exstrophy on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Bladder exstrophy is a
 Modern therapy is aimed at surgical reconstruction of the bladder and genitalia. Both males and females are born with this anomaly. Treatment is similar.
In males treatments have been:
In the modern staged repair of exstrophy (MSRE) the initial step is closure of the abdominal wall, often requiring a pelvic
Modern therapy is aimed at surgical reconstruction of the bladder and genitalia. Both males and females are born with this anomaly. Treatment is similar.
In males treatments have been:
In the modern staged repair of exstrophy (MSRE) the initial step is closure of the abdominal wall, often requiring a pelvic
congenital
A birth defect, also known as a congenital disorder, is an abnormal condition that is present at birth regardless of its cause. Birth defects may result in disabilities that may be physical, intellectual, or developmental. The disabilities can ...
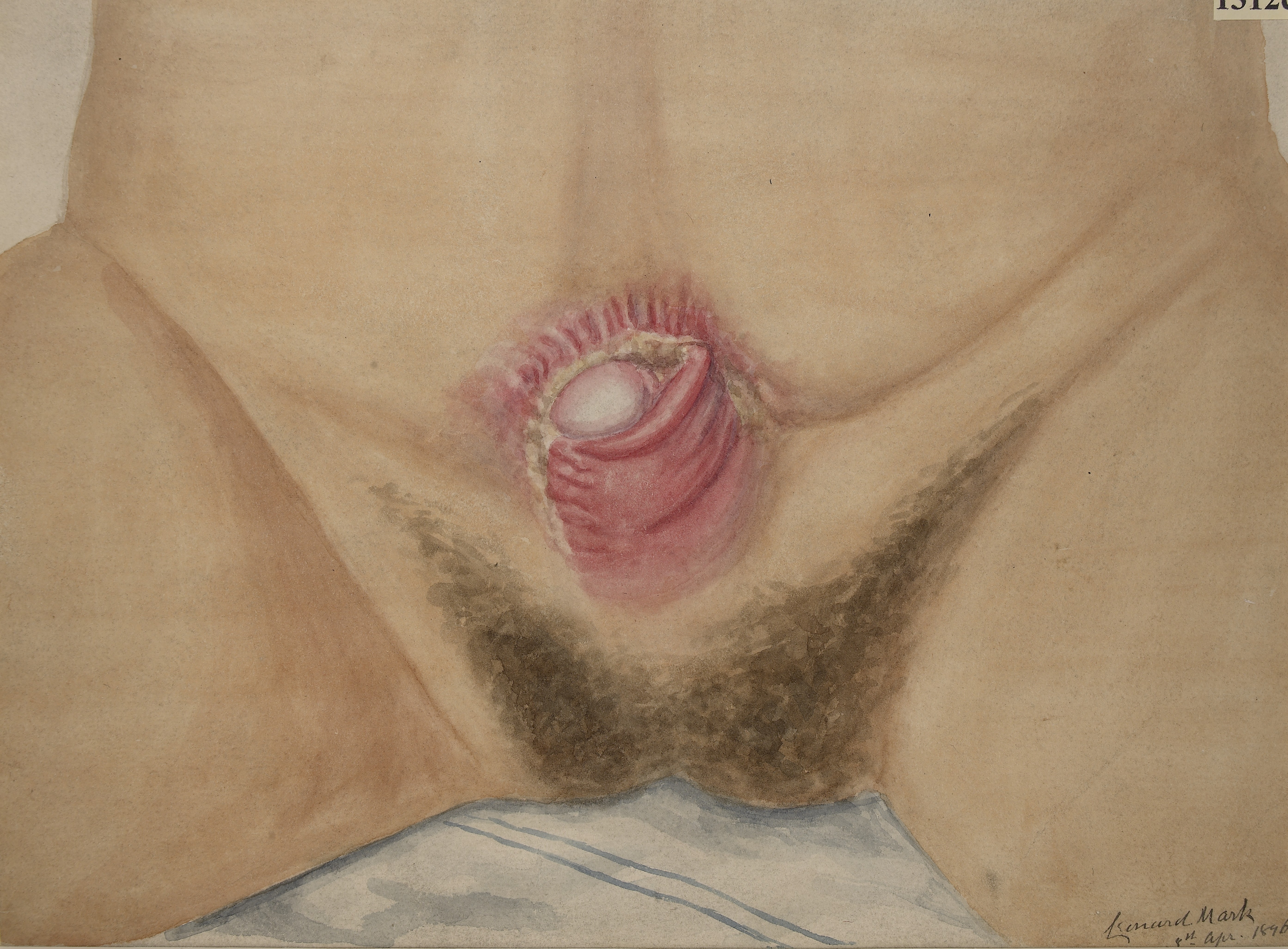
anomaly that exists along the spectrum of the exstrophy-epispadias complex, and most notably involves protrusion of the urinary bladder
The urinary bladder, or simply bladder, is a hollow organ in humans and other vertebrates that stores urine from the kidneys before disposal by urination. In humans the bladder is a distensible organ that sits on the pelvic floor. Urine enters ...
