|
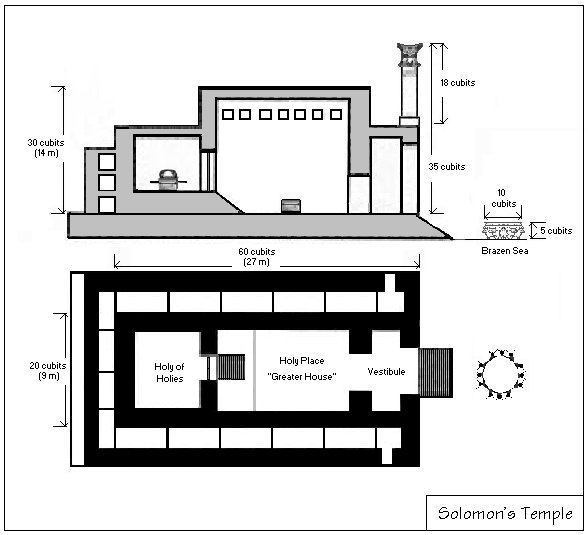
1 Kings 6
1 Kings 6 is the sixth chapter of the Books of Kings in the Hebrew Bible or the First Book of Kings in the Old Testament of the Christian Bible. The book is a compilation of various annals recording the acts of the kings of Israel and Judah by a Deuteronomic compiler in the seventh century BCE, with a supplement added in the sixth century BCE. This chapter belongs to the section focusing on the reign of Solomon over the unified kingdom of Judah and Israel (1 Kings 1 to 11). The focus of this chapter is the reign of Solomon, the king of Israel. Text This chapter was originally written in the Hebrew language and since the 16th century is divided into 38 verses. Textual witnesses Some early manuscripts containing the text of this chapter in Hebrew are of the Masoretic Text tradition, which includes the Codex Cairensis (895), Aleppo Codex (10th century), and Codex Leningradensis (1008). There is also a translation into Koine Greek known as the Septuagint, made in the last fe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Books Of Kings
The Book of Kings (, '' Sēfer Məlāḵīm'') is a book in the Hebrew Bible, found as two books (1–2 Kings) in the Old Testament of the Christian Bible. It concludes the Deuteronomistic history, a history of Israel also including the books of Joshua, Judges and Samuel. Biblical commentators believe the Books of Kings were written to provide a theological explanation for the destruction of the Kingdom of Judah by Babylon in c. 586 BCE and to provide a foundation for a return from Babylonian exile.Sweeney, p1/ref> The two books of Kings present a history of ancient Israel and Judah, from the death of King David to the release of Jehoiachin from imprisonment in Babylon—a period of some 400 years (). Scholars tend to treat the books as consisting of a first edition from the late 7th century BCE and of a second and final edition from the mid-6th century BCE.Fretheim, p. 7 Contents The Jerusalem Bible divides the two Books of Kings into eight sections: *1 Kings 1:1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Codex Sinaiticus
The Codex Sinaiticus (Shelfmark: London, British Library, Add MS 43725), designated by siglum [Aleph] or 01 (in the Gregory-Aland numbering of New Testament manuscripts), δ 2 (in the von Soden numbering of New Testament manuscripts), or Sinai Bible is a 4th-century Christian manuscript of a Greek Bible, containing the majority of the Greek Old Testament, including the Apocrypha, and the Greek New Testament, with both the Epistle of Barnabas and the Shepherd of Hermas included. It is written in uncial letters on parchment. It is one of the four great uncial codices (these being manuscripts which originally contained the whole of both the Old and New Testaments). Along with Codex Alexandrinus and Codex Vaticanus, it is one of the earliest and most complete manuscripts of the Bible, and contains the oldest complete copy of the New Testament. It is a historical treasure, and using the study of comparative writing styles (palaeography), it has been dated to the mid-4th cen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
King Of Sidon
The King of Sidon was the ruler of Sidon, an ancient Phoenician city in what is now Lebanon. Scholars have pieced together the fragmented list from various archaeological finds since the 19th century. Egyptian period * c.1700s BC Zimrida * c. 1300s BC Zimredda of Sidon / Zimrida IISidon : a study in oriental history 1907, Appendix 1: Kings of Sidon, p. 155-156. * c. 1300s BC Iab-nilud Assyrian period * 680–677 BCPersian period Eshmunazar Dynasty * 575–550 BC |
Phoenicia
