Ezekiel 40 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Ezekiel 40 is the fortieth chapter of the

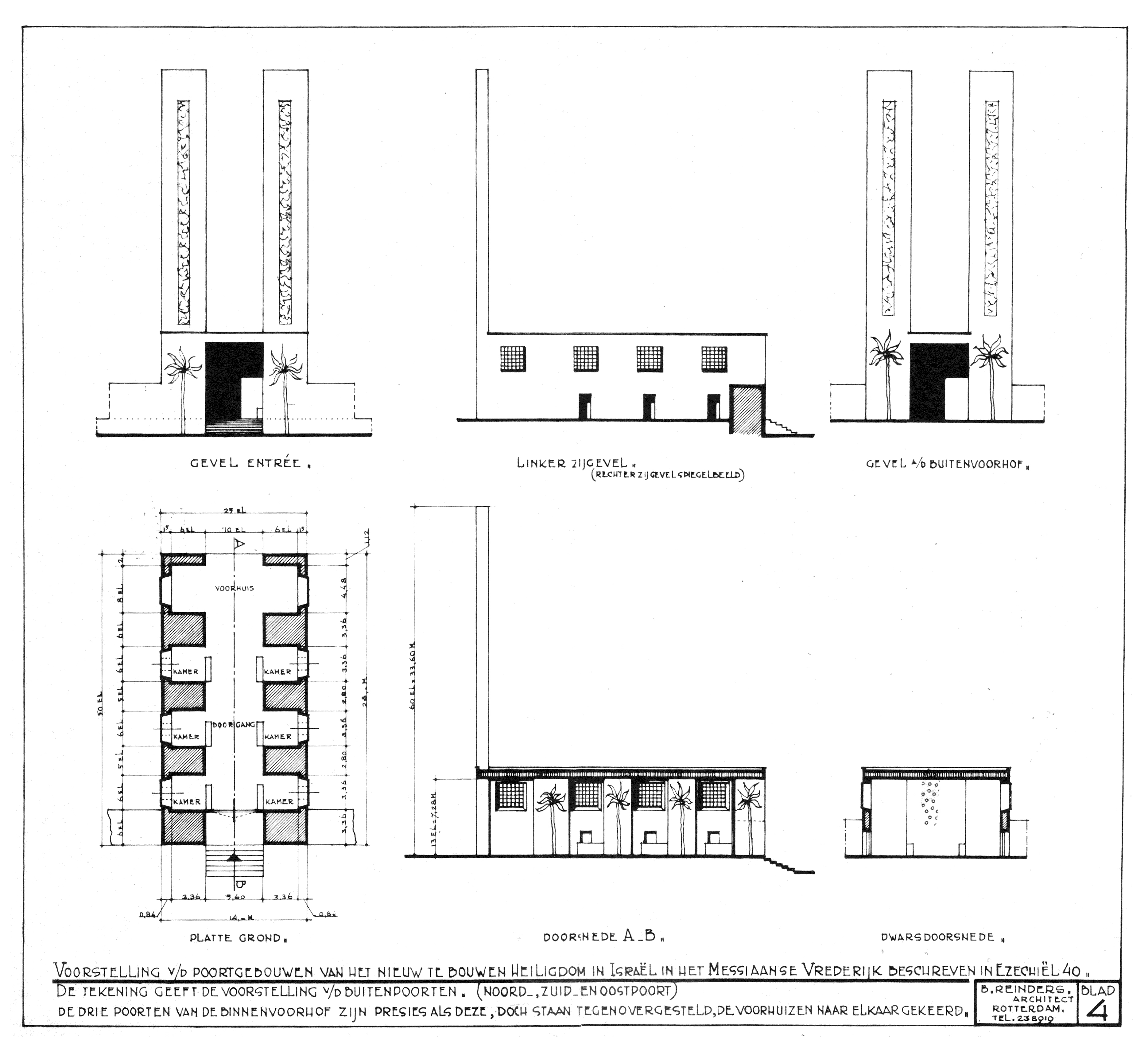 Ezekiel records the blueprint of the eastern gateway (which is similar to northern and southern gates) based on the action of the man acting as his guide:
: ''Then he went to the gateway which faced east; and he went up its stairs and measured the threshold of the gateway, which was one rod wide, and the other threshold was one rod wide. Each gate chamber was one rod long and one rod wide; between the gate chambers was a space of five cubits; and the threshold of the gateway by the vestibule of the inside gate was one rod.''
: ''He also measured the vestibule of the inside gate, one rod. Then he measured the vestibule of the gateway, eight cubits; and the gateposts, two cubits. The vestibule of the gate was on the inside.''
: ''In the eastern gateway were three gate chambers on one side and three on the other; the three were all the same size; also the gateposts were of the same size on this side and that side.''
: ''He measured the width of the entrance to the gateway, ten cubits; and the length of the gate, thirteen cubits.''
: ''There was a space in front of the gate chambers, one cubit on this side and one cubit on that side; the gate chambers were six cubits on this side and six cubits on that side.''
: ''Then he measured the gateway from the roof of one gate chamber to the roof of the other; the width was twenty-five cubits, as door faces door.''
: ''He measured the gateposts, sixty cubits high, and the court all around the gateway extended to the gatepost.''
: ''From the front of the entrance gate to the front of the vestibule of the inner gate was fifty cubits.''
: ''There were beveled window frames in the gate chambers and in their intervening archways on the inside of the gateway all around, and likewise in the vestibules. There were windows all around on the inside. And on each gatepost were palm trees.''
The Jerusalem Bible argues that "these elaborate gates" would be built "to enable a watch to be kept on those who enter" in order to ensure that the Temple could be kept pure from foreigners and sinners.Jerusalem Bible (1966), Footnote c at Ezekiel 40:16
Ezekiel records the blueprint of the eastern gateway (which is similar to northern and southern gates) based on the action of the man acting as his guide:
: ''Then he went to the gateway which faced east; and he went up its stairs and measured the threshold of the gateway, which was one rod wide, and the other threshold was one rod wide. Each gate chamber was one rod long and one rod wide; between the gate chambers was a space of five cubits; and the threshold of the gateway by the vestibule of the inside gate was one rod.''
: ''He also measured the vestibule of the inside gate, one rod. Then he measured the vestibule of the gateway, eight cubits; and the gateposts, two cubits. The vestibule of the gate was on the inside.''
: ''In the eastern gateway were three gate chambers on one side and three on the other; the three were all the same size; also the gateposts were of the same size on this side and that side.''
: ''He measured the width of the entrance to the gateway, ten cubits; and the length of the gate, thirteen cubits.''
: ''There was a space in front of the gate chambers, one cubit on this side and one cubit on that side; the gate chambers were six cubits on this side and six cubits on that side.''
: ''Then he measured the gateway from the roof of one gate chamber to the roof of the other; the width was twenty-five cubits, as door faces door.''
: ''He measured the gateposts, sixty cubits high, and the court all around the gateway extended to the gatepost.''
: ''From the front of the entrance gate to the front of the vestibule of the inner gate was fifty cubits.''
: ''There were beveled window frames in the gate chambers and in their intervening archways on the inside of the gateway all around, and likewise in the vestibules. There were windows all around on the inside. And on each gatepost were palm trees.''
The Jerusalem Bible argues that "these elaborate gates" would be built "to enable a watch to be kept on those who enter" in order to ensure that the Temple could be kept pure from foreigners and sinners.Jerusalem Bible (1966), Footnote c at Ezekiel 40:16
Ezekiel 40 Hebrew with Parallel EnglishEzekiel 40 Hebrew with Rashi's Commentary
Ezekiel 40 English Translation with Parallel Latin Vulgate
{{DEFAULTSORT:Ezekiel 40 40
Book of Ezekiel
The Book of Ezekiel is the third of the Latter Prophets in the Tanakh and one of the major prophetic books, following Isaiah and Jeremiah. According to the book itself, it records six visions of the prophet Ezekiel, exiled in Babylon, during t ...
in the Hebrew Bible
The Hebrew Bible or Tanakh (;"Tanach"
''Random House Webster's Unabridged Dictionary''. Hebrew: ''Tān ...
or the ''Random House Webster's Unabridged Dictionary''. Hebrew: ''Tān ...
Old Testament
The Old Testament (often abbreviated OT) is the first division of the Christian biblical canon, which is based primarily upon the 24 books of the Hebrew Bible or Tanakh, a collection of ancient religious Hebrew writings by the Israelites. The ...
of the Christian
Christians () are people who follow or adhere to Christianity, a monotheistic Abrahamic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus Christ. The words ''Christ'' and ''Christian'' derive from the Koine Greek title ''Christós'' (Χρι ...
Bible
The Bible (from Koine Greek , , 'the books') is a collection of religious texts or scriptures that are held to be sacred in Christianity, Judaism, Samaritanism, and many other religions. The Bible is an anthologya compilation of texts of a ...
. This book contains the prophecies attributed to the prophet
In religion, a prophet or prophetess is an individual who is regarded as being in contact with a divine being and is said to speak on behalf of that being, serving as an intermediary with humanity by delivering messages or teachings from the s ...
/priest
A priest is a religious leader authorized to perform the sacred rituals of a religion, especially as a mediatory agent between humans and one or more deities. They also have the authority or power to administer religious rites; in particu ...
Ezekiel
Ezekiel (; he, יְחֶזְקֵאל ''Yəḥezqēʾl'' ; in the Septuagint written in grc-koi, Ἰεζεκιήλ ) is the central protagonist of the Book of Ezekiel in the Hebrew Bible.
In Judaism, Christianity, and Islam, Ezekiel is acknow ...
, and is one of the Books of the Prophets
Nevi'im (; he, נְבִיאִים ''Nəvīʾīm'', Tiberian: ''Năḇīʾīm,'' "Prophets", literally "spokespersons") is the second major division of the Hebrew Bible (the ''Tanakh''), lying between the Torah (instruction) and Ketuvim (wri ...
. The Jerusalem Bible
''The Jerusalem Bible'' (JB or TJB) is an English translation of the Bible published in 1966 by Darton, Longman & Todd. As a Catholic Bible, it includes 73 books: the 39 books shared with the Hebrew Bible, along with the seven deuterocanonical ...
refers to the final section of Ezekiel, chapters 40- 48, as "the Torah of Ezekiel". This chapter describes Ezekiel's vision of a future Temple
A temple (from the Latin ) is a building reserved for spiritual rituals and activities such as prayer and sacrifice. Religions which erect temples include Christianity (whose temples are typically called churches), Hinduism (whose temples ...
.
Text
The original text was written in theHebrew language
Hebrew (; ; ) is a Northwest Semitic language of the Afroasiatic language family. Historically, it is one of the spoken languages of the Israelites and their longest-surviving descendants, the Jews and Samaritans. It was largely preserved ...
. This chapter is divided into 49 verses.
Textual witnesses
Some early manuscripts containing the text of this chapter inHebrew
Hebrew (; ; ) is a Northwest Semitic language of the Afroasiatic language family. Historically, it is one of the spoken languages of the Israelites and their longest-surviving descendants, the Jews and Samaritans. It was largely preserved ...
are of the Masoretic Text
The Masoretic Text (MT or 𝕸; he, נֻסָּח הַמָּסוֹרָה, Nūssāḥ Hammāsōrā, lit. 'Text of the Tradition') is the authoritative Hebrew and Aramaic text of the 24 books of the Hebrew Bible (Tanakh) in Rabbinic Judaism. ...
tradition, which includes the Codex Cairensis
The Codex Cairensis (also: ''Codex Prophetarum Cairensis'', ''Cairo Codex of the Prophets'') is a Hebrew manuscript containing the complete text of the Hebrew Bible's Nevi'im (Prophets). It has traditionally been described as "the oldest dated He ...
(895), the Petersburg Codex of the Prophets (916), Aleppo Codex
The Aleppo Codex ( he, כֶּתֶר אֲרָם צוֹבָא, romanized: , lit. 'Crown of Aleppo') is a medieval bound manuscript of the Hebrew Bible. The codex was written in the city of Tiberias in the tenth century CE (circa 920) under the ...
(10th century), Codex Leningradensis
The Leningrad Codex ( la, Codex Leningradensis [Leningrad Book]; he, כתב יד לנינגרד) is the oldest complete manuscript of the Hebrew Bible in Hebrew, using the Masoretic Text and Tiberian vocalization. According to its colopho ...
