Experimental Advanced Superconducting Tokamak on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

 The Experimental Advanced Superconducting Tokamak (EAST), also known as HT-7U (Hefei Tokamak 7 Upgrade), is an experimental
The Experimental Advanced Superconducting Tokamak (EAST), also known as HT-7U (Hefei Tokamak 7 Upgrade), is an experimental
People's Daily article
- Note that EAST is not the "world's first experimental nuclear fusion device".
{{coords, 31.91174, 117.14682, display=title Tokamaks Buildings and structures in Hefei Nuclear power in China 2006 in Hefei ur:مصنوعی سورج

 The Experimental Advanced Superconducting Tokamak (EAST), also known as HT-7U (Hefei Tokamak 7 Upgrade), is an experimental
The Experimental Advanced Superconducting Tokamak (EAST), also known as HT-7U (Hefei Tokamak 7 Upgrade), is an experimental superconducting
Superconductivity is a set of physical properties observed in superconductors: materials where electrical resistance vanishes and magnetic fields are expelled from the material. Unlike an ordinary metallic conductor, whose resistance decreases g ...
tokamak
A tokamak (; ) is a device which uses a powerful magnetic field generated by external magnets to confine plasma (physics), plasma in the shape of an axially symmetrical torus. The tokamak is one of several types of magnetic confinement fusi ...
magnetic fusion energy reactor in Hefei
Hefei is the Capital city, capital of Anhui, China. A prefecture-level city, it is the political, economic, and cultural center of Anhui. Its population was 9,369,881 as of the 2020 census. Its built-up (or ''metro'') area is made up of four u ...
, China. Operated by the Hefei Institutes of Physical Science conducting its experiments for the Chinese Academy of Sciences
The Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS; ) is the national academy for natural sciences and the highest consultancy for science and technology of the People's Republic of China. It is the world's largest research organization, with 106 research i ...
, EAST began its operations in 2006. EAST is part of the international ITER program after China joined the initiative in 2003 and acts as a testbed for ITER technologies. On January 20, 2025, it sustained plasma for 1066 seconds.
It is the first tokamak to utilize superconducting
Superconductivity is a set of physical properties observed in superconductors: materials where electrical resistance vanishes and magnetic fields are expelled from the material. Unlike an ordinary metallic conductor, whose resistance decreases g ...
toroidal and poloidal magnets.
History
EAST followed China's first superconducting tokamak device, dubbed HT-7, built by the Institute of Plasma Physics in partnership withRussia
Russia, or the Russian Federation, is a country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia. It is the list of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the world, and extends across Time in Russia, eleven time zones, sharing Borders ...
in the early 1990s. It was first proposed in 1996 and approved in 1998. According to a 2003 schedule, buildings and site facilities were to be constructed by 2003. Tokamak assembly was to take place from 2003 through 2005. Construction was completed in March 2006.
According to official reports, the project's budget is CNY ¥300 million (approximately US$37 million), some 1/15 to 1/20 the cost of a comparable reactor built in other countries.
Phase I
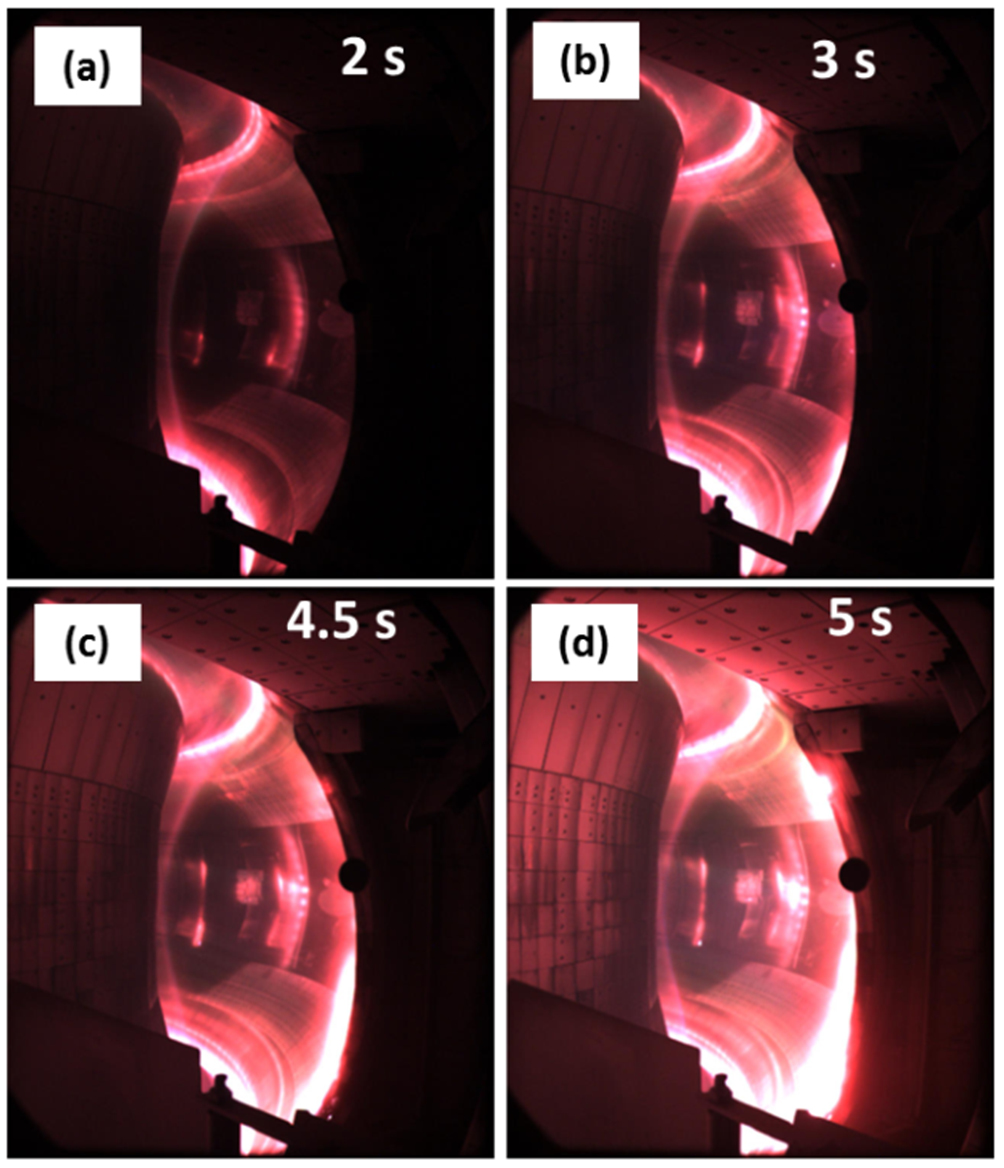
EAST entered its first commissioning phase around March 2006. Shortly after, in-vessel components and diagnostics were assembled. During initial operation, EAST was able to successfully generate its first plasma on September 28, 2006 in a nearly three second long test, reaching an electric current of 200 kiloamperes. By January 2007, the reactor had progressed to creating a plasma that could last nearly five seconds and generate currents up to 500 kiloamperes. Three years later, EAST was able to achieve a key milestone on November 7, 2010, achieving an H-mode plasma by low hybrid wave (LHW) injection alone. This was shortly followed by further success, where EAST became the first tokamak to successfully sustain H-Mode plasma for over 30 seconds at ~50 millionKelvin