Phoenicia () was an ancient thalassocratic civilization originating in the Levant region of the eastern Mediterranean, primarily located in modern Lebanon. The territory of the Phoenician city-states extended and shrank throughout their history, and they possessed several enclaves such as Arwad and Tell Sukas (modern Syria). The core region in which the Phoenician culture developed and thrived stretched from Tripoli and Byblos in northern Lebanon to Mount Carmel in modern Israel. At their height, the Phoenician possessions in the Eastern Mediterranean stretched from the Orontes River mouth to Ashkelon. Beyond its homeland, the Phoenician civilization extended to the Mediterranean from Cyprus to the Iberian Peninsula. The Phoenicians were a Semitic-speaking people of somewhat unknown origin who emerged in the Levant around 3000 BC. The term ''Phoenicia'' is an ancient Greek exonym that most likely described one of their most famous exports, a dye also known as Tyrian purpl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eshmunazar II
Eshmunazar II ( Phoenician: 𐤀𐤔𐤌𐤍𐤏𐤆𐤓 ', a theophoric name meaning 'Eshmun helps') was the Phoenician King of Sidon (). He was the grandson of king Eshmunazar I, and a vassal king of the Achaemenid Empire. He reigned after his father Tabnit I on the throne of Sidon. He died at the premature age of 14, and was succeeded by his cousin Bodashtart. The king is known from his sarcophagus, decorated with two inscriptions in the Phoenician script. It is housed in the Louvre Museum. Etymology Eshmunazar is the Latinized form of the Phoenician theophoric name , meaning "Eshmun helps". Variable spellings include: ʾEšmunʿazor, ʾšmnʿzr, Achmounazar, Ashmounazar, Ashmunazar, Ashmunezer, Echmounazar, Echmounazor, Eschmoun-ʿEzer, Eschmunazar, Eshmnʿzr, Eshmunazor, Esmounazar, Esmunasar, Esmunazar, Ešmunʿazor, Ešmunazar, Ešmunazor. Chronology The absolute chronology of the Kings of Sidon from the dynasty of Eshmunazar I has been much discussed in the liter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eshmunazar II Sarcophagus
The Eshmunazar II sarcophagus is a 6th-century BC sarcophagus unearthed in 1855 in the "Phoenician Necropolis", a hypogeum (underground tomb) complex in the southern area of the city of Sidon in modern-day Lebanon. The sarcophagus was discovered by members of the French consulate in Sidon and was donated to the Louvre. The Eshmunazar II sarcophagus has two sets of Canaanite and Aramaic inscriptions, Phoenician inscriptions, one on its lid and the other on its trough, under the sarcophagus head. The lid engraving was of great significance upon its discovery; it was the first Phoenician language inscription to be discovered in Phoenicia, Phoenicia proper, the most detailed Phoenician text ever found anywhere up to that point, and is today the second longest extant Phoenician inscription after the one discovered at Karatepe bilingual, Karatepe. Eshmunazar II (Phoenician: ', a theophoric name meaning 'Eshmun helps') was a Phoenician King of Sidon and the son of King Tabnit. His sa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cheshvan
Marcheshvan ( he, מַרְחֶשְׁוָן, Hebrew language#Modern Hebrew, Standard , Tiberian vocalization, Tiberian ; from Akkadian language, Akkadian , literally, 'eighth month'), sometimes shortened to Cheshvan (, Hebrew language#Modern Hebrew, Standard Tiberian vocalization, Tiberian ), is the second month of the civil year (which starts on 1 Tishrei), and the eighth month of the ecclesiastical year (which starts on 1 Nisan) on the Hebrew calendar. In a regular () year, Marcheshvan has 29 days, but because of the Hebrew calendar#Rosh Hashanah postponement rules, Rosh Hashanah postponement rules, in some years, an additional day is added to Marcheshvan to make the year a "full" () year. Marcheshvan occurs in October–November in the Gregorian calendar. The Hebrew Bible, before the Babylonian Exile, refers to the month as Bul (). In Sidon, the reference to is also made on the Sarcophaugus of Eshmunazar II dated to the early 5th century BC. Etymology Compared to its Akkadian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mark 11