(1008).
There is also a translation into Koine Greek
Koine Greek (; Koine el, ἡ κοινὴ διάλεκτος, hē koinè diálektos, the common dialect; ), also known as Hellenistic Greek, common Attic, the Alexandrian dialect, Biblical Greek or New Testament Greek, was the common supra-reg ...
known as the Septuagint
The Greek Old Testament, or Septuagint (, ; from the la, septuaginta, lit=seventy; often abbreviated ''70''; in Roman numerals, LXX), is the earliest extant Greek translation of books from the Hebrew Bible. It includes several books beyond th ...
, made in the last few centuries BC. Extant ancient manuscripts of the Septuagint
The Greek Old Testament, or Septuagint (, ; from the la, septuaginta, lit=seventy; often abbreviated ''70''; in Roman numerals, LXX), is the earliest extant Greek translation of books from the Hebrew Bible. It includes several books beyond th ...
version include Codex Vaticanus
The Codex Vaticanus ( The Vatican, Bibl. Vat., Vat. gr. 1209), designated by siglum B or 03 (in the Gregory-Aland numbering), δ 1 ( von Soden), is a fourth-century Christian manuscript of a Greek Bible, containing the majority of the Greek Old ...
(B; B; 4th century), Codex Alexandrinus
The Codex Alexandrinus (London, British Library, Royal MS 1. D. V-VIII), designated by the siglum A or 02 (in the Gregory-Aland numbering of New Testament manuscripts), δ 4 (in the von Soden numbering of New Testament manuscripts), is a manu ...
(A; A; 5th century) and Codex Marchalianus
Codex Marchalianus designated by siglum Q is a 6th-century Greek manuscript copy of the Greek version of the Hebrew Bible (Tanakh or Old Testament) known as the Septuagint. The text was written on vellum in uncial letters. Palaeographically it ...
(Q; Q; 6th century).

The beginning of the temple measurements (40:1–5)
This is the beginning of Ezekiel's final vision which he dated to the start of a Jubilee year, "in the 25th year of our exile"verse 1
Verse may refer to:
Poetry
* Verse, an occasional synonym for poetry
* Verse, a metrical structure, a stanza
* Blank verse, a type of poetry having regular meter but no rhyme
* Free verse, a type of poetry written without the use of strict ...
). In this vision Ezekiel is transported to the land of Israel (cf. Ezekiel 8:3), where he is placed on 'a very high mountain on which was a structure like a city to the south' (verse 2), evidently referring to Mount Zion (exalted as in Isaiah 2:2 and Micah 4:1) and a new city to replace the devastated Jerusalem. A man gleaming 'like bronze' (verse 3; cf. ; 1:27; ) appears with a measuring rod to measure the various dimensions of the temple complex and instructs Ezekiel to record the measurements to be passed on to the Israelites. The measuring actions continues to Ezekiel 42, but this single vision comprises the last nine chapters of the book (chapter 40–48), as Ezekiel tours the restored, pure temple and then watches the Divine Warrior's return and enthronement (in contrast to the vision in chapters 8–11, which record Ezekiel touring the defiled temple before watching the departure of the Warrior).
Verse 1
: ''In the twenty-fifth year of our captivity, at the beginning of the year, on the tenth day of the month, in the fourteenth year after the city was captured,'' : ''on the very same day the hand of the Lord was upon me; and He took me there.'' * The date corresponds to the 25th anniversary of Ezekiel's exile, April 28, 573 BCE, which is also the date given in an analysis by German theologian Bernhard Lang. The Jerusalem Bible notes the date as September–October 573. According to theTalmud
The Talmud (; he, , Talmūḏ) is the central text of Rabbinic Judaism and the primary source of Jewish religious law (''halakha'') and Jewish theology. Until the advent of modernity, in nearly all Jewish communities, the Talmud was the cente ...
( ''b. Arak.'' 12a), this date falls on the Day of Atonement (Yom Kippur) and marks the start of the seventeenth (and last) Jubilee year
A jubilee is a particular anniversary of an event, usually denoting the 25th, 40th, 50th, 60th, and the 70th anniversary. The term is often now used to denote the celebrations associated with the reign of a monarch after a milestone number of ...
in history.
Verse 4
: ''And the man said to me,'' :: ''"Son of man, look with your eyes and hear with your ears,'' ::: ''and fix your mind on everything I show you;'' :: ''for you were brought here so that I might show them to you.'' ::: ''Declare to the house of Israel everything you see."'' * "Son of man" (Hebrew: בן־אדם ''-''): this phrase is used 93 times to address Ezekiel.Verse 5
: ''Now there was a wall all around the outside of the temple.'' : ''In the man's hand was a measuring rod six cubits long, each being a cubit and a handbreadth;'' : ''and he measured the width of the wall structure, one rod; and the height, one rod.'' * "A cubit and a handbreadth": acubit
The cubit is an ancient unit of length based on the distance from the elbow to the tip of the middle finger. It was primarily associated with the Sumerians, Egyptians, and Israelites. The term ''cubit'' is found in the Bible regarding No ...
is about "44.4 cm or 17.5 in."; a handbreadth (or "four fingers thick") is about "7.4 cm or 2.9 in." Epiphanius of Salamis
Epiphanius of Salamis ( grc-gre, Ἐπιφάνιος; c. 310–320 – 403) was the bishop of Salamis, Cyprus, at the end of the 4th century. He is considered a saint and a Church Father by both the Eastern Orthodox and Catholic Churches. He gai ...
, in his treatise ''On Weights and Measures
''On Weights and Measures'' is a historical, lexical, metrological, and geographical treatise compiled in 392 AD in Constantia by Epiphanius of Salamis (c. 315–403). The greater part of the work is devoted to a discussion on Greek and Roma ...
'', describes that: "the part from the elbow to the wrist and the palm of the hand is called the cubit, the middle finger of the cubit measure being also extended at the same time and there being added below (it) the span, that is, of the hand, taken all together."
The Eastern Gateway of the Temple (40:6–16)
 Ezekiel records the blueprint of the eastern gateway (which is similar to northern and southern gates) based on the action of the man acting as his guide:
: ''Then he went to the gateway which faced east; and he went up its stairs and measured the threshold of the gateway, which was one rod wide, and the other threshold was one rod wide. Each gate chamber was one rod long and one rod wide; between the gate chambers was a space of five cubits; and the threshold of the gateway by the vestibule of the inside gate was one rod.''
: ''He also measured the vestibule of the inside gate, one rod. Then he measured the vestibule of the gateway, eight cubits; and the gateposts, two cubits. The vestibule of the gate was on the inside.''
: ''In the eastern gateway were three gate chambers on one side and three on the other; the three were all the same size; also the gateposts were of the same size on this side and that side.''
: ''He measured the width of the entrance to the gateway, ten cubits; and the length of the gate, thirteen cubits.''
: ''There was a space in front of the gate chambers, one cubit on this side and one cubit on that side; the gate chambers were six cubits on this side and six cubits on that side.''
: ''Then he measured the gateway from the roof of one gate chamber to the roof of the other; the width was twenty-five cubits, as door faces door.''
: ''He measured the gateposts, sixty cubits high, and the court all around the gateway extended to the gatepost.''
: ''From the front of the entrance gate to the front of the vestibule of the inner gate was fifty cubits.''
: ''There were beveled window frames in the gate chambers and in their intervening archways on the inside of the gateway all around, and likewise in the vestibules. There were windows all around on the inside. And on each gatepost were palm trees.''
The Jerusalem Bible argues that "these elaborate gates" would be built "to enable a watch to be kept on those who enter" in order to ensure that the Temple could be kept pure from foreigners and sinners.Jerusalem Bible (1966), Footnote c at Ezekiel 40:16
Ezekiel records the blueprint of the eastern gateway (which is similar to northern and southern gates) based on the action of the man acting as his guide:
: ''Then he went to the gateway which faced east; and he went up its stairs and measured the threshold of the gateway, which was one rod wide, and the other threshold was one rod wide. Each gate chamber was one rod long and one rod wide; between the gate chambers was a space of five cubits; and the threshold of the gateway by the vestibule of the inside gate was one rod.''
