|
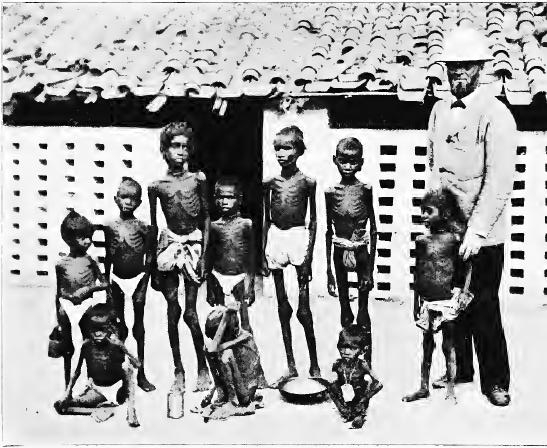
Rairakhol State
Rairakhol State ( or, ରେଢ଼ାଖୋଲ ରାଜ୍ୟ) was a princely state during the British Raj in what is today India. It was one of the Chota Nagpur States and had its capital at Rairakhol (Redhakhol), located in the present-day Sambalpur district of Odisha. It had an area of and a population of 26,888 in 1901, the average revenue was Rs.55,000 in 1904. Most of the state was covered by forest where wild elephants used to roam. Rairakhol State's inhabitants spoke mostly the Odia language, although there were also large Kol people groups speaking Munda and Oraon language. The Chasa caste was the predominant caste in the state. History Although records are obscure but according to traditions, around 17th century a branch of Kadamba dynasty of the Bonai State was ruling in the region and the chiefs were feudatories of the Bamra State until the 18th century, when the rulers of the Sambalpur State freed it from its dependence. During the 19th century, Raja Bishan Cha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British India
The provinces of India, earlier presidencies of British India and still earlier, presidency towns, were the administrative divisions of British governance on the Indian subcontinent. Collectively, they have been called British India. In one form or another, they existed between 1612 and 1947, conventionally divided into three historical periods: *Between 1612 and 1757 the East India Company set up Factory (trading post), factories (trading posts) in several locations, mostly in coastal India, with the consent of the Mughal emperors, Maratha Empire or local rulers. Its rivals were the merchant trading companies of Portugal, Denmark, the Netherlands, and France. By the mid-18th century, three ''presidency towns'': Madras, Bombay and Calcutta, had grown in size. *During the period of Company rule in India (1757–1858), the company gradually acquired sovereignty over large parts of India, now called "presidencies". However, it also increasingly came under British government over ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chasa Caste
Chasa is a community from the Indian state of Odisha. Chasas were traditionally cultivators but are now engaged in several professions. The Odia word ''chasa'' means farmer. They are third largest caste by population in Odisha. History The Orh/Oda Chasas claim that they were the first tribe to settle in Odisha, and that they began to cultivate the land. They claim that Odisha is named after them. They are classified as Shudra in the Hindu caste system. The association between Chasas and their occupation of manual labour (ploughing) was used to stigmatize the Chasas and distinguish them from the upper castes as late as the early 19th century. "''Chasa''" was considered to be a "generic derogatory term for cultivators", in contrast to the ''sabhya bhabya Gan'' "sophisticated people". Around the turn of the 20th century, Chasas were small farmers and marginal raiyats. In modern day Odisha, the Chasas are among the dominant castes in most villages, and are landowners and econo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Princely States Of Odisha
A prince is a male ruler (ranked below a king, grand prince, and grand duke) or a male member of a monarch's or former monarch's family. ''Prince'' is also a title of nobility (often highest), often hereditary, in some European states. The female equivalent is a princess. The English word derives, via the French word ''prince'', from the Latin noun , from (first) and (head), meaning "the first, foremost, the chief, most distinguished, noble ruler, prince". Historical background The Latin word (older Latin *prīsmo-kaps, literally "the one who takes the first lace/position), became the usual title of the informal leader of the Roman senate some centuries before the transition to empire, the ''princeps senatus''. Emperor Augustus established the formal position of monarch on the basis of principate, not dominion. He also tasked his grandsons as summer rulers of the city when most of the government were on holiday in the country or attending religious rituals, and, for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
