Extracellular Volume on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 In
In

 The extracellular fluid provides the medium for the exchange of substances between the ECF and the cells, and this can take place through dissolving, mixing and transporting in the fluid medium. Substances in the ECF include dissolved gases, nutrients, and electrolytes, all needed to maintain life. The ECF also contains materials
The extracellular fluid provides the medium for the exchange of substances between the ECF and the cells, and this can take place through dissolving, mixing and transporting in the fluid medium. Substances in the ECF include dissolved gases, nutrients, and electrolytes, all needed to maintain life. The ECF also contains materials
 There is a significant difference between the concentrations of
There is a significant difference between the concentrations of

 The arterial blood plasma, interstitial fluid and lymph interact at the level of the blood
The arterial blood plasma, interstitial fluid and lymph interact at the level of the blood
Britannica.comBiology-online.org
{{Authority control Body fluids Cell biology
 In
In cell biology
Cell biology (also cellular biology or cytology) is a branch of biology that studies the structure, function, and behavior of cells. All living organisms are made of cells. A cell is the basic unit of life that is responsible for the living a ...
, extracellular fluid (ECF) denotes all body fluid
Body fluids, bodily fluids, or biofluids, sometimes body liquids, are liquids within the human body. In lean healthy adult men, the total body water is about 60% (60–67%) of the total body weight; it is usually slightly lower in women (52-55%) ...
outside the cells
Cell most often refers to:
* Cell (biology), the functional basic unit of life
Cell may also refer to:
Locations
* Monastic cell, a small room, hut, or cave in which a religious recluse lives, alternatively the small precursor of a monastery w ...
of any multicellular organism
A multicellular organism is an organism that consists of more than one cell, in contrast to unicellular organism.
All species of animals, land plants and most fungi are multicellular, as are many algae, whereas a few organisms are partially un ...
. Total body water
In physiology, body water is the water content of an animal body that is contained in the tissues, the blood, the bones and elsewhere. The percentages of body water contained in various fluid compartments add up to total body water (TBW). This wa ...
in healthy adults is about 60% (range 45 to 75%) of total body weight; women and the obese typically have a lower percentage than lean men. Extracellular fluid makes up about one-third of body fluid, the remaining two-thirds is intracellular fluid
The human body and even its individual body fluids may be conceptually divided into various fluid compartments, which, although not literally anatomic compartments, do represent a real division in terms of how portions of the body's water, solut ...
within cells. The main component of the extracellular fluid is the interstitial fluid that surrounds cells.
Extracellular fluid is the internal environment of all multicellular animals, and in those animals with a blood
Blood is a body fluid in the circulatory system of humans and other vertebrates that delivers necessary substances such as nutrients and oxygen to the cells, and transports metabolic waste products away from those same cells. Blood in th ...
circulatory system
The blood circulatory system is a system of organs that includes the heart, blood vessels, and blood which is circulated throughout the entire body of a human or other vertebrate. It includes the cardiovascular system, or vascular system, tha ...
, a proportion of this fluid is blood plasma
Blood plasma is a light amber-colored liquid component of blood in which blood cells are absent, but contains proteins and other constituents of whole blood in suspension. It makes up about 55% of the body's total blood volume. It is the ...
. Plasma and interstitial fluid are the two components that make up at least 97% of the ECF. Lymph
Lymph (from Latin, , meaning "water") is the fluid that flows through the lymphatic system, a system composed of lymph vessels (channels) and intervening lymph nodes whose function, like the venous system, is to return fluid from the tissues ...
makes up a small percentage of the interstitial fluid. The remaining small portion of the ECF includes the transcellular fluid
In cell biology, extracellular fluid (ECF) denotes all body fluid outside the cells of any multicellular organism. Total body water in healthy adults is about 60% (range 45 to 75%) of total body weight; women and the obese typically have a lower ...
(about 2.5%). The ECF can also be seen as having two components – plasma and lymph as a delivery system, and interstitial fluid for water and solute exchange with the cells.
The extracellular fluid, in particular the interstitial fluid, constitutes the body's internal environment that bathes all of the cells
Cell most often refers to:
* Cell (biology), the functional basic unit of life
Cell may also refer to:
Locations
* Monastic cell, a small room, hut, or cave in which a religious recluse lives, alternatively the small precursor of a monastery w ...
in the body. The ECF composition is therefore crucial for their normal functions, and is maintained by a number of homeostatic mechanisms involving negative feedback
Negative feedback (or balancing feedback) occurs when some function of the output of a system, process, or mechanism is fed back in a manner that tends to reduce the fluctuations in the output, whether caused by changes in the input or by othe ...
. Homeostasis regulates, among others, the pH, sodium
Sodium is a chemical element with the symbol Na (from Latin ''natrium'') and atomic number 11. It is a soft, silvery-white, highly reactive metal. Sodium is an alkali metal, being in group 1 of the periodic table. Its only stable ...
, potassium
Potassium is the chemical element with the symbol K (from Neo-Latin '' kalium'') and atomic number19. Potassium is a silvery-white metal that is soft enough to be cut with a knife with little force. Potassium metal reacts rapidly with atmosp ...
, and calcium
Calcium is a chemical element with the symbol Ca and atomic number 20. As an alkaline earth metal, calcium is a reactive metal that forms a dark oxide-nitride layer when exposed to air. Its physical and chemical properties are most similar t ...
concentrations in the ECF. The volume of body fluid, blood glucose
Glycaemia, also known as blood sugar level, blood sugar concentration, or blood glucose level is the measure of glucose concentrated in the blood of humans or other animals. Approximately 4 grams of glucose, a simple sugar, is present in the bl ...
, oxygen
Oxygen is the chemical element with the symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group in the periodic table, a highly reactive nonmetal, and an oxidizing agent that readily forms oxides with most elements as we ...
, and carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide ( chemical formula ) is a chemical compound made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in the gas state at room temperature. In the air, carbon dioxide is t ...
levels are also tightly homeostatically maintained.
The volume of extracellular fluid in a young adult male of 70 kg (154 lbs) is 20% of body weight – about fourteen litres. Eleven litres is interstitial fluid and the remaining three litres is plasma.
Components
The main component of the extracellular fluid (ECF) is the interstitial fluid, or tissue fluid, which surrounds the cells in the body. The other major component of the ECF is the intravascular fluid of thecirculatory system
The blood circulatory system is a system of organs that includes the heart, blood vessels, and blood which is circulated throughout the entire body of a human or other vertebrate. It includes the cardiovascular system, or vascular system, tha ...
called blood plasma
Blood plasma is a light amber-colored liquid component of blood in which blood cells are absent, but contains proteins and other constituents of whole blood in suspension. It makes up about 55% of the body's total blood volume. It is the ...
. The remaining small percentage of ECF includes the transcellular fluid. These constituents are often called fluid compartments
The human body and even its individual body fluids may be conceptually divided into various fluid compartments, which, although not literally anatomic compartments, do represent a real division in terms of how portions of the body's water, solut ...
. The volume of extracellular fluid in a young adult male of 70 kg, is 20% of body weight – about fourteen litres.
Interstitial fluid
The interstitial fluid is essentially comparable to plasma. The interstitial fluid and plasma make up about 97% of the ECF, and a small percentage of this islymph
Lymph (from Latin, , meaning "water") is the fluid that flows through the lymphatic system, a system composed of lymph vessels (channels) and intervening lymph nodes whose function, like the venous system, is to return fluid from the tissues ...
.
Interstitial fluid is the body fluid between blood vessels and cells, containing nutrients from capillaries
A capillary is a small blood vessel from 5 to 10 micrometres (μm) in diameter. Capillaries are composed of only the tunica intima, consisting of a thin wall of simple squamous endothelial cells. They are the smallest blood vessels in the body: ...
by diffusion and holding waste products discharged by cells due to metabolism
Metabolism (, from el, μεταβολή ''metabolē'', "change") is the set of life-sustaining chemical reactions in organisms. The three main functions of metabolism are: the conversion of the energy in food to energy available to run c ...
. 11 litres of the ECF is interstitial fluid and the remaining three litres is plasma. Plasma and interstitial fluid are very similar because water, ions, and small solutes are continuously exchanged between them across the walls of capillaries, through pores and capillary clefts.
Interstitial fluid consists of a water solvent containing sugars, salts, fatty acids, amino acids, coenzymes, hormones, neurotransmitters, white blood cells and cell waste-products. This solution accounts for 26% of the water in the human body. The composition of interstitial fluid depends upon the exchanges between the cells in the biological tissue and the blood.Widmaier, Eric P., Hershel Raff, Kevin T. Strang, and Arthur J. Vander. "Body Fluid Compartments." ''Vander's Human Physiology: The Mechanisms of Body Function''. 14th ed. New York: McGraw-Hill, 2016. 400-401. Print. This means that tissue fluid has a different composition in different tissues and in different areas of the body.
The plasma that filters through the blood capillaries into the interstitial fluid does not contain red blood cells or platelets as they are too large to pass through but can contain some white blood cells to help the immune system.
Once the extracellular fluid collects into small vessels (lymph capillaries
Lymph capillaries or lymphatic capillaries are tiny, thin-walled microvessels located in the spaces between cells (except in the central nervous system and non-vascular tissues) which serve to drain and process extracellular fluid. Upon enteri ...
