Exe Bridge on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Old Exe Bridge is a ruined medieval
 A stone bridge was promoted by Nicholas and Walter Gervase, father and son and prominent local residents. The Gervases were well-off merchants. Walter was subsequently elected
A stone bridge was promoted by Nicholas and Walter Gervase, father and son and prominent local residents. The Gervases were well-off merchants. Walter was subsequently elected
 The size of the bridge's piers and the reclamation of land on the Exeter side reduced the width of the river by more than half, which increased the force of the water acting on the bridge, causing damage. The bridge is known to have been repaired several times throughout its life. The earliest repairs are impossible to date, but a partial collapse was recorded during a storm in 1286, and again in 1384, when several people were killed. It was rebuilt on both occasions. Later repairs can be dated by the stone used—they were made with Heavitree
The size of the bridge's piers and the reclamation of land on the Exeter side reduced the width of the river by more than half, which increased the force of the water acting on the bridge, causing damage. The bridge is known to have been repaired several times throughout its life. The earliest repairs are impossible to date, but a partial collapse was recorded during a storm in 1286, and again in 1384, when several people were killed. It was rebuilt on both occasions. Later repairs can be dated by the stone used—they were made with Heavitree

 Repairs and maintenance of the bridge were provided for from the proceeds of land bought by the Gervases at the time the bridge was built, and the funds were administered by bridge wardens. The wardens were responsible for the upkeep of the bridge until 1769, when the responsibility was passed to the Exeter
Repairs and maintenance of the bridge were provided for from the proceeds of land bought by the Gervases at the time the bridge was built, and the funds were administered by bridge wardens. The wardens were responsible for the upkeep of the bridge until 1769, when the responsibility was passed to the Exeter
File:Mediaeval Exe Bridge (10).JPG
File:Medieval bridge, Exeter (9204).jpg
File:Exeter medieval bridge.jpg
 About half of the bridge's original length survives unburied—eight and a half arches over about . Another three and a half arches, spanning remain buried. The visible arches vary in span from to . Two of them form the crypt of the bridge chapel, St Edmund's Church. It spanned the river diagonally in a north-westerly direction from what is now Exeter city centre to St Thomas (now a suburb of Exeter but originally outside the city), terminating outside St Thomas's Church, which was built at around the same time. The bridge was wide on average. The roadway on the bridge was about wide between the
About half of the bridge's original length survives unburied—eight and a half arches over about . Another three and a half arches, spanning remain buried. The visible arches vary in span from to . Two of them form the crypt of the bridge chapel, St Edmund's Church. It spanned the river diagonally in a north-westerly direction from what is now Exeter city centre to St Thomas (now a suburb of Exeter but originally outside the city), terminating outside St Thomas's Church, which was built at around the same time. The bridge was wide on average. The roadway on the bridge was about wide between the

 Bridge chapels were common in the Middle Ages, when religion was a significant part of daily life. The chapel provided travellers a place to pray or to give thanks for a safe journey, and the alms collected were often used towards the maintenance of the bridge. A church was built on the Exe Bridge, across two of the bridge arches, and dedicated to St Edmund the Martyr. The church was built with the bridge, and its structure is an integral part of it; it had an entrance on the bridge and possibly a second entrance underneath. The first record of a bridge chaplain is from 1196, suggesting that the church may have already been built by that date. A record of the completed church exists from 1214, when it was mentioned in a list of churches in Exeter, along with St Thomas's Church. It had a rectangular plan, long by wide. Its south wall rested on the north side (right-hand side when crossing from the Exeter side) of the bridge and its side walls rested on the cutwaters while the north wall was supported by piers rising from the riverbed which had their own cutwaters. The bridge arch below the aisle was blocked in the 17th century, showing that by that time the river did not flow under the church.Brown, pp. 16–17. A
Bridge chapels were common in the Middle Ages, when religion was a significant part of daily life. The chapel provided travellers a place to pray or to give thanks for a safe journey, and the alms collected were often used towards the maintenance of the bridge. A church was built on the Exe Bridge, across two of the bridge arches, and dedicated to St Edmund the Martyr. The church was built with the bridge, and its structure is an integral part of it; it had an entrance on the bridge and possibly a second entrance underneath. The first record of a bridge chaplain is from 1196, suggesting that the church may have already been built by that date. A record of the completed church exists from 1214, when it was mentioned in a list of churches in Exeter, along with St Thomas's Church. It had a rectangular plan, long by wide. Its south wall rested on the north side (right-hand side when crossing from the Exeter side) of the bridge and its side walls rested on the cutwaters while the north wall was supported by piers rising from the riverbed which had their own cutwaters. The bridge arch below the aisle was blocked in the 17th century, showing that by that time the river did not flow under the church.Brown, pp. 16–17. A
arch bridge
An arch bridge is a bridge with abutments at each end shaped as a curved arch. Arch bridges work by transferring the weight of the bridge and its loads partially into a horizontal thrust restrained by the abutments at either side. A viaduct ...