through a defect in the abdominal wall. Its presentation is variable, often including abnormalities of the bony pelvis, pelvic floor
The pelvic floor or pelvic diaphragm is composed of muscle fibers of the levator ani, the coccygeus muscle, and associated connective tissue which span the area underneath the pelvis. The pelvic diaphragm is a muscular partition formed by the lev ...
, and genitalia. The underlying embryologic mechanism leading to bladder exstrophy is unknown, though it is thought to be in part due to failed reinforcement of the cloacal membrane
The cloacal membrane is the membrane that covers the embryonic cloaca during the development of the urinary and reproductive organs.
It is formed by ectoderm and endoderm coming into contact with each other. As the human embryo grows and caudal ...
by underlying mesoderm
The mesoderm is the middle layer of the three germ layers that develops during gastrulation in the very early development of the embryo of most animals. The outer layer is the ectoderm, and the inner layer is the endoderm.Langman's Medical E ...
.
Exstrophy means the inversion of a hollow organ.
Signs and symptoms
The classic manifestation of bladder exstrophy presents with: * A defect in the abdominal wall occupied by both the exstrophied bladder as well as a portion of theurethra
The urethra (from Greek οὐρήθρα – ''ourḗthrā'') is a tube that connects the urinary bladder to the urinary meatus for the removal of urine from the body of both females and males. In human females and other primates, the urethra con ...
* A flattened puborectal sling
The levator ani is a broad, thin muscle group, situated on either side of the pelvis. It is formed from three muscle components: the pubococcygeus, the iliococcygeus, and the puborectalis.
It is attached to the inner surface of each side of t ...
* Separation of the pubic symphysis
The pubic symphysis is a secondary cartilaginous joint between the left and right superior rami of the pubis of the hip bones. It is in front of and below the urinary bladder. In males, the suspensory ligament of the penis attaches to the pubic ...
* Shortening of a pubic rami
* External rotation of the pelvis.
Females frequently have a displaced and narrowed vaginal orifice
In mammals, the vagina is the elastic, muscular part of the female genital tract. In humans, it extends from the vestibule to the cervix. The outer vaginal opening is normally partly covered by a thin layer of mucosal tissue called the hymen ...
, a bifid
Bifid refers to something that is split or cleft into two parts. It may refer to:
* Bifid, a variation in the P wave, R wave, or T wave in an echocardiogram in which a wave which usually has a single peak instead has two separate peaks
* Bifid ci ...
clitoris
The clitoris ( or ) is a female sex organ present in mammals, ostriches and a limited number of other animals. In humans, the visible portion – the glans – is at the front junction of the labia minora (inner lips), above the ope ...
, and divergent labia
The labia are part of the female genitalia; they are the major externally visible portions of the vulva. In humans, there are two pairs of labia: the ''labia majora'' (or the outer labia) are larger and thicker, while the ''labia minora'' are fol ...
.
Cause
The cause is not yet clinically established but is thought to be in part due to failed reinforcement of the cloacal membrane by underlying mesoderm.Diagnosis
In a small retrospective study of 25 pregnancies five factors were found to be strongly associated with a prenatal diagnosis of bladder exstrophy: * Inability to visualize the bladder on ultrasound * A lower abdominal bulge * A small penis with anteriorly displaced scrotum * A low set umbilical insertion * Abnormal widening of the iliac crests While a diagnosis of bladder exstrophy was made retrospectively in a majority of pregnancies, in only three cases was a prenatal diagnosis made.Management
The extreme rarity of the disease limits the surgical opportunities to practice the complex closure required in these patients. For this reason, patients have the best outcomes when the bladder closures are performed at high volume centers where surgical and nursing teams have extensive experience in caring for the disease. The highest volume center in the United States, and the world, is the Johns Hopkins Hospital in Baltimore, Maryland; they have seen over 1300 exstrophy patients in the past 50 years. Upon delivery, the exposed bladder is irrigated and a non-adherent film is placed to prevent as much contact with the external environment as possible. In the event the child was not born at a medical center with an appropriate exstrophy support team then transfer will likely follow. Upon transfer, or for those infants born at a medical center able to care for bladder exstrophy, imaging may take place in the first few hours of life prior to the child undergoing surgery. Primary (immediate) closure is indicated only in those patients with a bladder of appropriate size, elasticity, and contractility as those patients are most likely to develop a bladder of adequate capacity after early surgical intervention. Conditions that are absolute contraindications despite bladder adequacy include duplication of the penis or scrotum and significant bilateralhydronephrosis
Hydronephrosis describes hydrostatic dilation of the renal pelvis and calyces as a result of obstruction to urine flow downstream. Alternatively, hydroureter describes the dilation of the ureter, and hydronephroureter describes the dilation of t ...
