Feudatory States Of Orissa on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Orissa Tributary States, also known as the Garhjats and as the Orissa Feudatory States, were a group of 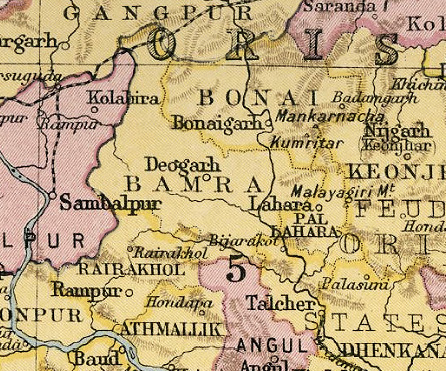
princely state
A princely state (also called native state or Indian state) was a nominally sovereign entity of the British Raj, British Indian Empire that was not directly governed by the British, but rather by an Indian ruler under a form of indirect rule, ...
s of British India
The provinces of India, earlier presidencies of British India and still earlier, presidency towns, were the administrative divisions of British governance on the Indian subcontinent. Collectively, they have been called British India. In one ...
now part of the present-day Indian state of Odisha
Odisha (English: , ), formerly Orissa ( the official name until 2011), is an Indian state located in Eastern India. It is the 8th largest state by area, and the 11th largest by population. The state has the third largest population of ...
.
The Orissa Tributary States were located in the Garhjat Hills
The Garhjat Hills is a mountain range formed by a series low-lying hills, plateaux, ridges and meadows that stretch into Odisha from the Utkal Plains in the Chotanagpur region of Jharkhand and the Chhattisgarh Plains. The range, also known as t ...
, the hilly and former heavily forested region of eastern Orissa, on the border with present-day Chhattisgarh
Chhattisgarh (, ) is a landlocked state in Central India. It is the ninth largest state by area, and with a population of roughly 30 million, the seventeenth most populous. It borders seven states – Uttar Pradesh to the north, Madhya Prade ...
and Jharkhand
Jharkhand (; ; ) is a state in eastern India. The state shares its border with the states of West Bengal to the east, Chhattisgarh to the west, Uttar Pradesh to the northwest, Bihar to the north and Odisha to the south. It has an area of . It ...
states.

History
In the 18th century, the entire region came under the control of theMaratha Empire
The Maratha Empire, also referred to as the Maratha Confederacy, was an early modern Indian confederation that came to dominate much of the Indian subcontinent in the 18th century. Maratha rule formally began in 1674 with the coronation of Shi ...
, in particular the Bhonsle
The Bhonsle (or Bhonsale, Bhosale, Bhosle) are a prominent group within the Maratha clan system of kunbi origin. They claimed descent from the Sisodia Rajputs but were likely Kunbi tiller-plainsmen.
History Earliest members
The earliest a ...
maharajas of Nagpur
Nagpur (pronunciation: Help:IPA/Marathi, aːɡpuːɾ is the third largest city and the winter capital of the Indian state of Maharashtra. It is the 13th largest city in India by population and according to an Oxford's Economics report, Nag ...
. Meanwhile, the British
British may refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories, and Crown Dependencies.
** Britishness, the British identity and common culture
* British English, ...
had become established in Bengal
Bengal ( ; bn, বাংলা/বঙ্গ, translit=Bānglā/Bôngô, ) is a geopolitical, cultural and historical region in South Asia, specifically in the eastern part of the Indian subcontinent at the apex of the Bay of Bengal, predom ...
, and were expanding their influence into the lowland tracts of Orissa. The British and the Marathas came into conflict in the late 18th century, and at the conclusion of the Second Anglo-Maratha War
}
The Second Anglo-Maratha War (1803–1805) was the second conflict between the British East India Company and the Maratha Empire in India.
Background
The British had supported the "fugitive" Peshwa Raghunathrao in the First Anglo-Maratha War, ...
in 1803, the Maharaja of Nagpur ceded Orissa to the British. Some of the former Maratha territory was ruled directly by the British, and attached to the Bengal Presidency
The Bengal Presidency, officially the Presidency of Fort William and later Bengal Province, was a subdivision of the British Empire in India. At the height of its territorial jurisdiction, it covered large parts of what is now South Asia and ...
; other territories became princely state
A princely state (also called native state or Indian state) was a nominally sovereign entity of the British Raj, British Indian Empire that was not directly governed by the British, but rather by an Indian ruler under a form of indirect rule, ...
s, under the control of local rulers under a treaty of subsidiary alliance
A subsidiary alliance, in South Asian history, was a tributary alliance between a South Asian state and a European East India Company.
Under this system, an Indian ruler who formed a treaty with the company in question would be provided wi ...
to the British monarch following the annexation
Annexation (Latin ''ad'', to, and ''nexus'', joining), in international law, is the forcible acquisition of one state's territory by another state, usually following military occupation of the territory. It is generally held to be an illegal act ...
in 1803. The local chiefs' status was recognised by the British as 'tributary chiefs' and their estates became the 'Tributary Mahals' of Orissa.
These territories were managed the Political Department and were not subject to any regular Settlement and Revenue system. Originally there were nineteen Tributary States, but two of them were confiscated and annexed by the British; Angul State
Angul (also known as Anugul) is a town and a municipality and the headquarters of Angul district in the state of Odisha, India. Angul has an average elevation of above sea level.
The total geographical area of the district is 6232 km2. ...
in 1847 for the rebellion of its Raja when he opposed the British officers that had been sent to suppress the Meriah sacrifice among the Khonds
Khonds (also spelt Kondha, Kandha etc.) are an indigenous Adivasi tribal community in India. Traditionally hunter-gatherers, they are divided into the hill-dwelling Khonds and plain-dwelling Khonds for census purposes; All the Khonds identify ...
, and Banki State in 1840, after its ruler had been convicted of murder.
The status of the Orissa Tributary States, the largest of which were Mayurbhanj
Mayurbhanj district is one of the 30 districts in Odisha state in eastern India. It is the largest district of Odisha by area. Its headquarters are at Baripada. Other major towns are Rairangpur, Karanjia and Udala. , it is the third-most-popu ...
, Keonjhar
Kendujhar is a town with municipality in Kendujhar District in the Indian state of Odisha. It is the administrative headquarters of the Kendujhar district, and it is one of the fifth scheduled areas of Odisha.
Climate
Politics
Mohan char ...
, Dhenkanal
Dhenkanal is a town and a municipality in Dhenkanal district in the state of Odisha, India.
Geography
Dhenkanal is at . It has an average elevation of 80 metres (262 feet).
Demographics
As per the 2011 India census, Dhenkanal had a p ...
, Baudh, and Nayagarh
Nayagarh is both a town and the municipality headquarters of the Nayagarh district in the Indian state of Odisha.
Geography
Nayagarh is located at with an average elevation of 178 metres (584 feet).
It was the Rukhi mountain to the south a ...
, was unclear until 1888, when the Secretary of State for India
His (or Her) Majesty's Principal Secretary of State for India, known for short as the India Secretary or the Indian Secretary, was the British Cabinet minister and the political head of the India Office responsible for the governance of th ...
accepted the view that they did not form part of British India, and modified powers were handed over to the Orissa chiefs under the control of a superintendent.
In 1905 five Oriya-speaking states of Bamra
Bamra State or Bamanda State, covering an area of 5149 km2, was one of the princely states of India during the period of the British Raj, its capital was in Debagarh (Deogarh). Bamra State acceded to India in 1948.
The state was located i ...
, Rairakhol
Redhakholis a town and a notified area council in Sambalpur district in the Indian state of Odisha.It has the following banks: Canara Bank, DCB Bank, State Bank of India, Union Bank, Utkal Gramin Bank, and Central Bank. Redhakhol town, which ...
, Sonpur, Patna
Patna (
), historically known as Pataliputra, is the capital and largest city of the state of Bihar in India. According to the United Nations, as of 2018, Patna had a population of 2.35 million, making it the 19th largest city in India. ...
, and Kalahandi State
Kalahandi State, also known as Karond State, was one of the princely states of India during the period of the British Raj. It was recognized as a state in 1874 and had its capital in Bhawanipatna. Its last ruler signed the accession to the India ...
) were added from the Central Provinces
The Central Provinces was a province of British India. It comprised British conquests from the Mughals and Marathas in central India, and covered parts of present-day Madhya Pradesh, Chhattisgarh and Maharashtra states. Its capital was Nagpur. ...
and two states, Gangpur
Gangpur is a census town in Burdwan II CD Block in Bardhaman Sadar North subdivision of Purba Bardhaman district in West Bengal, India.
Geography
Location
The location code of Gangpur Villa is 320193, according to the 2011 census. The dista ...
and Bonai
Bonai State ( or, ବଣାଇ), was a princely state during the British Raj in what is today India. It was one of the Chota Nagpur States and had its capital at Bonaigarh,Malleson, G. B.: An historical sketch of the native states of India, Londo ...
, from the Chota Nagpur States
The Chota Nagpur Tributary States or Chota Nagpur States were a group of non-salute states (minor princely states) at the time of British Raj, located on the Chhota Nagpur Plateau. British suzerainty over the states was exercised through the g ...
. With the addition of these states, the total area was and the population was 3,173,395 per the 1901 census.
In 1912, the province of Bihar and Orissa
Bihar and Orissa was a province of British India, which included the present-day Indian states of Bihar, Jharkhand, and Odisha. The territories were conquered by the British in the 18th and 19th centuries, and were governed by the then Indian Ci ...
was detached from Bengal, and the Orissa Tributary States were under the authority of the governor of Bihar and Orissa. In 1936 Orissa became a separate province, but the Orissa Tributary States were merged into the Eastern States Agency
The Eastern States Agency was an agency or grouping of princely states in eastern India, during the latter years of the Indian Empire. It was created in 1933, by the unification of the former Chhattisgarh States Agency and the Orissa States Agen ...
, which was under the direct authority of the Governor-General of India
The Governor-General of India (1773–1950, from 1858 to 1947 the Viceroy and Governor-General of India, commonly shortened to Viceroy of India) was the representative of the monarch of the United Kingdom and after Indian independence in 1 ...
rather than that of the provincial governor. After the Indian independence in 1947, the rulers of the states acceded to the Government of India
The Government of India (ISO: ; often abbreviated as GoI), known as the Union Government or Central Government but often simply as the Centre, is the national government of the Republic of India, a federal democracy located in South Asia, c ...
. They established the Eastern States Union
The Eastern States Union was a short-lived (1947–48) union of princely states in newly independent India that gathered most of the princely states of the former Orissa Tributary States and Chhattisgarh States Agency in order to fill the vacuu ...
in the same year. Their aim was to establish a unit that would be large enough to exist as a separate state within the Indian Union Union of India or Indian Union may refer to:
* The country of India
* Dominion of India (1947–1950)
* The Government of India, whose legal name is "Union of India" as per Article 300 of the Indian constitution
* Political integration of India
...
.Frederick George Bailey, ''Politics and Social Change: Orissa in 1959''. p. 179 But the union failed and the former Orissa Tributary States, except the Oriya speaking princely states of Saraikela
Saraikela (also spelled Seraikella) is the district headquarters and a nagar panchayat in the Seraikela Sadar subdivision of the Seraikela Kharsawan district in the Indian state of Jharkhand. It was formerly the capital of the Odia Saraikela St ...
and Kharsawan
Kharsawan garh is a town and a notified area in the Seraikela Sadar subdivision of the Seraikela Kharsawan district in the Indian state of Jharkhand.
History
Kharsawan (also spelt as Kharsuan) was founded around 1650. It was one of the Oriya P ...
, were integrated into the state of Orissa.
Princely states
The list of princely states under Orissa States Agency:See also
*Sambalpur State
Sambalpur State, also known as Hirakhand Kingdom was a sovereign state founded in the 1570 CE. It ruled over a vast kingdom spread across Western Odisha and Eastern Chhattisgarh in central-eastern India prior to the Maratha occupation in 1800 AD ...
* Banki State
*Eastern States Agency
The Eastern States Agency was an agency or grouping of princely states in eastern India, during the latter years of the Indian Empire. It was created in 1933, by the unification of the former Chhattisgarh States Agency and the Orissa States Agen ...
*Chota Nagpur Tributary States
The Chota Nagpur Tributary States or Chota Nagpur States were a group of non-salute states (minor princely states) at the time of British Raj, located on the Chhota Nagpur Plateau. British suzerainty over the states was exercised through the g ...
*Political integration of India
After the Indian independence in 1947, the dominion of India was divided into two sets of territories, one under direct British rule, and the other under the suzerainty of the British Crown, with control over their internal affairs remaining i ...
References
{{Princely states of the Eastern States Agency Princely states of Odisha Bengal Presidency 1888 establishments in India