Fetal Movement on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Fetal movement refers to motion of a
Fetal movement refers to motion of a
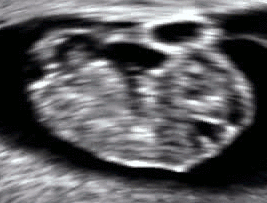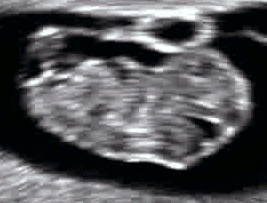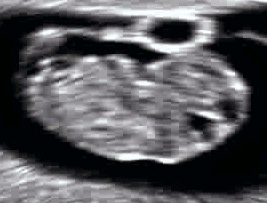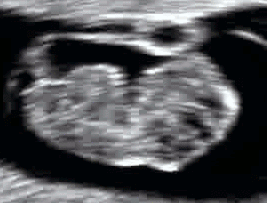 Even before the fetal stage begins, a six-week-old human
Even before the fetal stage begins, a six-week-old human
"Prenatal and Early Postnatal Development of Human Motor Behavior"
in ''Handbook of brain and behaviour in human development'', Kalverboer and Gramsbergen eds., pp. 415-418 (2001 Kluwer Academic Publishers): "The first movements to occur are sideward bendings of the head....At 9-10 weeks postmestrual age complex and generalized movements occur. These are the so-called general movements (Prechtl et al., 1979) and the startles. Both include the whole body, but the general movements are slower and have a complex sequence of involved body parts, while the startle is a quick, phasic movement of all limbs and trunk and neck." Movement of hands, hips and knees have been observed at nine weeks, stretches and yawns at ten weeks, and isolated limb movements beginning shortly thereafter.Prechtl, Heinz
"Prenatal and Early Postnatal Development of Human Motor Behavior"
in ''Handbook of brain and behaviour in human development'', Kalverboer and Gramsbergen eds., pp. 415-418 (2001 Kluwer Academic Publishers): "At 9-10 weeks postmenstrual age complex and generalized movements occur... olated movements of one arm or leg emerge 1 week later."
from
 Fetal movement refers to motion of a
Fetal movement refers to motion of a fetus
A fetus or foetus (; plural fetuses, feti, foetuses, or foeti) is the unborn offspring that develops from an animal embryo. Following embryonic development the fetal stage of development takes place. In human prenatal development, fetal deve ...
caused by its own muscle
Skeletal muscles (commonly referred to as muscles) are organs of the vertebrate muscular system and typically are attached by tendons to bones of a skeleton. The muscle cells of skeletal muscles are much longer than in the other types of muscl ...
activity. Locomotor activity begins during the late embryo
An embryo is an initial stage of development of a multicellular organism. In organisms that reproduce sexually, embryonic development is the part of the life cycle that begins just after fertilization of the female egg cell by the male spe ...
logical stage and changes in nature throughout development
Development or developing may refer to:
Arts
*Development hell, when a project is stuck in development
*Filmmaking, development phase, including finance and budgeting
*Development (music), the process thematic material is reshaped
* Photograph ...
. Muscles begin to move as soon as they are innervated
A nerve is an enclosed, cable-like bundle of nerve fibers (called axons) in the peripheral nervous system.
A nerve transmits electrical impulses. It is the basic unit of the peripheral nervous system. A nerve provides a common pathway for the e ...
. These first movements are not reflexive, but arise from self-generated nerve impulses originating in the spinal cord
The spinal cord is a long, thin, tubular structure made up of nervous tissue, which extends from the medulla oblongata in the brainstem to the lumbar region of the vertebral column (backbone). The backbone encloses the central canal of the spi ...
. As the nervous system
In biology, the nervous system is the highly complex part of an animal that coordinates its actions and sensory information by transmitting signals to and from different parts of its body. The nervous system detects environmental changes th ...
matures, muscles can move in response to stimuli.
Generally speaking, fetal motility can be classified as either elicited or spontaneous, and spontaneous movements may be triggered by either the spine or the brain. Whether a movement is supraspinally determined can be inferred by comparison to movements of an anencephalic
Anencephaly is the absence of a major portion of the brain, skull, and scalp that occurs during embryonic development. It is a cephalic disorder that results from a neural tube defect that occurs when the rostral (head) end of the neural tube fail ...
fetus.
This article primarily deals with voluntary and reflex
In biology, a reflex, or reflex action, is an involuntary, unplanned sequence or action and nearly instantaneous response to a stimulus.
Reflexes are found with varying levels of complexity in organisms with a nervous system. A reflex occurs ...
movements. Ages are given as age from fertilization rather than as gestational age
In obstetrics, gestational age is a measure of the age of a pregnancy which is taken from the beginning of the woman's last menstrual period (LMP), or the corresponding age of the gestation as estimated by a more accurate method if available. Su ...