) it is considered to be lymph, and the vessels that carry it back to the blood are called the lymphatic vessels. The lymphatic system returns protein and excess interstitial fluid to the circulation.
The ionic composition of the interstitial fluid and blood plasma vary due to the Gibbs–Donnan effect
The Gibbs–Donnan effect (also known as the Donnan's effect, Donnan law, Donnan equilibrium, or Gibbs–Donnan equilibrium) is a name for the behaviour of charged particles near a semi-permeable membrane that sometimes fail to distribute evenly ...
. This causes a slight difference in the concentration of cations and anions between the two fluid compartments.
Transcellular fluid
Transcellular fluid is formed from the transport activities of cells, and is the smallest component of extracellular fluid. These fluids are contained withinepithelial
Epithelium or epithelial tissue is one of the four basic types of animal tissue, along with connective tissue, muscle tissue and nervous tissue. It is a thin, continuous, protective layer of compactly packed cells with a little intercellu ...
lined spaces. Examples of this fluid are cerebrospinal fluid
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is a clear, colorless body fluid found within the tissue that surrounds the brain and spinal cord of all vertebrates.
CSF is produced by specialised ependymal cells in the choroid plexus of the ventricles of the bra ...
, aqueous humor
The aqueous humour is a transparent water-like fluid similar to plasma, but containing low protein concentrations. It is secreted from the ciliary body, a structure supporting the lens of the eyeball. It fills both the anterior and the posteri ...
in the eye, serous fluid
In physiology, serous fluid or serosal fluid (originating from the Medieval Latin word ''serosus'', from Latin ''serum'') is any of various body fluids resembling serum, that are typically pale yellow or transparent and of a benign nature. The fl ...
in the serous membranes lining body cavities
A body cavity is any space or compartment, or potential space, in an animal body. Cavities accommodate organs and other structures; cavities as potential spaces contain fluid.
The two largest human body cavities are the ventral body cavity, and ...
, perilymph
Perilymph is an extracellular fluid located within the inner ear. It is found within the scala tympani and scala vestibuli of the cochlea. The ionic composition of perilymph is comparable to that of plasma and cerebrospinal fluid. The major ca ...
and endolymph
Endolymph is the fluid contained in the membranous labyrinth of the inner ear. The major cation in endolymph is potassium, with the values of sodium and potassium concentration in the endolymph being 0.91 mM and 154 mM, respectively. ...
in the inner ear, and joint fluid. Due to the varying locations of transcellular fluid, the composition changes dramatically. Some of the electrolytes present in the transcellular fluid are sodium
Sodium is a chemical element with the symbol Na (from Latin ''natrium'') and atomic number 11. It is a soft, silvery-white, highly reactive metal. Sodium is an alkali metal, being in group 1 of the periodic table. Its only stable ...
ions, chloride ion
The chloride ion is the anion (negatively charged ion) Cl−. It is formed when the element chlorine (a halogen) gains an electron or when a compound such as hydrogen chloride is dissolved in water or other polar solvents. Chloride salt ...
s, and bicarbonate
In inorganic chemistry, bicarbonate ( IUPAC-recommended nomenclature: hydrogencarbonate) is an intermediate form in the deprotonation of carbonic acid. It is a polyatomic anion with the chemical formula .
Bicarbonate serves a crucial bioch ...
ions.
Function
 The extracellular fluid provides the medium for the exchange of substances between the ECF and the cells, and this can take place through dissolving, mixing and transporting in the fluid medium. Substances in the ECF include dissolved gases, nutrients, and electrolytes, all needed to maintain life. The ECF also contains materials
The extracellular fluid provides the medium for the exchange of substances between the ECF and the cells, and this can take place through dissolving, mixing and transporting in the fluid medium. Substances in the ECF include dissolved gases, nutrients, and electrolytes, all needed to maintain life. The ECF also contains materials secreted 440px
Secretion is the movement of material from one point to another, such as a secreted chemical substance from a cell or gland. In contrast, excretion is the removal of certain substances or waste products from a cell or organism. The classica ...
from cells in soluble form, but which quickly coalesces into fibres (e.g. collagen, reticular, and elastic fibres) or precipitates out into a solid or semisolid form (e.g. proteoglycans
Proteoglycans are proteins that are heavily glycosylated. The basic proteoglycan unit consists of a "core protein" with one or more covalently attached glycosaminoglycan (GAG) chain(s). The point of attachment is a serine (Ser) residue to wh ...
which form the bulk of cartilage, and the components of bone
A bone is a rigid organ that constitutes part of the skeleton in most vertebrate animals. Bones protect the various other organs of the body, produce red and white blood cells, store minerals, provide structure and support for the body, an ...