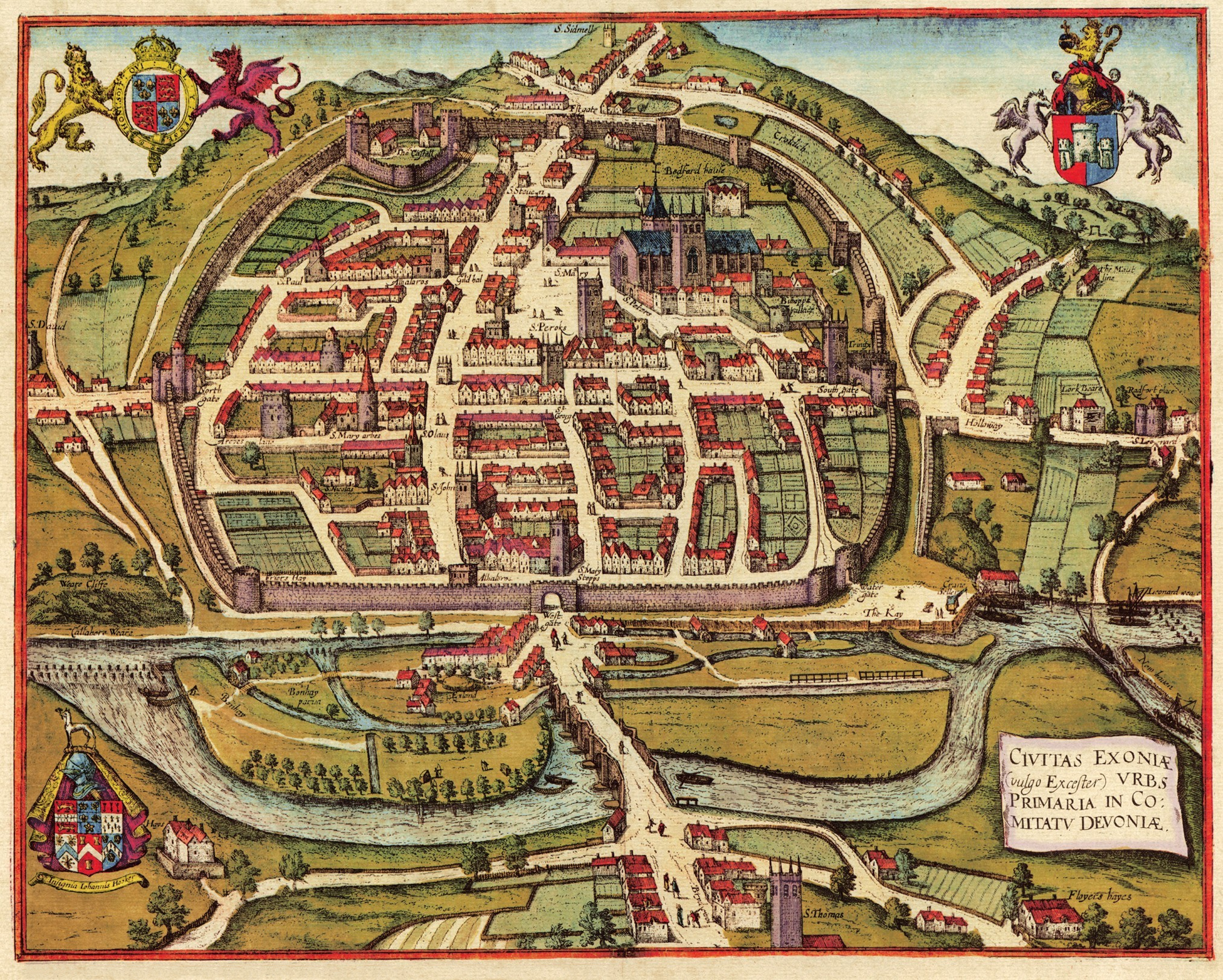
in Exeter in south west England. Construction of the bridge began in 1190, and was completed by 1214. The bridge is the oldest surviving bridge of its size in England and the oldest bridge in Britain with a chapel still on it. It replaced several rudimentary crossings which had been in use sporadically since Roman times. The project was the idea of Nicholas and Walter Gervase, father and son and influential local merchants, who travelled the country to raise funds. No known records survive of the bridge's builders. The result was a bridge at least long, which probably had 17 or 18 arches, carrying the road diagonally from the west gate of the city wall across the River Exe
The River Exe ( ) in England rises at Exe Head, near the village of Simonsbath, on Exmoor in Somerset, from the Bristol Channel coast, but flows more or less directly due south, so that most of its length lies in Devon. It flows for 60 mile ...
and its wide, marshy flood plain.
