European Wars Of Religion on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The European wars of religion were a series of wars waged in
The European wars of religion were a series of wars waged in
 The
The
 After numerous minor incidents and provocations from both sides, a Catholic priest was executed in the Thurgau in May 1528, and the Protestant pastor J. Keyser was burned at the stake in Schwyz in 1529. The last straw was the installation of a Catholic
After numerous minor incidents and provocations from both sides, a Catholic priest was executed in the Thurgau in May 1528, and the Protestant pastor J. Keyser was burned at the stake in Schwyz in 1529. The last straw was the installation of a Catholic
 Following the
Following the
 By 1617, Germany was bitterly divided, and it was clear that
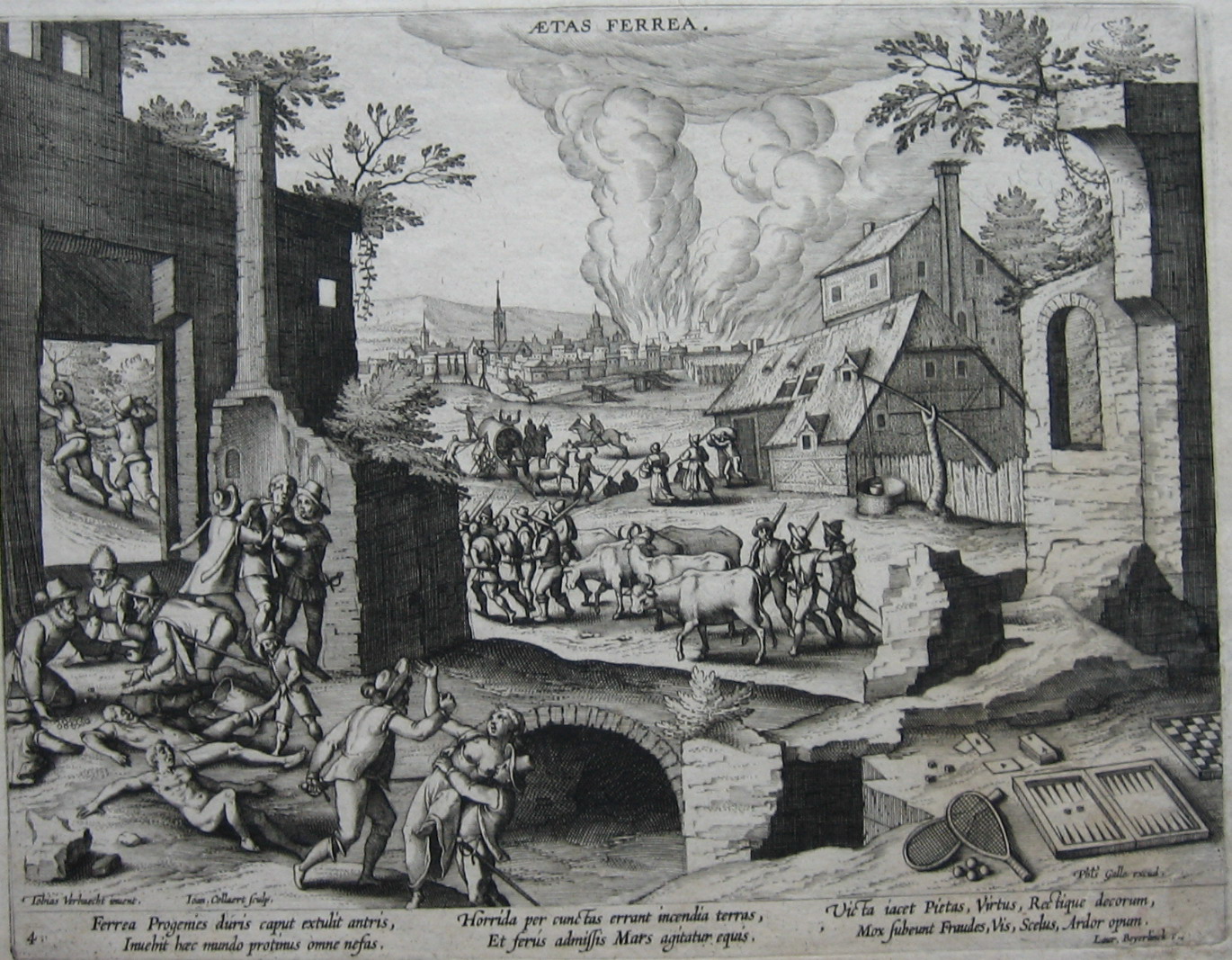
By 1617, Germany was bitterly divided, and it was clear that  The major impact of the Thirty Years' War, in which mercenary armies were extensively used, was the devastation of entire regions scavenged bare by the foraging armies. Episodes of widespread
The major impact of the Thirty Years' War, in which mercenary armies were extensively used, was the devastation of entire regions scavenged bare by the foraging armies. Episodes of widespread
 Philip gave full power to Alva in 1567. Alva's judgment was that of a soldier trained in Spanish discipline and piety. His object was to crush the rebels without mercy on the basis that every concession strengthens the opposition. Alva hand-picked an army of 10,000 men. He issued them the finest in armor while attending to their baser needs by hiring 2,000 prostitutes. Alva installed himself as Governor General and appointed a
Philip gave full power to Alva in 1567. Alva's judgment was that of a soldier trained in Spanish discipline and piety. His object was to crush the rebels without mercy on the basis that every concession strengthens the opposition. Alva hand-picked an army of 10,000 men. He issued them the finest in armor while attending to their baser needs by hiring 2,000 prostitutes. Alva installed himself as Governor General and appointed a  While Alva rested, he sent his son Don Fadrique to revenge the Beggar's atrocities. Don Fadrique's troops indiscriminately sacked homes, monasteries and churches. They stole the jewels and costly robes of the religious. They trampled consecrated hosts, butchered men and violated women. No distinction was made between Catholic or Protestant. His army crushed the weak defenses of
While Alva rested, he sent his son Don Fadrique to revenge the Beggar's atrocities. Don Fadrique's troops indiscriminately sacked homes, monasteries and churches. They stole the jewels and costly robes of the religious. They trampled consecrated hosts, butchered men and violated women. No distinction was made between Catholic or Protestant. His army crushed the weak defenses of
 Philip's half brother, the famous Don John, was placed in charge of the Spanish troops who, feeling cheated at not being able to pillage Zeirikzee, mutinied and began a campaign of indiscriminate plunder and violence. This "
Philip's half brother, the famous Don John, was placed in charge of the Spanish troops who, feeling cheated at not being able to pillage Zeirikzee, mutinied and began a campaign of indiscriminate plunder and violence. This "
 In a pattern soon to become familiar in the Netherlands and Scotland, underground
In a pattern soon to become familiar in the Netherlands and Scotland, underground 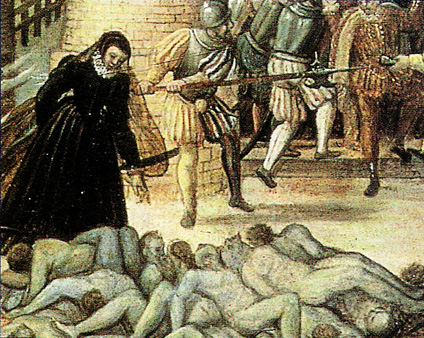 The Protestant army laid siege to several cities in the
The Protestant army laid siege to several cities in the
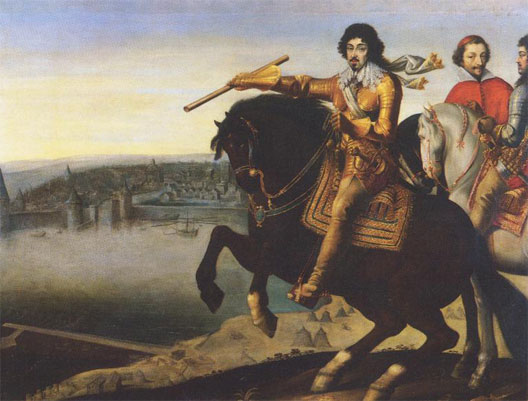 The King knew that he had to take Paris if he stood any chance of ruling all of France, and this was no easy task. The Catholic League's presses and supporters continued to spread stories about atrocities committed against Catholic priests and the laity in Protestant England, such as the Forty Martyrs of England and Wales. The city prepared to fight to the death rather than accept a Calvinist king. The Battle of Ivry, fought on 14 March 1590, was another victory for the king, and Henry's forces went on to lay siege to Paris, but the siege was broken by Spanish support. Realising that his predecessor had been right and that there was no prospect of a Protestant king succeeding in Catholic Paris, Henry reputedly uttered the famous phrase ''Paris vaut bien une messe'' ("Paris is well worth a Mass"). He was formally received into the Roman Catholic Church in 1593 and was crowned at Chartres in 1594.
Some members of the League fought on, but enough Catholics were won over by the King's conversion to increasingly isolate the diehards. The Spanish withdrew from France under the terms of the Peace of Vervins. Henry was faced with the task of rebuilding a shattered and impoverished Kingdom and reuniting France under a single authority. The wars concluded in 1598, when Henry IV issued the Edict of Nantes, which granted a degree of religious toleration to Protestants.
France, although always ruled by a Catholic monarch, had played a major part in supporting the Protestants in Germany and the Netherlands against their dynastic rivals, the Habsburgs. The period of the French Wars of Religion effectively removed France's influence as a major European power, allowing the Catholic forces in the Holy Roman Empire to regroup and recover.
The King knew that he had to take Paris if he stood any chance of ruling all of France, and this was no easy task. The Catholic League's presses and supporters continued to spread stories about atrocities committed against Catholic priests and the laity in Protestant England, such as the Forty Martyrs of England and Wales. The city prepared to fight to the death rather than accept a Calvinist king. The Battle of Ivry, fought on 14 March 1590, was another victory for the king, and Henry's forces went on to lay siege to Paris, but the siege was broken by Spanish support. Realising that his predecessor had been right and that there was no prospect of a Protestant king succeeding in Catholic Paris, Henry reputedly uttered the famous phrase ''Paris vaut bien une messe'' ("Paris is well worth a Mass"). He was formally received into the Roman Catholic Church in 1593 and was crowned at Chartres in 1594.
Some members of the League fought on, but enough Catholics were won over by the King's conversion to increasingly isolate the diehards. The Spanish withdrew from France under the terms of the Peace of Vervins. Henry was faced with the task of rebuilding a shattered and impoverished Kingdom and reuniting France under a single authority. The wars concluded in 1598, when Henry IV issued the Edict of Nantes, which granted a degree of religious toleration to Protestants.
France, although always ruled by a Catholic monarch, had played a major part in supporting the Protestants in Germany and the Netherlands against their dynastic rivals, the Habsburgs. The period of the French Wars of Religion effectively removed France's influence as a major European power, allowing the Catholic forces in the Holy Roman Empire to regroup and recover.
 Charles II of England, Charles II landed in Scotland at Garmouth in Moray on 23 June 1650 and signed the 1638 National Covenant and the 1643 Solemn League and Covenant immediately after coming ashore. With his original Scottish Royalist followers and his new Covenanter allies, King Charles II became the greatest threat facing the new English republic. In response to the threat, Cromwell left some of his lieutenants in Ireland to continue the suppression of the Irish Royalists and returned to England.
Cromwell arrived in Scotland on 22 July 1650 and proceeded to lay siege to Edinburgh. By the end of August disease and a shortage of supplies had reduced his army, and he had to order a retreat towards his base at Dunbar. A Scottish army, assembled under the command of David Leslie (Scottish general), David Leslie, tried to block the retreat, but Cromwell defeated them at the Battle of Dunbar (1650), Battle of Dunbar on 3 September. Cromwell's army then took Edinburgh, and by the end of the year his army had occupied much of southern Scotland.
In July 1651, Cromwell's forces crossed the Firth of Forth into Fife and defeated the Scots at the Battle of Inverkeithing (20 July 1651). The New Model Army advanced towards Perth, Scotland, Perth, which allowed Charles, at the head of the Scottish army, to move south into England. Cromwell followed Charles into England, leaving George Monck to finish the campaign in Scotland. Monck took Stirling on 14 August and Dundee on 1 September. In 1652, the army finished off the remnants of Royalist resistance, under the terms of the "Tender of Union".
In late 1688, William of Orange successfully invaded England. After the Convention of Estates (1689), Convention of Estates deposed the Catholic king James II of England, James VII on 11 April 1689, they offered the royal title to William and his wife Mary II of England, Mary (the Protestant daughter of James), which they accepted on 11 May 1689. During the subsequent
Charles II of England, Charles II landed in Scotland at Garmouth in Moray on 23 June 1650 and signed the 1638 National Covenant and the 1643 Solemn League and Covenant immediately after coming ashore. With his original Scottish Royalist followers and his new Covenanter allies, King Charles II became the greatest threat facing the new English republic. In response to the threat, Cromwell left some of his lieutenants in Ireland to continue the suppression of the Irish Royalists and returned to England.
Cromwell arrived in Scotland on 22 July 1650 and proceeded to lay siege to Edinburgh. By the end of August disease and a shortage of supplies had reduced his army, and he had to order a retreat towards his base at Dunbar. A Scottish army, assembled under the command of David Leslie (Scottish general), David Leslie, tried to block the retreat, but Cromwell defeated them at the Battle of Dunbar (1650), Battle of Dunbar on 3 September. Cromwell's army then took Edinburgh, and by the end of the year his army had occupied much of southern Scotland.
In July 1651, Cromwell's forces crossed the Firth of Forth into Fife and defeated the Scots at the Battle of Inverkeithing (20 July 1651). The New Model Army advanced towards Perth, Scotland, Perth, which allowed Charles, at the head of the Scottish army, to move south into England. Cromwell followed Charles into England, leaving George Monck to finish the campaign in Scotland. Monck took Stirling on 14 August and Dundee on 1 September. In 1652, the army finished off the remnants of Royalist resistance, under the terms of the "Tender of Union".
In late 1688, William of Orange successfully invaded England. After the Convention of Estates (1689), Convention of Estates deposed the Catholic king James II of England, James VII on 11 April 1689, they offered the royal title to William and his wife Mary II of England, Mary (the Protestant daughter of James), which they accepted on 11 May 1689. During the subsequent
 The European wars of religion were a series of wars waged in
The European wars of religion were a series of wars waged in Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a Continent#Subcontinents, subcontinent of Eurasia ...
during the 16th, 17th and early 18th centuries. Fought after the Protestant Reformation
The Reformation (alternatively named the Protestant Reformation or the European Reformation) was a major movement within Western Christianity in 16th-century Europe that posed a religious and political challenge to the Catholic Church and in ...
began in 1517, the wars disrupted the religious and political order in the Catholic
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
countries of Europe, or Christendom
Christendom historically refers to the Christian states, Christian-majority countries and the countries in which Christianity dominates, prevails,SeMerriam-Webster.com : dictionary, "Christendom"/ref> or is culturally or historically intertwine ...
. Other motives during the wars involved revolt, territorial ambitions and great power conflicts. By the end of the Thirty Years' War
The Thirty Years' War was one of the longest and most destructive conflicts in European history
The history of Europe is traditionally divided into four time periods: prehistoric Europe (prior to about 800 BC), classical antiquity (80 ...
(1618–1648), Catholic France had allied with the Protestant forces against the Catholic Habsburg monarchy
The Habsburg monarchy (german: Habsburgermonarchie, ), also known as the Danubian monarchy (german: Donaumonarchie, ), or Habsburg Empire (german: Habsburgerreich, ), was the collection of empires, kingdoms, duchies, counties and other polities ...
. The wars were largely ended by the Peace of Westphalia
The Peace of Westphalia (german: Westfälischer Friede, ) is the collective name for two peace treaties signed in October 1648 in the Westphalian cities of Osnabrück and Münster. They ended the Thirty Years' War (1618–1648) and brought pea ...
(1648), which established a new political order that is now known as Westphalian sovereignty
Westphalian sovereignty, or state sovereignty, is a principle in international law that each state has exclusive sovereignty over its territory. The principle underlies the modern international system of sovereign states and is enshrined in the Un ...
.
The conflicts began with the minor Knights' Revolt
The Knights' Revolt (27 August 15226 May 1523) was a short-lived revolt by several German Protestant, imperial knights, led by Franz von Sickingen, against Charles V, Holy Roman Emperor. It has been called the Poor Barons' Rebellion as it inspi ...
(1522), followed by the larger German Peasants' War
The German Peasants' War, Great Peasants' War or Great Peasants' Revolt (german: Deutscher Bauernkrieg) was a widespread popular revolt in some German-speaking areas in Central Europe from 1524 to 1525. It failed because of intense oppositio ...
(1524–1525) in the Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a Polity, political entity in Western Europe, Western, Central Europe, Central, and Southern Europe that developed during the Early Middle Ages and continued until its Dissolution of the Holy Roman Empire, dissolution i ...
. Warfare intensified after the Catholic Church began the Counter-Reformation
The Counter-Reformation (), also called the Catholic Reformation () or the Catholic Revival, was the period of Catholic resurgence that was initiated in response to the Protestant Reformation. It began with the Council of Trent (1545–1563) a ...
in 1545 against the growth of Protestantism
Protestantism is a branch of Christianity that follows the theological tenets of the Protestant Reformation, a movement that began seeking to reform the Catholic Church from within in the 16th century against what its followers perceived to b ...
. The conflicts culminated in the Thirty Years' War, which devastated Germany and killed one third of its population, a mortality rate
Mortality rate, or death rate, is a measure of the number of deaths (in general, or due to a specific cause) in a particular population, scaled to the size of that population, per unit of time. Mortality rate is typically expressed in units of de ...
twice that of World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
. The Peace of Westphalia broadly resolved the conflicts by recognising three separate Christian traditions in the Holy Roman Empire: Roman Catholicism, Lutheranism
Lutheranism is one of the largest branches of Protestantism, identifying primarily with the theology of Martin Luther, the 16th-century German monk and Protestant Reformers, reformer whose efforts to reform the theology and practice of the Cathol ...
, and Calvinism
Calvinism (also called the Reformed Tradition, Reformed Protestantism, Reformed Christianity, or simply Reformed) is a major branch of Protestantism that follows the theological tradition and forms of Christian practice set down by John Cal ...
.Treaty of Münster 1648 Although many European leaders were sickened by the bloodshed by 1648, smaller religious wars continued to be waged until the 1710s, including the Wars of the Three Kingdoms
The Wars of the Three Kingdoms were a series of related conflicts fought between 1639 and 1653 in the kingdoms of Kingdom of England, England, Kingdom of Scotland, Scotland and Kingdom of Ireland, Ireland, then separate entities united in a pers ...
(1639–1651) in the British Isles
The British Isles are a group of islands in the North Atlantic Ocean off the north-western coast of continental Europe, consisting of the islands of Great Britain, Ireland, the Isle of Man, the Inner and Outer Hebrides, the Northern Isles, ...
, the Savoyard–Waldensian wars
The Savoyard–Waldensian wars were a series of conflicts between the community of Waldensians (also known as Vaudois) and the Savoyard troops in the Duchy of Savoy from 1655 to 1690. The Piedmontese Easter in 1655 sparked the conflict. It was la ...
(1655–1690), and the Toggenburg War
The Toggenburg War, also known as the Second War of Villmergen or the Swiss Civil War of 1712, was a Swiss civil war during the Old Swiss Confederacy from 12 April to 11 August 1712. The Catholic "inner cantons" and the Imperial Abbey of Saint ...
(1712) in the Western Alps
The Western Alps are the western part of the Alpine Range including the southeastern part of France (e.g. Savoie), the whole of Monaco, the northwestern part of Italy (i.e. Piedmont and the Aosta Valley) and the southwestern part of Switzerland ( ...
.
Definitions and discussions
The European wars of religion are also known as the Wars of the Reformation. In 1517,Martin Luther
Martin Luther (; ; 10 November 1483 – 18 February 1546) was a German priest, theologian, author, hymnwriter, and professor, and Order of Saint Augustine, Augustinian friar. He is the seminal figure of the Reformation, Protestant Refo ...
's ''Ninety-five Theses
The ''Ninety-five Theses'' or ''Disputation on the Power and Efficacy of Indulgences''-The title comes from the 1517 Basel pamphlet printing. The first printings of the ''Theses'' use an incipit rather than a title which summarizes the content ...
'' took only two months to spread throughout Europe with the help of the printing press, overwhelming the abilities of Holy Roman Emperor Charles V and the papacy to contain it. In 1521, Luther was excommunicated
Excommunication is an institutional act of religious censure used to end or at least regulate the communion of a member of a congregation with other members of the religious institution who are in normal communion with each other. The purpose ...
, sealing the schism within Western Christendom
Western Christianity is one of two sub-divisions of Christianity (Eastern Christianity being the other). Western Christianity is composed of the Latin Church and Western Protestantism, together with their offshoots such as the Old Catholic C ...
between the Roman Catholic Church
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
and the Lutheran
Lutheranism is one of the largest branches of Protestantism, identifying primarily with the theology of Martin Luther, the 16th-century German monk and reformer whose efforts to reform the theology and practice of the Catholic Church launched th ...
s and opening the door for other Protestant
Protestantism is a Christian denomination, branch of Christianity that follows the theological tenets of the Reformation, Protestant Reformation, a movement that began seeking to reform the Catholic Church from within in the 16th century agai ...
s to resist the power of the papacy
The pope ( la, papa, from el, πάππας, translit=pappas, 'father'), also known as supreme pontiff ( or ), Roman pontiff () or sovereign pontiff, is the bishop of Rome (or historically the patriarch of Rome), head of the worldwide Cathol ...
.
Although most of the wars ended with the Peace of Westphalia
The Peace of Westphalia (german: Westfälischer Friede, ) is the collective name for two peace treaties signed in October 1648 in the Westphalian cities of Osnabrück and Münster. They ended the Thirty Years' War (1618–1648) and brought pea ...
in 1648, religious conflicts continued to be fought in Europe until at least the 1710s. These included the Savoyard–Waldensian wars
The Savoyard–Waldensian wars were a series of conflicts between the community of Waldensians (also known as Vaudois) and the Savoyard troops in the Duchy of Savoy from 1655 to 1690. The Piedmontese Easter in 1655 sparked the conflict. It was la ...
(1655–1690), the Nine Years' War
The Nine Years' War (1688–1697), often called the War of the Grand Alliance or the War of the League of Augsburg, was a conflict between France and a European coalition which mainly included the Holy Roman Empire (led by the Habsburg monarch ...
(1688–1697, including the Glorious Revolution
The Glorious Revolution; gd, Rèabhlaid Ghlòrmhor; cy, Chwyldro Gogoneddus , also known as the ''Glorieuze Overtocht'' or ''Glorious Crossing'' in the Netherlands, is the sequence of events leading to the deposition of King James II and ...
and the Williamite War in Ireland
The Williamite War in Ireland (1688–1691; ga, Cogadh an Dá Rí, "war of the two kings"), was a conflict between Jacobite supporters of deposed monarch James II and Williamite supporters of his successor, William III. It is also called th ...
), and the War of the Spanish Succession
The War of the Spanish Succession was a European great power conflict that took place from 1701 to 1714. The death of childless Charles II of Spain in November 1700 led to a struggle for control of the Spanish Empire between his heirs, Phil ...
(1701–1714). Whether these should be included in the European wars of religion depends on how one defines a " war of religion", and whether these wars can be considered "European" (i.e. international rather than domestic).Onnekink, pp. 9–10.
The religious nature of the wars has also been debated, and contrasted with other factors at play, such as national, dynastic (e.g. they could often simultaneously be characterised as wars of succession
A war of succession is a war prompted by a succession crisis in which two or more individuals claim the right of successor to a deceased or deposed monarch. The rivals are typically supported by factions within the royal court. Foreign powe ...
), and financial interests. Scholars have pointed out that some European wars of this period were not caused by disputes occasioned by the Reformation, such as the Italian Wars
The Italian Wars, also known as the Habsburg–Valois Wars, were a series of conflicts covering the period 1494 to 1559, fought mostly in the Italian peninsula, but later expanding into Flanders, the Rhineland and the Mediterranean Sea. The pr ...
(1494–1559, only involving Catholics), as well as the Northern Seven Years' War
The Northern Seven Years' War (also known as the ''Nordic Seven Years' War'', the ''First Northern War'' or the ''Seven Years War in Scandinavia'') was fought between the Kingdom of Sweden and a coalition of Denmark–Norway, Lübeck, and Polan ...
(1563–1570, only involving Lutherans). Others emphasise the fact that cross-religious alliances existed, such as the Lutheran duke Maurice of Saxony
Maurice (21 March 1521 – 9 July 1553) was Duke (1541–47) and later Elector (1547–53) of Saxony. His clever manipulation of alliances and disputes gained the Albertine branch of the Wettin dynasty extensive lands and the electoral dignity.
...
assisting the Catholic emperor Charles V Charles V may refer to:
* Charles V, Holy Roman Emperor (1500–1558)
* Charles V of Naples (1661–1700), better known as Charles II of Spain
* Charles V of France (1338–1380), called the Wise
* Charles V, Duke of Lorraine (1643–1690)
* Infan ...
in the first Schmalkaldic War
The Schmalkaldic War (german: link=no, Schmalkaldischer Krieg) was the short period of violence from 1546 until 1547 between the forces of Emperor Charles V of the Holy Roman Empire (simultaneously King Charles I of Spain), commanded by the Duk ...
in 1547 in order to become the Saxon elector instead of John Frederick, his Lutheran cousin, while the Catholic king Henry II of France
Henry II (french: Henri II; 31 March 1519 – 10 July 1559) was King of France from 31 March 1547 until his death in 1559. The second son of Francis I and Duchess Claude of Brittany, he became Dauphin of France upon the death of his elder bro ...
supported the Lutheran cause in the Second Schmalkaldic War in 1552 to secure French bases in modern-day Lorraine
Lorraine , also , , ; Lorrain: ''Louréne''; Lorraine Franconian: ''Lottringe''; german: Lothringen ; lb, Loutrengen; nl, Lotharingen is a cultural and historical region in Northeastern France, now located in the administrative region of Gr ...
. The ''Encyclopædia Britannica
The (Latin for "British Encyclopædia") is a general knowledge English-language encyclopaedia. It is published by Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc.; the company has existed since the 18th century, although it has changed ownership various time ...
'' maintains that " hewars of religion of this period erefought mainly for confessional security and political gain."
In the late 20th century, a number of revisionist historians such as William M. Lamont regarded the English Civil War
The English Civil War (1642–1651) was a series of civil wars and political machinations between Parliamentarians (" Roundheads") and Royalists led by Charles I ("Cavaliers"), mainly over the manner of England's governance and issues of re ...
(1642–1651) as a religious war, with John Morrill (1993) stating: "The English Civil War was not the first European revolution: it was the last of the Wars of Religion." This view has been criticised by various pre-, post- and anti-revisionist historians. Glen Burgess (1998) examined political propaganda written by the Parliamentarian politicians and clerics at the time, noting that many were or may have been motivated by their Puritan religious beliefs to support the war against the perceived Catholic king Charles I of England
Charles I (19 November 1600 – 30 January 1649) was King of England, Scotland, and Ireland from 27 March 1625 until Execution of Charles I, his execution in 1649. He was born into the House of Stuart as the second son of King James VI of ...
, but tried to express and legitimise their opposition and rebellion in terms of a legal revolt against a monarch who had violated crucial constitutional principles and thus had to be overthrown. They even warned their Parliamentarian allies to not make overt use of religious arguments in making their case for war against the king. In some cases, it may be argued that they hid their pro-Anglican and anti-Catholic motives behind legal parliance, for example by emphasising that the Church of England
The Church of England (C of E) is the established Christian church in England and the mother church of the international Anglican Communion. It traces its history to the Christian church recorded as existing in the Roman province of Britain ...
was the legally established religion: "Seen in this light, the defenses of Parliament's war, with their apparent legal-constitutional thrust, are not at all ways of saying that the struggle was not religious. On the contrary, they are ways of saying that it was." Burgess concluded: " e Civil War left behind it just the sort of evidence that we could reasonably expect a war of religion to leave."
Overview of the wars
Individual conflicts that may be distinguished within this topic include: * Pre-Reformation wars: ** The Oldcastle Revolt (1414) in England (sometimes considered to have "foreshadowed the wars of religion") ** TheHussite Wars
The Hussite Wars, also called the Bohemian Wars or the Hussite Revolution, were a series of civil wars fought between the Hussites and the combined Catholic forces of Holy Roman Emperor Sigismund, the Papacy, European monarchs loyal to the Cat ...
(1419–1434) in the Lands of the Bohemian Crown
The Lands of the Bohemian Crown were a number of incorporated states in Central Europe during the medieval and early modern periods connected by feudal relations under the Bohemian kings. The crown lands primarily consisted of the Kingdom of B ...
* Conflicts immediately connected with the Reformation:
** The Knights' Revolt
The Knights' Revolt (27 August 15226 May 1523) was a short-lived revolt by several German Protestant, imperial knights, led by Franz von Sickingen, against Charles V, Holy Roman Emperor. It has been called the Poor Barons' Rebellion as it inspi ...
(1522–1523) in the Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a Polity, political entity in Western Europe, Western, Central Europe, Central, and Southern Europe that developed during the Early Middle Ages and continued until its Dissolution of the Holy Roman Empire, dissolution i ...
Onnekink, p. 2.
** The First Dalecarlian Rebellion (1524–1525) in Sweden
Sweden, formally the Kingdom of Sweden,The United Nations Group of Experts on Geographical Names states that the country's formal name is the Kingdom of SwedenUNGEGN World Geographical Names, Sweden./ref> is a Nordic country located on ...
.
** The German Peasants' War
The German Peasants' War, Great Peasants' War or Great Peasants' Revolt (german: Deutscher Bauernkrieg) was a widespread popular revolt in some German-speaking areas in Central Europe from 1524 to 1525. It failed because of intense oppositio ...
(1524–1526) in the Holy Roman Empire
** The Second Dalecarlian Rebellion (1527–1528) in Sweden
Sweden, formally the Kingdom of Sweden,The United Nations Group of Experts on Geographical Names states that the country's formal name is the Kingdom of SwedenUNGEGN World Geographical Names, Sweden./ref> is a Nordic country located on ...
.
** The Wars of Kappel
The wars of Kappel (''Kappelerkriege'') is a collective term for two armed conflicts fought near Kappel am Albis between the Catholic and the Protestant cantons of the Old Swiss Confederacy during the Reformation in Switzerland.
First War
Th ...
(1529–1531) in the Old Swiss Confederacy
The Old Swiss Confederacy or Swiss Confederacy (German language, Modern German: ; historically , after the Swiss Reformation, Reformation also , "Confederation of the Swiss") was a loose confederation of independent small states (, German or ...
** The Tudor conquest of Ireland
The Tudor conquest (or reconquest) of Ireland took place under the Tudor dynasty, which held the Kingdom of England during the 16th century. Following a failed rebellion against the crown by Silken Thomas, the Earl of Kildare, in the 1530s, He ...
(1529–1603) on the Catholic population of Ireland by the Tudor kings of England
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Wales to its west and Scotland to its north. The Irish Sea lies northwest and the Celtic Sea to the southwest. It is separated from continental Europe b ...
and their Protestant allies
*** The Kildare Rebellion (1534–1535)
*** The First Desmond Rebellion (1569–1573)
*** The Second Desmond Rebellion
The Second Desmond Rebellion (1579–1583) was the more widespread and bloody of the two Desmond Rebellions in Ireland launched by the FitzGerald Dynasty of Desmond in Munster against English rule. The second rebellion began in July 1579 when ...
(1579–1583)
*** The Nine Years' War
The Nine Years' War (1688–1697), often called the War of the Grand Alliance or the War of the League of Augsburg, was a conflict between France and a European coalition which mainly included the Holy Roman Empire (led by the Habsburg monarch ...
(1593–1603)
** The Third Dalecarlian Rebellion (1531–1533) in Sweden
Sweden, formally the Kingdom of Sweden,The United Nations Group of Experts on Geographical Names states that the country's formal name is the Kingdom of SwedenUNGEGN World Geographical Names, Sweden./ref> is a Nordic country located on ...
.
** The War of Two Kings (1531–1532) in the Kalmar Union
The Kalmar Union (Danish language, Danish, Norwegian language, Norwegian, and sv, Kalmarunionen; fi, Kalmarin unioni; la, Unio Calmariensis) was a personal union in Scandinavia, agreed at Kalmar in Sweden, that from 1397 to 1523 joined under ...
(Denmark and Norway)
** The Count's Feud
The Count's Feud ( da, Grevens Fejde), also called the Count's War, was a war of succession that raged in Denmark in 1534–36 and brought about the Reformation in Denmark. In the international context, it was part of the European wars of relig ...
(1534–1536) in the Kalmar Union
The Kalmar Union (Danish language, Danish, Norwegian language, Norwegian, and sv, Kalmarunionen; fi, Kalmarin unioni; la, Unio Calmariensis) was a personal union in Scandinavia, agreed at Kalmar in Sweden, that from 1397 to 1523 joined under ...
(Denmark and Norway)
** The Münster rebellion
Münster (; nds, Mönster) is an independent city (''Kreisfreie Stadt'') in North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. It is in the northern part of the state and is considered to be the cultural centre of the Westphalia region. It is also a state distr ...
(1534–1535) in the Prince-Bishopric of Münster
The Prince-Bishopric of Münster (german: Fürstbistum Münster; Bistum Münster, Hochstift Münster) was a large ecclesiastical principality in the Holy Roman Empire, located in the northern part of today's North Rhine-Westphalia and western Low ...
** The Anabaptist riot (1535) in Amsterdam
Amsterdam ( , , , lit. ''The Dam on the River Amstel'') is the Capital of the Netherlands, capital and Municipalities of the Netherlands, most populous city of the Netherlands, with The Hague being the seat of government. It has a population ...
** Olav Engelbrektsson's rebellion (1536–1537) in Norway
** Bigod's rebellion (1537) in England
** The Dacke War
The Dacke War ( sv, Dackefejden) was a peasant uprising led by Nils Dacke in Småland, Sweden, in 1542 against the rule of Gustav Vasa. Dacke and his followers were dissatisfied with the heavy tax burden, the introduction of Lutheranism, and the ...
(1542–1543) in Sweden
* Conflicts after the death of Martin Luther:
** The Schmalkaldic War
The Schmalkaldic War (german: link=no, Schmalkaldischer Krieg) was the short period of violence from 1546 until 1547 between the forces of Emperor Charles V of the Holy Roman Empire (simultaneously King Charles I of Spain), commanded by the Duk ...
(1546–1547) in the Holy Roman Empire
** The Prayer Book Rebellion
The Prayer Book Rebellion or Western Rising was a popular revolt in Cornwall and Devon in 1549. In that year, the ''Book of Common Prayer'', presenting the theology of the English Reformation, was introduced. The change was widely unpopular, ...
(1549) in England
** The Battle of Sauðafell
The Battle of Sauðafell (''Orrustan á Sauðafelli'') occurred in 1550, when the forces of Catholic Bishop Jón Arason clashed with the forces of Daði Guðmundsson of Snóksdalur.
Location
Sauðafell was an important part of Daði's fief in ...
(1550) on Iceland
** The Second Schmalkaldic War or Princes' Revolt (1552–1555)Onnekink, p. 3.
** Wyatt's rebellion (1554) in England over Mary I of England
Mary I (18 February 1516 – 17 November 1558), also known as Mary Tudor, and as "Bloody Mary" by her Protestant opponents, was Queen of England and Ireland from July 1553 and Queen of Spain from January 1556 until her death in 1558. Sh ...
's decision to marry the Catholic non-English prince Philip II of Spain
Philip II) in Spain, while in Portugal and his Italian kingdoms he ruled as Philip I ( pt, Filipe I). (21 May 152713 September 1598), also known as Philip the Prudent ( es, Felipe el Prudente), was King of Spain from 1556, King of Portugal from ...
. Mary's repression of the rebellion earned her the nickname "Bloody Mary" amongst Protestants.
** The French Wars of Religion
The French Wars of Religion is the term which is used in reference to a period of civil war between French Catholic Church, Catholics and Protestantism, Protestants, commonly called Huguenots, which lasted from 1562 to 1598. According to estim ...
(1562–1598) in France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of Overseas France, overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, Pacific Ocean, Pac ...
** The Eighty Years' War
The Eighty Years' War or Dutch Revolt ( nl, Nederlandse Opstand) ( c.1566/1568–1648) was an armed conflict in the Habsburg Netherlands between disparate groups of rebels and the Spanish government. The causes of the war included the Refo ...
(1566/68–1648) in the Low Countries
The term Low Countries, also known as the Low Lands ( nl, de Lage Landen, french: les Pays-Bas, lb, déi Niddereg Lännereien) and historically called the Netherlands ( nl, de Nederlanden), Flanders, or Belgica, is a coastal lowland region in N ...
** The Cologne War
The Cologne War (german: Kölner Krieg, Kölnischer Krieg, Truchsessischer Krieg; 1583–88) was a conflict between Protestant and Catholic factions that devastated the Electorate of Cologne, a historical ecclesiastical principality of the Holy ...
(1583–1588) in the Electorate of Cologne
The Electorate of Cologne (german: Kurfürstentum Köln), sometimes referred to as Electoral Cologne (german: Kurköln, links=no), was an ecclesiastical principality of the Holy Roman Empire that existed from the 10th to the early 19th century. ...
** The Strasbourg Bishops' War
The Strasbourg Bishops' War (German: ''Bischöflicher Krieg'' or ''Straßburger Kapitelstreit'';Gerhard Taddey: ''Straßburger Kapitelstreit''. In: Gerhard Taddey (ed.): ''Lexikon der deutschen Geschichte. Personen, Ereignisse, Institutionen. Von ...
(1592–1604) in the Prince-Bishopric of Strasbourg
The Prince-Bishopric of Strasburg (german: Fürstbistum Straßburg; gsw-FR, Fìrschtbischofsìtz Strossburi(g)) was an ecclesiastical principality of the Holy Roman Empire from the 13th century until 1803. During the late 17th century, most of ...
** The War against Sigismund
The war against Sigismund ( sv, Kriget mot Sigismund) was a war between Duke Charles, later known as King Charles IX of Sweden, and Sigismund, who was at the time the King of both Sweden and the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth (that is, the K ...
(1598–1599) in the Polish–Swedish union
The Polish–Swedish union was a short-lived personal union between the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth and the Kingdom of Sweden between 1592 and 1599. It began when Sigismund III Vasa, elected King of Poland and Grand Duke of Lithuania, was c ...
** The Bocskai uprising (1604–1606) in Hungary and Transylvania
** The War of the Jülich Succession
The War of the Jülich Succession was a war of succession in the United Duchies of Jülich-Cleves-Berg. It lasted between 10 June 1609 and 24 October 1610, resumed in May 1614 and finally ended on 13 October 1614. The first round of the conflict ...
(1609–10, 1614) in the United Duchies of Jülich-Cleves-Berg
The so-called United Duchies of Jülich-Cleves-Berg was a territory in the Holy Roman Empire between 1521 and 1666, formed from the personal union of the duchies of Jülich, Cleves and Berg.
The name was resurrected after the Congress of Vienn ...
* The Thirty Years' War
The Thirty Years' War was one of the longest and most destructive conflicts in European history
The history of Europe is traditionally divided into four time periods: prehistoric Europe (prior to about 800 BC), classical antiquity (80 ...
(1618–1648), affecting the Holy Roman Empire including the Habsburg monarchy
The Habsburg monarchy (german: Habsburgermonarchie, ), also known as the Danubian monarchy (german: Donaumonarchie, ), or Habsburg Empire (german: Habsburgerreich, ), was the collection of empires, kingdoms, duchies, counties and other polities ...
and Bohemia and Moravia
The Protectorate of Bohemia and Moravia; cs, Protektorát Čechy a Morava; its territory was called by the Nazis ("the rest of Czechia"). was a partially annexed territory of Nazi Germany established on 16 March 1939 following the German occ ...
, France, Denmark-Norway and Sweden
Sweden, formally the Kingdom of Sweden,The United Nations Group of Experts on Geographical Names states that the country's formal name is the Kingdom of SwedenUNGEGN World Geographical Names, Sweden./ref> is a Nordic country located on ...
** Bohemian Revolt
The Bohemian Revolt (german: Böhmischer Aufstand; cs, České stavovské povstání; 1618–1620) was an uprising of the Bohemian estates against the rule of the Habsburg dynasty that began the Thirty Years' War. It was caused by both religi ...
(1618–1620) between the Protestant nobility of the Bohemian Crown and their Catholic Habsburg king. This revolt started the Thirty Years' War, causing additional conflicts elsewhere in Europe, and subsuming other already ongoing conflicts.
** Hessian War
The Hessian War (german: Hessenkrieg), in its wider sense sometimes also called the Hessian Wars (''Hessenkriege''), was a drawn out conflict that took place between 1567 and 1648, sometimes pursued through diplomatic means, sometimes by military ...
(1567–1648) between the Lutheran Landgraviate of Hesse-Darmstadt
The Landgraviate of Hesse-Darmstadt (german: Landgrafschaft Hessen-Darmstadt) was a State of the Holy Roman Empire, ruled by a younger branch of the House of Hesse. It was formed in 1567 following the division of the Landgraviate of Hesse betwee ...
(member of the Catholic League) and the Calvinist Landgraviate of Hesse-Kassel
The Landgraviate of Hesse-Kassel (german: Landgrafschaft Hessen-Kassel), spelled Hesse-Cassel during its entire existence, was a state in the Holy Roman Empire that was directly subject to the Emperor. The state was created in 1567 when the Lan ...
(member of the Protestant Union)
* The Huguenot rebellions
The Huguenot rebellions, sometimes called the Rohan Wars after the Huguenot leader Henri de Rohan, were a series of rebellions of the 1620s in which French Calvinist Protestants (Huguenots), mainly located in southwestern France, revolted agains ...
(1621–1629) in France
* The Wars of the Three Kingdoms
The Wars of the Three Kingdoms were a series of related conflicts fought between 1639 and 1653 in the kingdoms of Kingdom of England, England, Kingdom of Scotland, Scotland and Kingdom of Ireland, Ireland, then separate entities united in a pers ...
(1639–1651), affecting England
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Wales to its west and Scotland to its north. The Irish Sea lies northwest and the Celtic Sea to the southwest. It is separated from continental Europe b ...
, Scotland
Scotland (, ) is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. Covering the northern third of the island of Great Britain, mainland Scotland has a border with England to the southeast and is otherwise surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean to the ...
and Ireland
Ireland ( ; ga, Éire ; Ulster Scots dialect, Ulster-Scots: ) is an island in the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic Ocean, in Northwestern Europe, north-western Europe. It is separated from Great Britain to its east by the North Channel (Grea ...
** Bishops' Wars
The 1639 and 1640 Bishops' Wars () were the first of the conflicts known collectively as the 1639 to 1653 Wars of the Three Kingdoms, which took place in Scotland, England and Ireland. Others include the Irish Confederate Wars, the First and ...
(1639–1640)
** English Civil War
The English Civil War (1642–1651) was a series of civil wars and political machinations between Parliamentarians (" Roundheads") and Royalists led by Charles I ("Cavaliers"), mainly over the manner of England's governance and issues of re ...
(1642–1651)
** Scotland in the Wars of the Three Kingdoms
Between 1639 and 1653, Scotland was involved in the Wars of the Three Kingdoms, a series of wars starting with the Bishops Wars (between Scotland and England), the Irish Rebellion of 1641, the English Civil War (and its extension in Scotland ...
(1644–1651)
** Irish Confederate Wars
The Irish Confederate Wars, also called the Eleven Years' War (from ga, Cogadh na hAon-déag mBliana), took place in Ireland between 1641 and 1653. It was the Irish theatre of the Wars of the Three Kingdoms, a series of civil wars in the kin ...
(1641–1653) and the Cromwellian conquest of Ireland
The Cromwellian conquest of Ireland or Cromwellian war in Ireland (1649–1653) was the re-conquest of Ireland by the forces of the English Parliament, led by Oliver Cromwell, during the Wars of the Three Kingdoms. Cromwell invaded Ireland wi ...
(1649–1653)Onnekink, p. 7.
* The post-Westphalian wars:
** The Düsseldorf Cow War (1651)
** The Savoyard–Waldensian wars
The Savoyard–Waldensian wars were a series of conflicts between the community of Waldensians (also known as Vaudois) and the Savoyard troops in the Duchy of Savoy from 1655 to 1690. The Piedmontese Easter in 1655 sparked the conflict. It was la ...
(1655–1690) beginning with the Piedmontese Easter
The Piedmontese Easter (Italian: ''Pasque piemontesi'', French: ''Pâques piémontaises'' or ''Pâques vaudoises'') was a series of massacres on Waldensians (also known as Waldenses or Vaudois) by Savoyard troops in the Duchy of Savoy in 1655.
...
(''Pasque piemontesi'') of April 1655, in the Duchy of Savoy
The Duchy of Savoy ( it, Ducato di Savoia; french: Duché de Savoie) was a country in Western Europe that existed from 1416.
It was created when Sigismund, Holy Roman Emperor, raised the County of Savoy into a duchy for Amadeus VIII. The duc ...
** The First War of Villmergen
The First War of Villmergen Encarta-encyclopedie Winkler Prins (1993–2002) s.v. "Zwitserland. §5.2 Reformatie". Microsoft Corporation/Het Spectrum. was a Swiss religious war which lasted from 5 January until 7 March 1656, at the time of the Ol ...
(1656) in the Old Swiss Confederacy
** The Second Anglo-Dutch War
The Second Anglo-Dutch War or the Second Dutch War (4 March 1665 – 31 July 1667; nl, Tweede Engelse Oorlog "Second English War") was a conflict between Kingdom of England, England and the Dutch Republic partly for control over the seas a ...
(1665–1667) between England and the Dutch Republic
** The Nine Years' War
The Nine Years' War (1688–1697), often called the War of the Grand Alliance or the War of the League of Augsburg, was a conflict between France and a European coalition which mainly included the Holy Roman Empire (led by the Habsburg monarch ...
(1688–1697)
*** The Glorious Revolution
The Glorious Revolution; gd, Rèabhlaid Ghlòrmhor; cy, Chwyldro Gogoneddus , also known as the ''Glorieuze Overtocht'' or ''Glorious Crossing'' in the Netherlands, is the sequence of events leading to the deposition of King James II and ...
(1688–1689)
*** The Williamite War in Ireland
The Williamite War in Ireland (1688–1691; ga, Cogadh an Dá Rí, "war of the two kings"), was a conflict between Jacobite supporters of deposed monarch James II and Williamite supporters of his successor, William III. It is also called th ...
(1688–1691)
*** The Jacobite rising of 1689
The Jacobite rising of 1689 was a conflict fought primarily in the Scottish Highlands, whose objective was to put James II & VII back on the throne, following his deposition by the November 1688 Glorious Revolution. Named after "Jacobus", the L ...
in Scotland saw Roman Catholics and Anglican Tories supporting the deposed Catholic king James Stuart take up arms against the newly enthroned Calvinist William of Orange and his Presbyterian Covenanter allies; the religious component may be regarded as secondary to the dynastic factor, however.
** The War of the Spanish Succession
The War of the Spanish Succession was a European great power conflict that took place from 1701 to 1714. The death of childless Charles II of Spain in November 1700 led to a struggle for control of the Spanish Empire between his heirs, Phil ...
(1701–1714) across Europe had a strong religious component
** The War in the Cevennes (1702–1710) in France
** The Toggenburg War
The Toggenburg War, also known as the Second War of Villmergen or the Swiss Civil War of 1712, was a Swiss civil war during the Old Swiss Confederacy from 12 April to 11 August 1712. The Catholic "inner cantons" and the Imperial Abbey of Saint ...
(Second War of Villmergen) (1712) in the Old Swiss Confederacy
Holy Roman Empire
 The
The Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a Polity, political entity in Western Europe, Western, Central Europe, Central, and Southern Europe that developed during the Early Middle Ages and continued until its Dissolution of the Holy Roman Empire, dissolution i ...
, encompassing present-day Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwe ...
and surrounding territory, was the area most devastated by the wars of religion. The Empire was a fragmented collection of practically independent states with an elected Holy Roman Emperor
The Holy Roman Emperor, originally and officially the Emperor of the Romans ( la, Imperator Romanorum, german: Kaiser der Römer) during the Middle Ages, and also known as the Roman-German Emperor since the early modern period ( la, Imperat ...
as their titular ruler; after the 14th century, this position was usually held by a Habsburg. The Austrian House of Habsburg
The House of Habsburg (), alternatively spelled Hapsburg in Englishgerman: Haus Habsburg, ; es, Casa de Habsburgo; hu, Habsburg család, it, Casa di Asburgo, nl, Huis van Habsburg, pl, dom Habsburgów, pt, Casa de Habsburgo, la, Domus Hab ...
, who remained Catholic, was a major European power in its own right, ruling over some eight million subjects in present-day Germany, Austria
Austria, , bar, Östareich officially the Republic of Austria, is a country in the southern part of Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine states, one of which is the capital, Vienna, the most populous ...
, Bohemia
Bohemia ( ; cs, Čechy ; ; hsb, Čěska; szl, Czechy) is the westernmost and largest historical region of the Czech Republic. Bohemia can also refer to a wider area consisting of the historical Lands of the Bohemian Crown ruled by the Bohem ...
and Hungary
Hungary ( hu, Magyarország ) is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Spanning of the Carpathian Basin, it is bordered by Slovakia to the north, Ukraine to the northeast, Romania to the east and southeast, Serbia to the south, Croatia a ...
. The Empire also contained regional powers, such as Bavaria
Bavaria ( ; ), officially the Free State of Bavaria (german: Freistaat Bayern, link=no ), is a state in the south-east of Germany. With an area of , Bavaria is the largest German state by land area, comprising roughly a fifth of the total lan ...
, the Electorate of Saxony
The Electorate of Saxony, also known as Electoral Saxony (German: or ), was a territory of the Holy Roman Empire from 1356–1806. It was centered around the cities of Dresden, Leipzig and Chemnitz.
In the Golden Bull of 1356, Emperor Charles ...
, the Margraviate of Brandenburg
The Margraviate of Brandenburg (german: link=no, Markgrafschaft Brandenburg) was a major principality of the Holy Roman Empire from 1157 to 1806 that played a pivotal role in the history of Germany and Central Europe.
Brandenburg developed out o ...
, the Electorate of the Palatinate
The Electoral Palatinate (german: Kurpfalz) or the Palatinate (), officially the Electorate of the Palatinate (), was a state that was part of the Holy Roman Empire. The electorate had its origins under the rulership of the Counts Palatine of ...
, the Landgraviate of Hesse
The Landgraviate of Hesse (german: Landgrafschaft Hessen) was a principality of the Holy Roman Empire. It existed as a single entity from 1264 to 1567, when it was divided among the sons of Philip I, Landgrave of Hesse.
History
In the early Mid ...
, the Archbishopric of Trier
The Diocese of Trier, in English historically also known as ''Treves'' (IPA "tɾivz") from French ''Trèves'', is a Latin Church ecclesiastical territory or diocese of the Catholic church in Germany.Württemberg
Württemberg ( ; ) is a historical German territory roughly corresponding to the cultural and linguistic region of Swabia. The main town of the region is Stuttgart.
Together with Baden and Hohenzollern, two other historical territories, Würt ...
. A vast number of minor independent duchies, free imperial cities, abbeys, bishoprics, and small lordships of sovereign families rounded out the Empire.
Lutheranism
Lutheranism is one of the largest branches of Protestantism, identifying primarily with the theology of Martin Luther, the 16th-century German monk and Protestant Reformers, reformer whose efforts to reform the theology and practice of the Cathol ...
, from its inception at Wittenberg
Wittenberg ( , ; Low Saxon language, Low Saxon: ''Wittenbarg''; meaning ''White Mountain''; officially Lutherstadt Wittenberg (''Luther City Wittenberg'')), is the fourth largest town in Saxony-Anhalt, Germany. Wittenberg is situated on the Ri ...
in 1517, found a ready reception in Germany, as well as German-speaking parts of Hussite
The Hussites ( cs, Husité or ''Kališníci''; "Chalice People") were a Czech proto-Protestant Christian movement that followed the teachings of reformer Jan Hus, who became the best known representative of the Bohemian Reformation.
The Hussit ...
Bohemia (where the Hussite Wars
The Hussite Wars, also called the Bohemian Wars or the Hussite Revolution, were a series of civil wars fought between the Hussites and the combined Catholic forces of Holy Roman Emperor Sigismund, the Papacy, European monarchs loyal to the Cat ...
took place from 1419 to 1434, and Hussites remained a majority of the population until the 1620 Battle of White Mountain
), near Prague, Bohemian Confederation(present-day Czech Republic)
, coordinates =
, territory =
, result = Imperial-Spanish victory
, status =
, combatants_header =
, combatant1 = Catholic L ...
). The preaching of Martin Luther
Martin Luther (; ; 10 November 1483 – 18 February 1546) was a German priest, theologian, author, hymnwriter, and professor, and Order of Saint Augustine, Augustinian friar. He is the seminal figure of the Reformation, Protestant Refo ...
and his many followers raised tensions across Europe. In Northern Germany
Northern Germany (german: link=no, Norddeutschland) is a linguistic, geographic, socio-cultural and historic region in the northern part of Germany which includes the coastal states of Schleswig-Holstein, Mecklenburg-Vorpommern and Lower Saxony an ...
, Luther adopted the tactic of gaining the support of the local princes and city elites in his struggle to take over and re-establish the church along Lutheran lines. The Elector of Saxony
The Electorate of Saxony, also known as Electoral Saxony (German: or ), was a territory of the Holy Roman Empire from 1356–1806. It was centered around the cities of Dresden, Leipzig and Chemnitz.
In the Golden Bull of 1356, Emperor Charles ...
, the Landgrave of Hesse
The Landgraviate of Hesse (german: Landgrafschaft Hessen) was a principality of the Holy Roman Empire. It existed as a single entity from 1264 to 1567, when it was divided among the sons of Philip I, Landgrave of Hesse.
History
In the early Mi ...
, and other North German princes not only protected Luther from retaliation from the edict of outlawry
An outlaw, in its original and legal meaning, is a person declared as outside the protection of the law. In pre-modern societies, all legal protection was withdrawn from the criminal, so that anyone was legally empowered to persecute or kill them ...
issued by the Holy Roman Emperor, Charles V
Charles V, french: Charles Quint, it, Carlo V, nl, Karel V, ca, Carles V, la, Carolus V (24 February 1500 – 21 September 1558) was Holy Roman Emperor and Archduke of Austria from 1519 to 1556, King of Spain (Crown of Castile, Castil ...
, but also used state power to enforce the establishment of Lutheran worship in their lands, in what is called the Magisterial Reformation
The Magisterial Reformation "denotes the Lutheran, Calvinist eformed and Anglican churches" and how these denominations "related to secular authorities, such as princes, magistrates, or city councils", i.e. "the magistracy". While the Radical Refo ...
. Church property was seized, and Catholic worship was forbidden in most territories that adopted the Lutheran Reformation. The political conflicts thus engendered within the Empire led almost inevitably to war.
The Knights' Revolt
The Knights' Revolt (27 August 15226 May 1523) was a short-lived revolt by several German Protestant, imperial knights, led by Franz von Sickingen, against Charles V, Holy Roman Emperor. It has been called the Poor Barons' Rebellion as it inspi ...
of 1522 was a revolt by a number of Protestant and religious humanist German knights led by Franz von Sickingen, against the Roman Catholic Church and the Holy Roman Emperor. It has also been called the "Poor Barons' Rebellion". The revolt was short-lived but would inspire the bloody German Peasants' War of 1524–1526.
Rebellions of Anabaptists and other radicals
The first large-scale wave of violence was engendered by the more radical wing of the Reformation movement, whose adherents wished to extend the wholesale reform of the Church into a similarly wholesale reform of society in general. This was a step that the princes supporting Luther were not willing to countenance. TheGerman Peasants' War
The German Peasants' War, Great Peasants' War or Great Peasants' Revolt (german: Deutscher Bauernkrieg) was a widespread popular revolt in some German-speaking areas in Central Europe from 1524 to 1525. It failed because of intense oppositio ...
of 1524/1525 was a popular revolt
This is a chronological list of conflicts in which peasants played a significant role.
Background
The history of peasant wars spans over two thousand years. A variety of factors fueled the emergence of the peasant revolt phenomenon, including:
...
inspired by the teachings of the radical reformers. It consisted of a series of economic as well as religious revolts by Anabaptist
Anabaptism (from New Latin language, Neo-Latin , from the Greek language, Greek : 're-' and 'baptism', german: Täufer, earlier also )Since the middle of the 20th century, the German-speaking world no longer uses the term (translation: "Re- ...
peasant
A peasant is a pre-industrial agricultural laborer or a farmer with limited land-ownership, especially one living in the Middle Ages under feudalism and paying rent, tax, fees, or services to a landlord. In Europe, three classes of peasants ...
s, townsfolk and nobles
Nobility is a social class found in many societies that have an aristocracy. It is normally ranked immediately below royalty. Nobility has often been an estate of the realm with many exclusive functions and characteristics. The characteristi ...
. The conflict took place mostly in southern, western and central areas of modern Germany but also affected areas in neighboring modern Switzerland, Austria and the Netherlands (for example, the 1535 Anabaptist riot in Amsterdam). At its height, in the spring and summer of 1525, it involved an estimated 300,000 peasant insurgents. Contemporary estimates put the dead at 100,000. It was Europe's largest and most widespread popular uprising before the 1789 French Revolution
The French Revolution ( ) was a period of radical political and societal change in France that began with the Estates General of 1789 and ended with the formation of the French Consulate in November 1799. Many of its ideas are considere ...
.
Because of their revolutionary political ideas, radical reformers like Thomas Müntzer
Thomas Müntzer ( – 27 May 1525) was a German preacher and theologian of the early Reformation whose opposition to both Martin Luther and the Roman Catholic Church led to his open defiance of late-feudal authority in central Germany. Müntzer w ...
were compelled to leave the Lutheran cities of North Germany in the early 1520s. They spread their revolutionary religious and political doctrines into the countryside of Bohemia, Southern Germany, and Switzerland. Starting as a revolt against feudal oppression, the peasants' uprising became a war against all constituted authorities, and an attempt to establish by force an ideal Christian commonwealth. The total defeat of the insurgents at Frankenhausen on 15 May 1525, was followed by the execution of Müntzer and thousands of his peasant followers. Martin Luther
Martin Luther (; ; 10 November 1483 – 18 February 1546) was a German priest, theologian, author, hymnwriter, and professor, and Order of Saint Augustine, Augustinian friar. He is the seminal figure of the Reformation, Protestant Refo ...
rejected the demands of the insurgents and upheld the right of Germany's rulers to suppress the uprisings, setting out his views in his polemic '' Against the Murderous, Thieving Hordes of Peasants''. This played a major part in the rejection of his teachings by many German peasants, particularly in the south.
After the Peasants' War, a second and more determined attempt to establish a theocracy
Theocracy is a form of government in which one or more deity, deities are recognized as supreme ruling authorities, giving divine guidance to human intermediaries who manage the government's daily affairs.
Etymology
The word theocracy origina ...
was made at Münster
Münster (; nds, Mönster) is an independent city (''Kreisfreie Stadt'') in North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. It is in the northern part of the state and is considered to be the cultural centre of the Westphalia region. It is also a state distr ...
, in Westphalia
Westphalia (; german: Westfalen ; nds, Westfalen ) is a region of northwestern Germany and one of the three historic parts of the state of North Rhine-Westphalia. It has an area of and 7.9 million inhabitants.
The territory of the regio ...
(1532–1535). Here a group of prominent citizens, including the Lutheran
Lutheranism is one of the largest branches of Protestantism, identifying primarily with the theology of Martin Luther, the 16th-century German monk and reformer whose efforts to reform the theology and practice of the Catholic Church launched th ...
pastor turned Anabaptist
Anabaptism (from New Latin language, Neo-Latin , from the Greek language, Greek : 're-' and 'baptism', german: Täufer, earlier also )Since the middle of the 20th century, the German-speaking world no longer uses the term (translation: "Re- ...
Bernhard Rothmann
Bernhard (or Bernard) Rothmann (c. 1495 – c. 1535) was a 16th-century radical and Anabaptist leader in the city of Münster. He was born in Stadtlohn, Westphalia, around 1495.
Overview
In the late 1520s Bernard Rothmann became the leader for re ...
, Jan Matthys
Jan Matthys (also known as ''Jan Matthias'', ''Johann Mathyszoon'', ''Jan Mattijs'', ''Jan Matthijszoon''; c. 1500 – 5 April 1534) was a charismatic Anabaptist leader of the Münster Rebellion, regarded by his followers as a prophet.
Matthys w ...
, and Jan Bockelson ("John of Leiden") had little difficulty in obtaining possession of the town on 5 January 1534. Matthys identified Münster as the "New Jerusalem
In the Book of Ezekiel in the Hebrew Bible, New Jerusalem (, ''YHWH šāmmā'', YHWH sthere") is Ezekiel's prophetic vision of a city centered on the rebuilt Holy Temple, the Third Temple, to be established in Jerusalem, which would be the c ...
", and preparations were made to not only hold what had been gained, but to proceed from Münster toward the conquest of the world.
Claiming to be the successor of David
David (; , "beloved one") (traditional spelling), , ''Dāwūd''; grc-koi, Δαυΐδ, Dauíd; la, Davidus, David; gez , ዳዊት, ''Dawit''; xcl, Դաւիթ, ''Dawitʿ''; cu, Давíдъ, ''Davidŭ''; possibly meaning "beloved one". w ...
, John of Leiden
John of Leiden (born Johan Beukelszoon; 2 February 1509 – 22 January 1536) was a Dutch Anabaptist leader. In 1533 he moved to Münster, capital of the Prince-Bishopric of Münster, where he became an influential prophet, turned the city into ...
was installed as king
King is the title given to a male monarch in a variety of contexts. The female equivalent is queen, which title is also given to the consort of a king.
*In the context of prehistory, antiquity and contemporary indigenous peoples, the tit ...
. He legalized polygamy
Crimes
Polygamy (from Late Greek (') "state of marriage to many spouses") is the practice of marrying multiple spouses. When a man is married to more than one wife at the same time, sociologists call this polygyny. When a woman is married ...
and took sixteen wives, one of whom he personally beheaded in the marketplace. Community of goods
Common ownership refers to holding the assets of an organization, enterprise or community indivisibly rather than in the names of the individual members or groups of members as common property.
Forms of common ownership exist in every economi ...
was also established. After obstinate resistance, the town was taken by the besiegers on 24 June 1535, and then Leiden and some of his more prominent followers were executed in the marketplace.
Swiss Confederacy
In 1529 under the lead ofHuldrych Zwingli
Huldrych or Ulrich Zwingli (1 January 1484 – 11 October 1531) was a leader of the Reformation in Switzerland, born during a time of emerging Swiss patriotism and increasing criticism of the Swiss mercenary system. He attended the Unive ...
, the Protestant canton and city of Zürich
Zürich () is the list of cities in Switzerland, largest city in Switzerland and the capital of the canton of Zürich. It is located in north-central Switzerland, at the northwestern tip of Lake Zürich. As of January 2020, the municipality has 43 ...
had concluded with other Protestant cantons a defence alliance, the ''Christliches Burgrecht
A Burgrecht (''ius burgense, ius civile'') was a medieval agreement, most commonly in southern Germany and northern German-speaking Switzerland. It came to refer to an agreement between a town and surrounding settlements or to include the specifi ...
'', which also included the cities of Konstanz
Konstanz (, , locally: ; also written as Constance in English) is a university city with approximately 83,000 inhabitants located at the western end of Lake Constance in the south of Germany. The city houses the University of Konstanz and was th ...
and Strasbourg
Strasbourg (, , ; german: Straßburg ; gsw, label=Bas Rhin Alsatian, Strossburi , gsw, label=Haut Rhin Alsatian, Strossburig ) is the prefecture and largest city of the Grand Est region of eastern France and the official seat of the Eu ...
. The Catholic cantons in response had formed an alliance with Ferdinand of Austria.
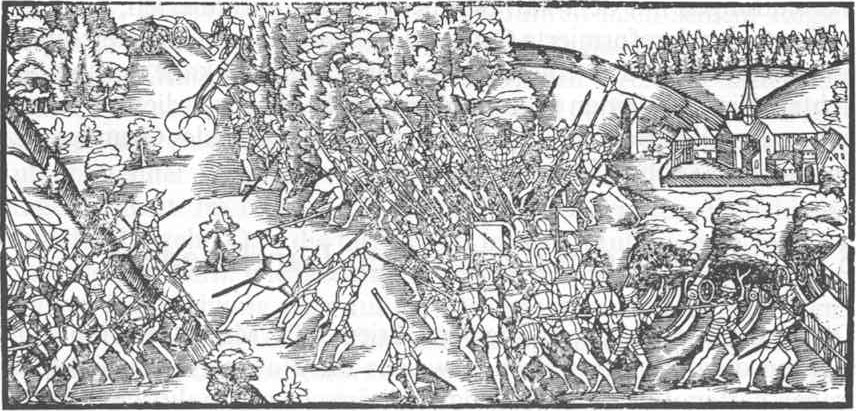
 After numerous minor incidents and provocations from both sides, a Catholic priest was executed in the Thurgau in May 1528, and the Protestant pastor J. Keyser was burned at the stake in Schwyz in 1529. The last straw was the installation of a Catholic
After numerous minor incidents and provocations from both sides, a Catholic priest was executed in the Thurgau in May 1528, and the Protestant pastor J. Keyser was burned at the stake in Schwyz in 1529. The last straw was the installation of a Catholic vogt
During the Middle Ages, an (sometimes given as modern English: advocate; German: ; French: ) was an office-holder who was legally delegated to perform some of the secular responsibilities of a major feudal lord, or for an institution such as ...
at Baden, and Zürich declared war on 8 June ( First War of Kappel), occupied the Thurgau and the territories of the Abbey of St. Gall
The Abbey of Saint Gall (german: Abtei St. Gallen) is a dissolved abbey (747–1805) in a Catholic religious complex in the city of St. Gallen in Switzerland. The Carolingian-era monastery existed from 719, founded by Saint Othmar on the spot ...
, and marched to Kappel at the border to Zug
, neighboring_municipalities = Cham, Baar, Walchwil, Steinhausen, Unterägeri
, twintowns = Fürstenfeld (Austria), Kalesija (Bosnia-Herzegowina)
Zug (Standard German: , Alemannic German: ; french: Zoug it, Zugo r ...
. Open war was avoided by means of a peace agreement (''Erster Landfriede
Under the law of the Holy Roman Empire, a ''Landfrieden'' or ''Landfriede'' (Latin: ''constitutio pacis'', ''pax instituta'' or ''pax jurata'', variously translated as "land peace", or "public peace") was a contractual waiver of the use of legiti ...
'') that was not exactly favourable to the Catholic side, which had to dissolve its alliance with the Austrian Habsburg
The House of Habsburg (), alternatively spelled Hapsburg in Englishgerman: Haus Habsburg, ; es, Casa de Habsburgo; hu, Habsburg család, it, Casa di Asburgo, nl, Huis van Habsburg, pl, dom Habsburgów, pt, Casa de Habsburgo, la, Domus Hab ...
s. Tensions remained essentially unresolved.
On 11 October 1531, the Catholic cantons decisively defeated the forces of Zürich in the Second War of Kappel
The Second War of Kappel (german: Zweiter Kappelerkrieg) was an armed conflict in 1531 between the Catholic and the Protestant cantons of the Old Swiss Confederacy during the Reformation in Switzerland.
Cause
The tensions between the two part ...
. The Zürich troops had little support from allied Protestant cantons, and Huldrych Zwingli was killed on the battlefield, along with twenty-four other pastors. After the defeat, the forces of Zürich regrouped and attempted to occupy the Zugerberg, and some of them camped on the ''Gubel'' hill near Menzingen
Menzingen is a municipality in the canton of Zug in Switzerland.
History
Menzingen is first mentioned around 1217-22 as ''Meincingin''.
The traditionalist Society of Saint Pius X, which is said to have broken with the Vatican over "doctrinal ...
. A small force of Aegeri succeeded in routing the camp, and the demoralized Zürich force had to retreat, forcing the Protestants to agree to a peace treaty to their disadvantage. Switzerland was to be divided into a patchwork of Protestant and Catholic cantons, with the Protestants tending to dominate the larger cities, and the Catholics the more rural areas.
In 1656, tensions between Protestants and Catholics re-emerged and led to the outbreak of the First War of Villmergen
The First War of Villmergen Encarta-encyclopedie Winkler Prins (1993–2002) s.v. "Zwitserland. §5.2 Reformatie". Microsoft Corporation/Het Spectrum. was a Swiss religious war which lasted from 5 January until 7 March 1656, at the time of the Ol ...
. The Catholics were victorious and able to maintain their political dominance. The Toggenburg War
The Toggenburg War, also known as the Second War of Villmergen or the Swiss Civil War of 1712, was a Swiss civil war during the Old Swiss Confederacy from 12 April to 11 August 1712. The Catholic "inner cantons" and the Imperial Abbey of Saint ...
in 1712 was a conflict between Catholic and Protestant cantons. According to the Peace of Aarau of 11 August 1712 and the Peace of Baden of 16 June 1718, the war ended with the end of Catholic hegemony. The Sonderbund War
The Sonderbund War (german: Sonderbundskrieg, fr , Guerre du Sonderbund, it , Guerra del Sonderbund) of November 1847 was a civil war in Switzerland, then still a relatively loose confederacy of cantons. It ensued after seven Catholic cantons ...
of 1847 was also based on religion.
Schmalkaldic Wars and other early conflicts
 Following the
Following the Diet of Augsburg
The Diet of Augsburg were the meetings of the Imperial Diet of the Holy Roman Empire held in the German city of Augsburg. Both an Imperial City and the residence of the Augsburg prince-bishops, the town had hosted the Estates in many such sess ...
in 1530, the Emperor demanded that all religious innovations not authorized by the Diet be abandoned by 15 April 1531. Failure to comply would result in prosecution by the Imperial Court. In response, the Lutheran princes who had set up Protestant churches in their own realms met in the town of Schmalkalden
Schmalkalden () is a town in the Schmalkalden-Meiningen district, in the southwest of the state of Thuringia, Germany. It is on the southern slope of the Thuringian Forest at the Schmalkalde river, a tributary to the Werra. , the town had a popula ...
in December 1530. Here they banded together to form the Schmalkaldic League
The Schmalkaldic League (; ; or ) was a military alliance of Lutheran princes within the Holy Roman Empire during the mid-16th century.
Although created for religious motives soon after the start of the Reformation, its members later came to ...
(german: Schmalkaldischer Bund), an alliance
An alliance is a relationship among people, groups, or states that have joined together for mutual benefit or to achieve some common purpose, whether or not explicit agreement has been worked out among them. Members of an alliance are called ...
designed to protect themselves from the Imperial action. Its members eventually intended the League to replace the Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a Polity, political entity in Western Europe, Western, Central Europe, Central, and Southern Europe that developed during the Early Middle Ages and continued until its Dissolution of the Holy Roman Empire, dissolution i ...
itself, and each state was to provide 10,000 infantry and 2,000 cavalry for mutual defense. In 1532 the Emperor, pressed by external troubles, stepped back from confrontation, offering the " Peace of Nuremberg", which suspended all action against the Protestant states pending a General Council of the Church. The moratorium kept peace in the German lands for over a decade, yet Protestantism became further entrenched, and spread, during its term.
The peace finally ended in the Schmalkaldic War
The Schmalkaldic War (german: link=no, Schmalkaldischer Krieg) was the short period of violence from 1546 until 1547 between the forces of Emperor Charles V of the Holy Roman Empire (simultaneously King Charles I of Spain), commanded by the Duk ...
(german: Schmalkaldischer Krieg), a brief conflict between 1546 and 1547 between the forces of Charles V Charles V may refer to:
* Charles V, Holy Roman Emperor (1500–1558)
* Charles V of Naples (1661–1700), better known as Charles II of Spain
* Charles V of France (1338–1380), called the Wise
* Charles V, Duke of Lorraine (1643–1690)
* Infan ...
and the princes of the Schmalkaldic League. The conflict ended with the advantage of the Catholics, and the Emperor was able to impose the Augsburg Interim
The Augsburg Interim (full formal title: ''Declaration of His Roman Imperial Majesty on the Observance of Religion Within the Holy Empire Until the Decision of the General Council'') was an imperial decree ordered on 15 May 1548 at the 1548 Diet ...
, a compromise allowing slightly modified worship, and supposed to remain in force until the conclusion of a General Council of the Church. However various Protestant elements rejected the Interim, and the Second Schmalkaldic War broke out in 1552, which would last until 1555.
The Peace of Augsburg (1555), signed by Charles V, Holy Roman Emperor
Charles V, french: Charles Quint, it, Carlo V, nl, Karel V, ca, Carles V, la, Carolus V (24 February 1500 – 21 September 1558) was Holy Roman Emperor and Archduke of Austria from 1519 to 1556, King of Spain (Crown of Castile, Castil ...
, confirmed the result of the 1526 Diet of Speyer and ended the violence between the Lutherans
Lutheranism is one of the largest branches of Protestantism, identifying primarily with the theology of Martin Luther, the 16th-century German monk and reformer whose efforts to reform the theology and practice of the Catholic Church launched ...
and the Catholics in Germany. It stated that:
* German princes could choose the religion (Lutheranism or Catholicism) of their realms according to their conscience. The citizens of each state were forced to adopt the religion of their rulers (the principle of ''cuius regio, eius religio
() is a Latin phrase which literally means "whose realm, their religion" – meaning that the religion of the ruler was to dictate the religion of those ruled. This legal principle marked a major development in the collective (if not individual ...
'').
* Lutherans living in an ''ecclesiastical state'' (under the control of a bishop) could continue to practice their faith.
* Lutherans could keep the territory that they had captured from the Catholic Church since the Peace of Passau
Holy Roman Emperor Charles V had won a victory against Protestant forces in the Schmalkaldic War of 1547. Many Protestant princes were unhappy with the religious terms of the Augsburg Interim imposed after this victory. In January 1552, led by Maur ...
in 1552.
* The ecclesiastical leaders of the Catholic Church (bishops) that had converted to Lutheranism were required to give up their territories.
Religious tensions remained strong throughout the second half of the 16th century. The Peace of Augsburg began to unravel as some bishops converting to Protestantism refused to give up their bishoprics
In church governance, a diocese or bishopric is the ecclesiastical district under the jurisdiction of a bishop.
History
In the later organization of the Roman Empire, the increasingly subdivided provinces were administratively associat ...
. This was evident from the Cologne War
The Cologne War (german: Kölner Krieg, Kölnischer Krieg, Truchsessischer Krieg; 1583–88) was a conflict between Protestant and Catholic factions that devastated the Electorate of Cologne, a historical ecclesiastical principality of the Holy ...
(1582–83), a conflict initiated when the prince-archbishop of the city converted to Calvinism. Religious tensions also broke into violence in the German free city of Donauwörth
Donauwörth () is a town and the capital of the Donau-Ries district in Swabia, Bavaria, Germany. It is said to have been founded by two fishermen where the rivers Danube (Donau) and Wörnitz meet. The city is part of the scenic route called "Roman ...
in 1606, when the Lutheran majority barred the Catholic residents from holding a procession, provoking a riot. This prompted intervention by Duke Maximilian of Bavaria on behalf of the Catholics.
By the end of the 16th century the Rhine
), Surselva, Graubünden, Switzerland
, source1_coordinates=
, source1_elevation =
, source2 = Rein Posteriur/Hinterrhein
, source2_location = Paradies Glacier, Graubünden, Switzerland
, source2_coordinates=
, so ...
lands and those of southern Germany remained largely Catholic, while Lutherans predominated in the north, and Calvinists dominated in west-central Germany, Switzerland, and the Netherlands. The latter formed the League of Evangelical Union in 1608.
Thirty Years' War
Matthias Matthias is a name derived from the Greek Ματθαίος, in origin similar to Matthew.
People
Notable people named Matthias include the following:
In religion:
* Saint Matthias, chosen as an apostle in Acts 1:21–26 to replace Judas Iscariot
* ...
, Holy Roman Emperor and King of Bohemia
Bohemia ( ; cs, Čechy ; ; hsb, Čěska; szl, Czechy) is the westernmost and largest historical region of the Czech Republic. Bohemia can also refer to a wider area consisting of the historical Lands of the Bohemian Crown ruled by the Bohem ...
, would die without an heir. His lands would therefore fall to his nearest male relative, his cousin Ferdinand of Styria
Styria (german: Steiermark ; Serbo-Croatian and sl, ; hu, Stájerország) is a state (''Bundesland'') in the southeast of Austria. With an area of , Styria is the second largest state of Austria, after Lower Austria. Styria is bordered to ...
. Ferdinand, having been educated by the Jesuits
The Society of Jesus ( la, Societas Iesu; abbreviation: SJ), also known as the Jesuits (; la, Iesuitæ), is a religious order (Catholic), religious order of clerics regular of pontifical right for men in the Catholic Church headquartered in Rom ...
, was a staunch Catholic. The rejection of Ferdinand as Crown Prince by the mostly Hussite
The Hussites ( cs, Husité or ''Kališníci''; "Chalice People") were a Czech proto-Protestant Christian movement that followed the teachings of reformer Jan Hus, who became the best known representative of the Bohemian Reformation.
The Hussit ...
Bohemia triggered the Thirty Years' War in 1618, when his representatives were defenestrated in Prague.
The Thirty Years' War
The Thirty Years' War was one of the longest and most destructive conflicts in European history
The history of Europe is traditionally divided into four time periods: prehistoric Europe (prior to about 800 BC), classical antiquity (80 ...
was fought between 1618 and 1648, principally on the territory of today's Germany, and involved most of the major European powers
A great power is a sovereign state that is recognized as having the ability and expertise to exert its influence on a global scale. Great powers characteristically possess military and economic strength, as well as diplomatic and soft power inf ...
. Beginning as a religious conflict between Protestants
Protestantism is a branch of Christianity that follows the theological tenets of the Protestant Reformation, a movement that began seeking to reform the Catholic Church from within in the 16th century against what its followers perceived to b ...
and Catholics
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
in the Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a Polity, political entity in Western Europe, Western, Central Europe, Central, and Southern Europe that developed during the Early Middle Ages and continued until its Dissolution of the Holy Roman Empire, dissolution i ...
, it gradually developed into a general war involving much of Europe, for reasons not necessarily related to religion. The war marked a continuation of the France-Habsburg rivalry for pre-eminence in Europe, which led later to direct war between France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of Overseas France, overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, Pacific Ocean, Pac ...
and Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = ''Plus ultra'' (Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, i ...
. Military intervention by external powers such as Denmark and Sweden on the Protestant side increased the duration of the war and the extent of its devastation. In the latter stages of the war, Catholic France, fearful of an increase in Habsburg power, also intervened on the Protestant side.
 The major impact of the Thirty Years' War, in which mercenary armies were extensively used, was the devastation of entire regions scavenged bare by the foraging armies. Episodes of widespread
The major impact of the Thirty Years' War, in which mercenary armies were extensively used, was the devastation of entire regions scavenged bare by the foraging armies. Episodes of widespread famine
A famine is a widespread scarcity of food, caused by several factors including war, natural disasters, crop failure, Demographic trap, population imbalance, widespread poverty, an Financial crisis, economic catastrophe or government policies. Th ...
and disease
A disease is a particular abnormal condition that negatively affects the structure or function of all or part of an organism, and that is not immediately due to any external injury. Diseases are often known to be medical conditions that a ...
devastated the population of the German states and, to a lesser extent, the Low Countries
The term Low Countries, also known as the Low Lands ( nl, de Lage Landen, french: les Pays-Bas, lb, déi Niddereg Lännereien) and historically called the Netherlands ( nl, de Nederlanden), Flanders, or Belgica, is a coastal lowland region in N ...
and Italy, while bankrupting many of the powers involved. The war ended with the Treaty of Münster Treaty of Münster refers to two treaties signed in 1648, and forming part of the Peace of Westphalia ending the Thirty Years' War:
* Peace of Münster
The Peace of Münster was a treaty between the Lords States General of the Seven United N ...
, a part of the wider Peace of Westphalia
The Peace of Westphalia (german: Westfälischer Friede, ) is the collective name for two peace treaties signed in October 1648 in the Westphalian cities of Osnabrück and Münster. They ended the Thirty Years' War (1618–1648) and brought pea ...
.
During the war, Germany's population was reduced by 30% on average. In the territory of Brandenburg
Brandenburg (; nds, Brannenborg; dsb, Bramborska ) is a states of Germany, state in the northeast of Germany bordering the states of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Lower Saxony, Saxony-Anhalt, and Saxony, as well as the country of Poland. With an ar ...
, the losses had amounted to half, while in some areas an estimated two thirds of the population died. The population of the Czech lands
The Czech lands or the Bohemian lands ( cs, České země ) are the three historical regions of Bohemia, Moravia, and Czech Silesia. Together the three have formed the Czech part of Czechoslovakia since 1918, the Czech Socialist Republic since 1 ...
declined by a third. The Swedish
Swedish or ' may refer to:
Anything from or related to Sweden, a country in Northern Europe. Or, specifically:
* Swedish language, a North Germanic language spoken primarily in Sweden and Finland
** Swedish alphabet, the official alphabet used by ...
army alone, which was no greater a ravager than the other armies of the Thirty Years' War, destroyed 2,000 castles, 18,000 villages and 1,500 towns during its tenure of 17 years in Germany. For decades armies and armed bands had roamed Germany like packs of wolves, slaughtering the populace like sheep. One band of marauders even styled themselves as "Werewolves". Huge damage was done to monasteries, churches and other religious institutions. The war had proved disastrous for the German-speaking parts of the Holy Roman Empire. Germany lost population and territory, and was henceforth further divided into hundreds of largely impotent semi-independent states. The Imperial power retreated to Austria and the Habsburg lands. The Netherlands and Switzerland were confirmed independent. The peace institutionalised the Catholic, Lutheran, Calvinist religious divide in Germany, with populations either converting, or moving to areas controlled by rulers of their own faith.
One authority puts France's losses against Austria at 80,000 killed or wounded and against Spain (including the years 1648–1659, after Westphalia) at 300,000 dead or disabled. Sweden and Finland lost, by one calculation, 110,000 dead from all causes. Another 400,000 Germans, British, and other nationalities died in Swedish service.
Low Countries
During the 16th and 17th centuries, the Netherlands, orLow Countries
The term Low Countries, also known as the Low Lands ( nl, de Lage Landen, french: les Pays-Bas, lb, déi Niddereg Lännereien) and historically called the Netherlands ( nl, de Nederlanden), Flanders, or Belgica, is a coastal lowland region in N ...
, were engaged in a seemingly futile struggle for independence against the most dominant power of the times, Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = ''Plus ultra'' (Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, i ...
. The most politically significant turn of events came when Charles V of Spain transferred sovereignty of the Low Countries to his son Philip II Philip II may refer to:
* Philip II of Macedon (382–336 BC)
* Philip II (emperor) (238–249), Roman emperor
* Philip II, Prince of Taranto (1329–1374)
* Philip II, Duke of Burgundy (1342–1404)
* Philip II, Duke of Savoy (1438-1497)
* Philip ...
. At this point in history the Low Countries were a loosely associated cluster of provinces. Philip II mishandled his responsibility through a series of bungled diplomatic maneuvers. Unlike his father, he had no basic understanding of the people placed under his direction. Charles V spoke the language; Philip II did not. Charles V was raised in Brussels; Philip II was considered a foreigner.
The religious element was a decisive factor in the development of hostilities despite the fact that the Dutch people at the time were overwhelmingly Roman Catholic. Their theological basis was in the liberal tradition of Erasmus versus the conservative line of the Spanish Church. Nevertheless, Protestant religions, especially Calvinism, seeped into the Low Countries during the early part of the 16th century due to the fact that it was a major center for trade. This period was also known for the Inquisition
The Inquisition was a group of institutions within the Catholic Church whose aim was to combat heresy, conducting trials of suspected heretics. Studies of the records have found that the overwhelming majority of sentences consisted of penances, ...
. Under Charles’ reign, the Low Countries were subjected to the papal form of the Inquisition where laws were rarely enforced. An incident at Rotterdam involving the rescue of several heretics from burning at the stake made Philip introduce the Spanish form of the Inquisition. This did little to promote allegiance to Spain.
Calvinism thrived in the mercantile atmosphere of the Low Countries. Businessmen liked the role of the laity in Calvinist congregations. The Roman Catholic church was viewed as an unyielding patriarch, and the pompous hierarchy of the Roman Catholic church was resented even though Catholicism had respect as an important social, moral, and political force. Merchants welcomed the "new" religion. Not to be taken lightly was the imposition of taxes on the businesses and people of the Low Countries. The taxation was unilateral in nature: it was levied by a foreign political entity and the benefit derived from the taxes went to Spain. Spain was building an empire, and the low Countries paid dearly.
In 1559, Philip appointed Margaret of Parma
Margaret of Parma (; 5 July 1522 – 18 January 1586) was Governor of the Netherlands from 1559 to 1567 and from 1578 to 1582. She was the illegitimate daughter of the then 22-year-old Holy Roman Emperor Charles V and Johanna Maria van der G ...
as governess. She held little power since her authority had been carefully limited by advisors designated by Philip. This was a means of preserving absolute control over the Low Countries and it was an excellent vehicle to promote the spread of the Inquisition. Hardly a day passed without an execution. Protestant authorities substantiate a number of accounts associated with the "justice" of Philip. One account reveals an incident where an Anabaptist was hacked to death with seven blows of a rusty sword in the presence of his wife, who died at the horror of the sight. Another tells of an enraged man who interrupted Christmas Mass, took the host, and trampled it. He was put to torture by having his right hand and foot burned away to the bane. His tongue was torn out, he was suspended over a fire and was slowly roasted to death. Margaret interceded but the atrocities continued. Even the Catholics now joined with Protestants as Philip stated that he would rather sacrifice a hundred thousand lives than change his policy. Some diplomacy was used and when a compromise was reached on 6 May 1566, Philip eased off. During the ensuing lull, Protestants brought their worship into the open. A group called the "Beggars" grew in strength and proceeded to raise a sizable army.
On 6 August 1566, Philip signed a formal instrument declaring that his offer of pardon had been gotten from him against his will. He claimed that he was not bound by the compromise of 6 May and a few days later, Philip assured the Pope that any suspension of the Inquisition was subject to papal approval. The destruction of thirty churches and monasteries followed. Protestants entered cathedrals smashing holy objects, breaking up altars and statues and smashing stained glass windows. Bodies were exhumed and corpses were stripped. Numbers of malcontents drank sacramental wine and burned missals. One Count fed the Eucharistic wafers to his parrot in defiance. It was well known that most Protestant leaders condemned the violence perpetrated by the angry mobs, but the pillage and destruction of property was considered far less criminal than burning heretics at the stake. On the political front, William of Orange saw the opportunity to amass support for a large scale insurrection aimed at procuring independence from Spain. Philip became dissatisfied with Margaret, and seized the opportunity to relieve her. The choice was crucial. Instead of selecting a successor trained in handling diplomacy, Philip sent the Duke of Alva
Duke is a male title either of a monarch ruling over a duchy, or of a member of royalty, or nobility. As rulers, dukes are ranked below emperors, kings, grand princes, grand dukes, and sovereign princes. As royalty or nobility, they are ranke ...
to crush the malcontents.
Duke of Alba (Alva)

 Philip gave full power to Alva in 1567. Alva's judgment was that of a soldier trained in Spanish discipline and piety. His object was to crush the rebels without mercy on the basis that every concession strengthens the opposition. Alva hand-picked an army of 10,000 men. He issued them the finest in armor while attending to their baser needs by hiring 2,000 prostitutes. Alva installed himself as Governor General and appointed a
Philip gave full power to Alva in 1567. Alva's judgment was that of a soldier trained in Spanish discipline and piety. His object was to crush the rebels without mercy on the basis that every concession strengthens the opposition. Alva hand-picked an army of 10,000 men. He issued them the finest in armor while attending to their baser needs by hiring 2,000 prostitutes. Alva installed himself as Governor General and appointed a Council of Troubles
The Council of Troubles (usual English translation of nl, Raad van Beroerten, or es, Tribunal de los Tumultos, or french: Conseil des Troubles) was the special tribunal instituted on 9 September 1567 by Fernando Álvarez de Toledo, 3rd Duke of ...
which the terrified Protestants renamed "The Council of Blood". There were nine members: seven Dutch and two Spanish. Only the two Spanish members had the power to vote, with Alva personally retaining the right of final decision on any case that interested him. Through a network of spies and informers, hardly a family in Flanders did not mourn some member arrested or killed. One morning, 1,500 were seized in their sleep and sent to jail. There were short trials held, often on the spot, for 40 or 50 at a time. In January 1568, 84 people were executed from Valenciennes alone. William of Orange decided to strike back at Spain, having organized three armies. He lost every battle and the Eighty Years' War was underway (1568–1648).
The Duke of Alva had money sent from Spain but it was intercepted by English privateers who were beginning to establish England as a viable world power. The Queen of England sent her apologies as a matter of diplomatic courtesy while unofficially enjoying Spain's troubles. Alva responded to his financial bind by imposing a new series of taxes. There was a 1% levy on all property, due immediately. He enforced a 5% perpetual tax on every transfer of realty and a 10% perpetual tax on every sale. This was Alva's downfall. Catholics, as well as Protestants, opposed him for eroding the foundations of business upon which the Dutch economy was built. What followed was a series of mutual confiscation of property as England and Spain played international cat-and-mouse.
Two new forces emerged to oppose Spain. Seizing upon the term, Beggars, used earlier in a derogatory manner by Margaret of Parma, the Dutch rebels formed the Wild Beggars and the Beggars of the Sea. The Wild Beggars pillaged churches and monasteries, cutting off the noses and ears of priests and monks. The Beggars of the Sea took to pirating under commission from William of Orange. William, who raised another army after a series of earlier defeats, again battled the Spanish without a single victory. He could neither control his troops nor deal with the fanatic Beggars. There existed no true unity between Catholics, Calvinists, and Protestants against Alva. The Beggars, who were nearly all ardent Calvinists, showed against the Catholics the same ferocity that the Inquisition and the Council of Blood had shown against rebels and heretics. Their captives were often given a choice between Calvinism and death. They unhesitatingly killed those who clung to the old faith, sometimes after incredible tortures. One Protestant historian wrote:
Zutphen
Zutphen () is a city and municipality located in the province of Gelderland, Netherlands. It lies some 30 km northeast of Arnhem, on the eastern bank of the river Ijssel at the point where it is joined by the Berkel. First mentioned in the 1 ...
and put nearly every man in town to death, hanging some by the feet while drowning 500 others. Sometime later after brief resistance, little Naarden
Naarden () is a List of cities in the Netherlands by province, city and former List of municipalities of the Netherlands, municipality in the Gooi region in the Provinces of the Netherlands, province of North Holland, Netherlands. It has been part ...
surrendered to the Spaniards. They greeted the victorious soldiers with tables set with feasts. The soldiers ate, drank, then killed every person in the town. Don Fadrique's army later attempted to besiege Alkmaar
Alkmaar () is a city and municipality in the Netherlands, located in the province of North Holland, about 30 km north of Amsterdam. Alkmaar is well known for its traditional cheese market. For tourists, it is a popular cultural destination. The ...
but the rebels won by opening the dikes and routing the Spanish troops. When Don Fadrique came to Haarlem
Haarlem (; predecessor of ''Harlem'' in English) is a city and municipality in the Netherlands. It is the capital of the province of North Holland. Haarlem is situated at the northern edge of the Randstad, one of the most populated metropoli ...
a brutal battle ensued. Haarlem was a Calvinist center that was known for its enthusiastic support of the rebels. A garrison of 4,000 troops defended the city with such intensity that Don Fadrique contemplated withdrawing. His father, Alva, threatened to disown him if he stopped the siege, so the barbarities intensified. Each army hung captives on crosses facing the enemy. The Dutch defenders taunted the Spanish besiegers by staging parodies of Catholic rituals on the cities ramparts.
William sent 3,000 men in an effort to relieve Haarlem. They were destroyed and subsequent efforts to save the city were futile. After seven months, when the city's inhabitants had been reduced to eating weeds and heather, the city surrendered (11 July 1573). Most of the 1,600 surviving defenders were put to death and 400 leading citizens were executed. Those that were spared were shown mercy only because they agreed to pay a fine of 250,000 guilders, a sizable sum even by today's standards. This was considered the last and most costly victory of Alva's regime. The Bishop of Namur estimated that in seven years, Alva had done more to harm Catholicism than Luther or Calvin had done in a generation. A new Governor of the Netherlands followed.
Division
 Philip's half brother, the famous Don John, was placed in charge of the Spanish troops who, feeling cheated at not being able to pillage Zeirikzee, mutinied and began a campaign of indiscriminate plunder and violence. This "
Philip's half brother, the famous Don John, was placed in charge of the Spanish troops who, feeling cheated at not being able to pillage Zeirikzee, mutinied and began a campaign of indiscriminate plunder and violence. This "Spanish Fury
A Spanish Fury (or the Spanish Terror) was one of a number of violent sackings of cities in the Low Countries, mostly by Spanish Habsburg armies, that occurred in the years 1572–1579 during the Dutch Revolt. In some cases the sack did not fol ...
" was used by William to reinforce his arguments to ally all the Netherlands' Provinces with him. The Union of Brussels was formed only to be dissolved later out of intolerance towards the religious diversity of its members. Calvinists began their wave of uncontrolled atrocities aimed at the Catholics. This divisiveness gave Spain the opportunity to send Alexander Farnese, Duke of Parma
Alexander Farnese ( it, Alessandro Farnese, es, Alejandro Farnesio; 27 August 1545 – 3 December 1592) was an Italian noble and condottiero and later a general of the Spanish army, who was Duke of Parma, Piacenza and Castro from 1586 to 1592 ...
with 20,000 well-trained troops into the Netherlands. Groningen, Breda, Campen, Antwerp, and Brussels, among others, were put to siege.
Farnese, the son of Margaret of Parma, was the ablest general of Spain. In January 1579, a group of Catholic nobles formed a League for the protection of their religion and property. Later that same month Friesland, Gelderland, Groningen, Holland, Overijssel, Utrecht and Zeeland formed the United Provinces which became the Dutch Netherlands
)
, anthem = ( en, "William of Nassau")
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name = Kingdom of the Netherlands
, established_title = Before independence
, established_date = Spanish Netherl ...
of today. The remaining provinces became the Spanish Netherlands
Spanish Netherlands (Spanish: Países Bajos Españoles; Dutch: Spaanse Nederlanden; French: Pays-Bas espagnols; German: Spanische Niederlande.) (historically in Spanish: ''Flandes'', the name "Flanders" was used as a ''pars pro toto'') was the Ha ...
and in the 19th century became Belgium
Belgium, ; french: Belgique ; german: Belgien officially the Kingdom of Belgium, is a country in Northwestern Europe. The country is bordered by the Netherlands to the north, Germany to the east, Luxembourg to the southeast, France to th ...
. Farnese soon regained nearly all the Southern provinces for Spain.
Further north, the city of Maastricht
Maastricht ( , , ; li, Mestreech ; french: Maestricht ; es, Mastrique ) is a city and a municipality in the southeastern Netherlands. It is the capital and largest city of the province of Limburg. Maastricht is located on both sides of the ...
was besieged on 12 March 1579. Farnese's attackers tunneled an extensive network of passages in order to enter the city beneath its walled defenses. The defenders dug tunnels to meet them. Battles were fought fiercely in caverns with limited maneuvering capabilities. Hundreds of besiegers were scalded or choked to death when boiling water was poured into the tunnels or fires were lit to fill them with smoke. In an attempt to mine the city, 500 of Farnese's own men were killed when the explosives detonated prematurely. It took more than four months but the besiegers finally breached the wall and entered the city at night. Catching the exhausted defenders sleeping, they massacred 6,000 men, women and children. Of the city's 30,000 population, only 400 survived. Farnese repeopled it with Walloon Catholics.
Maastricht was a major disaster for the Protestant cause and the Dutch began to turn on William of Orange. After several unsuccessful attempts, William was assassinated in 1584 and died penniless. Spain had taken the upper hand on land but the Beggars still controlled the sea. Queen Elizabeth of England began to aid the Northern provinces and actually sent troops there in 1585. While Philip wasted Farnese with ridiculous and useless battles against England
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Wales to its west and Scotland to its north. The Irish Sea lies northwest and the Celtic Sea to the southwest. It is separated from continental Europe b ...
and France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of Overseas France, overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, Pacific Ocean, Pac ...
, Spain had become spread too thin. The Spanish Armada
The Spanish Armada (a.k.a. the Enterprise of England, es, Grande y Felicísima Armada, links=no, lit=Great and Most Fortunate Navy) was a Spanish fleet that sailed from Lisbon in late May 1588, commanded by the Duke of Medina Sidonia, an aris ...
suffered defeat at the hands of the English in 1588 and the situation in the Netherlands became increasingly difficult to manage.
Maurice of Nassau
Maurice of Orange ( nl, Maurits van Oranje; 14 November 1567 – 23 April 1625) was '' stadtholder'' of all the provinces of the Dutch Republic except for Friesland from 1585 at the earliest until his death in 1625. Before he became Prince ...
, William's son, had studied mathematics and applied the latest techniques in science to ballistics and siege warfare. He recaptured Deventer
Deventer (; Sallands: ) is a city and municipality in the Salland historical region of the province of Overijssel, Netherlands. In 2020, Deventer had a population of 100,913. The city is largely situated on the east bank of the river IJssel, bu ...
, Groningen
Groningen (; gos, Grunn or ) is the capital city and main municipality of Groningen province in the Netherlands. The ''capital of the north'', Groningen is the largest place as well as the economic and cultural centre of the northern part of t ...
, Nijmegen
Nijmegen (;; Spanish and it, Nimega. Nijmeegs: ''Nimwèège'' ) is the largest city in the Dutch province of Gelderland and tenth largest of the Netherlands as a whole, located on the Waal river close to the German border. It is about 6 ...
and Zutphen
Zutphen () is a city and municipality located in the province of Gelderland, Netherlands. It lies some 30 km northeast of Arnhem, on the eastern bank of the river Ijssel at the point where it is joined by the Berkel. First mentioned in the 1 ...
.
In 1592, Farnese died of wounds and exhaustion. Philip II died in 1598. As the period of sieges subsided, the War of Liberation continued. Archduke Albert and Isabel of Austria were given sovereign rights in the Netherlands forming a truce in 1609 that gave the Dutch a brief respite from war. But, in 1621, 12 years later, the war resumed when the Netherlands reverted to Spain when Albert and Isabel died childless. This period never experienced the fury of the early sieges; however, the struggle for independence went on. Attacks on Dutch border towns were made by Spinola Spinola is a surname. Notable people with the surname include:
* Agostino Spinola (d. 1537), Italian cardinal
* Alberto Spinola (born 1943), Italian water polo player
* Ambrogio Spinola, 1st Marquis of the Balbases (1569–1630), Genoese banker an ...
, an Italian banker who pledged allegiance to Spain. Spain made progress in trying to suppress the Dutch but the Dutch recovered. They were financially supported by France and the money was poured into ships since Spain's control of the seas had been broken by England. Deeply involved in the Thirty Years' War
The Thirty Years' War was one of the longest and most destructive conflicts in European history
The history of Europe is traditionally divided into four time periods: prehistoric Europe (prior to about 800 BC), classical antiquity (80 ...
, Spain decided to yield everything to the Dutch in order to be free to fight the French. The Treaty of Münster Treaty of Münster refers to two treaties signed in 1648, and forming part of the Peace of Westphalia ending the Thirty Years' War:
* Peace of Münster
The Peace of Münster was a treaty between the Lords States General of the Seven United N ...
was signed on 30 January 1648, ending the War of Liberation.
France
In 1532, KingFrancis I Francis I or Francis the First may refer to:
* Francesco I Gonzaga (1366–1407)
* Francis I, Duke of Brittany (1414–1450), reigned 1442–1450
* Francis I of France (1494–1547), King of France, reigned 1515–1547
* Francis I, Duke of Saxe-Lau ...
intervened politically and militarily in support of Protestant German princes against the Habsburgs, as did King Henry II in 1551; both kings firmly repressed attempts to spread Lutheran ideas within France. An organised influx of Calvinist preachers from Geneva
Geneva ( ; french: Genève ) frp, Genèva ; german: link=no, Genf ; it, Ginevra ; rm, Genevra is the List of cities in Switzerland, second-most populous city in Switzerland (after Zürich) and the most populous city of Romandy, the French-speaki ...
and elsewhere during the 1550s succeeded in setting up hundreds of underground Calvinist congregations in France.
1560s
Calvinist
Calvinism (also called the Reformed Tradition, Reformed Protestantism, Reformed Christianity, or simply Reformed) is a major branch of Protestantism that follows the theological tradition and forms of Christian practice set down by John Ca ...
preaching and the formation of covert alliances with members of the nobility quickly led to more direct action to gain political and religious control. The prospect of taking over rich church properties and monastic lands had led nobles in many parts of Europe to support a princely Reformation. Added to this was the Calvinist teaching that leading citizens had the duty to overthrow what they perceive as an ungodly ruler (i.e. one who was not supportive of Calvinism). In March 1560, the "Amboise conspiracy
The Amboise conspiracy, also called Tumult of Amboise, was a failed attempt by a Huguenot faction in France to gain control over the young king Francis II and to reverse the policies of the current administration of Francis, Duke of Guise and Cha ...
", or "Tumult of Amboise", was an attempt on the part of a group of disaffected nobles to abduct the young king Francis II and eliminate the Catholic House of Guise
The House of Guise (pronunciation: �ɥiz Dutch: ''Wieze, German: Wiese'') was a prominent French noble family, that was involved heavily in the French Wars of Religion. The House of Guise was the founding house of the Principality of Joinvill ...
. It was foiled when their plans were discovered. The first major instances of systematic Protestant destruction of images and statues in Catholic churches occurred in Rouen
Rouen (, ; or ) is a city on the River Seine in northern France. It is the prefecture of the Regions of France, region of Normandy (administrative region), Normandy and the Departments of France, department of Seine-Maritime. Formerly one of ...
and La Rochelle
La Rochelle (, , ; Poitevin-Saintongeais: ''La Rochéle''; oc, La Rochèla ) is a city on the west coast of France and a seaport on the Bay of Biscay, a part of the Atlantic Ocean. It is the capital of the Charente-Maritime department. With ...
in 1560. The following year, the attacks extended to over 20 cities and towns, and would, in turn, incite Catholic urban groups to massacres and riots in Sens
Sens () is a Communes of France, commune in the Yonne Departments of France, department in Bourgogne-Franche-Comté in north-central France, 120 km from Paris.
Sens is a Subprefectures in France, sub-prefecture and the second city of the d ...
, Cahors
Cahors (; oc, Caors ) is a commune in the western part of Southern France. It is the smallest prefecture among the 13 departments that constitute the Occitanie Region. The main city of the Lot department and the historical center of the Quer ...
, Carcassonne
Carcassonne (, also , , ; ; la, Carcaso) is a French fortified city in the department of Aude, in the region of Occitanie. It is the prefecture of the department.
Inhabited since the Neolithic, Carcassonne is located in the plain of the ...
, Tours
Tours ( , ) is one of the largest cities in the region of Centre-Val de Loire, France. It is the Prefectures in France, prefecture of the Departments of France, department of Indre-et-Loire. The Communes of France, commune of Tours had 136,463 ...
and other cities.
In December 1560, Francis II died, and Catherine de' Medici
Catherine de' Medici ( it, Caterina de' Medici, ; french: Catherine de Médicis, ; 13 April 1519 – 5 January 1589) was an Florentine noblewoman born into the Medici family. She was Queen of France from 1547 to 1559 by marriage to King ...
became regent for her young son Charles IX. Although a Roman Catholic
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
*Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*'' Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a lette ...
, she was prepared to deal favourably with the Huguenot
The Huguenots ( , also , ) were a religious group of French Protestants who held to the Reformed, or Calvinist, tradition of Protestantism. The term, which may be derived from the name of a Swiss political leader, the Genevan burgomaster Be ...
House of Bourbon
The House of Bourbon (, also ; ) is a European dynasty of French origin, a branch of the Capetian dynasty, the royal House of France. Bourbon kings first ruled France and Navarre in the 16th century. By the 18th century, members of the Spanis ...
. She therefore supported religious toleration in the shape of the Edict of Saint-Germain
The Edict of Saint-Germain, also known as the Edict of January, was a landmark decree of tolerance promulgated by the regent of France, Catherine de' Medici, in January 1562. The act represented the culmination of several years of slowly libera ...
(January 1562), which allowed the Huguenots to worship publicly outside of towns and privately inside of them. On 1 March, a faction of the Guise family's retainers attacked an illegal Calvinist service in Wassy-sur-Blaise
Wassy () is a commune in the Haute-Marne department in north-eastern France. Its population, as of 2019, is 2,819. Wassy has been twinned with the German town of Eppingen in north-west Baden-Württemberg since 1967.
History
On 1 March 1562, a ...
in Champagne
Champagne (, ) is a sparkling wine originated and produced in the Champagne wine region of France under the rules of the appellation, that demand specific vineyard practices, sourcing of grapes exclusively from designated places within it, spe ...
. As hostilities broke out, the Edict was revoked.
This provoked the First War. The Bourbons, with English support and led by Louis I de Bourbon, Prince de Condé Louis may refer to:
* Louis (coin)
* Louis (given name), origin and several individuals with this name
* Louis (surname)
* Louis (singer), Serbian singer
* HMS ''Louis'', two ships of the Royal Navy
See also
Derived or associated terms
* Lewis ( ...
, and Admiral Coligny
Gaspard de Coligny (16 February 1519 – 24 August 1572), Seigneur de Châtillon, was a French nobleman, Admiral of France, and Huguenot leader during the French Wars of Religion. He served under kings Francis I and Henry II during the Ita ...
, began to seize and garrison strategic towns along the Loire
The Loire (, also ; ; oc, Léger, ; la, Liger) is the longest river in France and the 171st longest in the world. With a length of , it drains , more than a fifth of France's land, while its average discharge is only half that of the Rhône ...
. The Battle of Dreux
The Battle of Dreux was fought on 19 December 1562 between Catholics and Huguenots. The Catholics were led by Anne de Montmorency while Louis I, Prince of Condé, led the Huguenots. Though commanders from both sides were captured, the French Cat ...
and the battle of Orléans
Orléans (;"Orleans"
(US) and Francis, Duke of Guise Francis de Lorraine II, the first Prince of Joinville, also Duke of Guise and Duke of Aumale (french: François de Lorraine; 17 February 1519 – 24 February 1563), was a French general and statesman. A prominent leader during the Italian War of ...
was assassinated, and Catherine's fears that the war might drag on led her to mediate a truce and the (US) and Francis, Duke of Guise Francis de Lorraine II, the first Prince of Joinville, also Duke of Guise and Duke of Aumale (french: François de Lorraine; 17 February 1519 – 24 February 1563), was a French general and statesman. A prominent leader during the Italian War of ...
Edict of Amboise
The Edict of Amboise, also known as the Edict of Pacification, was signed at the Château of Amboise on 19 March 1563 by Catherine de' Medici, acting as regent for her son Charles IX of France. The Edict ended the first stage of the French War ...
(1563), which again provided for a controlled religious toleration of Protestant worship.
However, this was generally regarded as unsatisfactory by both Catholics and Protestants. The political temperature of the surrounding lands was rising, as religious unrest grew in the Netherlands. The Huguenots tried to gain French government support for intervention against the Spanish forces arriving in the Netherlands. Failing this, Protestant troops then made an unsuccessful attempt to capture and take control of King Charles IX at Meaux in 1567. This provoked a further outbreak of hostilities (the Second War), which ended in another unsatisfactory truce, the Peace of Longjumeau
The Peace of Longjumeau (also known as the Treaty of Longjumeau or the Edict of Longjumeau) was signed on 23 March 1568 by Charles IX of France and Catherine de' Medici. The edict brought to an end the brief second French Wars of Religion with t ...
(March 1568).
In September of that year, war again broke out (the Third War). Catherine and Charles decided this time to ally themselves with the House of Guise. The Huguenot army was under the command of Louis I de Bourbon, prince de Condé Louis may refer to:
* Louis (coin)
* Louis (given name), origin and several individuals with this name
* Louis (surname)
* Louis (singer), Serbian singer
* HMS ''Louis'', two ships of the Royal Navy
See also
Derived or associated terms
* Lewis ( ...
, and aided by forces from south-eastern France and a contingent of Protestant militias from Germany—including 14,000 mercenary ''reiter
''Reiter'' or ''Schwarze Reiter'' ("black riders", anglicized ''swart reiters'') were a type of cavalry in 16th to 17th century Central Europe including Holy Roman Empire, Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, Tsardom of Russia, and others.
...
s'' led by the Calvinist Duke of Zweibrücken. After the Duke was killed in action, he was succeeded by the Count of Mansfeld
Peter Ernst, Graf von Mansfeld (german: Peter Ernst Graf von Mansfeld; c. 158029 November 1626), or simply Ernst von Mansfeld, was a German military commander who, despite being a Catholic, fought for the Protestants during the early years of the ...
and the Dutch William of Orange and his brothers Louis and Henry. Much of the Huguenots' financing came from Queen Elizabeth I of England
Elizabeth I (7 September 153324 March 1603) was List of English monarchs, Queen of England and List of Irish monarchs, Ireland from 17 November 1558 until her death in 1603. Elizabeth was the last of the five House of Tudor monarchs and is ...
. The Catholics were commanded by the Duke d'Anjou (later King Henry III) and assisted by troops from Spain, the Papal States
The Papal States ( ; it, Stato Pontificio, ), officially the State of the Church ( it, Stato della Chiesa, ; la, Status Ecclesiasticus;), were a series of territories in the Italian Peninsula under the direct sovereign rule of the pope fro ...
and the Grand Duchy of Tuscany
The Grand Duchy of Tuscany ( it, Granducato di Toscana; la, Magnus Ducatus Etruriae) was an Italian monarchy that existed, with interruptions, from 1569 to 1859, replacing the Republic of Florence. The grand duchy's capital was Florence. In th ...
.
 The Protestant army laid siege to several cities in the
The Protestant army laid siege to several cities in the Poitou
Poitou (, , ; ; Poitevin: ''Poetou'') was a province of west-central France whose capital city was Poitiers. Both Poitou and Poitiers are named after the Pictones Gallic tribe.
Geography
The main historical cities are Poitiers (historical c ...
and Saintonge
Saintonge may refer to:
*County of Saintonge, a historical province of France on the Atlantic coast
*Saintonge (region), a region of France corresponding to the historical province
Places
*Saint-Genis-de-Saintonge, a commune in the Charente-Mari ...
regions (to protect La Rochelle
La Rochelle (, , ; Poitevin-Saintongeais: ''La Rochéle''; oc, La Rochèla ) is a city on the west coast of France and a seaport on the Bay of Biscay, a part of the Atlantic Ocean. It is the capital of the Charente-Maritime department. With ...
), and then Angoulême
Angoulême (; Poitevin-Saintongeais: ''Engoulaeme''; oc, Engoleime) is a communes of France, commune, the Prefectures of France, prefecture of the Charente Departments of France, department, in the Nouvelle-Aquitaine region of southwestern Franc ...
and Cognac
Cognac ( , also , ) is a variety of brandy named after the Communes of France, commune of Cognac, France. It is produced in the surrounding wine-growing region in the Departments of France, departments of Charente and Charente-Maritime.
Cog ...
. At the Battle of Jarnac
The Battle of Jarnac on 13 March 1569 was an encounter during the French Wars of Religion between the Catholic forces of Marshal Gaspard de Saulx, sieur de Tavannes, and the Huguenots led by Louis I de Bourbon, prince de Condé The two forces met ...
(16 March 1569), the Prince de Condé was killed, forcing Admiral de Coligny
Gaspard de Coligny (16 February 1519 – 24 August 1572), Seigneur de Châtillon, was a French nobleman, Admiral of France, and Huguenot leader during the French Wars of Religion. He served under kings Francis I and Henry II during the Ita ...
to take command of the Protestant forces. Coligny and his troops retreated to the south-west and regrouped with Gabriel, comte de Montgomery
Gabriel de Lorges, Count of Montgomery, Lord of Lorges and Ducey (5 May 153026 June 1574), was a French nobleman of Scottish extraction and captain of the Scots Guard of King Henry II of France. He is remembered for mortally injuring Henry II i ...
, and in spring of 1570 they pillaged Toulouse
Toulouse ( , ; oc, Tolosa ) is the prefecture of the French department of Haute-Garonne and of the larger region of Occitania. The city is on the banks of the River Garonne, from the Mediterranean Sea, from the Atlantic Ocean and from Par ...
, cut a path through the south of France and went up the Rhone valley to La Charité-sur-Loire
La Charité-sur-Loire (before 1961: ''La Charité'') is a commune in the Nièvre department and Bourgogne-Franche-Comté region of eastern France.
Geography
La Charité-sur-Loire lies on the right, eastern bank of the river Loire, about 25 km no ...
. The staggering royal debt and Charles IX's desire to seek a peaceful solution led to the Peace of Saint-Germain-en-Laye
The Peace of Saint-Germain-en-Laye was signed on 8 August 1570 by Charles IX of France, Gaspard II de Coligny and Jeanne d'Albret, and ended the 1568 to 1570 Third Civil War, part of the French Wars of Religion.
The Peace went much further tha ...
(8 August 1570), which once more allowed some concessions to the Huguenots. In 1572, rising tensions between local Catholics and Protestant forces attending the wedding of the Protestant Henry of Navarre, and the King's sister, Marguerite de Valois, culminated in the Saint Bartholomew's Day Massacre
The St. Bartholomew's Day massacre (french: Massacre de la Saint-Barthélemy) in 1572 was a targeted group of assassinations and a wave of Catholic mob violence, directed against the Huguenots (French Calvinist Protestants) during the French War ...
. This led to the Fourth and Fifth Civil wars in 1572 and 1573–1576.
Henry III
Henry of Anjou was crowned KingHenry III of France
Henry III (french: Henri III, né Alexandre Édouard; pl, Henryk Walezy; lt, Henrikas Valua; 19 September 1551 – 2 August 1589) was King of France from 1574 until his assassination in 1589, as well as King of Poland and Grand Duke of ...
in 1575, at Reims
Reims ( , , ; also spelled Rheims in English) is the most populous city in the French department of Marne, and the 12th most populous city in France. The city lies northeast of Paris on the Vesle river, a tributary of the Aisne.
Founded by ...
, but hostilities—the Fifth War—had already flared up again. Henry soon found himself in the difficult position of trying to maintain royal authority in the face of feuding warlord
A warlord is a person who exercises military, economic, and political control over a region in a country without a strong national government; largely because of coercive control over the armed forces. Warlords have existed throughout much of h ...
s who refused to compromise. In 1576, the King signed the Edict of Beaulieu
The Edict of Beaulieu (also known at the time as the Peace of Monsieur) was promulgated from Beaulieu-lès-Loches on 6 May 1576 by Henry III of France, who was pressured by Alençon's support of the Protestant army besieging Paris that spring.
Th ...
, granting minor concessions to the Calvinists, but a brief Sixth Civil War took place in 1577. Henry I, Duke of Guise
Henry I, Prince of Joinville, Duke of Guise, Count of Eu (31 December 1550 – 23 December 1588), sometimes called ('Scarface'), was the eldest son of Francis, Duke of Guise, and Anna d'Este. His maternal grandparents were Ercole II d'Este, Du ...
, formed the Catholic League to protect the Catholic cause in France. Further hostilities—the Seventh War (1579–1580)—ended in the stalemate of the Treaty of Fleix
The Treaty of Fleix (also known as the Edict of Fleix and the Peace of Fleix) was signed on 26 November 1580 by Henry III of France in Le Fleix. Negotiated by François, Duke of Anjou, who wished to focus military efforts on the Netherlands, the ...
.
The fragile compromise came to an end in 1584, when the King's youngest brother and heir presumptive, François, Duke of Anjou
''Monsieur'' Francis, Duke of Anjou and Alençon (french: Hercule François; 18 March 1555 – 10 June 1584) was the youngest son of King Henry II of France and Catherine de' Medici.
Early years
He was scarred by smallpox at age eight, an ...
, died. As Henry III had no son, under Salic Law
The Salic law ( or ; la, Lex salica), also called the was the ancient Frankish civil law code compiled around AD 500 by the first Frankish King, Clovis. The written text is in Latin and contains some of the earliest known instances of Old Du ...
, the next heir to the throne was the Calvinist Prince Henry of Navarre
Henry IV (french: Henri IV; 13 December 1553 – 14 May 1610), also known by the epithets Good King Henry or Henry the Great, was King of Navarre (as Henry III) from 1572 and King of France from 1589 to 1610. He was the first monarch ...
. Under pressure from the Duke of Guise, Henry III reluctantly issued an edict suppressing Protestantism and annulling Henry of Navarre's right to the throne.
In December 1584, the Duke of Guise signed the Treaty of Joinville
The Treaty of Joinville was signed in secret on 31 December 1584 by the Catholic League, led by France's first family of Catholic nobles, the House of Guise, and Habsburg Spain.
Treaty provisions
In the treaty:
* Philip II of Spain agreed to fi ...
on behalf of the Catholic League with Philip II of Spain
Philip II) in Spain, while in Portugal and his Italian kingdoms he ruled as Philip I ( pt, Filipe I). (21 May 152713 September 1598), also known as Philip the Prudent ( es, Felipe el Prudente), was King of Spain from 1556, King of Portugal from ...
, who supplied a considerable annual grant to the League. The situation degenerated into the Eighth War (1585–1589). Henry of Navarre again sought foreign aid from the German princes and Elizabeth I of England
Elizabeth I (7 September 153324 March 1603) was List of English monarchs, Queen of England and List of Irish monarchs, Ireland from 17 November 1558 until her death in 1603. Elizabeth was the last of the five House of Tudor monarchs and is ...
. Meanwhile, the solidly Catholic people of Paris, under the influence of the Committee of Sixteen, were becoming dissatisfied with Henry III and his failure to defeat the Calvinists. On 12 May 1588, a popular uprising raised barricades on the streets of Paris, and Henry III fled the city. The Committee of Sixteen took complete control of the government and welcomed the Duke of Guise to Paris. The Guises then proposed a settlement with a cipher as heir and demanded a meeting of the Estates-General, which was to be held in Blois
Blois ( ; ) is a commune and the capital city of Loir-et-Cher department, in Centre-Val de Loire, France, on the banks of the lower Loire river between Orléans and Tours.
With 45,898 inhabitants by 2019, Blois is the most populated city of the ...
.
King Henry decided to strike first. On 23 December 1588 at the Château de Blois
A château (; plural: châteaux) is a manor house or residence of the lord of the manor, or a fine country house of nobility or gentry, with or without fortifications, originally, and still most frequently, in French-speaking regions.
Nowaday ...
, Henry of Guise and his brother, the Cardinal de Guise, were lured into a trap and were murdered. The Duke of Guise had been highly popular in France, and the league declared open war against King Henry. The Parliament of Paris
The Parliament of Paris (french: Parlement de Paris) was the oldest ''parlement'' in the Kingdom of France, formed in the 14th century. It was fixed in Paris by Philip IV of France in 1302. The Parliament of Paris would hold sessions inside the ...
instituted criminal charges against the King, who now joined forces with his cousin, Henry of Navarre, to war against the League.
Charles of Lorraine, Duke of Mayenne
Charles of Lorraine, Duke of Mayenne (26 March 1554 – 3 October 1611), or Charles de Guise, was a French nobleman of the house of Guise and a military leader of the Catholic League, which he headed during the French Wars of Religion, followi ...
, then became the leader of the Catholic League. League presses began printing anti-royalist tracts under a variety of pseudonyms, while the Sorbonne
Sorbonne may refer to:
* Sorbonne (building), historic building in Paris, which housed the University of Paris and is now shared among multiple universities.
*the University of Paris (c. 1150 – 1970)
*one of its components or linked institution, ...
proclaimed that it was just and necessary to depose Henry III. In July 1589, in the royal camp at Saint-Cloud
Saint-Cloud () is a commune in the western suburbs of Paris, France, from the centre of Paris. Like other communes of Hauts-de-Seine such as Marnes-la-Coquette, Neuilly-sur-Seine and Vaucresson, Saint-Cloud is one of France's wealthiest towns ...
, a monk named Jacques Clément
Jacques Clément (1567 – 1 August 1589) was a French conspirator and the assassin of King Henry III.
He was born at Serbonnes, in today's Yonne ''département'', in Burgundy, and became a Dominican lay brother.
During the French Wars of Re ...
gained an audience with the King and drove a long knife into his spleen. Clément was executed on the spot, taking with him the information of who, if anyone, had hired him. On his deathbed, Henry III called for Henry of Navarre and begged him, in the name of Statecraft, to become a Catholic, citing the brutal warfare that would ensue if he refused. In keeping with Salic Law
The Salic law ( or ; la, Lex salica), also called the was the ancient Frankish civil law code compiled around AD 500 by the first Frankish King, Clovis. The written text is in Latin and contains some of the earliest known instances of Old Du ...
, he named Henry as his heir.
Henry IV
The situation on the ground in 1589 was that KingHenry IV of France
Henry IV (french: Henri IV; 13 December 1553 – 14 May 1610), also known by the epithets Good King Henry or Henry the Great, was King of Navarre (as Henry III) from 1572 and King of France from 1589 to 1610. He was the first monarc ...
, as Navarre had become, held the south and west, and the Catholic League the north and east. The leadership of the Catholic League had devolved to the Duke de Mayenne, who was appointed Lieutenant-General of the kingdom. He and his troops controlled most of rural Normandy. However, in September 1589, Henry inflicted a severe defeat on the Duke at the Battle of Arques. Henry's army swept through Normandy, taking town after town throughout the winter.
 The King knew that he had to take Paris if he stood any chance of ruling all of France, and this was no easy task. The Catholic League's presses and supporters continued to spread stories about atrocities committed against Catholic priests and the laity in Protestant England, such as the Forty Martyrs of England and Wales. The city prepared to fight to the death rather than accept a Calvinist king. The Battle of Ivry, fought on 14 March 1590, was another victory for the king, and Henry's forces went on to lay siege to Paris, but the siege was broken by Spanish support. Realising that his predecessor had been right and that there was no prospect of a Protestant king succeeding in Catholic Paris, Henry reputedly uttered the famous phrase ''Paris vaut bien une messe'' ("Paris is well worth a Mass"). He was formally received into the Roman Catholic Church in 1593 and was crowned at Chartres in 1594.
Some members of the League fought on, but enough Catholics were won over by the King's conversion to increasingly isolate the diehards. The Spanish withdrew from France under the terms of the Peace of Vervins. Henry was faced with the task of rebuilding a shattered and impoverished Kingdom and reuniting France under a single authority. The wars concluded in 1598, when Henry IV issued the Edict of Nantes, which granted a degree of religious toleration to Protestants.
France, although always ruled by a Catholic monarch, had played a major part in supporting the Protestants in Germany and the Netherlands against their dynastic rivals, the Habsburgs. The period of the French Wars of Religion effectively removed France's influence as a major European power, allowing the Catholic forces in the Holy Roman Empire to regroup and recover.
The King knew that he had to take Paris if he stood any chance of ruling all of France, and this was no easy task. The Catholic League's presses and supporters continued to spread stories about atrocities committed against Catholic priests and the laity in Protestant England, such as the Forty Martyrs of England and Wales. The city prepared to fight to the death rather than accept a Calvinist king. The Battle of Ivry, fought on 14 March 1590, was another victory for the king, and Henry's forces went on to lay siege to Paris, but the siege was broken by Spanish support. Realising that his predecessor had been right and that there was no prospect of a Protestant king succeeding in Catholic Paris, Henry reputedly uttered the famous phrase ''Paris vaut bien une messe'' ("Paris is well worth a Mass"). He was formally received into the Roman Catholic Church in 1593 and was crowned at Chartres in 1594.
Some members of the League fought on, but enough Catholics were won over by the King's conversion to increasingly isolate the diehards. The Spanish withdrew from France under the terms of the Peace of Vervins. Henry was faced with the task of rebuilding a shattered and impoverished Kingdom and reuniting France under a single authority. The wars concluded in 1598, when Henry IV issued the Edict of Nantes, which granted a degree of religious toleration to Protestants.
France, although always ruled by a Catholic monarch, had played a major part in supporting the Protestants in Germany and the Netherlands against their dynastic rivals, the Habsburgs. The period of the French Wars of Religion effectively removed France's influence as a major European power, allowing the Catholic forces in the Holy Roman Empire to regroup and recover.
Denmark–Norway
Denmark
In 1524, King Christian II of Denmark, Christian II converted to Lutheranism and encouraged Lutheran preachers to enter Denmark despite the opposition of the Danish diet of 1524. Following the death of King Frederick I of Denmark, Frederick I in 1533, Count's Feud, war broke out between Catholic followers of Count Christoph of Oldenburg and the firmly Lutheran Christian III of Denmark, Count Christian of Holstein. After losing his main support in Lübeck, Christoph quickly fell to defeat, finally losing his last stronghold of Copenhagen in 1536. Lutheranism was immediately established, the Catholic bishops were imprisoned, and monastic and church lands were soon confiscated to pay for the armies that had brought Christian to power. In Denmark, this increased royal revenues by 300%.Norway, Faroe Islands, and Iceland
Christian III established Lutheranism by force in Norway in 1537, Faroe Islands in Catholic Church in the Faroe Islands#Protestant Reformation, 1540, and Iceland in Battle of Sauðafell, 1550. In 1536/1537, he also made Norway a Denmark-Norway, puppet state under the Danish crown. It would be a puppet state until 1814, when Frederick VI of Denmark, Frederick VI renounced his claims to the Crown of Norway in favor of the King of Sweden as part of the Treaty of Kiel.Thirty Years' War
In 1625, as part of theThirty Years' War
The Thirty Years' War was one of the longest and most destructive conflicts in European history
The history of Europe is traditionally divided into four time periods: prehistoric Europe (prior to about 800 BC), classical antiquity (80 ...
, Christian IV of Denmark, Christian IV, who was also the Duke of Holstein, agreed to help the Lutheran rulers of neighbouring Lower Saxony against the forces of the Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a Polity, political entity in Western Europe, Western, Central Europe, Central, and Southern Europe that developed during the Early Middle Ages and continued until its Dissolution of the Holy Roman Empire, dissolution i ...
by intervening militarily. Denmark's cause was aided by France, which, together with England, had agreed to help subsidize the war. Christian had himself appointed war leader of the Lower Saxon Alliance and raised an army of 20,000–35,000 mercenaries. Christian, however, was forced to retire before the combined forces of Imperial generals Albrecht von Wallenstein and General Tilly, Tilly. Wallenstein's army marched north, occupying Mecklenburg, Pomerania, and ultimately Jutland. However, lacking a fleet, he was unable to take the Danish capital on the island of Zealand (Denmark), Zealand. Peace negotiations were concluded in the Treaty of Lübeck in 1629, which stated that Christian IV could keep his control over Denmark-Norway if he would abandon his support for the Protestant German states.
Great Britain and Ireland
The Reformation came to Britain and Ireland with King Henry VIII of England's breach with the Catholic Church in 1533. At this time there were only a limited number of Protestants among the general population, and these were mostly living in the towns of the South and the East of England. With the state-ordered break with the Pope in Rome, the Church in England, Wales and Ireland was placed under the rule of the King and Parliament. The first major changes to doctrine and practice took place under Vicar-General Thomas Cromwell, and the newly appointed Protestant-leaning Archbishop of Canterbury, Thomas Cranmer. The first challenge to the institution of these reforms came from Ireland, where "Silken" Thomas FitzGerald, 10th Earl of Kildare, Thomas Fitzgerald cited the controversy to justify his armed uprising of 1534. The young Fitzgerald failed to gain much local support, however, and in October a 1,600 strong army of English and Welshmen arrived in Ireland, along with four modern siege-guns. The following year Fitzgerald was blasted into submission, and in August he was induced to surrender. Shortly after this episode, local resistance to the reforms emerged in England. The dissolution of the monasteries, which began in 1536, provoked a violent northern Catholic rebellion in the Pilgrimage of Grace, which was eventually put down with much bloodshed. The reformation continued to be imposed on an often unwilling population with the aid of stern laws that made it treason, punishable by death, to oppose the King's actions with respect to religion. The next major armed resistance took place in thePrayer Book Rebellion
The Prayer Book Rebellion or Western Rising was a popular revolt in Cornwall and Devon in 1549. In that year, the ''Book of Common Prayer'', presenting the theology of the English Reformation, was introduced. The change was widely unpopular, ...
of 1549, which was an unsuccessful rising in western England against the enforced substitution of Cranmer's English language service for the Latin Catholic Mass.
Following the restoration of Catholicism under Queen Mary I of England
Mary I (18 February 1516 – 17 November 1558), also known as Mary Tudor, and as "Bloody Mary" by her Protestant opponents, was Queen of England and Ireland from July 1553 and Queen of Spain from January 1556 until her death in 1558. Sh ...
in 1553, there was a brief unsuccessful Protestant rising in the south-east of England.
Scottish Reformation
The Reformation in Scotland began in conflict. Fiery Calvinist preacher John Knox returned to Scotland in 1560, having been exiled for his part in the assassination of Cardinal Beaton. He proceeded to Dundee where a large number of Protestant sympathisers and noblemen had gathered. Knox was declared an outlaw by the Queen Regent, Mary of Guise, but the Protestants went at once to Perth, Scotland, Perth, a walled town that could be defended in case of a siege. At the church of St John the Baptist, Knox preached a fiery sermon that provoked an iconoclastic riot. A mob poured into the church and it was entirely gutted. In the pattern of Calvinist riots in France and the Netherlands, the mob then attacked two friaries in the town, looting their gold and silver and smashing images. Mary of Guise gathered those nobles loyal to her and a small French army. With Protestant reinforcements arriving from neighbouring counties, the queen regent retreated to Dunbar. By now, Calvinist mobs had overrun much of Central Lowlands, central Scotland, destroying monasteries and Catholic churches as they went. On 30 June, the Protestants occupied Edinburgh, though they were only able to hold it for a month. Even before their arrival, the mob had already sacked the churches and the friaries. On 1 July, Knox preached from the pulpit of St Giles' Cathedral, St Giles', the most influential in the capital. Knox negotiated by letter with William Cecil, 1st Baron Burghley, Elizabeth I of England, Elizabeth's chief advisor, for English support. When additional French troops arrived in Leith, Edinburgh's seaport, the Protestants responded by retaking Edinburgh. This time, on 24 October 1559, the Scottish nobility formally deposed Mary of Guise from the regency. Her secretary, William Maitland of Lethington, defected to the Protestant side, bringing his administrative skills. For the final stage of the revolution, Maitland appealed to Scottish patriotism to fight French domination. Support from England finally arrived and by the end of March, a significant English army joined the Scottish Protestant forces. The sudden death of Mary of Guise in Edinburgh Castle on 10 June 1560 paved the way for the signing of the Treaty of Edinburgh, and the withdrawal of French and English troops from Scotland, leaving the Scottish Calvinists in control on the ground. Catholicism was forcibly suppressed. The return of Mary, Queen of Scots, to Scotland in 1560, led to further tension between her and the Protestant Lords of the Congregation. Mary claimed to favour religious toleration on the French model, however the Protestant establishment feared a reestablishment of Catholicism, and sought with English help to neutralise or depose Mary. Mary's marriage to a leading Catholic precipitated Mary's half-brother, the Earl of Moray, to join with other Protestant Lords in open rebellion. Mary set out for Stirling on 26 August 1565 to confront them. Moray and the rebellious lords were routed and fled into exile; the decisive military action becoming known as the Chaseabout Raid. In 1567, Mary was captured by another rebellious force at the Battle of Carberry Hill and imprisoned in Loch Leven Castle, where she was forced to abdicate the Scottish throne in favour of her one-year-old son James. Mary escaped from Loch Leven (Kinross), Loch Leven the following year, and once again managed to raise a small army. After her army's defeat at the Battle of Langside on 13 May, she fled to England, where she was imprisoned by Queen Elizabeth I of England, Elizabeth. Her son James I of England, James VI was raised as a Protestant, later becoming King of England as well as Scotland. The Rising of the North from 1569 to 1570 was an unsuccessful attempt by Catholic nobles from Northern England to depose Queen Elizabeth I and replace her with Mary, Queen of Scots.English Civil War
England
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Wales to its west and Scotland to its north. The Irish Sea lies northwest and the Celtic Sea to the southwest. It is separated from continental Europe b ...
, Scotland
Scotland (, ) is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. Covering the northern third of the island of Great Britain, mainland Scotland has a border with England to the southeast and is otherwise surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean to the ...
and Kingdom of Ireland, Ireland, in personal union under the Stuart king, James I of England, James I & VI, continued Elizabeth I's policy of providing military support to European Protestants in the Netherlands and France. King Charles I of England, Charles I decided to send an expeditionary force to relieve the French Huguenots whom Royal French forces held besieged in La Rochelle
La Rochelle (, , ; Poitevin-Saintongeais: ''La Rochéle''; oc, La Rochèla ) is a city on the west coast of France and a seaport on the Bay of Biscay, a part of the Atlantic Ocean. It is the capital of the Charente-Maritime department. With ...
. However tax-raising authority for these wars was getting harder and harder to raise from parliament.
In 1638 the Scottish National Covenant was signed by aggrieved presbyterian lords and commoners. A Scottish rebellion, known as the Bishops War, soon followed, leading to the defeat of a weak royalist counter-force in 1640. The rebels went on to capture Newcastle upon Tyne, further weakening King Charles' authority.
In October 1641, a major rebellion broke out in Ireland. Charles soon needed to raise more money to suppress this Irish rebellion of 1641, Irish Rebellion. Meanwhile, English Puritans and Scottish Calvinism, Calvinists intensely opposed the king's main religious policy of unifying the Church of England
The Church of England (C of E) is the established Christian church in England and the mother church of the international Anglican Communion. It traces its history to the Christian church recorded as existing in the Roman province of Britain ...
and the Church of Scotland under a form of High Church Anglicanism. This, its opponents believed, was far too catholic in form, and based on the authority of bishops.
The English parliament refused to vote enough money for Charles to defeat the Scots without the King giving up much of his authority and reforming the English church along more Calvinist lines. This the king refused, and deteriorating relations led to the outbreak of war in 1642. The first pitched battle of the war, fought at Battle of Edgehill, Edgehill on 23 October 1642, proved inconclusive, and both the Royalists and Parliamentarians claimed it as a victory. The second field action of the war was a stand-off at Turnham Green (Battle), Turnham Green, and Charles was forced to withdraw to Oxford, which would serve as his base for the remainder of the war.
In general, the early part of the war went well for the Royalists. The turning-point came in the late summer and early autumn of 1643, when the Earl of Essex's army forced the king to raise the siege of Gloucester and then brushed the Royalist army aside at the First Battle of Newbury on 20 September 1643. In an attempt to gain an advantage in numbers Charles negotiated a ceasefire with the Catholic rebels in Ireland, freeing up English troops to fight on the Royalist side in England. Simultaneously Parliament offered concessions to the Scots in return for their aid and assistance.
With the help of the Scots, Parliament won at Battle of Marston Moor, Marston Moor (2 July 1644), gaining York and much of the north of England. Oliver Cromwell's conduct in this battle proved decisive, and demonstrated his leadership potential. In 1645 Parliament passed the Self-denying Ordinance, by which all members of either House of Parliament laid down their commands, allowing the re-organization of its main forces into the New Model Army. By 1646 Charles had been forced to surrender himself to the Scots, and the parliamentary forces were in control of England. Charles was executed in 1649, and the monarchy was not English Restoration, restored until 1660. Even then, religious strife continued through the Glorious Revolution
The Glorious Revolution; gd, Rèabhlaid Ghlòrmhor; cy, Chwyldro Gogoneddus , also known as the ''Glorieuze Overtocht'' or ''Glorious Crossing'' in the Netherlands, is the sequence of events leading to the deposition of King James II and ...
and thereafter.
Ireland
The wars of religion in Ireland took place in the context of a country that had already rebelled frequently against English rule in the previous decades. In 1534, Thomas FitzGerald, 10th Earl of Kildare, Thomas Fitzgerald, known as Silken Thomas, had led what was called the Silken Thomas Rebellion. In the province of Ulster in the North of the country, Shane O'Neill (Irish chieftain), Shane O'Neill's Rebellion occurred from 1558 to 1567, and in the South of the Country the Desmond Rebellions occurred in 1569–1573 and 1579–1583 in the province of Munster. Ireland entered into a continuous state of war with the Irish Rebellion of 1641, rebellion of 1641, with most of the island controlled by the Confederate Ireland, Irish Confederates. Increasingly threatened by the armies of the English Parliament after Charles I's arrest in 1648, the Confederates signed a treaty of alliance with the English Royalists. The joint Royalist and Confederate forces under James Butler, 1st Duke of Ormonde, the Duke of Ormonde attempted to eliminate the Parliamentary army holding Dublin, but their opponents routed them at the Battle of Rathmines (2 August 1649). As the former Member of Parliament Admiral Robert Blake blockaded Prince Rupert's fleet in Kinsale, Oliver Cromwell could land at Dublin on 15 August 1649 with an army to quell the Royalist alliance in Ireland. Cromwell's suppression of the Royalists in Ireland during 1649 still has a strong resonance for many Irish people. The siege of Drogheda and massacre of nearly 3,500 people—comprising around 2,700 Royalist soldiers and all the men in the town carrying arms, including civilians, prisoners, and Catholic priests—became one of the historical memories that has driven Irish-English and Catholic-Protestant strife during the last three centuries. However, the massacre has significance mainly as a symbol of the Irish perception of Cromwellian cruelty, as far more people died in the subsequent guerrilla warfare and scorched-earth fighting in the country than at infamous massacres such as Drogheda and Wexford. The Parliament of England, Parliamentarian conquest of Ireland ground on for another four years until 1653, when the last Irish Confederate and Royalist troops surrendered. Historians have estimated that up to 30% of Ireland's population either died or had gone into exile by the end of the wars. The victors confiscated almost all Irish Catholic-owned land in the wake of the conquest and distributed it to the Parliament's creditors, to the Parliamentary soldiers who served in Ireland, and to English people who had settled there before the war.Scotland
The execution of Charles I of England, Charles I altered the dynamics of the Scotland in the Wars of the Three Kingdoms, Civil War in Scotland, which had raged between Royalists and Covenanters since 1644. By 1649, the struggle had left the Royalists there in disarray, and their erstwhile leader, the James Graham, 1st Marquess of Montrose, Marquess of Montrose, had gone into exile. However, Montrose, who had raised a mercenary force in Norway, later returned but did not succeed in raising many Highland clans, and the Covenanters defeated his army at the Battle of Carbisdale 1650, Battle of Carbisdale in Ross-shire on 27 April 1650. The victors captured Montrose shortly afterwards and took him to Edinburgh. On 20 May, the Scottish Parliament sentenced him to death and had him hanged the next day. Charles II of England, Charles II landed in Scotland at Garmouth in Moray on 23 June 1650 and signed the 1638 National Covenant and the 1643 Solemn League and Covenant immediately after coming ashore. With his original Scottish Royalist followers and his new Covenanter allies, King Charles II became the greatest threat facing the new English republic. In response to the threat, Cromwell left some of his lieutenants in Ireland to continue the suppression of the Irish Royalists and returned to England.
Cromwell arrived in Scotland on 22 July 1650 and proceeded to lay siege to Edinburgh. By the end of August disease and a shortage of supplies had reduced his army, and he had to order a retreat towards his base at Dunbar. A Scottish army, assembled under the command of David Leslie (Scottish general), David Leslie, tried to block the retreat, but Cromwell defeated them at the Battle of Dunbar (1650), Battle of Dunbar on 3 September. Cromwell's army then took Edinburgh, and by the end of the year his army had occupied much of southern Scotland.
In July 1651, Cromwell's forces crossed the Firth of Forth into Fife and defeated the Scots at the Battle of Inverkeithing (20 July 1651). The New Model Army advanced towards Perth, Scotland, Perth, which allowed Charles, at the head of the Scottish army, to move south into England. Cromwell followed Charles into England, leaving George Monck to finish the campaign in Scotland. Monck took Stirling on 14 August and Dundee on 1 September. In 1652, the army finished off the remnants of Royalist resistance, under the terms of the "Tender of Union".
In late 1688, William of Orange successfully invaded England. After the Convention of Estates (1689), Convention of Estates deposed the Catholic king James II of England, James VII on 11 April 1689, they offered the royal title to William and his wife Mary II of England, Mary (the Protestant daughter of James), which they accepted on 11 May 1689. During the subsequent
Charles II of England, Charles II landed in Scotland at Garmouth in Moray on 23 June 1650 and signed the 1638 National Covenant and the 1643 Solemn League and Covenant immediately after coming ashore. With his original Scottish Royalist followers and his new Covenanter allies, King Charles II became the greatest threat facing the new English republic. In response to the threat, Cromwell left some of his lieutenants in Ireland to continue the suppression of the Irish Royalists and returned to England.
Cromwell arrived in Scotland on 22 July 1650 and proceeded to lay siege to Edinburgh. By the end of August disease and a shortage of supplies had reduced his army, and he had to order a retreat towards his base at Dunbar. A Scottish army, assembled under the command of David Leslie (Scottish general), David Leslie, tried to block the retreat, but Cromwell defeated them at the Battle of Dunbar (1650), Battle of Dunbar on 3 September. Cromwell's army then took Edinburgh, and by the end of the year his army had occupied much of southern Scotland.
In July 1651, Cromwell's forces crossed the Firth of Forth into Fife and defeated the Scots at the Battle of Inverkeithing (20 July 1651). The New Model Army advanced towards Perth, Scotland, Perth, which allowed Charles, at the head of the Scottish army, to move south into England. Cromwell followed Charles into England, leaving George Monck to finish the campaign in Scotland. Monck took Stirling on 14 August and Dundee on 1 September. In 1652, the army finished off the remnants of Royalist resistance, under the terms of the "Tender of Union".
In late 1688, William of Orange successfully invaded England. After the Convention of Estates (1689), Convention of Estates deposed the Catholic king James II of England, James VII on 11 April 1689, they offered the royal title to William and his wife Mary II of England, Mary (the Protestant daughter of James), which they accepted on 11 May 1689. During the subsequent Jacobite rising of 1689
The Jacobite rising of 1689 was a conflict fought primarily in the Scottish Highlands, whose objective was to put James II & VII back on the throne, following his deposition by the November 1688 Glorious Revolution. Named after "Jacobus", the L ...
, instigated by James' Roman Catholic and Anglican Tory supporters, the Calvinist forces in the south and lowlands of Scotland triumphed. Despite this defeat, many Scottish Highland clans remained either Catholic or Episcopalian in sympathy. The Catholic Clan MacDonald was subject to the 1691 Glencoe Massacre for being late in pledging loyalty to the new Protestant king William II. Highland clans also rallied to the support of Catholic claimants to the British throne in later, failed Jacobite risings of the erstwhile Stuart James Francis Edward Stuart, King James III in 1715 and Charles Edward Stuart in 1745.
Other
The Pilgrimage of Grace was a popular revolt in late medieval Europe, popular rising in Yorkshire in 1536–37 against Henry VIII's break with the Roman Catholic Church. Bigod's rebellion was an armed rebellion by Roman Catholicism in England and Wales, English Roman Catholics in Cumberland and Westmorland against Henry VIII of England, King Henry VIII ofEngland
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Wales to its west and Scotland to its north. The Irish Sea lies northwest and the Celtic Sea to the southwest. It is separated from continental Europe b ...
and the English Reformation Parliament, English Parliament.
Death toll
These figures include the deaths of civilians from infectious disease, diseases,famine
A famine is a widespread scarcity of food, caused by several factors including war, natural disasters, crop failure, Demographic trap, population imbalance, widespread poverty, an Financial crisis, economic catastrophe or government policies. Th ...
, etc., as well as deaths of soldiers in battle and possible wikt:massacre, massacres and genocide.
The wars listed were the most severe in casualties; the remaining religious conflicts in Europe lasted for only a few years, a year, or less and/or were much less violent. Huguenot rebellions
The Huguenot rebellions, sometimes called the Rohan Wars after the Huguenot leader Henri de Rohan, were a series of rebellions of the 1620s in which French Calvinist Protestants (Huguenots), mainly located in southwestern France, revolted agains ...
were possibly the most damaging conflict after the German Peasants' War
The German Peasants' War, Great Peasants' War or Great Peasants' Revolt (german: Deutscher Bauernkrieg) was a widespread popular revolt in some German-speaking areas in Central Europe from 1524 to 1525. It failed because of intense oppositio ...
and may have taken up to 100,000 lives.
Religious situation pre- and post-European wars
At the Reformation's zenith around 1590, Protestant governments and/or cultures controlled about half of the European territory; however, as a result of Catholic reconquests, only about one fifth was left in 1690.See also
* Concordat of Worms * English Reformation * Northern Crusades * Ottoman wars in EuropeNotes
References
Bibliography
* * Greengrass, Mark. ''The European Reformation 1500–1618''. Longman, 1998. * Diarmaid MacCulloch, MacCulloch, Diarmaid. ''The Reformation: A History''. New York: Penguin 2003. * {{DEFAULTSORT:European Wars Of Religion European wars of religion, Protestant Reformation 16th-century conflicts 17th-century conflicts 18th-century conflicts 16th century in Europe 17th century in Europe 18th century in Europe 16th-century Christianity 17th-century Christianity 18th-century Christianity 16th-century Protestantism 17th-century Protestantism 18th-century Protestantism