). These and many other substances occur, especially in association with various proteoglycans to form the extracellular matrix
In biology, the extracellular matrix (ECM), also called intercellular matrix, is a three-dimensional network consisting of extracellular macromolecules and minerals, such as collagen, enzymes, glycoproteins and hydroxyapatite that provide struc ...
or the "filler" substance between the cells throughout the body. These substances occur in the extracellular space, and are therefore all bathed or soaked in ECF, without being part of the ECF.
Oxygenation
One of the main roles of extracellular fluid is to facilitate the exchange of molecular oxygen from blood to tissue cells and for carbon dioxide, CO2, produced in cell mitochondria, back to the blood. Since carbon dioxide is about 20 times more soluble in water than oxygen, it can relatively easily diffuse in the aqueous fluid between cells and blood. However, hydrophobic molecular oxygen has very poor water solubility and prefers hydrophobic lipid crystalline structures. As a result of this, plasma lipoproteins can carry significantly more O2 than in the surrounding aqueous medium. Ifhemoglobin
Hemoglobin (haemoglobin BrE) (from the Greek word αἷμα, ''haîma'' 'blood' + Latin ''globus'' 'ball, sphere' + ''-in'') (), abbreviated Hb or Hgb, is the iron-containing oxygen-transport metalloprotein present in red blood cells (erythrocyte ...
in erythrocytes is the main transporter of oxygen in the blood
Blood is a body fluid in the circulatory system of humans and other vertebrates that delivers necessary substances such as nutrients and oxygen to the cells, and transports metabolic waste products away from those same cells. Blood in th ...
, plasma lipoproteins may be its only carrier in the ECF.
The oxygen-carrying capacity of lipoproteins, OCCL, reduces in ageing
Ageing ( BE) or aging ( AE) is the process of becoming older. The term refers mainly to humans, many other animals, and fungi, whereas for example, bacteria, perennial plants and some simple animals are potentially biologically immortal. In ...
or in inflammation
Inflammation (from la, wikt:en:inflammatio#Latin, inflammatio) is part of the complex biological response of body tissues to harmful stimuli, such as pathogens, damaged cells, or Irritation, irritants, and is a protective response involving im ...
. This results in changes of ECF functions, reduction of tissue O2 supply and contributes to development of tissue hypoxia. These changes in lipoproteins are caused by oxidative or inflammatory damage.
Regulation
The internal environment is stabilised in the process ofhomeostasis
In biology, homeostasis (British English, British also homoeostasis) Help:IPA/English, (/hɒmɪə(ʊ)ˈsteɪsɪs/) is the state of steady internal, physics, physical, and chemistry, chemical conditions maintained by organism, living systems. Thi ...
. Complex homeostatic mechanisms operate to regulate and keep the composition of the ECF stable. Individual cells can also regulate their internal composition by various mechanisms.
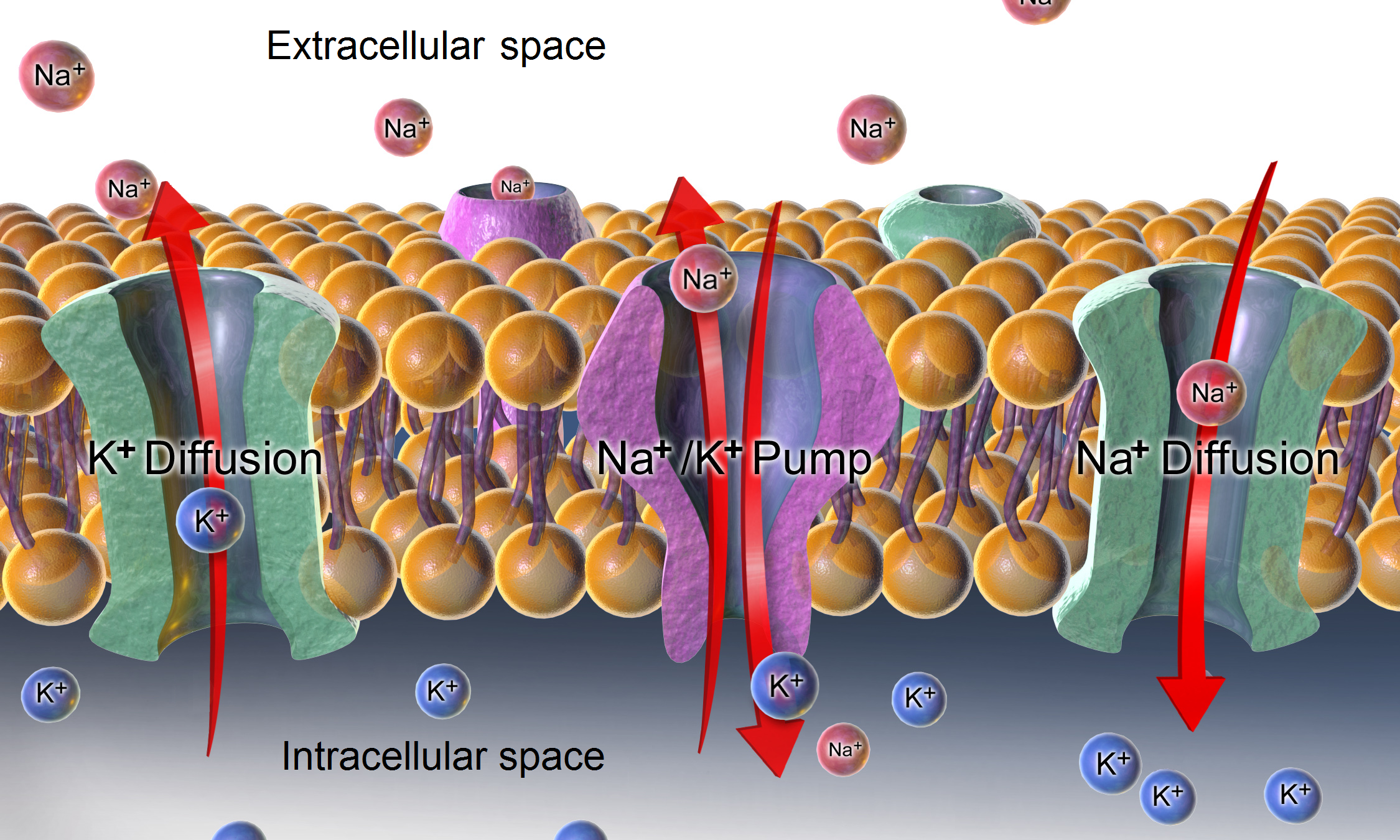
 There is a significant difference between the concentrations of
There is a significant difference between the concentrations of sodium
Sodium is a chemical element with the symbol Na (from Latin ''natrium'') and atomic number 11. It is a soft, silvery-white, highly reactive metal. Sodium is an alkali metal, being in group 1 of the periodic table. Its only stable ...