St Edmund's Church, the bridge chapel, was built into the bridge at the time of its construction, and St Thomas's Church was built on the riverbank at about the same time. The Exe Bridge is unusual among British medieval bridges for having had secular buildings on it as well as the chapel. Timber-framed shops, with houses above, were in place from at least the early 14th century, and later in the bridge's life, all but the most central section carried buildings. As the river silted up, land was reclaimed, allowing a wall to be built from the side of St Edmund's which protected a row of houses and shops which became known as Frog Street. Walter Gervase also commissioned a chantry chapel
A chantry is an ecclesiastical term that may have either of two related meanings:
# a chantry service, a Christian liturgy of prayers for the dead, which historically was an obiit, or
# a chantry chapel, a building on private land, or an area i ...
, built opposite the church, which came into use after 1257 and continued until the Reformation
The Reformation (alternatively named the Protestant Reformation or the European Reformation) was a major movement within Western Christianity in 16th-century Europe that posed a religious and political challenge to the Catholic Church and in ...
in the mid-16th century.
The medieval bridge collapsed and had to be partially rebuilt several times throughout its life; the first recorded rebuilding was in 1286. By 1447 the bridge was severely dilapidated, and the mayor of Exeter appealed for funds to repair it. By the 16th century, it was again in need of repairs. Nonetheless, the bridge was in use for almost 600 years, until a replacement was built in 1778 and the arches across the river were demolished. That bridge was itself replaced in 1905, and again in 1969 by a pair of bridges. During construction of the twin bridges, eight and a half arches of the medieval bridge were uncovered and restored, some of which had been buried for nearly 200 years, and the surrounds were landscaped into a public park. Several more arches are buried under modern buildings. The bridge's remains are a scheduled monument
In the United Kingdom, a scheduled monument is a nationally important archaeological site or historic building, given protection against unauthorised change.
The various pieces of legislation that legally protect heritage assets from damage and d ...
and grade II listed building
In the United Kingdom, a listed building or listed structure is one that has been placed on one of the four statutory lists maintained by Historic England in England, Historic Environment Scotland in Scotland, in Wales, and the Northern Irel ...
.
Background
Exeter was founded asIsca Dumnoniorum
Isca Dumnoniorum, also known simply as Isca, was originally a Roman legionary fortress for the Second Augustan Legion (established ) in the Roman province of Britannia at the site of present-day Exeter in Devon.
The town grew up around this ...
by the Romans in the first century CE. It became an important administrative centre for the south west of England, but travel further west (to the remainder of Devon
Devon ( , historically known as Devonshire , ) is a ceremonial and non-metropolitan county in South West England. The most populous settlement in Devon is the city of Plymouth, followed by Devon's county town, the city of Exeter. Devo ...
and the whole of Cornwall
Cornwall (; kw, Kernow ) is a historic county and ceremonial county in South West England. It is recognised as one of the Celtic nations, and is the homeland of the Cornish people. Cornwall is bordered to the north and west by the Atlantic ...
) required crossing the River Exe
The River Exe ( ) in England rises at Exe Head, near the village of Simonsbath, on Exmoor in Somerset, from the Bristol Channel coast, but flows more or less directly due south, so that most of its length lies in Devon. It flows for 60 mile ...
. At Exeter, the Exe was naturally broad and shallow, making this the lowest reliable crossing point before the river's tidal estuary. There are records of a crossing from Roman times, most likely in the form of a timber bridge. No trace of any Roman bridge survives; it is likely that, once replaced, the bridge deck was simply left to degrade and any masonry supports would have been washed away by floodwaters.
Bridge building was sparse in England through the Early Middle Ages (the period following the decline of the Roman Empire until after the Norman conquest of England in the late 11th century).Hayman, pp. 9–10. Work on the Pont d'Avignon in the south of France began in the 1170s. London Bridge, over the River Thames
The River Thames ( ), known alternatively in parts as the River Isis, is a river that flows through southern England including London. At , it is the longest river entirely in England and the second-longest in the United Kingdom, after the R ...
on the opposite side of England, was begun around the same time, and was completed in 1209. Several similar bridges were constructed across England in this era, of which Exeter's, London's, and the Dee Bridge in Chester were among the largest examples. Only one other bridge of a similar age survives in Devon, at Clyst St Mary, just east of Exeter; another exists at Yeolmbridge
Yeolmbridge is a village in Cornwall (but within the boundaries of the historic county of Devon), two and a half miles north of Launceston.
Yeolm Bridge
The village takes its name from the bridge, Yeolm Bridge which crosses the River Otter ...
, historically in Devon but now in Cornwall.
