Foothills (North Carolina) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
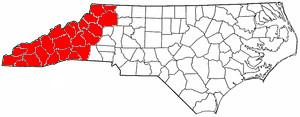 Western North Carolina (often abbreviated as WNC) is the
Western North Carolina (often abbreviated as WNC) is the
 The southwestern and far west part of Western North Carolina all lie within the
The southwestern and far west part of Western North Carolina all lie within the
 The Foothills is a
The Foothills is a
 The region has three major public universities:
The region has three major public universities:
 Western North Carolina (often abbreviated as WNC) is the
Western North Carolina (often abbreviated as WNC) is the region
In geography, regions, otherwise referred to as zones, lands or territories, are areas that are broadly divided by physical characteristics (physical geography), human impact characteristics (human geography), and the interaction of humanity and t ...
of North Carolina
North Carolina () is a state in the Southeastern region of the United States. The state is the 28th largest and 9th-most populous of the United States. It is bordered by Virginia to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the east, Georgia and So ...
which includes the Appalachian Mountains
The Appalachian Mountains, often called the Appalachians, (french: Appalaches), are a system of mountains in eastern to northeastern North America. The Appalachians first formed roughly 480 million years ago during the Ordovician Period. They ...
; it is often known geographically as the state's Mountain Region. It contains the highest mountains in the Eastern United States
The Eastern United States, commonly referred to as the American East, Eastern America, or simply the East, is the region of the United States to the east of the Mississippi River. In some cases the term may refer to a smaller area or the East C ...
, with 125 peaks rising to over 5,000 feet (1,500 meters) in elevation. Mount Mitchell
Mount Mitchell, known in Cherokee as Attakulla, is the highest peak of the Appalachian Mountains and the highest peak in mainland eastern North America. It is located near Burnsville in Yancey County, North Carolina in the Black Mountain subra ...
at 6,684 feet (2,037 meters), is the highest peak of the Appalachian Mountains
The Appalachian Mountains, often called the Appalachians, (french: Appalaches), are a system of mountains in eastern to northeastern North America. The Appalachians first formed roughly 480 million years ago during the Ordovician Period. They ...
and mainland eastern North America
North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere and almost entirely within the Western Hemisphere. It is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South America and the Car ...
. The population of the region, as measured by the 2010 U.S. Census
The United States census of 2010 was the twenty-third United States national census. National Census Day, the reference day used for the census, was April 1, 2010. The census was taken via mail-in citizen self-reporting, with enumerators servin ...
, is 1,473,241, which is approximately 15% of North Carolina's total population.
Located east of the Tennessee
Tennessee ( , ), officially the State of Tennessee, is a landlocked state in the Southeastern region of the United States. Tennessee is the 36th-largest by area and the 15th-most populous of the 50 states. It is bordered by Kentucky to th ...
state line and west of the Piedmont
it, Piemontese
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 =
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographics1_title1 =
, demographics1_info1 =
, demographics1_title2 ...
, Western North Carolina contains few major urban centers. Asheville
Asheville ( ) is a city in, and the county seat of, Buncombe County, North Carolina. Located at the confluence of the French Broad and Swannanoa rivers, it is the largest city in Western North Carolina, and the state's 11th-most populous cit ...
, located in the region's center, is the area's largest city and most prominent commercial hub. The Foothills
Foothills or piedmont are geographically defined as gradual increases in elevation at the base of a mountain range, higher hill range or an upland area. They are a transition zone between plains and low relief hills and the adjacent topograp ...
region of the state is loosely defined as the area along Western North Carolina's eastern boundary; this region consists of a transitional terrain of hills between the Appalachians and Piedmont Plateau
The Piedmont is a plateau region located in the Eastern United States. It is situated between the Atlantic coastal plain and the main Appalachian Mountains, stretching from New York in the north to central Alabama in the south. The Piedmont ...
of central North Carolina.
Areas in the northwest portion of the Western North Carolina region, including Boone and Blowing Rock Blowing Rock may refer to:
* The town of Blowing Rock, North Carolina
** The rocky outcropping Blowing Rock (land feature), near the town of the same name
* Blowing Rock, Virginia, an unincorporated community
* Caribbean island belonging to Anguil ...
, commonly use the nickname "The High Country". The term Land of the Sky (or Land-of-Sky) is a common nickname for the Asheville
Asheville ( ) is a city in, and the county seat of, Buncombe County, North Carolina. Located at the confluence of the French Broad and Swannanoa rivers, it is the largest city in Western North Carolina, and the state's 11th-most populous cit ...
area. The term is derived from the title of the novel, ''Land of the Sky
''The Land of the Sky, or, adventures in mountain by-ways'' (1876) is a novel by American author Frances Christine Fisher Tiernan, who published under the pseudonym Christian Reid. She published more than 50 novels, most notably this one.
The na ...
'' (1876), written by Mrs. Frances Tiernan, under the pseudonym Christian Reid
Frances Tiernan (, Fisher; pen name, Christian Reid; July 5, 1846 – March 24, 1920) was an American author who wrote more than 50 novels, most notably '' The Land of the Sky''. Reared as a Roman Catholic, she grew up in the Southern United Stat ...
. She often refers in this book to the Great Smoky Mountains
The Great Smoky Mountains (, ''Equa Dutsusdu Dodalv'') are a mountain range rising along the Tennessee–North Carolina border in the southeastern United States. They are a subrange of the Appalachian Mountains, and form part of the Blue Ridge ...
and Blue Ridge Mountains
The Blue Ridge Mountains are a physiographic province of the larger Appalachian Mountains range. The mountain range is located in the Eastern United States, and extends 550 miles southwest from southern Pennsylvania through Maryland, West Virgin ...
, the two main ranges
In the Hebrew Bible and in the Old Testament, the word ranges has two very different meanings.
Leviticus
In Leviticus 11:35, ranges probably means a cooking furnace for two or more pots, as the Hebrew word here is in the dual number; or perhaps ...
in Western North Carolina. The Asheville area regional government body, the Land-of-Sky Regional Council, uses this nickname.
The federally recognized Eastern Band of Cherokee Indians
The Eastern Band of Cherokee Indians (EBCI), (Cherokee language, Cherokee: ᏣᎳᎩᏱ ᏕᏣᏓᏂᎸᎩ, ''Tsalagiyi Detsadanilvgi'') is a Federally recognized tribe, federally recognized Indian Tribe based in Western North Carolina in the U ...
(EBCI) have a reservation in this region known as Qualla Boundary
The Qualla Boundary or The Qualla is territory held as a land trust by the United States government for the federally recognized Eastern Band of Cherokee Indians, who reside in western North Carolina. The area is part of the large historic Chero ...
; it is situated adjacent to the Great Smoky Mountains National Park
Great Smoky Mountains National Park is an American national park in the southeastern United States, with parts in North Carolina and Tennessee. The park straddles the ridgeline of the Great Smoky Mountains, part of the Blue Ridge Mountains, whi ...
. Their capital is at Cherokee, North Carolina
Cherokee ( chr, ᏣᎳᎩ, translit=Tsalagi) is a census-designated place (CDP) in Swain County, North Carolina, Swain and Jackson County, North Carolina, Jackson counties in Western North Carolina, United States, within the Qualla Boundar ...
. This region, taking in today's southeastern Tennessee, western North and South Carolina, and northeastern Georgia, is considered the homeland of the historic Cherokee. Many of the people were forcibly removed in the late 1830s in the Trail of Tears
The Trail of Tears was an ethnic cleansing and forced displacement of approximately 60,000 people of the "Five Civilized Tribes" between 1830 and 1850 by the United States government. As part of the Indian removal, members of the Cherokee, ...
to Indian Territory
The Indian Territory and the Indian Territories are terms that generally described an evolving land area set aside by the Federal government of the United States, United States Government for the relocation of Native Americans in the United St ...