.
Some sources contend that there is no voluntary movement until after birth. Other sources say that purposive movement begins months earlier.Becher, Julie-Claire. (Royal College of Physicians of Edinburgh and Royal College of Physicians and Surgeons of Glasgow October 2004): "Purposive movement depends on brain maturation. This begins at about 18 weeks' gestation and progressively replaces reflex movements, which disappear by about 8 months after birth....Reflexes are very different from purposeful voluntary movements which develop during the first year of life." 3D ultrasound has been used to create motion pictures of fetal movement, which are called "4D ultrasound".
Movement during development
First trimester
Embryonic stage
 Even before the fetal stage begins, a six-week-old human
Even before the fetal stage begins, a six-week-old human embryo
An embryo is an initial stage of development of a multicellular organism. In organisms that reproduce sexually, embryonic development is the part of the life cycle that begins just after fertilization of the female egg cell by the male spe ...
can arch its back and neck.Vaughan, p. 207. By seven weeks, movement in the arms and legs can be detected by ultrasound
Ultrasound is sound waves with frequency, frequencies higher than the upper audible limit of human hearing range, hearing. Ultrasound is not different from "normal" (audible) sound in its physical properties, except that humans cannot hea ...
.
Fetal stage
The parts of the fetal brain that control movement will not fully form until late in the second trimester, and the first part of the third trimester. Control of movement is limited at birth, and purposeful voluntary movements develop during the long period up until puberty. According to an overview produced by theRoyal College of Physicians of Edinburgh
The Royal College of Physicians of Edinburgh (RCPE) is a medical royal college in Scotland. It is one of three organisations that sets the specialty training standards for physicians in the United Kingdom. It was established by Royal charter ...
, purposive movement begins at about 18 weeks, gradually replacing reflex movements, and purposeful voluntary movements then develop further after birth.
In these early movements, the limbs move together; they begin to move independently by the ninth week as the controlling neuron
A neuron, neurone, or nerve cell is an electrically excitable cell that communicates with other cells via specialized connections called synapses. The neuron is the main component of nervous tissue in all animals except sponges and placozoa. N ...
s in the spinal cord develop. At week 11, the fetus can open its mouth and suck its fingers; at week 12, it begins to swallow
The swallows, martins, and saw-wings, or Hirundinidae, are a family of passerine songbirds found around the world on all continents, including occasionally in Antarctica. Highly adapted to aerial feeding, they have a distinctive appearance. The ...
amniotic fluid
The amniotic fluid is the protective liquid contained by the amniotic sac of a gravid amniote. This fluid serves as a cushion for the growing fetus, but also serves to facilitate the exchange of nutrients, water, and biochemical products betwee ...
.Vaughan 1996, p. 74.
In addition to sideward bendings of the head, complex and generalized movements occur at the beginning of the fetal stage, with movements and startles that involve the whole body.Prechtl, Heinz"Prenatal and Early Postnatal Development of Human Motor Behavior"
in ''Handbook of brain and behaviour in human development'', Kalverboer and Gramsbergen eds., pp. 415-418 (2001 Kluwer Academic Publishers): "The first movements to occur are sideward bendings of the head....At 9-10 weeks postmestrual age complex and generalized movements occur. These are the so-called general movements (Prechtl et al., 1979) and the startles. Both include the whole body, but the general movements are slower and have a complex sequence of involved body parts, while the startle is a quick, phasic movement of all limbs and trunk and neck." Movement of hands, hips and knees have been observed at nine weeks, stretches and yawns at ten weeks, and isolated limb movements beginning shortly thereafter.Prechtl, Heinz
"Prenatal and Early Postnatal Development of Human Motor Behavior"
in ''Handbook of brain and behaviour in human development'', Kalverboer and Gramsbergen eds., pp. 415-418 (2001 Kluwer Academic Publishers): "At 9-10 weeks postmenstrual age complex and generalized movements occur... olated movements of one arm or leg emerge 1 week later."
Second trimester
By about the twelfth week, the fetus is able to kick and curl its toes, and may grasp its feet or scratch itself with its fingernails. It can also move in response to atouch
In physiology, the somatosensory system is the network of neural structures in the brain and body that produce the perception of touch (haptic perception), as well as temperature (thermoception), body position (proprioception), and pain. It is ...
on its skin.Vaughan 1996, p. 209. Also starting about week 12, the thoracic diaphragm
The thoracic diaphragm, or simply the diaphragm ( grc, διάφραγμα, diáphragma, partition), is a sheet of internal Skeletal striated muscle, skeletal muscle in humans and other mammals that extends across the bottom of the thoracic cavit ...
moves up and down as if the fetus were breathing, but this movement disappears about week 16 and does not resume until the third trimester.
Movements such as kicking continue, and the mother usually feels movement for the first time, an event called quickening
In pregnancy terms, quickening is the moment in pregnancy when the pregnant woman starts to feel the fetus' movement in the uterus.
Medical facts
The first natural sensation of quickening may feel like a light tapping or fluttering. These sensat ...
, during the fifth month.Vaughan 1996, p. 134. Around this time, limb movements become more complex, with flexing of the joint
A joint or articulation (or articular surface) is the connection made between bones, ossicles, or other hard structures in the body which link an animal's skeletal system into a functional whole.Saladin, Ken. Anatomy & Physiology. 7th ed. McGraw ...
s and ribs. This activity assists with proper joint development. Women who have already given birth have more relaxed uterine muscles that are consequently more sensitive to fetal motion, and for them fetal motion can sometimes be felt as early as 14 weeks.
By about week 21, the fetus begins to develop a regular schedule of movement. The startle reflex is present in half of all fetuses by week 24 and in all fetuses by week 28. Movement is restricted around this time because the fetus has grown so large it has little space for kicking or changing body position.
Third trimester
In later pregnancy, a complex motion called "stepping" develops. This movement consists of circular "bicycling" motion of legs, which helps the fetus move to a head-downposition
Position often refers to:
* Position (geometry), the spatial location (rather than orientation) of an entity
* Position, a job or occupation
Position may also refer to:
Games and recreation
* Position (poker), location relative to the dealer
* ...
in preparation for birth.
Variation in activity level
Fetuses aged 14 to 18 weeks show a pronouncedcircadian rhythm
A circadian rhythm (), or circadian cycle, is a natural, internal process that regulates the sleep–wake cycle and repeats roughly every 24 hours. It can refer to any process that originates within an organism (i.e., Endogeny (biology), endogeno ...
in their activity level, which can be detected both by fetal electrocardiogram and by measuring locomotor activity. Active and quiet periods for the fetus do not correspond to those of the mother; fetuses are most active from 9 a.m. to 2 p.m. and again from 7 p.m. to 4 a.m. During the last four to six weeks before birth
Birth is the act or process of bearing or bringing forth offspring, also referred to in technical contexts as parturition. In mammals, the process is initiated by hormones which cause the muscular walls of the uterus to contract, expelling the f ...
, most of the fetus's kicking and jabbing movements occur while it is sleep
Sleep is a sedentary state of mind and body. It is characterized by altered consciousness, relatively inhibited sensory activity, reduced muscle activity and reduced interactions with surroundings. It is distinguished from wakefulness by a de ...
ing lightly.
Monitoring fetal movement
After quickening, a pregnant woman may choose to count the number and types of movements she feels her fetus make. This tally is informally known as a ''kick count''. TheAmerican Pregnancy Association
American Pregnancy Association is a non-profit organization that is working to improve reproductive wellness through education. It is based in Irving, Texas, U.S.
History
American Pregnancy Association was founded in 1995 as America's Pregnancy ...
states that advantages of conducting kick counts range from giving a pregnant woman an opportunity to bond with her baby to reducing the risk of stillbirth
Stillbirth is typically defined as fetal death at or after 20 or 28 weeks of pregnancy, depending on the source. It results in a baby born without signs of life. A stillbirth can result in the feeling of guilt or grief in the mother. The term ...
; kick counts are especially recommended in high risk pregnancies.American Pregnancy Association, 2007. However, instructing women to monitor fetal movements is potentially associated with increased maternal anxiety.RCOG release: Reduced fetal movements – New Green-top Guidelinefrom
Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists
The Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists (RCOG) is a professional association based in London, United Kingdom. Its members, including people with and without medical degrees, work in the field of obstetrics and gynaecology, that is ...
. Date published: 25/02/2011 70% of pregnancies with a single episode of reduced fetal movements are uncomplicated.
In the UK, the Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists say that if you think your baby has stopped moving or is moving less and you are over 28 weeks pregnant you should contact your midwife. Do not wait until the next day to contact the hospital or midwife.
Notes
References
* * *{{cite book , title = How Life Begins: The Science of Life in the Womb , last = Vaughan , first = Christopher , year = 1996 , publisher =Times Books
Times Books (previously the New York Times Book Company) is a publishing imprint owned by the New York Times Company and licensed to Henry Holt and Company.
Times Books began as the New York Times Book Company in 1969, when The New York Times Com ...
(Random House
Random House is an American book publisher and the largest general-interest paperback publisher in the world. The company has several independently managed subsidiaries around the world. It is part of Penguin Random House, which is owned by Germ ...
) , location = New York , isbn = 978-0-8129-2103-8 , url-access = registration , url = https://archive.org/details/howlifebeginssci00vaug
Vertebrate developmental biology
Human pregnancy
Tests during pregnancy
Articles containing video clips