Until the 12th century, the Exe was crossed by a ford
Ford commonly refers to:
* Ford Motor Company, an automobile manufacturer founded by Henry Ford
* Ford (crossing), a shallow crossing on a river
Ford may also refer to:
Ford Motor Company
* Henry Ford, founder of the Ford Motor Company
* Ford F ...
, which was notoriously treacherous and was supplemented by a ferry for foot passengers. According to John Hooker John Hooker may refer to:
*John Hooker (English constitutionalist) (c. 1527–1601), English writer, solicitor, antiquary, civic administrator and advocate of republican government
*John Lee Hooker (1912–2001), American blues singer-songwriter an ...
, chamberlain of Exeter, who wrote a history of the city in the 16th century (around 400 years after the bridge was built), a rudimentary timber bridge existed at the site but this was also treacherous, particularly in the winter when the river was in flood. Hooker describes how pedestrians were washed off the bridge on several occasions and swept to their deaths.Meller, p. 64.
History
Construction
 A stone bridge was promoted by Nicholas and Walter Gervase, father and son and prominent local residents. The Gervases were well-off merchants. Walter was subsequently elected
A stone bridge was promoted by Nicholas and Walter Gervase, father and son and prominent local residents. The Gervases were well-off merchants. Walter was subsequently elected mayor of Exeter
This is a chronological list of the Mayors and Lord Mayors of the city of Exeter, England.
The role of Mayor was granted the dignity and style of Lord Mayor by letters patent dated 1 May 2002 as the result of a competition to celebrate the G ...
several times and had his parents buried in the chapel on the Exe Bridge upon their deaths (the exact dates of which are unknown); he died in 1252. The exact dates of the bridge's construction are not known, but construction began around 1190. Stone bridges often took two decades or more to complete in the Middle Ages, and the Exe Bridge was not complete until around 1210.Brierley. p. 130.Harrison, pp. 177–178. Walter travelled the country soliciting donations. According to Hooker, the Gervases raised £10,000 through public donations for the construction of a stone bridge and the purchase of land which would provide an income for the bridge's upkeep. No records survive of the people responsible for the design and construction of the bridge. There is a record of a bridge chaplain in 1196, which W. G. Hoskins, professor of English local history, believed to mean that the bridge was at least partially built by then. It was certainly complete by 1214, when a record exists of St Edmund's Church, which was built on the bridge.Brown, pp. 6–7.
The bridge was at least longBrown, pp. 8–9. (some studies have suggested it was longer, up to Harrison, p. 112.) and consisted of possibly 17 or 18 arches; some accounts suggest there could have been as few as 12 arches, though the number appears to have varied over time with repairs. It crossed the Exe diagonally, starting from close to the West Gate of the city walls, and continued across the marshy banks which were prone to flooding.Brierley. p. 131. The foundations were created using piles of timber, reinforced with iron and lead and driven in tightly enough to form a solid base. In the shallower water closer to the banks, rubble and gravel were simply tipped onto the river bed. After part of the bridge was demolished in the 18th century, some of the piles were removed and found to be jet black and extremely solid, having been underwater for some 500 years.
Medieval history
 The size of the bridge's piers and the reclamation of land on the Exeter side reduced the width of the river by more than half, which increased the force of the water acting on the bridge, causing damage. The bridge is known to have been repaired several times throughout its life. The earliest repairs are impossible to date, but a partial collapse was recorded during a storm in 1286, and again in 1384, when several people were killed. It was rebuilt on both occasions. Later repairs can be dated by the stone used—they were made with Heavitree
The size of the bridge's piers and the reclamation of land on the Exeter side reduced the width of the river by more than half, which increased the force of the water acting on the bridge, causing damage. The bridge is known to have been repaired several times throughout its life. The earliest repairs are impossible to date, but a partial collapse was recorded during a storm in 1286, and again in 1384, when several people were killed. It was rebuilt on both occasions. Later repairs can be dated by the stone used—they were made with Heavitree breccia
Breccia () is a rock composed of large angular broken fragments of minerals or rocks cemented together by a fine-grained matrix.
The word has its origins in the Italian language, in which it means "rubble". A breccia may have a variety of ...
, a local stone not quarried until the mid 14th century (approximately 150 years after the bridge was built). By 1447, the bridge was recorded as being severely dilapidated—Richard Izacke
Richard Izacke (16241698) of Devon was an antiquarian and lawyer who served as Chamberlain of the City of Exeter. His history, ''Antiquities of the City of Exeter'', was first published in 1677.
Biography
Baptised on 8 February 1624 at Ottery St ...
, the chamberlain of Exeter in the mid 17th century, wrote that it "was now in great decay, the stone work thereof being much foundred, and the higher part being all of timber was consumed and worn away".Brierley, pp. 135–136.
Shortly after this report, the mayor, John Shillingford, appealed for funds to rebuild it. He approached John Kemp
John Kemp ( – 22 March 1454, surname also spelled Kempe) was a medieval English cardinal, Archbishop of Canterbury, and Lord Chancellor of England.
Biography
Kemp was the son of Thomas Kempe, a gentleman of Ollantigh, in the parish ...
, the Archbishop of York
The archbishop of York is a senior bishop in the Church of England, second only to the archbishop of Canterbury. The archbishop is the diocesan bishop of the Diocese of York and the metropolitan bishop of the province of York, which covers th ...
, with whom he was acquainted and who was an executor of the estate of the recently deceased Henry Beaufort
Cardinal Henry Beaufort (c. 1375 – 11 April 1447), Bishop of Winchester, was an English prelate and statesman who held the offices of Bishop of Lincoln (1398) then Bishop of Winchester (1404) and was from 1426 a Cardinal of the Church of Ro ...
, the famously wealthy Bishop of Winchester. Kemp promised a contribution but the process was frustrated by Shillingford's sudden death in 1458. In 1539, one of the central arches collapsed and was repaired using stone from St Nicholas' Priory but there was still no refurbishment of the whole structure.
Later history

 Repairs and maintenance of the bridge were provided for from the proceeds of land bought by the Gervases at the time the bridge was built, and the funds were administered by bridge wardens. The wardens were responsible for the upkeep of the bridge until 1769, when the responsibility was passed to the Exeter
Repairs and maintenance of the bridge were provided for from the proceeds of land bought by the Gervases at the time the bridge was built, and the funds were administered by bridge wardens. The wardens were responsible for the upkeep of the bridge until 1769, when the responsibility was passed to the Exeter turnpike trust
Turnpike trusts were bodies set up by individual acts of Parliament, with powers to collect road tolls for maintaining the principal roads in Britain from the 17th but especially during the 18th and 19th centuries. At the peak, in the 1830s, ...
by Act of Parliament. The trust was dissolved in 1884 and responsibility for the bridge and its estate passed to Exeter City Council
Exeter City Council is the council and local government of the city of Exeter, Devon.
History
Proposed unitary authority status
The government proposed that the city should become an independent unitary authority within Devon, much like neighb ...
.Brierley, p. 136. The bridge wardens kept detailed records on rolls of parchment, of which most rolls from 1343 to 1711 survive, forming the most complete set of records for a bridge in Britain except those for London Bridge. The bridge estate grew to a considerable size. The records show that it leased 15 shops on the bridge, and over 50 other properties elsewhere in Exeter, including mills and agricultural land, all providing an income for maintenance and repairs. The wardens and their successors in the turnpike trust also collected toll
Toll may refer to:
Transportation
* Toll (fee) a fee charged for the use of a road or waterway
** Road pricing, the modern practice of charging for road use
** Road toll (historic), the historic practice of charging for road use
** Shadow toll, ...
s from carts using the bridge from outside the city (citizens of Exeter were exempt from the tolls).Brown, pp. 12–13.
By the late 18th century, congestion around the bridge became a cause for concern. An Act of Parliament in 1773 empowered the trustees to repair or rebuild the bridge but events overtook the planned repairs when, in December 1775, a fire broke out in the Fortune of War, a pub
A pub (short for public house) is a kind of drinking establishment which is licensed to serve alcoholic drinks for consumption on the premises. The term ''public house'' first appeared in the United Kingdom in late 17th century, and was ...
built on the bridge. The fire consumed the pub and a neighbouring house. The pub provided cheap accommodation to local vagrants and it was believed that upwards of 30 people may have been inside at the time of the fire; at least nine bodies were recovered after the fire was extinguished.
Plans for widening the medieval bridge were considered but dismissed. The spans across the river were demolished following the completion of a new, three-arch masonry bridge by Joseph Dixon in 1778. Construction of the replacement bridge began in 1770 and suffered a major setback in 1775 when floodwaters washed away much of the part-built structure and damaged its foundations. This bridge was built on a different alignment, just upstream from the medieval bridge and crossing on a shorter, horizontal line. By then, the marshland over which several of the medieval arches were built had been reclaimed and the river was restricted to a width of . The medieval arches on the Exeter bank were left intact and eventually buried or incorporated into buildings. The 19th-century bridge was itself demolished and replaced with a three-hinged steel arch bridge in 1905, built by Sir John Wolfe Barry, who was also responsible for London's Tower Bridge
Tower Bridge is a Grade I listed combined bascule and suspension bridge in London, built between 1886 and 1894, designed by Horace Jones and engineered by John Wolfe Barry with the help of Henry Marc Brunel. It crosses the River Thames clos ...
. Barry's bridge lasted about 65 years before it was demolished in favour of a pair of reinforced concrete bridges, which opened in 1969 and 1972.