and potassium
Potassium is the chemical element with the symbol K (from Neo-Latin '' kalium'') and atomic number19. Potassium is a silvery-white metal that is soft enough to be cut with a knife with little force. Potassium metal reacts rapidly with atmosp ...
ions inside and outside the cell. The concentration of sodium ions is considerably higher in the extracellular fluid than in the intracellular fluid. The converse is true of the potassium ion concentrations inside and outside the cell. These differences cause all cell membrane
The cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane (PM) or cytoplasmic membrane, and historically referred to as the plasmalemma) is a biological membrane that separates and protects the interior of all cells from the outside environment (the ...
s to be electrically charged, with the positive charge on the outside of the cells and the negative charge on the inside. In a resting neuron (not conducting an impulse) the membrane potential
Membrane potential (also transmembrane potential or membrane voltage) is the difference in electric potential between the interior and the exterior of a biological cell. That is, there is a difference in the energy required for electric charge ...
is known as the resting potential A relatively static membrane potential which is usually referred to as the ground value for trans-membrane voltage.
The relatively static membrane potential of quiescent cells is called the resting membrane potential (or resting voltage), as opp ...
, and between the two sides of the membrane is about -70 mV.
This potential is created by sodium-potassium pumps in the cell membrane, which pump sodium ions out of the cell, into the ECF, in return for potassium ions which enter the cell from the ECF. The maintenance of this difference in the concentration of ions between the inside of the cell and the outside, is critical to keep normal cell volumes stable, and also to enable some cells to generate action potential
An action potential occurs when the membrane potential of a specific cell location rapidly rises and falls. This depolarization then causes adjacent locations to similarly depolarize. Action potentials occur in several types of animal cells, ...
s.
In several cell types voltage-gated ion channel
Voltage-gated ion channels are a class of transmembrane proteins that form ion channels that are activated by changes in the electrical membrane potential near the channel. The membrane potential alters the conformation of the channel proteins, ...
s in the cell membrane can be temporarily opened under specific circumstances for a few microseconds at a time. This allows a brief inflow of sodium ions into the cell (driven in by the sodium ion concentration gradient that exists between the outside and inside of the cell). This causes the cell membrane to temporarily depolarize (lose its electrical charge) forming the basis of action potentials.
The sodium ions in the ECF also play an important role in the movement of water from one body compartment to the other. When tears are secreted, or saliva is formed, sodium ions are pumped from the ECF into the ducts in which these fluids are formed and collected. The water content of these solutions results from the fact water follows the sodium ions (and accompanying anion
An ion () is an atom or molecule with a net electrical charge.
The charge of an electron is considered to be negative by convention and this charge is equal and opposite to the charge of a proton, which is considered to be positive by conve ...
s) osmotically. The same principle applies to the formation of many other body fluid
Body fluids, bodily fluids, or biofluids, sometimes body liquids, are liquids within the human body. In lean healthy adult men, the total body water is about 60% (60–67%) of the total body weight; it is usually slightly lower in women (52-55%) ...
s.
Calcium ions have a great propensity to bind to proteins. This changes the distribution of electrical charges on the protein, with the consequence that the 3D (or tertiary) structure of the protein is altered. The normal shape, and therefore function of very many of the extracellular proteins, as well as the extracellular portions of the cell membrane proteins is dependent on a very precise ionized calcium concentration in the ECF. The proteins that are particularly sensitive to changes in the ECF ionized calcium concentration are several of the clotting factors
Coagulation, also known as clotting, is the process by which blood changes from a liquid to a gel, forming a blood clot. It potentially results in hemostasis, the cessation of blood loss from a damaged vessel, followed by repair. The mechanism ...
in the blood plasma, which are functionless in the absence of calcium ions, but become fully functional on the addition of the correct concentration of calcium salts. The voltage gated sodium ion channels in the cell membranes of nerves and muscle have an even greater sensitivity to changes in the ECF ionized calcium concentration. Relatively small decreases in the plasma ionized calcium levels (hypocalcemia
Hypocalcemia is a medical condition characterized by low calcium levels in the blood serum. The normal range of blood calcium is typically between 2.1–2.6 mmol/L (8.8–10.7 mg/dL, 4.3–5.2 mEq/L) while levels less than 2.1 mm ...
) cause these channels to leak sodium into the nerve cells or axons, making them hyper-excitable, thus causing spontaneous muscle spasms (tetany
Tetany or tetanic seizure is a medical sign consisting of the involuntary contraction of muscles, which may be caused by disorders that increase the action potential frequency of muscle cells or the nerves that innervate them.
Muscle cramps cause ...
) and paraesthesia
Paresthesia is an abnormal sensation of the skin (tingling, pricking, chilling, burning, numbness) with no apparent physical cause. Paresthesia may be transient or chronic, and may have any of dozens of possible underlying causes. Paresthesias ar ...
(the sensation of "pins and needles") of the extremities and round the mouth. When the plasma ionized calcium rises above normal (hypercalcemia
Hypercalcemia, also spelled hypercalcaemia, is a high calcium (Ca2+) level in the blood serum. The normal range is 2.1–2.6 mmol/L (8.8–10.7 mg/dL, 4.3–5.2 mEq/L), with levels greater than 2.6 mmol/L defined as hypercalce ...
) more calcium is bound to these sodium channels having the opposite effect, causing lethargy, muscle weakness, anorexia, constipation and labile emotions.
The tertiary structure of proteins is also affected by the pH of the bathing solution. In addition, the pH of the ECF affects the proportion of the total amount of calcium in the plasma which occurs in the free, or ionized form, as opposed to the fraction that is bound to protein and phosphate ions. A change in the pH of the ECF therefore alters the ionized calcium concentration of the ECF. Since the pH of the ECF is directly dependent on the partial pressure of carbon dioxide in the ECF, hyperventilation
Hyperventilation is irregular breathing that occurs when the rate or tidal volume of breathing eliminates more carbon dioxide than the body can produce. This leads to hypocapnia, a reduced concentration of carbon dioxide dissolved in the blood. ...
, which lowers the partial pressure of carbon dioxide in the ECF, produces symptoms that are almost indistinguishable from low plasma ionized calcium concentrations.
The extracellular fluid is constantly "stirred" by the circulatory system
The blood circulatory system is a system of organs that includes the heart, blood vessels, and blood which is circulated throughout the entire body of a human or other vertebrate. It includes the cardiovascular system, or vascular system, tha ...
, which ensures that the watery environment which bathes the body's cells is virtually identical throughout the body. This means that nutrients can be secreted into the ECF in one place (e.g. the gut, liver, or fat cells) and will, within about a minute, be evenly distributed throughout the body. Hormones are similarly rapidly and evenly spread to every cell in the body, regardless of where they are secreted into the blood. Oxygen taken up by the lungs from the alveolar air is also evenly distributed at the correct partial pressure to all the cells of the body. Waste products are also uniformly spread to the whole of the ECF, and are removed from this general circulation at specific points (or organs), once again ensuring that there is generally no localized accumulation of unwanted compounds or excesses of otherwise essential substances (e.g. sodium ions, or any of the other constituents of the ECF). The only significant exception to this general principle is the plasma in the vein
Veins are blood vessels in humans and most other animals that carry blood towards the heart. Most veins carry deoxygenated blood from the tissues back to the heart; exceptions are the pulmonary and umbilical veins, both of which carry oxygenate ...