The kelvin (symbol: K) is the base unit for temperature in the International System of Units (SI). The Kelvin scale is an absolute temperature scale that starts at the lowest possible temperature (absolute zero), taken to be 0 K. By de ...
in May of 2011.
Phase II
The second phase of EAST was formally entered through a ribbon-cutting ceremony for the EAST auxiliary heating system project, which was held on November 29, 2011. After a nearly 20-month long upgrading break since September 2012, EAST commenced for the first round of experiments in May 2014. A year later, EAST was reporting currents of up to 1 Megaampere, as well as stable H-mode plasma for 6.4 seconds. Then, almost two years later, EAST was able to break records when it managed to maintain a plasma pulse for 102 seconds at ~50 million °C (90 million °F). During this test, EAST was able to generate a Plasma with currents of 400 kiloamperes with a density of about 2.4 x 1019/m3. It was observed that the temperature was slowly increasing during this test. more data in screen shot Building on this success, EAST became the first tokamak to successfully sustain H-Mode plasma for more than one minute at ~50 million °C (90 million °F) on November 2, 2016. In July of 2017, it was also the first tokamak to sustain said plasma for more than 100 seconds at the same temperature. The following year, EAST reached a milestone of ~100 million °C (180 million °F) electron temperature on November 12, 2018. During May of 2021, it reached an electron temperature of 120 million °C electron temperature for 101 seconds. On December 30, 2021, a long-pulse high-parameter plasma operation of 1056 seconds was realized, setting another world record for the operation of the Tokamak experimental device. EAST achieved the world's first 403-second steady-state H-mode plasma on April 12, 2023. EAST then broke its record several years later on January 20, 2025, when it sustained plasma for 1066 seconds.Physics objectives
China is a member of the ITER consortium, and EAST is a testbed for ITER technologies. EAST was designed to test: *Superconducting
Superconductivity is a set of physical properties observed in superconductors: materials where electrical resistance vanishes and magnetic fields are expelled from the material. Unlike an ordinary metallic conductor, whose resistance decreases g ...
Niobium-titanium poloidal field magnets
A magnet is a material or object that produces a magnetic field. This magnetic field is invisible but is responsible for the most notable property of a magnet: a force that pulls on other ferromagnetic materials, such as iron, steel, nickel, ...
, making it the first tokamak with superconducting toroidal and poloidal magnets
* Non-inductive current drive
* Pulses of up to 102 seconds with 0.5 MA plasma current
* Schemes for controlling plasma instabilities through real-time diagnostics
* Materials for diverters and plasma facing components
* Operation with ''β''N = 2 and confinement factor ''H''89 > 2
Tokamak parameters
See also
* ASDEX Upgrade * China Fusion Engineering Test Reactor (CFETR) * HL-2M *List of fusion experiments
Experiments directed toward developing fusion power are invariably done with dedicated machines which can be classified according to the principles they use to confine the plasma (physics), plasma fuel and keep it hot.
The major division is bet ...
* ITER
* Joint European Torus
The Joint European Torus (JET) was a magnetically confined plasma physics experiment, located at Culham Centre for Fusion Energy in Oxfordshire, UK. Based on a tokamak design, the fusion research facility was a joint European project with the ...
* JT-60
* KSTAR
References
External links
* - Official website of EAST Fusion Facility - Chinese Academy of SciencePeople's Daily article
- Note that EAST is not the "world's first experimental nuclear fusion device".
{{coords, 31.91174, 117.14682, display=title Tokamaks Buildings and structures in Hefei Nuclear power in China 2006 in Hefei ur:مصنوعی سورج