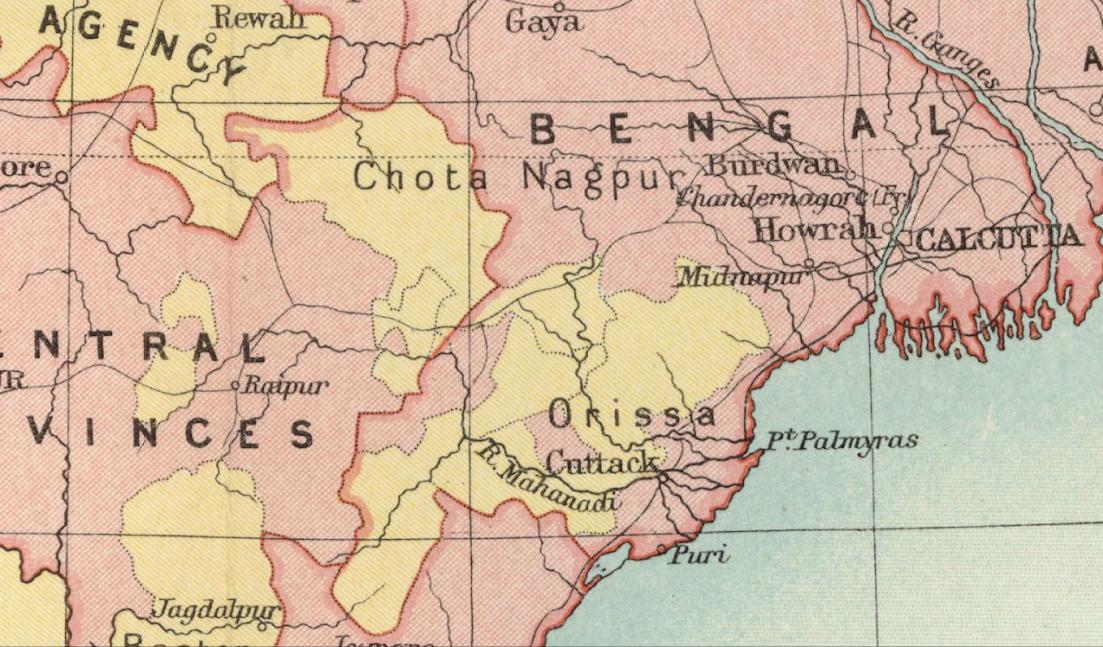
Orissa Tributary States
The Orissa Tributary States, also known as the Garhjats and as the Orissa Feudatory States, were a group of princely states of British India now part of the present-day Indian state of Odisha. The Orissa Tributary States were located in the Garhjat Hills, the hilly and former heavily forested region of eastern Orissa, on the border with present-day Chhattisgarh and Jharkhand states. History In the 18th century, the entire region came under the control of the Maratha Empire, in particular the Bhonsle maharajas of Nagpur. Meanwhile, the British had become established in Bengal, and were expanding their influence into the lowland tracts of Orissa. The British and the Marathas came into conflict in the late 18th century, and at the conclusion of the Second Anglo-Maratha War in 1803, the Maharaja of Nagpur ceded Orissa to the British. Some of the former Maratha territory was ruled directly by the British, and attached to the Bengal Presidency; other territories became princely sta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eastern States Agency
The Eastern States Agency was an agency or grouping of princely states in eastern India, during the latter years of the Indian Empire. It was created in 1933, by the unification of the former Chhattisgarh States Agency and the Orissa States Agency; the agencies remained intact within the grouping. In 1936, the Bengal States Agency was added. History Since the 19th century the princely states and the tributary states of Orissa and Chhota Nagpur were not part of Bengal, but British relations with them were managed by its government through the Bengal Presidency. The Eastern States Agency was created on 1 April 1933. This agency dealt with forty-two princely states in eastern India, located in the present-day Indian states of Chhattisgarh, Jharkhand, Odisha, West Bengal and Tripura. Before the creation of the Eastern States Agency in 1933, twenty-three native states of the former Orissa Tributary States and Chhota Nagpur States were under the suzerainty of the British provi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bengal Presidency
The Bengal Presidency, officially the Presidency of Fort William and later Bengal Province, was a subdivision of the British Empire in India. At the height of its territorial jurisdiction, it covered large parts of what is now South Asia and Southeast Asia. Bengal proper covered the ethno-linguistic region of Bengal (present-day Bangladesh and the Indian state of West Bengal). Calcutta, the city which grew around Fort William, was the capital of the Bengal Presidency. For many years, the Governor of Bengal was concurrently the Viceroy of India and Calcutta was the de facto capital of India until 1911. The Bengal Presidency emerged from trading posts established in Mughal Bengal during the reign of Emperor Jahangir in 1612. The East India Company (HEIC), a British monopoly with a Royal Charter, competed with other European companies to gain influence in Bengal. After the decisive overthrow of the Nawab of Bengal in 1757 and the Battle of Buxar in 1764, the HEIC expanded ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central Provinces
The Central Provinces was a province of British India. It comprised British conquests from the Mughals and Marathas in central India, and covered parts of present-day Madhya Pradesh, Chhattisgarh and Maharashtra states. Its capital was Nagpur. Its Summer Capital was Pachmarhi. It became the Central Provinces and Berar in 1903. The Central Provinces was formed in 1861 by the merger of the Saugor and Nerbudda Territories and Nagpur Province. The district of Nimar which was administered by the Central India Agency was added in 1864. It was almost an island encircled by a sea of "native States" such as Bhopal State and Rewa State to the north, the Chota Nagpur States and Kalahandi State to the east, and the Nizam's territories of Hyderabad to the south and Berar to the west. Geography The Central Provinces was landlocked, occupying the mountain ranges, plateaus, and river valleys in the centre of the Indian Subcontinent. The northernmost portion of the state extended onto the Bun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chhattisgarh Division
Chhattisgarh Division was an administrative division of the Central Provinces of British India. It was located in the east of the Central Provinces and encompassed the upper Mahanadi River basin, in the central part of present-day Chhattisgarh state of India. With the advent of the British the town of Raipur, headquarters of Chhattisgarh Division, gained prominence over Ratanpur, the historical capital of the territory. The Central Provinces became the Central Provinces and Berar in 1936 until the Independence of India.The major languages spoken are Chhattisgarhi, Odia, Hindi and numerous tribal languages. History Chhattisgarh Division was occupied by the Bhonsle Marathas and incorporated into the Kingdom of Nagpur in the 18th century. The Kingdom of Nagpur was annexed to British India in 1853, becoming Nagpur Province. In 1861 Nagpur Province was merged with the Saugor and Nerbudda Territories to form the Central Provinces. All the princely states of the Central Provinces were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sanad (deed)
In common law, a deed is any legal instrument in writing which passes, affirms or confirms an interest, right, or property and that is signed, attested, delivered, and in some jurisdiction (area), jurisdictions, seal (emblem), sealed. It is commonly associated with transferring (conveyancing) title (property), title to property. The deed has a greater presumption of validity and is less Rebuttable presumption, rebuttable than an instrument signed by the party to the deed. A deed can be unilateral or bilateral. Deeds include conveyancing, conveyances, Contract, commissions, licenses, patents, diplomas, and conditionally power of attorney, powers of attorney if executed as deeds. The deed is the modern descendant of the medieval charter, and delivery is thought to symbolically replace the ancient ceremony of livery of seisin. The traditional phrase ''signed, sealed and delivered'' refers to the practice of seals; however, attesting witnesses have replaced seals to some extent. Agr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sambalpur State
Sambalpur State, also known as Hirakhand Kingdom was a sovereign state founded in the 1570 CE. It ruled over a vast kingdom spread across Western Odisha and Eastern Chhattisgarh in central-eastern India prior to the Maratha occupation in 1800 AD. From 1849 AD it was integrated with British Raj as a princely state, British District. Its capital was present-day Sambalpur city in Western Odisha. History Sambalpur State was founded in mid 16th century by Balarama Deva, a Rajput from Chauhan dynasty and younger brother of Patna State, kingdom of Patna ruler Raja Narsingh Deva. In 1570 CE, the Patna State, kingdom of Patna, ruled by the Chauhan dynasty was bifurcated. The southern portion of the Ang River was ruled by Narasingh Deva and his brother Balaram Deva received the northern side of the river of Sambalpur region. Balaram Deb established his new capital at Sambalpur. Sambalpur was ruled by the Chauhan dynasty till 1800. The kingdom of Sambalpur was also known as Hirakhand and S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bamra State
Bamra State or Bamanda State, covering an area of 5149 km2, was one of the princely states of India during the period of the British Raj, its capital was in Debagarh (Deogarh). Bamra State acceded to India in 1948. The state was located in a hilly area between the Mahanadi valley and the Chhota Nagpur Plateau. Most of its territory was forest, producing timber and lac but said to be rich in iron ore. The most important river was the Brahmani River. The state was one of the five Orissa Tributary States which were transferred from the Central Provinces to Bengal on the reconstitution of that province in October 1905. The capital is situated at Deogarh. History As per the documents preserved by the courts and legends of the historical events, the first ruler of the Bamra state Saraju Gangadeb was the son of the local Eastern Ganga dynasty administrator of Patna region Hattahamir Deb, who was the son of Eastern Ganga ruler Bhanudeva II. Hattahamir Deb was overthrown in 1360 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)