scarcely surpassed anywhere."
[Engelhardt 1908, pp. 3–18] These animals multiplied beyond the settler's expectations, often overrunning pastures and extending well-beyond the domains of the missions. The giant herds of horses and cows took well to the climate and the extensive pastures of the Coastal California region, but at a heavy price for the California Native American people. The uncontrolled spread of these new herds, and associated
invasive exotic plant species, quickly exhausted the
native plants
In biogeography, a native species is indigenous to a given region or ecosystem if its presence in that region is the result of only local natural evolution (though often popularised as "with no human intervention") during history. The term is equi ...
in the grasslands, and the
chaparral and woodlands that the Indians depended on for their seed, foliage, and bulb harvests. The grazing-overgrazing problems were also recognized by the Spaniards, who periodically had extermination parties cull and kill thousands of excess livestock, when herd populations grew beyond their control or the land's capacity. Years with a severe drought did this also.
Mission kitchens and
bakeries
A bakery is an establishment that produces and sells flour-based food baked in an oven such as bread, cookies, cakes, donuts, pastries, and pies. Some retail bakeries are also categorized as cafés, serving coffee and tea to customers who wish ...
prepared and served thousands of meals each day.
Candles
A candle is an ignitable wick embedded in wax, or another flammable solid substance such as tallow, that provides light, and in some cases, a fragrance. A candle can also provide heat or a method of keeping time.
A person who makes candles i ...
,
soap
Soap is a salt of a fatty acid used in a variety of cleansing and lubricating products. In a domestic setting, soaps are surfactants usually used for washing, bathing, and other types of housekeeping. In industrial settings, soaps are use ...
,
grease, and
ointment
A topical medication is a medication that is applied to a particular place on or in the body. Most often topical medication means application to body surfaces such as the skin or mucous membranes to treat ailments via a large range of classes ...
s were all made from
tallow
Tallow is a rendering (industrial), rendered form of beef or mutton fat, primarily made up of triglycerides.
In industry, tallow is not strictly defined as beef or mutton fat. In this context, tallow is animal fat that conforms to certain techn ...
(
rendered animal
fat
In nutrition science, nutrition, biology, and chemistry, fat usually means any ester of fatty acids, or a mixture of such chemical compound, compounds, most commonly those that occur in living beings or in food.
The term often refers spec ...
) in large vats located just outside the west wing. Also situated in this general area were vats for dyeing
wool
Wool is the textile fibre obtained from sheep and other mammals, especially goats, rabbits, and camelids. The term may also refer to inorganic materials, such as mineral wool and glass wool, that have properties similar to animal wool.
As ...
and
tanning
Tanning may refer to:
*Tanning (leather), treating animal skins to produce leather
*Sun tanning, using the sun to darken pale skin
**Indoor tanning, the use of artificial light in place of the sun
**Sunless tanning, application of a stain or dye t ...
leather
Leather is a strong, flexible and durable material obtained from the tanning, or chemical treatment, of animal skins and hides to prevent decay. The most common leathers come from cattle, sheep, goats, equine animals, buffalo, pigs and hogs, ...
, and primitive
loom
A loom is a device used to weave cloth and tapestry. The basic purpose of any loom is to hold the warp threads under tension to facilitate the interweaving of the weft threads. The precise shape of the loom and its mechanics may vary, but th ...
s for
weaving
Weaving is a method of textile production in which two distinct sets of yarns or threads are interlaced at right angles to form a fabric or cloth. Other methods are knitting, crocheting, felting, and braiding or plaiting. The longitudinal th ...
. Large ''bodegas'' (warehouses) provided long-term storage for preserved foodstuffs and other treated materials.

Each mission had to fabricate virtually all of its construction materials from local materials. Workers in the ''carpintería'' (
carpentry
Carpentry is a skilled trade and a craft in which the primary work performed is the cutting, shaping and installation of building materials during the construction of buildings, ships, timber bridges, concrete formwork, etc. Carpenters tr ...
shop) used crude methods to shape beams, lintels, and other structural elements; more skilled artisans carved doors, furniture, and wooden implements. For certain applications bricks (''ladrillos'') were fired in
oven
upA double oven
A ceramic oven
An oven is a tool which is used to expose materials to a hot environment. Ovens contain a hollow chamber and provide a means of heating the chamber in a controlled way. In use since antiquity, they have been us ...
s (
kilns
A kiln is a thermally insulated chamber, a type of oven, that produces temperatures sufficient to complete some process, such as hardening, drying, or chemical changes. Kilns have been used for millennia to turn objects made from clay int ...
) to strengthen them and make them more resistant to the elements; when ''tejas'' (roof tiles) eventually replaced the conventional ''jacal'' roofing (densely packed reeds) they were placed in the kilns to harden them as well. Glazed ceramic pots, dishes, and canisters were also made in mission kilns.
Prior to the establishment of the missions, the native peoples knew only how to utilize bone, seashells, stone, and wood for building, tool making, weapons, and so forth. The missionaries established manual training in European skills and methods; in agriculture, mechanical arts, and the raising and care of livestock. Everything consumed and otherwise utilized by the natives was produced at the missions under the supervision of the padres; thus, the neophytes not only supported themselves, but after 1811 sustained the entire military and civil government of California. The
foundry
A foundry is a factory that produces metal castings. Metals are cast into shapes by melting them into a liquid, pouring the metal into a mold, and removing the mold material after the metal has solidified as it cools. The most common metals pr ...
at Mission San Juan Capistrano was the first to introduce the Indians to the
Iron Age
The Iron Age is the final epoch of the three-age division of the prehistory and protohistory of humanity. It was preceded by the Stone Age (Paleolithic, Mesolithic, Neolithic) and the Bronze Age (Chalcolithic). The concept has been mostly appl ...
. The
blacksmith
A blacksmith is a metalsmith who creates objects primarily from wrought iron or steel, but sometimes from #Other metals, other metals, by forging the metal, using tools to hammer, bend, and cut (cf. tinsmith). Blacksmiths produce objects such ...
used the mission's
forges (California's first) to
smelt
Smelt may refer to:
* Smelting, chemical process
* The common name of various fish:
** Smelt (fish), a family of small fish, Osmeridae
** Australian smelt in the family Retropinnidae and species ''Retropinna semoni''
** Big-scale sand smelt ''At ...
and fashion
iron
Iron () is a chemical element with symbol Fe (from la, ferrum) and atomic number 26. It is a metal that belongs to the first transition series and group 8 of the periodic table. It is, by mass, the most common element on Earth, right in f ...
into everything from basic tools and hardware (such as
nails) to crosses, gates, hinges, even
cannon
A cannon is a large- caliber gun classified as a type of artillery, which usually launches a projectile using explosive chemical propellant. Gunpowder ("black powder") was the primary propellant before the invention of smokeless powder ...
for mission defense. Iron in particular was a commodity that the mission acquired solely through trade, as the missionaries had neither the know-how nor technology to
mine
Mine, mines, miners or mining may refer to:
Extraction or digging
* Miner, a person engaged in mining or digging
*Mining, extraction of mineral resources from the ground through a mine
Grammar
*Mine, a first-person English possessive pronoun
...
and process metal
ore
Ore is natural rock or sediment that contains one or more valuable minerals, typically containing metals, that can be mined, treated and sold at a profit.Encyclopædia Britannica. "Ore". Encyclopædia Britannica Online. Retrieved 7 April 2 ...
s.
No study of the missions is complete without mention of their extensive
water supply
Water supply is the provision of water by public utilities, commercial organisations, community endeavors or by individuals, usually via a system of pumps and pipes. Public water supply systems are crucial to properly functioning societies. Thes ...
systems. Stone ''zanjas'' (
aqueducts
Aqueduct may refer to:
Structures
*Aqueduct (bridge), a bridge to convey water over an obstacle, such as a ravine or valley
*Navigable aqueduct, or water bridge, a structure to carry navigable waterway canals over other rivers, valleys, railw ...
, sometimes spanning miles, brought
fresh water
Fresh water or freshwater is any naturally occurring liquid or frozen water containing low concentrations of dissolved salts and other total dissolved solids. Although the term specifically excludes seawater and brackish water, it does include ...
from a nearby river or spring to the mission site. Open or covered lined ditches and/or baked clay pipes, joined together with
lime mortar
Lime mortar or torching is composed of lime and an aggregate such as sand, mixed with water. The ancient Egyptians were the first to use lime mortars, which they used to plaster their temples. In addition, the Egyptians also incorporated various ...
or
bitumen
Asphalt, also known as bitumen (, ), is a sticky, black, highly viscous liquid or semi-solid form of petroleum. It may be found in natural deposits or may be a refined product, and is classed as a pitch. Before the 20th century, the term a ...
, gravity-fed the water into large
cistern
A cistern (Middle English ', from Latin ', from ', "box", from Greek ', "basket") is a waterproof receptacle for holding liquids, usually water. Cisterns are often built to catch and store rainwater. Cisterns are distinguished from wells by t ...
s and fountains, and emptied into waterways where the force of the water was used to turn grinding wheels and other simple machinery, or dispensed for use in cleaning. Water used for drinking and cooking was allowed to trickle through alternate layers of sand and charcoal to remove the impurities. One of the best-preserved mission water systems is at Mission Santa Barbara.
History
Beginning in 1492 with the voyages of
Christopher Columbus
Christopher Columbus
* lij, Cristoffa C(or)ombo
* es, link=no, Cristóbal Colón
* pt, Cristóvão Colombo
* ca, Cristòfor (or )
* la, Christophorus Columbus. (; born between 25 August and 31 October 1451, died 20 May 1506) was a ...
, the
Kingdom of Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = ''Plus ultra'' (Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, i ...
sought to establish missions to convert indigenous people in ''Nueva España'' (''
New Spain
New Spain, officially the Viceroyalty of New Spain ( es, Virreinato de Nueva España, ), or Kingdom of New Spain, was an integral territorial entity of the Spanish Empire, established by Habsburg Spain during the Spanish colonization of the Am ...
''), which consisted of the Caribbean, Mexico, and most of what is now the
Southwestern United States
The Southwestern United States, also known as the American Southwest or simply the Southwest, is a geographic and cultural region of the United States that generally includes Arizona, New Mexico, and adjacent portions of California, Colorado, Ne ...
) to
Roman Catholicism
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwide . It is am ...
. This would facilitate
colonization
Colonization, or colonisation, constitutes large-scale population movements wherein migrants maintain strong links with their, or their ancestors', former country – by such links, gain advantage over other inhabitants of the territory. When ...
of these lands
awarded
An award, sometimes called a distinction, is something given to a recipient as a token of recognition of excellence in a certain field. When the token is a medal, ribbon or other item designed for wearing, it is known as a decoration.
An award ...
to Spain by the
Catholic Church
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
, including that region later known as ''Alta California''.
[
The Spanish claim to the Pacific Northwest dated back to a 1493 papal bull ('']Inter caetera
''Inter caetera'' ('Among other orks) was a papal bull issued by Pope Alexander VI on the 4 May () 1493, which granted to the Catholic Monarchs King Ferdinand II of Aragon and Queen Isabella I of Castile all lands to the "west and south" o ...
'') and rights contained in the 1494 Treaty of Tordesillas
The Treaty of Tordesillas, ; pt, Tratado de Tordesilhas . signed in Tordesillas, Spain on 7 June 1494, and authenticated in Setúbal, Portugal, divided the newly discovered lands outside Europe between the Portuguese Empire and the Spanish Emp ...
; in these two formal acts, Spain gave itself the exclusive right to colonize all of the Western Hemisphere (excluding Brazil), including all of the west coast of North America.[The term ''Alta California'' as applies to the mission chain founded by Serra refers specifically to the modern-day United States State of ]California
California is a U.S. state, state in the Western United States, located along the West Coast of the United States, Pacific Coast. With nearly 39.2million residents across a total area of approximately , it is the List of states and territori ...
.[Leffingwell: The Rev. ]Antonio de la Ascensión
Antonio is a masculine given name of Etruscan origin deriving from the root name Antonius. It is a common name among Romance language-speaking populations as well as the Balkans and Lusophone Africa. It has been among the top 400 most popular male ...
, a Carmelite
, image =
, caption = Coat of arms of the Carmelites
, abbreviation = OCarm
, formation = Late 12th century
, founder = Early hermits of Mount Carmel
, founding_location = Mount Car ...
who visited San Diego with Vizcaíno's 1602 expedition, "surveyed the area and concluded that the land was fertile, the fish plentiful, and gold abundant." Ascensión was convinced that California's potential wealth and strategic location merited colonization, and in 1620 recommended in a letter to Madrid
Madrid ( , ) is the capital and most populous city of Spain. The city has almost 3.4 million inhabitants and a metropolitan area population of approximately 6.7 million. It is the second-largest city in the European Union (EU), and ...
that missions be established in the region, a venture that would involve military as well as religious personnel.
Early Spanish exploration
Only 48 years after Columbus discovered the Americas for Europe,
Francisco Vázquez de Coronado
Francisco Vázquez de Coronado y Luján (; 1510 – 22 September 1554) was a Spanish conquistador and explorer who led a large expedition from what is now Mexico to present-day Kansas through parts of the southwestern United States between 15 ...
set out from Compostela, New Spain on February 23, 1540, at the head of a large expedition. Accompanied by 400 European men-at-arms (mostly Spaniards), 1,300 to 2,000 Mexican Indian allies, several Indian and African slaves, and four Franciscan friars, he traveled from
Mexico
Mexico (Spanish: México), officially the United Mexican States, is a country in the southern portion of North America. It is bordered to the north by the United States; to the south and west by the Pacific Ocean; to the southeast by Guatema ...
through parts of the southwestern
United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territorie ...
to present-day
Kansas
Kansas () is a state in the Midwestern United States. Its capital is Topeka, and its largest city is Wichita. Kansas is a landlocked state bordered by Nebraska to the north; Missouri to the east; Oklahoma to the south; and Colorado to the ...
between 1540 and 1542. Two years later on 27 June 1542,
Juan Rodriguez Cabrillo
''Juan'' is a given name, the Spanish and Manx versions of ''John''. It is very common in Spain and in other Spanish-speaking communities around the world and in the Philippines, and also (pronounced differently) in the Isle of Man. In Spanish, t ...
set out from
Navidad, Mexico and sailed up the coast of Baja California and into the region of Alta California.