Mark 11 is the eleventh chapter of the Gospel of Mark in the New Testament of the Christian Bible, beginning Jesus' final week before His death as He arrives in Jerusalem for the coming Passover. It contains the stories of Jesus' entry into Jerusalem, His cursing of the fig tree, His conflict with the Temple money changers, and His argument with the chief priests and elders about his authority. Text The original text was written in Koine Greek. This chapter is divided into 33 verses. Textual witnesses Some early manuscripts containing the text of this chapter are: *Codex Vaticanus (325-350; complete) *Codex Sinaiticus (330-360; complete) *Codex Bezae (~400; complete) *Codex Alexandrinus (400-440; complete) * Codex Ephraemi Rescriptus (~450; complete) Timescale Verses 1-11 reflect the events commemorated by Christians on Palm Sunday. Verses 12-19 take place "the next day", and end that evening. Verses 20-33 commence early ( gr, πρωῒ, ''prói''), the following morning. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Micah 3
Micah 3 is the third chapter of the Book of Micah in the Hebrew Bible or the Old Testament of the Christian Bible. This book contains the prophecies attributed to the prophet Micah, and is a part of the Book of the Twelve Minor Prophets. Text The original text was written in the Hebrew language. This chapter is divided into 12 verses. Textual versions Some early manuscripts containing the text of this chapter in Hebrew are of the Masoretic Text tradition, which includes the Codex Cairensis (895), the Petersburg Codex of the Prophets (916), Codex Leningradensis (1008). Fragments cumulatively containing all verses of this chapter were found among the Dead Sea Scrolls, including 4Q82 (4QXIIg; 25 BCE) with extant verses 12; and Wadi Murabba'at Minor Prophets (Mur88; MurXIIProph; 75-100 CE) with extant verses 1‑12. There is also a translation into Koine Greek known as the Septuagint, made in the last few centuries BCE. Extant ancient manuscripts of the Septuagint version includ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jeremiah 7
Jeremiah 7 is the seventh chapter of the Book of Jeremiah in the Hebrew Bible or the Old Testament of the Christian Bible. This book contains prophecies attributed to the prophet Jeremiah, and is one of the Books of the Prophets. Chapters 7 to 10 constitute an address delivered by Jeremiah at the gate of the Temple in Jerusalem.Streane, A. W. (1913)Cambridge Bible for Schools and Collegeson Jeremiah 7, accessed 4 January 2019 Text The original text of this chapter, as with the rest of the Book of Jeremiah, was written in Hebrew language. Since the division of the Bible into chapters and verses in the late medieval period, this chapter is divided into 34 verses. Textual witnesses Some early manuscripts containing the text of this chapter in Hebrew are of the Masoretic Text tradition, which includes the Codex Cairensis (895), the Petersburg Codex of the Prophets (916), Aleppo Codex (10th century), Codex Leningradensis (1008). Some fragments containing parts of this chapter wer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2 Kings 19
2 Kings 19 is the nineteenth chapter of the second part of the Books of Kings in the Hebrew Bible or the Second Book of Kings in the Old Testament of the Christian Bible. The book is a compilation of various annals recording the acts of the kings of Israel and Judah by a Deuteronomic compiler in the seventh century BC, with a supplement added in the sixth century BC. This chapter records the invasion of Assyrian to Judah during the reign of Hezekiah, the king of Judah, a part of the section comprising 2 Kings 18:1 to 20:21, with a parallel version in Isaiah 36– 39. Text This chapter was originally written in the Hebrew language. It is divided into 37 verses. Textual witnesses Some early manuscripts containing the text of this chapter in Hebrew are of the Masoretic Text tradition, which includes the Codex Cairensis (895), Aleppo Codex (10th century), and Codex Leningradensis (1008). There is also a translation into Koine Greek known as the Septuagint, made in the last few ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |