
Family (from la, familia) is a
group
A group is a number of persons or things that are located, gathered, or classed together.
Groups of people
* Cultural group, a group whose members share the same cultural identity
* Ethnic group, a group whose members share the same ethnic ide ...
of people related either by
consanguinity
Consanguinity ("blood relation", from Latin '' consanguinitas'') is the characteristic of having a kinship with another person (being descended from a common ancestor).
Many jurisdictions have laws prohibiting people who are related by blood fr ...
(by recognized birth) or
affinity
Affinity may refer to:
Commerce, finance and law
* Affinity (law), kinship by marriage
* Affinity analysis, a market research and business management technique
* Affinity Credit Union, a Saskatchewan-based credit union
* Affinity Equity Par ...
(by marriage or other relationship). The purpose of the family is to maintain the well-being of its members and of society. Ideally, families offer
predictability
Predictability is the degree to which a correct prediction or forecast of a system's state can be made, either qualitatively or quantitatively.
Predictability and causality
Causal determinism has a strong relationship with predictability. Per ...
, structure, and safety as members mature and learn to participate in the community. Historically, most human societies use family as the primary locus of
attachment, nurturance, and
socialization
In sociology, socialization or socialisation (see spelling differences) is the process of internalizing the norms and ideologies of society. Socialization encompasses both learning and teaching and is thus "the means by which social and cul ...
.
Anthropologists classify most family organizations as
matrifocal
A matrifocal family structure is one where mothers head families and fathers play a less important role in the home and in bringing up children.
Definition
The concept of the matrifocal family was introduced to the study of Caribbean societie ...
(a mother and her children), patrifocal (a father and his children),
conjugal (a wife, her husband, and children, also called the
nuclear family),
avuncular
The avunculate, sometimes called avunculism or avuncularism, is any social institution where a special relationship exists between an uncle and his sisters' children. This relationship can be formal or informal, depending on the society. Early a ...
(a man, his sister, and her children), or
extended (in addition to parents and children, may include grandparents, aunts, uncles, or cousins).
The field of
genealogy
Genealogy () is the study of families, family history, and the tracing of their lineages. Genealogists use oral interviews, historical records, genetic analysis, and other records to obtain information about a family and to demonstrate kin ...
aims to trace family lineages through history. The family is also an important economic unit studied in
family economics
Family economics applies economic concepts such as production, division of labor, distribution, and decision making to the family. It is used to explain outcomes unique to family—such as marriage, the decision to have children, fertility, po ...
. The word "families" can be used metaphorically to create more inclusive categories such as
community
A community is a social unit (a group of living things) with commonality such as place, norms, religion, values, customs, or identity. Communities may share a sense of place situated in a given geographical area (e.g. a country, village, ...
,
nation
A nation is a community of people formed on the basis of a combination of shared features such as language, history, ethnicity, culture and/or society. A nation is thus the collective Identity (social science), identity of a group of people unde ...
hood, and
global village
Global village describes the phenomenon of the entire world becoming more interconnected as the result of the propagation of media technologies throughout the world. The term was coined by Canadian media theorist Marshall McLuhan in his books ' ...
.
Social

One of the primary functions of the family involves providing a framework for the production and reproduction of persons
biologically
Biology is the scientific study of life. It is a natural science with a broad scope but has several unifying themes that tie it together as a single, coherent field. For instance, all organisms are made up of cells that process hereditary i ...
and socially. This can occur through the sharing of material substances (such as food); the giving and receiving of care and nurture (
nurture kinship
The concept of nurture kinship in the anthropological study of human social relationships (kinship) highlights the extent to which such relationships are brought into being through the performance of various acts of nurture between individuals. A ...
); jural rights and obligations; and moral and sentimental ties.
[Schneider, David 1984 ''A Critique of the Study of Kinship''. Ann Arbor: ]University of Michigan Press
The University of Michigan Press is part of Michigan Publishing at the University of Michigan Library. It publishes 170 new titles each year in the humanities and social sciences. Titles from the press have earned numerous awards, including ...
. p. 182 Thus, one's experience of one's family shifts over time. From the perspective of
children, the family is a "family of orientation": the family serves to locate children socially and plays a major role in their
enculturation and socialization. From the point of view of the parent(s), the family is a "family of procreation", the goal of which is to produce, enculturate and socialize children. However, producing children is not the only function of the family; in societies with a sexual division of labor,
marriage
Marriage, also called matrimony or wedlock, is a culturally and often legally recognized union between people called spouses. It establishes rights and obligations between them, as well as between them and their children, and between ...
, and the resulting relationship between two people, it is necessary for the formation of an economically productive
household
A household consists of two or more persons who live in the same dwelling. It may be of a single family or another type of person group. The household is the basic unit of analysis in many social, microeconomic and government models, and is i ...
.
C. C. Harris notes that the western conception of family is ambiguous and confused with the
household
A household consists of two or more persons who live in the same dwelling. It may be of a single family or another type of person group. The household is the basic unit of analysis in many social, microeconomic and government models, and is i ...
, as revealed in the different contexts in which the word is used.
Olivia Harris states this confusion is not accidental, but indicative of the familial ideology of
capitalist
Capitalism is an economic system based on the private ownership of the means of production and their operation for profit. Central characteristics of capitalism include capital accumulation, competitive markets, price system, priva ...
,
western
Western may refer to:
Places
*Western, Nebraska, a village in the US
*Western, New York, a town in the US
*Western Creek, Tasmania, a locality in Australia
*Western Junction, Tasmania, a locality in Australia
*Western world, countries that id ...
countries that pass social legislation that insists members of a
nuclear family should live together, and that those not so related should not live together; despite the ideological and legal pressures, a large percentage of families do not conform to the ideal
nuclear family type.
Size

The
total fertility rate
The total fertility rate (TFR) of a population is the average number of children that would be born to a woman over her lifetime if:
# she were to experience the exact current age-specific fertility rates (ASFRs) through her lifetime
# she were t ...
of women varies from country to country, from a high of 6.76 children born/woman in
Niger
)
, official_languages =
, languages_type = National languages[Singapore
Singapore (), officially the Republic of Singapore, is a sovereign island country and city-state in maritime Southeast Asia. It lies about one degree of latitude () north of the equator, off the southern tip of the Malay Peninsula, bor ...](_blank)
(as of 2015).
Fertility is low in most
Eastern European
Eastern Europe is a subregion of the European continent. As a largely ambiguous term, it has a wide range of geopolitical, geographical, ethnic, cultural, and socio-economic connotations. The vast majority of the region is covered by Russia, whi ...
and
Southern European
Southern Europe is the southern region of Europe. It is also known as Mediterranean Europe, as its geography is essentially marked by the Mediterranean Sea. Definitions of Southern Europe include some or all of these countries and regions: Alba ...
countries, and high in most
sub-Saharan African countries.
In some cultures, the mother's preference of family size influences that of the children through early adulthood.
A parent's number of children strongly correlates with the number of children that their children will eventually have.
Types

Although early western
cultural anthropologist
Cultural anthropology is a branch of anthropology focused on the study of cultural variation among humans. It is in contrast to social anthropology, which perceives cultural variation as a subset of a posited anthropological constant. The portman ...
s and
sociologists considered family and
kinship to be universally associated with relations by "blood" (based on ideas common in their own cultures) later research
has shown that many societies instead understand family through ideas of living together, the sharing of food (e.g.
milk kinship
Milk kinship, formed during nursing by a non-biological mother, was a form of fostering allegiance with fellow community members. This particular form of kinship did not exclude particular groups, such that Social class, class and other hierarcha ...
) and sharing care and
nurture
Nature versus nurture is a long-standing debate in biology and society about the balance between two competing factors which determine fate: genetics (nature) and environment (nurture). The alliterative expression "nature and nurture" in English h ...
.
Sociologists have a special interest in the function and status of family forms in stratified (especially
capitalist
Capitalism is an economic system based on the private ownership of the means of production and their operation for profit. Central characteristics of capitalism include capital accumulation, competitive markets, price system, priva ...
) societies.
According to the work of scholars
Max Weber,
Alan Macfarlane
Alan Donald James Macfarlane (born 20 December 1941 in Shillong, Meghalaya, India) is an anthropologist and historian, and a Professor Emeritus of King's College, Cambridge. He is the author or editor of 20 books and numerous articles on th ...
,
Steven Ozment
Steven Edgar Ozment (February 21, 1939 – December 12, 2019) was an American historian of early modern and modern Germany, the European family, and the Protestant Reformation. From 1990 to 2015, he was the McLean Professor of Ancient and Modern Hi ...
,
Jack Goody and
Peter Laslett
Thomas Peter Ruffell Laslett (18 December 1915 – 8 November 2001) was an English historian.
Biography
Laslett was the son of a Baptist minister and was born in Bedford on 18 December 1915. Although he spent much of his childhood in Oxford, ...
, the huge transformation that led to modern marriage in Western democracies was "fueled by the religio-cultural value system provided by elements of
Judaism
Judaism ( he, ''Yahăḏūṯ'') is an Abrahamic, monotheistic, and ethnic religion comprising the collective religious, cultural, and legal tradition and civilization of the Jewish people. It has its roots as an organized religion in t ...
, early
Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus of Nazareth. It is the world's largest and most widespread religion with roughly 2.38 billion followers representing one-third of the global pop ...
,
Roman Catholic
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
* Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
* Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*'' Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a let ...
canon law
Canon law (from grc, κανών, , a 'straight measuring rod, ruler') is a set of ordinances and regulations made by ecclesiastical authority (church leadership) for the government of a Christian organization or church and its members. It is th ...
and the
Protestant Reformation
The Reformation (alternatively named the Protestant Reformation or the European Reformation) was a major movement within Western Christianity in 16th-century Europe that posed a religious and political challenge to the Catholic Church and ...
".
Much sociological,
historical and
anthropological
Anthropology is the scientific study of humanity, concerned with human behavior, human biology, cultures, societies, and linguistics, in both the present and past, including past human species. Social anthropology studies patterns of behav ...
research dedicates itself to the understanding of this variation, and of changes in the family that form over time. Levitan claims:
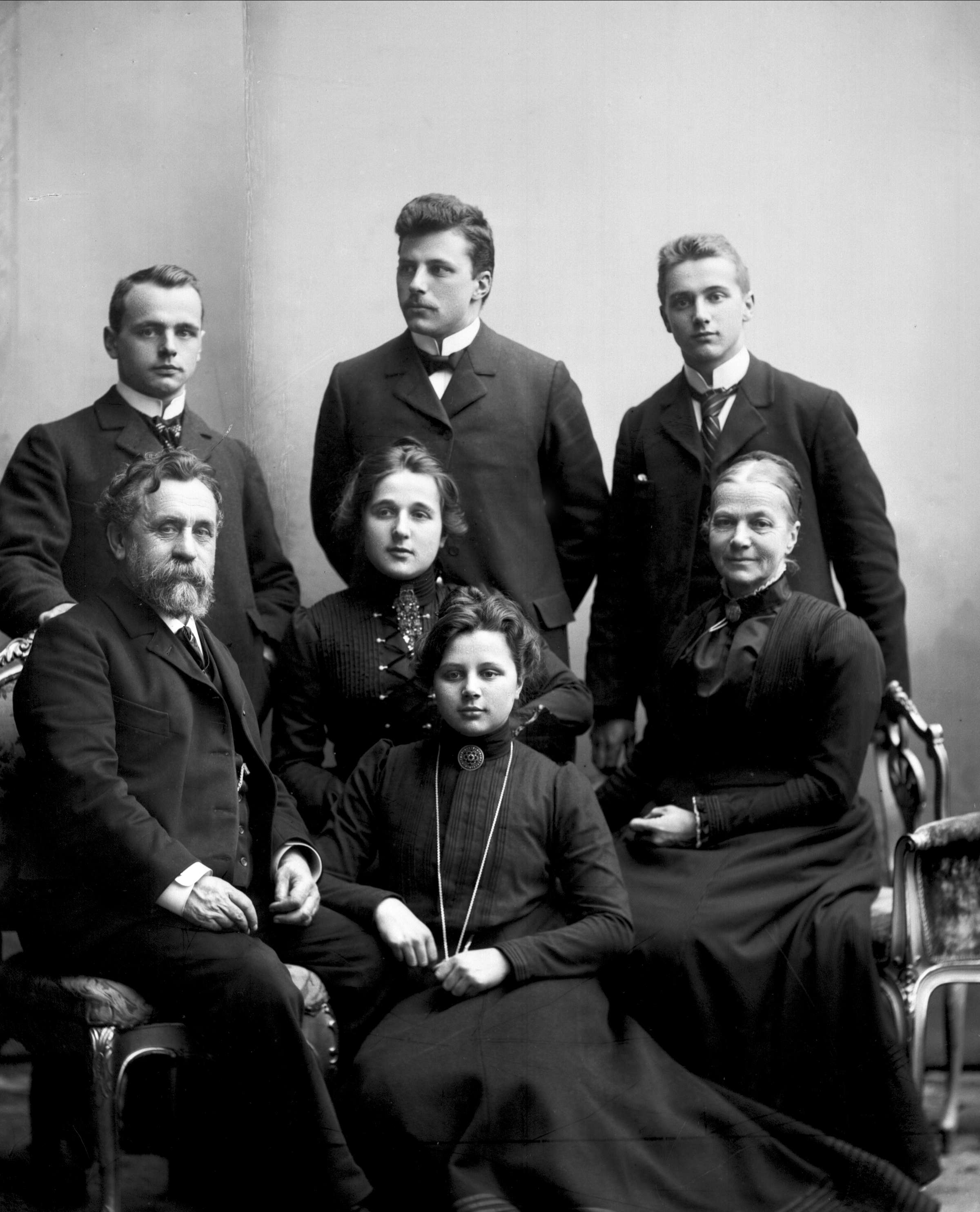
Multigenerational family
Historically, the most common family type was one in which grandparents, parents, and children lived together as a single unit. For example, the household might include the owners of a farm, one (or more) of their adult children, the adult child's spouse, and the adult child's own children (the owners' grandchildren). Members of the extended family are not included in this family group. Sometimes, "skipped" generation families, such as a grandparents living with their grandchildren, are included.
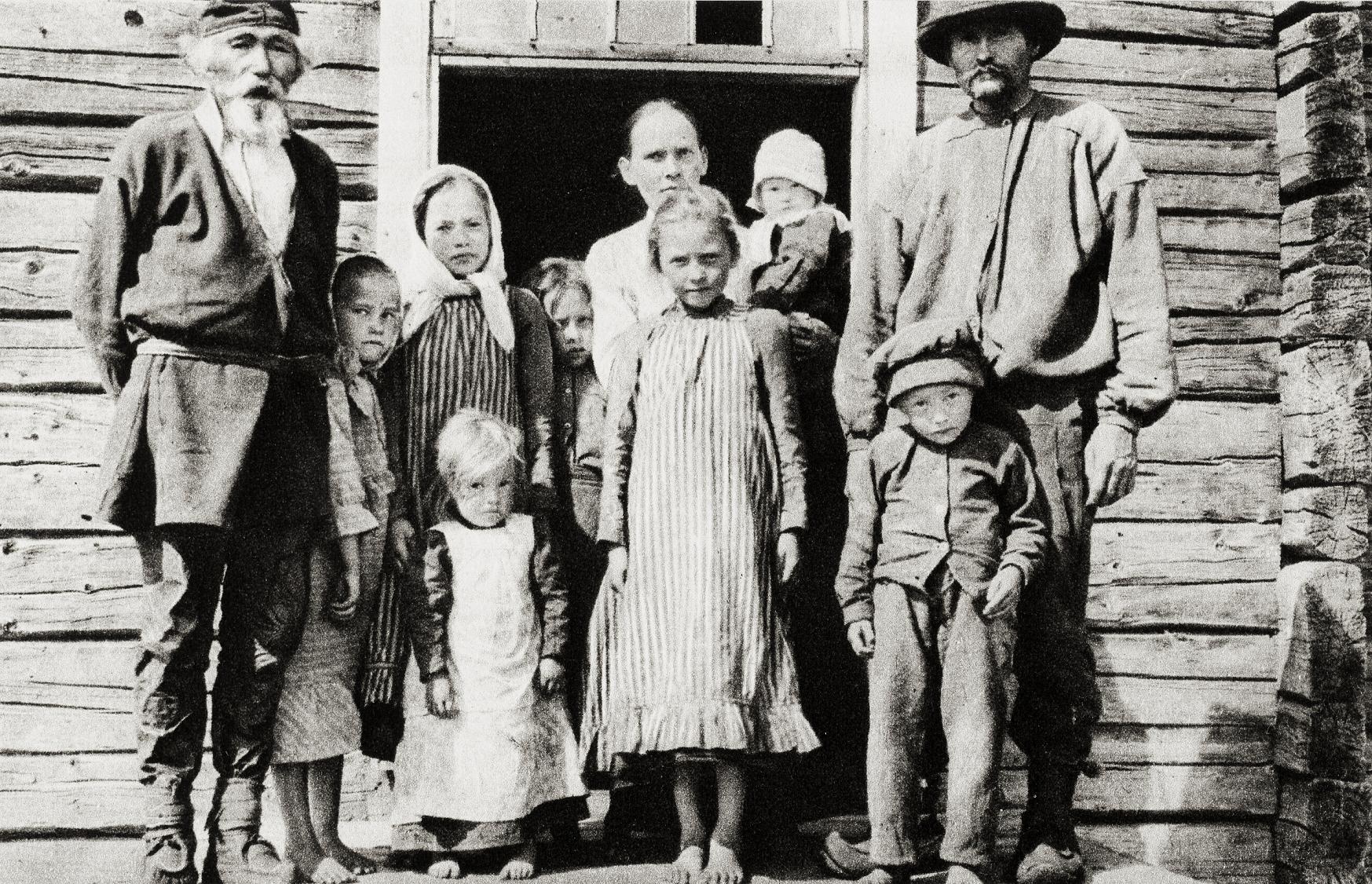

In the US, this arrangement declined after
World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing ...
, reaching a low point in 1980, when about one out of every eight people in the US lived in a multigenerational family.
The numbers have risen since then, with one in five people in the US living in a multigenerational family as of 2016. The increasing popularity is partly driven by
demographic change
Demography () is the statistical study of populations, especially human beings.
Demographic analysis examines and measures the dimensions and dynamics of populations; it can cover whole societies or groups defined by criteria such as edu ...
s and the economic shifts associated with the
Boomerang Generation
Boomerang Generation, in Western culture, is the generation of young adults graduating high school and college in the 21st century. They are so named for the percentage of whom choose to share a home with their parents after previously living on t ...
.
Multigenerational households are less common in Canada, where about 6% of people living in Canada were living in multigenerational families as of 2016, but the proportion of multigenerational households was increasing rapidly, driven by increasing numbers of Aboriginal families, immigrant families, and high housing costs in some regions.
Conjugal (nuclear) family
The term "
nuclear family" is commonly used to refer to conjugal families. A "
conjugal" family includes only the spouses and unmarried children who are not of age. Some sociologists distinguish between conjugal families (relatively independent of the kindred of the parents and of other families in general) and nuclear families (which maintain relatively close ties with their kindred).
Other family structures – with (for example)
blended parents,
single parent
A single parent is a person who has a child or children but does not have a spouse or live-in partner to assist in the upbringing or support of the child. Reasons for becoming a single parent include divorce, break-up, abandonment, becoming wid ...
s, and
domestic partnerships – have begun to challenge the normality of the nuclear family.
Single-parent family
A ''
single-parent family
A single parent is a person who has a child or children but does not have a spouse or live-in partner to assist in the upbringing or support of the child. Reasons for becoming a single parent include divorce, break-up, abandonment, becoming wi ...
'' consists of one parent together with their children, where the parent is either widowed, divorced (and not remarried), or never married. The parent may have
sole custody
Sole custody is a child custody arrangement whereby only one parent has custody of a child. In the most common use of the term, sole custody refers to a context in which one parent has sole physical custody of a child.
Types of custody
Depending ...
of the children, or separated parents may have a
shared-parenting arrangement where the children divide their time (possibly equally) between two different single-parent families or between one single-parent family and one
blended family
A stepfamily is a family where at least one parent has children that are not biologically related to their spouse. Either parent, or both, may have children from previous relationships or marriages. Two known classifications for stepfamilies i ...
. As compared to sole custody, physical, mental and social well-being of children may be improved by shared-parenting arrangements and by children having greater access to both parents. The number of single-parent families have been increasing, and about half of all children in the United States will live in a single-parent family at some point before they reach the age of 18. Most single-parent families are headed by a mother, but the number of single-parent families headed by fathers is increasing.
Matrifocal family
A "matrifocal" family consists of a
mother
]
A mother is the female parent of a child. A woman may be considered a mother by virtue of having given birth, by raising a child who may or may not be her biological offspring, or by supplying her ovum for fertilisation in the case of ges ...
and her children.
Generally, these children are her biological offspring, although adoption of children occurs in nearly every society. This kind of family occurs commonly where women have the resources to rear their children by themselves, or where men are more
Mobility (disambiguation), mobile than women. As a definition, "a family or domestic group is matrifocal when it is centred on a woman and her children. In this case, the father(s) of these children are intermittently present in the life of the group and occupy a secondary place. The children's mother is not necessarily the wife of one of the children's fathers." The name, matrifocal, was coined in Guiana but it is defined differently in other countries. For Nayar families, the family have the male as the "center" or the head of the family, either the step-father/father/brother, rather than the mother.
Extended family



The term "
extended family
An extended family is a family that extends beyond the nuclear family of parents and their children to include aunts, uncles, grandparents, cousins or other relatives, all living nearby or in the same household. Particular forms include the stem ...
" is also common, especially in the United States. This term has two distinct meanings:
# It serves as a synonym of "consanguinal family" (consanguine means "of the same blood").
# In societies dominated by the conjugal family, it refers to "
kindred" (an egocentric network of relatives that extends beyond the domestic group) who do not belong to the conjugal family.
These types refer to ideal or normative structures found in particular societies. Any society will exhibit some variation in the actual composition and conception of families.
Historically, ''
extended families
An extended family is a family that extends beyond the nuclear family of parents and their children to include aunts, uncles, grandparents, cousins or other relatives, all living nearby or in the same household. Particular forms include the stem a ...
'' were the basic family unit in the
Catholic culture
Christian culture generally includes all the cultural practices which have developed around the religion of Christianity. There are variations in the application of Christian beliefs in different cultures and traditions.
Christian culture has i ...
and
countries (such as
Southern Europe
Southern Europe is the southern region of Europe. It is also known as Mediterranean Europe, as its geography is essentially marked by the Mediterranean Sea. Definitions of Southern Europe include some or all of these countries and regions: Alba ...
and
Latin America
Latin America or
* french: Amérique Latine, link=no
* ht, Amerik Latin, link=no
* pt, América Latina, link=no, name=a, sometimes referred to as LatAm is a large cultural region in the Americas where Romance languages — languages derived f ...
),
and in Asian,
Middle Eastern and
Eastern Orthodox
Eastern Orthodoxy, also known as Eastern Orthodox Christianity, is one of the three main branches of Chalcedonian Christianity, alongside Catholicism and Protestantism.
Like the Pentarchy of the first millennium, the mainstream (or " canonical ...
countries.
Family of choice
The term
family of choice
A family of choice, also known as chosen family, found family, kith and kin, or hānai family is a term that refers to a non-biologically related group of people established to provide ongoing social support. Unlike a "family of origin" (the biol ...
, also sometimes referred to as "chosen family" or "found family", is common within the
LGBT community, veterans, individuals who have suffered abuse, and those who have no contact with biological "parents". It refers to the group of people in an individual's life that satisfies the typical role of family as a support system. The term differentiates between the "family of origin" (the biological family or that in which people are raised) and those that actively assume that ideal role.
The family of choice may or may not include some or all of the members of the family of origin. This family is not one that follows the "normal" familial structure like having a father, a mother, and children. This is family is a group of people that rely on each other like a family of origin would. This terminology stems from the fact that many
LGBT
' is an initialism that stands for lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender. In use since the 1990s, the initialism, as well as some of its common variants, functions as an umbrella term for sexuality and gender identity.
The LGBT term ...
individuals, upon
coming out, face rejection or shame from the families they were raised in.
The term family of choice is also used by individuals in the 12 step communities, who create close-knit "family" ties through the recovery process.
As a family system, families of choice face unique issues. Without legal safeguards, families of choice may struggle when medical, educational or governmental institutions fail to recognize their legitimacy.
If members of the chosen family have been disowned by their family of origin, they may experience surrogate grief, displacing anger, loss, or anxious attachment onto their new family.
Blended family
The term ''blended family'' or ''
stepfamily
A stepfamily is a family where at least one parent has children that are not biologically related to their spouse. Either parent, or both, may have children from previous relationships or marriages. Two known classifications for stepfamilies i ...
'' describes families with mixed parents: one or both parents remarried, bringing children of the former family into the new family. Also in sociology, particularly in the works of social psychologist
Michael Lamb, ''traditional family'' refers to "a middle-class family with a bread-winning father and a stay-at-home mother, married to each other and raising their biological children," and ''nontraditional'' to exceptions to this rule. Most of the US households are now non-traditional under this definition. Critics of the term "traditional family" point out that in most cultures and at most times, the
extended family
An extended family is a family that extends beyond the nuclear family of parents and their children to include aunts, uncles, grandparents, cousins or other relatives, all living nearby or in the same household. Particular forms include the stem ...
model has been most common, not the nuclear family, though it has had a longer tradition in England than in other parts of Europe and Asia which contributed large numbers of immigrants to the Americas. The nuclear family became the most common form in the U.S. in the 1960s and 1970s.
In terms of communication patterns in families, there are a certain set of beliefs within the family that reflect how its members should communicate and interact. These family communication patterns arise from two underlying sets of beliefs. One being conversation orientation (the degree to which the importance of communication is valued) and two, conformity orientation (the degree to which families should emphasize similarities or differences regarding attitudes, beliefs, and values).
Blended families is complex, ranging from stepfamilies to cohabitating families (an individual living with guardians who are not married with step or half siblings). While it's not too different from stepfamilies, cohabiting families pose a prevalent psychological effect on youths. Some adolescents would be prone to "acts of delinquency," and experiencing problems in school ranging from a decrease in academic performance to increased problematic behavior. It coincides with other researches on the trajectories of stepfamilies where some experienced familyhood, but others lacking connection. Emotional detachment from members within stepfamilies contributes to this uncertainty, furthering the tension that these families may establish. The transition from an old family to a new family that falls under blended families would also become problematic as the activities that were once performed in the old family may not transfer well within the new family for adolescents.
Monogamous family
A monogamous family is based on a legal or social
monogamy
Monogamy ( ) is a form of dyadic relationship in which an individual has only one partner during their lifetime. Alternately, only one partner at any one time (serial monogamy) — as compared to the various forms of non-monogamy (e.g., polyg ...
. In this case, an individual has only one (official) partner during their lifetime or at any one time (i.e.
serial monogamy
Monogamy ( ) is a form of dyadic relationship in which an individual has only one partner during their lifetime. Alternately, only one partner at any one time ( serial monogamy) — as compared to the various forms of non-monogamy (e.g., pol ...
).
[Cf. "Monogamy" in ''Britannica World Language Dictionary'', R.C. Preble (ed.), Oxford-London 1962, p. 1275:''1. The practice or principle of marrying only once. opp. to digamy now ''rare'' 2. The condition, rule or custom of being married to only one ]person
A person ( : people) is a being that has certain capacities or attributes such as reason, morality, consciousness or self-consciousness, and being a part of a culturally established form of social relations such as kinship, ownership of prope ...
at a time (opp. to polygamy or bigamy) 1708. 3. Zool. The habit of living in pairs, or having only one mate''; The same text repeats ''The Shorter Oxford English Dictionary'', W. Little, H.W. Fowler, J. Coulson (ed.), C.T. Onions (rev. & ed.,) Oxford 1969, 3rd edition, vol. 1, p. 1275
OED Online
March 2010. Oxford University Press. 23 Jun. 2010 Cf
Monogamy
in Merriam-Webster Dictionary This means that a person may not have several different legal spouses at the same time, as this is usually prohibited by
bigamy
In cultures where monogamy is mandated, bigamy is the act of entering into a marriage with one person while still legally married to another. A legal or de facto separation of the couple does not alter their marital status as married persons. I ...
laws, (the act of entering into a marriage with one person while still legally married to another) in jurisdictions that require monogamous marriages.
Polygamous family

Polygamy
Crimes
Polygamy (from Late Greek (') "state of marriage to many spouses") is the practice of marriage, marrying multiple spouses. When a man is married to more than one wife at the same time, sociologists call this polygyny. When a woman is ...
is a marriage that includes more than two partners.
When a man is married to more than one wife at a time, the relationship is called
polygyny
Polygyny (; from Neoclassical Greek πολυγυνία (); ) is the most common and accepted form of polygamy around the world, entailing the marriage of a man with several women.
Incidence
Polygyny is more widespread in Africa than in any ...
; and when a woman is married to more than one husband at a time, it is called
polyandry
Polyandry (; ) is a form of polygamy in which a woman takes two or more husbands at the same time. Polyandry is contrasted with polygyny, involving one male and two or more females. If a marriage involves a plural number of "husbands and wives ...
. If a marriage includes multiple husbands and wives, it can be called
polyamory
Polyamory () is the practice of, or desire for, romantic relationships with more than one partner at the same time, with the informed consent of all partners involved. People who identify as polyamorous may believe in open relationships wi ...
,
group or conjoint marriage.
[
]Polygyny
Polygyny (; from Neoclassical Greek πολυγυνία (); ) is the most common and accepted form of polygamy around the world, entailing the marriage of a man with several women.
Incidence
Polygyny is more widespread in Africa than in any ...
is a form of plural marriage, in which a man is allowed more than one wife . In modern countries that permit polygamy, polygyny is typically the only form permitted. Polygyny is practiced primarily (but not only) in parts of the Middle East and Africa; and is often associated with Islam, however, there are certain conditions in Islam that must be met to perform polygyny.
Polyandry
Polyandry (; ) is a form of polygamy in which a woman takes two or more husbands at the same time. Polyandry is contrasted with polygyny, involving one male and two or more females. If a marriage involves a plural number of "husbands and wives ...
is a form of marriage whereby a woman takes two or more husbands at the same time.Nepal
Nepal (; ne, :ne:नेपाल, नेपाल ), formerly the Federal Democratic Republic of Nepal ( ne,
सङ्घीय लोकतान्त्रिक गणतन्त्र नेपाल ), is a landlocked country in S ...
, in parts of China and in parts of northern India. Polyandry is most common in societies marked by high male mortality or where males will often be apart from the rest of the family for a considerable period of time.
Kinship terminology
Degrees of kinship

 A first-degree relative is one who shares 50% of your DNA through direct inheritance, such as a full sibling, parent or progeny.
There is another measure for the degree of relationship, which is determined by counting up generations to the first common ancestor and back down to the target individual, which is used for various genealogical and legal purposes.
A first-degree relative is one who shares 50% of your DNA through direct inheritance, such as a full sibling, parent or progeny.
There is another measure for the degree of relationship, which is determined by counting up generations to the first common ancestor and back down to the target individual, which is used for various genealogical and legal purposes.
Terminologies

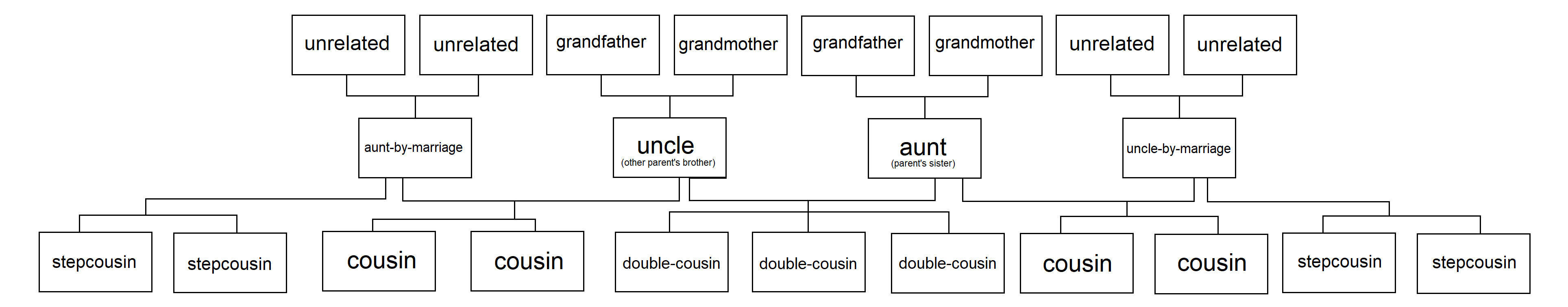 In his book ''
In his book ''Systems of Consanguinity and Affinity of the Human Family
''Systems of Consanguinity and Affinity of the Human Family'' is an 1871 book written by Lewis Henry Morgan (1818 - 1881) and published by the Smithsonian Institution. It is considered foundational for the discipline of anthropology and particular ...
'', anthropologist Lewis Henry Morgan
Lewis Henry Morgan (November 21, 1818 – December 17, 1881) was a pioneering American anthropologist and social theorist who worked as a railroad lawyer. He is best known for his work on kinship and social structure, his theories of social evol ...
(1818–1881) performed the first survey of kinship terminologies in use around the world. Although much of his work is now considered dated, he argued that kinship terminologies reflect different sets of distinctions. For example, most kinship terminologies distinguish between sexes (the difference between a brother and a sister) and between generations (the difference between a child and a parent). Moreover, he argued, kinship terminologies distinguish between relatives by blood and marriage
Marriage, also called matrimony or wedlock, is a culturally and often legally recognized union between people called spouses. It establishes rights and obligations between them, as well as between them and their children, and between ...
(although recently some anthropologists have argued that many societies define kinship in terms other than "blood").
Morgan made a distinction between kinship systems that use ''classificatory'' terminology and those that use ''descriptive'' terminology. Classificatory systems are generally and erroneously understood to be those that "class together" with a single term relatives who actually do not have the same type of relationship to ego. (What defines "same type of relationship" under such definitions seems to be genealogical relationship. This is problematic given that any genealogical description, no matter how standardized, employs words originating in a folk understanding of kinship.) What Morgan's terminology actually differentiates are those (classificatory) kinship systems that do not distinguish lineal and collateral relationships and those (descriptive) kinship systems that do. Morgan, a lawyer, came to make this distinction in an effort to understand Seneca
Seneca may refer to:
People and language
* Seneca (name), a list of people with either the given name or surname
* Seneca people, one of the six Iroquois tribes of North America
** Seneca language, the language of the Seneca people
Places Extrat ...
inheritance practices. A Seneca man's effects were inherited by his sisters' children rather than by his own children. Morgan identified six basic patterns of kinship terminologies:
* Hawaiian: only distinguishes relatives based upon sex and generation.
* Sudanese: no two relatives share the same term.
* Eskimo: in addition to distinguishing relatives based upon sex and generation, also distinguishes between lineal relatives and collateral relatives.
* Iroquois
The Iroquois ( or ), officially the Haudenosaunee ( meaning "people of the longhouse"), are an Iroquoian-speaking confederacy of First Nations peoples in northeast North America/ Turtle Island. They were known during the colonial years to ...
: in addition to sex and generation, also distinguishes between siblings of opposite sexes in the parental generation.
* Crow
A crow is a bird of the genus '' Corvus'', or more broadly a synonym for all of ''Corvus''. Crows are generally black in colour. The word "crow" is used as part of the common name of many species. The related term "raven" is not pinned scientifica ...
: a matrilineal system with some features of an Iroquois system, but with a "skewing" feature in which generation is "frozen" for some relatives.
* Omaha: like a Crow system but patrilineal.
Roles


 Most Western societies employ Eskimo kinship terminology. This kinship terminology commonly occurs in societies with strong conjugal, where families have a degree of relative mobility. Typically, societies with conjugal families also favor
Most Western societies employ Eskimo kinship terminology. This kinship terminology commonly occurs in societies with strong conjugal, where families have a degree of relative mobility. Typically, societies with conjugal families also favor neolocal Neolocal residence is a type of post-marital residence in which a newly married couple resides separately from both the husband's natal household and the wife's natal household. Neolocal residence forms the basis of most developed nations, especiall ...
residence; thus upon marriage, a person separates from the nuclear family of their childhood (family of orientation) and forms a new nuclear family (family of procreation). Such systems generally assume that the mother's husband is also the biological father. The system uses highly descriptive terms for the nuclear family and progressively more classificatory Classification is a process related to categorization, the process in which ideas and objects are recognized, differentiated and understood.
Classification is the grouping of related facts into classes.
It may also refer to:
Business, organizat ...
as the relatives become more and more collateral.
Nuclear family