Parts of the medieval bridge were exposed when a German bomb exploded nearby during the Exeter Blitz in the Second World War. More arches were revealed during the construction of the modern bridges. The 20th-century engineers were careful to site the new bridges and their approach roads away from the line of the medieval bridge. At this time, part of Frog Street (a road on the river bank) was abandoned. During the work, an old brewery and several adjoining buildings along the street were demolished to make way for a new road scheme connecting with the twin bridges. One timber-framed house became known as "the House that Moved
The House That Moved is a historic building in Exeter, originally built in the late Middle Ages and structure relocation, relocated in 1961 when the entire street it was on was demolished to make way for a new bypass (road), bypass road linked to ...
" after it was saved from demolition and wheeled to a new position. The demolition uncovered five of the medieval arches and, after further excavation, another three and a half arches were exposed, estimated to be around half the original length of the bridge. Exeter City Council commissioned local stonemasons to restore the stonework, then landscaped the area around the arches into a public park to display the uncovered arches, which were in remarkably good condition, having been buried for around 200 years. The bases of several of the demolished arches survive on the riverbed, and about of bridge is buried under Edmund Street and the modern bank of the Exe. What remains is the oldest surviving bridge of its size in England and the oldest with a chapel still on the bridge in Britain. As such, the bridge is a scheduled monument
In the United Kingdom, a scheduled monument is a nationally important archaeological site or historic building, given protection against unauthorised change.
The various pieces of legislation that legally protect heritage assets from damage and d ...
and a grade II listed building
In the United Kingdom, a listed building or listed structure is one that has been placed on one of the four statutory lists maintained by Historic England in England, Historic Environment Scotland in Scotland, in Wales, and the Northern Irel ...
, providing it legal protection from modification or demolition.
Architecture
 About half of the bridge's original length survives unburied—eight and a half arches over about . Another three and a half arches, spanning remain buried. The visible arches vary in span from to . Two of them form the crypt of the bridge chapel, St Edmund's Church. It spanned the river diagonally in a north-westerly direction from what is now Exeter city centre to St Thomas (now a suburb of Exeter but originally outside the city), terminating outside St Thomas's Church, which was built at around the same time. The bridge was wide on average. The roadway on the bridge was about wide between the
About half of the bridge's original length survives unburied—eight and a half arches over about . Another three and a half arches, spanning remain buried. The visible arches vary in span from to . Two of them form the crypt of the bridge chapel, St Edmund's Church. It spanned the river diagonally in a north-westerly direction from what is now Exeter city centre to St Thomas (now a suburb of Exeter but originally outside the city), terminating outside St Thomas's Church, which was built at around the same time. The bridge was wide on average. The roadway on the bridge was about wide between the parapet
A parapet is a barrier that is an extension of the wall at the edge of a roof, terrace, balcony, walkway or other structure. The word comes ultimately from the Italian ''parapetto'' (''parare'' 'to cover/defend' and ''petto'' 'chest/breast'). ...
s at its peak, wide enough for two carts to pass side by side—unusually wide for a medieval bridge. The parapets are lost but some of the medieval paving survives, along with other, later, paving.
The surviving arches are up to high. The piers are rounded in the downstream direction but feature cutwater
In architecture, a starling (or sterling) is a defensive bulwark, usually built with pilings or bricks, surrounding the supports (or piers) of a bridge or similar construction. Starlings may be shaped to ease the flow of the water around the brid ...
s (streamlined brickwork intended to reduce the impact of the water on the piers) facing upstream. Above the cutwaters were originally triangular recesses forming refuges for pedestrians to allow carts to pass. Local trap stone was used for the faces of the arches, behind which is gravel and rubble contained within a box of wooden stakes which were driven into the ground and the riverbed. Other stones found include sandstone
Sandstone is a clastic sedimentary rock composed mainly of sand-sized (0.0625 to 2 mm) silicate grains. Sandstones comprise about 20–25% of all sedimentary rocks.
Most sandstone is composed of quartz or feldspar (both silicates ...
and limestone
Limestone ( calcium carbonate ) is a type of carbonate sedimentary rock which is the main source of the material lime. It is composed mostly of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different crystal forms of . Limestone forms whe ...
from East Devon, and Heavitree breccia for later repairs. Dendrochronology (tree-ring dating) has established that the oldest of these stakes came from trees felled between 1190 and 1210.
The arches are a mix of Norman-style semi-circles and the pointed Gothic style
Gothic or Gothics may refer to:
People and languages
*Goths or Gothic people, the ethnonym of a group of East Germanic tribes
**Gothic language, an extinct East Germanic language spoken by the Goths
** Crimean Gothic, the Gothic language spoken ...
. All are supported by ribbed vault
Vault may refer to:
* Jumping, the act of propelling oneself upwards
Architecture
* Vault (architecture), an arched form above an enclosed space
* Bank vault, a reinforced room or compartment where valuables are stored
* Burial vault (enclosure ...
s. The pointed arches became fashionable at about the same time as work started on the bridge and there was some suggestion that the variation was the result of repairs, but archaeological studies in the 20th century proved that the bridge was built with both types of arch. The pointed arches have five ribs, each about wide and spaced between and apart; the rounded arches have three ribs, ranging from to wide and to apart.Brierley, pp. 137–138.
Churches

 Bridge chapels were common in the Middle Ages, when religion was a significant part of daily life. The chapel provided travellers a place to pray or to give thanks for a safe journey, and the alms collected were often used towards the maintenance of the bridge. A church was built on the Exe Bridge, across two of the bridge arches, and dedicated to St Edmund the Martyr. The church was built with the bridge, and its structure is an integral part of it; it had an entrance on the bridge and possibly a second entrance underneath. The first record of a bridge chaplain is from 1196, suggesting that the church may have already been built by that date. A record of the completed church exists from 1214, when it was mentioned in a list of churches in Exeter, along with St Thomas's Church. It had a rectangular plan, long by wide. Its south wall rested on the north side (right-hand side when crossing from the Exeter side) of the bridge and its side walls rested on the cutwaters while the north wall was supported by piers rising from the riverbed which had their own cutwaters. The bridge arch below the aisle was blocked in the 17th century, showing that by that time the river did not flow under the church.Brown, pp. 16–17. A
Bridge chapels were common in the Middle Ages, when religion was a significant part of daily life. The chapel provided travellers a place to pray or to give thanks for a safe journey, and the alms collected were often used towards the maintenance of the bridge. A church was built on the Exe Bridge, across two of the bridge arches, and dedicated to St Edmund the Martyr. The church was built with the bridge, and its structure is an integral part of it; it had an entrance on the bridge and possibly a second entrance underneath. The first record of a bridge chaplain is from 1196, suggesting that the church may have already been built by that date. A record of the completed church exists from 1214, when it was mentioned in a list of churches in Exeter, along with St Thomas's Church. It had a rectangular plan, long by wide. Its south wall rested on the north side (right-hand side when crossing from the Exeter side) of the bridge and its side walls rested on the cutwaters while the north wall was supported by piers rising from the riverbed which had their own cutwaters. The bridge arch below the aisle was blocked in the 17th century, showing that by that time the river did not flow under the church.Brown, pp. 16–17. A seal
Seal may refer to any of the following:
Common uses
* Pinniped, a diverse group of semi-aquatic marine mammals, many of which are commonly called seals, particularly:
** Earless seal, or "true seal"
** Fur seal
* Seal (emblem), a device to imp ...
of the bridge was made for use by the bridge wardens, probably shortly after its opening, showing the outline of St Edmund's Church (or possibly the chantry chapel
A chantry is an ecclesiastical term that may have either of two related meanings:
# a chantry service, a Christian liturgy of prayers for the dead, which historically was an obiit, or
# a chantry chapel, a building on private land, or an area i ...
) with houses on either side. The oldest known document with the seal on was addressed to the mayor of Exeter in either 1256 or 1264.
The church was extended several times during the bridge's lifetime. By the end of the 14th century, accumulated silt on the Exeter side allowed a portion of land to be reclaimed, leaving the west wall of the church above dry land. Thus, the north wall was partially demolished to allow an aisle to be added, adding to the width of the church. Work on a bell tower began in 1449 after Edmund Lacey
Edmund Lacey (or Lacy; died 1455) was a medieval Bishop of Hereford and Bishop of Exeter in England.
Lacey was educated at University College, Oxford, where he was a mature commoner, then Fellow, and subsequently Master of the College from 1 ...
, the Bishop of Exeter, offered indulgence
In the teaching of the Catholic Church, an indulgence (, from , 'permit') is "a way to reduce the amount of punishment one has to undergo for sins". The ''Catechism of the Catholic Church'' describes an indulgence as "a remission before God of ...
s in exchange for financial contributions. Indulgences, in which senior clergymen offered reduced time in purgatory
Purgatory (, borrowed into English via Anglo-Norman and Old French) is, according to the belief of some Christian denominations (mostly Catholic), an intermediate state after physical death for expiatory purification. The process of purgatory ...
in exchange for acts of charity, were a common method of funding bridges in the Middle Ages.Brierley, p. 133. Further extensions followed in the 16th century, by which time the area of land reclaimed from the river had grown, and several of the bridge arches were on dry land. It is likely that there was little or no water flowing under the arches supporting the church by this point, except during winter floods. The church was struck by lightning in 1800 and largely rebuilt in 1834, then severely damaged in a fire in 1882 and repaired the following year, though retaining much of the ancient stonework. Another fire in 1969 left the church in a ruinous state, and it was partially demolished in 1975, when most of the later additions were removed but the medieval stonework was preserved. Although ruined, the tower survives at its original height—the only intact part of the church.
On the opposite side of the bridge was a smaller chantry chapel (a chapel employing a priest to pray for a given period of time after a person's death, to aid that person's passage to heaven), built for Walter Gervase and dedicated to the Blessed Virgin Mary
Mary; arc, ܡܪܝܡ, translit=Mariam; ar, مريم, translit=Maryam; grc, Μαρία, translit=María; la, Maria; cop, Ⲙⲁⲣⲓⲁ, translit=Maria was a first-century Jews, Jewish woman of Nazareth, the wife of Saint Joseph, Jose ...
. Upon his death in 1257, Gervase left an endowment of 50 shillings a year for a priest to hold three services a week to pray for him, his father, and his family. The chapel continued in use until at least 1537 but was destroyed in 1546 during the dissolution of the monasteries. Only stone fragments from the foundations survive. According to Hooker, Gervase and his wife were buried in another chapel, attached to St Edmund's Church, in which there was a "handsome monument" to Gervase's memory. This chapel was alienated from the church during the Reformation
The Reformation (alternatively named the Protestant Reformation or the European Reformation) was a major movement within Western Christianity in 16th-century Europe that posed a religious and political challenge to the Catholic Church and in ...
and converted into a private house; the monument was removed and defaced. Only the foundations of the chapel remained by the 19th century.
At the western end of the bridge (on dry land) was St Thomas's Church, built at a similar time to the bridge. The exact date of construction is unknown, but it was dedicated to St Thomas Becket, who was canonised in 1173, and the first known record of it dates from 1191. It became the parish church for Cowick (most of the area is now known as St Thomas) in 1261. The church was swept away in a major flood at the beginning of the 15th century and rebuilt further away from the river. The new building, on Cowick Street, was consecrated in 1412. It underwent significant rebuilding in the 17th and 19th centuries after it was set alight during the English Civil War
The English Civil War (1642–1651) was a series of civil wars and political machinations between Parliamentarians (" Roundheads") and Royalists led by Charles I ("Cavaliers"), mainly over the manner of England's governance and issues of re ...
. The church is a grade I listed building.
Secular buildings
Bridge chapels were common on medieval bridges but secular buildings were not. Around 135 major stone bridges were built in Britain in the medieval era. Most, though not all, had some form of bridge chapel either on the bridge itself or on the approach, but only 12 are documented as having secular buildings on the bridge, of which the only surviving example with buildings intact is High Bridge inLincoln
Lincoln most commonly refers to:
* Abraham Lincoln (1809–1865), the sixteenth president of the United States
* Lincoln, England, cathedral city and county town of Lincolnshire, England
* Lincoln, Nebraska, the capital of Nebraska, U.S.
* Lincol ...
. The Exe Bridge had timber-framed houses on it from early in its life—the earliest record is of two shops, with houses above, from 1319. At the height of development, all but the six arches in the middle of the river supported buildings. They were built with their front walls resting on the parapets of the bridge and the rest of the building supported by wooden posts in the riverbed, until they were demolished in 1881.
In the later 13th century, silty deposits had built up on the Exeter side of the bridge, allowing the land to be reclaimed for two buildings which backed onto the river and fronted onto what became Frog Street. Archaeological evidence suggests that one of the two was possibly a tannery
Tanning may refer to:
*Tanning (leather), treating animal skins to produce leather
*Sun tanning, using the sun to darken pale skin
**Indoor tanning, the use of artificial light in place of the sun
**Sunless tanning, application of a stain or dye t ...
. The houses were demolished in the post-medieval era but the foundations survived. Several buildings were constructed next to the bridge on the Exeter side, protected from the river by a wall which extended from the west side of the church.Brown, pp. 22–23.
See also
*List of bridges in the United Kingdom
Bridges in the United Kingdom is a link page for any road bridges or footbridges in the United Kingdom.
Railway bridges are listed under: List of railway bridges and viaducts in the United Kingdom.
Canal aqueducts are listed under: List of can ...
References
Bibliography
* * * * * * * * * * * * *Citations
Further reading
* {{Cite book , last=Brown , first=Stewart , title=The Medieval Exe Bridge, St Edmund's Church, and Excavation of Waterfront Houses, Exeter , date=2019 , publisher=Devon Archaeological Society , isbn=978-0-9527899-2-5 , location=Exeter Bridges in Devon Grade II listed bridges Scheduled monuments in Devon Bridges completed in the 13th century Buildings and structures in Exeter Bridges with buildings Arch bridges in the United Kingdom 1190 establishments in England Grade II listed buildings in Devon Former toll bridges in England