: ''He also measured the vestibule of the inside gate, one rod. Then he measured the vestibule of the gateway, eight cubits; and the gateposts, two cubits. The vestibule of the gate was on the inside.''
: ''In the eastern gateway were three gate chambers on one side and three on the other; the three were all the same size; also the gateposts were of the same size on this side and that side.''
: ''He measured the width of the entrance to the gateway, ten cubits; and the length of the gate, thirteen cubits.''
: ''There was a space in front of the gate chambers, one cubit on this side and one cubit on that side; the gate chambers were six cubits on this side and six cubits on that side.''
: ''Then he measured the gateway from the roof of one gate chamber to the roof of the other; the width was twenty-five cubits, as door faces door.''
: ''He measured the gateposts, sixty cubits high, and the court all around the gateway extended to the gatepost.''
: ''From the front of the entrance gate to the front of the vestibule of the inner gate was fifty cubits.''
: ''There were beveled window frames in the gate chambers and in their intervening archways on the inside of the gateway all around, and likewise in the vestibules. There were windows all around on the inside. And on each gatepost were palm trees.''
The Jerusalem Bible argues that "these elaborate gates" would be built "to enable a watch to be kept on those who enter" in order to ensure that the Temple could be kept pure from foreigners and sinners.Jerusalem Bible (1966), Footnote c at Ezekiel 40:16
See also
*Israel
Israel (; he, יִשְׂרָאֵל, ; ar, إِسْرَائِيل, ), officially the State of Israel ( he, מְדִינַת יִשְׂרָאֵל, label=none, translit=Medīnat Yīsrāʾēl; ), is a country in Western Asia. It is situated ...
*Levi
Levi (; ) was, according to the Book of Genesis, the third of the six sons of Jacob and Leah (Jacob's third son), and the founder of the Israelite Tribe of Levi (the Levites, including the Kohanim) and the great-grandfather of Aaron, Moses and M ...
*New Jerusalem Dead Sea Scroll Discovered among the Dead Sea Scrolls near Qumran, Israel, were fragments of a scroll which describes New Jerusalem in minute detail. The New Jerusalem Scroll appears to contain an apocalyptic vision, an eschatological vision of the city and the te ...
*Third Temple
The "Third Temple" ( he, , , ) refers to a hypothetical rebuilt Temple in Jerusalem. It would succeed Solomon's Temple and the Second Temple, the former having been destroyed during the Babylonian siege of Jerusalem in and the latter havin ...
*Zadok
Zadok (or Zadok HaKohen, also spelled Ṣadok, Ṣadoc, Zadoq, Tzadok, or Tsadoq; he, צָדוֹק הַכֹּהֵן, meaning "Righteous, Justified") was a Kohen (priest), biblically recorded to be a descendant from Eleazar the son of Aaron (). H ...
*Related Bible
The Bible (from Koine Greek , , 'the books') is a collection of religious texts or scriptures that are held to be sacred in Christianity, Judaism, Samaritanism, and many other religions. The Bible is an anthologya compilation of texts of a ...
parts: 1 Kings 6, 2 Chronicles 3, Isaiah 2
Isaiah 2 is the second chapter of the Book of Isaiah in the Hebrew Bible or the Old Testament of the Christian Bible. This book contains the prophecies attributed to the prophet Isaiah, and is one of the Books of the Prophets.
Text
The ori ...
, Ezekiel 33
Ezekiel 33 is the thirty-third chapter of the Book of Ezekiel in the Hebrew Bible or the Old Testament of the Christian Bible. This book contains the prophecies attributed to the prophet/priest Ezekiel, and is one of the Books of the Prophets. ...
, Ezekiel 41, Ezekiel 48, Daniel 10, Revelation 21
Revelation 21 is the twenty-first chapter of the Book of Revelation in the New Testament of the Christian Bible. This chapter contains the accounts of "the new heaven and the new earth", followed by the appearance of the New Jerusalem the Bride.
...
Notes
References
Sources
* * * * * * * *External links
Jewish
Ezekiel 40 Hebrew with Parallel English
Christian
Ezekiel 40 English Translation with Parallel Latin Vulgate
{{DEFAULTSORT:Ezekiel 40 40