 The system emphasizes the nuclear family. Members of the nuclear family use highly descriptive kinship terms, identifying directly only the husband, wife, mother, father, son, daughter, brother, and sister. All other relatives are grouped together into categories. Members of the nuclear family may be lineal or collateral. Kin, for whom these are family, refer to them in descriptive terms that build on the terms used within the nuclear family or use the nuclear family term directly.
Nuclear family of orientation
*
The system emphasizes the nuclear family. Members of the nuclear family use highly descriptive kinship terms, identifying directly only the husband, wife, mother, father, son, daughter, brother, and sister. All other relatives are grouped together into categories. Members of the nuclear family may be lineal or collateral. Kin, for whom these are family, refer to them in descriptive terms that build on the terms used within the nuclear family or use the nuclear family term directly.
Nuclear family of orientation
* Brother
A brother is a man or boy who shares one or more parents with another; a male sibling. The female counterpart is a sister. Although the term typically refers to a familial relationship, it is sometimes used endearingly to refer to non-familia ...
: the male child of a parent.
* Sister
A sister is a woman or a girl who shares one or more parents with another individual; a female sibling. The male counterpart is a brother. Although the term typically refers to a family, familial relationship, it is sometimes used endearingly to r ...
: the female child of a parent.
* Father
A father is the male parent of a child. Besides the paternal bonds of a father to his children, the father may have a parental, legal, and social relationship with the child that carries with it certain rights and obligations. An adoptive fathe ...
: a male parent.
** Grandfather
Grandparents, individually known as grandmother and grandfather, are the parents of a person's father or mother – paternal or maternal. Every sexually-reproducing living organism who is not a genetic chimera has a maximum of four genetic ...
: the father of a parent.
* Mother
]
A mother is the female parent of a child. A woman may be considered a mother by virtue of having given birth, by raising a child who may or may not be her biological offspring, or by supplying her ovum for fertilisation in the case of ges ...
: a female parent.
** Grandmother
Grandparents, individually known as grandmother and grandfather, are the parents of a person's father or mother – paternal or maternal. Every sexually-reproducing living organism who is not a genetic chimera has a maximum of four genetic gra ...
: the mother of a parent.
Nuclear conjugal family
* Husband: a male spouse.
* Wife
A wife (plural, : wives) is a female in a marital relationship. A woman who has separated from her partner continues to be a wife until the marriage is legally Dissolution (law), dissolved with a divorce judgement. On the death of her partner, ...
: a female spouse.
* Son
A son is a male offspring; a boy or a man in relation to his parents. The female counterpart is a daughter. From a biological perspective, a son constitutes a first degree relative.
Social issues
In pre-industrial societies and some current c ...
: a male child of the parent(s).
** Grandson: a child's son.
* Daughter
A daughter is a female offspring; a girl or a woman in relation to her parents. Daughterhood is the state of being someone's daughter. The male counterpart is a son. Analogously the name is used in several areas to show relations between group ...
: a female child of the parent(s).
** Granddaughter: a child's daughter.
Nuclear non-lineal family
* Spouse: husband or wife
** Stepparent
A stepfamily is a family where at least one parent has children that are not biologically related to their spouse. Either parent, or both, may have children from previous relationships or marriages. Two known classifications for stepfamilies i ...
: a spouse of a parent that is not a biological parent
* Sibling: sister or brother
** Half-sibling
A sibling is a relative that shares at least one parent with the subject. A male sibling is a brother and a female sibling is a sister. A person with no siblings is an only child.
While some circumstances can cause siblings to be raised separat ...
: a sibling with whom the subject shares only one biological parent
** Step-sibling: a child of a parent that is not a biological parent
Collateral relatives
A sibling is a collateral relative with a minimal removal. For collateral relatives with one additional removal, one generation more distant from a common ancestor on one side, more classificatory terms come into play. These terms (Aunt
An aunt is a woman who is a sibling of a parent or married to a sibling of a parent. Aunts who are related by birth are second-degree relatives. Known alternate terms include auntie or aunty. Children in other cultures and families may re ...
, Uncle
An uncle is usually defined as a male relative who is a sibling of a parent or married to a sibling of a parent. Uncles who are related by birth are second-degree relatives. The female counterpart of an uncle is an aunt, and the reciprocal rela ...
, Niece
In the lineal kinship system used in the English-speaking world, a niece or nephew is a child of the subject's sibling or sibling-in-law. The converse relationship, the relationship from the niece or nephew's perspective, is that of an ...
, and Nephew) do not build on the terms used within the nuclear family as most are not traditionally members of the household. These terms do not traditionally differentiate between a collateral relatives and a person married to a collateral relative (both collateral and aggregate). Collateral relatives with additional removals on each side are Cousin
Most generally, in the lineal kinship system used in the English-speaking world, a cousin is a type of familial relationship in which two relatives are two or more familial generations away from their most recent common ancestor. Commonly, ...
s. This is the most classificatory term and can be distinguished by degrees of collaterality and by generation (removal).
When only the subject has the additional removal, the relative is the subject's parents' siblings, the terms Aunt and Uncle are used for female and male relatives respectively. When only the relative has the additional removal, the relative is the subjects siblings child, the terms Niece and Nephew are used for female and male relatives respectively. The spouse of a biological aunt or uncle is an aunt or uncle, and the nieces and nephews of a spouse are nieces and nephews. With further removal by the subject for aunts and uncles and by the relative for nieces and nephews the prefix "grand-" modifies these terms. With further removal the prefix becomes "great-grand-," adding another "great-" for each additional generation. For large numbers of generations a number can be substituted, for example, "fourth great-grandson", "four-greats grandson" or "four-times-great-grandson".
When the subject and the relative have an additional removal they are cousins. A cousin with minimal removal is a first cousin, i.e. the child of the subjects uncle or aunt. Degrees of collaterality and removals are used to more precisely describe the relationship between cousins. The degree is the number of generations subsequent to the common ancestor before a parent of one of the cousins is found, while the removal is the difference between the number of generations from each cousin to the common ancestor (the difference between the generations the cousins are from).
Aggregate relatives
English-speakers mark relationships by marriage (except for wife/husband) with the tag "-in-law". The mother and father of one's spouse become one's mother-in-law and father-in-law; the wife of one's son becomes one's daughter-in-law and the husband of one's daughter becomes one's son-in-law. The term "sister-in-law
A sibling-in-law is the spouse of one's sibling, or the sibling of one's spouse, or the person who is married to the sibling of one's spouse.Cambridge Dictionaries Online.Family: non-blood relations.
More commonly, a sibling-in-law is referred ...
" refers to two essentially different relationships, either the wife of one's brother, or the sister of one's spouse. "Brother-in-law
A sibling-in-law is the spouse of one's sibling, or the sibling of one's spouse, or the person who is married to the sibling of one's spouse.Cambridge Dictionaries Online.Family: non-blood relations.
More commonly, a sibling-in-law is referre ...
" is the husband of one's sister, or the brother of one's spouse. The terms "half-brother" and "half-sister" indicate siblings who share only one biological parent. The term " aunt-in-law" is the wife of one's uncle, or the aunt of one's spouse. "Uncle-in-law
An uncle is usually defined as a male relative who is a sibling of a parent or married to a sibling of a parent. Uncles who are related by birth are second-degree relatives. The female counterpart of an uncle is an aunt, and the reciprocal rela ...
" is the husband of one's aunt, or the uncle of one's spouse. "Cousin-in-law
Most generally, in the lineal kinship system used in the English-speaking world, a cousin is a type of familial relationship in which two relatives are two or more familial generations away from their most recent common ancestor. Commonly, ...
" is the spouse of one's cousin, or the cousin of one's spouse. The term "niece-in-law
In the lineal kinship system used in the English-speaking world, a niece or nephew is a child of the subject's sibling or sibling-in-law. The converse relationship, the relationship from the niece or nephew's perspective, is that of an ...
" is the wife of one's nephew, or the niece of one's spouse. " Nephew-in-law" is the husband of one's niece, or the nephew of one's spouse. The grandmother and grandfather of one's spouse become one's grandmother-in-law and grandfather-in-law; the wife of one's grandson becomes one's granddaughter-in-law and the husband of one's granddaughter becomes one's grandson-in-law.
In Indian English a sibling in law who is the spouse of your sibling can be referred to as a co-sibling (specificity a co-sister
Types of kinship
Patrilineal
Patrilineality
Patrilineality, also known as the male line, the spear side or agnatic kinship, is a common kinship system in which an individual's family membership derives from and is recorded through their father's lineage. It generally involves the inheritan ...
, also known as ''the male line'' or ''agnatic kinship'', is a form of kinship system in which an individual's family membership derives from and is traced through his or her father's lineage
Lineage may refer to:
Science
* Lineage (anthropology), a group that can demonstrate its common descent from an apical ancestor or a direct line of descent from an ancestor
* Lineage (evolution), a temporal sequence of individuals, populati ...
. It generally involves the inheritance
Inheritance is the practice of receiving private property, titles, debts, entitlements, privileges, rights, and obligations upon the death of an individual. The rules of inheritance differ among societies and have changed over time. Officia ...
of property, rights, names, or titles by persons related through male
Male (symbol: ♂) is the sex of an organism that produces the gamete (sex cell) known as sperm, which fuses with the larger female gamete, or ovum, in the process of fertilization.
A male organism cannot reproduce sexually without access to ...
kin.
A patriline ("father line") is a person's father, and additional ancestors that are traced only through males. One's patriline is thus a record of descent from a man in which the individuals in all intervening generations are male. In cultural anthropology, a patrilineage is a consanguineal
Consanguinity ("blood relation", from Latin '' consanguinitas'') is the characteristic of having a kinship with another person (being descended from a common ancestor).
Many jurisdictions have laws prohibiting people who are related by blood fr ...
male and female kinship group
Family (from la, familia) is a group of people related either by consanguinity (by recognized birth) or affinity (by marriage or other relationship). The purpose of the family is to maintain the well-being of its members and of society. Ideall ...
, each of whose members is descended from the common ancestor through male forebears.
Matrilineal

Matrilineality
Matrilineality is the tracing of kinship through the female line. It may also correlate with a social system in which each person is identified with their matriline – their mother's lineage – and which can involve the inheritance ...
is a form of kinship system in which an individual's family membership derives from and is traced through his or her mother's lineage
Lineage may refer to:
Science
* Lineage (anthropology), a group that can demonstrate its common descent from an apical ancestor or a direct line of descent from an ancestor
* Lineage (evolution), a temporal sequence of individuals, populati ...
.
It may also correlate with a societal system
In sociology, a social system is the patterned network of relationships constituting a coherent whole that exist between individuals, groups, and institutions. It is the formal structure of role and status that can form in a small, stable group. ...
in which each person is identified with their matriline—their mother's lineage
Lineage may refer to:
Science
* Lineage (anthropology), a group that can demonstrate its common descent from an apical ancestor or a direct line of descent from an ancestor
* Lineage (evolution), a temporal sequence of individuals, populati ...
—and which can involve the inheritance
Inheritance is the practice of receiving private property, titles, debts, entitlements, privileges, rights, and obligations upon the death of an individual. The rules of inheritance differ among societies and have changed over time. Officia ...
of property and titles. A matriline is a line of descent from a female
Female ( symbol: ♀) is the sex of an organism that produces the large non-motile ova (egg cells), the type of gamete (sex cell) that fuses with the male gamete during sexual reproduction.
A female has larger gametes than a male. Females ...
ancestor to a descendant in which the individuals in all intervening generations are mothersin other words, a "mother line".
In a matrilineal descent system, an individual is considered to belong to the same descent group
Descent may refer to:
As a noun Genealogy and inheritance
* Common descent, concept in evolutionary biology
* Kinship, one of the major concepts of cultural anthropology
**Pedigree chart or family tree
**Ancestry
**Lineal descendant
**Heritage
** ...
as her or his mother. This matrilineal descent pattern is in contrasts to the more common pattern of patrilineal descent pattern.
Bilateral descent
Bilateral descent
Bilateral descent is a system of family lineage in which the relatives on the mother's side and father's side are equally important for emotional ties or for transfer of property or wealth. It is a family arrangement where descent and inheritan ...
is a form of kinship system in which an individual's family membership derives from and is traced through both the paternal and maternal sides. The relatives on the mother's side and father's side are equally important for emotional ties or for transfer of property or wealth. It is a family arrangement where descent and inheritance are passed equally through both parents. Families who use this system trace descent through both parents simultaneously and recognize multiple ancestors, but unlike with cognatic descent it is not used to form descent groups.
Traditionally, this is found among some groups in West Africa, India, Australia, Indonesia, Melanesia
Melanesia (, ) is a subregion of Oceania in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It extends from Indonesia's New Guinea in the west to Fiji in the east, and includes the Arafura Sea.
The region includes the four independent countries of Fiji, Va ...
, Malaysia and Polynesia
Polynesia () "many" and νῆσος () "island"), to, Polinisia; mi, Porinihia; haw, Polenekia; fj, Polinisia; sm, Polenisia; rar, Porinetia; ty, Pōrīnetia; tvl, Polenisia; tkl, Polenihia (, ) is a subregion of Oceania, made up of ...
. Anthropologists believe that a tribal structure based on bilateral descent helps members live in extreme environments because it allows individuals to rely on two sets of families dispersed over a wide area.
History of theories
Early scholars of family history applied Darwin's biological theory of evolution
Evolution is change in the heritable characteristics of biological populations over successive generations. These characteristics are the expressions of genes, which are passed on from parent to offspring during reproduction. Variatio ...
in their theory of evolution of family systems.Lewis H. Morgan
Lewis Henry Morgan (November 21, 1818 – December 17, 1881) was a pioneering American anthropologist and social theorist who worked as a railroad lawyer. He is best known for his work on kinship and social structure, his theories of social ev ...
published ''Ancient Society
''Ancient Society'' is an 1877 book by the American anthropologist Lewis H. Morgan. Building on the data about kinship and social organization presented in his 1871 '' Systems of Consanguinity and Affinity of the Human Family'', Morgan develops ...
'' in 1877 based on his theory of the three stages of human progress from Savagery through Barbarism to Civilization
A civilization (or civilisation) is any complex society characterized by the development of a state, social stratification, urbanization, and symbolic systems of communication beyond natural spoken language (namely, a writing system).
...
. Morgan's book was the "inspiration for '' published in 1884.
Engels expanded Morgan's hypothesis that economical factors caused the transformation of primitive community into a class-divided society. Engels' theory of resource
Resource refers to all the materials available in our environment which are technologically accessible, economically feasible and culturally sustainable and help us to satisfy our needs and wants. Resources can broadly be classified upon their ...
control, and later that of Karl Marx
Karl Heinrich Marx (; 5 May 1818 – 14 March 1883) was a German philosopher, economist, historian, sociologist, political theorist, journalist, critic of political economy, and socialist revolutionary. His best-known titles are the 1848 ...
, was used to explain the cause and effect of change in family structure and function. The popularity of this theory was largely unmatched until the 1980s, when other sociological theories, most notably structural functionalism
Structural functionalism, or simply functionalism, is "a framework for building theory that sees society as a complex system whose parts work together to promote solidarity and stability".
This approach looks at society through a macro-level o ...
, gained acceptance.
The nuclear family in industrial society
 Contemporary society generally views the family as a haven from the world, supplying absolute fulfillment. Zinn and Eitzen discuss the image of the "family as haven ... a place of
Contemporary society generally views the family as a haven from the world, supplying absolute fulfillment. Zinn and Eitzen discuss the image of the "family as haven ... a place of intimacy
An intimate relationship is an interpersonal relationship that involves physical or emotional intimacy. Although an intimate relationship is commonly a sexual relationship, it may also be a non-sexual relationship involving family, friends, or ...
, love
Love encompasses a range of strong and positive emotional and mental states, from the most sublime virtue or good habit, the deepest interpersonal affection, to the simplest pleasure. An example of this range of meanings is that the love o ...
and trust
Trust often refers to:
* Trust (social science), confidence in or dependence on a person or quality
It may also refer to:
Business and law
* Trust law, a body of law under which one person holds property for the benefit of another
* Trust (bus ...
where individuals may escape
Escape or Escaping may refer to:
Computing
* Escape character, in computing and telecommunication, a character which signifies that what follows takes an alternative interpretation
** Escape sequence, a series of characters used to trigger some so ...
the competition of dehumanizing forces in modern society".
During industrialization, " e family as a repository of warmth and tenderness (embodied by the mother) stands in opposition to the competitive and aggressive world of commerce (embodied by the father). The family's task was to protect against the outside world."[Zinn and Eitzen (1987) ]
Diversity in American families
'', p. 3 However, Zinn and Eitzen note, "The protective image of the family has waned in recent years as the ideals of family fulfillment have taken shape. Today, the family is more compensatory than protective. It supplies what is vitally needed but missing in other social arrangements."divorce
Divorce (also known as dissolution of marriage) is the process of terminating a marriage or marital union. Divorce usually entails the canceling or reorganizing of the legal duties and responsibilities of marriage, thus dissolving the ...
. They respond to this, saying, "there is no golden age of the family gleaming at us in the far back historical past."[Zinn and Eitzen (1987) ]
Diversity in American families
'', p. 8 "Desertion by spouses, illegitimate children, and other conditions that are considered characteristics of modern times existed in the past as well."
The postmodern family
 Others argue that whether or not one views the family as "declining" depends on one's definition of "family". "Married couples have dropped below half of all American households. This drop is shocking from traditional forms of the family system. Only a fifth of households were following traditional ways of having married couples raising a family together." In the Western World, marriages are no longer
Others argue that whether or not one views the family as "declining" depends on one's definition of "family". "Married couples have dropped below half of all American households. This drop is shocking from traditional forms of the family system. Only a fifth of households were following traditional ways of having married couples raising a family together." In the Western World, marriages are no longer arranged
In music, an arrangement is a musical adaptation of an existing composition. Differences from the original composition may include reharmonization, melodic paraphrasing, orchestration, or formal development. Arranging differs from orchest ...
for economic, social or political gain, and children are no longer expected to contribute to family income. Instead, people choose mates based on love
Love encompasses a range of strong and positive emotional and mental states, from the most sublime virtue or good habit, the deepest interpersonal affection, to the simplest pleasure. An example of this range of meanings is that the love o ...
. This increased role of love indicates a societal shift toward favoring emotional fulfilment and relationships within a family, and this shift necessarily weakens the institution of the family.
Margaret Mead considers the family as a main safeguard to continuing human progress. Observing, "Human beings have learned, laboriously, to be human", she adds: "we hold our present form of humanity on trust, ndit is possible to lose it" ... "It is not without significance that the most successful large-scale abrogations of the family have occurred not among simple savages, living close to the subsistence edge, but among great nations and strong empires, the resources of which were ample, the populations huge, and the power almost unlimited"
Many countries (particularly Western) have, in recent years, changed their family laws in order to accommodate diverse family models. For instance, in the United Kingdom, in Scotland, the ''Family Law (Scotland) Act 2006'' provides cohabitants with some limited rights. In 2010, Ireland enacted the Civil Partnership and Certain Rights and Obligations of Cohabitants Act 2010. There have also been moves at an international level, most notably, the Council of Europe ''European Convention on the Legal Status of Children Born out of Wedlock'' which came into force in 1978. Countries which ratify it must ensure that children born outside marriage are provided with legal rights as stipulated in the text of this convention. The convention was ratified by the UK in 1981 and by Ireland in 1988.
In the United States, one in five mothers has children by different fathers; among mothers with two or more children the figure is higher, with 28% having children with at least two different men. Such families are more common among Blacks and Hispanics and among the lower socioeconomic class.
However, in western society, the single parent family has been growing more accepted and has begun to make an impact on culture. Single parent families are more commonly single mother families than single father. These families sometimes face difficult issues besides the fact that they have to rear their children on their own, for example, low income making it difficult to pay for rent, child care, and other necessities for a healthy and safe home.
Furthermore, there are families that consist of two mothers, two fathers, non-binary, trans, and queer folks raising children. This is made possible due to surrogacy, IVF, IUI, adoption, and other processes.
Domestic violence
Domestic violence (DV) is violence that happens within the family. The legal and social understanding of the concept of DV differs by culture. The definition of the term "domestic violence" varies, depending on the context in which it is used. It may be defined differently in medical, legal, political or social contexts. The definitions have varied over time, and vary in different parts of the world.
The Convention on preventing and combating violence against women and domestic violence states that:
In 1993, the United Nations Declaration on the Elimination of Violence against Women identified domestic violence as one of three contexts in which violence against women occurs, describing it as:
Family violence
Family violence is a broader definition, often used to include child abuse, elder abuse, and other violent acts between family members.[Wallace, p. 2]
Child abuse is defined by the World Health Organization, WHO as:
There exists legislation to prevent and punish the occurrence of these offences. There are laws regarding familial sexual activity, which states that it is a criminal offence to have any kind of sexual relationship between one's grandparent, parent, sibling, aunt or uncle.
Elder abuse is, according to the WHO: "a single, or repeated act, or lack of appropriate action, occurring within any relationship where there is an expectation of trust which causes harm or distress to an older person".
Parental abuse of children (child abuse)
Child abuse is the physical, sexual or emotional maltreatment or neglect of a child or children. In the United States, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) and the Department for Children and Families (DCF) define child maltreatment as any act or series of acts of commission or omission by a parent or other caregiver that results in harm, potential for harm, or threat of harm to a child.
Parental abuse by children
Abuse of parents by their children is a common but under reported and under-researched subject. A factor why this subject is under-researched is because of the overshadowing effect caused by parents abusing their children instead. Parents are quite often subject to levels of childhood aggression in excess of normal childhood aggressive outbursts, typically in the form of verbal abuse, verbal or physical abuse, physical abuse. Parents feel a sense of shame and humiliation to have that problem, so they rarely seek help and it is usually little or no help available anyway.
Elder abuse
Elder abuse is "a single, or repeated act, or lack of appropriate action, occurring within any relationship where there is an expectation of trust, which causes harm or distress to an older person". This definition has been adopted by the World Health Organization from a definition put forward by Action on Elder Abuse in the UK. Laws protecting the elderly from abuse are similar to, and related to, laws protecting dependent adults from abuse.
The core element to the harm of elder abuse is the "expectation of trust" of the older person toward their abuser. Thus, it includes harms by people the older person knows or with whom they have a relationship, such as a spouse, partner or family member, a friend or neighbor, or people that the older person relies on for services. Many forms of elder abuse are recognized as types of domestic violence or family violence.
Forced and child marriage
Forced and child marriages are practiced in certain regions of the world, particularly in Asia and Africa, and these types of marriages are associated with a high rate of domestic violence.marriage
Marriage, also called matrimony or wedlock, is a culturally and often legally recognized union between people called spouses. It establishes rights and obligations between them, as well as between them and their children, and between ...
where one or both spouses are under 18.
The concept of family honour
Family honor is an abstract concept involving the perceived quality of worthiness and respectability that affects the social standing and the self-evaluation of a group of related people, both corporately and individually.
Economic issues
A family is often part of a sharing economy with common ownership.
Dowry, bride price and dower
 Dowry is property (money, goods, or estate) that a wife or wife's family gives to her husband when the wife and husband marry. Offering dowry was common in many cultures historically (including in Europe and North America), but this practice today is mostly restricted to some areas primarily in the Indian subcontinent.
Bride price, (also bride wealth or bride token), is property paid by the groom or his family to the parents of a woman upon the marriage of their daughter to the groom. It is practiced mostly in Sub-Saharan Africa, parts of South-East Asia (Thailand, Cambodia), and parts of Central Asia.
Dower is property given to the bride herself by the groom at the time of marriage, and which remains under her ownership and control.
Dowry is property (money, goods, or estate) that a wife or wife's family gives to her husband when the wife and husband marry. Offering dowry was common in many cultures historically (including in Europe and North America), but this practice today is mostly restricted to some areas primarily in the Indian subcontinent.
Bride price, (also bride wealth or bride token), is property paid by the groom or his family to the parents of a woman upon the marriage of their daughter to the groom. It is practiced mostly in Sub-Saharan Africa, parts of South-East Asia (Thailand, Cambodia), and parts of Central Asia.
Dower is property given to the bride herself by the groom at the time of marriage, and which remains under her ownership and control.
Property regimes and taxation
In some countries married couples benefit from various taxation advantages not available to a single person or to unmarried couples. For example, spouses may be allowed to average their combined incomes. Some jurisdictions recognize common law marriage or ''de facto'' relations for this purposes. In some jurisdictions there is also an option of civil partnership or domestic partnership.
Different property regimes exist for spouses. In many countries, each marriage partner has the choice of keeping their property community property, separate or combining properties. In the latter case, called community property, when the marriage ends by divorce each owns half. In lieu of a will (law), will or trust law, trust, property owned by the deceased generally is inherited by the surviving spouse.
Rights and laws
Reproductive rights
 Reproductive rights are legal rights and freedoms relating to reproduction and reproductive health. These include the right to decide on issues regarding the number of children born, family planning, contraception, and private life, free from coercion and discrimination; as well as the right to access health services and adequate information. According to UNFPA, reproductive rights "include the right to decide the number, timing and spacing of children, the right to voluntarily marry and establish a family, and the right to the highest attainable standard of health, among others". Family planning refers to the factors that may be considered by individuals and couples in order for them to control their fertility, anticipate and attain the desired number of children and the spacing and timing of their births.
The state and church have been, and still are in some countries, involved in controlling the size of families, often using coercive methods, such as bans on contraception or abortion (where the policy is a natalist one—for example through tax on childlessness) or conversely, discriminatory policies against large families or even forced abortions (e.g., China's one-child policy in place from 1978 to 2015). Forced sterilization has often targeted ethnic minority groups, such as Roma women in Eastern Europe, or indigenous women in Peru (during the 1990s).
Reproductive rights are legal rights and freedoms relating to reproduction and reproductive health. These include the right to decide on issues regarding the number of children born, family planning, contraception, and private life, free from coercion and discrimination; as well as the right to access health services and adequate information. According to UNFPA, reproductive rights "include the right to decide the number, timing and spacing of children, the right to voluntarily marry and establish a family, and the right to the highest attainable standard of health, among others". Family planning refers to the factors that may be considered by individuals and couples in order for them to control their fertility, anticipate and attain the desired number of children and the spacing and timing of their births.
The state and church have been, and still are in some countries, involved in controlling the size of families, often using coercive methods, such as bans on contraception or abortion (where the policy is a natalist one—for example through tax on childlessness) or conversely, discriminatory policies against large families or even forced abortions (e.g., China's one-child policy in place from 1978 to 2015). Forced sterilization has often targeted ethnic minority groups, such as Roma women in Eastern Europe, or indigenous women in Peru (during the 1990s).
Parents' rights
The Parents' rights movement, parents' rights movement is a movement whose members are primarily interested in issues affecting parents and children related to family law, specifically parental rights and obligations. Mothers' rights movements focus on maternal health, workplace issues such as labor rights, breastfeeding, and rights in family law. The fathers' rights movement is a movement whose members are primarily interested in issues related to family law, including child custody and child support, that affect fathers and their children.[#FRALR, Collier & Sheldon, 2006, pp. 1–26.]
Children's rights
Children's rights are the human rights of children, with particular attention to the rights of special protection and care afforded to minors, including their right to association with both parents, their right to human identity, their right to be provided in regard to their other basic needs, and their right to be free from violence and abuse.
Marriage rights
Each jurisdiction has its own marriage laws. These laws differ significantly from country to country; and these laws are often controversial. Areas of controversy include women's rights as well as same-sex marriage.
Legal reforms
Legal reforms to family laws have taken place in many countries during the past few decades. These dealt primarily with gender equality within marriage and with divorce laws. Women have been given equal rights in marriage in many countries, reversing older family laws based on the dominant legal role of the husband. Coverture, which was enshrined in the common law of England and the US for several centuries and throughout most of the 19th century, was abolished. In some European countries the changes that lead to gender equality were slower. The period of 1975–1979 saw a major overhaul of family laws in countries such as Italy, Spain, Austria,[''Contemporary Western European Feminism'', by Gisela Kaplan, p. 133] West Germany, and Portugal. In 1978, the Council of Europe passed the ''Resolution (78) 37 on equality of spouses in civil law''. Among the last European countries to establish full gender equality in marriage were Switzerland. In 1985, a referendum guaranteed women legal equality with men within marriage. The new reforms came into force in January 1988. In Greece, in 1983, legislation was passed guaranteeing equality between spouses, abolishing dowry, and ending legal discrimination against illegitimate children. In 1981, Spain abolished the requirement that married women must have their husbands' permission to initiate judicial proceedings
Health

Family medicine
Family medicine is a medical specialty devoted to comprehensive health care for people of all ages; it is based on knowledge of the patient in the context of the family and the community, emphasizing disease prevention and health promotion. The importance of family medicine is being increasingly recognized.
Maternal mortality
Maternal mortality or maternal death is defined by World Health Organization, WHO as "the death of a woman while pregnant or within 42 days of termination of pregnancy, irrespective of the duration and site of the pregnancy, from any cause related to or aggravated by the pregnancy or its management but not from accidental or incidental causes."
Infant and child mortality
Infant mortality is the death of a child less than one year of age. Child mortality is the death of a child before the child's fifth birthday. Like maternal mortality, infant and child mortality were common throughout history, but have decreased significantly in modern times.
Politics

 While in many parts of the world family policies seek to promote a gender-equal organization of the family life, in others the male-dominated family continues to be the official policy of the authorities, which is also supported by law. For instance, the Civil Code of Iran states at Article 1105: "In relations between husband and wife; the position of the head of the family is the exclusive right of the husband".
In some parts of the world, some governments promote a specific form of family, such as that based on traditional family values. The term "family values" is often used in political discourse in some countries, its general meaning being that of traditional or cultural values that pertain to the family's structure, function, roles, beliefs, attitudes, and ideals, usually involving the "traditional family"—a middle class, middle-class family with a breadwinner father and a homemaker mother, raising their biological children. Any deviation from this family model is considered a "nontraditional family". These family ideals are often advanced through policies such as marriage promotion. Some jurisdictions outlaw practices which they deem as socially or religiously unacceptable, such as fornication, cohabitation or adultery.
While in many parts of the world family policies seek to promote a gender-equal organization of the family life, in others the male-dominated family continues to be the official policy of the authorities, which is also supported by law. For instance, the Civil Code of Iran states at Article 1105: "In relations between husband and wife; the position of the head of the family is the exclusive right of the husband".
In some parts of the world, some governments promote a specific form of family, such as that based on traditional family values. The term "family values" is often used in political discourse in some countries, its general meaning being that of traditional or cultural values that pertain to the family's structure, function, roles, beliefs, attitudes, and ideals, usually involving the "traditional family"—a middle class, middle-class family with a breadwinner father and a homemaker mother, raising their biological children. Any deviation from this family model is considered a "nontraditional family". These family ideals are often advanced through policies such as marriage promotion. Some jurisdictions outlaw practices which they deem as socially or religiously unacceptable, such as fornication, cohabitation or adultery.
Work-family balance
Work-family balance is a concept involving proper prioritizing between work/career and family life. It includes issues relating to the way how work and families intersect and influence each other. At a political level, it is reflected through policies such maternity leave and paternity leave. Since the 1950s, social scientists as well as feminists have increasingly criticized gendered arrangements of work and care, and the male breadwinner role, and policies are increasingly targeting men as fathers, as a tool of changing gender relations.
Protection of private and family life
Article 8 of the European Convention on Human Rights provides a right to respect for one's "private and family life, his home and his privacy of correspondence, correspondence", subject to certain restrictions that are "in accordance with law" and "necessary in a democratic society".
Criticism
An early opponent of the family was Socrates whose position was outlined by Plato in ''The Republic''. In Book 5 of ''The Republic'', Socrates tells his interlocutors that a just city is one in which citizens have no family ties.
The family being such a deep-rooted and much-venerated institution, few intellectuals have ventured to speak against it. Familialism has been atypically defined as a "social structure where ... a family's values are held in higher esteem than the values of the individual members of the family". In-group favoritism, Favoritism granted to relatives regardless of wikt:merit, merit is called nepotism.
The Russian-American Rationalism, rationalist and Individualism, individualist philosopher, novelist and playwright Ayn Rand compared partiality towards consanguinity
Consanguinity ("blood relation", from Latin '' consanguinitas'') is the characteristic of having a kinship with another person (being descended from a common ancestor).
Many jurisdictions have laws prohibiting people who are related by blood fr ...
with racism, as a small-scale manifestation of the latter.[ Said i]
one of the lectures
Ayn Rand delivered. "The worship of the family is merely racism, like a crudely primitive first installment on the worship of the tribe. It places the accident of birth above a man's values and duty to the tribe above a man's right to his own life." Additionally, she spoke in favor of childfree lifestyle, while following it herself.
The family and social justice
One of the controversies regarding the family is the application of the concept of social justice to the private sphere of family relations, in particular with regard to the rights of women and children's rights, children. Throughout much of the history, most philosophers who advocated for social justice focused on the public political arena, not on the family structures; with the family often being seen as a separate entity which needed to be protected from outside state intrusion. One notable exception was John Stuart Mill, who, in his work ''The Subjection of Women'', advocated for greater rights for women within marriage and family. Second wave feminists argued that the personal is political, stating that there are strong connections between personal experiences and the larger social and political structures. In the context of the feminist movement of the 1960s and 1970s, this was a challenge to the nuclear family and family values, as they were understood then.[Angela Harutyunyan, Kathrin Hörschelmann, Malcolm Miles (2009) ''Public Spheres After Socialism']
pp. 50–51
Feminists focused on domestic violence, arguing that the reluctance—in law or in practice—of the state to intervene and offer protection to women who have been abused within the family, is in violation of women's human rights, and is the result of an ideology which places family relations outside the conceptual framework of human rights.
Global trends in family composition
Statistics from an infographic by Olivier Ballou showed that,
See also
* Childlessness
* Familialism
* Family economics
* Household
* Nepotism
* Parent
* Stepfamily
* Voluntary childlessness
Notes
References
Citations
Sources
* Race, Class, & Gender: An Anthology, 9th edition. Editors: Margaret L. Anderson and Patricia Hill Collins. Cengage Learning.
Bibliography
*
*
*
* Esping-Andersen, Gøsta (2009). The incomplete revolution: Adapting welfare states to women's new roles. Cambridge: ''Polity Press''.
*
* Forbes, Scott, ''A Natural History of Families'', (Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press, 2005),
* Foucault, Michel (1978). ''The History of Sexuality: Volume I: An Introduction''. (New York: Vintage Books).
* Paul Gilroy, Gilroy, Paul "Identity Belonging and the Critique of Pure Sameness" in Gilroy, Paul (2000) ''Against Race: Imagining Political Culture Beyond the Color Line'', (Cambridge, Mass.: Belknap Press of Harvard University Press), Ch. I.3, pp. 97–133
* Jack Goody, Goody, Jack
The Development of the Family and Marriage in Europe
'' (Cambridge University Press, 1980); translated into Spanish, French, Italian, Portuguese.
* Mock, Douglas W., ''More Than Kin and Less Than Kind'', (Belknap Press, 2004),
* David M. Schneider, Schneider, David M., ''American Kinship: a cultural approach'' (Chicago: University of Chicago Press, 1980).
*
*
External links
*
{{Authority control
Family,
Society
 Family (from la, familia) is a
Family (from la, familia) is a  One of the primary functions of the family involves providing a framework for the production and reproduction of persons
One of the primary functions of the family involves providing a framework for the production and reproduction of persons  The
The  Although early western
Although early western  In the US, this arrangement declined after
In the US, this arrangement declined after 

 The term "
The term "

 A first-degree relative is one who shares 50% of your DNA through direct inheritance, such as a full sibling, parent or progeny.
There is another measure for the degree of relationship, which is determined by counting up generations to the first common ancestor and back down to the target individual, which is used for various genealogical and legal purposes.
A first-degree relative is one who shares 50% of your DNA through direct inheritance, such as a full sibling, parent or progeny.
There is another measure for the degree of relationship, which is determined by counting up generations to the first common ancestor and back down to the target individual, which is used for various genealogical and legal purposes.

 In his book ''
In his book ''

 Most Western societies employ Eskimo kinship terminology. This kinship terminology commonly occurs in societies with strong conjugal, where families have a degree of relative mobility. Typically, societies with conjugal families also favor
Most Western societies employ Eskimo kinship terminology. This kinship terminology commonly occurs in societies with strong conjugal, where families have a degree of relative mobility. Typically, societies with conjugal families also favor 
 The system emphasizes the nuclear family. Members of the nuclear family use highly descriptive kinship terms, identifying directly only the husband, wife, mother, father, son, daughter, brother, and sister. All other relatives are grouped together into categories. Members of the nuclear family may be lineal or collateral. Kin, for whom these are family, refer to them in descriptive terms that build on the terms used within the nuclear family or use the nuclear family term directly.
Nuclear family of orientation
*
The system emphasizes the nuclear family. Members of the nuclear family use highly descriptive kinship terms, identifying directly only the husband, wife, mother, father, son, daughter, brother, and sister. All other relatives are grouped together into categories. Members of the nuclear family may be lineal or collateral. Kin, for whom these are family, refer to them in descriptive terms that build on the terms used within the nuclear family or use the nuclear family term directly.
Nuclear family of orientation
* 
 Others argue that whether or not one views the family as "declining" depends on one's definition of "family". "Married couples have dropped below half of all American households. This drop is shocking from traditional forms of the family system. Only a fifth of households were following traditional ways of having married couples raising a family together." In the Western World, marriages are no longer
Others argue that whether or not one views the family as "declining" depends on one's definition of "family". "Married couples have dropped below half of all American households. This drop is shocking from traditional forms of the family system. Only a fifth of households were following traditional ways of having married couples raising a family together." In the Western World, marriages are no longer  Dowry is property (money, goods, or estate) that a wife or wife's family gives to her husband when the wife and husband marry. Offering dowry was common in many cultures historically (including in Europe and North America), but this practice today is mostly restricted to some areas primarily in the Indian subcontinent.
Bride price, (also bride wealth or bride token), is property paid by the groom or his family to the parents of a woman upon the marriage of their daughter to the groom. It is practiced mostly in Sub-Saharan Africa, parts of South-East Asia (Thailand, Cambodia), and parts of Central Asia.
Dower is property given to the bride herself by the groom at the time of marriage, and which remains under her ownership and control.
Dowry is property (money, goods, or estate) that a wife or wife's family gives to her husband when the wife and husband marry. Offering dowry was common in many cultures historically (including in Europe and North America), but this practice today is mostly restricted to some areas primarily in the Indian subcontinent.
Bride price, (also bride wealth or bride token), is property paid by the groom or his family to the parents of a woman upon the marriage of their daughter to the groom. It is practiced mostly in Sub-Saharan Africa, parts of South-East Asia (Thailand, Cambodia), and parts of Central Asia.
Dower is property given to the bride herself by the groom at the time of marriage, and which remains under her ownership and control.

 While in many parts of the world family policies seek to promote a gender-equal organization of the family life, in others the male-dominated family continues to be the official policy of the authorities, which is also supported by law. For instance, the Civil Code of Iran states at Article 1105: "In relations between husband and wife; the position of the head of the family is the exclusive right of the husband".
In some parts of the world, some governments promote a specific form of family, such as that based on traditional family values. The term "family values" is often used in political discourse in some countries, its general meaning being that of traditional or cultural values that pertain to the family's structure, function, roles, beliefs, attitudes, and ideals, usually involving the "traditional family"—a middle class, middle-class family with a breadwinner father and a homemaker mother, raising their biological children. Any deviation from this family model is considered a "nontraditional family". These family ideals are often advanced through policies such as marriage promotion. Some jurisdictions outlaw practices which they deem as socially or religiously unacceptable, such as fornication, cohabitation or adultery.
While in many parts of the world family policies seek to promote a gender-equal organization of the family life, in others the male-dominated family continues to be the official policy of the authorities, which is also supported by law. For instance, the Civil Code of Iran states at Article 1105: "In relations between husband and wife; the position of the head of the family is the exclusive right of the husband".
In some parts of the world, some governments promote a specific form of family, such as that based on traditional family values. The term "family values" is often used in political discourse in some countries, its general meaning being that of traditional or cultural values that pertain to the family's structure, function, roles, beliefs, attitudes, and ideals, usually involving the "traditional family"—a middle class, middle-class family with a breadwinner father and a homemaker mother, raising their biological children. Any deviation from this family model is considered a "nontraditional family". These family ideals are often advanced through policies such as marriage promotion. Some jurisdictions outlaw practices which they deem as socially or religiously unacceptable, such as fornication, cohabitation or adultery.