.
Surgery
 Modern therapy is aimed at surgical reconstruction of the bladder and genitalia. Both males and females are born with this anomaly. Treatment is similar.
In males treatments have been:
In the modern staged repair of exstrophy (MSRE) the initial step is closure of the abdominal wall, often requiring a pelvic
Modern therapy is aimed at surgical reconstruction of the bladder and genitalia. Both males and females are born with this anomaly. Treatment is similar.
In males treatments have been:
In the modern staged repair of exstrophy (MSRE) the initial step is closure of the abdominal wall, often requiring a pelvic osteotomy
An osteotomy is a surgical operation whereby a bone is cut to shorten or lengthen it or to change its alignment. It is sometimes performed to correct a hallux valgus, or to straighten a bone that has healed crookedly following a fracture. It is ...
. This leaves the patient with penile epispadias and urinary incontinence
Urinary incontinence (UI), also known as involuntary urination, is any uncontrolled leakage of urine. It is a common and distressing problem, which may have a large impact on quality of life. It has been identified as an important issue in geria ...
. At approximately 2–3 years of age, the patient then undergoes repair of the epispadias after testosterone
Testosterone is the primary sex hormone and anabolic steroid in males. In humans, testosterone plays a key role in the development of Male reproductive system, male reproductive tissues such as testes and prostate, as well as promoting secondar ...
stimulation. Finally, bladder neck repair usually occurs around the age of 4–5 years, though this is dependent upon a bladder with adequate capacity and, most importantly, an indication that the child is interested in becoming continent. In some of the bladder reconstructions, the bladder is augmented with the addition of a segment of the large intestines to increase the volume capacity of the reconstructed bladder.
In the complete primary repair of exstrophy (CPRE) the bladder closure is combined with an epispadias repair, in an effort to decrease costs and morbidity. This technique has, however, led to significant loss of penile and corporal tissue, particularly in younger patients.
In females treatment has included:
Surgical reconstruction of the clitoris, which is separated into two distinct bodies. Surgical reconstruction to correct the split of the mons, redefine the structure of the bladder neck and urethra. Vaginoplasty
Vaginoplasty is any surgical procedure that results in the construction or reconstruction of the vagina. It is a type of genitoplasty. Pelvic organ prolapse is often treated with one or more surgeries to repair the vagina. Sometimes a vaginoplas ...
will correct the anteriorly displaced vagina. If the anus is involved, it is also repaired. Fertility remains and women who were born with bladder exstrophy usually develop prolapse due to the weaker muscles of the pelvic floor.
Prognosis
The most important criterion for improving long-term prognosis is success of the initial closure. If a patient requires more than one closure their chance of continence drops off precipitously with each additional closure - at just two closures the chance of voiding continence is just 17%. Even with successful surgery, people may have long-term complications. Some of the most common include: *Vesicoureteral reflux
Vesicoureteral reflux (VUR), also known as vesicoureteric reflux, is a condition in which urine flows retrograde, or backward, from the bladder into one or both ureters and then to the renal calyx or kidneys. Urine normally travels in one directi ...
* Bladder spasm
Overactive bladder (OAB) is a condition where there is a frequent feeling of needing to urinate to a degree that it negatively affects a person's life. The frequent need to urinate may occur during the day, at night, or both. If there is loss ...
* Bladder calculus
A bladder stone is a stone found in the urinary bladder.
Signs and symptoms
Bladder stones are small mineral deposits that can form in the bladder. In most cases bladder stones develop when the urine becomes very concentrated or when one is d ...
* Urinary tract infections
A urinary tract infection (UTI) is an infection that affects part of the urinary tract. When it affects the lower urinary tract it is known as a bladder infection (cystitis) and when it affects the upper urinary tract it is known as a kidney ...
Epidemiology
Occurring at a rate between 1 in 10,000 to 1 in 50,000 with a male-to-female ratio of 2.3-6:1, bladder exstrophy is relatively rare. For those individuals with bladder exstrophy who maintain their ability to reproduce, the risk of bladder exstrophy in their children is approximately 500-fold greater than the general population.References
External links
{{Congenital malformations of urinary system Urinary bladder disorders Congenital disorders of urinary system Rare diseases