Secret English claims
Unknown to Spain,
Sir Francis Drake
Sir Francis Drake ( – 28 January 1596) was an English explorer, sea captain, privateer, slave trader, naval officer, and politician. Drake is best known for his circumnavigation of the world in a single expedition, from 1577 to 1580 (t ...
, an English privateer who raided Spanish treasure ships and colonial settlements, claimed the Alta California region as
Nova Albion
New Albion, also known as ''Nova Albion'' (in reference to Albion, an archaic name for Britain), was the name of the continental area north of Mexico claimed by Francis Drake, Sir Francis Drake for Kingdom of England, England when he landed on ...
for the
English Crown
This list of kings and reigning queens of the Kingdom of England begins with Alfred the Great, who initially ruled Wessex, one of the seven Anglo-Saxon kingdoms which later made up modern England. Alfred styled himself King of the Anglo-Sax ...
in 1579, a full generation before the first English landing in
Jamestown in 1607. During his
circumnavigation of the world, Drake anchored in a harbor just north of present-day San Francisco, California, establishing friendly relations with the
Coastal Miwok and claiming the territory for
Queen Elizabeth I
Elizabeth I (7 September 153324 March 1603) was Queen of England and Ireland from 17 November 1558 until her death in 1603. Elizabeth was the last of the five House of Tudor monarchs and is sometimes referred to as the "Virgin Queen".
El ...
. However, Drake sailed back to England and England (and later Britain) never pressed for any sort of claim regarding the region.
[Morrison, p. 214]
Russian exploration
However, it wasn't until 1741 that the Spanish monarchy of
King Philip V was stimulated to consider how to protect his claims to Alta California. Philip was spurred on when the territorial ambitions of
Tsarist Russia Tsarist Russia may refer to:
* Grand Duchy of Moscow (1480–1547)
*Tsardom of Russia (1547–1721)
*Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire and the final period of the Russian monarchy from 1721 to 1917, ruling across large parts of ...
were expressed in the
Vitus Bering
Vitus Jonassen Bering (baptised 5 August 1681 – 19 December 1741),All dates are here given in the Julian calendar, which was in use throughout Russia at the time. also known as Ivan Ivanovich Bering, was a Danish cartographer and explorer in ...
expedition along the western coast on the North American continent.
[Chapman: "It is usually stated that the Spanish court at Madrid received reports about Russian aggression in the Pacific northwest, and sent orders to meet them by the occupation of Alta California, wherefore the expeditions of 1769 were made. This view contains only a smattering of the truth. It is evident from ]osé de
In demonology, Ose (Pronounced /ˈɒze/), is a Great President of Hell, ruling three legions of demons (thirty to other authors, and Pseudomonarchia Daemonum gives no number of legions). He makes men wise in all liberal sciences and gives true ans ...
Gálvez's correspondence of 1768 that he and arlos Francisco de
Arlos is a commune in the Haute-Garonne department in southwestern France.
Population
See also
*Communes of the Haute-Garonne department
The following is a list of the 586 communes of the French department of Haute-Garonne.
The communes coo ...
Croix had discussed the advisability of an immediate expedition to Monterey, long before any word came from Spain about the Russian activities."[Bennett: California had been visited a number of times since Cabrillo's discovery in 1542, which initially included notable expeditions led by Englishmen ]Francis Drake
Sir Francis Drake ( – 28 January 1596) was an English explorer, sea captain, privateer, slave trader, naval officer, and politician. Drake is best known for his circumnavigation of the world in a single expedition, from 1577 to 1580 (t ...
in 1579 and Thomas Cavendish
Sir Thomas Cavendish (1560 – May 1592) was an English explorer and a privateer known as "The Navigator" because he was the first who deliberately tried to emulate Sir Francis Drake and raid the Spanish towns and ships in the Pacific and retu ...
1587, and later on by Woodes Rogers
Woodes Rogers ( 1679 – 15 July 1732) was an English sea captain, privateer, Atlantic slave trade, slave trader and, from 1718, the first List of colonial heads of the Bahamas, Royal Governor of the Bahamas. He is known as the captain of ...
(1710), George Shelvocke
George Shelvocke (baptised 1 April 167530 November 1742) was an English Royal Navy officer and later privateer who in 1726 wrote ''A Voyage Round the World by Way of the Great South Sea'' based on his exploits. It includes an account of how his s ...
(1719), James Cook
James Cook (7 November 1728 Old Style date: 27 October – 14 February 1779) was a British explorer, navigator, cartographer, and captain in the British Royal Navy, famous for his three voyages between 1768 and 1779 in the Pacific Ocean an ...
(1778), and finally George Vancouver
Captain George Vancouver (22 June 1757 – 10 May 1798) was a British Royal Navy officer best known for his 1791–1795 expedition, which explored and charted North America's northwestern Pacific Coast regions, including the coasts of what a ...
in 1792. Spanish explorer Sebastián Vizcaíno
Sebastián Vizcaíno (1548–1624) was a Spanish soldier, entrepreneur, explorer, and diplomat whose varied roles took him to New Spain, the Baja California peninsula, the California coast and Asia.
Early career
Vizcaíno was born in 154 ...
made landfall in San Diego Bay
San Diego Bay is a natural harbor and deepwater port located in San Diego County, California near the U.S.–Mexico border. The bay, which is long and wide, is the third largest of the three large, protected natural bays on California's of c ...
in 1602, and the famed ''conquistador
Conquistadors (, ) or conquistadores (, ; meaning 'conquerors') were the explorer-soldiers of the Spanish and Portuguese Empires of the 15th and 16th centuries. During the Age of Discovery, conquistadors sailed beyond Europe to the Americas, O ...
'' Hernán Cortés
Hernán Cortés de Monroy y Pizarro Altamirano, 1st Marquess of the Valley of Oaxaca (; ; 1485 – December 2, 1547) was a Spanish ''conquistador'' who led an expedition that caused the fall of the Aztec Empire and brought large portions of w ...
explored the California Gulf Coast in 1735.
Spanish expansion
California represents the "high-water mark" of Spanish expansion in North America as the last and northernmost colony on the continent. The mission system arose in part from the need to control Spain's ever-expanding holdings in the New World. Realizing that the colonies required a literate population base that the mother country could not supply, the Spanish government (with the cooperation of the Church) established a network of missions to convert the
indigenous population
Indigenous peoples are culturally distinct ethnic groups whose members are directly descended from the earliest known inhabitants of a particular geographic region and, to some extent, maintain the language and culture of those original people ...
to Christianity. They aimed to make converts and tax-paying citizens of those they conquered.
[Bennett 1897a, p. 10][Bennett: "Other pioneers have blazed the way for civilization by the torch and the bullet, and the red man has disappeared before them; but it remained for the Spanish priests to undertake to preserve the Indian and seek to make his existence compatible with a higher civilization."] To make them into Spanish citizens and productive inhabitants, the Spanish government and the Church required the indigenous people to learn Spanish language and vocational skills along with Christian teachings.
Estimates for the pre-contact indigenous population in California are based on a number of different sources and vary substantially, from 133,000,
to 225,000,
to
as high as 705,000 from more than 100 separate tribes or nations.
[Kroeber: "In the matter of population, too, the effect of Caucasian contact cannot be wholly slighted, since all statistics date from a late period. The disintegration of Native numbers and Native culture have proceeded hand in hand, but in very different rations according to locality. The determination of population strength before the arrival of whites is, on the other hand, of considerable significance toward the understanding of Indian culture, on account of the close relations which are manifest between type of culture and density of population."][Chapman, p. 383: "...there may have been about 133,000 ative inhabitantsin what is now the state as a whole, and 70,000 in or near the conquered area. The missions included only the Indians of given localities, though it is true that they were situated on the best lands and in the most populous centres. Even in the vicinity of the missions, there were some unconverted groups, however." See ]Population of Native California
The population of Native California refers to the population of Indigenous peoples of California. Estimates prior to and after European contact have varied substantially. Pre-contact estimates range from 133,000 to 705,000 with some recent schol ...
.
On January 29, 1767, Spain's
King Charles III
Charles III (Charles Philip Arthur George; born 14 November 1948) is King of the United Kingdom and the 14 other Commonwealth realms. He was the longest-serving heir apparent and Prince of Wales and, at age 73, became the oldest person to a ...
ordered the new governor
Gaspar de Portolá
Gaspar de Portolá y Rovira (January 1, 1716 – October 10, 1786) was a Spanish military officer, best known for leading the Portolá expedition into California and for serving as the first List of governors of California before 1850, Governor ...
to
forcibly expel the
Jesuits
The Society of Jesus ( la, Societas Iesu; abbreviation: SJ), also known as the Jesuits (; la, Iesuitæ), is a religious order (Catholic), religious order of clerics regular of pontifical right for men in the Catholic Church headquartered in Rom ...
, who operated under the authority of the Pope and had established a chain of fifteen
missions on the
Baja California Peninsula.
[Bennett: Due to the isolation of the Baja California missions, the decree for expulsion did not arrive in June 1767, as it did in the rest of New Spain, but was delayed until the new governor, Portolà, arrived with the news on November 30. Jesuits from the operating missions gathered in Loreto, whereupon they left for exile on February 3, 1768.] ''Visitador General''
José de Gálvez
José is a predominantly Spanish and Portuguese form of the given name Joseph. While spelled alike, this name is pronounced differently in each language: Spanish ; Portuguese (or ).
In French, the name ''José'', pronounced , is an old vernacul ...
engaged the
Franciscan
The Franciscans are a group of related Mendicant orders, mendicant Christianity, Christian Catholic religious order, religious orders within the Catholic Church. Founded in 1209 by Italian Catholic friar Francis of Assisi, these orders include t ...
s, under the leadership of Friar
Junípero Serra
Junípero Serra y Ferrer (; ; ca, Juníper Serra i Ferrer; November 24, 1713August 28, 1784) was a Spanish Roman Catholic priest and missionary of the Franciscan Order
, image = FrancescoCoA PioM.svg
, image_size ...
, to take charge of those outposts on March 12, 1768. The ''padres'' closed or consolidated several of the existing settlements, and also founded
Misión San Fernando Rey de España de Velicatá
:''Another mission bearing the name San Fernando Rey de España is located in the Mission Hills neighborhood of Los Angeles, California.''
Mission San Fernando Velicatá ( es, Misión San Fernando Rey de España de Velicatá) was a Spanish miss ...
(the only Franciscan mission in all of Baja California) and the nearby
Visita de la Presentación
The Visita de la Presentación was a Catholic visita located in Baja California Sur, Mexico. The visita was founded by Franciscan missionary Francisco Palóu in 1769 as an extension of Misión San Francisco Javier de Viggé-Biaundó.
Overview
...
in 1769. This plan, however, changed within a few months after Gálvez received the following orders: "Occupy and fortify San Diego and Monterey for God and the King of Spain." The Church ordered the priests of the
Dominican Order
The Order of Preachers ( la, Ordo Praedicatorum) abbreviated OP, also known as the Dominicans, is a Catholic mendicant order of Pontifical Right for men founded in Toulouse, France, by the Spanish priest, saint and mystic Dominic of Cal ...
to take charge of the Baja California missions so the Franciscans could concentrate on founding new missions in Alta California.
Mission period (1769–1833)

On July 14, 1769 Gálvez sent the
Portolá expedition
thumbnail, 250px, Point of San Francisco Bay Discovery
The Portolá expedition ( es, Expedición de Portolá) was a Spanish voyage of exploration in 1769–1770 that was the first recorded European land entry and exploration of the interior of t ...
out from Loreto to explore lands to the north. Leader
Gaspar de Portolá
Gaspar de Portolá y Rovira (January 1, 1716 – October 10, 1786) was a Spanish military officer, best known for leading the Portolá expedition into California and for serving as the first List of governors of California before 1850, Governor ...
was accompanied by a group of Franciscans led by
Junípero Serra
Junípero Serra y Ferrer (; ; ca, Juníper Serra i Ferrer; November 24, 1713August 28, 1784) was a Spanish Roman Catholic priest and missionary of the Franciscan Order
, image = FrancescoCoA PioM.svg
, image_size ...
. Serra's plan was to extend the string of missions north from the Baja California peninsula, connected by an established road and spaced a day's travel apart. The first Alta California mission and presidio were founded at San Diego, the second at Monterey.
En route to Monterey, the Rev. Francisco Gómez and the Rev.
Juan Crespí
Joan Crespí or Juan Crespí (1 March 1721 – 1 January 1782) was a Franciscan missionary and explorer of Las Californias.
Biography
A native of Majorca, Crespí entered the Franciscan order at the age of seventeen. He came to New Spain in ...
came across a Native settlement wherein two young girls were dying: one, a baby, said to be "dying at its mother's breast," the other a small girl suffering of burns. On July 22, Gómez baptized the baby, naming her ''Maria Magdalena'', while Crespí baptized the older child, naming her ''Margarita''. These were the first recorded baptisms in Alta California. Crespi dubbed the spot ''
Los Cristianos
Los Cristianos is a town in Spain with a population of 21,235 (2017), situated on the south coast of the Canary Island of Tenerife. Located in the municipality of Arona, Tenerife, Arona between the cone of the mountain Chayofita and the greater mou ...
''.
[Engelhardt: Today, the site (located at on ]Marine Corps Base Camp Pendleton
Marine Corps Base Camp Pendleton is the major West Coast base of the United States Marine Corps and is one of the largest Marine Corps bases in the United States. It is on the Southern California coast in San Diego County and is bordered by Oc ...
in San Diego County
San Diego County (), officially the County of San Diego, is a county in the southwestern corner of the U.S. state of California. As of the 2020 census, the population was 3,298,634, making it California's second-most populous county and the fi ...
) is in Los Christianitos ("The Little Christians") Canyon, and is designated as ''La Christiana'' California Historical Landmark
A California Historical Landmark (CHL) is a building, structure, site, or place in California that has been determined to have statewide historical landmark significance.
Criteria
Historical significance is determined by meeting at least one of ...
br>#562
. The group continued northward but missed Monterey Harbor and returned to San Diego on January 24, 1770. Near the end of 1769 the Portolá expedition had reached its most northerly point at present-day
San Francisco
San Francisco (; Spanish language, Spanish for "Francis of Assisi, Saint Francis"), officially the City and County of San Francisco, is the commercial, financial, and cultural center of Northern California. The city proper is the List of Ca ...
. In following years, the
Spanish Crown
, coatofarms = File:Coat_of_Arms_of_Spanish_Monarch.svg
, coatofarms_article = Coat of arms of the King of Spain
, image = Felipe_VI_in_2020_(cropped).jpg
, incumbent = Felipe VI
, incumbentsince = 19 Ju ...
sent a number of follow-up expeditions to explore more of Alta California.
Spain also settled the
California
California is a U.S. state, state in the Western United States, located along the West Coast of the United States, Pacific Coast. With nearly 39.2million residents across a total area of approximately , it is the List of states and territori ...
region with a number of African and
mulatto
(, ) is a racial classification to refer to people of mixed African and European ancestry. Its use is considered outdated and offensive in several languages, including English and Dutch, whereas in languages such as Spanish and Portuguese is ...
Catholics, including at least ten of the recently re-discovered
Los Pobladores
Los pobladores del pueblo de los Ángeles (English language, English: ''The townspeople of Los Angeles'') refers to the 44 original settlers and 4 soldiers from New Spain (Mexico) who founded the Pueblo de Los Ángeles, Pueblo de Nuestra Señora l ...
, the founders of
Los Angeles
Los Angeles ( ; es, Los Ángeles, link=no , ), often referred to by its initials L.A., is the largest city in the state of California and the second most populous city in the United States after New York City, as well as one of the world' ...
in 1781.

Structure
Each mission was to be turned over to a
secular clergy
In Christianity, the term secular clergy refers to deacons and priests who are not monastics or otherwise members of religious life. A secular priest (sometimes known as a diocesan priest) is a priest who commits themselves to a certain geogra ...
and all the common mission lands distributed amongst the native population within ten years after its founding, a policy that was based upon Spain's experience with the more advanced tribes in Mexico, Central America, and
Peru
, image_flag = Flag of Peru.svg
, image_coat = Escudo nacional del Perú.svg
, other_symbol = Great Seal of the State
, other_symbol_type = Seal (emblem), National seal
, national_motto = "Fi ...
. In time, it became apparent to the Rev. Serra and his associates that the
natives
Indigenous peoples are culturally distinct ethnic groups whose members are directly descended from the earliest known inhabitants of a particular geographic region and, to some extent, maintain the language and culture of those original people ...
on the northern frontier in Alta California required a much longer period of acclimatization.
None of the California missions ever attained complete
self-sufficiency
Self-sustainability and self-sufficiency are overlapping states of being in which a person or organization needs little or no help from, or interaction with, others. Self-sufficiency entails the self being enough (to fulfill needs), and a self-s ...
, and required continued (albeit modest) financial support from mother Spain. Mission development was therefore financed out of ''El Fondo Piadoso de las Californias'' (''The
Pious Fund of the Californias
The Pious Fund of the Californias ( es, Fondo Piadoso de las Californias) is a fund, originating in 1697, to sponsor the Roman Catholic Jesuit Spanish missions in Baja California, and Franciscan Spanish missions in Alta California in the Vic ...
'', which originated in 1697 and consisted of voluntary donations from individuals and religious bodies in Mexico to members of the
Society of Jesus
, image = Ihs-logo.svg
, image_size = 175px
, caption = ChristogramOfficial seal of the Jesuits
, abbreviation = SJ
, nickname = Jesuits
, formation =
, founders ...
) to enable the missionaries to propagate the Catholic Faith in
the area then known as California. Starting with the onset of the
Mexican War of Independence
The Mexican War of Independence ( es, Guerra de Independencia de México, links=no, 16 September 1810 – 27 September 1821) was an armed conflict and political process resulting in Mexico's independence from Spain. It was not a single, co ...
in 1810, this support largely disappeared, and missions and converts were left on their own. As of 1800, native labor had made up the backbone of the colonial economy.
Arguably "the worst epidemic of the Spanish Era in California" was known to be the
measles
Measles is a highly contagious infectious disease caused by measles virus. Symptoms usually develop 10–12 days after exposure to an infected person and last 7–10 days. Initial symptoms typically include fever, often greater than , cough, ...
epidemic of 1806, wherein one-quarter of the mission Native American population of the
San Francisco Bay Area
The San Francisco Bay Area, often referred to as simply the Bay Area, is a populous region surrounding the San Francisco, San Pablo, and Suisun Bay estuaries in Northern California. The Bay Area is defined by the Association of Bay Area Go ...
died of the measles or related complications between March and May of that year. In 1811, the Spanish Viceroy in Mexico sent an ''interrogatorio'' (questionnaire) to all of the missions in Alta California regarding the customs, disposition, and condition of the Mission Indians. The replies, which varied greatly in the length, spirit, and even the value of the information contained therein, were collected and prefaced by the Father-Presidente with a short general statement or abstract; the compilation was thereupon forwarded to the viceregal government.
[Kroeber: "Some of the missionaries evidently regarded compliance with the instructions of the questionnaire as an official requirement which was perfunctorily performed. In many cases no answers were given various questions at certain of the missions."] The contemporary nature of the responses, no matter how incomplete or biased some may be, are nonetheless of considerable value to modern
ethnologists
Ethnology (from the grc-gre, ἔθνος, meaning 'nation') is an academic field that compares and analyzes the characteristics of different peoples and the relationships between them (compare cultural, social, or sociocultural anthropology). ...
.

Russian colonization of the Americas
The Russian colonization of North America covers the period from 1732 to 1867, when the Russian Empire laid claim to northern Pacific Coast territories in the Americas. Russian colonial possessions in the Americas are collectively known as Russi ...
reached its southernmost point with the 1812 establishment of
Fort Ross
Fort Ross (Russian: Форт-Росс, Kashaya ''mé·ṭiʔni''), originally Fortress Ross ( pre-reformed Russian: Крѣпость Россъ, tr. ''Krepostʹ Ross''), is a former Russian establishment on the west coast of North America in ...
(''krepost' rus''), an agricultural, scientific, and
fur-trading settlement located in present-day
Sonoma County, California
Sonoma County () is a county (United States), county located in the U.S. state of California. As of the 2020 United States Census, its population was 488,863. Its county seat and largest city is Santa Rosa, California, Santa Rosa. It is to the n ...
. In November and December 1818, several of the missions were attacked by
Hipólito Bouchard
Hippolyte or Hipólito Bouchard (15 January 1780 – 4 January 1837) was a French-born Argentine sailor and corsair who fought for Argentina, Chile, and Peru.
During his first campaign as an Argentine corsair he attacked the Spanish colonies ...
, "California's only pirate."
[There is a great contrast between the legacy of Bouchard in Argentina versus his reputation in the United States. In Buenos Aires, Bouchard is honored as a brave patriot, while in California he is most often remembered as a pirate, and not a privateer. See ]Hippolyte Bouchard
Hippolyte or Hipólito Bouchard (15 January 1780 – 4 January 1837) was a French-born Argentine sailor and corsair who fought for Argentina, Chile, and Peru.
During his first campaign as an Argentine corsair he attacked the Spanish colonies o ...
. A French
privateer
A privateer is a private person or ship that engages in maritime warfare under a commission of war. Since robbery under arms was a common aspect of seaborne trade, until the early 19th century all merchant ships carried arms. A sovereign or deleg ...
sailing under the flag of
Argentina
Argentina (), officially the Argentine Republic ( es, link=no, República Argentina), is a country in the southern half of South America. Argentina covers an area of , making it the second-largest country in South America after Brazil, th ...
, ''Pirata Buchar'' (as Bouchard was known to the locals) worked his way down the California coast, conducting raids on the installations at Monterey,
Santa Barbara, and San Juan Capistrano, with limited success. Upon hearing of the attacks, many mission priests (along with a few government officials) sought refuge at
Mission Nuestra Señora de la Soledad
Mission Nuestra Señora de la Soledad ( es, Misión Nuestra Señora de la Soledad), commonly known as Mission Soledad, is a Spanish mission located in Soledad, California. The mission was founded by the Franciscan order on October 9, 1791 to con ...
, the mission chain's most isolated outpost. Ironically,
Mission Santa Cruz
Mission Santa Cruz (''La Misión de la Exaltación de la Santa Cruz'', which translates as the Mission of the Exaltation of the Holy Cross), was the twelfth of twenty-one Spanish missions in California (today's U.S. state), established by the Fr ...
(though ultimately ignored by the marauders) was ignominiously sacked and vandalized by local residents who were entrusted with securing the church's valuables.
By 1819, Spain decided to limit its "reach" in the New World to
Northern California
Northern California (colloquially known as NorCal) is a geographic and cultural region that generally comprises the northern portion of the U.S. state of California. Spanning the state's northernmost 48 counties, its main population centers incl ...
due to the costs involved in sustaining these remote outposts; the northernmost settlement therefore is
Mission San Francisco Solano
Mission San Francisco Solano was the 21st, last, and northernmost mission in Alta California. It was named for Saint Francis Solanus. It was the only mission built in Alta California after Mexico gained independence from Spain. The difficulty of ...
, founded in Sonoma in 1823.
[Hittell, p. 499][Hittell: "...it ission San Francisco Solanowas quite frequently known as the mission of Sonoma. From the beginning it was rather a military than a religious establishment—a sort of outpost or barrier, first against the Russians and afterwards against the Americans; but still a large adobe church was built and Indians were baptized."]
The
Chumash people revolted against the Spanish presence in 1824. The Chumash planned a coordinated rebellion at three missions. Due to an incident with a soldier at Mission Santa Inés, the rebellion began on Saturday, February 21. The Chumash withdrew from Mission Santa Inés upon the arrival of military reinforcements, then attacked Mission La Purisima from inside, forced the garrison to surrender, and allowed the garrison, their families, and the mission priest to depart for Santa Inés. The next day, the Chumash of Mission Santa Barbara captured the mission from within without bloodshed, repelled a military attack on the mission, and then retreated from the mission to the hills. The Chumash continued to occupy Mission La Purisima until a Mexican military unit attacked people on March 16 and forced them to surrender. Two military expeditions were sent after the Chumash in the hills; the first did not find them and the second negotiated with the Chumash and convinced a majority to return to the missions by June 28.
An attempt to found a twenty-second mission in
Santa Rosa
Santa Rosa is the Italian, Portuguese and Spanish name for Saint Rose.
Santa Rosa may also refer to:
Places Argentina
*Santa Rosa, Mendoza, a city
* Santa Rosa, Tinogasta, Catamarca
* Santa Rosa, Valle Viejo, Catamarca
*Santa Rosa, La Pampa
* Sa ...
in 1827 was aborted.
[Hittell: "By that time, it was found that the Russians were not such undesirable neighbors as in 1817 it was thought they might become...the Russian scare, for the time being at least was over; and as for the old enthusiasm for new spiritual conquests, there was none left."][Bennett 1897b, p. 154: "Up to 1817 the 'spiritual conquest' of California had been confined to the territory south of San Francisco Bay. And this, it might be said, was as far as possible under the mission system. There had been a few years prior to that time certain alarming incursions of the Russians, which distressed Spain, and it was ordered that missions be started across the bay."][Chapman: "...the Russians and the English were by no means the only foreign peoples who threatened Spain's domination of the Pacific coast. The Indians and the Chinese had their opportunity before Spain appeared upon the scene. The Japanese were at one time a potential concern, and the Portuguese and Dutch voyagers occasionally gave Spain concern. The French for many years were the most dangerous enemy of all, but with their disappearance from North America in 1763, as a result of their defeat in the ]Seven Years' War
The Seven Years' War (1756–1763) was a global conflict that involved most of the European Great Powers, and was fought primarily in Europe, the Americas, and Asia-Pacific. Other concurrent conflicts include the French and Indian War (1754� ...
, they were no longer a menace. The people of the United States were eventually to become the most powerful outstanding element." In 1833 the final group of missionaries arrived in Alta California. These were Mexican-born (rather than Spaniards), and had been trained at the
Apostolic College of Our Lady of Guadalupe in Zacatecas. Among these friars was
Francisco García Diego y Moreno
Francisco García Diego y Moreno, OFM, (17 September 1785 – 30 April 1846) was the first bishop of the Diocese of the Californias.
Early episcopal appointments
In 1801, he received the habit of Francis at the missionary College of Guadalupe ...
, who would become the first bishop of the Diocese of Both Californias. These friars would bear the brunt of the changes brought on by secularization and the U.S. occupation, and many would be marked by allegations of corruption.
Secularization
As the Mexican republic matured, calls for the
secularization
In sociology, secularization (or secularisation) is the transformation of a society from close identification with religious values and institutions toward non-religious values and secular institutions. The ''secularization thesis'' expresses the ...
("
disestablishment
The separation of church and state is a philosophical and jurisprudential concept for defining political distance in the relationship between religious organizations and the state. Conceptually, the term refers to the creation of a secular stat ...
") of the missions increased.
[Robinson: The ''cortes'' (legislature) of New Spain issued a decree in 1813 for at least partial secularization that affected all missions in America and was to apply to all outposts that had operated for ten years or more; however, the decree was never enforced in California.]
José María de Echeandía
José María de Echeandía (?–1871) was twice Mexican governor of Alta California from 1825 to 1831 and again from 1832 to 1833. He was the only governor of California that lived in San Diego.José Bandini, in a note to Governor Echeandía or t ...
, the first native Mexican elected Governor of Alta California issued a "Proclamation of Emancipation" (or "''Prevenciónes de Emancipacion''") on July 25, 1826. All Indians within the military districts of San Diego, Santa Barbara, and
Monterey
Monterey (; es, Monterrey; Ohlone: ) is a city located in Monterey County on the southern edge of Monterey Bay on the U.S. state of California's Central Coast. Founded on June 3, 1770, it functioned as the capital of Alta California under both ...
who were found qualified were freed from missionary rule and made eligible to become Mexican citizens. Those who wished to remain under mission tutelage were exempted from most forms of corporal punishment.
[Catholic historian Zephyrin Engelhardt referred to Echeandía as "...an avowed enemy of the religious orders."] By 1830 even the neophyte populations themselves appeared confident in their own abilities to operate the mission ranches and farms independently; the ''padres'', however, doubted the capabilities of their charges in this regard.
Accelerating immigration, both Mexican and foreign, increased pressure on the Alta California government to seize the mission properties and dispossess the natives in accordance with Echeandía's directive.
[Settlers made numerous false claims to diminish the natives' abilities: "The Indians are by nature slovenly and indolent," stated one newcomer. "They have unfeelingly appropriated the region," claimed another.] Despite the fact that Echeandía's emancipation plan was met with little encouragement from the novices who populated the southern missions, he was nonetheless determined to test the scheme on a large scale at Mission San Juan Capistrano. To that end, he appointed a number of ''comisionados'' (commissioners) to oversee the emancipation of the Indians. The Mexican government passed legislation on December 20, 1827 that mandated the expulsion of all Spaniards younger than sixty years of age from Mexican territories; Governor Echeandía nevertheless intervened on behalf of some of the missionaries to prevent their deportation once the law took effect in California.
Governor
José Figueroa
José Figueroa (1792 – 29 September 1835), was a General and the Mexican Governor of Alta California from 1833 to 1835. He wrote the first book to be published in California.
Background and governorship
Figueroa was a Mestizo of Spanish a ...
(who took office in 1833) initially attempted to keep the mission system intact, but the
Mexican Congress
The Congress of the Union ( es, Congreso de la Unión, ), formally known as the General Congress of the United Mexican States (''Congreso General de los Estados Unidos Mexicanos''), is the legislature of the federal government of Mexico cons ...
passed ''
An Act for the Secularization of the Missions of California'' on August 17, 1833 when liberal
Valentín Gómez Farías
Valentín Gómez Farías (; 14 February 1781 – 5 July 1858) was a Mexican physician and liberal politician who became president of Mexico twice, first in 1833, during the period of the First Mexican Republic, and again in 1846, during the ...
was in office.
[Yenne, pp. 18–19][Yenne: In 1833, Figueroa replaced the Spanish-born Franciscan ''padres'' at all of the settlements north of Mission San Antonio de Padua with Mexican-born Franciscan priests from the ]College of Guadalupe de Zacatecas The College of Guadalupe de Zacatecas was a Roman Catholic Franciscan missionary college, or seminary (''Colegio Apostolico''), founded in Guadalupe, Zacatecas (Mexico) by the Order of Friars Minor between 1703 and 1707. The institution was establis ...
. In response, Father-Presidente Narciso Durán Narcís Duran (in Catalan), commonly known as Narciso Durán, OFM (December 16, 1776 in Empúries, Catalonia, Spain – June 4, 1846 in Santa Barbara, Alta California, Mexico) was a Franciscan friar and missionary. He arrived in California in 1806 ...
transferred the headquarters of the Alta California Mission System to Mission Santa Bárbara, where it remained until 1846.
The Act also provided for the colonization of both Alta and Baja California, the expenses of this latter move to be borne by the proceeds gained from the sale of the mission property to private interests.
For instance, after Mexican Independence, the Mexican government confiscated Franciscan lands and decommissioned them. This, however, did not see the end of Native plight since Further dislocation and abuse occurred under Mexican control. Most of the confiscated Franscians lands were given out as grants to white settlers or well connected Mexicans, while Native Californians continued to occupy the land as a labor force.
Mission San Juan Capistrano was the very first to feel the effects of secularization when, on August 9, 1834 Governor Figueroa issued his "Decree of Confiscation." Nine other settlements quickly followed, with six more in 1835;
San Buenaventura and San Francisco de Asís were among the last to succumb, in June and December 1836, respectively. The
Franciscan
The Franciscans are a group of related Mendicant orders, mendicant Christianity, Christian Catholic religious order, religious orders within the Catholic Church. Founded in 1209 by Italian Catholic friar Francis of Assisi, these orders include t ...
s soon thereafter abandoned most of the missions, taking with them almost everything of value, after which the locals typically plundered the mission buildings for construction materials. Former mission pasture lands were divided into large land grants called ''ranchos'', greatly increasing the number of private land holdings in Alta California.
Rancho period (1834–1849)
In spite of this neglect, the Indian towns at
San Juan Capistrano
San Juan Capistrano (Spanish for "St. John of Capistrano") is a city in Orange County, California, located along the Orange Coast. The population was 34,593 at the 2010 census.
San Juan Capistrano was founded by the Spanish in 1776, when St. ...
,
San Dieguito, and
Las Flores did continue on for some time under a provision in ''Gobernador'' Echeandía's 1826 Proclamation that allowed for the partial conversion of missions to ''pueblos''. According to one estimate, the native population in and around the missions proper was approximately 80,000 at the time of the confiscation; others claim that the
statewide population had dwindled to approximately 100,000 by the early 1840s, due in no small part to the natives' exposure to European diseases, and from the Franciscan practice of cloistering women in the ''convento'' and controlling sexuality during the child-bearing age. (
Baja California Territory
Baja California Territory (Territorio de Baja California) was a Mexican territory from 1824 to 1931, that encompassed the Baja California Peninsula of present-day northwestern Mexico. It replaced the Baja California Province (1773–1824) of ...
experienced a similar reduction in native population resulting from Spanish colonization efforts there).
 Pío de Jesús Pico
Pío de Jesús Pico, the last Mexican Governor of Alta California, found upon taking office that there were few funds available to carry on the affairs of the province. He prevailed upon the assembly to pass a decree authorizing the renting or the sale of all mission property, reserving only the church, a curate's house, and a building for a courthouse. The expenses of conducting the services of the church were to be provided from the proceeds, but there was no disposition made as to what should be done to secure the funds for that purpose. After secularization, Father-Presidente Narciso Durán transferred the missions' headquarters to Santa Bárbara, thereby making Mission Santa Bárbara the repository of some 3,000 original documents that had been scattered through the California missions. The Mission archive is the oldest library in the State of California that still remains in the hands of its founders, the Franciscans (it is the only mission where they have maintained an uninterrupted presence). Beginning with the writings of
Hubert Howe Bancroft
Hubert Howe Bancroft (May 5, 1832 – March 2, 1918) was an American historian and ethnologist who wrote, published and collected works concerning the western United States, Texas, California, Alaska, Mexico, Central America and British Columbi ...
, the library has served as a center for historical study of the missions for more than a century. In 1895 journalist and historian
Charles Fletcher Lummis
Charles Fletcher Lummis (March 1, 1859, in Lynn, Massachusetts – November 25, 1928, in Los Angeles, California) was a United States journalist, and an activist for Indian rights and historic preservation. A traveler in the American Southwest, h ...
criticized the Act and its results, saying:
California statehood (1850 and beyond)

Precise figures relating to the population decline of California indigenes are not available. One writer,
Gregory Orfalea
Gregory Orfalea is an American writer, the author or editor of nine books, including his most recent works, the biography ''Journey to the Sun: Junipero Serra's Dream and the Founding of California'' (Scribner, 2014) and a short story colle ...
, estimates that pre-contact population was reduced by 33 percent during Spanish and Mexican rule, mostly through introduction of European diseases, but much more after the United States takeover in 1848. By 1870, the loss of indigenous lives had become catastrophic. Up to 80 percent died, leaving a population of about 30,000 in 1870. Orfalea claims that nearly half of the native deaths after 1848 were murder.
[
In 1837–38, a major smallpox epidemic devastated native tribes north of San Francisco Bay, in the jurisdiction of Mission San Francisco Solano. General ]Mariano Vallejo
Don Mariano Guadalupe Vallejo (4 July 1807 – 18 January 1890) was a Californio general, statesman, and public figure. He was born a subject of Spain, performed his military duties as an officer of the Republic of Mexico, and shaped the transi ...
estimated that 70,000 died from the disease. Vallejo's ally, chief Sem-Yeto
Sem-Yeto () was a leader of the Suisunes, a Patwin people of the Suisun Bay region of northern California. Baptized as Francisco Solano and also known as Chief Solano, he was a notable Native American leader in Alta California because of his ...
, was one of the few natives to be vaccinated, and one of the few to survive.
When the mission properties were secularized between 1834 and 1838, the approximately 15,000 resident ''neophytes'' lost whatever protection the mission system afforded them. While under the secularization laws the natives were to receive up to one-half of the mission properties, this never happened. The natives lost whatever stock and movable property they may have accumulated. When California became a U.S. state, California law stripped them of legal title to the land. In the Act of September 30, 1850, Congress
A congress is a formal meeting of the representatives of different countries, constituent states, organizations, trade unions, political parties, or other groups. The term originated in Late Middle English to denote an encounter (meeting of a ...
appropriated funds to allow the President to appoint three Commissioners, O. M. Wozencraft
Oliver M. Wozencraft (July 26, 1814 – November 22, 1887) was a prominent early American settler in California. He had substantial involvement in negotiating Aboriginal title in California, treaties between California Native American Indi ...
, Redick McKee and George W. Barbour, to study the California situation and "...negotiate treaties with the various Indian tribes of California." Treaty negotiations ensued during the period between March 19, 1851 and January 7, 1852, during which the Commission interacted with 402 Indian chiefs and headmen (representing approximately one-third to one-half of the California tribes) and entered into eighteen treaties.
California Senator William M. Gwin
William McKendree Gwin (October 9, 1805 – September 3, 1885) was an American medical doctor and politician who served in elected office in Mississippi and California. In California he shared the distinction, along with John C. Frémont, of bein ...
's Act of March 3, 1851 created the Public Land Commission
The California Land Act of 1851 (), enacted following the Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo and the admission of California as a state in 1850, established a three-member Public Land Commission to determine the validity of prior Spanish and Mexican la ...
, whose purpose was to determine the validity of Spanish and Mexican land grant
A land grant is a gift of real estate—land or its use privileges—made by a government or other authority as an incentive, means of enabling works, or as a reward for services to an individual, especially in return for military service. Grants ...
s in California. On February 19, 1853 Archbishop
In Christian denominations, an archbishop is a bishop of higher rank or office. In most cases, such as the Catholic Church, there are many archbishops who either have jurisdiction over an ecclesiastical province in addition to their own archdi ...
J.S. Alemany filed petitions for the return of all former mission lands in the state. Ownership of (essentially exact area of land occupied by the original mission buildings, cemeteries, and gardens) was subsequently conveyed to the Church, along with the '' Cañada de los Pinos'' (or College Rancho) in Santa Barbara County
Santa Barbara County, California, officially the County of Santa Barbara, is located in Southern California. As of the 2020 census, the population was 448,229. The county seat is Santa Barbara, and the largest city is Santa Maria.
Santa Barba ...
comprising , and ''La Laguna
LA most frequently refers to Los Angeles, the second largest city in the United States.
La, LA, or L.A. may also refer to:
Arts and entertainment Music
* La (musical note), or A, the sixth note
* "L.A.", a song by Elliott Smith on ''Figure ...
'' in San Luis Obispo County
San Luis Obispo County (), officially the County of San Luis Obispo, is a county on the Central Coast of California. As of the 2020 census, the population was 282,424. The county seat is San Luis Obispo.
Junípero Serra founded the Mission ...
, consisting of . As the result of a U.S. government
The federal government of the United States (U.S. federal government or U.S. government) is the national government of the United States, a federal republic located primarily in North America, composed of 50 states, a city within a fede ...
investigation in 1873, a number of Indian reservation
An Indian reservation is an area of land held and governed by a federally recognized Native American tribal nation whose government is accountable to the United States Bureau of Indian Affairs and not to the state government in which it ...
s were assigned by executive proclamation in 1875. The commissioner of Indian affairs reported in 1879 that the number of Mission Indians
Mission Indians are the indigenous peoples of California who lived in Southern California and were forcibly relocated from their traditional dwellings, villages, and homelands to live and work at 15 Franciscan missions in Southern California and ...
in the state was down to around 3,000.
Legacy and Native American controversy
There is controversy over the California Department of Education's treatment of the missions in the Department's elementary curriculum; in the tradition of historical revisionism
In historiography, historical revisionism is the reinterpretation of a historical account. It usually involves challenging the orthodox (established, accepted or traditional) views held by professional scholars about a historical event or times ...
, it has been alleged that the curriculum "waters down" the harsh treatment of Native Americans. Some modern anthropologists
An anthropologist is a person engaged in the practice of anthropology. Anthropology is the study of aspects of humans within past and present societies. Social anthropology, cultural anthropology and philosophical anthropology study the norms and v ...
cite a cultural bias on the part of the missionaries that blinded them to the natives' plight and caused them to develop strong negative opinions of the California Indians.[Hittell: "Boscana himself and his brother missionaries were men of narrow range of thought, continually seeking among the superstitions of the natives for resemblances of the true faith and ever ready to catch at the slightest hints and magnify them into complicated dogmas corresponding afar of those which they themselves taught."] European diseases like influenza
Influenza, commonly known as "the flu", is an infectious disease caused by influenza viruses. Symptoms range from mild to severe and often include fever, runny nose, sore throat, muscle pain, headache, coughing, and fatigue. These symptoms ...
, measles
Measles is a highly contagious infectious disease caused by measles virus. Symptoms usually develop 10–12 days after exposure to an infected person and last 7–10 days. Initial symptoms typically include fever, often greater than , cough, ...
, tuberculosis
Tuberculosis (TB) is an infectious disease usually caused by '' Mycobacterium tuberculosis'' (MTB) bacteria. Tuberculosis generally affects the lungs, but it can also affect other parts of the body. Most infections show no symptoms, in ...
, gonorrhea
Gonorrhea, colloquially known as the clap, is a sexually transmitted infection (STI) caused by the bacterium '' Neisseria gonorrhoeae''. Infection may involve the genitals, mouth, or rectum. Infected men may experience pain or burning with ...
, and dysentery
Dysentery (UK pronunciation: , US: ), historically known as the bloody flux, is a type of gastroenteritis that results in bloody diarrhea. Other symptoms may include fever, abdominal pain, and a feeling of incomplete defecation. Complications ...
caused a significant population reduction from the first encounter through the 19th century as California Native Americans had no immunity to these diseases. These deaths, however, where only made worse by the treatment Native Californians faced at the hands of Settlers. Associate professor Benjamin Madly at the University of California, Los Angeles states:
"Between 1846 and 1870, California’s Indian population plunged from perhaps 150,000 to 30,000. Diseases, dislocation, and starvation caused many of these deaths. However, abduction, unfree labor, mass death on reservations, individual homicides, battles, and massacres also took thousands of lives and hindered reproduction"
The impact that the original Spanish system of colonization had on modern day California cannot be overstated. Although the certain cooperation between Church and State that was part and parcel of the original California mission system was soon discarded by the Mexican government, it nonetheless provided a foundation upon which later forms of government would soon be established. The early missions and their sub-missions formed the nuclei of what would later become the major metropolitan areas of San Francisco
San Francisco (; Spanish language, Spanish for "Francis of Assisi, Saint Francis"), officially the City and County of San Francisco, is the commercial, financial, and cultural center of Northern California. The city proper is the List of Ca ...
and Los Angeles
Los Angeles ( ; es, Los Ángeles, link=no , ), often referred to by its initials L.A., is the largest city in the state of California and the second most populous city in the United States after New York City, as well as one of the world' ...
, as well as many other smaller municipalities. In addition to clearing the way for Spanish, Mexican, and later American settlers, the early Spanish mission system established the viability of the early Western economies of cattle and agriculture which survive in modern form in the state to this day. The Spanish mission system acted to "settle and Westernize" California, but unfortunately did so very much at the ''expense'' of the earlier Native American Culture
Native American cultures across the United States are notable for their wide variety and diversity of lifestyles, regalia, art forms and beliefs. The culture of indigenous North America is usually defined by the concept of the Pre-Columbian ...
of California that had preceded the Spanish mission system.
Mission administration, locations and military districts
System Father-Presidentes
* The Rev. Junípero Serra
Junípero Serra y Ferrer (; ; ca, Juníper Serra i Ferrer; November 24, 1713August 28, 1784) was a Spanish Roman Catholic priest and missionary of the Franciscan Order
, image = FrancescoCoA PioM.svg
, image_size ...
(1769–1784)
* The Rev. Francisco Palóu
Francesc Palou (in Catalan) or Francisco Palóu (1723–1789) was a Spanish Franciscan missionary, administrator and historian on the Baja California Peninsula and in Alta California. Palóu made significant contributions to the Alta California ...
(''presidente pro tempore
''Pro tempore'' (), abbreviated ''pro tem'' or ''p.t.'', is a Latin phrase which best translates to "for the time being" in English. This phrase is often used to describe a person who acts as a ''locum tenens'' (placeholder) in the absence of ...
'') (1784–1785)
* The Rev. Fermín Francisco de Lasuén Fermín or Fermin may refer to:
* Fermin, Spanish saint
* Fermin (name), Spanish name and surname
* Fermin IV
Fermin (also Firmin, from Latin ''Firminus''; Spanish ''Fermín'') was a legendary holy man and martyr, traditionally venerated as the c ...
(1785–1803)
* The Rev. Pedro Estévan Tápis
Pedro is a masculine given name. Pedro is the Spanish, Portuguese, and Galician name for ''Peter''. Its French equivalent is Pierre while its English and Germanic form is Peter.
The counterpart patronymic surname of the name Pedro, meaning " ...
(1803–1812)
* The Rev. José Francisco de Paula Señan
Father José Francisco de Paula Señan (March 3, 1760 – August 24, 1823) was a Spanish missionary to the Americas.
Life
He was born in Barcelona, Spain and entered the Franciscan Order in 1774. In 1784 he was incorporated in the missionary C ...
(1812–1815)
* The Rev. Mariano Payéras
Mariano is a masculine name from the Romance languages, corresponding to the feminine Mariana.
It is an Italian, Spanish and Portuguese variant of the Roman Marianus which derived from Marius, and Marius derived from the Roman god Mars (see also ...
(1815–1820)
* The Rev. José Francisco de Paula Señan (1820–1823)
* The Rev. Vicente Francisco de Sarría Father Vicente Francisco de Sarría (1767 Etxebarri, Spain – 1835 Soledad, California, Soledad) was a History of the Basques, Basque missionary to the Americas.
Venture into Alta California
Father Sarría baptized John Gilroy (California), Jo ...
(1823–1824)
* The Rev. Narciso Durán Narcís Duran (in Catalan), commonly known as Narciso Durán, OFM (December 16, 1776 in Empúries, Catalonia, Spain – June 4, 1846 in Santa Barbara, Alta California, Mexico) was a Franciscan friar and missionary. He arrived in California in 1806 ...
(1824–1827)
* The Rev. José Bernardo Sánchez
Father José Bernardo Sánchez (September 7, 1778 – January 15, 1833) was a Spanish missionary in colonial Mexico and Alta California.
Early life
Born in Robledillo de Mohernando, Old Castile, Spain, Sánchez became a Franciscan on October ...
(1827–1831)
* The Rev. Narciso Durán (1831–1838)
* The Rev. José Joaquin Jimeno
Father José Joaquin Jimeno (1804–1856) was a Spanish missionary to the Americas.
Father Jimeno is known to have traveled with Father Mariano Payeras to San Jacinto, a distant rancho of Mission San Luis Rey de Francia in September 1821. He ...
(1838–1844)
* The Rev. Narciso Durán (1844–1846)
The "Father-Presidente" was the head of the Catholic missions in Alta and Baja California. He was appointed by the College of San Fernando de Mexico The College of San Fernando de México was a Roman Catholic Franciscan missionary college, or seminary (''Colegio Apostólico''), founded in Spanish colonial Mexico City by the Franciscan Order of Friars Minor on October 15, 1734.
The institution w ...
until 1812, when the position became known as the "Commissary Prefect" who was appointed by the Commissary General of the Indies (a Franciscan residing in Spain). Beginning in 1831, separate individuals were elected to oversee Upper and Lower California.
Mission headquarters
 *
* Mission San Diego de Alcalá
Mission Basilica San Diego de Alcalá ( es, Misión San Diego de Alcalá) was the second Franciscan founded mission in The Californias (after San Fernando de Velicata), a province of New Spain. Located in present-day San Diego, California, it w ...
(1769–1771)
* Mission San Carlos Borromeo de Carmelo (1771–1815)
* Mission La Purísima Concepción*(1815–1819)
* Mission San Carlos Borromeo de Carmelo (1819–1824)
* Mission San José*(1824–1827)
* Mission San Carlos Borromeo de Carmelo (1827–1830)
* Mission San José*(1830–1833)
* Mission Santa Barbara (1833–1846)
† The Rev. Payeras and the Rev. Durán remained at their resident missions during their terms as ''Father-Presidente'', therefore those settlements became the de facto
''De facto'' ( ; , "in fact") describes practices that exist in reality, whether or not they are officially recognized by laws or other formal norms. It is commonly used to refer to what happens in practice, in contrast with ''de jure'' ("by la ...
headquarters (until 1833, when all mission records were permanently relocated to Santa Barbara).[In 1833 Figueroa replaced the ''padres'' at all of the settlements north of Mission San Antonio de Padua with Mexican-born Franciscan priests from the ]College of Guadalupe de Zacatecas The College of Guadalupe de Zacatecas was a Roman Catholic Franciscan missionary college, or seminary (''Colegio Apostolico''), founded in Guadalupe, Zacatecas (Mexico) by the Order of Friars Minor between 1703 and 1707. The institution was establis ...
. In response, Father-Presidente Narciso Durán Narcís Duran (in Catalan), commonly known as Narciso Durán, OFM (December 16, 1776 in Empúries, Catalonia, Spain – June 4, 1846 in Santa Barbara, Alta California, Mexico) was a Franciscan friar and missionary. He arrived in California in 1806 ...
transferred the headquarters of the Alta California Mission System to Mission Santa Bárbara, where they remained until 1846.
Mission locations
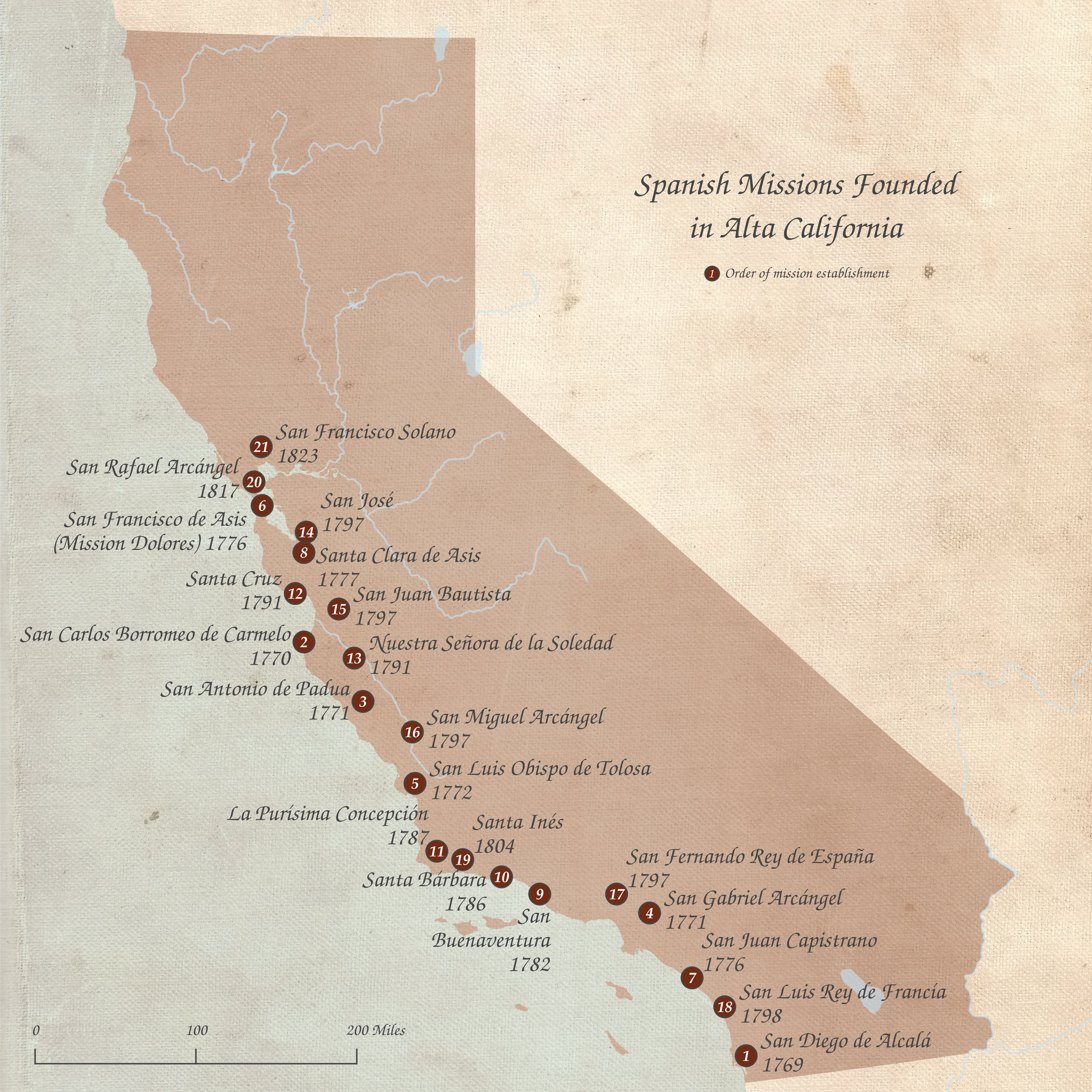 There were 21 missions accompanied by military outposts in
There were 21 missions accompanied by military outposts in Alta California
Alta California ('Upper California'), also known as ('New California') among other names, was a province of New Spain, formally established in 1804. Along with the Baja California peninsula, it had previously comprised the province of , but ...
from San Diego
San Diego ( , ; ) is a city on the Pacific Ocean coast of Southern California located immediately adjacent to the Mexico–United States border. With a 2020 population of 1,386,932, it is the List of United States cities by population, eigh ...
to Sonoma, California. To facilitate travel between them on horse and foot, the mission settlements were situated approximately 30 miles (48 kilometers) apart, about one day's journey
A day's journey in pre-modern literature, including the Bible, ancient geographers and ethnographers such as Herodotus, is a measurement of distance.
In the Bible, it is not as precisely defined as other Biblical measurements of distance; the dis ...
on horseback, or three days on foot. The entire trail eventually became a 600-mile (966-kilometer) long "California Mission Trail." Heavy freight movement was practical only via water. Tradition has it that the padres sprinkled mustard
Mustard may refer to:
Food and plants
* Mustard (condiment), a paste or sauce made from mustard seeds used as a condiment
* Mustard plant, one of several plants, having seeds that are used for the condiment
** Mustard seed, seeds of the mustard p ...
seeds along the trail to mark it with bright yellow flowers.
Following the old Camino Real northwards, from San Diego
San Diego ( , ; ) is a city on the Pacific Ocean coast of Southern California located immediately adjacent to the Mexico–United States border. With a 2020 population of 1,386,932, it is the List of United States cities by population, eigh ...
through to the northernmost mission in Sonoma, California
Sonoma is a city in Sonoma County, California, United States, located in the North Bay region of the San Francisco Bay Area. Sonoma is one of the principal cities of California's Wine Country and the center of the Sonoma Valley AVA. Sonoma's p ...
, north of San Francisco Bay
San Francisco Bay is a large tidal estuary in the U.S. state of California, and gives its name to the San Francisco Bay Area. It is dominated by the big cities of San Francisco, San Jose, and Oakland.
San Francisco Bay drains water from a ...
, the missions were:
Military districts
 During the Mission Period Alta California was divided into four military districts. Each was garrisoned (''comandancias'') by a presidio strategically placed along the California coast to protect the missions and other Spanish settlements in Upper California. Each of these functioned as a base of military operations for a specific region. They were independent of one another and were organized from south to north as follows:
* El Presidio Real de San Diego founded on July 16, 1769 – responsible for the defense of all installations located within the First Military District (the missions at San Diego, San Luis Rey, San Juan Capistrano, and San Gabriel);
* El Presidio Real de Santa Bárbara founded on April 12, 1782 – responsible for the defense of all installations located within the Second Military District (the missions at San Fernando, San Buenaventura, Santa Barbara, Santa Inés, and La Purísima, along with ''El Pueblo de Nuestra Señora la Reina de los Ángeles del Río de Porciúncula'' os Angeles;
* El Presidio Real de San Carlos de Monterey (''El Castillo'') founded on June 3, 1770 – responsible for the defense of all installations located within the Third Military District (the missions at San Luis Obispo, San Miguel, San Antonio, Soledad, San Carlos, and San Juan Bautista, along with ''Villa Branciforte'' anta Cruz; and
* El Presidio Real de San Francisco founded on December 17, 1776 – responsible for the defense of all installations located within the Fourth Military District (the missions at Santa Cruz, San José, Santa Clara, San Francisco, San Rafael, and Solano, along with ''El Pueblo de San José de Guadalupe'' an Jose.
* El Presidio de Sonoma, or "Sonoma Barracks" (a collection of guardhouses, storerooms, living quarters, and an
During the Mission Period Alta California was divided into four military districts. Each was garrisoned (''comandancias'') by a presidio strategically placed along the California coast to protect the missions and other Spanish settlements in Upper California. Each of these functioned as a base of military operations for a specific region. They were independent of one another and were organized from south to north as follows:
* El Presidio Real de San Diego founded on July 16, 1769 – responsible for the defense of all installations located within the First Military District (the missions at San Diego, San Luis Rey, San Juan Capistrano, and San Gabriel);
* El Presidio Real de Santa Bárbara founded on April 12, 1782 – responsible for the defense of all installations located within the Second Military District (the missions at San Fernando, San Buenaventura, Santa Barbara, Santa Inés, and La Purísima, along with ''El Pueblo de Nuestra Señora la Reina de los Ángeles del Río de Porciúncula'' os Angeles;
* El Presidio Real de San Carlos de Monterey (''El Castillo'') founded on June 3, 1770 – responsible for the defense of all installations located within the Third Military District (the missions at San Luis Obispo, San Miguel, San Antonio, Soledad, San Carlos, and San Juan Bautista, along with ''Villa Branciforte'' anta Cruz; and
* El Presidio Real de San Francisco founded on December 17, 1776 – responsible for the defense of all installations located within the Fourth Military District (the missions at Santa Cruz, San José, Santa Clara, San Francisco, San Rafael, and Solano, along with ''El Pueblo de San José de Guadalupe'' an Jose.
* El Presidio de Sonoma, or "Sonoma Barracks" (a collection of guardhouses, storerooms, living quarters, and an observation tower
An observation tower is a structure used to view events from a long distance and to create a full 360 degree range of vision to conduct long distance observations. Observation towers are usually at least tall and are made from stone, iron, an ...
) was established in 1836 by Mariano Guadalupe Vallejo
Don Mariano Guadalupe Vallejo (4 July 1807 – 18 January 1890) was a Californio general, statesman, and public figure. He was born a subject of Spain, performed his military duties as an officer of the Republic of Mexico, and shaped the trans ...
(the "Commandante-General of the Northern Frontier of Alta California") as a part of Mexico's strategy to halt Russian incursions into the region. The Sonoma Presidio became the new headquarters of the Mexican Army in California, while the remaining ''presidios'' were essentially abandoned and, in time, fell into ruins.
An ongoing power struggle between church and state grew increasingly heated and lasted for decades. Originating as a feud between the Rev. Serra and Pedro Fages
Pedro Fages (1734–1794) was a Spanish soldier, explorer, first Lieutenant Governor of the Californias under Gaspar de Portolá. Fages claimed the governorship after Portolá's death, acting as governor in opposition to the official governor ...
(the military governor of Alta California from 1770 to 1774, who regarded the Spanish installations in California as military institutions first and religious outposts second), the uneasy relationship persisted for more than sixty years.[Bennett: "...Junípero had in California insisted that the military should be subservient to the priests, that the conquest was spiritual, not temporal..."] Dependent upon one another for their very survival, military leaders and mission ''padres'' nevertheless adopted conflicting stances regarding everything from land rights, the allocation of supplies, protection of the missions, the criminal propensities of the soldiers, and (in particular) the status of the native populations.[Engelhardt: "Recruited from the scum of society in Mexico, frequently convicts and jailbirds, it is not surprising that the mission guards, leather-jacket soldiers, as they were called, should be guilty of...crimes at nearly all the Missions...In truth, the guards counted among the worst obstacles to missionary progress. The wonder is, that the missionaries nevertheless succeeded so well in attracting converts."]
Present-day California missions

Building restoration
California is home to the greatest number of well-preserved missions found in any U.S. state.[Morrison: That the buildings in the California mission chain are in large part intact is due in no small measure to their relatively recent construction; Mission San Diego de Alcalá was founded more than two centuries after the establishment of the Mission of Nombre de Dios in ]St. Augustine, Florida
St. Augustine ( ; es, San Agustín ) is a city in the Southeastern United States and the county seat of St. Johns County on the Atlantic coast of northeastern Florida. Founded in 1565 by Spanish explorers, it is the oldest continuously inhabit ...
in 1565 and 170 years following the founding of Mission San Gabriel del Yunque in present-day Santa Fe, New Mexico
Santa Fe ( ; , Spanish for 'Holy Faith'; tew, Oghá P'o'oge, Tewa for 'white shell water place'; tiw, Hulp'ó'ona, label=Tiwa language, Northern Tiwa; nv, Yootó, Navajo for 'bead + water place') is the capital of the U.S. state of New Mexico. ...
in 1598. The missions are collectively the best-known historic
History (derived ) is the systematic study and the documentation of the human activity. The time period of event before the invention of writing systems is considered prehistory. "History" is an umbrella term comprising past events as well ...
element of the coastal regions of California:
* Most of the missions are still owned and operated by some entity within the Catholic Church.
* Three of the missions are still run under the auspices of the Franciscan
The Franciscans are a group of related Mendicant orders, mendicant Christianity, Christian Catholic religious order, religious orders within the Catholic Church. Founded in 1209 by Italian Catholic friar Francis of Assisi, these orders include t ...
Order (Santa Barbara, San Miguel Arcángel, and San Luis Rey de Francia)
* Four of the missions (San Diego de Alcalá, San Carlos Borromeo de Carmelo, San Francisco de Asís, and San Juan Capistrano) have been designated minor basilica
In the Catholic Church, a basilica is a designation given by the Pope to a church building. Basilicas are distinguished for ceremonial purposes from other churches. The building need not be a basilica in the architectural sense (a rectangular ...
s by the Holy See
The Holy See ( lat, Sancta Sedes, ; it, Santa Sede ), also called the See of Rome, Petrine See or Apostolic See, is the jurisdiction of the Pope in his role as the bishop of Rome. It includes the apostolic episcopal see of the Diocese of Rome ...
due to their cultural, historic, architectural, and religious importance.
* Mission La Purísima Concepción, Mission San Francisco Solano, and the one remaining mission-era structure of Mission Santa Cruz are owned and operated by the California Department of Parks and Recreation
The California Department of Parks and Recreation, more commonly known as California State Parks, manages the California state parks system. The system administers 279 separate park units on 1.4 million acres (570,000 hectares), with over 280 ...
as State Historic Parks;
* Seven mission sites are designated National Historic Landmark
A National Historic Landmark (NHL) is a building, district, object, site, or structure that is officially recognized by the United States government for its outstanding historical significance. Only some 2,500 (~3%) of over 90,000 places listed ...
s, fourteen are listed in the National Register of Historic Places
The National Register of Historic Places (NRHP) is the United States federal government's official list of districts, sites, buildings, structures and objects deemed worthy of preservation for their historical significance or "great artistic v ...
, and all are designated as California Historical Landmark
A California Historical Landmark (CHL) is a building, structure, site, or place in California that has been determined to have statewide historical landmark significance.
Criteria
Historical significance is determined by meeting at least one of ...
s for their historic, architectural, and archaeological significance.
 Because virtually all of the artwork at the missions served either a devotional or didactic purpose, there was no underlying reason for the mission residents to record their surroundings graphically; visitors, however, found them to be objects of curiosity. During the 1850s a number of artists found gainful employment as draftsmen attached to expeditions sent to map the Pacific coastline and the border between California and Mexico (as well as plot practical railroad routes); many of the drawings were reproduced as
Because virtually all of the artwork at the missions served either a devotional or didactic purpose, there was no underlying reason for the mission residents to record their surroundings graphically; visitors, however, found them to be objects of curiosity. During the 1850s a number of artists found gainful employment as draftsmen attached to expeditions sent to map the Pacific coastline and the border between California and Mexico (as well as plot practical railroad routes); many of the drawings were reproduced as lithograph
Lithography () is a planographic method of printing originally based on the immiscibility of oil and water. The printing is from a stone (lithographic limestone) or a metal plate with a smooth surface. It was invented in 1796 by the German a ...
s in the expedition reports.
In 1875 American illustrator
An illustrator is an artist who specializes in enhancing writing or elucidating concepts by providing a visual representation that corresponds to the content of the associated text or idea. The illustration may be intended to clarify complicat ...
Henry Chapman Ford began visiting each of the twenty-one mission sites, where he created a historically important portfolio of watercolors, oils, and etchings. His depictions of the missions were (in part) responsible for the revival of interest in the state's Spanish heritage, and indirectly for the restoration of the missions. The 1880s saw the appearance of a number of articles on the missions in national publications and the first books on the subject; as a result, a large number of artists did one or more mission paintings, though few attempted a series.
The popularity of the missions also stemmed largely from Helen Hunt Jackson
Helen Hunt Jackson (pen name, H.H.; born Helen Maria Fiske; October 15, 1830 – August 12, 1885) was an American poet and writer who became an activist on behalf of improved treatment of Indigenous peoples of the Americas, Native Americans by t ...
's 1884 novel ''Ramona
''Ramona'' is a 1884 American novel written by Helen Hunt Jackson. Set in Southern California after the Mexican–American War, it portrays the life of a mixed-race Scottish– Native American orphan girl, who suffers racial discrimination and ...
'' and the subsequent efforts of Charles Fletcher Lummis
Charles Fletcher Lummis (March 1, 1859, in Lynn, Massachusetts – November 25, 1928, in Los Angeles, California) was a United States journalist, and an activist for Indian rights and historic preservation. A traveler in the American Southwest, h ...
, William Randolph Hearst
William Randolph Hearst Sr. (; April 29, 1863 – August 14, 1951) was an American businessman, newspaper publisher, and politician known for developing the nation's largest newspaper chain and media company, Hearst Communications. His flamboya ...
, and other members of the "Landmarks Club of Southern California" to restore three of the southern missions in the early 20th century (San Juan Capistrano, San Diego de Alcalá, and San Fernando; the Pala ''Asistencia'' was also restored by this effort).[Thompson: In the words of Charles Lummis, the historic structures "...were falling to ruin with frightful rapidity, their roofs being breached or gone, the adobe walls melting under the winter rains."] Lummis wrote in 1895,
In acknowledgement of the magnitude of the restoration efforts required and the urgent need to have acted quickly to prevent further or even total degradation, Lummis went on to state, It is no exaggeration to say that human power could not have restored these four missions had there been a five-year delay in the attempt.
In 1911 author John Steven McGroarty
John Steven McGroarty (August 20, 1862 – August 7, 1944) was a poet, ''Los Angeles Times'' columnist, and author who also served two terms as a United States Democratic Party, Democratic Congressman from California from 1935 to 1939.
__TOC_ ...
penned ''The Mission Play'', a three-hour pageant describing the California missions from their founding in 1769 through secularization in 1834, and ending with their "final ruin" in 1847.
 Today, the missions exist in varying degrees of architectural integrity and structural soundness. The most common extant features at the mission grounds include the church building and an ancillary ''convento'' (
Today, the missions exist in varying degrees of architectural integrity and structural soundness. The most common extant features at the mission grounds include the church building and an ancillary ''convento'' (convent
A convent is a community of monks, nuns, religious brothers or, sisters or priests. Alternatively, ''convent'' means the building used by the community. The word is particularly used in the Catholic Church, Lutheran churches, and the Anglican ...
) wing. In some cases (in San Rafael, Santa Cruz, and Soledad, for example), the current buildings are replicas constructed on or near the original site. Other mission compounds remain relatively intact and true to their original, Mission Era construction.
A notable example of an intact complex is the now-threatened Mission San Miguel Arcángel: its chapel retains the original interior mural
A mural is any piece of graphic artwork that is painted or applied directly to a wall, ceiling or other permanent substrate. Mural techniques include fresco, mosaic, graffiti and marouflage.
Word mural in art
The word ''mural'' is a Spani ...
s created by Salinan
The Salinan are a Native American tribe whose ancestral territory is in the southern Salinas Valley and the Santa Lucia Range in the Central Coast of California. Today, the Salinan governments are now working toward federal tribal recognition f ...
Indians under the direction of Esteban Munras Esteban () is a Spanish male given name, derived from Greek Στέφανος (Stéphanos) and related to the English names Steven and Stephen. Although in its original pronunciation the accent is on the penultimate syllable, English-speakers tend t ...
, a Spanish artist and last Spanish diplomat to California. This structure was closed to the public from 2003 to 2009 due to severe damage from the San Simeon earthquake. Many missions have preserved (or in some cases reconstructed) historic features in addition to chapel buildings.
The missions have earned a prominent place in California's historic consciousness, and a steady stream of tourists from all over the world visit them. In recognition of that fact, on November 30, 2004 President George W. Bush
George Walker Bush (born July 6, 1946) is an American politician who served as the 43rd president of the United States from 2001 to 2009. A member of the Republican Party, Bush family, and son of the 41st president George H. W. Bush, he ...
signed HR 1446, the ''California Mission Preservation Act'', into law. The measure provided $10 million over a five-year period to the California Missions Foundation for projects related to the physical preservation of the missions, including structural rehabilitation, stabilization, and conservation of mission art and artifacts. The California Missions Foundation, a volunteer, tax-exempt organization, was founded in 1998 by Richard Ameil, an eighth generation Californian. A change to the California Constitution
The Constitution of California ( es, Constitución de California) is the primary organizing law for the U.S. state of California, describing the duties, powers, structures and functions of the government of California. California's original co ...
has also been proposed that would allow the use of State funds in restoration efforts.[Coronado and Ignatin]
Structures gallery
File:La Purisima Mission 156.jpg, Mission La Purísima Concepción
Mission (from Latin ''missio'' "the act of sending out") may refer to:
Organised activities Religion
*Christian mission, an organized effort to spread Christianity
*Mission (LDS Church), an administrative area of The Church of Jesus Christ of ...
, located northeast of Lompoc
Lompoc ( ; Chumash: ''Lum Poc'') is a city in Santa Barbara County, California. Located on the Central Coast, Lompoc has a population of 43,834 as of July 2021.
Lompoc has been inhabited for thousands of years by the Chumash people, who called ...
.
File:Nuestra Senora del la Soledad chapel.JPG, Mission Nuestra Señora de la Soledad
Mission Nuestra Señora de la Soledad ( es, Misión Nuestra Señora de la Soledad), commonly known as Mission Soledad, is a Spanish mission located in Soledad, California. The mission was founded by the Franciscan order on October 9, 1791 to con ...
, located south of Soledad.
File:Mission San Antonio de Padua modern.jpg, Mission San Antonio de Padua
Mission San Antonio de Padua is a Spanish mission established by the Franciscan order in present-day Monterey County, California, near the present-day town of Jolon. Founded on July 14, 1771, it was the third mission founded in Alta California ...
, located northwest of Jolon
Jolon (; Spanish: ''Jolón''; Salinan: ''Xolon'') is small unincorporated village in southern Monterey County, California. Jolon is located in the San Antonio River Valley, west of Salinas Valley.
The origins of Jolon date to 1771, when the Spa ...
.
File:Mission Santa Barbara01.jpg, Mission Santa Barbara
Mission Santa Barbara ( es, link=no, Misión de Santa Bárbara) is a Spanish mission in Santa Barbara, California. Often referred to as the ‘Queen of the Missions,’ it was founded by Padre Fermín Lasuén for the Franciscan order on December ...
, located in Santa Barbara.
File:Mission San Buenaventura.jpg, Mission San Buenaventura
Mission San Buenaventura ( es, Misión San Buenaventura), formally known as the Mission Basilica of San Buenaventura, is a Catholic parish and basilica in the Archdiocese of Los Angeles. The parish church in the city of Ventura, California, Unite ...
, located in Ventura.
File:MissionCarmelSEGL2.jpg, Mission San Carlos Borromeo de Carmelo
Mission San Carlos Borromeo del Río Carmelo, or Misión de San Carlos Borromeo de Carmelo, first built in 1797, is one of the most authentically restored Catholic mission churches in California. Located at the mouth of Carmel Valley, Californi ...
, located south of Carmel
Carmel may refer to:
* Carmel (biblical settlement), an ancient Israelite town in Judea
* Mount Carmel, a coastal mountain range in Israel overlooking the Mediterranean Sea
* Carmelites, a Roman Catholic mendicant religious order
Carmel may also ...
.
File:Mission Santa Clara.jpg, Mission Santa Clara de Asís
Mission Santa Clara de Asís ( es, Misión Santa Clara de Asís) is a Spanish mission in the city of Santa Clara, California. The mission, which was the eighth in California, was founded on January 12, 1777, by the Franciscan order. Named for ...
, located in Santa Clara.
File:MissionSantaCruzCalifornia.jpg, Scale replica of Mission Santa Cruz
Mission Santa Cruz (''La Misión de la Exaltación de la Santa Cruz'', which translates as the Mission of the Exaltation of the Holy Cross), was the twelfth of twenty-one Spanish missions in California (today's U.S. state), established by the Fr ...
chapel, located in Santa Cruz.
File:Mission San Diego de Alcalá - church.jpg, Mission San Diego de Alcalá
Mission Basilica San Diego de Alcalá ( es, Misión San Diego de Alcalá) was the second Franciscan founded mission in The Californias (after San Fernando de Velicata), a province of New Spain. Located in present-day San Diego, California, it w ...
, located in San Diego
San Diego ( , ; ) is a city on the Pacific Ocean coast of Southern California located immediately adjacent to the Mexico–United States border. With a 2020 population of 1,386,932, it is the List of United States cities by population, eigh ...
.
File:2007 Mission San Fernando.jpg, Mission San Fernando Rey de España
Mission San Fernando Rey de España is a Spanish mission in the Mission Hills community of Los Angeles, California. The mission was founded on 8 September 1797 at the site of Achooykomenga, and was the seventeenth of the twenty-one Spanish mis ...
, located in Mission Hills (Los Angeles).
File:San Francisco de Asis--Mission Dolores.JPG, Mission San Francisco de Asís
Mission San Francisco de Asís ( es, Misión San Francisco de Asís), commonly known as Mission Dolores (as it was founded near the Dolores creek), is a Spanish Californian mission and the oldest surviving structure in San Francisco. Located i ...
, located in San Francisco
San Francisco (; Spanish language, Spanish for "Francis of Assisi, Saint Francis"), officially the City and County of San Francisco, is the commercial, financial, and cultural center of Northern California. The city proper is the List of Ca ...
.
File:Mission San Francisco Solano.jpg, Mission San Francisco Solano
Mission San Francisco Solano was the 21st, last, and northernmost mission in Alta California. It was named for Saint Francis Solanus. It was the only mission built in Alta California after Mexico gained independence from Spain. The difficulty of ...
, located in Sonoma.
File:Mission San Gabriel 4-15-05 6611.JPG, Mission San Gabriel Arcángel
Mission San Gabriel Arcángel ( es, Misión de San Gabriel Arcángel) is a Californian mission and historic landmark in San Gabriel, California. It was founded by Spaniards of the Franciscan order on "The Feast of the Birth of Mary," September ...
, located in San Gabriel.
File:Mission StInes.jpg, Mission Santa Inés
Mission Santa Inés (sometimes spelled Santa Ynez) was a Spanish mission in the present-day city of Solvang, California, and named after St. Agnes of Rome. Founded on September 17, 1804, by Father Estévan Tapís of the Franciscan order, the m ...
, located in Solvang.
File:Mission San Jose April 2011 001.jpg, Mission San José Mission San José may refer to:
*Mission San José (California), a Spanish mission in Fremont, California
* Mission San Jose, Fremont, California, a neighborhood
*Mission San Jose High School, a high school in Fremont, California
*Mission San José ...
, located in Fremont.
File:Mission San Juan Bautista.jpg, Mission San Juan Bautista
Mission San Juan Bautista is a Spanish mission in San Juan Bautista, San Benito County, California. Founded on June 24, 1797 by Fermín Lasuén of the Franciscan order, the mission was the fifteenth of the Spanish missions established in presen ...
, located in San Juan Bautista.
File:Mission San Juan Capistrano.jpg, Mission San Juan Capistrano
Mission San Juan Capistrano ( es, Misión San Juan Capistrano) is a Spanish mission in San Juan Capistrano, Orange County, California. Founded November 1, 1776 in colonial ''Las Californias'' by Spanish Catholic missionaries of the Franciscan O ...
, located in San Juan Capistrano
San Juan Capistrano (Spanish for "St. John of Capistrano") is a city in Orange County, California, located along the Orange Coast. The population was 34,593 at the 2010 census.
San Juan Capistrano was founded by the Spanish in 1776, when St. ...
.
File:MissionSanLuisEntrance.jpg, Mission San Luis Obispo de Tolosa
Mission San Luis Obispo de Tolosa ( es, Misión San Luis Obispo de Tolosa) is a Spanish mission founded September 1, 1772 by Father Junípero Serra in San Luis Obispo, California. Named after Saint Louis of Anjou, the bishop of Toulouse, the m ...
, located in San Luis Obispo
San Luis Obispo (; Spanish for " St. Louis the Bishop", ; Chumash: ''tiłhini'') is a city and county seat of San Luis Obispo County, in the U.S. state of California. Located on the Central Coast of California, San Luis Obispo is roughly halfwa ...
.
File:Mission San Luis Rey de Francia current.jpg, Mission San Luis Rey de Francia
Mission San Luis Rey de Francia ( es, Misión San Luis Rey de Francia) is a former Spanish mission in San Luis Rey, a neighborhood of Oceanside, California. This Mission lent its name to the Luiseño tribe of Mission Indians.
At its prime, M ...
, located in Oceanside.
File:MissionSanMiguelPlaza2008.JPG, Mission San Miguel Arcángel
Mission San Miguel Arcángel is a Spanish mission in San Miguel, California. It was established on July 25, 1797 by the Franciscan order, on a site chosen specifically due to the large number of Salinan Indians that inhabited the area, whom the ...
, located in San Miguel.
File:Saint Raphael Church San Rafael CA.jpg, Mission San Rafael Arcángel
Mission San Rafael Arcángel is a Spanish mission in San Rafael, California. It was founded in 1817 as a medical '' asistencia'' ("sub-mission") of Mission San Francisco de Asís. It was a hospital to treat sick Native Americans, making it Alta ...
, located in San Rafael.
See also
On California Missions:
* List of Spanish missions in California
Franciscan priests established 21 missions between 1769 and 1833 in Alta California, accompanied by military outposts. Their goal was to spread Christianity among the local Native Americans, as well as to affirm Spanish, and later Mexican, cl ...
* San Antonio de Pala Asistencia
The San Antonio de Pala Asistencia, or the "Pala Mission", was founded on June 13, 1816 as an asistencia or "sub-mission" to Mission San Luis Rey de Francia, some twenty miles inland upstream from the latter mission on the San Luis Rey River. Pa ...
, not a full mission, but still serving the Pala reservation
On California history:
* Juan Bautista de Anza National Historic Trail
The Juan Bautista de Anza National Historic Trail is a trail extending from Nogales on the U.S.-Mexico border in Arizona, through the California desert and coastal areas in Southern California and the Central Coast region to San Francisco.htt ...
* History of California through 1899
Human history in California began when indigenous Americans first arrived some 13,000 years ago. Coastal exploration by the Spanish began in the 16th century, with further European settlement along the coast and in the inland valleys following ...
* History of the west coast of North America
The human history of the west coast of North America is believed to stretch back to the arrival of the earliest people over the Bering Strait, or alternately along a now-submerged coastal plain, through the development of significant List of pre- ...
* Mission Vieja
The Mission Vieja or Misión Vieja or the Old Mission was the first Spanish mission in the San Gabriel Valley. Mission Vieja was built in 1771 by what would become the fathers of the Mission San Gabriel Arcángel. The Mission Vieja site was d ...
On general missionary history:
* Catholic Church and the Age of Discovery
The Catholic Church during the Age of Discovery inaugurated a major effort to spread Christianity in the New World and to convert the indigenous peoples of the Americas and other indigenous peoples. The evangelical effort was a major part of, and ...
* History of Christian Missions
This timeline of Christian missions chronicles the global expansion of Christianity through a listing of the most significant missionary outreach events.
Apostolic Age
Earliest dates must all be considered approximate
* 33 – Great Commissi ...
* List of the oldest churches in Mexico
The following is a list of the oldest extant church in each of the administrative divisions of Mexico. The first place of Christian worship in what would become Mexico was in what is now known as La Antigua, Veracruz, founded by the Spanish in 1519 ...
* Missionary
A missionary is a member of a Religious denomination, religious group which is sent into an area in order to promote its faith or provide services to people, such as education, literacy, social justice, health care, and economic development.Tho ...
On colonial Spanish American history:
* Spanish colonization of the Americas
Spain began colonizing the Americas under the Crown of Castile and was spearheaded by the Spanish . The Americas were invaded and incorporated into the Spanish Empire, with the exception of Brazil, British America, and some small regions ...
* California mission clash of cultures
The California mission clash of cultures occurred at the Spanish Missions in California during the Spanish Las Californias- New Spain and Mexican Alta California eras of control, with lasting consequences after American statehood. The Missions w ...
* Indian Reductions
Reductions ( es, reducciones, also called ; , pl. ) were settlements created by Spanish rulers and Roman Catholic missionaries in Spanish America and the Spanish East Indies (the Philippines). In Portuguese-speaking Latin America, such red ...
* California Genocide
The California genocide was the killing of thousands of indigenous peoples of California by United States government agents and private citizens in the 19th century. It began following the American Conquest of California from Mexico, and the ...
* Native Americans in the United States
Native Americans, also known as American Indians, First Americans, Indigenous Americans, and other terms, are the Indigenous peoples of the mainland United States ( Indigenous peoples of Hawaii, Alaska and territories of the United State ...
Notes
References
Sources
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
Further reading
Books
*
*
*
*
*
* Crespí, Juan: ''A Description of Distant Roads: Original Journals of the First Expedition into California, 1796–1770'', edited and translated by Alan K. Brown, San Diego State University Press, 2001,
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
Articles and archives
Early California Population Project (ECPP)
The Huntington Library
The Huntington Library, Art Museum and Botanical Gardens, known as The Huntington, is a collections-based educational and research institution established by Henry E. Huntington (1850–1927) and Arabella Huntington (c.1851–1924) in San Mar ...
, 2006. Provides public access to all the information contained in California's historic mission registers.
California Missions
article at the ''Catholic Encyclopedia
The ''Catholic Encyclopedia: An International Work of Reference on the Constitution, Doctrine, Discipline, and History of the Catholic Church'' (also referred to as the ''Old Catholic Encyclopedia'' and the ''Original Catholic Encyclopedia'') i ...
''
The California Missions
2001.
Matrimonial Investigation records of the San Gabriel Mission
Claremont Colleges
The Claremont Colleges (known colloquially as the 7Cs) are a consortium of seven private institutions of higher education located in Claremont, California, United States. They comprise five undergraduate colleges (the 5Cs)—Pomona College, Scr ...
Digital Library, 2008, 169 records digitized and searchable by priest name or by the names of the couple requesting marriage.
''Junipero Serra, the Vatican, & Enslavement Theology''
Preview of Fogel, Daniel. ISM Press Books. Offers a critical perspective on the missions' impact on California's Indians.
MissionTour
Tom Simondi, 2001–2005.
James, George Wharton, 1913. eText at Project Gutenberg
Project Gutenberg (PG) is a Virtual volunteering, volunteer effort to digitize and archive cultural works, as well as to "encourage the creation and distribution of eBooks."
It was founded in 1971 by American writer Michael S. Hart and is the ...
.
The San Diego Founders Trail
2001–2008 website.
Faigin, Daniel P. California Highways, 1996–2004
Almanac: California Missions
GAzis-SAx, Joel, 1999.
External links
The California Frontier Project: Dedicated the early California, including the Spanish missionsCalifornia Mission Studies Association
California's Spanish Missions
The California Missions Trail
California Department of Parks and Recreation
* ttp://www.californias-missions.org/ Tricia Anne Weber: The Spanish Missions of California
''Album of Views of the Missions of California''
Souvenir Publishing Company, San Francisco, Los Angeles, 1890s.
''The Missions of California''
by Eugene Leslie Smyth, Chicago: Alexander Belford & Co., 1899.
California Historical Society
California Mission Visitors GuideCalifornia Missions: A Journey Along the El Camino Real
(exhibit at The California Museum
The California Museum is the state history museum of California, located in its capital city of Sacramento. It is dedicated to Californian history and the stories of California. The museum is home to the California Hall of Fame and has more t ...
)
National Register of Historic Places: Early History of the California Coast: List of Sites
California Mission Sketches by Henry Miller, 1856
an
Finding Aid to the Documents relating to Missions of the Californias : typescript, 1768–1802
at The Bancroft Library
The Bancroft Library in the center of the campus of the University of California, Berkeley, is the university's primary special-collections library. It was acquired from its founder, Hubert Howe Bancroft, in 1905, with the proviso that it retai ...
*
{{DEFAULTSORT:Spanish Missions In California
The Californias
California Mission Indians
Archaeological sites in California
History of Catholicism in the United States
Native American history of California
California genocide
Junípero Serra
 The Spanish missions in California ( es, Misiones españolas en California) comprise a
series of 21 religious outposts or missions established between 1769 and 1833 in what is now the U.S. state of
The Spanish missions in California ( es, Misiones españolas en California) comprise a
series of 21 religious outposts or missions established between 1769 and 1833 in what is now the U.S. state of  In addition to the ''presidio'' (royal fort) and ''pueblo'' (town), the ''misión'' was one of the three major agencies employed by the Spanish sovereign to extend its borders and consolidate its
In addition to the ''presidio'' (royal fort) and ''pueblo'' (town), the ''misión'' was one of the three major agencies employed by the Spanish sovereign to extend its borders and consolidate its  Although the missions were considered temporary ventures by the Spanish
Although the missions were considered temporary ventures by the Spanish  The Alta California missions, known as
The Alta California missions, known as  To the ''padres'', a baptized Indian person was no longer free to move about the country, but had to labor and worship at the mission under the strict observance of the priests and overseers, who herded them to daily masses and labors. If an Indian did not report for their duties for a period of a few days, they were searched for, and if it was discovered that they had left without permission, they were considered runaways. Large-scale military expeditions were organized to round up the escaped neophytes. Sometimes, the Franciscans allowed neophytes to escape the missions, or they would allow them to visit their home village. However, the Franciscans would only allow this so that they could secretly follow the neophytes. Upon arriving to the village and capturing the runaways, they would take back Indians to the missions, sometimes as many as 200 to 300 Indians.
A total of 20,355 natives were "attached" to the California missions in 1806 (the highest figure recorded during the Mission Period); under Mexican rule the number rose to 21,066 (in 1824, the record year during the entire era of the Franciscan missions).Chapman: "Over the hills of the Coast Range, in the valleys of the Sacramento and San Joaquin, north of San Francisco Bay, and in the Sierra Nevadas of the south there were untold thousands whom the mission system never reached...they were as if in a world apart from the narrow strip of coast which was all there was of the Spanish California." During the entire period of Mission rule, from 1769 to 1834, the Franciscans baptized 53,600 adult Indians and buried 37,000. Dr. Cook estimates that 15,250 or 45% of the population decrease was caused by disease. Two epidemics of
To the ''padres'', a baptized Indian person was no longer free to move about the country, but had to labor and worship at the mission under the strict observance of the priests and overseers, who herded them to daily masses and labors. If an Indian did not report for their duties for a period of a few days, they were searched for, and if it was discovered that they had left without permission, they were considered runaways. Large-scale military expeditions were organized to round up the escaped neophytes. Sometimes, the Franciscans allowed neophytes to escape the missions, or they would allow them to visit their home village. However, the Franciscans would only allow this so that they could secretly follow the neophytes. Upon arriving to the village and capturing the runaways, they would take back Indians to the missions, sometimes as many as 200 to 300 Indians.
A total of 20,355 natives were "attached" to the California missions in 1806 (the highest figure recorded during the Mission Period); under Mexican rule the number rose to 21,066 (in 1824, the record year during the entire era of the Franciscan missions).Chapman: "Over the hills of the Coast Range, in the valleys of the Sacramento and San Joaquin, north of San Francisco Bay, and in the Sierra Nevadas of the south there were untold thousands whom the mission system never reached...they were as if in a world apart from the narrow strip of coast which was all there was of the Spanish California." During the entire period of Mission rule, from 1769 to 1834, the Franciscans baptized 53,600 adult Indians and buried 37,000. Dr. Cook estimates that 15,250 or 45% of the population decrease was caused by disease. Two epidemics of  The work day was six hours, interrupted by dinner (lunch) around 11:00 a.m. and a two-hour ''siesta'', and ended with evening prayers and the
The work day was six hours, interrupted by dinner (lunch) around 11:00 a.m. and a two-hour ''siesta'', and ended with evening prayers and the  Livestock was raised, not only for the purpose of obtaining meat, but also for wool, leather, and tallow, and for cultivating the land. In 1832, at the height of their prosperity, the missions collectively owned:
* 151,180 head of
Livestock was raised, not only for the purpose of obtaining meat, but also for wool, leather, and tallow, and for cultivating the land. In 1832, at the height of their prosperity, the missions collectively owned:
* 151,180 head of  Each mission had to fabricate virtually all of its construction materials from local materials. Workers in the ''carpintería'' (
Each mission had to fabricate virtually all of its construction materials from local materials. Workers in the ''carpintería'' ( On July 14, 1769 Gálvez sent the
On July 14, 1769 Gálvez sent the 

 Pío de Jesús Pico, the last Mexican Governor of Alta California, found upon taking office that there were few funds available to carry on the affairs of the province. He prevailed upon the assembly to pass a decree authorizing the renting or the sale of all mission property, reserving only the church, a curate's house, and a building for a courthouse. The expenses of conducting the services of the church were to be provided from the proceeds, but there was no disposition made as to what should be done to secure the funds for that purpose. After secularization, Father-Presidente Narciso Durán transferred the missions' headquarters to Santa Bárbara, thereby making Mission Santa Bárbara the repository of some 3,000 original documents that had been scattered through the California missions. The Mission archive is the oldest library in the State of California that still remains in the hands of its founders, the Franciscans (it is the only mission where they have maintained an uninterrupted presence). Beginning with the writings of
Pío de Jesús Pico, the last Mexican Governor of Alta California, found upon taking office that there were few funds available to carry on the affairs of the province. He prevailed upon the assembly to pass a decree authorizing the renting or the sale of all mission property, reserving only the church, a curate's house, and a building for a courthouse. The expenses of conducting the services of the church were to be provided from the proceeds, but there was no disposition made as to what should be done to secure the funds for that purpose. After secularization, Father-Presidente Narciso Durán transferred the missions' headquarters to Santa Bárbara, thereby making Mission Santa Bárbara the repository of some 3,000 original documents that had been scattered through the California missions. The Mission archive is the oldest library in the State of California that still remains in the hands of its founders, the Franciscans (it is the only mission where they have maintained an uninterrupted presence). Beginning with the writings of  Precise figures relating to the population decline of California indigenes are not available. One writer,
Precise figures relating to the population decline of California indigenes are not available. One writer,  *
*  There were 21 missions accompanied by military outposts in
There were 21 missions accompanied by military outposts in  During the Mission Period Alta California was divided into four military districts. Each was garrisoned (''comandancias'') by a presidio strategically placed along the California coast to protect the missions and other Spanish settlements in Upper California. Each of these functioned as a base of military operations for a specific region. They were independent of one another and were organized from south to north as follows:
* El Presidio Real de San Diego founded on July 16, 1769 – responsible for the defense of all installations located within the First Military District (the missions at San Diego, San Luis Rey, San Juan Capistrano, and San Gabriel);
* El Presidio Real de Santa Bárbara founded on April 12, 1782 – responsible for the defense of all installations located within the Second Military District (the missions at San Fernando, San Buenaventura, Santa Barbara, Santa Inés, and La Purísima, along with ''El Pueblo de Nuestra Señora la Reina de los Ángeles del Río de Porciúncula'' os Angeles;
* El Presidio Real de San Carlos de Monterey (''El Castillo'') founded on June 3, 1770 – responsible for the defense of all installations located within the Third Military District (the missions at San Luis Obispo, San Miguel, San Antonio, Soledad, San Carlos, and San Juan Bautista, along with ''Villa Branciforte'' anta Cruz; and
* El Presidio Real de San Francisco founded on December 17, 1776 – responsible for the defense of all installations located within the Fourth Military District (the missions at Santa Cruz, San José, Santa Clara, San Francisco, San Rafael, and Solano, along with ''El Pueblo de San José de Guadalupe'' an Jose.
* El Presidio de Sonoma, or "Sonoma Barracks" (a collection of guardhouses, storerooms, living quarters, and an
During the Mission Period Alta California was divided into four military districts. Each was garrisoned (''comandancias'') by a presidio strategically placed along the California coast to protect the missions and other Spanish settlements in Upper California. Each of these functioned as a base of military operations for a specific region. They were independent of one another and were organized from south to north as follows:
* El Presidio Real de San Diego founded on July 16, 1769 – responsible for the defense of all installations located within the First Military District (the missions at San Diego, San Luis Rey, San Juan Capistrano, and San Gabriel);
* El Presidio Real de Santa Bárbara founded on April 12, 1782 – responsible for the defense of all installations located within the Second Military District (the missions at San Fernando, San Buenaventura, Santa Barbara, Santa Inés, and La Purísima, along with ''El Pueblo de Nuestra Señora la Reina de los Ángeles del Río de Porciúncula'' os Angeles;
* El Presidio Real de San Carlos de Monterey (''El Castillo'') founded on June 3, 1770 – responsible for the defense of all installations located within the Third Military District (the missions at San Luis Obispo, San Miguel, San Antonio, Soledad, San Carlos, and San Juan Bautista, along with ''Villa Branciforte'' anta Cruz; and
* El Presidio Real de San Francisco founded on December 17, 1776 – responsible for the defense of all installations located within the Fourth Military District (the missions at Santa Cruz, San José, Santa Clara, San Francisco, San Rafael, and Solano, along with ''El Pueblo de San José de Guadalupe'' an Jose.
* El Presidio de Sonoma, or "Sonoma Barracks" (a collection of guardhouses, storerooms, living quarters, and an 
 Because virtually all of the artwork at the missions served either a devotional or didactic purpose, there was no underlying reason for the mission residents to record their surroundings graphically; visitors, however, found them to be objects of curiosity. During the 1850s a number of artists found gainful employment as draftsmen attached to expeditions sent to map the Pacific coastline and the border between California and Mexico (as well as plot practical railroad routes); many of the drawings were reproduced as
Because virtually all of the artwork at the missions served either a devotional or didactic purpose, there was no underlying reason for the mission residents to record their surroundings graphically; visitors, however, found them to be objects of curiosity. During the 1850s a number of artists found gainful employment as draftsmen attached to expeditions sent to map the Pacific coastline and the border between California and Mexico (as well as plot practical railroad routes); many of the drawings were reproduced as  Today, the missions exist in varying degrees of architectural integrity and structural soundness. The most common extant features at the mission grounds include the church building and an ancillary ''convento'' (
Today, the missions exist in varying degrees of architectural integrity and structural soundness. The most common extant features at the mission grounds include the church building and an ancillary ''convento'' (