, but others remained; their descendants make up the EBCI, among the largest of recognized tribes. Sixteen earthwork mounds or their sites, built by indigenous peoples, have been listed in state archeological records in the eleven westernmost counties. Archeological and related research in the early 21st century has revealed that there may be as many as 50 such prehistoric mounds in this area, which were long central to Cherokee towns and culture.
Subregions
Far West
 The southwestern and far west part of Western North Carolina all lie within the
The southwestern and far west part of Western North Carolina all lie within the Appalachian Mountain
The Appalachian Mountains, often called the Appalachians, (french: Appalaches), are a system of mountains in eastern to northeastern North America. The Appalachians first formed roughly 480 million years ago during the Ordovician Period. They ...
chain. Mt. Mitchell, the highest peak in the state, as well as eastern North America
North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere and almost entirely within the Western Hemisphere. It is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South America and the Car ...
, is located here. Asheville
Asheville ( ) is a city in, and the county seat of, Buncombe County, North Carolina. Located at the confluence of the French Broad and Swannanoa rivers, it is the largest city in Western North Carolina, and the state's 11th-most populous cit ...
is the major urban hub of far western North Carolina. This area also includes a few hydroelectric projects managed by the Tennessee Valley Authority
The Tennessee Valley Authority (TVA) is a federally owned electric utility corporation in the United States. TVA's service area covers all of Tennessee, portions of Alabama, Mississippi, and Kentucky, and small areas of Georgia, North Carolina ...
, including Fontana Dam
Fontana Dam is a hydroelectric dam on the Little Tennessee River in Swain and Graham counties, North Carolina, United States. The dam is operated by the Tennessee Valley Authority, which built the dam in the early 1940s to satisfy the skyrocketin ...
. Tourism, especially outdoor ventures such as canoeing, whitewater rafting, camping, and fishing are important for many local economies.
High Country
The northern counties in Western North Carolina are commonly known as the state's High Country. Centered on Boone, the High Country has the area's most popularski resort
A ski resort is a resort developed for skiing, snowboarding, and other winter sports. In Europe, most ski resorts are towns or villages in or adjacent to a ski area – a mountainous area with pistes (ski trails) and a ski lift system. In North ...
s, including Ski Beech, Appalachian Ski Mountain, and Sugar Mountain. The area also features such attractions, historical sites, and geological formations as Linville Caverns
Linville Caverns are privately owned active limestone caverns located in northern McDowell County, North Carolina, just south of the village of Linville Falls, on U.S. Highway 221. The caverns are open to the public year-round for guided tours. L ...
, Grandfather Mountain
Grandfather Mountain is a mountain, a non-profit attraction, and a North Carolina state park
near Linville, North Carolina. At 5,946 feet (1,812 m), it is the highest peak on the eastern escarpment of the Blue Ridge Mountains, one of the major ch ...
, and Blowing Rock Blowing Rock may refer to:
* The town of Blowing Rock, North Carolina
** The rocky outcropping Blowing Rock (land feature), near the town of the same name
* Blowing Rock, Virginia, an unincorporated community
* Caribbean island belonging to Anguil ...
. Education, skiing, tourism, and Christmas tree
A Christmas tree is a decorated tree, usually an evergreen conifer, such as a spruce, pine or fir, or an artificial tree of similar appearance, associated with the celebration of Christmas. The custom was further developed in early modern ...
farming are among this area's most prominent industries, although agriculture
Agriculture or farming is the practice of cultivating plants and livestock. Agriculture was the key development in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created food surpluses that enabled people to ...
and raising livestock
Livestock are the domesticated animals raised in an agricultural setting to provide labor and produce diversified products for consumption such as meat, eggs, milk, fur, leather, and wool. The term is sometimes used to refer solely to animals ...
also remain important. The counties that make up the High Country are: Alleghany, Ashe, Avery, Mitchell
Mitchell may refer to:
People
*Mitchell (surname)
*Mitchell (given name)
Places Australia
* Mitchell, Australian Capital Territory, a light-industrial estate
* Mitchell, New South Wales, a suburb of Bathurst
* Mitchell, Northern Territo ...
, Watauga Watauga can refer to:
;Places
*Watauga, Kentucky
* Watauga County, North Carolina
* Watauga, South Dakota
* Watauga, Tennessee
* Watauga, Texas
;Bodies of Water
* Watauga Lake in Tennessee
* The Watauga River in North Carolina and Tennessee
;Shi ...
, Wilkes, and Yancey.
Foothills
 The Foothills is a
The Foothills is a region
In geography, regions, otherwise referred to as zones, lands or territories, are areas that are broadly divided by physical characteristics (physical geography), human impact characteristics (human geography), and the interaction of humanity and t ...
of transitional terrain between the Piedmont Plateau
The Piedmont is a plateau region located in the Eastern United States. It is situated between the Atlantic coastal plain and the main Appalachian Mountains, stretching from New York in the north to central Alabama in the south. The Piedmont ...
and the Appalachian Mountains
The Appalachian Mountains, often called the Appalachians, (french: Appalaches), are a system of mountains in eastern to northeastern North America. The Appalachians first formed roughly 480 million years ago during the Ordovician Period. They ...
, extending from the lower edge of the Blue Ridge escarpment into the upper Catawba, Yadkin, Broad, Saluda, and Savannah River valleys. The eastern slopes of the Blue Ridge drop sharply to the foothills section, going from 3,500–4,000 feet (1,000–1,200 m) at the top to 1,000–1,500 feet at the base. The foothills region contains numerous lower peaks and isolated mountain ranges, such as the South Mountains, Brushy Mountains, and Stone Mountain State Park
Stone Mountain State Park is a North Carolina state park in Alleghany County and Wilkes County, North Carolina.
Stone Mountain
The centerpiece of the park is Stone Mountain, a dome of exposed granite (specifically a quartz diorite to g ...
. The foothills are divided into many small river and creek valleys where much of the region's population lives. Although no large cities are located in the foothills, the subregion contains many smaller cities and towns.
These towns were often developed by European Americans
European Americans (also referred to as Euro-Americans) are Americans of European ancestry. This term includes people who are descended from the first European settlers in the United States as well as people who are descended from more recent Eu ...
around a single industry, such as furniture
Furniture refers to movable objects intended to support various human activities such as seating (e.g., stools, chairs, and sofas), eating (tables), storing items, eating and/or working with an item, and sleeping (e.g., beds and hammocks). Fu ...
or textiles
Textile is an umbrella term that includes various fiber-based materials, including fibers, yarns, filaments, threads, different fabric types, etc. At first, the word "textiles" only referred to woven fabrics. However, weaving is not the ...
, which depended on local waterpower as their energy sources. Since the late 20th century
The 20th (twentieth) century began on
January 1, 1901 ( MCMI), and ended on December 31, 2000 ( MM). The 20th century was dominated by significant events that defined the modern era: Spanish flu pandemic, World War I and World War II, nuclear ...
, many of these industries and their associated jobs have moved offshore to other countries due to globalization
Globalization, or globalisation (Commonwealth English; see spelling differences), is the process of interaction and integration among people, companies, and governments worldwide. The term ''globalization'' first appeared in the early 20t ...
, although they still remain prevalent in some foothill areas. The towns that depended upon them economically, often suffered from job and population losses of people moving to areas of more economic opportunity. Some areas of the foothills are developing newer economies, including manufacturing
Manufacturing is the creation or production of goods with the help of equipment, labor, machines, tools, and chemical or biological processing or formulation. It is the essence of secondary sector of the economy. The term may refer to a r ...
, food distribution
Food distribution is the process where a general population is supplied with food. The Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) considers food distribution as a subset of the food system. The process and methodology behind food distribution varies ...
, utilities
A public utility company (usually just utility) is an organization that maintains the infrastructure for a public service (often also providing a service using that infrastructure). Public utilities are subject to forms of public control and r ...
, and health care
Health care or healthcare is the improvement of health via the prevention, diagnosis, treatment, amelioration or cure of disease, illness, injury, and other physical and mental impairments in people. Health care is delivered by health profe ...
. Many farmers in the northern foothills are poultry
Poultry () are domesticated birds kept by humans for their eggs, their meat or their feathers. These birds are most typically members of the superorder Galloanserae (fowl), especially the order Galliformes (which includes chickens, quails, a ...
farmers. Vineyard
A vineyard (; also ) is a plantation of grape-bearing vines, grown mainly for winemaking, but also raisins, table grapes and non-alcoholic grape juice. The science, practice and study of vineyard production is known as viticulture. Vineyards ...
s have been developed, along with associated winemaking
Winemaking or vinification is the production of wine, starting with the selection of the fruit, its fermentation into alcohol, and the bottling of the finished liquid. The history of wine-making stretches over millennia. The science of wine and ...
and popular retail
Retail is the sale of goods and services to consumers, in contrast to wholesaling, which is sale to business or institutional customers. A retailer purchases goods in large quantities from manufacturers, directly or through a wholesaler, and t ...
.
Among the towns of the foothills region are: Elkin, Forest City, Glen Alpine Glean Alpine may mean:
* Glen Alpine, New South Wales, Australia
* Glen Alpine, North Carolina, United States
* Glen Alpine, Nova Scotia, Canada
* Glen Alpine, Toowoomba
Glen Alpine is a heritage-listed villa at 32–36 East Street, Redwood, ...
, Granite Falls, Hudson
Hudson may refer to:
People
* Hudson (given name)
* Hudson (surname)
* Henry Hudson, English explorer
* Hudson (footballer, born 1986), Hudson Fernando Tobias de Carvalho, Brazilian football right-back
* Hudson (footballer, born 1988), Hudso ...
, Lake Lure
Lake Lure is a town in Rutherford County, North Carolina, United States. In 2020 the town population was 1,634. Lake Lure was incorporated in 1927, and acquired the lake after which it is named in 1965.
History
In 1902, Dr. Lucius B. Morse and ...
, Rutherfordton, Spindale, Tryon, and Valdese; and the cities of Hickory
Hickory is a common name for trees composing the genus ''Carya'', which includes around 18 species. Five or six species are native to China, Indochina, and India (Assam), as many as twelve are native to the United States, four are found in Mexi ...
, Lenoir Lenoir may refer to:
Locations:
* Lenoir, North Carolina, United States
* Lenoir County, North Carolina, United States
* Lenoir City, Tennessee
In Universities:
* Lenoir-Rhyne University
* Lenoir Dining Hall, a dining hall at the University of N ...
, Marion Marion may refer to:
People
*Marion (given name)
*Marion (surname)
*Marion Silva Fernandes, Brazilian footballer known simply as "Marion"
*Marion (singer), Filipino singer-songwriter and pianist Marion Aunor (born 1992)
Places Antarctica
* Mari ...
, Mount Airy, Shelby, and Morganton. "The southern mountains" refer to the counties bordering South Carolina. The cities/towns of Hendersonville, Brevard, and Columbus
Columbus is a Latinized version of the Italian surname "''Colombo''". It most commonly refers to:
* Christopher Columbus (1451-1506), the Italian explorer
* Columbus, Ohio, capital of the U.S. state of Ohio
Columbus may also refer to:
Places ...
are within this area.
Higher education
Appalachian State University
Appalachian State University (; Appalachian, App State, App, or ASU) is a public university in Boone, North Carolina. It was founded as a teachers college in 1899 by brothers B. B. and D. D. Dougherty and the latter's wife, Lillie Shull Dough ...
in Boone, Western Carolina University
Western Carolina University (WCU) is a public university in Cullowhee, North Carolina. It is part of the University of North Carolina system.
The fifth oldest institution of the sixteen four-year universities in the UNC system, WCU was founded t ...
in Cullowhee
Cullowhee
, from the North Carolina Collection website at the , and UNC Asheville in Asheville. All three are part of the
 The
The
 The
The
Retrieved: May 15, 2009. In 2003, Appalachian North Carolina— which included most counties of Western North Carolina and two counties in central North Carolina— had a three-year average unemployment rate of 6%, compared with 6.2% statewide and 5.5% nationwide. In 2002, Appalachian North Carolina had a per capita market income of $21,168, compared with $23,443 statewide and $26,420 nationwide. In 2000, Appalachian North Carolina had a poverty rate of 11.7%, compared to 12.3% statewide and 12.4% nationwide. Only Graham County was designated as "Distressed" in North Carolina. Six— Cherokee, McDowell, Mitchell, Rutherford, Swain, and Yancey— were designated "at-risk." Forsyth County (which is usually grouped as part of central North Carolina) was the only county given the "attainment" designation. Four— Buncombe, Davie, Henderson, and Polk— were designated "competitive." Most Western North Carolina counties were designated "transitional," meaning they lagged behind the national average on one of the three key indicators. Graham County had Appalachian North Carolina's highest poverty rating, with 19.5% of its residents living below the poverty line. Forsyth had Appalachian North Carolina's highest per capita income at $26,987. Watauga County's unemployment rate of 2.3% was lowest of all 420 counties in the Appalachian region. The changes brought by increased tourism and population growth from retirees and persons migrating to the region have been double-edged. Local businesses have benefited from increased economic revenue, but increases in costs of living and loss of natural habitat to development, can degrade the quality of life for which the region has become notable.
 There are 82
There are 82
 Western North Carolina is generally considered to consist of 23 counties.
The counties commonly included in the region are as follows:
# Alleghany County
# Ashe County
#
Western North Carolina is generally considered to consist of 23 counties.
The counties commonly included in the region are as follows:
# Alleghany County
# Ashe County
#
, from the North Carolina Collection website at the , and UNC Asheville in Asheville. All three are part of the
University of North Carolina system
The University of North Carolina is the multi-campus public university system for the state of North Carolina. Overseeing the state's 16 public universities and the NC School of Science and Mathematics, it is commonly referred to as the UNC Sys ...
.
Several small, private colleges and universities are also located in the region. Mars Hill University
Mars Hill University is a private Christian university in Mars Hill, North Carolina. The university offers 35 undergraduate majors and includes a school of nursing and graduate schools in education, criminal justice, and management. From 1859 to ...
is located north of Asheville. Founded in 1856, it is the oldest college or university in Western North Carolina. Montreat College
Montreat College (pronounced "mon-treet") is a private, Christian college in Montreat, North Carolina. Founded in 1916, Montreat College offers associate, bachelor's, and master's degree programs for traditional and adult students. The college's m ...
, affiliated with the Presbyterian Church
Presbyterianism is a part of the Reformed tradition within Protestantism that broke from the Roman Catholic Church in Scotland by John Knox, who was a priest at St. Giles Cathedral (Church of Scotland). Presbyterian churches derive their nam ...
, is located east of Asheville. Lees-McRae College, located in Banner Elk
Banner Elk is a town in Avery County, North Carolina, United States. The population was 1,028 at the 2010 census. Banner Elk is home to Lees–McRae College.
History
The area surrounding the Elk River was inhabited by the Cherokee before weste ...
, is also affiliated with the Presbyterian Church
Presbyterianism is a part of the Reformed tradition within Protestantism that broke from the Roman Catholic Church in Scotland by John Knox, who was a priest at St. Giles Cathedral (Church of Scotland). Presbyterian churches derive their nam ...
. Warren Wilson College
Warren Wilson College (WWC) is a private liberal arts college in Swannanoa, North Carolina. It is known for its curriculum that combines academics, work, and service as every student must complete a requisite course of study, work an on-campus ...
, located in Swannanoa, is noted for its strong pro-environment policies and for being one of the nine work colleges
Work colleges are colleges in the United States that require students to work and integrate that work into the college learning experience. A work college is a public or private non-profit, four-year degree-granting institution with a commitment t ...
in the United States. Brevard College
Brevard College is a private college in Brevard, North Carolina. The college grants the Bachelor of Arts or Bachelor of Science degree.
History
Brevard College was named for Ephraim Brevard, a teacher and one of the local leaders that produce ...
, located in Brevard, is affiliated with the United Methodist Church
The United Methodist Church (UMC) is a worldwide mainline Protestant denomination based in the United States, and a major part of Methodism. In the 19th century, its main predecessor, the Methodist Episcopal Church, was a leader in evangelical ...
. Lenoir-Rhyne University, located in Hickory, is a private liberal arts university affiliated with the Evangelical Lutheran Church in America
The Evangelical Lutheran Church in America (ELCA) is a mainline Protestant Lutheran church headquartered in Chicago, Illinois. The ELCA was officially formed on January 1, 1988, by the merging of three Lutheran church bodies. , it has approxim ...
.
Several community college
A community college is a type of educational institution. The term can have different meanings in different countries: many community colleges have an "open enrollment" for students who have graduated from high school (also known as senior sec ...
systems serve the region, including Asheville-Buncombe Technical Community College, Blue Ridge Community College, Caldwell Community College & Technical Institute
Caldwell Community College and Technical Institute (CCC&TI) is a public community college serving residents of Caldwell and Watauga counties in North Carolina. CCC&TI is part of the North Carolina Community College System.
CCC&TI offers two ful ...
, Catawba Valley Community College
Catawba Valley Community College is a public community college in Hickory, North Carolina. The college, established April 3, 1958, is part of the North Carolina Community College System. The main campus covers and includes 16 buildings. The col ...
, Haywood Community College
Haywood Community College is a community college in Clyde, North Carolina. It is part of the North Carolina Community College System. Established in 1965, the college offers associate degree programs and online courses in programs such as forest ...
, Isothermal Community College
Isothermal Community College (ICC) is a public community college in Spindale, North Carolina. Named after its location in the thermal belt, an area in the foothills of Western North Carolina with significantly milder temperatures than its immedia ...
, Mayland Community College, McDowell Technical Community College
McDowell Technical Community College is a public community college in Marion, North Carolina. It is part of the North Carolina Community College System.
History
McDowell Technical Community College was founded in 1964 as a satellite of Ashevill ...
, Southwestern Community College, Tri-County Community College, Western Piedmont Community College
Western Piedmont Community College is a public community college in Morganton, North Carolina. It was chartered on April 2, 1964, as a member of the North Carolina Community College System
The North Carolina Community College System (Sy ...
, and Wilkes Community College
Wilkes Community College (WCC) is a public community college in Wilkesboro, North Carolina. It is part of the North Carolina Community College System and serves the people of Wilkes, Ashe and Alleghany counties, and beyond. The college is best k ...
.
Transportation
Highways
Interstates
Three majorInterstate highway
The Dwight D. Eisenhower National System of Interstate and Defense Highways, commonly known as the Interstate Highway System, is a network of controlled-access highways that forms part of the National Highway System in the United States. Th ...
s cross the region: Interstate 40
Interstate 40 (I-40) is a major east–west Interstate Highway running through the south-central portion of the United States. At a length of , it is the third-longest Interstate Highway in the country, after I-90 and I-80. From west to ea ...
, which traverses east-west, Interstate 77
Interstate 77 (I-77) is a north–south Interstate Highway in the eastern United States. It traverses diverse terrain, from the mountainous state of West Virginia to the rolling farmlands of North Carolina and Ohio. It largely supplants the ...
, which runs north-south through the northeastern section of Western North Carolina, and Interstate 26
Interstate 26 (I-26) is a main route of the Interstate Highway System in the Southeastern United States. Nominally east–west, as indicated by its even number, I-26 runs from the junction of U.S. Route 11W (US 11W) and US 23 in ...
, which traverses north-south (although it is classified as an east-west highway for most of its route and is signed as such). Interstate 240 is the only auxiliary interstate route in the region, and it serves downtown Asheville.
U.S. Highways
US 421, a multi-lane expressway, is the major highway in the northwestern part of the state. US 19, US 23, US 64, US 74, and US 441 are the major highways in the far western part of the region.US 70
U.S. Route 70 or U.S. Highway 70 (US 70) is an east–west United States highway that runs for from eastern North Carolina to east-central Arizona. It is a major east–west highway of the Southeastern, Southern and Southwestern United States. ...
runs east through the area, connecting Hickory and Asheville. US 221
U.S. Route 221 (US 221) is a spur of U.S. Route 21. It travels from Perry, Florida, at US 19/ US 98/ US 27 Alternate to Lynchburg, Virginia, at US 29 Business (Lynchburg Expressway). It travels through the states ...
also runs through the area. This highway, which begins in Perry, Florida
Perry is a city in Taylor County, Florida, Taylor County, Florida, United States. As of 2010, the population recorded by the U.S. Census Bureau is 7,017.
It is the county seat. The city was named for Madison Perry, fourth Governors of Florida, Gov ...
, connects the town of Rutherfordton to Jefferson. US 321 runs north from Hickory to Watauga and Avery counties before entering Tennessee.
Blue Ridge Parkway
 The
The Blue Ridge Parkway
The Blue Ridge Parkway is a National Parkway and All-American Road in the United States, noted for its scenic beauty. The parkway, which is America's longest linear park, runs for through 29 Virginia and North Carolina counties, linking Shenand ...
, a National Scenic Byway
A National Scenic Byway is a road recognized by the United States Department of Transportation for one or more of six "intrinsic qualities": archeological, cultural, historic, natural, recreational, and scenic. The program was established by Co ...
that is 469 miles long, runs through western North Carolina, starting in Virginia and ending near the Great Smoky Mountains National Park
Great Smoky Mountains National Park is an American national park in the southeastern United States, with parts in North Carolina and Tennessee. The park straddles the ridgeline of the Great Smoky Mountains, part of the Blue Ridge Mountains, whi ...
.
Railroads
Two major class 1 railroads serve the region,CSX
CSX Transportation , known colloquially as simply CSX, is a Class I freight railroad operating in the Eastern United States and the Canadian provinces of Ontario and Quebec. The railroad operates approximately 21,000 route miles () of track. ...
and Norfolk Southern
The Norfolk Southern Railway is a Railroad classes, Class I freight railroad in the United States formed in 1982 with the merger of Norfolk and Western Railway and Southern Railway (U.S.), Southern Railway. With headquarters in Atlanta, the ...
. In addition, two tourist railroad
A heritage railway or heritage railroad (US usage) is a railway operated as living history to re-create or preserve railway scenes of the past. Heritage railways are often old railway lines preserved in a state depicting a period (or periods) i ...
s also operate in the area, the Tweetsie Railroad theme park and the Great Smoky Mountains Railroad
The Great Smoky Mountains Railroad is a freight and heritage railroad based in Bryson City, North Carolina, United States. Since late 1999, the railroad is currently owned and operated by American Heritage Railways, Inc., which also owns and ...
.
Airports
Asheville Regional Airport
Asheville Regional Airport is a Class C airport near Interstate 26 near the town of Fletcher, south of downtown Asheville, in the U.S. state of North Carolina, United States. It is owned by the Greater Asheville Regional Airport Authority. Th ...
(AVL), located southeast of the city of Asheville in Fletcher
Fletcher may refer to:
People
* Fletcher (occupation), a person who fletches arrows, the origin of the surname
* Fletcher (singer) (born 1994), American actress and singer-songwriter
* Fletcher (surname)
* Fletcher (given name)
Places
United ...
, serves the area with non-stop jet service to Charlotte, North Carolina
Charlotte ( ) is the most populous city in the U.S. state of North Carolina. Located in the Piedmont region, it is the county seat of Mecklenburg County. The population was 874,579 at the 2020 census, making Charlotte the 16th-most populo ...
; LaGuardia Airport
LaGuardia Airport is a civil airport in East Elmhurst, Queens, New York City. Covering , the facility was established in 1929 and began operating as a public airport in 1939. It is named after former New York City mayor Fiorello La Guardia. ...
in New York City
New York, often called New York City or NYC, is the List of United States cities by population, most populous city in the United States. With a 2020 population of 8,804,190 distributed over , New York City is also the L ...
and nearby Newark, New Jersey
Newark ( , ) is the most populous city in the U.S. state of New Jersey and the seat of Essex County and the second largest city within the New York metropolitan area.Houston
Houston (; ) is the most populous city in Texas, the most populous city in the Southern United States, the fourth-most populous city in the United States, and the sixth-most populous city in North America, with a population of 2,304,580 in ...
, Texas
Texas (, ; Spanish language, Spanish: ''Texas'', ''Tejas'') is a state in the South Central United States, South Central region of the United States. At 268,596 square miles (695,662 km2), and with more than 29.1 million residents in 2 ...
; Atlanta, Georgia
Atlanta ( ) is the capital and most populous city of the U.S. state of Georgia. It is the seat of Fulton County, the most populous county in Georgia, but its territory falls in both Fulton and DeKalb counties. With a population of 498,715 ...
; Orlando Sanford International Airport
Orlando Sanford International Airport is in Sanford, Florida, United States, near Orlando. It was built as Naval Air Station Sanford, a Master Jet Base for carrier-based attack and reconnaissance aircraft, and was used by the U.S. Navy until 1 ...
near Orlando, Florida
Orlando () is a city in the U.S. state of Florida and is the county seat of Orange County, Florida, Orange County. In Central Florida, it is the center of the Greater Orlando, Orlando metropolitan area, which had a population of 2,509,831, acco ...
; Philadelphia, Pennsylvania
Philadelphia, often called Philly, is the largest city in the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, the sixth-largest city in the U.S., the second-largest city in both the Northeast megalopolis and Mid-Atlantic regions after New York City. Sinc ...
; Detroit, Michigan
Detroit ( , ; , ) is the largest city in the U.S. state of Michigan. It is also the largest U.S. city on the United States–Canada border, and the seat of government of Wayne County. The City of Detroit had a population of 639,111 at ...
; and O'Hare International Airport
Chicago O'Hare International Airport , sometimes referred to as, Chicago O'Hare, or simply O'Hare, is the main international airport serving Chicago, Illinois, located on the city's Northwest Side, approximately northwest of the Chicago Loop, ...
in Chicago
(''City in a Garden''); I Will
, image_map =
, map_caption = Interactive Map of Chicago
, coordinates =
, coordinates_footnotes =
, subdivision_type = Country
, subdivision_name ...
, Illinois
Illinois ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Midwestern United States, Midwestern United States. Its largest metropolitan areas include the Chicago metropolitan area, and the Metro East section, of Greater St. Louis. Other smaller metropolita ...
.
Economy
Tourism
Tourism is travel for pleasure or business; also the theory and practice of touring (disambiguation), touring, the business of attracting, accommodating, and entertaining tourists, and the business of operating tour (disambiguation), tours. Th ...
is a major part of the economy
An economy is an area of the production, distribution and trade, as well as consumption of goods and services. In general, it is defined as a social domain that emphasize the practices, discourses, and material expressions associated with the ...
in the area, which contains half of the Great Smoky Mountains National Park
Great Smoky Mountains National Park is an American national park in the southeastern United States, with parts in North Carolina and Tennessee. The park straddles the ridgeline of the Great Smoky Mountains, part of the Blue Ridge Mountains, whi ...
as well as the Nantahala and Pisgah national forests. Several lake
A lake is an area filled with water, localized in a basin, surrounded by land, and distinct from any river or other outlet that serves to feed or drain the lake. Lakes lie on land and are not part of the ocean, although, like the much large ...
s and dam
A dam is a barrier that stops or restricts the flow of surface water or underground streams. Reservoirs created by dams not only suppress floods but also provide water for activities such as irrigation, human consumption, industrial use, a ...
s are scattered throughout Western North Carolina, such as Lake Lure
Lake Lure is a town in Rutherford County, North Carolina, United States. In 2020 the town population was 1,634. Lake Lure was incorporated in 1927, and acquired the lake after which it is named in 1965.
History
In 1902, Dr. Lucius B. Morse and ...
and Fontana Dam
Fontana Dam is a hydroelectric dam on the Little Tennessee River in Swain and Graham counties, North Carolina, United States. The dam is operated by the Tennessee Valley Authority, which built the dam in the early 1940s to satisfy the skyrocketin ...
. Many visitors travel to the region every summer and autumn from major cities to escape hot weather
Weather is the state of the atmosphere, describing for example the degree to which it is hot or cold, wet or dry, calm or stormy, clear or cloudy. On Earth, most weather phenomena occur in the lowest layer of the planet's atmosphere, the ...
elsewhere and see the leaves
A leaf (plural, : leaves) is any of the principal appendages of a vascular plant plant stem, stem, usually borne laterally aboveground and specialized for photosynthesis. Leaves are collectively called foliage, as in "autumn foliage", wh ...
change colors. The timber industry is also a major economic sector.
Appalachian Regional Commission
 The
The Appalachian Regional Commission
The Appalachian Regional Commission (ARC) is a United States federal–state partnership that works with the people of Appalachia to create opportunities for self-sustaining economic development and improved quality of life. Congress established A ...
was formed in 1965 to aid economic development in the Appalachian region, which was lagging far behind the rest of the nation on most economic indicators. The Appalachian region, as currently defined by the Commission, includes 420 counties in 13 states, including 29 counties in North Carolina. The Commission classifies each county according to five economic qualifications— distressed, at-risk, transitional, competitive, or attainment. "Distressed" counties are considered the most economically endangered and "attainment" counties are the most economically prosperous. The three indicators used for such classification are three-year average unemployment rate, market income per capita, and poverty rate.Appalachian Regional Commission Online Resource CenterRetrieved: May 15, 2009. In 2003, Appalachian North Carolina— which included most counties of Western North Carolina and two counties in central North Carolina— had a three-year average unemployment rate of 6%, compared with 6.2% statewide and 5.5% nationwide. In 2002, Appalachian North Carolina had a per capita market income of $21,168, compared with $23,443 statewide and $26,420 nationwide. In 2000, Appalachian North Carolina had a poverty rate of 11.7%, compared to 12.3% statewide and 12.4% nationwide. Only Graham County was designated as "Distressed" in North Carolina. Six— Cherokee, McDowell, Mitchell, Rutherford, Swain, and Yancey— were designated "at-risk." Forsyth County (which is usually grouped as part of central North Carolina) was the only county given the "attainment" designation. Four— Buncombe, Davie, Henderson, and Polk— were designated "competitive." Most Western North Carolina counties were designated "transitional," meaning they lagged behind the national average on one of the three key indicators. Graham County had Appalachian North Carolina's highest poverty rating, with 19.5% of its residents living below the poverty line. Forsyth had Appalachian North Carolina's highest per capita income at $26,987. Watauga County's unemployment rate of 2.3% was lowest of all 420 counties in the Appalachian region. The changes brought by increased tourism and population growth from retirees and persons migrating to the region have been double-edged. Local businesses have benefited from increased economic revenue, but increases in costs of living and loss of natural habitat to development, can degrade the quality of life for which the region has become notable.
Topography
 There are 82
There are 82 mountain
A mountain is an elevated portion of the Earth's crust, generally with steep sides that show significant exposed bedrock. Although definitions vary, a mountain may differ from a plateau in having a limited Summit (topography), summit area, and ...
peak Peak or The Peak may refer to:
Basic meanings Geology
* Mountain peak
** Pyramidal peak, a mountaintop that has been sculpted by erosion to form a point Mathematics
* Peak hour or rush hour, in traffic congestion
* Peak (geometry), an (''n''-3)-di ...
s between 5,000 and 6,000 feet (1,500–1,800 m) in elevation
The elevation of a geographic location is its height above or below a fixed reference point, most commonly a reference geoid, a mathematical model of the Earth's sea level as an equipotential gravitational surface (see Geodetic datum § Vert ...
in western North Carolina, and 43 peaks rise to over . Among the subranges of the Appalachian Mountains located in western North Carolina are the Great Smoky Mountains
The Great Smoky Mountains (, ''Equa Dutsusdu Dodalv'') are a mountain range rising along the Tennessee–North Carolina border in the southeastern United States. They are a subrange of the Appalachian Mountains, and form part of the Blue Ridge ...
, Blue Ridge Mountains
The Blue Ridge Mountains are a physiographic province of the larger Appalachian Mountains range. The mountain range is located in the Eastern United States, and extends 550 miles southwest from southern Pennsylvania through Maryland, West Virgin ...
, South Mountains, Brushy Mountains, Sauratown Mountains
The Sauratown Mountains, which are sometimes called "the mountains away from the mountains", are an isolated mountain range located within Stokes and Surry counties in the U.S. state of North Carolina. The vast majority of the range is located i ...
, Great Balsam Mountains
The Great Balsam Mountains, or Balsam Mountains, are in the mountain region of western North Carolina, United States. The Great Balsams are a subrange of the Blue Ridge Mountains, which in turn are a part of the Appalachian Mountains. The most f ...
, Great Craggy Mountains
The Great Craggy Mountains, commonly called the Craggies, are a mountain range in western North Carolina, United States. They are a subrange of the Blue Ridge Mountains and encompass an area of approx. 194 sq mi (503 km²). They are situated ...
, the Plott Balsams
The Plott Balsams are a mountain range in western North Carolina, in the southeastern United States. They are part of the Blue Ridge Mountain Province of the Southern Appalachian Mountains. The Plott Balsams stretch from the city of Sylva in t ...
, and the Black Mountains. Mount Mitchell
Mount Mitchell, known in Cherokee as Attakulla, is the highest peak of the Appalachian Mountains and the highest peak in mainland eastern North America. It is located near Burnsville in Yancey County, North Carolina in the Black Mountain subra ...
, in the Black Mountains, is, at , the highest point in eastern North America
North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere and almost entirely within the Western Hemisphere. It is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South America and the Car ...
. Valley and foothills locations typically range from AMSL
Height above mean sea level is a measure of the vertical distance (height, elevation or altitude) of a location in reference to a historic mean sea level taken as a vertical datum. In geodesy, it is formalized as ''orthometric heights''.
The comb ...
.
The major rivers in the region include the French Broad River
The French Broad River is a river in the U.S. states of North Carolina and Tennessee. It flows from near the town of Rosman in Transylvania County, North Carolina, into Tennessee, where its confluence with the Holston River at Knoxville forms ...
, Nolichucky River
The Nolichucky River is a river that flows through Western North Carolina and East Tennessee, in the southeastern United States. Traversing the Pisgah National Forest and the Cherokee National Forest in the Blue Ridge Mountains, the river's wate ...
, Watauga River
The Watauga River () is a large stream of western North Carolina and East Tennessee. It is long with its headwaters in Linville Gap to the South Fork Holston River at Boone Lake.
Course
The Watauga River rises from a spring near the base ...
, Little Tennessee River
The Little Tennessee River is a tributary of the Tennessee River that flows through the Blue Ridge Mountains from Georgia (U.S. state), Georgia, into North Carolina, and then into Tennessee, in the southeastern United States. It drains portio ...
, and Hiwassee River
The Hiwassee River has its headwaters on the north slope of Rocky Mountain in Towns County in the northern area of the State of Georgia. It flows northward into North Carolina before turning westward into Tennessee, flowing into the Tennessee Riv ...
flowing into the Tennessee River valley; the New River flowing into the Ohio River valley; and the headwaters and upper valleys of the Catawba River
The Catawba River originates in Western North Carolina and flows into South Carolina, where it later becomes known as the Wateree River. The river is approximately 220 miles (350 km) long. It rises in the Appalachian Mountains and drains into ...
, Yadkin River
The Yadkin River is one of the longest rivers in North Carolina, flowing . It rises in the northwestern portion of the state near the Blue Ridge Parkway's Thunder Hill Overlook. Several parts of the river are impounded by dams for water, po ...
, Broad River, and Saluda River
The Saluda River is a principal tributary of the Congaree River, about 200 mi (320 km) long, in northern and western South Carolina in the United States. Via the Congaree River, it is part of the watershed of the Santee River, which f ...
flowing through the foothills towards the Atlantic. The Eastern Continental Divide
The Eastern Continental Divide, Eastern Divide or Appalachian Divide is a hydrographic divide in eastern North America that separates the easterly Atlantic Seaboard watershed from the westerly Gulf of Mexico watershed. The divide nearly span ...
runs through the region, dividing Tennessee
Tennessee ( , ), officially the State of Tennessee, is a landlocked state in the Southeastern region of the United States. Tennessee is the 36th-largest by area and the 15th-most populous of the 50 states. It is bordered by Kentucky to th ...
-bound stream
A stream is a continuous body of water, body of surface water Current (stream), flowing within the stream bed, bed and bank (geography), banks of a channel (geography), channel. Depending on its location or certain characteristics, a stream ...
s from those flowing through the Carolinas
The Carolinas are the U.S. states of North Carolina and South Carolina, considered collectively. They are bordered by Virginia to the north, Tennessee to the west, and Georgia to the southwest. The Atlantic Ocean is to the east.
Combining Nort ...
.
Area
Counties
 Western North Carolina is generally considered to consist of 23 counties.
The counties commonly included in the region are as follows:
# Alleghany County
# Ashe County
#
Western North Carolina is generally considered to consist of 23 counties.
The counties commonly included in the region are as follows:
# Alleghany County
# Ashe County
# Avery County
Avery County is a county located in the U.S. state of North Carolina. As of the 2020 census, the population was 17,806. The county seat is Newland. The county seat was initially established in Elk Park when the county was first formed, but wa ...
# Buncombe County
Buncombe County is a County (United States), county located in the U.S. state of North Carolina. It is classified within Western North Carolina. The 2020 United States census, 2020 census reported the population was 269,452. Its county seat is A ...
# Burke County
# Caldwell County
# Cherokee County Cherokee County is the name of eight counties in the United States:
* Cherokee County, Alabama
* Cherokee County, Georgia
* Cherokee County, Iowa
* Cherokee County, Kansas
* Cherokee County, North Carolina
* Cherokee County, Oklahoma
* Cherokee Co ...
# Clay County Clay County is the name of 18 counties in the United States. Most are named for Henry Clay, U.S. Senator and statesman:
* Clay County, Alabama
* Clay County, Arkansas (named for John Clayton, and originally named Clayton County)
* Clay County, Flor ...
# Graham County
# Haywood County
# Henderson County
# Jackson County
# Macon County
# Madison County
# McDowell County
# Mitchell County
# Polk County Polk County is the name of twelve counties in the United States, all except two named after president of the United States James Knox Polk:
* Polk County, Arkansas
* Polk County, Florida
* Polk County, Georgia
* Polk County, Iowa
* Polk Count ...
# Rutherford County
# Swain County
Swain County is a county located on the far western border of the U.S. state of North Carolina. As of the 2020 census, the population was 14,117. Its county seat is Bryson City.
Four rivers flow through the mountainous terrain of Swain County: t ...
# Transylvania County
Transylvania County is a county in the U.S. state of North Carolina. As of the 2020 census the population is 32,986. Its county seat is Brevard.
Transylvania County comprises the Brevard Micropolitan Statistical Area, which is also included i ...
# Watauga County
Watauga County ( )
from the North Carolina Collection's website at the # Wilkes County #
 Listed below are communities often considered to be a part of Western North Carolina:
Listed below are communities often considered to be a part of Western North Carolina:
 *
*
from the North Carolina Collection's website at the # Wilkes County #
Yancey County
Yancey County is a county located in the U.S. state of North Carolina. As of the 2020 census, the population was 18,470. Its county seat is Burnsville.
This land was inhabited by the Cherokee prior to European settlement, as was much of the S ...
Other counties that fall under various definitions of Western North Carolina include: Alexander County, Catawba County
Catawba County is a County (United States), county in the U.S. state of North Carolina. As of the 2020 United States census, 2020 census, the population was 160,610. Its county seat is Newton, North Carolina, Newton, and its largest city is Hick ...
, Cleveland County
Cleveland ( ), officially the City of Cleveland, is a city in the United States, U.S. U.S. state, state of Ohio and the county seat of Cuyahoga County, Ohio, Cuyahoga County. Located in the northeastern part of the state, it is situated along ...
, Surry County and Yadkin County
Yadkin County is located in the U.S. state of North Carolina. As of the 2020 census, the population was 37,214. Its county seat is Yadkinville. Yadkin County is included in the Winston-Salem, NC Metropolitan Statistical Area, which is also inc ...
. When these counties are added, they form a total regional area of roughly 11,750 square miles (30,430 km²). This makes the region roughly the size of Massachusetts
Massachusetts (Massachusett language, Massachusett: ''Muhsachuweesut assachusett writing systems, məhswatʃəwiːsət'' English: , ), officially the Commonwealth of Massachusetts, is the most populous U.S. state, state in the New England ...
.
During the early 1800s the western counties in North Carolina included counties located in the piedmont region, to distinguish them from the eastern counties in North Carolina that were settled earlier. As the western counties became more populated, jurisdictions competed for representation in the North Carolina General Assembly
The North Carolina General Assembly is the Bicameralism, bicameral legislature of the Government of North Carolina, State government of North Carolina. The legislature consists of two chambers: the North Carolina Senate, Senate and the North Ca ...
and the Governor's office.
Cities and towns
 Listed below are communities often considered to be a part of Western North Carolina:
Listed below are communities often considered to be a part of Western North Carolina:
Over 40,000 inhabitants
*Asheville
Asheville ( ) is a city in, and the county seat of, Buncombe County, North Carolina. Located at the confluence of the French Broad and Swannanoa rivers, it is the largest city in Western North Carolina, and the state's 11th-most populous cit ...
* Hickory
Hickory is a common name for trees composing the genus ''Carya'', which includes around 18 species. Five or six species are native to China, Indochina, and India (Assam), as many as twelve are native to the United States, four are found in Mexi ...
(Located in the North Carolina foothills; contains small amounts of territory in Burke and Caldwell Counties)
Over 10,000 inhabitants
* Boone * Hendersonville *Lenoir Lenoir may refer to:
Locations:
* Lenoir, North Carolina, United States
* Lenoir County, North Carolina, United States
* Lenoir City, Tennessee
In Universities:
* Lenoir-Rhyne University
* Lenoir Dining Hall, a dining hall at the University of N ...
* Morganton
* Waynesville
Fewer than 10,000 inhabitants
 *
* Andrews Andrews may refer to:
Places Australia
*Andrews, Queensland
*Andrews, South Australia
United States
*Andrews, Florida (disambiguation), various places
*Andrews, Indiana
* Andrews, Nebraska
*Andrews, North Carolina
* Andrews, Oregon
* Andrews, Sou ...
* Bakersville
* Banner Elk
Banner Elk is a town in Avery County, North Carolina, United States. The population was 1,028 at the 2010 census. Banner Elk is home to Lees–McRae College.
History
The area surrounding the Elk River was inhabited by the Cherokee before weste ...
* Beech Mountain
Beech Mountain is a town in both Avery and Watauga counties in the U.S. state of North Carolina. As of the 2010 census, the town population was 320. The town is located atop Beech Mountain and is the highest town east of the Rocky Mountains ...
* Biltmore Forest
* Black Mountain
* Blowing Rock Blowing Rock may refer to:
* The town of Blowing Rock, North Carolina
** The rocky outcropping Blowing Rock (land feature), near the town of the same name
* Blowing Rock, Virginia, an unincorporated community
* Caribbean island belonging to Anguil ...
* Bostic
* Brevard
* Bryson City
Bryson City is a town in Swain County, North Carolina, Swain County, North Carolina in the United States. The population was 1558 as of the 2020 Census. It is the county seat of Swain County.
Located in what was historically the land of the Cherok ...
* Burnsville
* Cajah's Mountain
* Canton
* Cedar Rock
* Chimney Rock
* Clyde Clyde may refer to:
People
* Clyde (given name)
* Clyde (surname)
Places
For townships see also Clyde Township
Australia
* Clyde, New South Wales
* Clyde, Victoria
* Clyde River, New South Wales
Canada
* Clyde, Alberta
* Clyde, Ontario, a tow ...
* Columbus
Columbus is a Latinized version of the Italian surname "''Colombo''". It most commonly refers to:
* Christopher Columbus (1451-1506), the Italian explorer
* Columbus, Ohio, capital of the U.S. state of Ohio
Columbus may also refer to:
Places ...
* Connellys Springs
* Crossnore
* Dillsboro
* Drexel
* Elk Park
* Elkin
* Ellenboro
* Flat Rock
* Fletcher
Fletcher may refer to:
People
* Fletcher (occupation), a person who fletches arrows, the origin of the surname
* Fletcher (singer) (born 1994), American actress and singer-songwriter
* Fletcher (surname)
* Fletcher (given name)
Places
United ...
* Fontana Dam
Fontana Dam is a hydroelectric dam on the Little Tennessee River in Swain and Graham counties, North Carolina, United States. The dam is operated by the Tennessee Valley Authority, which built the dam in the early 1940s to satisfy the skyrocketin ...
* Forest City
* Forest Hills
* Franklin
Franklin may refer to:
People
* Franklin (given name)
* Franklin (surname)
* Franklin (class), a member of a historical English social class
Places Australia
* Franklin, Tasmania, a township
* Division of Franklin, federal electoral d ...
* Gamewell
* Glen Alpine Glean Alpine may mean:
* Glen Alpine, New South Wales, Australia
* Glen Alpine, North Carolina, United States
* Glen Alpine, Nova Scotia, Canada
* Glen Alpine, Toowoomba
Glen Alpine is a heritage-listed villa at 32–36 East Street, Redwood, ...
* Grandfather
Grandparents, individually known as grandmother and grandfather, are the parents of a person's father or mother – paternal or maternal. Every sexually-reproducing living organism who is not a genetic chimera has a maximum of four genetic ...
* Granite Falls
* Hayesville
* Highlands
Highland is a broad term for areas of higher elevation, such as a mountain range or mountainous plateau.
Highland, Highlands, or The Highlands, may also refer to:
Places Albania
* Dukagjin Highlands
Armenia
* Armenian Highlands
Australia
*Sou ...
* Hildebran
* Hot Springs
A hot spring, hydrothermal spring, or geothermal spring is a spring produced by the emergence of geothermally heated groundwater onto the surface of the Earth. The groundwater is heated either by shallow bodies of magma (molten rock) or by circ ...
* Hudson
Hudson may refer to:
People
* Hudson (given name)
* Hudson (surname)
* Henry Hudson, English explorer
* Hudson (footballer, born 1986), Hudson Fernando Tobias de Carvalho, Brazilian football right-back
* Hudson (footballer, born 1988), Hudso ...
* Jefferson Jefferson may refer to:
Names
* Jefferson (surname)
* Jefferson (given name)
People
* Thomas Jefferson (1743–1826), third president of the United States
* Jefferson (footballer, born 1970), full name Jefferson Tomaz de Souza, Brazilian foo ...
* Lake Lure
Lake Lure is a town in Rutherford County, North Carolina, United States. In 2020 the town population was 1,634. Lake Lure was incorporated in 1927, and acquired the lake after which it is named in 1965.
History
In 1902, Dr. Lucius B. Morse and ...
* Lake Santeetlah
Lake Santeetlah, part of the Tennessee River watershed, was created in 1928 when Alcoa dammed the Cheoah River as a means of generating hydroelectric power in Graham County, North Carolina. The reservoir is largely surrounded by the Cheoah Distric ...
* Lansing
Lansing () is the capital of the U.S. state of Michigan. It is mostly in Ingham County, although portions of the city extend west into Eaton County and north into Clinton County. The 2020 census placed the city's population at 112,644, makin ...
* Laurel Park
* Long View
* Maggie Valley
Maggie Valley is a town in Haywood County, North Carolina, United States. The population was 1,150 at the 2010 census. A popular tourist destination, it is home to Cataloochee Ski Area and the former Ghost Town in the Sky amusement park. Maggie V ...
* Marion Marion may refer to:
People
*Marion (given name)
*Marion (surname)
*Marion Silva Fernandes, Brazilian footballer known simply as "Marion"
*Marion (singer), Filipino singer-songwriter and pianist Marion Aunor (born 1992)
Places Antarctica
* Mari ...
* Mars Hill
* Marshall
Marshall may refer to:
Places
Australia
* Marshall, Victoria, a suburb of Geelong, Victoria
Canada
* Marshall, Saskatchewan
* The Marshall, a mountain in British Columbia
Liberia
* Marshall, Liberia
Marshall Islands
* Marshall Islands, an i ...
* Mills River
The Mills River is located in Transylvania and Henderson counties, North Carolina, United States is a tributary of the French Broad River. The river flows out of the Pisgah Ranger District of the Pisgah National Forest in two forks: the North F ...
* Montreat
* Murphy
Murphy () ( ga, Ua Murchadha) is an Irish surname and the most common surname in the Republic of Ireland.
Origins and variants
The surname is a variant of two Irish surnames: "Ó Murchadha"/"Ó Murchadh" (descendant of "Murchadh"), and "Mac ...
* Newland
* North Wilkesboro
North Wilkesboro is a town in Wilkes County, North Carolina, United States, approximately 80 miles north of Charlotte. The population was 4,131 at the 2020 US Census. North Wilkesboro is the birthplace and original home of Lowe's Home Improvemen ...
* Old Fort
* Rhodhiss
* Robbinsville
* Ronda
Ronda () is a town in the Spanish province of Málaga. It is located about west of the city of Málaga, within the autonomous community of Andalusia. Its population is about 35,000. Ronda is known for its cliff-side location and a deep chasm ...
* Rosman
* Ruth
Ruth (or its variants) may refer to:
Places
France
* Château de Ruthie, castle in the commune of Aussurucq in the Pyrénées-Atlantiques département of France
Switzerland
* Ruth, a hamlet in Cologny
United States
* Ruth, Alabama
* Ruth, Arka ...
* Rutherford College
* Rutherfordton
* Saluda
* Sawmills
A sawmill (saw mill, saw-mill) or lumber mill is a facility where logs are cut into lumber. Modern sawmills use a motorized saw to cut logs lengthwise to make long pieces, and crosswise to length depending on standard or custom sizes (dimensi ...
* Seven Devils
Seven Devils is a solitaire game in the style of Canfield played with two decks of playing cards. It is considered to be a very difficult solitaire game.Thomas WarfieldThe 4 Solitaire Games You Should Win Before You Die 24 March 2015.
Rul ...
* Sparta
Sparta ( Doric Greek: Σπάρτα, ''Spártā''; Attic Greek: Σπάρτη, ''Spártē'') was a prominent city-state in Laconia, in ancient Greece. In antiquity, the city-state was known as Lacedaemon (, ), while the name Sparta referre ...
* Spindale
* Spruce Pine
* Sugar Mountain
* Sylva
* Tryon
* Valdese
* Weaverville
* Webster
Webster may refer to:
People
*Webster (surname), including a list of people with the surname
*Webster (given name), including a list of people with the given name
Places Canada
*Webster, Alberta
*Webster's Falls, Hamilton, Ontario
United State ...
* West Jefferson
* Wilkesboro
* Woodfin
Important unincorporated communities
* Brasstown (site ofJohn C. Campbell Folk School
The John C. Campbell Folk School, also referred to as "The Folk School", is located in Brasstown, North Carolina, along the Cherokee County and Clay line. It is a non-profit adult educational organization based on non-competitive learning. Origin ...
)
* Cashiers
Cashiers is a census-designated place (CDP) and unincorporated village located in southern Jackson County, North Carolina, United States. As of the 2020 United States census, the community had a total population of 657, up from 157 at the 2010 c ...
(a popular tourist area)
* Cherokee
The Cherokee (; chr, ᎠᏂᏴᏫᏯᎢ, translit=Aniyvwiyaʔi or Anigiduwagi, or chr, ᏣᎳᎩ, links=no, translit=Tsalagi) are one of the indigenous peoples of the Southeastern Woodlands of the United States. Prior to the 18th century, t ...
(headquarters for the Eastern Band of the Cherokee
The Eastern Band of Cherokee Indians (EBCI), (Cherokee: ᏣᎳᎩᏱ ᏕᏣᏓᏂᎸᎩ, ''Tsalagiyi Detsadanilvgi'') is a federally recognized Indian Tribe based in Western North Carolina in the United States. They are descended from the smal ...
)
* Collettsville (located near Wilson Creek)
* Cullowhee
Cullowhee
, from the North Carolina Collection website at the (site of
, from the North Carolina Collection website at the (site of
Western Carolina University
Western Carolina University (WCU) is a public university in Cullowhee, North Carolina. It is part of the University of North Carolina system.
The fifth oldest institution of the sixteen four-year universities in the UNC system, WCU was founded t ...
's main campus)
* Deals Gap
Deals (previously stylized as ''DEAL$'') was an American chain of discount variety stores owned by Dollar Tree. The chain operated more than 221 stores located in shopping centers, malls (until 2015), and urban areas in 19 states throughout the U ...
(site of a nationally famous motorcycle and sportscar resort)
* Lake Junaluska
Lake Junaluska is a census-designated place (CDP) in Haywood County, North Carolina, United States, and a manmade lake in the Blue Ridge Mountains. It is part of the Asheville Metropolitan Statistical Area.
Lake Junaluska is named after nearby ...
(headquarters for the World Methodist Council
The World Methodist Council (WMC), founded in 1881, is a consultative body and association of churches in the Methodist tradition. It comprises 80 member denominations in 138 countries which together represent an estimated 80 million people; this ...
and site of a United Methodist
The United Methodist Church (UMC) is a worldwide mainline Protestant denomination based in the United States, and a major part of Methodism. In the 19th century, its main predecessor, the Methodist Episcopal Church, was a leader in evangelic ...
camp and conference center)
* Linville (a popular recreation area)
* Little Switzerland (located near Blue Ridge Parkway
The Blue Ridge Parkway is a National Parkway and All-American Road in the United States, noted for its scenic beauty. The parkway, which is America's longest linear park, runs for through 29 Virginia and North Carolina counties, linking Shenand ...
)
See also
* 828 area code *Appalachia
Appalachia () is a cultural region in the Eastern United States that stretches from the Southern Tier of New York State to northern Alabama and Georgia. While the Appalachian Mountains stretch from Belle Isle in Newfoundland and Labrador, Ca ...
* East Tennessee
East Tennessee is one of the three Grand Divisions of Tennessee defined in state law. Geographically and socioculturally distinct, it comprises approximately the eastern third of the U.S. state of Tennessee. East Tennessee consists of 33 count ...
* Geography of North Carolina
The geography of North Carolina falls naturally into three divisions — the Appalachian Mountains in the west (including the Blue Ridge and Great Smoky Mountains), the central Piedmont Plateau, and the eastern Atlantic Coastal Plain. North Caro ...
* North Carolina's 11th congressional district
North Carolina's 11th congressional district encompasses most of Western North Carolina. Since January 3, 2021, the district has been represented by Madison Cawthorn.
Redistricting
The 11th district has historically been known for its volat ...
* Piedmont Triad
The Piedmont Triad (or simply the Triad) is a metropolitan region in the north-central part of the U.S. state of North Carolina anchored by three cities: Greensboro, North Carolina, Greensboro, Winston-Salem, North Carolina, Winston-Salem, and H ...
References
External links
* {{Use mdy dates, date=December 2018 Geography of Appalachia Regions of North Carolina State of Franklin