s, where the concentrations of dissolved substances in individual veins differ, to varying degrees, from those in the rest of the ECF. However, this plasma is confined within the waterproof walls of the venous tubes, and therefore does not affect the interstitial fluid in which the body's cells live. When the blood from all the veins in the body mixes in the heart and lungs, the differing compositions cancel out (e.g. acidic blood from active muscles is neutralized by the alkaline blood homeostatically produced by the kidneys). From the left atrium
The atrium ( la, ātrium, , entry hall) is one of two upper chambers in the heart that receives blood from the circulatory system. The blood in the atria is pumped into the heart ventricles through the atrioventricular valves.
There are two ...
onward, to every organ in the body, the normal, homeostatically regulated values of all of the ECF's components are therefore restored.
Interaction between the blood plasma, interstitial fluid and lymph
 The arterial blood plasma, interstitial fluid and lymph interact at the level of the blood
The arterial blood plasma, interstitial fluid and lymph interact at the level of the blood capillaries
A capillary is a small blood vessel from 5 to 10 micrometres (μm) in diameter. Capillaries are composed of only the tunica intima, consisting of a thin wall of simple squamous endothelial cells. They are the smallest blood vessels in the body: ...
. The capillaries are permeable
Permeability, permeable, and semipermeable may refer to:
Chemistry
*Semipermeable membrane, a membrane which will allow certain molecules or ions to pass through it by diffusion
*Vascular permeability, the movement of fluids and molecules betwe ...
and water can move freely in and out. At the arteriolar end of the capillary the blood pressure is greater than the hydrostatic pressure
Fluid statics or hydrostatics is the branch of fluid mechanics that studies the condition of the equilibrium of a floating body and submerged body " fluids at hydrostatic equilibrium and the pressure in a fluid, or exerted by a fluid, on an i ...
in the tissues. Water will therefore seep out of the capillary into the interstitial fluid. The pores through which this water moves are large enough to allow all the smaller molecules (up to the size of small proteins such as insulin
Insulin (, from Latin ''insula'', 'island') is a peptide hormone produced by beta cells of the pancreatic islets encoded in humans by the ''INS'' gene. It is considered to be the main anabolic hormone of the body. It regulates the metabol ...
) to move freely through the capillary wall as well. This means that their concentrations across the capillary wall equalize, and therefore have no osmotic effect (because the osmotic pressure caused by these small molecules and ions – called the crystalloid osmotic pressure to distinguish it from the osmotic effect of the larger molecules that cannot move across the capillary membrane – is the same on both sides of capillary wall).
The movement of water out of the capillary at the arteriolar end causes the concentration of the substances that cannot cross the capillary wall to increase as the blood moves to the venular end of the capillary. The most important substances that are confined to the capillary tube are plasma albumin, the plasma globulins and fibrinogen
Fibrinogen (factor I) is a glycoprotein complex, produced in the liver, that circulates in the blood of all vertebrates. During tissue and vascular injury, it is converted enzymatically by thrombin to fibrin and then to a fibrin-based blood ...
. They, and particularly the plasma albumin, because of its molecular abundance in the plasma, are responsible for the so-called "oncotic" or "colloid" osmotic pressure which draws water back into the capillary, especially at the venular end.
The net effect of all of these processes is that water moves out of and back into the capillary, while the crystalloid substances in the capillary and interstitial fluids equilibrate. Since the capillary fluid is constantly and rapidly renewed by the flow of the blood, its composition dominates the equilibrium concentration that is achieved in the capillary bed. This ensures that the watery environment of the body's cells is always close to their ideal environment (set by the body's homeostats).
A small proportion of the solution that leaks out of the capillaries is not drawn back into the capillary by the colloid osmotic forces. This amounts to between 2-4 liters per day for the body as a whole. This water is collected by the lymphatic system
The lymphatic system, or lymphoid system, is an organ system in vertebrates that is part of the immune system, and complementary to the circulatory system. It consists of a large network of lymphatic vessels, lymph nodes, lymphatic or lymphoi ...
and is ultimately discharged into the left subclavian vein
The subclavian vein is a paired large vein, one on either side of the body, that is responsible for draining blood from the upper extremities, allowing this blood to return to the heart. The left subclavian vein plays a key role in the absorption ...
, where it mixes with the venous blood coming from the left arm, on its way to the heart. The lymph
Lymph (from Latin, , meaning "water") is the fluid that flows through the lymphatic system, a system composed of lymph vessels (channels) and intervening lymph nodes whose function, like the venous system, is to return fluid from the tissues ...
flows through lymph capillaries
Lymph capillaries or lymphatic capillaries are tiny, thin-walled microvessels located in the spaces between cells (except in the central nervous system and non-vascular tissues) which serve to drain and process extracellular fluid. Upon enteri ...
to lymph node
A lymph node, or lymph gland, is a kidney-shaped organ of the lymphatic system and the adaptive immune system. A large number of lymph nodes are linked throughout the body by the lymphatic vessels. They are major sites of lymphocytes that inc ...
s where bacteria and tissue debris are removed from the lymph, while various types of white blood cells
White blood cells, also called leukocytes or leucocytes, are the cells of the immune system that are involved in protecting the body against both infectious disease and foreign invaders. All white blood cells are produced and derived from mult ...
(mainly lymphocytes) are added to the fluid. In addition the lymph which drains the small intestine contains fat droplets called chylomicron
Chylomicrons (from the Greek χυλός, chylos, meaning ''juice'' (of plants or animals), and micron, meaning ''small particle''), also known as ultra low-density lipoproteins (ULDL), are lipoprotein particles that consist of triglycerides (8 ...
s after the ingestion of a fatty meal. This lymph is called chyle
Chyle (from the Greek word χυλός ''chylos'', "juice") is a milky bodily fluid
Body fluids, bodily fluids, or biofluids, sometimes body liquids, are liquids within the human body. In lean healthy adult men, the total body water is about 60 ...
which has a milky appearance, and imparts the name lacteal
A lacteal is a lymphatic capillary that absorbs dietary fats in the villi of the small intestine.
Triglycerides are emulsified by bile and hydrolyzed by the enzyme lipase, resulting in a mixture of fatty acids, di- and monoglycerides. These ...
s (referring to the milky appearance of their contents) to the lymph vessels of the small intestine.
Extracellular fluid may be mechanically guided in this circulation by the vesicles between other structures. Collectively this forms the interstitium
The interstitium is a contiguous fluid-filled space existing between a structural barrier, such as a cell membrane or the skin, and internal structures, such as organs, including muscles and the circulatory system. The fluid in this space is ...
, which may be considered a newly identified biological structure in the body. However, there is some debate over whether the interstitium is an organ.
Electrolytic constituents
Maincations
An ion () is an atom or molecule with a net electrical charge.
The charge of an electron is considered to be negative by convention and this charge is equal and opposite to the charge of a proton, which is considered to be positive by conve ...
:
*Sodium
Sodium is a chemical element with the symbol Na (from Latin ''natrium'') and atomic number 11. It is a soft, silvery-white, highly reactive metal. Sodium is an alkali metal, being in group 1 of the periodic table. Its only stable ...
(Na+) 136–146 mM
*Potassium
Potassium is the chemical element with the symbol K (from Neo-Latin '' kalium'') and atomic number19. Potassium is a silvery-white metal that is soft enough to be cut with a knife with little force. Potassium metal reacts rapidly with atmosp ...
(K+) 3.8–5.0 mM
*Calcium
Calcium is a chemical element with the symbol Ca and atomic number 20. As an alkaline earth metal, calcium is a reactive metal that forms a dark oxide-nitride layer when exposed to air. Its physical and chemical properties are most similar t ...
(Ca2+) 1.0–1.4 mM
Main anions
An ion () is an atom or molecule with a net electrical charge.
The charge of an electron is considered to be negative by convention and this charge is equal and opposite to the charge of a proton, which is considered to be positive by conve ...
:
*Chloride
The chloride ion is the anion (negatively charged ion) Cl−. It is formed when the element chlorine (a halogen) gains an electron or when a compound such as hydrogen chloride is dissolved in water or other polar solvents. Chloride s ...
(Cl−) 103–112 mM
*Bicarbonate
In inorganic chemistry, bicarbonate ( IUPAC-recommended nomenclature: hydrogencarbonate) is an intermediate form in the deprotonation of carbonic acid. It is a polyatomic anion with the chemical formula .
Bicarbonate serves a crucial bioch ...
(HCO3−) 22–28 mM
*Phosphate
In chemistry, a phosphate is an anion, salt, functional group or ester derived from a phosphoric acid. It most commonly means orthophosphate, a derivative of orthophosphoric acid .
The phosphate or orthophosphate ion is derived from phosph ...
(HPO42−) 0.8-1.4 mM
Guyton & Hall Textbook of Medical Physiology (page 5)
See also
* Effective circulating volume (ECV) *Fluid compartments
The human body and even its individual body fluids may be conceptually divided into various fluid compartments, which, although not literally anatomic compartments, do represent a real division in terms of how portions of the body's water, solut ...
References
External links
Britannica.com
{{Authority control Body fluids Cell biology