Flanders (, ;
Dutch
Dutch commonly refers to:
* Something of, from, or related to the Netherlands
* Dutch people ()
* Dutch language ()
Dutch may also refer to:
Places
* Dutch, West Virginia, a community in the United States
* Pennsylvania Dutch Country
People E ...
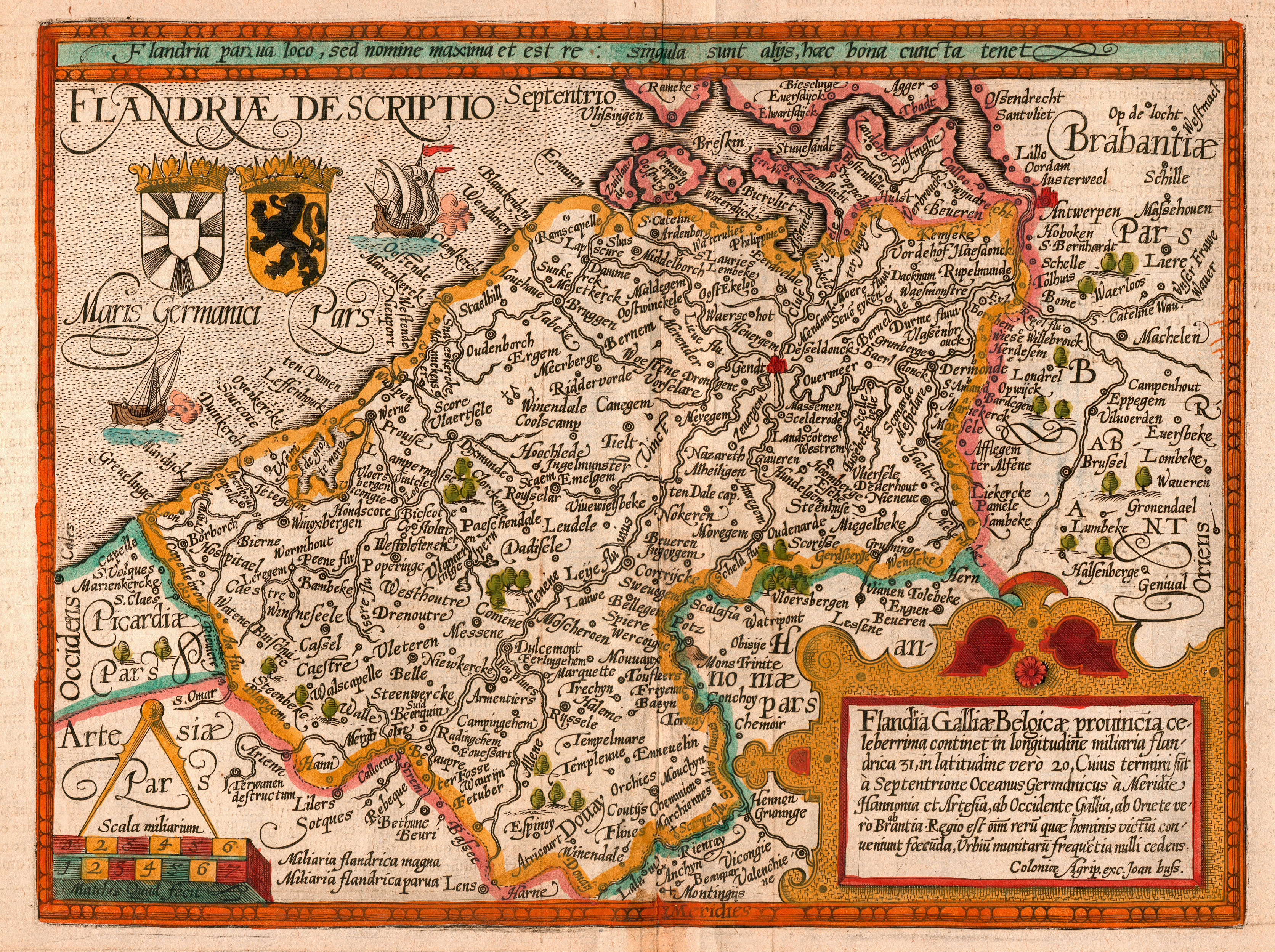
: ''Vlaanderen'' ) is the
Flemish
Flemish (''Vlaams'') is a Low Franconian dialect cluster of the Dutch language. It is sometimes referred to as Flemish Dutch (), Belgian Dutch ( ), or Southern Dutch (). Flemish is native to Flanders, a historical region in northern Belgium; ...
-speaking northern portion of
Belgium
Belgium, ; french: Belgique ; german: Belgien officially the Kingdom of Belgium, is a country in Northwestern Europe. The country is bordered by the Netherlands to the north, Germany to the east, Luxembourg to the southeast, France to th ...
and one of the
communities, regions and language areas of Belgium
Belgium is a federal state comprising three communities and three regions that are based on four language areas. For each of these subdivision types, the subdivisions together make up the entire country; in other words, the types overlap.
The la ...
. However, there are several overlapping definitions, including ones related to culture, language, politics, and history, and sometimes involving neighbouring countries. The
demonym
A demonym (; ) or gentilic () is a word that identifies a group of people (inhabitants, residents, natives) in relation to a particular place. Demonyms are usually derived from the name of the place (hamlet, village, town, city, region, province, ...
associated with Flanders is
Fleming, while the corresponding adjective is
Flemish
Flemish (''Vlaams'') is a Low Franconian dialect cluster of the Dutch language. It is sometimes referred to as Flemish Dutch (), Belgian Dutch ( ), or Southern Dutch (). Flemish is native to Flanders, a historical region in northern Belgium; ...
. The official capital of Flanders is the
City of Brussels
The City of Brussels (french: Ville de Bruxelles or alternatively ''Bruxelles-Ville'' ; nl, Stad Brussel or ''Brussel-Stad'') is the largest municipality and historical City centre, centre of the Brussels, Brussels-Capital Region, as well a ...
, although the
Brussels-Capital Region
Brussels (french: Bruxelles or ; nl, Brussel ), officially the Brussels-Capital Region (All text and all but one graphic show the English name as Brussels-Capital Region.) (french: link=no, Région de Bruxelles-Capitale; nl, link=no, Bruss ...
that includes it has an independent regional government. The powers of the government of Flanders consist, among others, of economic affairs in the
Flemish Region
The Flemish Region ( nl, Vlaams Gewest, ),; german: Flämische Region usually simply referred to as Flanders ( nl, link=no, Vlaanderen ) ; german: link=no, Flandern is one of the three regions of Belgium—alongside the Walloon Region and t ...
and the community aspects of Flanders life in Brussels, such as Flemish culture and education.
Geographically, Flanders is mainly flat, and has a small section of coast on the
North Sea
The North Sea lies between Great Britain, Norway, Denmark, Germany, the Netherlands and Belgium. An epeiric sea on the European continental shelf, it connects to the Atlantic Ocean through the English Channel in the south and the Norwegian S ...
. It borders the
French department
In the administrative divisions of France, the department (french: département, ) is one of the three levels of government under the national level ("territorial collectivities"), between the administrative regions and the communes. Ninety-s ...
of
Nord
Nord, a word meaning "north" in several European languages, may refer to:
Acronyms
* National Organization for Rare Disorders, an American nonprofit organization
* New Orleans Recreation Department, New Orleans, Louisiana, US
Film and televisi ...
to the south-west near the coast, the Dutch provinces of
Zeeland
, nl, Ik worstel en kom boven("I struggle and emerge")
, anthem = "Zeeuws volkslied"("Zeelandic Anthem")
, image_map = Zeeland in the Netherlands.svg
, map_alt =
, m ...
,
North Brabant
North Brabant ( nl, Noord-Brabant ; Brabantian: ; ), also unofficially called Brabant, is a province in the south of the Netherlands. It borders the provinces of South Holland and Gelderland to the north, Limburg to the east, Zeeland to the we ...
and
Limburg
Limburg or Limbourg may refer to:
Regions
* Limburg (Belgium), a province since 1839 in the Flanders region of Belgium
* Limburg (Netherlands), a province since 1839 in the south of the Netherlands
* Diocese of Limburg, Roman Catholic Diocese in ...
to the north and east, and the
Walloon provinces of
Hainaut,
Walloon Brabant
Walloon Brabant (french: Brabant wallon ; nl, Waals-Brabant ; wa, Roman Payis) is a province located in Belgium's French-speaking region of Wallonia. It borders on (clockwise from the North) the province of Flemish Brabant (Flemish Region) and ...
and
Liège
Liège ( , , ; wa, Lîdje ; nl, Luik ; german: Lüttich ) is a major city and municipality of Wallonia and the capital of the Belgian province of Liège.
The city is situated in the valley of the Meuse, in the east of Belgium, not far from b ...
to the south. Despite accounting for only 45% of Belgium's territory, it holds the country's largest population, with 6,653,062 (or 57%) out of 11,431,406 Belgian inhabitants living there. Much of Flanders is agriculturally fertile and densely populated at . The Brussels Region is an officially bilingual
enclave
An enclave is a territory (or a small territory apart of a larger one) that is entirely surrounded by the territory of one other state or entity. Enclaves may also exist within territorial waters. ''Enclave'' is sometimes used improperly to deno ...
within the Flemish Region. Flanders also has exclaves of its own:
Voeren
Voeren (; ) is a Flanders, Flemish Dutch language, Dutch-speaking Municipalities of Belgium, municipality with Municipalities with language facilities, facilities for the Walloons, French-speaking minority, located in the Belgium, Belgian provi ...
in the east is between Wallonia and the Netherlands and
Baarle-Hertog
(; french: Baerle-Duc, ) is a Flemish municipality of Belgium, much of which consists of a number of small Belgian enclaves fully surrounded by the Netherlands.
Parts of are surrounded by the Dutch province of North Brabant, but it is part of t ...
in the north consists of 22 exclaves surrounded by the Netherlands. Not including Brussels, there are five present-day
Flemish provinces:
Antwerp
Antwerp (; nl, Antwerpen ; french: Anvers ; es, Amberes) is the largest city in Belgium by area at and the capital of Antwerp Province in the Flemish Region. With a population of 520,504, ,
East Flanders
, native_name_lang =
, settlement_type = Province of Belgium
, image_flag = Flag of Oost-Vlaanderen.svg
, flag_size =
, image_shield = Wapen van O ...
,
Flemish Brabant
Flemish Brabant ( nl, Vlaams-Brabant ; french: Brabant flamand ) is a province of Flanders, one of the three regions of Belgium. It borders on (clockwise from the North) the Belgian provinces of Antwerp, Limburg, Liège, Walloon Brabant, Haina ...
,
Limburg
Limburg or Limbourg may refer to:
Regions
* Limburg (Belgium), a province since 1839 in the Flanders region of Belgium
* Limburg (Netherlands), a province since 1839 in the south of the Netherlands
* Diocese of Limburg, Roman Catholic Diocese in ...
and
West Flanders
)
, settlement_type = Province of Belgium
, image_flag = Flag of West Flanders.svg
, flag_size =
, image_shield = Wapen van West-Vlaanderen.svg
, shield_size =
, image_map ...
. The official language is Dutch. Other recognised languages are French and German.
The area of today's Flanders has figured prominently in European history since the
Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire a ...
. The original
County of Flanders
The County of Flanders was a historic territory in the Low Countries.
From 862 onwards, the counts of Flanders were among the original twelve peers of the Kingdom of France. For centuries, their estates around the cities of Ghent, Bruges and Ypr ...
stretched around AD 900 from the
Strait of Dover
The Strait of Dover or Dover Strait (french: Pas de Calais - ''Strait of Calais''), is the strait at the narrowest part of the English Channel, marking the boundary between the Channel and the North Sea, separating Great Britain from continent ...
to the
Scheldt
The Scheldt (french: Escaut ; nl, Schelde ) is a river that flows through northern France, western Belgium, and the southwestern part of Netherlands, the Netherlands, with its mouth at the North Sea. Its name is derived from an adjective corr ...
estuary
An estuary is a partially enclosed coastal body of brackish water with one or more rivers or streams flowing into it, and with a free connection to the open sea. Estuaries form a transition zone between river environments and maritime environment ...
and expanded from there. This county also still corresponds roughly with the modern-day Belgian provinces of West Flanders and East Flanders, along with neighbouring parts of France and the Netherlands. In this period, cities such as
Ghent
Ghent ( nl, Gent ; french: Gand ; traditional English: Gaunt) is a city and a municipality in the Flemish Region of Belgium. It is the capital and largest city of the East Flanders province, and the third largest in the country, exceeded in ...
and
Bruges
Bruges ( , nl, Brugge ) is the capital and largest City status in Belgium, city of the Provinces of Belgium, province of West Flanders in the Flemish Region of Belgium, in the northwest of the country, and the sixth-largest city of the countr ...
of the historic County of Flanders, and later
Antwerp
Antwerp (; nl, Antwerpen ; french: Anvers ; es, Amberes) is the largest city in Belgium by area at and the capital of Antwerp Province in the Flemish Region. With a population of 520,504, of the
Duchy of Brabant
The Duchy of Brabant was a State of the Holy Roman Empire established in 1183. It developed from the Landgraviate of Brabant and formed the heart of the historic Low Countries, part of the Burgundian Netherlands from 1430 and of the Habsburg Neth ...
made it one of the richest and most urbanised parts of Europe, trading, and weaving the
wool
Wool is the textile fibre obtained from sheep and other mammals, especially goats, rabbits, and camelids. The term may also refer to inorganic materials, such as mineral wool and glass wool, that have properties similar to animal wool.
As ...
of neighbouring lands into cloth for both domestic use and export. As a consequence, a very sophisticated culture developed, with impressive achievements in the arts and architecture, rivaling those of
northern Italy
Northern Italy ( it, Italia settentrionale, it, Nord Italia, label=none, it, Alta Italia, label=none or just it, Nord, label=none) is a geographical and cultural region in the northern part of Italy. It consists of eight administrative regions ...
.
Belgium was one of the centres of the 19th-century
Industrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution was the transition to new manufacturing processes in Great Britain, continental Europe, and the United States, that occurred during the period from around 1760 to about 1820–1840. This transition included going f ...
, but Flanders was at first overtaken by French-speaking Wallonia. In the second half of the 20th century, and due to massive national investments in port infrastructure, Flanders' economy modernised rapidly, and today Flanders and Brussels are much wealthier than Wallonia, being among the wealthiest regions in Europe and the world. In accordance with late 20th century
Belgian state reforms, Flanders was made into two political entities: the Flemish Region ( nl, link=no, Vlaams Gewest) and the
Flemish Community
The Flemish Community ( nl, Vlaamse Gemeenschap ; french: Communauté flamande ; german: Flämische Gemeinschaft ) is one of the three institutional communities of Belgium, established by the Belgian constitution and having legal responsibilitie ...
( nl, link=no, Vlaamse Gemeenschap). These entities were merged, although geographically the Flemish Community, which has a broader cultural mandate, covers Brussels, whereas the Flemish Region does not.
Terminology
Modern Belgium
The term "Flanders" has several main modern meanings:
* The "Flemish community" or "Flemish nation", i.e. the social, cultural and linguistic, scientific and educational, economical and political community of the
Flemings
The Flemish or Flemings ( nl, Vlamingen ) are a Germanic ethnic group native to Flanders, Belgium, who speak Dutch. Flemish people make up the majority of Belgians, at about 60%.
"''Flemish''" was historically a geographical term, as all inha ...
. It comprises 6.5 million Belgians (60%) who consider Dutch to be their mother tongue.
* The political subdivisions of Belgium: the
Flemish Region
The Flemish Region ( nl, Vlaams Gewest, ),; german: Flämische Region usually simply referred to as Flanders ( nl, link=no, Vlaanderen ) ; german: link=no, Flandern is one of the three regions of Belgium—alongside the Walloon Region and t ...
(competent in mainly economic matters) and the
Flemish Community
The Flemish Community ( nl, Vlaamse Gemeenschap ; french: Communauté flamande ; german: Flämische Gemeinschaft ) is one of the three institutional communities of Belgium, established by the Belgian constitution and having legal responsibilitie ...
(competent in mainly cultural matters). The first does not comprise Brussels (which forms a
Region by itself), whereas the latter does comprise the Dutch-speaking inhabitants of Brussels.
* The political institutions that govern both subdivisions: the operative body "
Flemish Government
The Flemish Government ( nl, Vlaamse regering ) is the executive branch of the Flemish Community and the Flemish Region of Belgium. It consists of a government cabinet, headed by the Minister-President and accountable to the Flemish Parliament, a ...
" and the legislative organ "
Flemish Parliament
The Flemish Parliament (Dutch: , formerly called Flemish Council or ''Vlaamse Raad'') constitutes the legislative power in Flanders for matters which fall within the competence of Flanders, both as a geographic region and as a cultural communi ...
".
* Within Belgian discussions, the two westernmost provinces of the Flemish Region,
West Flanders
)
, settlement_type = Province of Belgium
, image_flag = Flag of West Flanders.svg
, flag_size =
, image_shield = Wapen van West-Vlaanderen.svg
, shield_size =
, image_map ...
and
East Flanders
, native_name_lang =
, settlement_type = Province of Belgium
, image_flag = Flag of Oost-Vlaanderen.svg
, flag_size =
, image_shield = Wapen van O ...
, forming the central portion of the historic
County of Flanders
The County of Flanders was a historic territory in the Low Countries.
From 862 onwards, the counts of Flanders were among the original twelve peers of the Kingdom of France. For centuries, their estates around the cities of Ghent, Bruges and Ypr ...
.
Historical
The name originally applied to the ''
ancien régime
''Ancien'' may refer to
* the French word for "ancient, old"
** Société des anciens textes français
* the French for "former, senior"
** Virelai ancien
** Ancien Régime
** Ancien Régime in France
{{disambig ...
'' territory called the
County of Flanders
The County of Flanders was a historic territory in the Low Countries.
From 862 onwards, the counts of Flanders were among the original twelve peers of the Kingdom of France. For centuries, their estates around the cities of Ghent, Bruges and Ypr ...
, that existed from the 8th century (Latin ''Flandria'') until its absorption by the
French First Republic
In the history of France, the First Republic (french: Première République), sometimes referred to in historiography as Revolutionary France, and officially the French Republic (french: République française), was founded on 21 September 1792 ...
. Until the 1600s, this county also extended over parts of what are now France and the Netherlands.
* In France, one of the historically Flemish regions is now in the
Nord department. This is referred to as
French Flanders
French Flanders (french: La Flandre française) is a part of the historical County of Flanders in present-day France where a dialect of Dutch was or still is traditionally spoken. The region lies in the modern-day region of Hauts-de-France and r ...
, and can be divided into two smaller regions:
Walloon Flanders
Walloon Flanders (Dutch: ''Waals Vlaanderen'', French: ''Flandre wallonne'') was a semi-independent part of the County of Flanders, composed of the Burgrave, burgraviates of Lille, Douai and Orchies. It is sometimes referred to as ''Lille–Douai ...
and
Maritime Flanders (Westhoek). The first region was predominantly French-speaking already in the 1600s, the latter became so in the 20th century. The
city of Lille identifies itself as "Flemish", and this is reflected, for instance, in the name of its local railway station
TGV
The TGV (french: Train à Grande Vitesse, "high-speed train"; previously french: TurboTrain à Grande Vitesse, label=none) is France's intercity high-speed rail service, operated by SNCF. SNCF worked on a high-speed rail network from 1966 to 19 ...
''
Lille Flandres
Lille-Flandres station ( French: ''Gare de Lille-Flandres'', Dutch: ''Rijsel Vlaanderen'') is the main railway station of Lille, capital of French Flanders. It is a terminus for SNCF Intercity and regional trains. It opened in 1842 as the ''Gare ...
''.
* The historically Flemish region which became part of the
Dutch Republic
The United Provinces of the Netherlands, also known as the (Seven) United Provinces, officially as the Republic of the Seven United Netherlands (Dutch: ''Republiek der Zeven Verenigde Nederlanden''), and commonly referred to in historiography ...
, now part of the Dutch province of
Zeeland
, nl, Ik worstel en kom boven("I struggle and emerge")
, anthem = "Zeeuws volkslied"("Zeelandic Anthem")
, image_map = Zeeland in the Netherlands.svg
, map_alt =
, m ...
, sometimes called
Zeelandic Flanders
Zeelandic Flanders ( ; zea, Zeêuws-Vlaonderen; vls, Zêeuws-Vloandern)''Vlaanderen'' in isolation: . is the southernmost region of the province of Zeeland in the south-western Netherlands. It lies south of the Western Scheldt that separates t ...
.
Especially in international discussions, the significance of the County of Flanders and its
counts
Count (feminine: countess) is a historical title of nobility in certain European countries, varying in relative status, generally of middling rank in the hierarchy of nobility.L. G. Pine, Pine, L. G. ''Titles: How the King Became His Majesty'' ...
eroded over time, but the designation was used for a bigger territory. "Flanders" (and Latin "Belgium") were the first two common names used for the
Burgundian Netherlands
In the history of the Low Countries, the Burgundian Netherlands (french: Pays-Bas bourguignons, nl, Bourgondische Nederlanden, lb, Burgundeschen Nidderlanden, wa, Bas Payis borguignons) or the Burgundian Age is the period between 1384 and ...
. With the breakaway of the northern Netherlands in the
Early modern period, the term Flanders continued to be associated with the whole southern part of the
Low Countries
The term Low Countries, also known as the Low Lands ( nl, de Lage Landen, french: les Pays-Bas, lb, déi Niddereg Lännereien) and historically called the Netherlands ( nl, de Nederlanden), Flanders, or Belgica, is a coastal lowland region in N ...
― the
Southern
Southern may refer to:
Businesses
* China Southern Airlines, airline based in Guangzhou, China
* Southern Airways, defunct US airline
* Southern Air, air cargo transportation company based in Norwalk, Connecticut, US
* Southern Airways Express, M ...
,
Spanish
Spanish might refer to:
* Items from or related to Spain:
**Spaniards are a nation and ethnic group indigenous to Spain
**Spanish language, spoken in Spain and many Latin American countries
**Spanish cuisine
Other places
* Spanish, Ontario, Cana ...
or
Austrian Netherlands
The Austrian Netherlands nl, Oostenrijkse Nederlanden; french: Pays-Bas Autrichiens; german: Österreichische Niederlande; la, Belgium Austriacum. was the territory of the Burgundian Circle of the Holy Roman Empire between 1714 and 1797. The p ...
, which were the successors of the Burgundian state, and predecessors of modern Belgium.
Dutch-speaking part of Belgium
During the 19th and 20th centuries, it became increasingly common to refer more specifically to the Dutch-speaking part of Belgium as "Flanders". The linguistic limit between French and Dutch was recorded in the early '60s, from
Kortrijk
Kortrijk ( , ; vls, Kortryk or ''Kortrik''; french: Courtrai ; la, Cortoriacum), sometimes known in English as Courtrai or Courtray ( ), is a Belgian City status in Belgium, city and Municipalities in Belgium, municipality in the Flemish Regio ...
to
Maastricht
Maastricht ( , , ; li, Mestreech ; french: Maestricht ; es, Mastrique ) is a city and a municipality in the southeastern Netherlands. It is the capital and largest city of the province of Limburg. Maastricht is located on both sides of the ...
. Now, Flanders extends over the northern part of Belgium, including not only the Dutch-speaking Belgian parts of the medieval
Duchy of Brabant
The Duchy of Brabant was a State of the Holy Roman Empire established in 1183. It developed from the Landgraviate of Brabant and formed the heart of the historic Low Countries, part of the Burgundian Netherlands from 1430 and of the Habsburg Neth ...
, which was united with Flanders since the Middle Ages, but also
Belgian Limburg
Limburg ( nl, Limburg, ; li, Limburg or ''Wes-Limburg'' ; french: Limbourg, ) is a province in Belgium. It is the easternmost of the five Dutch-speaking provinces that together form the Region of Flanders, one of the three main political and c ...
, which corresponds closely to the medieval
County of Loon
The County of Loon ( , , ) was a county in the Holy Roman Empire, which corresponded approximately with the Belgian province of Limburg. It was named after the original seat of its count, Loon, which is today called Borgloon. During the middle ag ...
, which was never under Burgundian control.
The ambiguity between this wider cultural area and that of the County or Province still remains in discussions about the region. In most present-day contexts, however, the term Flanders is taken to refer to either the political, social, cultural, and linguistic community (and the corresponding official institution, the
Flemish Community
The Flemish Community ( nl, Vlaamse Gemeenschap ; french: Communauté flamande ; german: Flämische Gemeinschaft ) is one of the three institutional communities of Belgium, established by the Belgian constitution and having legal responsibilitie ...
), or the geographical area, one of the three institutional regions in Belgium, namely the
Flemish Region
The Flemish Region ( nl, Vlaams Gewest, ),; german: Flämische Region usually simply referred to as Flanders ( nl, link=no, Vlaanderen ) ; german: link=no, Flandern is one of the three regions of Belgium—alongside the Walloon Region and t ...
.
In the
history of art
The history of art focuses on objects made by humans for any number of spiritual, narrative, philosophical, symbolic, conceptual, documentary, decorative, and even functional and other purposes, but with a primary emphasis on its aesthetic vis ...
and other fields, the adjectives Flemish and
Netherlandish
The Low Countries comprise the coastal Rhine–Meuse–Scheldt delta region in Western Europe, whose definition usually includes the modern countries of Luxembourg, Belgium and the Netherlands. Both Belgium and the Netherlands derived their ...
are commonly used to designate all the artistic production in this area before about 1580, after which it refers specifically to the southern Netherlands. For example, the term "Flemish Primitives", now outdated in English but used in French, Dutch and other languages, is a synonym for "
Early Netherlandish painting
Early Netherlandish painting, traditionally known as the Flemish Primitives, refers to the work of artists active in the Burgundian and Habsburg Netherlands during the 15th- and 16th-century Northern Renaissance period. It flourished especiall ...
", and it is not uncommon to see
Mosan art
Mosan art is a regional style of art from the valley of the Meuse in present-day Belgium, the Netherlands, and Germany. Although in a broader sense the term applies to art from this region from all periods, it generally refers to Romanesque ar ...
categorized as Flemish art. In music the ''
Franco-Flemish School
The designation Franco-Flemish School, also called Netherlandish School, Burgundian School, Low Countries School, Flemish School, Dutch School, or Northern School, refers, somewhat imprecisely, to the style of polyphonic vocal music composition or ...
'' is also known as the ''Dutch School''.
Within this Dutch-speaking part of Belgium, French has never ceased to be spoken by some citizens and Jewish groups have been speaking
Yiddish
Yiddish (, or , ''yidish'' or ''idish'', , ; , ''Yidish-Taytsh'', ) is a West Germanic language historically spoken by Ashkenazi Jews. It originated during the 9th century in Central Europe, providing the nascent Ashkenazi community with a ver ...
in Antwerp for centuries. Today, Flanders's minority residents include 170 nationalities—the largest groups speaking French, English,
Berber
Berber or Berbers may refer to:
Ethnic group
* Berbers, an ethnic group native to Northern Africa
* Berber languages, a family of Afro-Asiatic languages
Places
* Berber, Sudan, a town on the Nile
People with the surname
* Ady Berber (1913–196 ...
,
Turkish
Turkish may refer to:
*a Turkic language spoken by the Turks
* of or about Turkey
** Turkish language
*** Turkish alphabet
** Turkish people, a Turkic ethnic group and nation
*** Turkish citizen, a citizen of Turkey
*** Turkish communities and mi ...
,
Arabic
Arabic (, ' ; , ' or ) is a Semitic languages, Semitic language spoken primarily across the Arab world.Semitic languages: an international handbook / edited by Stefan Weninger; in collaboration with Geoffrey Khan, Michael P. Streck, Janet C ...
, Spanish, Italian and
Polish
Polish may refer to:
* Anything from or related to Poland, a country in Europe
* Polish language
* Poles, people from Poland or of Polish descent
* Polish chicken
*Polish brothers (Mark Polish and Michael Polish, born 1970), American twin screenwr ...
.
History
Early history
When
Julius Caesar
Gaius Julius Caesar (; ; 12 July 100 BC – 15 March 44 BC), was a Roman general and statesman. A member of the First Triumvirate, Caesar led the Roman armies in the Gallic Wars before defeating his political rival Pompey in a civil war, and ...
conquered the area he described it as the less economically developed and more warlike part of ''
Gallia Belgica
Gallia Belgica ("Belgic Gaul") was a province of the Roman Empire located in the north-eastern part of Roman Gaul, in what is today primarily northern France, Belgium, and Luxembourg, along with parts of the Netherlands and Germany.
In 50 BC, af ...
''. His informants told him that especially in the east, the tribes claimed ancestral connections and kinship with the
"Germanic" peoples then east of the
Rhine
), Surselva, Graubünden, Switzerland
, source1_coordinates=
, source1_elevation =
, source2 = Rein Posteriur/Hinterrhein
, source2_location = Paradies Glacier, Graubünden, Switzerland
, source2_coordinates=
, so ...
. Under the
Roman empire
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, Βασιλεία τῶν Ῥωμαίων, Basileía tôn Rhōmaíōn) was the post-Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings around the Mediterr ...
the whole of ''Gallia Belgica'' became an administrative province. The future counties of Flanders and Brabant remained part of this province connected to what is now France, but in the east modern Limburg became part of the Rhine frontier province of ''
Germania Inferior
Germania Inferior ("Lower Germania") was a Roman province from AD 85 until the province was renamed Germania Secunda in the fourth century, on the west bank of the Rhine bordering the North Sea. The capital of the province was Colonia Agrippin ...
'' connected to what is now the Netherlands and Germany. ''Gallia Belgica'' and ''Germania Inferior'' were the two most northerly continental provinces of the
Roman empire
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, Βασιλεία τῶν Ῥωμαίων, Basileía tôn Rhōmaíōn) was the post-Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings around the Mediterr ...
.
In the future county of Flanders, the main
Belgic tribe
The Belgae () were a large confederation of tribes living in northern Gaul, between the English Channel, the west bank of the Rhine, and the northern bank of the river Seine, from at least the third century BC. They were discussed in depth by J ...
in early Roman times was the
Menapii
The Menapii were a Belgic tribe dwelling near the North Sea, around present-day Cassel, during the Iron Age and the Roman period.
Name Attestations
They are mentioned as ''Menapii'' by Caesar (mid-1st c. BC) and Orosius (early 5th c. AD), ...
, but also on the coast were the
Marsacii The Marsaci or Marsacii were a tribe in Roman imperial times, who lived within the area of the Rhine–Meuse–Scheldt delta, under Roman domination. (The river Meuse is the Maas in Dutch, and this name is also often used in English. In Latin sourc ...
and
Morini
The Morini (Gaulish: "sea folk, sailors") were a Belgic coastal tribe dwelling in the modern Pas de Calais region, around present-day Boulogne-sur-Mer, during the Iron Age and the Roman period.
Name
They are mentioned as ''Morini'' by Caesar ( ...
. In the central part of modern Belgium were the
Nervii
The Nervii were one of the most powerful Belgic tribes of northern Gaul at the time of its conquest by Rome. Their territory corresponds to the central part of modern Belgium, including Brussels, and stretched southwards into French Hainault. D ...
and in the east were the
Tungri
The Tungri (or Tongri, or Tungrians) were a tribe, or group of tribes, who lived in the Belgic part of Gaul, during the times of the Roman Empire. Within the Roman Empire, their territory was called the ''Civitas Tungrorum''. They were described by ...
. The Tungri especially were understood to have links to Germanic tribes east of the Rhine. Another notable Germanic group were the
Toxandrians
The Texandri (also Texuandri; later Toxandri, Toxiandri, Taxandri) were a Germanic people living between the Scheldt and Rhine rivers in the 1st century AD. They are associated with a region mentioned in the late 4th century as Texandria (also Toxi ...
who appear to have lived in the
Kempen region, in the northern parts of both the Nervian and Tungrian provinces, probably stretching into the modern Netherlands. The Roman administrative districts (''
civitates
In Ancient Rome, the Latin term (; plural ), according to Cicero in the time of the late Roman Republic, was the social body of the , or citizens, united by law (). It is the law that binds them together, giving them responsibilities () on th ...
'') of the Menapii, Nervii and Tungri therefore corresponded roughly with the medieval counties of Flanders, Brabant and
Loon
Loons (North American English) or divers (British / Irish English) are a group of aquatic birds found in much of North America and northern Eurasia. All living species of loons are members of the genus ''Gavia'', family Gaviidae and order Gavi ...
, and the modern Flemish provinces of East and West Flanders (Menapii), Brabant and Antwerp (the northern Nervii), and Belgian Limburg (Tungri). Brabant appears to have been home to relatively unpopulated forest area, the
Silva Carbonaria
Silva Carbonaria, the "charcoal forest", was the dense old-growth forest of beech and oak that formed a natural boundary during the Late Iron Age through Roman times into the Early Middle Ages across what is now western Wallonia. The Silva Carbon ...
, forming a natural boundary between northeast and southwest Belgium.
Linguistically, the tribes in this area were under
Celtic
Celtic, Celtics or Keltic may refer to:
Language and ethnicity
*pertaining to Celts, a collection of Indo-European peoples in Europe and Anatolia
**Celts (modern)
*Celtic languages
**Proto-Celtic language
* Celtic music
*Celtic nations
Sports Fo ...
influence in the south, and
Germanic influence in the east, but there is disagreement about what languages were spoken locally (apart from
Vulgar Latin
Vulgar Latin, also known as Popular or Colloquial Latin, is the range of non-formal Register (sociolinguistics), registers of Latin spoken from the Crisis of the Roman Republic, Late Roman Republic onward. Through time, Vulgar Latin would evolve ...
), and there may even have been an intermediate "
Nordwestblock
The Nordwestblock (German, "Northwest Block") is a hypothetical Northwestern European cultural region that some scholars propose as a prehistoric culture in the present-day Netherlands, Belgium, northern France, and northwestern Germany, in an ar ...
" language related to both. By the first century BC,
Germanic languages
The Germanic languages are a branch of the Indo-European language family spoken natively by a population of about 515 million people mainly in Europe, North America, Oceania and Southern Africa. The most widely spoken Germanic language, Engli ...
had become prevalent.
As Roman influence waned, Frankish populations settled east of the Silva Carbonaria, and eventually pushed through it under
Chlodio
Chlodio (probably died after 450), also Clodio, Clodius, Clodion, Cloio or Chlogio, was a Frankish king who attacked and then apparently ruled Roman-inhabited lands around Cambrai and Tournai, near the modern border of Belgium and France. He is k ...
. They had kings in each city (''civitas''). In the meantime, the Franks contributed to the Roman military. The first Merovingian king
Childeric I
Childeric I (; french: Childéric; la, Childericus; reconstructed Frankish: ''*Hildirīk''; – 481 AD) was a Frankish leader in the northern part of imperial Roman Gaul and a member of the Merovingian dynasty, described as a king (Latin ''rex ...
was king of the Franks in the military, who became leader of the administration of ''Belgica Secunda'', which included the ''civitas'' of the Menapii (the future county of Flanders). From there, his son
Clovis I
Clovis ( la, Chlodovechus; reconstructed Frankish: ; – 27 November 511) was the first king of the Franks to unite all of the Frankish tribes under one ruler, changing the form of leadership from a group of petty kings to rule by a single kin ...
managed to conquer both the Roman populations of northern France and the Frankish populations beyond the forest areas.
Historical Flanders
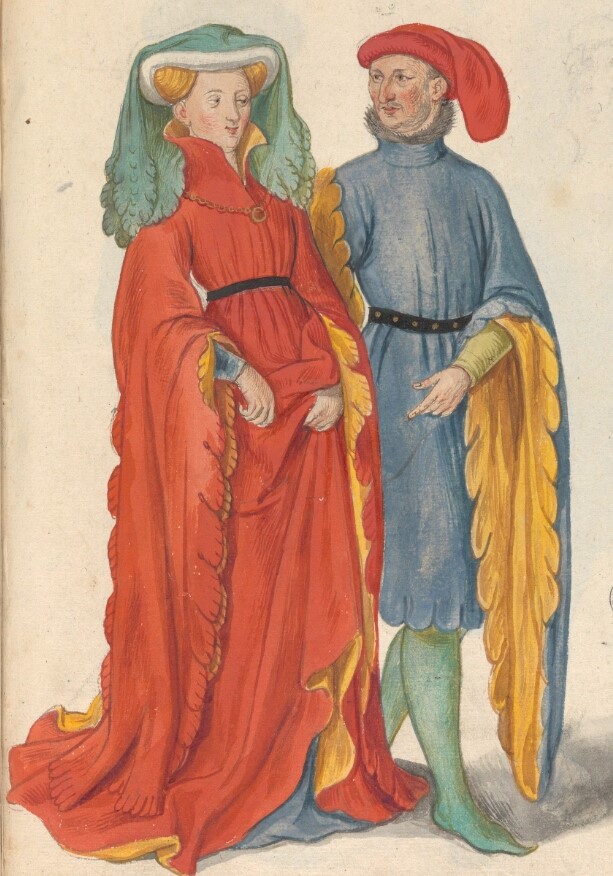

The County of Flanders was a
feudal
Feudalism, also known as the feudal system, was the combination of the legal, economic, military, cultural and political customs that flourished in Middle Ages, medieval Europe between the 9th and 15th centuries. Broadly defined, it was a wa ...
fief
A fief (; la, feudum) was a central element in medieval contracts based on feudal law. It consisted of a form of property holding or other rights granted by an Lord, overlord to a vassal, who held it in fealty or "in fee" in return for a for ...
in
West Francia
In medieval history, West Francia (Medieval Latin: ) or the Kingdom of the West Franks () refers to the western part of the Frankish Empire established by Charlemagne. It represents the earliest stage of the Kingdom of France, lasting from about ...
. The first certain Count in the comital family,
Baldwin I of Flanders
Baldwin I (probably 830s – 879), also known as Baldwin Iron Arm ( nl, Boudewijn met de IJzeren Arm; the epithet is first recorded in the 12th century), was the first margrave of Flanders, which evolved into the County of Flanders.
He was the ...
, is first reported in a document of 862, when he eloped with a daughter of his king
Charles the Bald
Charles the Bald (french: Charles le Chauve; 13 June 823 – 6 October 877), also known as Charles II, was a 9th-century king of West Francia (843–877), king of Italy (875–877) and emperor of the Carolingian Empire (875–877). After a ser ...
. The region developed as a medieval economic power with a large degree of political autonomy. While its trading cities remained strong, it was weakened and divided when districts fell under direct French royal rule in the late 12th century. The remaining parts of Flanders came under the rule of the counts of neighbouring imperial
Hainaut under
Baldwin V of Hainaut
Baldwin V of Hainaut (1150 – 17 December 1195) was count of Hainaut (1171–1195), margrave of Namur as Baldwin I (1189–1195) and count of Flanders as Baldwin VIII (1191–1195).
History
He was the son of Baldwin IV, Count of Hainaut. In the ...
in 1191.
During the late
Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire a ...
, Flanders's trading towns (notably
Ghent
Ghent ( nl, Gent ; french: Gand ; traditional English: Gaunt) is a city and a municipality in the Flemish Region of Belgium. It is the capital and largest city of the East Flanders province, and the third largest in the country, exceeded in ...
,
Bruges
Bruges ( , nl, Brugge ) is the capital and largest City status in Belgium, city of the Provinces of Belgium, province of West Flanders in the Flemish Region of Belgium, in the northwest of the country, and the sixth-largest city of the countr ...
and
Ypres
Ypres ( , ; nl, Ieper ; vls, Yper; german: Ypern ) is a Belgian city and municipality in the province of West Flanders. Though
the Dutch name is the official one, the city's French name is most commonly used in English. The municipality co ...
) made it one of the richest and most urbanized parts of Europe, weaving the
wool
Wool is the textile fibre obtained from sheep and other mammals, especially goats, rabbits, and camelids. The term may also refer to inorganic materials, such as mineral wool and glass wool, that have properties similar to animal wool.
As ...
of neighbouring lands into cloth for both domestic use and export. As a consequence, a sophisticated culture developed, with impressive art and architecture, rivaling those of northern Italy. Ghent, Bruges, Ypres and the
Franc of Bruges
The Brugse Vrije was a castellany in the county of Flanders, often called in English "the Franc of Bruges". It included the area around Bruges, and was bordered by the North Sea, the Westerschelde and the Yser river. The city of Bruges was separa ...
formed the
Four Members The Four members ( nl, Vier Leden) consisted of Bruges, Franc of Bruges, Ghent and Ypres gathered together in a medieval parliament. Together they exercised considerable power in Flanders.
During the Hundred Years' War, Jacob van Artevelde a prom ...
, a form of parliament that exercised considerable power in Flanders.
Increasingly powerful from the 12th century, the territory's autonomous urban
communes
An intentional community is a voluntary residential community which is designed to have a high degree of social cohesion and teamwork from the start. The members of an intentional community typically hold a common social, political, religious, ...
were instrumental in defeating a French attempt at annexation (1300–1302), finally defeating the French in the
Battle of the Golden Spurs
The Battle of the Golden Spurs ( nl, Guldensporenslag; french: Bataille des éperons d'or) was a military confrontation between the royal army of France and rebellious forces of the County of Flanders on 11 July 1302 during the Franco-Flemis ...
(11 July 1302), near
Kortrijk
Kortrijk ( , ; vls, Kortryk or ''Kortrik''; french: Courtrai ; la, Cortoriacum), sometimes known in English as Courtrai or Courtray ( ), is a Belgian City status in Belgium, city and Municipalities in Belgium, municipality in the Flemish Regio ...
. Two years later, the
uprising was defeated and Flanders indirectly remained part of the French Crown. Flemish prosperity waned in the following century, due to widespread European population decline following the
Black Death
The Black Death (also known as the Pestilence, the Great Mortality or the Plague) was a bubonic plague pandemic occurring in Western Eurasia and North Africa from 1346 to 1353. It is the most fatal pandemic recorded in human history, causi ...
of 1348, the disruption of trade during the Anglo-French
Hundred Years' War
The Hundred Years' War (; 1337–1453) was a series of armed conflicts between the kingdoms of Kingdom of England, England and Kingdom of France, France during the Late Middle Ages. It originated from disputed claims to the French Crown, ...
(1337–1453), and increased English cloth production. Flemish weavers had gone over to
Worstead
Worstead is a village and civil parish in the English county of Norfolk. It lies south of North Walsham, north of Wroxham, and north of Norwich. The village is served by Worstead railway station on the Bittern Line. For the purposes of local ...
and
North Walsham
North Walsham is a market town and civil parish in Norfolk, England, within the North Norfolk district.
Demography
The civil parish has an area of and in the 2011 census had a population of 12,634. For the purposes of local government, the pa ...
in Norfolk in the 12th century and established the woolen industry.
The County of Flanders started to take control of the neighbouring
County of Brabant
The Landgraviate of Brabant (1085–1183) was a small medieval fiefdom west of Brussels, consisting of the area between the Dender and Zenne rivers in the Low Countries, then part of the Holy Roman Empire.
Before 1085 the land had belonged ...
during the life of
Louis II, Count of Flanders
Louis II ( nl, Lodewijk van Male; french: Louis II de Flandre) (25 October 1330, Male – 30 January 1384, Lille), also known as Louis of Male, a member of the House of Dampierre, was Count of Flanders, Nevers and Rethel from 1346 as well as ...
(1330-1384), who fought his sister-in-law
Joanna, Duchess of Brabant
Joanna, Duchess of Brabant (24 June 1322 – 1 December 1406), also known as Jeanne, was a ruling Duchess (Duke) of Brabant from 1355 until her death. She was duchess of Brabant until the occupation of the duchy by her brother-in-law Louis II of ...
for control of it.
The entire area, straddling the ancient boundary of France and the Holy Roman Empire, later passed to
Philip the Bold
Philip II the Bold (; ; 17 January 1342 – 27 April 1404) was Duke of Burgundy and '' jure uxoris'' Count of Flanders, Artois and Burgundy. He was the fourth and youngest son of King John II of France and Bonne of Luxembourg.
Philip II was ...
in 1384, the
Duke of Burgundy
Duke of Burgundy (french: duc de Bourgogne) was a title used by the rulers of the Duchy of Burgundy, from its establishment in 843 to its annexation by France in 1477, and later by Holy Roman Emperors and Kings of Spain from the House of Habsburg ...
, with his capital in
Brussels
Brussels (french: Bruxelles or ; nl, Brussel ), officially the Brussels-Capital Region (All text and all but one graphic show the English name as Brussels-Capital Region.) (french: link=no, Région de Bruxelles-Capitale; nl, link=no, Bruss ...
. The titles were eventually more clearly united under his grandson
Philip the Good
Philip III (french: Philippe le Bon; nl, Filips de Goede; 31 July 1396 – 15 June 1467) was Duke of Burgundy from 1419 until his death. He was a member of a cadet line of the Valois dynasty, to which all 15th-century kings of France belonge ...
(1396 – 1467). This large Duchy passed in
1477
Year 1477 (Roman numerals, MCDLXXVII) was a common year starting on Wednesday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar.
Events
January–December
* January 5 – Battle of Nancy: Charles the Bold of Duchy of Burg ...
to the
Habsburg
The House of Habsburg (), alternatively spelled Hapsburg in Englishgerman: Haus Habsburg, ; es, Casa de Habsburgo; hu, Habsburg család, it, Casa di Asburgo, nl, Huis van Habsburg, pl, dom Habsburgów, pt, Casa de Habsburgo, la, Domus Hab ...
dynasty, and in
1556
__NOTOC__
Year 1556 ( MDLVI) was a leap year starting on Wednesday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar.
Events
January–June
* January 16 – Charles V, having already abdicated as Holy Roman Emperor, r ...
to the kings of Spain. Western and southern districts of Flanders were confirmed under French rule under successive treaties of
1659
Events
January–March
* January 14 – In the Battle of the Lines of Elvas, fought near the small city of Elvas in Portugal during the Portuguese Restoration War, the Spanish Army under the command of Luis Méndez de Haro suff ...
(Artois),
1668
Events
January–March
* January 23 – The Triple Alliance (1668), Triple Alliance of 1668 is formed between Kingdom of England, England, Sweden and the Dutch Republic, United Provinces of the Netherlands.
* February 13 &ndash ...
and
1678
Events
January–March
* January 10 – England and the Dutch Republic sign a mutual defense treaty in order to fight against France.
* January 27 – The first fire engine company (in what will become the United States) goe ...
.
The County of Loon, approximately the modern Flemish province of Limburg, remained independent of France, forming a part of the
Prince-Bishopric of Liège
The Prince-Bishopric of Liège or Principality of Liège was an Hochstift, ecclesiastical principality of the Holy Roman Empire that was situated for the most part in present-day Belgium. It was an Imperial State, Imperial Estate, so the List of ...
until the French Revolution, but surrounded by the Burgundians, and under their influence.
Low Countries
Beeldenstorm
In 1500,
Charles V Charles V may refer to:
* Charles V, Holy Roman Emperor (1500–1558)
* Charles V of Naples (1661–1700), better known as Charles II of Spain
* Charles V of France (1338–1380), called the Wise
* Charles V, Duke of Lorraine (1643–1690)
* Infan ...
was born in
Ghent
Ghent ( nl, Gent ; french: Gand ; traditional English: Gaunt) is a city and a municipality in the Flemish Region of Belgium. It is the capital and largest city of the East Flanders province, and the third largest in the country, exceeded in ...
. He inherited the
Seventeen Provinces
The Seventeen Provinces were the Imperial states of the Habsburg Netherlands in the 16th century. They roughly covered the Low Countries, i.e., what is now the Netherlands, Belgium, Luxembourg, and most of the French departments of Nord (Fre ...
(1506), Spain (1516) with its colonies and in 1519 was elected
Holy Roman Emperor
The Holy Roman Emperor, originally and officially the Emperor of the Romans ( la, Imperator Romanorum, german: Kaiser der Römer) during the Middle Ages, and also known as the Roman-German Emperor since the early modern period ( la, Imperat ...
. Charles V issued the
Pragmatic Sanction of 1549
The Pragmatic Sanction of 1549 was an edict, promulgated by Charles V, Holy Roman Emperor, reorganising the Seventeen Provinces of the present-day Netherlands, Belgium, and Luxembourg into one indivisible territory, while retaining existing custom ...
, which established the Low Countries as the Seventeen Provinces (or
Spanish Netherlands
Spanish Netherlands (Spanish: Países Bajos Españoles; Dutch: Spaanse Nederlanden; French: Pays-Bas espagnols; German: Spanische Niederlande.) (historically in Spanish: ''Flandes'', the name "Flanders" was used as a ''pars pro toto'') was the Ha ...
in its broad sense) as an entity separate from the
Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a Polity, political entity in Western Europe, Western, Central Europe, Central, and Southern Europe that developed during the Early Middle Ages and continued until its Dissolution of the Holy Roman Empire, dissolution i ...
and from France. In 1556 Charles V abdicated due to ill health (he suffered from crippling
gout
Gout ( ) is a form of inflammatory arthritis characterized by recurrent attacks of a red, tender, hot and swollen joint, caused by deposition of monosodium urate monohydrate crystals. Pain typically comes on rapidly, reaching maximal intensit ...
). Spain and the Seventeen Provinces went to his son,
Philip II of Spain
Philip II) in Spain, while in Portugal and his Italian kingdoms he ruled as Philip I ( pt, Filipe I). (21 May 152713 September 1598), also known as Philip the Prudent ( es, Felipe el Prudente), was King of Spain from 1556, King of Portugal from ...
.
Over the first half of the 16th century
Antwerp
Antwerp (; nl, Antwerpen ; french: Anvers ; es, Amberes) is the largest city in Belgium by area at and the capital of Antwerp Province in the Flemish Region. With a population of 520,504, grew to become the second-largest European city north of the
Alps
The Alps () ; german: Alpen ; it, Alpi ; rm, Alps ; sl, Alpe . are the highest and most extensive mountain range system that lies entirely in Europe, stretching approximately across seven Alpine countries (from west to east): France, Sw ...
by 1560. Antwerp was the richest city in Europe at this time. According to Luc-Normand Tellier "It is estimated that the port of Antwerp was earning the Spanish crown seven times more revenues than the
Americas
The Americas, which are sometimes collectively called America, are a landmass comprising the totality of North and South America. The Americas make up most of the land in Earth's Western Hemisphere and comprise the New World.
Along with th ...
."

Meanwhile, Protestantism had reached the Low Countries. Among the wealthy traders of Antwerp, the
Lutheran
Lutheranism is one of the largest branches of Protestantism, identifying primarily with the theology of Martin Luther, the 16th-century German monk and reformer whose efforts to reform the theology and practice of the Catholic Church launched th ...
beliefs of the German
Hanseatic
The Hanseatic League (; gml, Hanse, , ; german: label=German language, Modern German, Deutsche Hanse) was a Middle Ages, medieval commercial and defensive confederation of merchant guilds and market towns in Central Europe, Central and Norther ...
traders found appeal, perhaps partly for economic reasons. The spread of Protestantism in this city was aided by the presence of an
Augustinian Augustinian may refer to:
*Augustinians, members of religious orders following the Rule of St Augustine
*Augustinianism, the teachings of Augustine of Hippo and his intellectual heirs
*Someone who follows Augustine of Hippo
* Canons Regular of Sain ...
cloister (founded 1514) in the St. Andries quarter. Luther, an Augustinian himself, had taught some of the monks, and his works were in print by 1518. The first Lutheran martyrs came from Antwerp. The
Reformation
The Reformation (alternatively named the Protestant Reformation or the European Reformation) was a major movement within Western Christianity in 16th-century Europe that posed a religious and political challenge to the Catholic Church and in ...
resulted in consecutive but overlapping waves of reform: a Lutheran, followed by a militant
Anabaptist
Anabaptism (from New Latin language, Neo-Latin , from the Greek language, Greek : 're-' and 'baptism', german: Täufer, earlier also )Since the middle of the 20th century, the German-speaking world no longer uses the term (translation: "Re- ...
, then a
Mennonite
Mennonites are groups of Anabaptist Christian church communities of denominations. The name is derived from the founder of the movement, Menno Simons (1496–1561) of Friesland. Through his writings about Reformed Christianity during the Radic ...
, and finally a
Calvinistic
Calvinism (also called the Reformed Tradition, Reformed Protestantism, Reformed Christianity, or simply Reformed) is a major branch of Protestantism that follows the theological tradition and forms of Christian practice set down by John Calv ...
movement. These movements existed independently of each other.
Philip II Philip II may refer to:
* Philip II of Macedon (382–336 BC)
* Philip II (emperor) (238–249), Roman emperor
* Philip II, Prince of Taranto (1329–1374)
* Philip II, Duke of Burgundy (1342–1404)
* Philip II, Duke of Savoy (1438-1497)
* Philip ...
, a devout Catholic and self-proclaimed protector of the
Counter-Reformation
The Counter-Reformation (), also called the Catholic Reformation () or the Catholic Revival, was the period of Catholic resurgence that was initiated in response to the Protestant Reformation. It began with the Council of Trent (1545–1563) a ...
,
suppressed Calvinism in Flanders,
Brabant Brabant is a traditional geographical region (or regions) in the Low Countries of Europe. It may refer to:
Place names in Europe
* London-Brabant Massif, a geological structure stretching from England to northern Germany
Belgium
* Province of Bra ...
and Holland (what is now approximately
Belgian Limburg
Limburg ( nl, Limburg, ; li, Limburg or ''Wes-Limburg'' ; french: Limbourg, ) is a province in Belgium. It is the easternmost of the five Dutch-speaking provinces that together form the Region of Flanders, one of the three main political and c ...
was part of the
Prince-Bishopric of Liège
The Prince-Bishopric of Liège or Principality of Liège was an Hochstift, ecclesiastical principality of the Holy Roman Empire that was situated for the most part in present-day Belgium. It was an Imperial State, Imperial Estate, so the List of ...
and was Catholic ''de facto''). In 1566, the wave of
iconoclasm
Iconoclasm (from Ancient Greek, Greek: grc, wikt:εἰκών, εἰκών, lit=figure, icon, translit=eikṓn, label=none + grc, wikt:κλάω, κλάω, lit=to break, translit=kláō, label=none)From grc, wikt:εἰκών, εἰκών + wi ...
known as the ''
Beeldenstorm
''Beeldenstorm'' () in Dutch and ''Bildersturm'' in German (roughly translatable from both languages as 'attack on the images or statues') are terms used for outbreaks of destruction of religious images that occurred in Europe in the 16th centu ...
'' was a prelude to religious war between Catholics and Protestants, especially the Anabaptists. The ''Beeldenstorm'' started in what is now
French Flanders
French Flanders (french: La Flandre française) is a part of the historical County of Flanders in present-day France where a dialect of Dutch was or still is traditionally spoken. The region lies in the modern-day region of Hauts-de-France and r ...
, with open-air sermons ( nl, hagepreken) that spread through the Low Countries, first to Antwerp and Ghent, and from there further east and north.
The Eighty Years' War and its consequences
Subsequently, Philip II of Spain sent
the Duke of
Alba
''Alba'' ( , ) is the Scottish Gaelic name for Scotland. It is also, in English language historiography, used to refer to the polity of Picts and Scottish people, Scots united in the ninth century as the Kingdom of Alba, until it developed i ...
to the Provinces to repress the revolt. Alba recaptured the southern part of the Provinces, who signed the
Union of Atrecht
The Union of Arras (Dutch: ''Unie van Atrecht'', French: ''Union d'Arras'', Spanish: ''Unión de Arrás'') was an alliance between the County of Artois, the County of Hainaut and the city of Douai in the Habsburg Netherlands in early 1579 during ...
, which meant that they would accept the Spanish government on condition of more freedom. But the northern part of the provinces signed the
Union of Utrecht
The Union of Utrecht ( nl, Unie van Utrecht) was a treaty signed on 23 January 1579 in Utrecht, Netherlands, unifying the northern provinces of the Netherlands, until then under the control of Habsburg Spain.
History
The Union of Utrecht is r ...
and settled in 1581 the
Republic of the Seven United Netherlands
The United Provinces of the Netherlands, also known as the (Seven) United Provinces, officially as the Republic of the Seven United Netherlands (Dutch: ''Republiek der Zeven Verenigde Nederlanden''), and commonly referred to in historiography ...
. Spanish troops quickly started fighting the rebels, and the Spanish armies conquered the important trading cities of Bruges and Ghent. Antwerp, which was then the most important port in the world, also had to be conquered. But before the revolt was defeated, a war between Spain and England broke out, forcing Spanish troops to halt their advance. On 17 August 1585, Antwerp fell. This ended the Eighty Years' War for the (from now on)
Southern Netherlands
The Southern Netherlands, also called the Catholic Netherlands, were the parts of the Low Countries belonging to the Holy Roman Empire which were at first largely controlled by Habsburg Spain (Spanish Netherlands, 1556–1714) and later by the A ...
. The
United Provinces (the Northern Netherlands) fought on until 1648 – the
Peace of Westphalia
The Peace of Westphalia (german: Westfälischer Friede, ) is the collective name for two peace treaties signed in October 1648 in the Westphalian cities of Osnabrück and Münster. They ended the Thirty Years' War (1618–1648) and brought pea ...
.

During the war with England, the rebels from the north, strengthened by refugees from the south, started a campaign to reclaim areas lost to
Philip II Philip II may refer to:
* Philip II of Macedon (382–336 BC)
* Philip II (emperor) (238–249), Roman emperor
* Philip II, Prince of Taranto (1329–1374)
* Philip II, Duke of Burgundy (1342–1404)
* Philip II, Duke of Savoy (1438-1497)
* Philip ...
's Spanish troops. They conquered a considerable part of Brabant (the later
North Brabant
North Brabant ( nl, Noord-Brabant ; Brabantian: ; ), also unofficially called Brabant, is a province in the south of the Netherlands. It borders the provinces of South Holland and Gelderland to the north, Limburg to the east, Zeeland to the we ...
of the Netherlands), and the south bank of the Scheldt estuary (
Zeelandic Flanders
Zeelandic Flanders ( ; zea, Zeêuws-Vlaonderen; vls, Zêeuws-Vloandern)''Vlaanderen'' in isolation: . is the southernmost region of the province of Zeeland in the south-western Netherlands. It lies south of the Western Scheldt that separates t ...
), before being stopped by Spanish troops. The front at the end of this war stabilized and became the border between present-day Belgium and the Netherlands. The Dutch (as they later became known) had managed to reclaim enough of Spanish-controlled Flanders to close off the river
Scheldt
The Scheldt (french: Escaut ; nl, Schelde ) is a river that flows through northern France, western Belgium, and the southwestern part of Netherlands, the Netherlands, with its mouth at the North Sea. Its name is derived from an adjective corr ...
, effectively cutting Antwerp off from its trade routes.
The
fall of Antwerp
The Fall of Antwerp on 17 August 1585 took place during the Eighty Years' War, after a siege lasting over a year from July 1584 until August 1585. The city of Antwerp was the focal point of the Protestant-dominated Dutch Revolt, but was force ...
to the Spanish and the closing of the
Scheldt
The Scheldt (french: Escaut ; nl, Schelde ) is a river that flows through northern France, western Belgium, and the southwestern part of Netherlands, the Netherlands, with its mouth at the North Sea. Its name is derived from an adjective corr ...
caused considerable emigration. Many Calvinist merchants of Antwerp and other Flemish cities left Flanders and migrated north. Many of them settled in
Amsterdam
Amsterdam ( , , , lit. ''The Dam on the River Amstel'') is the Capital of the Netherlands, capital and Municipalities of the Netherlands, most populous city of the Netherlands, with The Hague being the seat of government. It has a population ...
, which was a smaller port, important only in the
Baltic trade
Baltic may refer to:
Peoples and languages
* Baltic languages, a subfamily of Indo-European languages, including Lithuanian, Latvian and extinct Old Prussian
*Balts (or Baltic peoples), ethnic groups speaking the Baltic languages and/or originati ...
. The Flemish exiles helped to rapidly transform Amsterdam into one of the world's most important ports. This is why the exodus is sometimes described as "''creating a new Antwerp''".
Flanders and Brabant, went into a period of relative decline from the time of the
Thirty Years War
The Thirty Years' War was one of the longest and List of wars and anthropogenic disasters by death toll, most destructive conflicts in History of Europe, European history, lasting from 1618 to 1648. Fought primarily in Central Europe, an es ...
.
In the Northern Netherlands, the mass emigration from Flanders and Brabant became an important driving force behind the
Dutch Golden Age
The Dutch Golden Age ( nl, Gouden Eeuw ) was a period in the history of the Netherlands, roughly spanning the era from 1588 (the birth of the Dutch Republic) to 1672 (the Rampjaar, "Disaster Year"), in which Dutch trade, science, and Dutch art, ...
.
Southern Netherlands (1581–1795)
Although arts remained relatively impressive for another century with
Peter Paul Rubens
Sir Peter Paul Rubens (; ; 28 June 1577 – 30 May 1640) was a Flemish artist and diplomat from the Duchy of Brabant in the Southern Netherlands (modern-day Belgium). He is considered the most influential artist of the Flemish Baroque traditio ...
(1577–1640) and
Anthony van Dyck
Sir Anthony van Dyck (, many variant spellings; 22 March 1599 – 9 December 1641) was a Brabantian Flemish Baroque artist who became the leading court painter in England after success in the Southern Netherlands and Italy.
The seventh c ...
, Flanders lost its former economic and intellectual power under Spanish, Austrian, and French rule. Heavy taxation and rigid imperial political control compounded the effects of industrial stagnation and Spanish-Dutch and Franco-Austrian conflict. The Southern Netherlands suffered severely under the
War of the Spanish Succession
The War of the Spanish Succession was a European great power conflict that took place from 1701 to 1714. The death of childless Charles II of Spain in November 1700 led to a struggle for control of the Spanish Empire between his heirs, Phil ...
. But under the reign of Empress Maria-Theresia, these lands again flourished economically. Influenced by
the Enlightenment
The Age of Enlightenment or the Enlightenment; german: Aufklärung, "Enlightenment"; it, L'Illuminismo, "Enlightenment"; pl, Oświecenie, "Enlightenment"; pt, Iluminismo, "Enlightenment"; es, La Ilustración, "Enlightenment" was an intel ...
, the Austrian Emperor
Joseph II
Joseph II (German: Josef Benedikt Anton Michael Adam; English: ''Joseph Benedict Anthony Michael Adam''; 13 March 1741 – 20 February 1790) was Holy Roman Emperor from August 1765 and sole ruler of the Habsburg lands from November 29, 1780 unt ...
was the first sovereign who had been in the Southern Netherlands since King Philip II of Spain left them in 1559.
French Revolution and Napoleonic France (1795–1815)
In 1794, the
French Republican Army started using Antwerp as the northernmost naval port of France.
The following year, France officially annexed Flanders as the ''
départements
A department (, ) is an administrative or political division in several countries. Departments are the first-level divisions of 11 countries, nine in the Americas and two in Africa. An additional 10 countries use departments as second-level divi ...
'' of
Lys,
Escaut,
Deux-Nèthes
Deux-Nèthes (, nl, Twee Neten) was a department of the First French Republic and of the First French Empire in present-day Belgium and the Netherlands. It was named after two branches of the river Nete (Grote Nete and Kleine Nete). The southern ...
,
Meuse-Inférieure
Meuse-Inférieure ( "Lower Meuse"; ; ) was a department of the French First Republic and French First Empire in present-day Belgium, Netherlands and Germany. It was named after the river Meuse. Its territory corresponded largely with the present-d ...
and
Dyle. Obligatory (French) army service for all men aged 16–25 years was a main reason for the uprising against the French in 1798, known as the ''Boerenkrijg'' (''Peasants' War''), with the heaviest fighting in the
Campine
The Campine ( French ) or De Kempen (Dutch ) is a natural region situated chiefly in north-eastern Belgium and parts of the south-eastern Netherlands which once consisted mainly of extensive moors, tracts of sandy heath, and wetlands. It encom ...
area.
United Kingdom of the Netherlands (1815–1830)
After the defeat of
Napoleon Bonaparte
Napoleon Bonaparte ; it, Napoleone Bonaparte, ; co, Napulione Buonaparte. (born Napoleone Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French military commander and political leader who ...
at the 1815
Battle of Waterloo
The Battle of Waterloo was fought on Sunday 18 June 1815, near Waterloo, Belgium, Waterloo (at that time in the United Kingdom of the Netherlands, now in Belgium). A French army under the command of Napoleon was defeated by two of the armie ...
in
Brabant Brabant is a traditional geographical region (or regions) in the Low Countries of Europe. It may refer to:
Place names in Europe
* London-Brabant Massif, a geological structure stretching from England to northern Germany
Belgium
* Province of Bra ...
, the
Congress of Vienna
The Congress of Vienna (, ) of 1814–1815 was a series of international diplomatic meetings to discuss and agree upon a possible new layout of the European political and constitutional order after the downfall of the French Emperor Napoleon B ...
(1815) gave sovereignty over the
Austrian Netherlands
The Austrian Netherlands nl, Oostenrijkse Nederlanden; french: Pays-Bas Autrichiens; german: Österreichische Niederlande; la, Belgium Austriacum. was the territory of the Burgundian Circle of the Holy Roman Empire between 1714 and 1797. The p ...
– Belgium minus the
East Cantons
Eupen-Malmedy is a small, predominantly German-speaking region in eastern Belgium. It consists of three administrative cantons around the towns of Eupen, Malmedy, and Sankt Vith which encompass some . Elsewhere in Belgium, the region is commonly ...
and Luxembourg – to the
United Netherlands (Dutch: ''Verenigde Nederlanden'') under Prince William I of Orange Nassau, making him
William I of the United Kingdom of the Netherlands. William I started rapid industrialisation of the southern parts of the Kingdom. But the political system failed to forge a true union between the north and south. Most of the southern
bourgeoisie
The bourgeoisie ( , ) is a social class, equivalent to the middle or upper middle class. They are distinguished from, and traditionally contrasted with, the proletariat by their affluence, and their great cultural and financial capital. They ...
was Roman Catholic and French-speaking, while the north was mainly Protestant and Dutch-speaking.
In 1815, the Dutch Senate was reinstated (Dutch: ''Eerste Kamer der Staaten Generaal''). The nobility, mainly coming from the south, became more and more estranged from their northern colleagues. Resentment grew between the Roman Catholics from the south and the Protestants from the north, and also between the powerful liberal bourgeoisie from the south and their more moderate colleagues from the north. On 25 August 1830 (after the showing of the opera '
La Muette de Portici
''La muette de Portici'' (''The Mute Girl of Portici'', or ''The Dumb Girl of Portici''), also called ''Masaniello'' () in some versions, is an opera in five acts by Daniel Auber, with a libretto by Germain Delavigne, revised by Eugène Scribe.
...
' of
Daniel Auber
Daniel-François-Esprit Auber (; 29 January 178212 May 1871) was a French composer and director of the Paris Conservatoire.
Born into an artistic family, Auber was at first an amateur composer before he took up writing operas professionally when ...
in Brussels) the
Belgian Revolution
The Belgian Revolution (, ) was the conflict which led to the secession of the southern provinces (mainly the former Southern Netherlands) from the United Kingdom of the Netherlands and the establishment of an independent Kingdom of Belgium.
T ...
sparked. On 4 October 1830, the
Provisional Government
A provisional government, also called an interim government, an emergency government, or a transitional government, is an emergency governmental authority set up to manage a political transition generally in the cases of a newly formed state or f ...
(Dutch: ''Voorlopig Bewind'') proclaimed its independence, which was later confirmed by the
National Congress that issued a new Liberal Constitution and declared the new state a
Constitutional Monarchy
A constitutional monarchy, parliamentary monarchy, or democratic monarchy is a form of monarchy in which the monarch exercises their authority in accordance with a constitution and is not alone in decision making. Constitutional monarchies dif ...
, under the House of
Saxe-Coburg
Saxe-Coburg (german: Sachsen-Coburg) was a duchy held by the Ernestine branch of the Wettin dynasty in today's Bavaria, Germany.
History
Ernestine Line
When Henry IV, Count of Henneberg – Schleusingen, died in 1347, the possessions of the ...
. Flanders now became part of the Kingdom of Belgium, which was recognized by the major European Powers on 20 January 1831. The cessation was recognized by the
United Kingdom of the Netherlands
The United Kingdom of the Netherlands ( nl, Verenigd Koninkrijk der Nederlanden; french: Royaume uni des Pays-Bas) is the unofficial name given to the Kingdom of the Netherlands as it existed between 1815 and 1839. The United Netherlands was cr ...
on 19 April 1839.
Kingdom of Belgium
In 1830, the
Belgian Revolution
The Belgian Revolution (, ) was the conflict which led to the secession of the southern provinces (mainly the former Southern Netherlands) from the United Kingdom of the Netherlands and the establishment of an independent Kingdom of Belgium.
T ...
led to the splitting up of the two countries. Belgium was confirmed as an independent state by the
Treaty of London of 1839, but deprived of the eastern half of Limburg (now Dutch Limburg), and the Eastern half of Luxembourg (now the Grand-Duchy of Luxembourg). Sovereignty over
Zeelandic Flanders
Zeelandic Flanders ( ; zea, Zeêuws-Vlaonderen; vls, Zêeuws-Vloandern)''Vlaanderen'' in isolation: . is the southernmost region of the province of Zeeland in the south-western Netherlands. It lies south of the Western Scheldt that separates t ...
, south of the
Westerscheldt
The Western Scheldt ( nl, Westerschelde) in the province of Zeeland in the southwestern Netherlands, is the estuary of the Scheldt river. This river once had several estuaries, but the others are now disconnected from the Scheldt, leaving the W ...
river delta, was left with the Kingdom of the Netherlands, which was allowed to levy a toll on all traffic to Antwerp harbour until 1863.
Rise of the Flemish Movement
In 1873, Dutch became an official language in public secondary schools. In 1898, Dutch and French were declared equal languages in laws and Royal orders. In 1930, the first Flemish university was opened.
The first official translation of the Belgian constitution in Dutch was not published until 1967.
World War I and its consequences
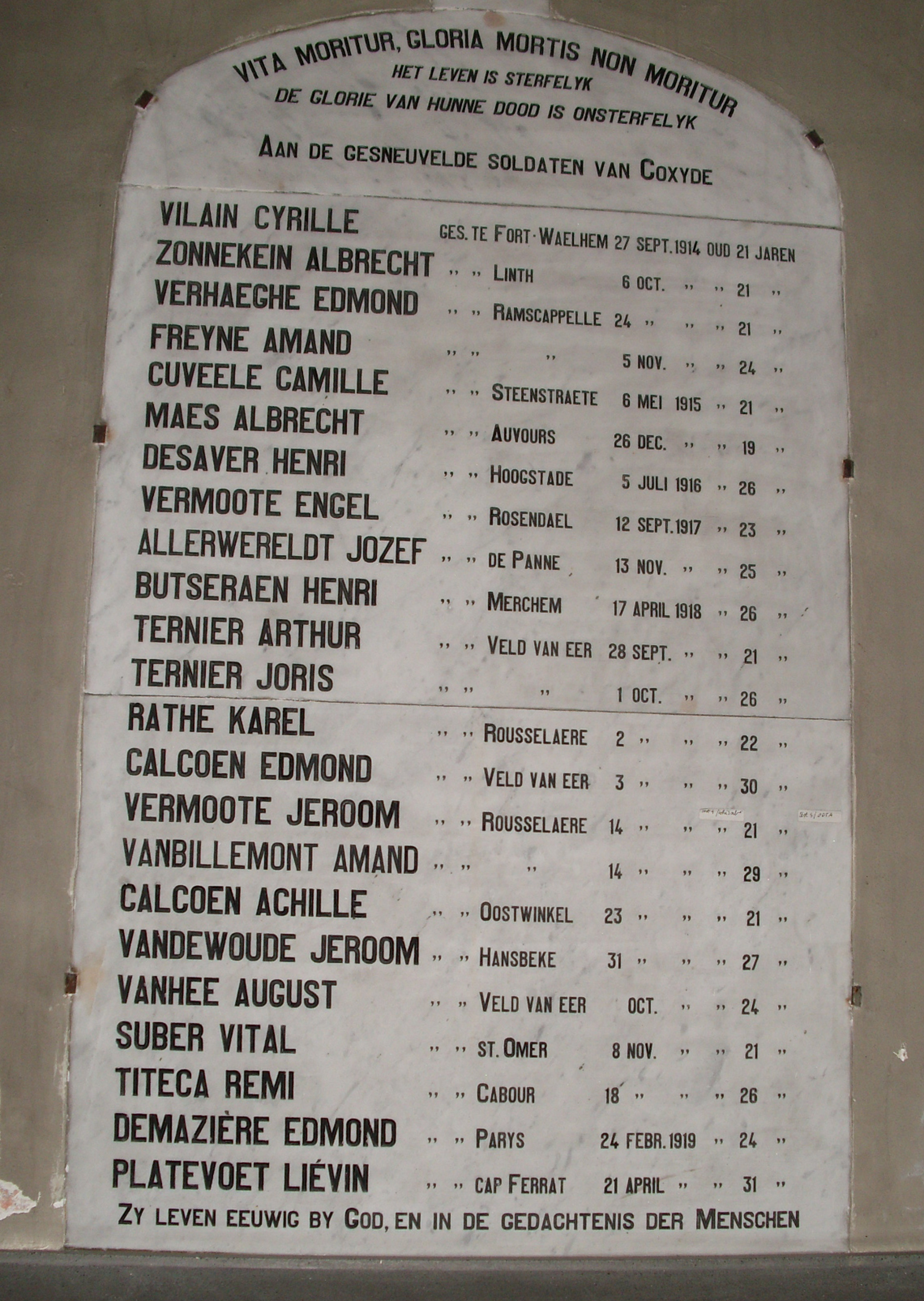
Flanders (and Belgium as a whole) saw some of the greatest loss of life on the
Western Front of the
First World War
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
, in particular from the three battles of
Ypres
Ypres ( , ; nl, Ieper ; vls, Yper; german: Ypern ) is a Belgian city and municipality in the province of West Flanders. Though
the Dutch name is the official one, the city's French name is most commonly used in English. The municipality co ...
.
The war strengthened Flemish identity and consciousness. The occupying German authorities took several Flemish-friendly measures. The resulting suffering of the war is remembered by Flemish organizations during the yearly
Yser pilgrimage in
Diksmuide
(; french: Dixmude, ; vls, Diksmude) is a Belgian city and municipality in the Flemish province of West Flanders. The municipality comprises the city of proper and the former communes of Beerst, Esen, Kaaskerke, Keiem, Lampernisse, Leke, N ...
at the monument of the
Yser Tower
The Yser Towers ( nl, IJzertoren) are a monument complex near the Yser river at Diksmuide, West Flanders in Belgium. The first tower was built in 1928–30 to commemorate the Belgian soldiers killed on the surrounding Yser Front during World War ...
.
Right-wing nationalism in the interbellum and World War II
During the interbellum and World War II, several right-wing fascist and/or national-socialistic parties emerged in Belgium. Since these parties were promised more rights for the Flemings by the German government during World War II, many of them collaborated with the Nazi regime. After the war, collaborators (or people who were ''Zwart'', "Black" during the war) were prosecuted and punished, among them many Flemish Nationalists whose main political goal had been the emancipation of Flanders. As a result, until today Flemish Nationalism is often associated with right-wing and sometimes fascist ideologies.
Flemish autonomy
After World War II, the differences between Dutch-speaking and French-speaking Belgians became clear in a number of conflicts, such as the
Royal Question, the question whether King Leopold III should return (which most Flemings supported but Walloons did not) and the use of Dutch in the
Catholic University of Leuven
University of Leuven or University of Louvain (french: Université de Louvain, link=no; nl, Universiteit Leuven, link=no) may refer to:
* Old University of Leuven (1425–1797)
* State University of Leuven (1817–1835)
* Catholic University of ...
. As a result, several
state reforms took place in the second half of the 20th century, which transformed the unitary Belgium into a federal state with
communities, regions and language areas. This resulted also in the establishment of a
Flemish Parliament
The Flemish Parliament (Dutch: , formerly called Flemish Council or ''Vlaamse Raad'') constitutes the legislative power in Flanders for matters which fall within the competence of Flanders, both as a geographic region and as a cultural communi ...
and
Government
A government is the system or group of people governing an organized community, generally a state.
In the case of its broad associative definition, government normally consists of legislature, executive, and judiciary. Government is a ...
. During the 1970s, all major political parties split into a Dutch and French-speaking party.
Several Flemish parties still advocate for more Flemish autonomy, some even for Flemish independence (see
Partition of Belgium
The partition of Belgium is a hypothetical situation, which has been discussed by both Belgian and international media, envisioning a split of Belgium along linguistic divisions, with the Flemish Community (Flanders) and the French-speaking Commu ...
), whereas the French-speakers would like to keep the current state as it is. Recent governments (such as
Verhofstadt I Government
The Verhofstadt I Government was the federal government of Belgium from 12 July 1999 to 12 July 2003.
It was the first government headed by Prime Minister Guy Verhofstadt (VLD). It consisted of the Flemish Liberals and Democrats (VLD), the Fre ...
) have transferred certain federal competences to the regional governments.
On 13 December 2006, a
spoof news broadcast by the Belgian Francophone public broadcasting station
RTBF
The ''Radio-télévision belge de la Communauté française'' (RTBF, ''Belgian Radio-television of the French Community'', branded as rtbf.be) is a public service broadcaster delivering radio and television services to the French-speaking Commu ...
announced that Flanders had decided to declare independence from Belgium.
The
2007 federal elections showed more support for Flemish autonomy, marking the start of the
2007–2011 Belgian political crisis
The 2007–2011 Belgian political crisis was a period of tense communal relations and political instability in Belgium, which was rooted in the differing opinions on state reform, and in the continued existence of the controversial electoral dis ...
. All the political parties that advocated a significant increase of Flemish autonomy gained votes as well as seats in the
Belgian federal parliament
The Federal Parliament is the bicameral parliament of Belgium. It consists of the Chamber of Representatives (Dutch: , french: Chambre des Représentants, german: Abgeordnetenkammer) and the Senate (Dutch: , french: Sénat, german: Senat). It sit ...
. This was especially the case for
Christian Democratic and Flemish
Christian Democratic and Flemish (, , CD&V) is a Flemish Christian-democratic political party in Belgium. The party has historical ties to both trade unionism ( ACV) and trade associations (UNIZO) and the Farmer's League. Until 2001, the party wa ...
and
New Flemish Alliance
The New Flemish Alliance ( nl, Nieuw-Vlaamse Alliantie, N-VA) is a Flemish nationalist and conservative political party in Belgium. The party was founded in 2001 by the right-leaning fraction of the centrist-nationalist People's Union (VU).
T ...
(N-VA) (who had participated on a shared
electoral list
An electoral list is a grouping of candidates for election, usually found in proportional or mixed electoral systems, but also in some plurality electoral systems. An electoral list can be registered by a political party (a party list) or can ...
). The trend continued during the
2009 regional elections, where CD&V and N-VA were the clear winners in Flanders, and N-VA became even the largest party in Flanders and Belgium during the
2010 federal elections, followed by the
longest-ever government formation after which the
Di Rupo I Government
The Di Rupo Government was the federal cabinet of Belgium sworn in on 6 December 2011, after a record-breaking 541 days of negotiations following the June 2010 elections. The government included social democrats ( sp.a/ PS), Christian democrats ...
was formed excluding N-VA. Eight parties agreed on a
sixth state reform which aim to solve the disputes between Flemings and French-speakers. However, the
2012 provincial and municipal elections continued the trend of N-VA becoming the biggest party in Flanders.
However, sociological studies show no parallel between the rise of nationalist parties and popular support for their agenda. Instead, a recent study revealed a majority in favour of returning regional competences to the federal level.
Government and politics

Both the
Flemish Community
The Flemish Community ( nl, Vlaamse Gemeenschap ; french: Communauté flamande ; german: Flämische Gemeinschaft ) is one of the three institutional communities of Belgium, established by the Belgian constitution and having legal responsibilitie ...
and the
Flemish Region
The Flemish Region ( nl, Vlaams Gewest, ),; german: Flämische Region usually simply referred to as Flanders ( nl, link=no, Vlaanderen ) ; german: link=no, Flandern is one of the three regions of Belgium—alongside the Walloon Region and t ...
are constitutional institutions of the Kingdom of Belgium, exercising certain powers within their jurisdiction, granted following a series of
state reforms. In practice, the Flemish Community and Region together form a single body, with its own
parliament
In modern politics, and history, a parliament is a legislative body of government. Generally, a modern parliament has three functions: Representation (politics), representing the Election#Suffrage, electorate, making laws, and overseeing ...
and
government
A government is the system or group of people governing an organized community, generally a state.
In the case of its broad associative definition, government normally consists of legislature, executive, and judiciary. Government is a ...
, as the Community legally absorbed the competences of the Region. The parliament is a directly elected legislative body composed of 124 representatives. The government consists of up to 11 members and is presided by a
Minister-President
A minister-president or minister president is the head of government in a number of European countries or subnational governments with a parliamentary or semi-presidential system of government where they preside over the council of ministers. It ...
, currently
Geert Bourgeois
Geert Albert Bourgeois (; born 6 July 1951) is a Belgian politician of the New Flemish Alliance (N-VA), which he founded in 2001, who is currently serving as a Member of the European Parliament since 2019. He previously served as the Minister-Pr ...
(
New Flemish Alliance
The New Flemish Alliance ( nl, Nieuw-Vlaamse Alliantie, N-VA) is a Flemish nationalist and conservative political party in Belgium. The party was founded in 2001 by the right-leaning fraction of the centrist-nationalist People's Union (VU).
T ...
) leading a coalition of his party (N-VA) with
Christen-Democratisch en Vlaams
Christian Democratic and Flemish (, , CD&V) is a Flemish Christian-democratic political party in Belgium. The party has historical ties to both trade unionism ( ACV) and trade associations (UNIZO) and the Farmer's League. Until 2001, the party wa ...
(CD&V) and
Open Vlaamse Liberalen en Democraten
french: Libéraux et démocrates flamands ouverts
, abbreviation = Open Vld
, logo =
, leader1_title = President
, leader1_name = Egbert Lachaert
, foundation = 1992 (VLD)2007 (Open Vld)
, predecessor = Pa ...
(Open VLD).
The area of the Flemish Community is represented on the maps above, including the area of the
Brussels-Capital Region
Brussels (french: Bruxelles or ; nl, Brussel ), officially the Brussels-Capital Region (All text and all but one graphic show the English name as Brussels-Capital Region.) (french: link=no, Région de Bruxelles-Capitale; nl, link=no, Bruss ...
(hatched on the relevant map). Roughly, the Flemish Community exercises competences originally oriented towards the individuals of the Community's language: culture (including audiovisual media),
education
Education is a purposeful activity directed at achieving certain aims, such as transmitting knowledge or fostering skills and character traits. These aims may include the development of understanding, rationality, kindness, and honesty. Va ...
, and the use of the language. Extensions to personal matters less directly associated with language comprise sports, health policy (curative and preventive medicine), and assistance to individuals (protection of youth, social welfare, aid to families, immigrant assistance services, etc.)
The area of the Flemish Region is represented on the maps above. It has a population of more than 6 million (excluding the Dutch-speaking community in the Brussels Region, grey on the map for it is not a part of the Flemish Region). Roughly, the Flemish Region is responsible for territorial issues in a broad sense, including economy, employment, agriculture, water policy, housing, public works, energy, transport, the environment, town and country planning, nature conservation, credit, and foreign trade. It supervises the provinces, municipalities, and intercommunal utility companies.
The number of Dutch-speaking
Flemish people
The Flemish or Flemings ( nl, Vlamingen ) are a Germanic ethnic group native to Flanders, Belgium, who speak Dutch. Flemish people make up the majority of Belgians, at about 60%.
"''Flemish''" was historically a geographical term, as all inhab ...
in the Capital Region is estimated to be between 11% and 15% (official figures do not exist as there is no language census and no official subnationality). According to a survey conducted by the
University of Louvain
A university () is an institution of higher (or tertiary) education and research which awards academic degrees in several academic disciplines. Universities typically offer both undergraduate and postgraduate programs. In the United States, the ...
(UCLouvain) in
Louvain-la-Neuve
Louvain-la-Neuve (, French for ''New Leuven''; wa, Li Noû Lovén) is a planned town in the municipality of Ottignies-Louvain-la-Neuve, Wallonia, Belgium, situated 30 km southeast of Brussels, in the province of Walloon Brabant. The town was ...
and published in June 2006, 51% of respondents from Brussels claimed to be bilingual, even if they do not have Dutch as their first language. They are governed by the Brussels Region for economics affairs and by the Flemish Community for educational and cultural issues.

As mentioned above, Flemish institutions such as the
Flemish Parliament
The Flemish Parliament (Dutch: , formerly called Flemish Council or ''Vlaamse Raad'') constitutes the legislative power in Flanders for matters which fall within the competence of Flanders, both as a geographic region and as a cultural communi ...
and
Government
A government is the system or group of people governing an organized community, generally a state.
In the case of its broad associative definition, government normally consists of legislature, executive, and judiciary. Government is a ...
, represent the Flemish Community and the Flemish Region. The region and the community thus ''de facto'' share the same parliament and the same government. All these institutions are based in Brussels. Nevertheless, both types of subdivisions (the Community and the Region) still exist legally and the distinction between both is important for the people living in Brussels. Members of the Flemish Parliament who were elected in the Brussels Region cannot vote on affairs belonging to the competences of the Flemish Region.
The
official language
An official language is a language given supreme status in a particular country, state, or other jurisdiction. Typically the term "official language" does not refer to the language used by a people or country, but by its government (e.g. judiciary, ...
for all Flemish institutions is
Dutch
Dutch commonly refers to:
* Something of, from, or related to the Netherlands
* Dutch people ()
* Dutch language ()
Dutch may also refer to:
Places
* Dutch, West Virginia, a community in the United States
* Pennsylvania Dutch Country
People E ...
. French enjoys a limited official recognition in
a dozen municipalities along the borders with French-speaking
Wallonia
Wallonia (; french: Wallonie ), or ; nl, Wallonië ; wa, Waloneye or officially the Walloon Region (french: link=no, Région wallonne),; nl, link=no, Waals gewest; wa, link=no, Redjon walone is one of the three regions of Belgium—alo ...
, and a large recognition in the bilingual Brussels Region. French is widely known in Flanders, with 59% claiming to know French according to a survey conducted by
UCLouvain in
Louvain-la-Neuve
Louvain-la-Neuve (, French for ''New Leuven''; wa, Li Noû Lovén) is a planned town in the municipality of Ottignies-Louvain-la-Neuve, Wallonia, Belgium, situated 30 km southeast of Brussels, in the province of Walloon Brabant. The town was ...
and published in June 2006.
Politics
Historically, the political parties reflected the
pillarisation
Pillarisation (from the nl, verzuiling) is the politico-denominational segregation of a society into groups by religion and associated political beliefs. These societies were (and in some areas, still are) vertically divided into two or more gr ...
(''verzuiling'') in Flemish society. The traditional political parties of the three pillars are
Christian-Democratic and Flemish
Christian Democratic and Flemish (, , CD&V) is a Flemish Christian-democratic political party in Belgium. The party has historical ties to both trade unionism ( ACV) and trade associations (UNIZO) and the Farmer's League. Until 2001, the party wa ...
(CD&V), the
Open Flemish Liberals and Democrats
french: Libéraux et démocrates flamands ouverts
, abbreviation = Open Vld
, logo =
, leader1_title = President
, leader1_name = Egbert Lachaert
, foundation = 1992 (VLD)2007 (Open Vld)
, predecessor = Pa ...
(Open Vld) and the
Socialist Party – Differently
Vooruit (Dutch for Forward, ) is a Flemish social democratic political party in Belgium. The party was known as the Flemish Socialist Party (1978–2001: ''Socialistische Partij'', SP; 2001–2021: ''Socialistische Partij Anders'', SP.A) until ...
(sp.a).
However, during the last half century, many new political parties were founded in Flanders. One of the first was the nationalist
People's Union, of which the right nationalist
Flemish Block
''Vlaams Blok'' ( en, Flemish Block, or VB) was the name of a Belgian far-right and secessionist political party with an anti-immigration platform.Erk, 2005, pp. 493-502. Its ideologies embraced Flemish nationalism, calling for the independence ...
(now
Flemish Interest
, ideology =
, predecessor = Vlaams Blok
, position =
, europarl = Identity and Democracy
, european = Identity and Democracy Party
, youth_wing = Vlaams Belang Jongeren
, colours =
, ...
) split off, and which later dissolved into the now-defunct Spirit or
Social Liberal Party, moderate nationalism rather left of the spectrum, on the one hand, and the
New Flemish Alliance
The New Flemish Alliance ( nl, Nieuw-Vlaamse Alliantie, N-VA) is a Flemish nationalist and conservative political party in Belgium. The party was founded in 2001 by the right-leaning fraction of the centrist-nationalist People's Union (VU).
T ...
(N-VA), more conservative but independentist, on the other hand. Other parties are the leftist alternative/ecological
Green
Green is the color between cyan and yellow on the visible spectrum. It is evoked by light which has a dominant wavelength of roughly 495570 Nanometre, nm. In subtractive color systems, used in painting and color printing, it is created by ...
party; the short-lived anarchistic libertarian spark
ROSSEM
Radical Reformists and Social Fighters for a Fairer Society ( nl, Radicale Omvormers en Sociale Strijders voor een Eerlijker Maatschappij, ROSSEM) is a Belgium, Belgian Libertarianism, libertarian political party founded in 1991 by the Flemish bu ...
and more recently the conservative-right liberal
List Dedecker
Libertarian, Direct, Democratic ( nl, Libertair, Direct, Democratisch; LDD) is a conservative-liberal, libertarian, right-wing populist Flemish political party in Belgium.
The party surprised commentators by winning five seats in the Chamber an ...
, founded by
Jean-Marie Dedecker
Jean-Marie Louis Dedecker (born 13 June 1952) is a Belgian politician.
In 1999 and 2003, Dedecker was directly elected to the Belgian Senate for the Flemish Liberals and Democrats (VLD). In 2004 Dedecker ran for a seat in the Flemish Parliament ...
, and the socialist
Workers' Party.
Particularly the
Flemish Block
''Vlaams Blok'' ( en, Flemish Block, or VB) was the name of a Belgian far-right and secessionist political party with an anti-immigration platform.Erk, 2005, pp. 493-502. Its ideologies embraced Flemish nationalism, calling for the independence ...
/
Flemish Interest
, ideology =
, predecessor = Vlaams Blok
, position =
, europarl = Identity and Democracy
, european = Identity and Democracy Party
, youth_wing = Vlaams Belang Jongeren
, colours =
, ...
has seen electoral success roughly around the turn of the century, and the
New Flemish Alliance
The New Flemish Alliance ( nl, Nieuw-Vlaamse Alliantie, N-VA) is a Flemish nationalist and conservative political party in Belgium. The party was founded in 2001 by the right-leaning fraction of the centrist-nationalist People's Union (VU).
T ...
during the last few elections, even becoming the largest party in the
2010 federal elections.
Flemish independence

For some inhabitants, Flanders is more than just a geographical area or the federal institutions (Flemish Community and Region). Supporters of the Flemish Movement even call it a nation and pursue Flemish independence, but most people (approximately 75%) living in Flanders say they are proud to be Belgian and opposed to the dissolution of Belgium. 20% is even ''very proud'', while some 25% are not proud and 8% is ''very not proud''. Mostly students claim to be proud of their nationality, with 90% of them saying so. Of the people older than 55, 31% claim to be proud of being a Belgian. Particular opposition to secession comes from women, people employed in
services
Service may refer to:
Activities
* Administrative service, a required part of the workload of university faculty
* Civil service, the body of employees of a government
* Community service, volunteer service for the benefit of a community or a pu ...
, the highest social classes and people from big families. Strongest of all opposing the notion are housekeepers—both housewives and house husbands.
In 2012, the Flemish government drafted a "Charter for Flanders" (''Handvest voor Vlaanderen'') of which the first article says ''"Vlaanderen is een deelstaat van de federale Staat België en maakt deel uit van de Europese Unie."'' ("Flanders is a
component state of the federal State of Belgium and is part of the European Union"). Although interpreted by many Flemish nationalists as a statement, this phrase is merely a quotation from the Belgian constitution and has no further legal value whatsoever.
Geography

Flanders shares its borders with Wallonia in the south, Brussels being an enclave within the Flemish Region. The rest of the border is shared with the
Netherlands
)
, anthem = ( en, "William of Nassau")
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name = Kingdom of the Netherlands
, established_title = Before independence
, established_date = Spanish Netherl ...
(
Zeelandic Flanders
Zeelandic Flanders ( ; zea, Zeêuws-Vlaonderen; vls, Zêeuws-Vloandern)''Vlaanderen'' in isolation: . is the southernmost region of the province of Zeeland in the south-western Netherlands. It lies south of the Western Scheldt that separates t ...
in
Zeeland
, nl, Ik worstel en kom boven("I struggle and emerge")
, anthem = "Zeeuws volkslied"("Zeelandic Anthem")
, image_map = Zeeland in the Netherlands.svg
, map_alt =
, m ...
,
North Brabant
North Brabant ( nl, Noord-Brabant ; Brabantian: ; ), also unofficially called Brabant, is a province in the south of the Netherlands. It borders the provinces of South Holland and Gelderland to the north, Limburg to the east, Zeeland to the we ...
and
Limburg
Limburg or Limbourg may refer to:
Regions
* Limburg (Belgium), a province since 1839 in the Flanders region of Belgium
* Limburg (Netherlands), a province since 1839 in the south of the Netherlands
* Diocese of Limburg, Roman Catholic Diocese in ...
) in the north and east, and with France (
French Flanders
French Flanders (french: La Flandre française) is a part of the historical County of Flanders in present-day France where a dialect of Dutch was or still is traditionally spoken. The region lies in the modern-day region of Hauts-de-France and r ...
in
Hauts-de-France
Hauts-de-France (; pcd, Heuts-d'Franche; , also ''Upper France'') is the northernmost Regions of France, region of France, created by the territorial reform of French regions in 2014, from a merger of Nord-Pas-de-Calais and Picardy. Its Prefectu ...
) and the
North Sea
The North Sea lies between Great Britain, Norway, Denmark, Germany, the Netherlands and Belgium. An epeiric sea on the European continental shelf, it connects to the Atlantic Ocean through the English Channel in the south and the Norwegian S ...
in the west.
Voeren
Voeren (; ) is a Flanders, Flemish Dutch language, Dutch-speaking Municipalities of Belgium, municipality with Municipalities with language facilities, facilities for the Walloons, French-speaking minority, located in the Belgium, Belgian provi ...
is an
exclave
An enclave is a territory (or a small territory apart of a larger one) that is entirely surrounded by the territory of one other state or entity. Enclaves may also exist within territorial waters. ''Enclave'' is sometimes used improperly to deno ...
of Flanders between Wallonia and the Netherlands, while
Baarle-Hertog
(; french: Baerle-Duc, ) is a Flemish municipality of Belgium, much of which consists of a number of small Belgian enclaves fully surrounded by the Netherlands.
Parts of are surrounded by the Dutch province of North Brabant, but it is part of t ...
in Flanders forms a complicated series of enclaves and exclaves with
Baarle-Nassau
Baarle-Nassau () is a municipality and town in the southern Netherlands, located in the province of North Brabant. It had a population of in . The town is the site of a complicated borderline between Belgium and the Netherlands, with 22 small ...
in the Netherlands. Germany, although bordering Wallonia and close to
Voeren
Voeren (; ) is a Flanders, Flemish Dutch language, Dutch-speaking Municipalities of Belgium, municipality with Municipalities with language facilities, facilities for the Walloons, French-speaking minority, located in the Belgium, Belgian provi ...
in Limburg, does not share a border with Flanders. The
German-speaking Community of Belgium
The German-speaking Community (german: links=no, Deutschsprachige Gemeinschaft, or DG; french: links=no, Communauté germanophone; nl, links=no, Duitstalige Gemeenschap), since 2017 also known as East Belgium (german: links=no, Ostbelgien), is ...
, also close to Voeren, does not border Flanders either. (The commune of
Plombières
Plombières (; german: Bleyberg or ''Bleiberg'', nl, Blieberg; wa, So-on-Mont-d'-Plomb) is a municipality of Wallonia located in the province of Liège, Belgium.
On 1 January 2006, Plombières had a total population of 10,401. The total are ...
, majority French speaking, lies between them.)
Flanders is a highly urbanised area, lying completely within the
Blue Banana
The Blue Banana (also known as the European Megalopolis or the Liverpool–Milan Axis) is a discontinuous corridor of urbanization spreading over Western and Central Europe, with a population of around 111 million. The conceptualisation of the ...
.
Antwerp
Antwerp (; nl, Antwerpen ; french: Anvers ; es, Amberes) is the largest city in Belgium by area at and the capital of Antwerp Province in the Flemish Region. With a population of 520,504, ,
Ghent
Ghent ( nl, Gent ; french: Gand ; traditional English: Gaunt) is a city and a municipality in the Flemish Region of Belgium. It is the capital and largest city of the East Flanders province, and the third largest in the country, exceeded in ...
,
Bruges
Bruges ( , nl, Brugge ) is the capital and largest City status in Belgium, city of the Provinces of Belgium, province of West Flanders in the Flemish Region of Belgium, in the northwest of the country, and the sixth-largest city of the countr ...
and
Leuven
Leuven (, ) or Louvain (, , ; german: link=no, Löwen ) is the capital and largest city of the province of Flemish Brabant in the Flemish Region of Belgium. It is located about east of Brussels. The municipality itself comprises the historic ...
are the largest cities of the
Flemish Region
The Flemish Region ( nl, Vlaams Gewest, ),; german: Flämische Region usually simply referred to as Flanders ( nl, link=no, Vlaanderen ) ; german: link=no, Flandern is one of the three regions of Belgium—alongside the Walloon Region and t ...
.
Antwerp
Antwerp (; nl, Antwerpen ; french: Anvers ; es, Amberes) is the largest city in Belgium by area at and the capital of Antwerp Province in the Flemish Region. With a population of 520,504, has a population of more than 500,000 citizens and is the largest city,
Ghent
Ghent ( nl, Gent ; french: Gand ; traditional English: Gaunt) is a city and a municipality in the Flemish Region of Belgium. It is the capital and largest city of the East Flanders province, and the third largest in the country, exceeded in ...
has a population of 250,000 citizens, followed by
Bruges
Bruges ( , nl, Brugge ) is the capital and largest City status in Belgium, city of the Provinces of Belgium, province of West Flanders in the Flemish Region of Belgium, in the northwest of the country, and the sixth-largest city of the countr ...
with 120,000 citizens and
Leuven
Leuven (, ) or Louvain (, , ; german: link=no, Löwen ) is the capital and largest city of the province of Flemish Brabant in the Flemish Region of Belgium. It is located about east of Brussels. The municipality itself comprises the historic ...
counts almost 100,000 citizens.
Brussels
Brussels (french: Bruxelles or ; nl, Brussel ), officially the Brussels-Capital Region (All text and all but one graphic show the English name as Brussels-Capital Region.) (french: link=no, Région de Bruxelles-Capitale; nl, link=no, Bruss ...
is a part of Flanders as far as community matters are concerned, but does not belong to the Flemish Region.
Flanders has two main geographical regions: the coastal
Yser
The Yser ( , ; nl, IJzer ) is a river that rises in French Flanders (the north of France), enters the Belgian province of West Flanders and flows through the '' Ganzepoot'' and into the North Sea at the town of Nieuwpoort.
The source of the Ys ...
basin plain in the north-west and a central plain. The first consists mainly of sand dunes and
clay
Clay is a type of fine-grained natural soil material containing clay minerals (hydrous aluminium phyllosilicates, e.g. kaolin, Al2 Si2 O5( OH)4).
Clays develop plasticity when wet, due to a molecular film of water surrounding the clay par ...
ey
alluvial
Alluvium (from Latin ''alluvius'', from ''alluere'' 'to wash against') is loose clay, silt, sand, or gravel that has been deposited by running water in a stream bed, on a floodplain, in an alluvial fan or beach, or in similar settings. Alluv ...
soils in the
polder
A polder () is a low-lying tract of land that forms an artificial hydrological entity, enclosed by embankments known as dikes. The three types of polder are:
# Land reclaimed from a body of water, such as a lake or the seabed
# Flood plains s ...
s. Polders are areas of land, close to or below sea level that have been reclaimed from the sea, from which they are protected by
dikes
Dyke (UK) or dike (US) may refer to:
General uses
* Dyke (slang), a slang word meaning "lesbian"
* Dike (geology), a subvertical sheet-like intrusion of magma or sediment
* Dike (mythology), ''Dikē'', the Greek goddess of moral justice
* Dikes, ...
or, a little further inland, by fields that have been drained with canals. With similar soils along the lowermost
Scheldt
The Scheldt (french: Escaut ; nl, Schelde ) is a river that flows through northern France, western Belgium, and the southwestern part of Netherlands, the Netherlands, with its mouth at the North Sea. Its name is derived from an adjective corr ...
basin starts the central plain, a smooth, slowly rising fertile area irrigated by many waterways that reaches an average height of about five metres (16.4 ft) above sea level with wide valleys of its rivers upstream as well as the
Campine
The Campine ( French ) or De Kempen (Dutch ) is a natural region situated chiefly in north-eastern Belgium and parts of the south-eastern Netherlands which once consisted mainly of extensive moors, tracts of sandy heath, and wetlands. It encom ...
region to the east having sandy soils at altitudes around thirty metres. Near its southern edges close to
Wallonia
Wallonia (; french: Wallonie ), or ; nl, Wallonië ; wa, Waloneye or officially the Walloon Region (french: link=no, Région wallonne),; nl, link=no, Waals gewest; wa, link=no, Redjon walone is one of the three regions of Belgium—alo ...
one can find slightly rougher land, richer in
calcium
Calcium is a chemical element with the symbol Ca and atomic number 20. As an alkaline earth metal, calcium is a reactive metal that forms a dark oxide-nitride layer when exposed to air. Its physical and chemical properties are most similar to ...
, with low hills reaching up to and small valleys, and at the eastern border with the Netherlands, in the
Meuse
The Meuse ( , , , ; wa, Moûze ) or Maas ( , ; li, Maos or ) is a major European river, rising in France and flowing through Belgium and the Netherlands before draining into the North Sea from the Rhine–Meuse–Scheldt delta. It has a t ...
basin, there are
marl
Marl is an earthy material rich in carbonate minerals, clays, and silt. When hardened into rock, this becomes marlstone. It is formed in marine or freshwater environments, often through the activities of algae.
Marl makes up the lower part o ...
caves (''mergelgrotten''). Its
exclave
An enclave is a territory (or a small territory apart of a larger one) that is entirely surrounded by the territory of one other state or entity. Enclaves may also exist within territorial waters. ''Enclave'' is sometimes used improperly to deno ...
around
Voeren
Voeren (; ) is a Flanders, Flemish Dutch language, Dutch-speaking Municipalities of Belgium, municipality with Municipalities with language facilities, facilities for the Walloons, French-speaking minority, located in the Belgium, Belgian provi ...
between the Dutch border and
Wallonia
Wallonia (; french: Wallonie ), or ; nl, Wallonië ; wa, Waloneye or officially the Walloon Region (french: link=no, Région wallonne),; nl, link=no, Waals gewest; wa, link=no, Redjon walone is one of the three regions of Belgium—alo ...
's
Liège Province
Liège (; wa, Lîdje ; nl, Luik ; german: Lüttich ) is the easternmost province of the Wallonia region of Belgium.
Liège Province is the only Belgian province that has borders with three countries. It borders (clockwise from the north) the Du ...
attains a maximum altitude of above sea level.
Administrative divisions
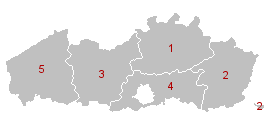
The present-day
Flemish Region
The Flemish Region ( nl, Vlaams Gewest, ),; german: Flämische Region usually simply referred to as Flanders ( nl, link=no, Vlaanderen ) ; german: link=no, Flandern is one of the three regions of Belgium—alongside the Walloon Region and t ...
covers and is divided into
five provinces,
22 arrondissements and
308 cities or municipalities.
The province of Flemish Brabant is the most recently created, being formed in 1995 after the splitting of the
province of Brabant
The Province of Brabant (, , ) was a province in Belgium from 1830 to 1995. It was created in 1815 as South Brabant, part of the United Kingdom of the Netherlands. In 1995, it was split into the Dutch-speaking Flemish Brabant, the French-speak ...
on a linguistic basis.
Most municipalities are made up of several former municipalities, now called ''
deelgemeente
A deelgemeente (, literally ''part-municipality'') or section ( French) is a subdivision of a municipality in Belgium and, until March 2014, in the Netherlands as well.
Belgium
Each municipality in Belgium that existed as a separate entity on 1 J ...
n''. The largest municipality (both in terms of population and area) is
Antwerp
Antwerp (; nl, Antwerpen ; french: Anvers ; es, Amberes) is the largest city in Belgium by area at and the capital of Antwerp Province in the Flemish Region. With a population of 520,504, , having more than half a million inhabitants. Its nine ''deelgemeenten'' have a special status and are called
districts
A district is a type of administrative division that, in some countries, is managed by the local government. Across the world, areas known as "districts" vary greatly in size, spanning regions or counties, several municipalities, subdivisions o ...
, which have an elected council and a college. While any municipality with more than 100,000 inhabitants can establish districts, only Antwerp did this so far. The smallest municipality (also both in terms of population and area) is
Herstappe
Herstappe (; ) is a Flemish municipality located in the Belgian province of Limburg. On January 1, 2016, Herstappe had a total population of 89. The total area is 1.35 km² which gives a population density of 66 inhabitants per km². It is t ...
(Limburg).

The
Flemish Community
The Flemish Community ( nl, Vlaamse Gemeenschap ; french: Communauté flamande ; german: Flämische Gemeinschaft ) is one of the three institutional communities of Belgium, established by the Belgian constitution and having legal responsibilitie ...
covers both the
Flemish Region
The Flemish Region ( nl, Vlaams Gewest, ),; german: Flämische Region usually simply referred to as Flanders ( nl, link=no, Vlaanderen ) ; german: link=no, Flandern is one of the three regions of Belgium—alongside the Walloon Region and t ...
and, together with the French Community, the
Brussels-Capital Region
Brussels (french: Bruxelles or ; nl, Brussel ), officially the Brussels-Capital Region (All text and all but one graphic show the English name as Brussels-Capital Region.) (french: link=no, Région de Bruxelles-Capitale; nl, link=no, Bruss ...
. Brussels, an enclave within the province of Flemish Brabant, is not divided into any province nor is it part of any. It coincides with the
Arrondissement of Brussels-Capital
The Arrondissement of Brussels-Capital ( nl, Arrondissement Brussel-Hoofdstad; french: Arrondissement de Bruxelles-Capitale; german: Verwaltungsbezirk Brüssel-Hauptstadt) is the only administrative arrondissement in the Brussels Capital Region ...
and includes
19 municipalities.
The
Flemish Government
The Flemish Government ( nl, Vlaamse regering ) is the executive branch of the Flemish Community and the Flemish Region of Belgium. It consists of a government cabinet, headed by the Minister-President and accountable to the Flemish Parliament, a ...
has its own local institutions in the Brussels-Capital Region, being the ''
Vlaamse Gemeenschapscommissie
The Vlaamse Gemeenschapscommissie (or VGC, or, in English, the Flemish Community Commission) is the local representative of the Flemish authorities in the Brussels-Capital Region, one of the three regions of Belgium. The VGC depends on the Flemish ...
'' (VGC), and its municipal antennae (''Gemeenschapscentra'', community centres for the Flemish community in Brussels). These institutions are independent from the educational, cultural and social institutions that depend directly on the Flemish Government. They exert, among others, all those cultural competences that outside Brussels fall under the provinces.
Climate
The climate is maritime
temperate
In geography, the temperate climates of Earth occur in the middle latitudes (23.5° to 66.5° N/S of Equator), which span between the tropics and the polar regions of Earth. These zones generally have wider temperature ranges throughout t ...
, with significant precipitation in all seasons (
Köppen climate classification
The Köppen climate classification is one of the most widely used climate classification systems. It was first published by German-Russian climatologist Wladimir Köppen (1846–1940) in 1884, with several later modifications by Köppen, notabl ...
: ''Cfb''; the average temperature is in January, and in July; the average precipitation is 65 millimetres (2.6 in) in January, and 78 millimetres (3.1 in) in July).
Economy


Total GDP of the Flemish Region in 2018 was €270 billion (
Eurostat
Eurostat ('European Statistical Office'; DG ESTAT) is a Directorate-General of the European Commission located in the Kirchberg, Luxembourg, Kirchberg quarter of Luxembourg City, Luxembourg. Eurostat's main responsibilities are to provide statis ...
figures). Per capita GDP at
purchasing power parity
Purchasing power parity (PPP) is the measurement of prices in different countries that uses the prices of specific goods to compare the absolute purchasing power of the countries' currency, currencies. PPP is effectively the ratio of the price of ...
was 20% above the EU average. Flemish productivity per capita is about 13% higher than that in
Wallonia
Wallonia (; french: Wallonie ), or ; nl, Wallonië ; wa, Waloneye or officially the Walloon Region (french: link=no, Région wallonne),; nl, link=no, Waals gewest; wa, link=no, Redjon walone is one of the three regions of Belgium—alo ...
, and wages are about 7% higher than in Wallonia.
Flanders was one of the first continental European areas to undergo the
Industrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution was the transition to new manufacturing processes in Great Britain, continental Europe, and the United States, that occurred during the period from around 1760 to about 1820–1840. This transition included going f ...
, in the 19th century. Initially, the modernization relied heavily on food processing and textile. However, by the 1840s the textile industry of Flanders was in severe crisis and there was famine in Flanders (1846–50). After World War II,
Antwerp
Antwerp (; nl, Antwerpen ; french: Anvers ; es, Amberes) is the largest city in Belgium by area at and the capital of Antwerp Province in the Flemish Region. With a population of 520,504, and
Ghent
Ghent ( nl, Gent ; french: Gand ; traditional English: Gaunt) is a city and a municipality in the Flemish Region of Belgium. It is the capital and largest city of the East Flanders province, and the third largest in the country, exceeded in ...
experienced a fast expansion of the
chemical
A chemical substance is a form of matter having constant chemical composition and characteristic properties. Some references add that chemical substance cannot be separated into its constituent elements by physical separation methods, i.e., wi ...
and petroleum industries. Flanders also attracted a large majority of foreign investments in Belgium. The
1973
Events January
* January 1 - The United Kingdom, the Republic of Ireland and Denmark enter the European Economic Community, which later becomes the European Union.
* January 15 – Vietnam War: Citing progress in peace negotiations, U.S. ...
and
1979 oil crises sent the economy into a recession. The steel industry remained in relatively good shape. In the 1980s and 90s, the economic centre of Belgium continued to shift further to Flanders and is now concentrated in the populous
Flemish Diamond
The Flemish Diamond ( nl, Vlaamse Ruit) is the Flemish reference to a network of four metropolitan areas in Belgium, three of which are in the central provinces of Flanders, together with the Brussels Capital Region.Note: The Flemish government ...
area. Nowadays, the Flemish economy is mainly service-oriented.
Belgium is a founding member of the
European Coal and Steel Community
The European Coal and Steel Community (ECSC) was a European organization created after World War II to regulate the coal and steel industries. It was formally established in 1951 by the Treaty of Paris, signed by Belgium, France, Italy, Luxembo ...
in 1951, which evolved into the present-day
European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational political and economic union of member states that are located primarily in Europe. The union has a total area of and an estimated total population of about 447million. The EU has often been des ...
. In 1999, the
euro
The euro ( symbol: €; code: EUR) is the official currency of 19 out of the member states of the European Union (EU). This group of states is known as the eurozone or, officially, the euro area, and includes about 340 million citizens . ...
, the single European currency, was introduced in Flanders. It replaced the
Belgian franc
The Belgian franc ( nl, Belgische frank, french: Franc belge, german: Belgischer Franken) was the currency of the Kingdom of Belgium from 1832 until 2002 when the Euro was introduced. It was subdivided into 100 subunits, each known as a in Dutch ...
in 2002.
The Flemish economy is strongly export-oriented, in particular of high value-added goods. The main imports are food products, machinery, rough diamonds, petroleum and petroleum products, chemicals, clothing and accessories, and textiles. The main exports are automobiles, food and food products, iron and steel, finished diamonds, textiles, plastics, petroleum products, and non-ferrous metals. Since 1922, Belgium and Luxembourg have been a single trade market within a
customs
Customs is an authority or agency in a country responsible for collecting tariffs and for controlling the flow of goods, including animals, transports, personal effects, and hazardous items, into and out of a country. Traditionally, customs ...
and
currency union
A currency union (also known as monetary union) is an intergovernmental agreement that involves two or more State (polity), states sharing the same currency. These states may not necessarily have any Economic integration#Stages, further integratio ...
—the
Belgium–Luxembourg Economic Union
The Belgium–Luxembourg Economic Union ( nl, Belgisch-Luxemburgse Economische Unie, french: Union économique belgo-luxembourgeoise, german: Belgisch-Luxemburgische Wirtschaftsunion, lb, Belsch-Lëtzebuerger Wirtschaftsunioun), abbreviated to B ...
. Its main trading partners are Germany, the Netherlands, France, the United Kingdom, Italy, the United States, and Spain.
Antwerp is the number one diamond market in the world, diamond exports account for roughly 1/10 of Belgian exports. The Antwerp-based
BASF
BASF Societas Europaea, SE () is a German multinational corporation, multinational chemical company and the List of largest chemical producers, largest chemical producer in the world. Its headquarters is located in Ludwigshafen, Germany.
The ...
plant is the largest BASF-base outside Germany, and accounts on its own for about 2% of Belgian exports. Other industrial and service activities in Antwerp include car manufacturing, telecommunications, photographic products.
Flanders is home to several science and technology institutes, such as
IMEC
Interuniversity Microelectronics Centre (IMEC) is an international research & development organization, active in the fields of nanoelectronics and digital technologies, with headquarters in Belgium. Luc Van den hove has served as President and ...
,
VITO
Vito is an Italian name that is derived from the Latin word "''vita''", meaning "life".
It is a modern form of the Latin name Vitus, meaning "life-giver," as in San Vito or Saint Vitus, the patron saint of dogs and a heroic figure in southern ...
,
Flanders DC Flanders District of Creativity or Flanders DC is a non-profit organization founded by the Flemish government, on 7 May 2004, centered around the design and fashion sector.
Goals
* Research: analysis of the role of creativity in the economic growt ...
and
Flanders Make
Flanders (, ; Dutch: ''Vlaanderen'' ) is the Flemish-speaking northern portion of Belgium and one of the communities, regions and language areas of Belgium. However, there are several overlapping definitions, including ones related to culture ...
.
Infrastructure
Flanders has developed an extensive transportation infrastructure of ports, canals, railways and highways. The
Port of Antwerp
The Port of Antwerp-Bruges is the port of the City of Antwerp. It is located in Flanders (Belgium), mainly in the province of Antwerp but also partially in the province of East Flanders. It is a seaport in the heart of Europe accessible to ...
is the second-largest in Europe, after
Rotterdam
Rotterdam ( , , , lit. ''The Dam on the River Rotte'') is the second largest city and municipality in the Netherlands. It is in the province of South Holland, part of the North Sea mouth of the Rhine–Meuse–Scheldt delta, via the ''"N ...
. Other ports are
Bruges-Zeebrugge,
Ghent
Ghent ( nl, Gent ; french: Gand ; traditional English: Gaunt) is a city and a municipality in the Flemish Region of Belgium. It is the capital and largest city of the East Flanders province, and the third largest in the country, exceeded in ...
and
Ostend
Ostend ( nl, Oostende, ; french: link=no, Ostende ; german: link=no, Ostende ; vls, Ostende) is a coastal city and municipality, located in the province of West Flanders in the Flemish Region of Belgium. It comprises the boroughs of Mariakerk ...
, of which Zeebrugge and Ostend are located at the .
Whereas railways are managed by the federal
National Railway Company of Belgium
french: Société nationale des chemins de fer belgesgerman: Nationale Gesellschaft der Belgischen Eisenbahnen
, type = Statutory corporation
, industry = Rail Transport
, foundation = 1926
, founder = Government of ...
, other public transport (
De Lijn
Vlaamse Vervoersmaatschappij De Lijn (English: Flemish transport company ''De Lijn''), usually known as De Lijn (, "The Line"), is a company run by the Flemish government in Belgium to provide public transportation with about 2240 buses and 399 tr ...
) and roads are managed by the Flemish region.
The main airport is
Brussels Airport
Brussels Airport, nl, Luchthaven Brussel, vls, Vliegpling Brussel, german: Flughafen Brüssel is an international airport northeast of Brussels, the capital of Belgium. In 2019, more than 26 million passengers arrived or departed at Bruss ...
, the only other civilian airport with scheduled services in Flanders is
Antwerp International Airport
Antwerp International Airport, french: Aéroport International d'Anvers, german: Flughafen Antwerpen is a small international airport serving the City of Antwerp in the Province of Antwerp in the Flemish Region of Belgium. Located south of t ...
, but there are two other ones with cargo or charter flights:
Ostend-Bruges International Airport and
Kortrijk-Wevelgem International Airport
Flanders International Airport, Flanders Airport or Kortrijk-Wevelgem International Airport is an airport located in the town of Wevelgem, West Flanders in the Flemish Region of Belgium and partly also in the Bissegem section of the city of Kor ...
, both in West Flanders.
Demographics
The highest population density is found in the area circumscribed by the
Brussels
Brussels (french: Bruxelles or ; nl, Brussel ), officially the Brussels-Capital Region (All text and all but one graphic show the English name as Brussels-Capital Region.) (french: link=no, Région de Bruxelles-Capitale; nl, link=no, Bruss ...
-
Antwerp
Antwerp (; nl, Antwerpen ; french: Anvers ; es, Amberes) is the largest city in Belgium by area at and the capital of Antwerp Province in the Flemish Region. With a population of 520,504, -
Ghent
Ghent ( nl, Gent ; french: Gand ; traditional English: Gaunt) is a city and a municipality in the Flemish Region of Belgium. It is the capital and largest city of the East Flanders province, and the third largest in the country, exceeded in ...
-
Leuven
Leuven (, ) or Louvain (, , ; german: link=no, Löwen ) is the capital and largest city of the province of Flemish Brabant in the Flemish Region of Belgium. It is located about east of Brussels. The municipality itself comprises the historic ...
agglomerations that surround Mechelen and is known as the
Flemish Diamond
The Flemish Diamond ( nl, Vlaamse Ruit) is the Flemish reference to a network of four metropolitan areas in Belgium, three of which are in the central provinces of Flanders, together with the Brussels Capital Region.Note: The Flemish government ...
, in other important urban centres as
Bruges
Bruges ( , nl, Brugge ) is the capital and largest City status in Belgium, city of the Provinces of Belgium, province of West Flanders in the Flemish Region of Belgium, in the northwest of the country, and the sixth-largest city of the countr ...
,
Roeselare
Roeselare (; french: Roulers, ; West Flemish: ''Roeseloare'') is a Belgian city and municipality in the Flemish province of West Flanders. The municipality comprises the city of Roeselare proper and the towns of Beveren, Oekene and Rumbeke.
The ...
and
Kortrijk
Kortrijk ( , ; vls, Kortryk or ''Kortrik''; french: Courtrai ; la, Cortoriacum), sometimes known in English as Courtrai or Courtray ( ), is a Belgian City status in Belgium, city and Municipalities in Belgium, municipality in the Flemish Regio ...
to the west, and notable centres
Turnhout
Turnhout () is a Belgium, Belgian Municipalities in Belgium, municipality and city located in the Flemish Region, Flemish Provinces of Belgium, province of Antwerp (province), Antwerp. The municipality comprises only the city of Turnhout proper. ...
and
Hasselt
Hasselt (, , ; la, Hasseletum, Hasselatum) is a Belgian city and municipality, and capital and largest city of the province of Limburg in the Flemish Region of Belgium. It is known for its former branding as "the city of taste", as well as its ...
to the east. On 1 January 2015, the Flemish Region had a population of 6,444,127 and about 15% of the 1,175,173 people in the Brussels Region are also considered Flemish.
Religion

The Belgian constitution provides for
freedom of religion
Freedom of religion or religious liberty is a principle that supports the freedom of an individual or community, in public or private, to manifest religion or belief in teaching, practice, worship, and observance. It also includes the freedom ...
, and the various governments in general respect this right in practice. Since independence,
Catholicism
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
, counterbalanced by strong
freethought
Freethought (sometimes spelled free thought) is an epistemological viewpoint which holds that beliefs should not be formed on the basis of authority, tradition, revelation, or dogma, and that beliefs should instead be reached by other methods ...
movements, has had an important role in Belgium's politics, since the 20th century in Flanders mainly via the Christian trade union
ACV and the
Christian Democratic and Flemish
Christian Democratic and Flemish (, , CD&V) is a Flemish Christian-democratic political party in Belgium. The party has historical ties to both trade unionism ( ACV) and trade associations (UNIZO) and the Farmer's League. Until 2001, the party wa ...
party (CD&V). According to the ''2001 Survey and Study of Religion'', about 47 percent of the Belgian population identify themselves as belonging to the Catholic Church, while Islam is the second-largest religion at 3.5 percent. A 2006 inquiry in Flanders, considered more religious than Wallonia, showed that 55% considered themselves religious, and 36% believed that God created the world.
Jews
have been present in Flanders for a long time, in particular
in Antwerp. More recently, Muslims have immigrated to Flanders, now forming the largest minority religion with about 3.9% in the Flemish Region and 25% in Brussels. The largest Muslim group is Moroccan in origin, while the second largest is Turkish in origin.
Education

Education is compulsory from the ages of six to 18, but most
Flemings
The Flemish or Flemings ( nl, Vlamingen ) are a Germanic ethnic group native to Flanders, Belgium, who speak Dutch. Flemish people make up the majority of Belgians, at about 60%.
"''Flemish''" was historically a geographical term, as all inha ...
continue to study until around 23. Among the
Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development
The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD; french: Organisation de coopération et de développement économiques, ''OCDE'') is an intergovernmental organization, intergovernmental organisation with 38 member countries ...
countries in 1999, Flanders had the third-highest proportion of 18- to 21-year-olds enrolled in
postsecondary education
Tertiary education, also referred to as third-level, third-stage or post-secondary education, is the educational level following the completion of secondary education. The World Bank, for example, defines tertiary education as including univers ...
. Flanders also scores very high in international comparative studies on education. Its secondary school students consistently rank among the top three for mathematics and science. However, the success is not evenly spread: ethnic minority youth score consistently lower, and the difference is larger than in most comparable countries.
Mirroring the historical political conflicts between the secular and Catholic segments of the population, the Flemish educational system is split into a secular branch controlled by the communities, the provinces, or the municipalities, and a
subsidised religious—mostly Catholic—branch. For the subsidised schools, the main costs such as the teacher's wages and building maintenance completely borne by the Flemish government. Subsidised schools are also free to determine their own teaching and examination methods, but in exchange, they must be able to prove that certain minimal terms are achieved by keeping records of the given lessons and exams. It should however be noted that—at least for the Catholic schools—the religious authorities have very limited power over these schools, neither do the schools have a lot of power on their own. Instead, the Catholic schools are a member of the Catholic umbrella organisation . The VSKO determines most practicalities for schools, like the advised schedules per study field. However, there's freedom of education in Flanders, which doesn't only mean that every pupil can choose his/her preferred school, but also that every organisation can found a school, and even be subsidised when abiding the different rules. This resulted also in some smaller school systems follow 'methodical pedagogies' (e.g.
Steiner,
Montessori
The Montessori method of education involves children's natural interests and activities rather than formal teaching methods. A Montessori classroom places an emphasis on hands-on learning and developing real-world skills. It emphasizes indepen ...
, or
Freinet) or serve the Jewish and Protestant minorities.
During the school year 2003–2004, 68.30% of the total population of children between the ages of six and 18 went to subsidized private schools (both religious schools or 'methodical pedagogies' schools).
The big freedom given to schools results in a constant competition to be the "best" school. The schools get certain reputations amongst parents and employers. So it's important for schools to be the best school since the subsidies depend on the number of pupils. This competition has been pinpointed as one of the main reasons for the high overall quality of the Flemish education. However, the importance of a school's reputation also makes schools more eager to expel pupils that don't perform well. Resulting in the ethnic differences and the well-known waterfall system: pupils start high in the perceived hierarchy, and then drop towards more professional oriented directions or "easier" schools when they can't handle the pressure any longer.
Healthcare
Healthcare is a federal matter, but the
Flemish Government
The Flemish Government ( nl, Vlaamse regering ) is the executive branch of the Flemish Community and the Flemish Region of Belgium. It consists of a government cabinet, headed by the Minister-President and accountable to the Flemish Parliament, a ...
is responsible for care, health education and
preventive care
Preventive healthcare, or prophylaxis, consists of measures taken for the purposes of disease prevention.Hugh R. Leavell and E. Gurney Clark as "the science and art of preventing disease, prolonging life, and promoting physical and mental hea ...
.
Culture
Language and literature

The standard language in Flanders is
Dutch
Dutch commonly refers to:
* Something of, from, or related to the Netherlands
* Dutch people ()
* Dutch language ()
Dutch may also refer to:
Places
* Dutch, West Virginia, a community in the United States
* Pennsylvania Dutch Country
People E ...
; spelling and grammar are regulated by a single authority, the
Dutch Language Union
The Dutch Language Union (Dutch: , NTU) is an international regulatory institution that governs issues regarding the Dutch language. It is best known for its spelling reforms which are promulgated by member states, grammar books, the Green Boo ...
(''Nederlandse Taalunie''), comprising a committee of ministers of the Flemish and Dutch governments, their advisory council of appointed experts, a controlling commission of 22 parliamentarians, and a secretariate.
The term
Flemish
Flemish (''Vlaams'') is a Low Franconian dialect cluster of the Dutch language. It is sometimes referred to as Flemish Dutch (), Belgian Dutch ( ), or Southern Dutch (). Flemish is native to Flanders, a historical region in northern Belgium; ...
can be applied to the Dutch spoken in Flanders; it shows many regional and local variations.
The biggest difference between Belgian Dutch and Dutch used in the Netherlands is in the pronunciation of words. The Dutch spoken in the north of the Netherlands is typically described as being "sharper", while Belgian Dutch is "softer". In Belgian Dutch, there are also fewer vowels pronounced as
diphthongs
A diphthong ( ; , ), also known as a gliding vowel, is a combination of two adjacent vowel sounds within the same syllable. Technically, a diphthong is a vowel with two different targets: that is, the tongue (and/or other parts of the speech o ...
. When it comes to spelling, Belgian Dutch language purists historically avoided writing words using a French spelling, or searched for specific translations of words derived from French, while the Dutch often retain the French spelling. For example, the Dutch word "punaise" (English: ''
Drawing pin
A drawing pin (in British English) or thumb tack (in North American English) is a short nail or pin used to fasten items to a wall or board for display and intended to be inserted by hand, usually using the thumb. A variety of names is used t ...
'') is derived directly from the French language. Belgian Dutch language purists have lobbied to accept the word "duimspijker" (literally: ''thumb spike'') as official Dutch, though the Dutch Language Union never accepted it as standard Dutch. Other proposals by purists were sometimes accepted, and sometimes reverted again in later spelling revisions. As language purists were quite often professionally involved in language (e.g. as a teacher), these unofficial purist translations are found more often in Belgian Dutch texts.
The earliest example of literature in non-
standardized dialects in the current area of Flanders is
Hendrik van Veldeke
Heinrich von Veldeke (aka: , Dutch language, Dutch Hendrik van Veldeke, born before or around 1150 – died after 1184) is the first writer in the Low Countries known by name who wrote in a European language other than Latin. He was born in Velde ...
's ''Eneas Romance'', the first courtly romance in a
Germanic language
The Germanic languages are a branch of the Indo-European language family spoken natively by a population of about 515 million people mainly in Europe, North America, Oceania and Southern Africa. The most widely spoken Germanic language, Engli ...
(12th century). With a writer of
Hendrik Conscience
Henri (Hendrik) Conscience (3 December 1812 – 10 September 1883) was a Belgian author. He is considered the pioneer of Dutch-language literature in Flanders, writing at a time when Belgium was dominated by the French language among the upper cl ...
's stature,
Flemish literature Flemish literature is literature from Flanders, historically a region comprising parts of present-day Belgium, France and the Netherlands. Until the early 19th century, this literature was regarded as an integral part of Dutch literature. After Bel ...
rose ahead of French literature in Belgium's early history.
Guido Gezelle
Guido Pieter Theodorus Josephus Gezelle (1 May 1830 – 27 November 1899) was an influential writer and poet and a Roman Catholic priest from Belgium. He is famous for the use of the West Flemish dialect.
Life
Gezelle was born in Bruges in ...
not only explicitly referred to his writings as Flemish but used it in many of his poems, and strongly defended it:
Original
from ''kleengedichtjes'' (1860?)Gij zegt dat 't vlaamsch te niet zal gaan:
't en zal!
dat 't waalsch gezwets zal boven slaan:
't en zal!
Dat hopen, dat begeren wij:
dat zeggen en dat zweren wij:
zoo lange als wij ons weren, wij:
't en zal, 't en zal,
't en zal!
; Translation
You say Flemish will fade away:
It shan't!
that Walloon twaddle will have its way:
It shan't!
This we hope, for this we hanker:
this we say and this we vow:
as long as we fight back, we:
It shan't, It shan't,
It shan't!
The distinction between
Dutch
Dutch commonly refers to:
* Something of, from, or related to the Netherlands
* Dutch people ()
* Dutch language ()
Dutch may also refer to:
Places
* Dutch, West Virginia, a community in the United States
* Pennsylvania Dutch Country
People E ...
and Flemish literature, often perceived politically, is also made on intrinsic grounds by some experts such as Kris Humbeeck, professor of Literature at the
University of Antwerp
The University of Antwerp ( nl, Universiteit Antwerpen) is a major Belgian university located in the city of Antwerp. The official abbreviation is ''UA'', but ''UAntwerpen'' is more recently used. The University of Antwerp has about 20,000 stud ...
.
[ ] Nevertheless, most
Dutch-language
Dutch ( ) is a West Germanic language spoken by about 25 million people as a first language and 5 million as a second language. It is the third most widely spoken Germanic language, after its close relatives German and English. ''Afrikaans'' ...
literature read (and appreciated to varying degrees) in Flanders is the same as that in the Netherlands.
Influential Flemish writers include
Ernest Claes
Andreas Ernestus Josephus Claes (24 October 1885 in Zichem – 2 September 1968 in Elsene) was a Belgian author. He is best known for his regional novels, including ''De Witte'' ("Whitey"), which was the source material for the first Flemish movie ...
,
Stijn Streuvels
Stijn Streuvels (3 October 1871, Heule, Kortrijk - 15 August 1969, Ingooigem, Anzegem), born Franciscus (Frank) Petrus Maria Lateur, was a Flemish Belgian writer.
Biography
He started writing at a very young age. He was inspired by his uncle, th ...
and
Felix Timmermans
Leopold Maximiliaan Felix Timmermans (5 July 1886 – 24 January 1947) is a much translated author from Flanders.
He was nominated for the Nobel Prize in Literature three times.
Life
Timmermans was born in the Belgian city of Lier, as the thi ...
. Their novels mostly describe rural life in Flanders in the 19th century and at beginning of the 20th. Widely read by the older generations, they are considered somewhat old-fashioned by present-day critics. Some famous Flemish writers of the early 20th century wrote in French, including Nobel Prize winners (1911)
Maurice Maeterlinck
Maurice Polydore Marie Bernard Maeterlinck (29 August 1862 – 6 May 1949), also known as Count (or Comte) Maeterlinck from 1932, was a Belgian playwright, poet, and essayist who was Flemish but wrote in French. He was awarded the Nobel Prize in ...
and
Emile Verhaeren
Emil or Emile may refer to:
Literature
*'' Emile, or On Education'' (1762), a treatise on education by Jean-Jacques Rousseau
* ''Émile'' (novel) (1827), an autobiographical novel based on Émile de Girardin's early life
*'' Emil and the Detecti ...
. They were followed by a younger generation, including
Paul van Ostaijen
Paul van Ostaijen (22 February 1896 – 18 March 1928) was a Belgian Dutch-language poet and writer.
Nickname
Van Ostaijen was born in Antwerp to Dutch father and Flemish mother. His nickname was ''Mister 1830'', derived from his habit of walki ...
and
Gaston Burssens, who ''
activated
"Activated" is a song by English singer Cher Lloyd. It was released on 22 July 2016 through Vixen Records. The song was made available to stream exclusively on ''Rolling Stone'' a day before to release (on 21 July 2016).
Background
In an interv ...
'' the
Flemish Movement
The Flemish Movement ( nl, Vlaamse Beweging) is an umbrella term which encompasses various political groups in the Belgian region of Flanders and, less commonly, in French Flanders. Ideologically, it encompasses groups which have sought to promo ...
.
[ Still widely read and translated into other languages (including English) are the novels of authors such as ]Willem Elsschot
Alphonsus Josephus de Ridder (7 May 1882 – 31 May 1960), was a Belgian writer and poet who wrote under the pseudonym Willem Elsschot (). One of the most prominent Flemish authors, his most famous work, ''Cheese'' (1933) is the most translated ...
, Louis Paul Boon
Louis Paul Boon (15 March 1912, in Aalst, Belgium, Aalst – 10 May 1979, in Erembodegem) was a Belgian writer of novels, poetry, pornography, columns and art criticism. He was also a painter. He is best known for the novels ''My Little War'' (1947 ...
and Hugo Claus
Hugo Maurice Julien Claus (; 5 April 1929 – 19 March 2008) was a leading Belgian author who published under his own name as well as various pseudonyms. Claus' literary contributions spanned the genres of drama, the novel, and poetry; he also l ...
. The recent crop of writers includes the novelists Tom Lanoye
Tom or TOM may refer to:
* Tom (given name), a diminutive of Thomas or Tomás or an independent Aramaic given name (and a list of people with the name)
Characters
* Tom Anderson, a character in ''Beavis and Butt-Head''
* Tom Beck, a character ...
and Herman Brusselmans
Herman Frans Martha Brusselmans (; born 9 October 1957) is a Belgian novelist, poet, playwright and columnist. He lives in Ghent. He is one of the best-selling authors in Flanders, but controversial at the same time for his profane language and ...
, and poets such as the married couple Herman de Coninck and Kristien Hemmerechts
Kristien Hemmerechts (born 27 August 1955) is a Belgian writer.
Life
Kristien Hemmerechts studied Germanic philology at the ''Katholieke Universiteit Brussel'' (KUB) and the Katholieke Universiteit Leuven (KUL). Afterwards, she studied litera ...
.
Languages
At the creation of the Belgian state, French was the only official language. Historically Flanders was a Dutch-speaking region. For a long period, French was used as a second language
A person's second language, or L2, is a language that is not the native language (first language or L1) of the speaker, but is learned later. A second language may be a neighbouring language, another language of the speaker's home country, or a fo ...
and, like elsewhere in Europe, commonly spoken among the aristocracy. There is still a French-speaking minority in Flanders, especially in the municipalities with language facilities
There are 27 municipalities with language facilities ( nl, faciliteitengemeenten; french: communes à facilités; german: Fazilitäten-Gemeinden) in Belgium which must offer linguistic services to residents in Dutch, French, or German in additio ...
, along the language border and the Brussels periphery
The Brussels Periphery (, i.e. the "Brussels Rim", or ''Vlaamse Rand'', i.e. the "Flemish Rim", or just ''De Rand'', "the Rim"; ) refers to 19 Flemish municipalities that encircle the Brussels-Capital Region. The Brussels Region is an enclave of ...
(Vlaamse Rand), though many of them are French-speakers that migrated to Flanders in recent decades.
In French Flanders
French Flanders (french: La Flandre française) is a part of the historical County of Flanders in present-day France where a dialect of Dutch was or still is traditionally spoken. The region lies in the modern-day region of Hauts-de-France and r ...
, French is the only official language and now the native language of the majority of the population, but there is still a minority of Dutch-speakers living there. French is also the primary language in the officially bilingual Brussels Capital Region
Brussels (french: Bruxelles or ; nl, Brussel ), officially the Brussels-Capital Region (All text and all but one graphic show the English name as Brussels-Capital Region.) (french: link=no, Région de Bruxelles-Capitale; nl, link=no, Bruss ...
, (see Francization of Brussels
The Francization of Brussels refers to the evolution, over the past two centuries, of this historically Dutch-speaking city into one where French has become the majority language and lingua franca. The main cause of this transition was the r ...
).
Many Flemings are also able to speak French, children in Flanders generally get their first French lessons in the 5th primary year (normally around 10 years). But the current lack of French outside the educational context makes it hard to maintain a decent level of French. As such, the proficiency of French is declining. Flemish pupils are also obligated to follow English lessons as their third language. Normally from the second secondary year (around 14 years old), but the ubiquity of English in movies, music, IT and even advertisements makes it easier to learn and maintain the English language.
Media
The public radio and television broadcaster in Flanders is VRT, which operates the TV channels één, Canvas
Canvas is an extremely durable plain-woven fabric used for making sails, tents, marquees, backpacks, shelters, as a support for oil painting and for other items for which sturdiness is required, as well as in such fashion objects as handbags ...
, Ketnet
Ketnet is a Dutch-language public children's television channel in Belgium owned and operated by the VRT, Flemish public broadcaster. It broadcasts a mix of locally produced and imported productions on the VRT3 channel from 6am until 8pm.
On 1 D ...
, OP12
OP12 (English: On 12) was the third channel of Belgium's VRT that featured evening broadcasts. The channel was launched on May 14, 2012 and closed on December 31, 2014. The channel's name was derived from the digital channel number that the s ...
and (together with the Netherlands) BVN
BVN (''Het beste van NPO'', "The best of NPO"), is a Dutch free-to-air television channel providing Dutch public-service television to viewers around the world.
It is a service of the public broadcasting company of the Netherlands, Nederlands ...
. Flemish provinces each have up to two TV channels as well. Commercial television broadcasters include vtm and Vier
Play4 is a Belgian-Flemish commercial television channel. It is part of SBS Belgium and production company Woestijnvis.
As of 2010, the channel has a market share of more than 7%.
The channel was formerly known as VIER from 17 September 2012 t ...
(VT4). Popular TV series are for example ''Thuis
''Thuis'' ( en, At Home) is a Belgian television soap opera, which airs on één, which is in the hands of VRT, the national broadcasting channel of the Dutch-speaking region of Belgium, Flanders.
''Thuis'' first aired on 23 December 1995, f ...
'' and '' F.C. De Kampioenen''.
The five most successful Flemish films were ''Loft
A loft is a building's upper storey or elevated area in a room directly under the roof (American usage), or just an attic: a storage space under the roof usually accessed by a ladder (primarily British usage). A loft apartment refers to large ...
'' (2008; 1,186,071 visitors), ''Koko Flanel
''Koko Flanel'' is a Belgian comedy movie directed by Stijn Coninx starring Urbanus, Bea Van Der Maat, Willeke van Ammelrooy, Herbert Flack and Ann Petersen. The movie was released in 1990 and was until 18 February 2009 the most successful F ...
'' (1990; 1,082,000 tickets sold), ''Hector
In Greek mythology, Hector (; grc, Ἕκτωρ, Hektōr, label=none, ) is a character in Homer's Iliad. He was a Trojan prince and the greatest warrior for Troy during the Trojan War. Hector led the Trojans and their allies in the defense o ...
'' (1987; 933,000 tickets sold), ''Daens Daens might refer to:
* Adolf Daens, Belgian Flemish priest and politician
* Pieter Daens (novel), a novel by Louis Paul Boon
*Daens (film)
''Daens'' is a 1992 Belgian period drama film directed by Stijn Coninx, after a novel by Louis Paul Bo ...
'' (1993; 848,000 tickets sold) and '' De Zaak Alzheimer'' (2003; 750,000 tickets sold). The first and last ones were directed by Erik Van Looy
Erik Ludovicus Maria Van Looy () is a Belgian film director known for his thriller movies.Erik Van Looy
IMDb He was bor ...
, and an American remake is being made of both of them, respectively ''The Loft
The Loft may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media
* The Loft (British band), a British indie band
* The Loft (Danish band), a Danish band
* ''The Loft'' (film) (2014) an American film
* The Loft (Sirius XM), a music channel on satellite r ...
'' (2012) and ''The Memory of a Killer
''The Alzheimer Case'' (also known as ''The Alzheimer Affair'' or ''The Memory of a Killer''; nl, De zaak Alzheimer) is a 2003 Belgian action thriller film directed by Erik Van Looy, based on the novel ''De zaak Alzheimer'' by Jef Geeraerts. It ...
''. The other three ones were directed by Stijn Coninx
Stijn, Baron Coninx (born 21 February 1957) is a Belgian film director.
Career
He studied film directing at HRITCS (currently Ritcs, at Erasmus Hogeschool Brussel). Baron Coninx is best known for his film ''Daens'', which was nominated for a ...
.
Newspapers are grouped under three main publishers: De Persgroep
DPG Media Group is a Belgian media company also active in the Netherlands and Denmark. It is owned by the Van Thillo family and employs some 6,000 people.
Divisions
The DPG Media Group operates through three national subsidiaries:
* DPG Media ...
with ''Het Laatste Nieuws
''Het Laatste Nieuws'' (; in English ''The Latest News'') is a Dutch-language newspaper based in Antwerp, Belgium. It was founded by Julius Hoste Sr. on 7 June 1888. It is now part of DPG Media, and is the most popular newspaper in Flanders and ...
'', the most popular newspaper in Flanders, ''De Morgen
''De Morgen'' (Dutch for ''The Morning'') is a Flemish newspaper with a circulation of 53,860. The paper is published in Antwerp, Belgium.
History and profile
''De Morgen'' originates from a merger in 1978 of two socialist newspapers ' (meaning ...
'' and ''De Tijd
''De Tijd'' (, ''The Times'') is a Belgian newspaper that mainly focuses on business and economics. It is printed on salmon pink paper since May 2009, following the example of its colleagues ''Financial Times'', ''Het Financieele Dagblad'', '' FT ...
''. Then Corelio
Mediahuis is a newspaper & magazine publishing, distribution, printing, TV, radio and online media company founded in 2014 with assets in Belgium, the Netherlands, Ireland, Luxembourg and Germany. Mediahuis publishes daily newspaper titles in Belg ...
with ', the oldest extant Flemish newspaper, ''Het Nieuwsblad
''Het Nieuwsblad'' (; en, The Newspaper) is a Flemish newspaper that mainly focusses on "a broad view" regarding politics, culture, economics, lifestyle, society and sports.
History and profile
In 1929, ''Het Nieuwsblad'' was published by ...
'' and ''De Standaard
''De Standaard'' (meaning ''The Standard'' in English) is a Flemish daily newspaper published in Belgium by Mediahuis (formerly Corelio and VUM). It was traditionally a Christian-Democratic paper, associated with the Christian-Democratic and F ...
''. Lastly, Concentra
Concentra Inc., is a national health care establishment founded in 1979 in Amarillo, Texas. The headquarters of the corporation is in Addison, Texas and runs approximately 520 urgent care locations across 44 states. The company is linked with ove ...
publishes ''Gazet van Antwerpen
The ''Gazet van Antwerpen'' (Antwerp Gazette, popularly named ''De Frut'', "sour head cheese") is a Belgian newspaper in Antwerp and Flanders, published by Concentra.
History and profile
''Gazet van Antwerpen'' was established in 1891. Its edit ...
'' and ''Het Belang van Limburg
''Het Belang van Limburg'' (Dutch; literally ''The Interest of Limburg'') is a Dutch language regional newspaper in Belgium.
History and profile
''Het Belang van Limburg'' was founded in 1933 as a merger of several weekly magazines. The paper ...
''.
Magazines include ''Knack
Knack or The Knack may refer to:
Music and entertainment
* The Knack, an American pop-rock band famous for their hit "My Sharona"
* The Knack (1960s US band), an American garage rock band active in the 1960s
* The Knack (UK band), a British freakb ...
'' and ''HUMO
''HUMO'' is a popular Dutch-language Belgian weekly radio and television supermarket tabloid.
History and profile
''Humoradio'' (meaning a portmanteau of 'humor' and 'radio' in English) was first published in 1936 as a Dutch-language counterpar ...
''.
Sports
 Association football (soccer) is one of the most popular sports in both parts of Belgium, together with cycling, tennis, swimming and judo.
In cycling, the
Association football (soccer) is one of the most popular sports in both parts of Belgium, together with cycling, tennis, swimming and judo.
In cycling, the Tour of Flanders
The Tour of Flanders ( nl, Ronde van Vlaanderen), also known as ''De Ronde'' (''"The Tour"''), is an annual road cycling race held in Belgium every spring. The most important cycling race in Flanders, it is part of the UCI World Tour and organi ...
is considered one of the five "Monuments
A monument is a type of structure that was explicitly created to commemorate a person or event, or which has become relevant to a social group as a part of their remembrance of historic times or cultural heritage, due to its artistic, hist ...
". Other "Flanders Classics
Flanders Classics is an official cooperation among the organizers of the classic cycle races held in Flanders. It was founded in 2009 " races include ''Dwars door Vlaanderen
Dwars door Vlaanderen ''( en, Across Flanders)'' is a semi-classic road bicycle race in Belgium, held annually since 1945. The race starts in Roeselare and finishes in Waregem, both in West Flanders. Since 2017 the event is included in the UCI W ...
'' and Gent–Wevelgem
Gent–Wevelgem, officially Gent–Wevelgem – In Flanders Fields, is a road bicycle racing, road cycling race in Belgium, held annually since 1934. It is one of the classic cycle races, classic races part of the Flemish Cycling Week, run in late ...
. Eddy Merckx
Édouard Louis Joseph, Baron Merckx (, ; born 17 June 1945), better known as Eddy Merckx, is a Belgian former professional road and track bicycle racer who is among the most successful riders in the history of competitive cycling. His victorie ...
is widely regarded as the greatest cyclist of all time, with five victories in the Tour de France
The Tour de France () is an annual men's multiple-stage bicycle race primarily held in France, while also occasionally passing through nearby countries. Like the other Grand Tours (the Giro d'Italia and the Vuelta a España), it consists ...
and numerous other cycling records. His hour speed record (set in 1972) stood for 12 years.
Jean-Marie Pfaff
Jean-Marie Pfaff (born 4 December 1953) is a Belgian former professional footballer who played as a goalkeeper who spent most of his professional career with Beveren and Bayern Munich. Pfaff was capped 64 times playing for Belgium, and particip ...
, a former Belgian goalkeeper, is considered one of the greatest in the history of football (soccer).Goalkeeping Greats
" Goalkeepersaredifferent.com. Retrieved on 2008
Kim Clijsters
Kim Antonie Lode Clijsters (; born 8 June 1983) is a Belgian former professional tennis player. Clijsters reached the world No. 1 ranking in both singles and doubles, having held both rankings simultaneously in 2003. She won six major titles, ...
(as well as the French-speaking Belgian
Justine Henin
Justine Henin (; born 1 June 1982) is a Belgian former professional tennis player. She spent a total of 117 weeks as the world No. 1 and was the year-end No. 1 in 2003, 2006 and 2007. Henin, coming from a country with limited success in te ...
) was
Player of the Year
Several sports leagues honour their best player with an award called Player of the Year (POY) . In the United States, this type of award is usually called a Most Valuable Player award.
Association football
In association football, this award is he ...
twice in the
Women's Tennis Association
The Women's Tennis Association (WTA) is the principal organizing body of women's professional tennis. It governs the WTA Tour which is the worldwide professional tennis tour for women and was founded to create a better future for women's tenni ...
as she was ranked the number one female tennis player.
Kim Gevaert
Kim Gevaert (born 5 August 1978 in Leuven) is a former sprint athlete and Olympic champion from Belgium.
Career
Her closest brush with a world title came in running 4/100 of a second behind three-time champion Gail Devers at the 2004 IAAF Wor ...
and
Tia Hellebaut
Tia Hellebaut (; born 16 February 1978 in Antwerp) is a retired Belgian track and field athlete, as well as a chemist, who started out in her sports career in the heptathlon, and afterwards specialized in the high jump event. She has cleared 2.05 ...
are notable track and field stars from Flanders.
The
1920 Summer Olympics
The 1920 Summer Olympics (french: Jeux olympiques d'été de 1920; nl, Olympische Zomerspelen van 1920; german: Olympische Sommerspiele 1920), officially known as the Games of the VII Olympiad (french: Jeux de la VIIe olympiade; nl, Spelen van ...
were held in Antwerp.
Jacques Rogge
Jacques Jean Marie Rogge, Count Rogge (, ; 2 May 1942 – 29 August 2021) was a Belgian sports administrator and physician who served as the eighth President of the International Olympic Committee (IOC) from 2001 to 2013. In 2013, Rogge beca ...
has been president of the
International Olympic Committee
The International Olympic Committee (IOC; french: link=no, Comité international olympique, ''CIO'') is a non-governmental sports organisation based in Lausanne, Switzerland. It is constituted in the form of an association under the Swiss ...
since 2001.
The Flemish government agency for sports is
Bloso
Sport Vlaanderen is the Flemish sports agency. Within Belgium, it is the Flemish counterpart of French-speaking ADEPS. Both agencies were founded in 1969 to succeed the state-founded national INEPS/NILOS.
Until 2016 Sport Vlaanderen was called Blo ...
.
Music
Flanders is known for its music festivals, like the annual
Rock Werchter
Rock Werchter is an annual music festival held in the village of Werchter, near Leuven, Belgium, since 1976 and is a large sized rock music festival. The 2003, 2005, 2006, 2007, 2012 and 2014 festivals received the Arthur award for ''best festiv ...
,
Tomorrowland
Tomorrowland is one of the many themed lands featured at all of the Magic Kingdom styled Disney theme parks around the world owned or licensed by The Walt Disney Company. Each version of the land is different and features numerous attractions t ...
and
Pukkelpop
Pukkelpop is an annual music festival that takes place near the city of Hasselt, Belgium, in mid- to late August. It is held within a large enclosure of fields and woodland—adjacent to a dual carriageway called ''Kempische Steenweg''—in the ...
. The
Gentse Feesten
The Gentse Feesten (; In Ghent dialect Gense Fieste "The Ghent Festival") is a music and theatre festival in the city of Ghent, Belgium. Besides stage events there are street acts such as mimes and buskers. The festival starts on the Friday before ...
is another very large yearly event.
The best-selling Flemish group or artist is the (Flemish-Dutch) group
2 Unlimited
2 Unlimited are a Belgian/Dutch dance music act, founded by Belgian producers/songwriters Jean-Paul De Coster and Phil Wilde in 1991 in Antwerp, Belgium. From 1991 to 1996, Dutch rapper Ray Slijngaard and Dutch vocalist Anita Doth fronted the a ...
, followed by (Italian-born)
Rocco Granata
Rocco Granata (born 16 August 1938) is an Italian-Belgian singer, songwriter, and accordionist.
Granata was born in Figline Vegliaturo, Calabria, southern Italy; but his parents immigrated to Belgium when he was aged ten. Rocco's father was a ...
,
Technotronic
Technotronic was a Belgian electronic music project formed in 1987 by Jo Bogaert, who originally gained popularity in Europe as a solo artist with various new beat projects, including Acts of Madmen and Nux Nemo. Together with rapper Manuela K ...
,
Helmut Lotti
Helmut Lotti (born Helmut Barthold Johannes Alma Lotigiers; 22 October 1969), is a Belgian tenorGoldsmith B (2009)Belgian tenor Helmut Lotti wants to find his own style ''WDEZ''. Retrieved 23 April 2010. and singer-songwriter. Lotti performs in ...
and
Vaya Con Dios.
The weekly charts of best-selling singles is the
Ultratop 50
Ultratop is an organization which generates and publishes the official record charts in Belgium. Ultratop is a non-profit organization, created on the initiative of the Belgian Entertainment Association (BEA), the Belgian member organization of ...
. "Kvraagetaan" by the
Fixkes
Fixkes is a Belgian band from Stabroek, near Antwerp. The band mixes
acoustic pop and rap in their music. In February 2007, they released their first official single, "Kvraagetaan". The single was a big success in Belgium and reached number 1 i ...
holds the current record for longest time at No. 1 on the chart.
See also
*
Burgundian Netherlands
In the history of the Low Countries, the Burgundian Netherlands (french: Pays-Bas bourguignons, nl, Bourgondische Nederlanden, lb, Burgundeschen Nidderlanden, wa, Bas Payis borguignons) or the Burgundian Age is the period between 1384 and ...
*
Count of Flanders
The count of Flanders was the ruler or sub-ruler of the county of Flanders, beginning in the 9th century. Later, the title would be held for a time, by the rulers of the Holy Roman Empire and Spain. During the French Revolution, in 1790, the co ...
*
Flemish Movement
The Flemish Movement ( nl, Vlaamse Beweging) is an umbrella term which encompasses various political groups in the Belgian region of Flanders and, less commonly, in French Flanders. Ideologically, it encompasses groups which have sought to promo ...
*
Flemish Parliament
The Flemish Parliament (Dutch: , formerly called Flemish Council or ''Vlaamse Raad'') constitutes the legislative power in Flanders for matters which fall within the competence of Flanders, both as a geographic region and as a cultural communi ...
*
Flemish Primitives
Early Netherlandish painting, traditionally known as the Flemish Primitives, refers to the work of artists active in the Burgundian Netherlands, Burgundian and Habsburg Netherlands during the 15th- and 16th-century Northern Renaissance period. ...
*
Seventeen Provinces
The Seventeen Provinces were the Imperial states of the Habsburg Netherlands in the 16th century. They roughly covered the Low Countries, i.e., what is now the Netherlands, Belgium, Luxembourg, and most of the French departments of Nord (Fre ...
Explanatory notes
References
Further reading
* De Vries, André. ''Flanders: a cultural history'' (Oxford University Press, 2007)
excerpt* Demets, Lisa, Jan Dumolyn, and Els De Paermentier. "Political ideology and the rewriting of history in fifteenth-century Flanders." ''BMGN-THE LOW COUNTRIES HISTORICAL REVIEW'' 134.1 (2019): 73-95
online*
* Humes, Samuel. ''Belgium: Long United, Long Divided'' (2014
online
External links
*
*
{{Authority control
Regions of Belgium
Autonomous regions
Divided regions
Dutch-speaking countries and territories
 The County of Flanders was a
The County of Flanders was a  Meanwhile, Protestantism had reached the Low Countries. Among the wealthy traders of Antwerp, the
Meanwhile, Protestantism had reached the Low Countries. Among the wealthy traders of Antwerp, the  During the war with England, the rebels from the north, strengthened by refugees from the south, started a campaign to reclaim areas lost to
During the war with England, the rebels from the north, strengthened by refugees from the south, started a campaign to reclaim areas lost to  Although arts remained relatively impressive for another century with
Although arts remained relatively impressive for another century with  Flanders (and Belgium as a whole) saw some of the greatest loss of life on the Western Front of the
Flanders (and Belgium as a whole) saw some of the greatest loss of life on the Western Front of the  Both the
Both the  As mentioned above, Flemish institutions such as the
As mentioned above, Flemish institutions such as the  For some inhabitants, Flanders is more than just a geographical area or the federal institutions (Flemish Community and Region). Supporters of the Flemish Movement even call it a nation and pursue Flemish independence, but most people (approximately 75%) living in Flanders say they are proud to be Belgian and opposed to the dissolution of Belgium. 20% is even ''very proud'', while some 25% are not proud and 8% is ''very not proud''. Mostly students claim to be proud of their nationality, with 90% of them saying so. Of the people older than 55, 31% claim to be proud of being a Belgian. Particular opposition to secession comes from women, people employed in
For some inhabitants, Flanders is more than just a geographical area or the federal institutions (Flemish Community and Region). Supporters of the Flemish Movement even call it a nation and pursue Flemish independence, but most people (approximately 75%) living in Flanders say they are proud to be Belgian and opposed to the dissolution of Belgium. 20% is even ''very proud'', while some 25% are not proud and 8% is ''very not proud''. Mostly students claim to be proud of their nationality, with 90% of them saying so. Of the people older than 55, 31% claim to be proud of being a Belgian. Particular opposition to secession comes from women, people employed in  Flanders shares its borders with Wallonia in the south, Brussels being an enclave within the Flemish Region. The rest of the border is shared with the
Flanders shares its borders with Wallonia in the south, Brussels being an enclave within the Flemish Region. The rest of the border is shared with the  The present-day
The present-day 
 Total GDP of the Flemish Region in 2018 was €270 billion (
Total GDP of the Flemish Region in 2018 was €270 billion ( The Belgian constitution provides for
The Belgian constitution provides for  Education is compulsory from the ages of six to 18, but most
Education is compulsory from the ages of six to 18, but most  The standard language in Flanders is
The standard language in Flanders is  Association football (soccer) is one of the most popular sports in both parts of Belgium, together with cycling, tennis, swimming and judo.
In cycling, the
Association football (soccer) is one of the most popular sports in both parts of Belgium, together with cycling, tennis, swimming and judo.
In cycling, the