|
Urinary Bladder Disorders
Urinary bladder disease includes urinary bladder inflammation such as cystitis, bladder rupture and bladder obstruction (tamponade). Cystitis is common, sometimes referred to as urinary tract infection (UTI) caused by bacteria, bladder rupture occurs when the bladder is overfilled and not emptied while bladder tamponade is a result of blood clot formation near the bladder outlet. Cystitis Cystitis is a urinary bladder inflammation that results from any one of a number of distinct syndromes. It is most commonly caused by a bacterial infection in which case it is referred to as a urinary tract infection. Bladder trauma Bladder rupture (rupture of bladder, ) may occur if the bladder is overfilled and not emptied. This can occur in the case of binge drinkers who have consumed large quantities of fluids, but are not conscious of the need to urinate due to stupor. This condition is very rare in women, but does occur. Signs and symptoms include localized pain and uraemia (poisoning due ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
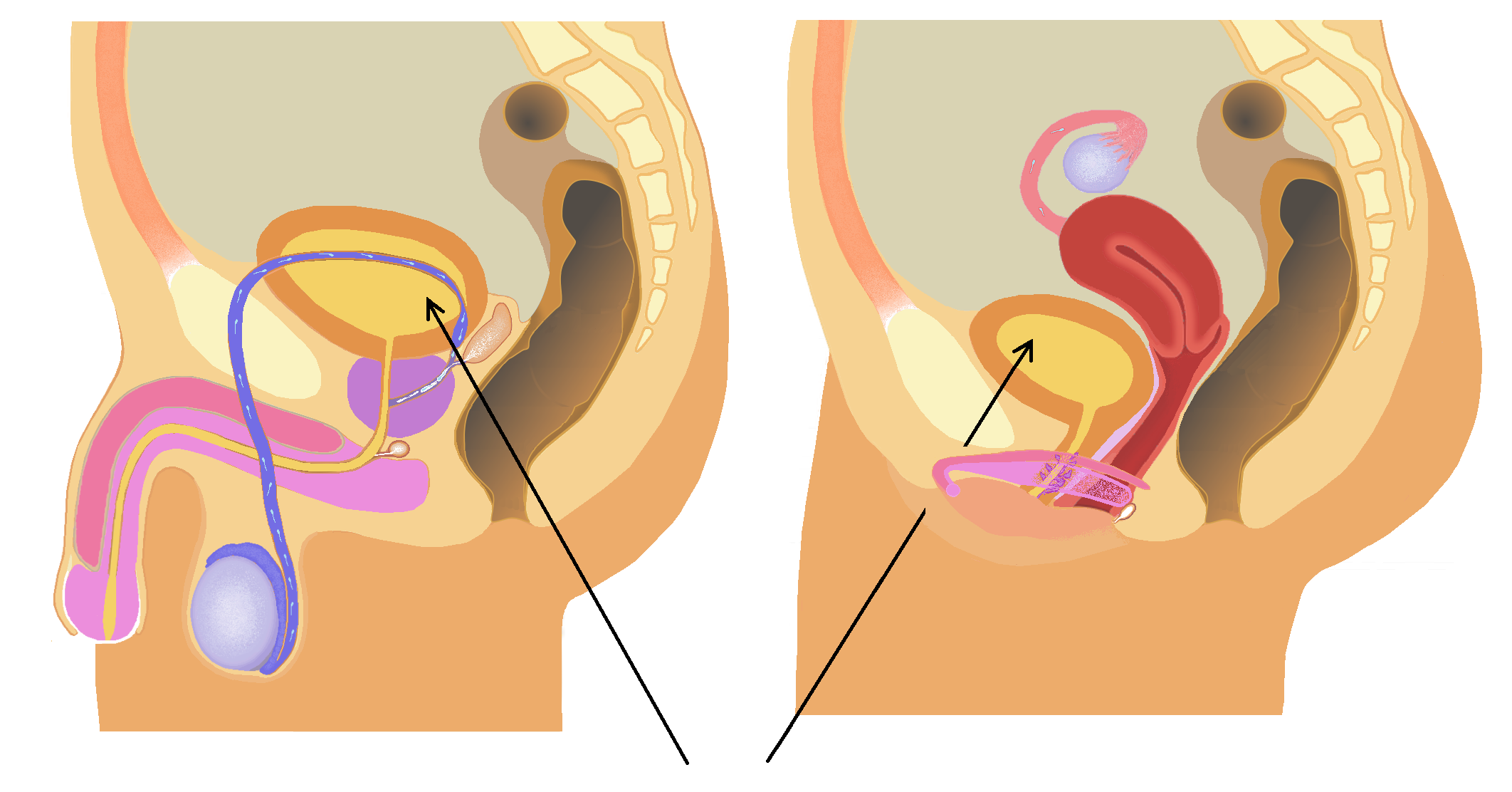
Urinary Bladder
The bladder () is a hollow organ in humans and other vertebrates that stores urine from the Kidney (vertebrates), kidneys. In placental mammals, urine enters the bladder via the ureters and exits via the urethra during urination. In humans, the bladder is a distensible organ that sits on the pelvic floor. The typical adult human bladder will hold between 300 and (10 and ) before the urge to empty occurs, but can hold considerably more. The Latin phrase for "urinary bladder" is ''vesica urinaria'', and the term ''vesical'' or prefix ''vesico-'' appear in connection with associated structures such as vesical veins. The modern Latin word for "bladder" – ''cystis'' – appears in associated terms such as cystitis (inflammation of the bladder). Structure In humans, the bladder is a hollow muscular organ situated at the base of the pelvis. In gross anatomy, the bladder can be divided into a broad (base), a body, an apex, and a neck. The apex (also called the vertex) is directed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Morbidity
A disease is a particular abnormal condition that adversely affects the structure or function of all or part of an organism and is not immediately due to any external injury. Diseases are often known to be medical conditions that are associated with specific signs and symptoms. A disease may be caused by external factors such as pathogens or by internal dysfunctions. For example, internal dysfunctions of the immune system can produce a variety of different diseases, including various forms of immunodeficiency, hypersensitivity, allergies, and autoimmune disorders. In humans, ''disease'' is often used more broadly to refer to any condition that causes pain, dysfunction, distress, social problems, or death to the person affected, or similar problems for those in contact with the person. In this broader sense, it sometimes includes injuries, disabilities, disorders, syndromes, infections, isolated symptoms, deviant behaviors, and atypical variations of structure and f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Underactive Bladder
Underactive bladder syndrome (UAB) describes symptoms of difficulty with bladder emptying, such as hesitancy to start the stream, a poor or intermittent stream, or sensations of incomplete bladder emptying. The physical finding of detrusor activity of insufficient strength or duration to ensure efficient bladder emptying is properly termed "detrusor underactivity" (DU). Historically, UAB and DU (as well as others such as 'bladder underactivity') have been often used interchangeably, leading to both terminologic and pathophysiologic confusion. Patients with underactive bladder have a diminished sense of bladder filling and consequently are often found to have DU as an underlying finding, however bladder outlet obstruction and less frequently volume hypersensitivity ("OAB") can be associated with UAB symptoms. Causes Without diagnostic evaluation, the cause of underactive bladder is unclear, as there are multiple possible causes. UAB symptoms can accurately reflect impaired bladd ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
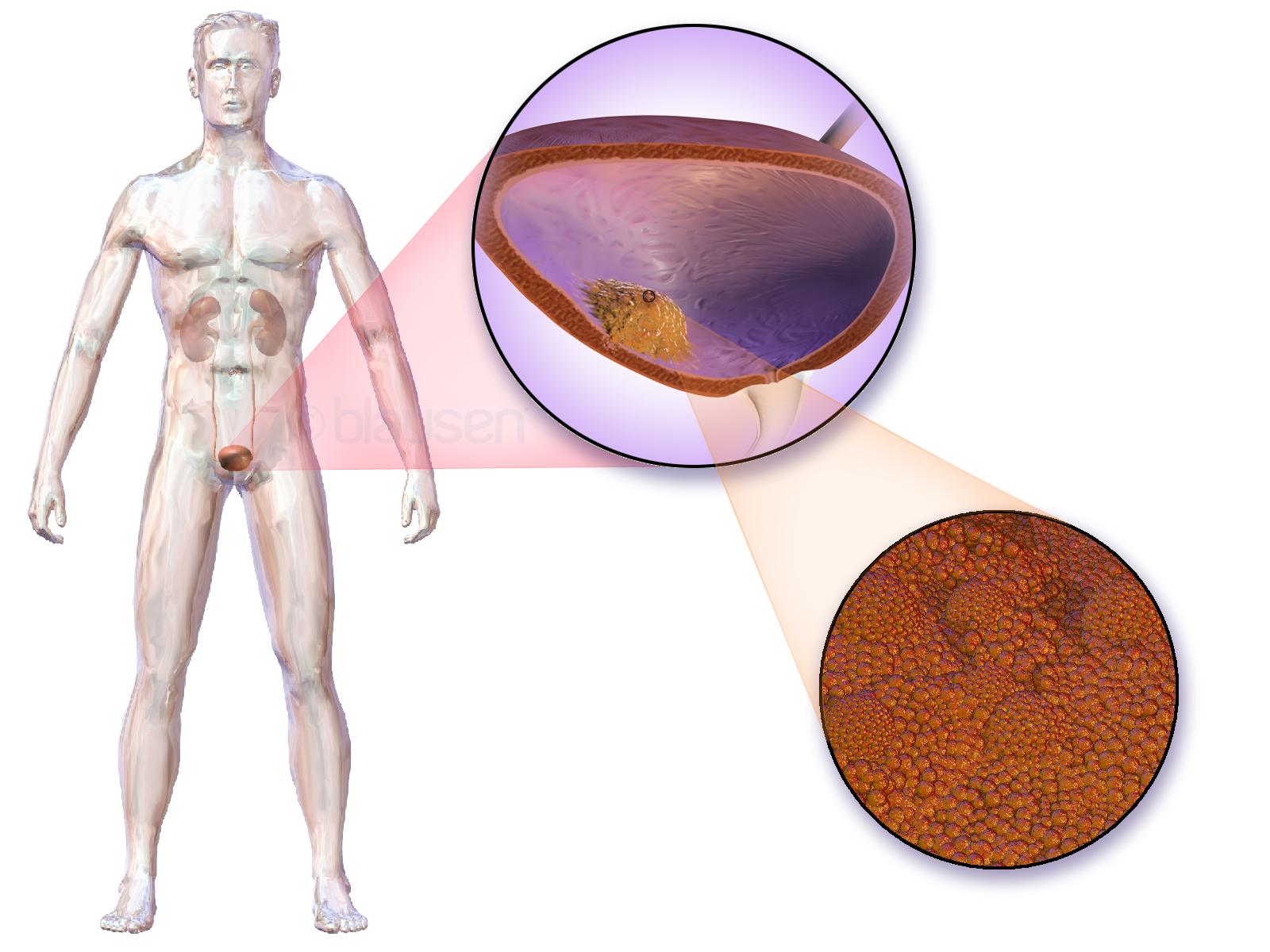
Bladder Cancer
Bladder cancer is the abnormal growth of cells in the bladder. These cells can grow to form a tumor, which eventually spreads, damaging the bladder and other organs. Most people with bladder cancer are diagnosed after noticing blood in their urine. Those suspected of having bladder cancer typically have their bladder inspected by a thin medical camera, a procedure called cystoscopy. Suspected tumors are removed and examined to determine if they are cancerous. Based on how far the tumor has spread, the cancer case is assigned a stage 0 to 4; a higher stage indicates a more widespread and dangerous disease. Those whose bladder tumors have not spread outside the bladder have the best prognoses. These tumors are typically surgically removed, and the person is treated with chemotherapy or one of several immune-stimulating therapies. Those whose tumors continue to grow, or whose tumors have penetrated the bladder muscle, often have their bladder surgically removed ( radical cy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tamponade
Tamponade () is the closure or blockage (as of a wound or body cavity) by or as if by a tampon, especially to stop bleeding. Tamponade is a useful method of stopping a hemorrhage. This can be achieved by applying an absorbent dressing directly into a wound, thereby absorbing excess blood and creating a blockage, or by applying direct pressure with a hand or a tourniquet. Not to be confused with a tamponade that occurs as a result of health problems. For example: cardiac tamponade is a condition where fluid collects in the pericardial sac increasing pressure within the pericardium which in turn prevents the ventricles from expanding fully significantly reducing the efficiency of the heart. It is considered a medical emergency and if left unchecked is fatal. Bladder tamponade is obstruction of the urinary bladder outlet due to heavy blood clot formation within it. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sepsis
Sepsis is a potentially life-threatening condition that arises when the body's response to infection causes injury to its own tissues and organs. This initial stage of sepsis is followed by suppression of the immune system. Common signs and symptoms include fever, tachycardia, increased heart rate, hyperventilation, increased breathing rate, and mental confusion, confusion. There may also be symptoms related to a specific infection, such as a cough with pneumonia, or dysuria, painful urination with a pyelonephritis, kidney infection. The very young, old, and people with a immunodeficiency, weakened immune system may not have any symptoms specific to their infection, and their hypothermia, body temperature may be low or normal instead of constituting a fever. Severe sepsis may cause organ dysfunction and significantly reduced blood flow. The presence of Hypotension, low blood pressure, high blood Lactic acid, lactate, or Oliguria, low urine output may suggest poor blood flow. Se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gram Negative
Gram-negative bacteria are bacteria that, unlike gram-positive bacteria, do not retain the crystal violet stain used in the Gram staining method of bacterial differentiation. Their defining characteristic is that their cell envelope consists of a thin peptidoglycan cell wall sandwiched between an inner (cytoplasmic) membrane and an outer membrane. These bacteria are found in all environments that support life on Earth. Within this category, notable species include the model organism ''Escherichia coli'', along with various pathogenic bacteria, such as ''Pseudomonas aeruginosa'', ''Chlamydia trachomatis'', and '' Yersinia pestis''. They pose significant challenges in the medical field due to their outer membrane, which acts as a protective barrier against numerous antibiotics (including penicillin), detergents that would normally damage the inner cell membrane, and the antimicrobial enzyme lysozyme produced by animals as part of their innate immune system. Furthermore, the outer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Urogenital Fistula
A urogenital fistula is an abnormal tract that exists between the urinary tract and bladder, ureters, or urethra. A urogenital fistula can occur between any of the organs and structures of the pelvic region. A fistula allows urine to continually exit through and out the urogenital tract. This can result in significant disability, interference with sexual activity, and other physical health issues, the effects of which may in turn have a negative impact on mental or emotional state, including an increase in social isolation. Urogenital fistulas vary in etiology (medical cause). Fistulas are usually caused by injury or surgery, but they can also result from malignancy, infection, prolonged and obstructed labor and deliver in childbirth, hysterectomy, radiation therapy or inflammation. Of the fistulas that develop from difficult childbirth, 97 percent occur in developing countries. Congenital urogenital fistulas are rare; only ten cases have been documented. Abnormal passageways can ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uraemia
Uremia is the condition of having high levels of urea in the blood. Urea is one of the primary components of urine. It can be defined as an excess in the blood of amino acid and protein metabolism end products, such as urea and creatinine, which would normally be excreted in the urine. ''Uremic syndrome'' can be defined as the terminal clinical manifestation of kidney failure (also called ''renal failure''). It is the signs, symptoms and results from laboratory tests which result from inadequate excretory, regulatory, and endocrine function of the kidneys. Both ''uremia'' and ''uremic syndrome'' have been used interchangeably to denote a very high plasma urea concentration that is the result of renal failure. The former denotation will be used for the rest of the article. Azotemia is a similar, less severe condition with high levels of urea, where the abnormality can be measured chemically but is not yet so severe as to produce symptoms. Uremia describes the pathological and sympt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inflammation
Inflammation (from ) is part of the biological response of body tissues to harmful stimuli, such as pathogens, damaged cells, or irritants. The five cardinal signs are heat, pain, redness, swelling, and loss of function (Latin ''calor'', ''dolor'', ''rubor'', ''tumor'', and ''functio laesa''). Inflammation is a generic response, and therefore is considered a mechanism of innate immunity, whereas adaptive immunity is specific to each pathogen. Inflammation is a protective response involving immune cells, blood vessels, and molecular mediators. The function of inflammation is to eliminate the initial cause of cell injury, clear out damaged cells and tissues, and initiate tissue repair. Too little inflammation could lead to progressive tissue destruction by the harmful stimulus (e.g. bacteria) and compromise the survival of the organism. However inflammation can also have negative effects. Too much inflammation, in the form of chronic inflammation, is associated with variou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stupor
Stupor is the lack of critical mental function and a level of consciousness, in which an affected person is almost entirely unresponsive and responds only to intense stimuli such as pain. The word derives from the Latin '' stupor'' ("numbness, insensibility"). Signs and symptoms Stupor is characterized by impaired reaction to external stimuli. Those in a stuporous state are rigid, mute and only appear to be conscious, as the eyes are open and follow surrounding objects. If not stimulated externally, a patient with stupor will appear to be in a sleepy state most of the time. In some extreme cases of severe depressive disorders the patient can become motionless, lose their appetite and become mute. Short periods of restricted responsivity can be achieved by intense stimulation (e.g. pain, bright light, loud noise, shock). Causes Stupor is associated with infectious diseases, complicated toxic states (e.g. heavy metals), severe hypothermia, mental illnesses (e.g. schizophren ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Binge Drinking
Binge drinking, or heavy episodic drinking, is drinking alcoholic beverages with an intention of becoming intoxicated by heavy consumption of alcohol over a short period of time, but definitions vary considerably. Binge drinking is a style of drinking that is popular in several countries worldwide, and overlaps somewhat with social drinking since it is often done in groups. The degree of intoxication however, varies between and within various cultures that engage in this practice. A binge on alcohol can occur over hours, last up to several days, or in the event of extended abuse, even weeks. Due to the long term effects of alcohol abuse, binge drinking is considered to be a major public health issue. Binge drinking is more common in males, during adolescence and young adulthood. Heavy regular binge drinking is associated with adverse effects on neurologic, cardiac, gastrointestinal, hematologic, immune, and musculoskeletal organ systems as well as increasing the risk of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |