Ethiopian Catholic Eparchy Of Bahir Dar-Dessie on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Ethiopians are the native inhabitants of
 In 980 BCE,
In 980 BCE,
 The kingdom enlarged its territory by the half of 4th century after conquering neighbor city
The kingdom enlarged its territory by the half of 4th century after conquering neighbor city
 Between 1769 and 1855, Ethiopia experienced a period of isolation referred to as the ''
Between 1769 and 1855, Ethiopia experienced a period of isolation referred to as the '' Emperor
Emperor
 An Italian occupation of Ethiopia following
An Italian occupation of Ethiopia following



The Burji, Konso and Beta Israel were sampled from Ethiopia. The Afroasiatic speaking Ethiopians sampled were cumulatively (Fig.5B) found to belong to: 71% in the "Cushitic" cluster, 6% in the "Saharan/Dogon" cluster, 5% in the "Niger Kordofanian" cluster, 3% each in the "Nilo-Saharan" and "Chadic Saharan" cluster, while the balance (12%) of their assignment was distributed among the remnant (9) Associated Ancestral Clusters (AAC's) found in Sub-Saharan Africa. The "Cushitic" cluster was also deemed "closest to the non-African AACs, consistent with an East African migration of modern humans out of Africa or a back-migration of non-Africans into Saharan and Eastern Africa."
Supplementary Material
/ref> Wilson et al. (2001), an autosomal DNA study based on cluster analysis that looked at a combined sample of Amhara and Oromo examining a single enzyme variant: drug metabolizing enzyme (DME) loci, found that 62% of Ethiopians fall into the same cluster of
 A composite look at most YDNA studies done so farMoran et al. (200
A composite look at most YDNA studies done so farMoran et al. (200
Y chromosome haplogroups of elite Ethiopian enduranceShenn et al. (200
Reconstruction of Patrilineages and Matrilineages of Samaritans and Other Israeli Populations From Y-Chromosome and Mitochondrial DNA Sequence Variation reveals that, out of a total of 459 males sampled from Ethiopia, approximately 58% of Y-chromosome haplotypes were found to belong to Haplogroup E (Y-DNA), Haplogroup E, of which 71% (41% of total) were characterized by one of its further downstream sub lineage known as
 The maternal ancestry of Ethiopians is similarly diverse. About half (52.2%) of Ethiopians belongs to
The maternal ancestry of Ethiopians is similarly diverse. About half (52.2%) of Ethiopians belongs to
Ethiopia
Ethiopia, , om, Itiyoophiyaa, so, Itoobiya, ti, ኢትዮጵያ, Ítiyop'iya, aa, Itiyoppiya officially the Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia, is a landlocked country in the Horn of Africa. It shares borders with Eritrea to the ...
, as well as the global diaspora of Ethiopia. Ethiopians constitute several component ethnic groups, many of which are closely related to ethnic groups in neighboring Eritrea and other parts of the Horn of Africa.
The first documented use of the name "Ethiopia" from Greek name
"Αἰθίοψ" (Ethiopian) was in the 4th century during the reign of Aksumite king Ezana
Ezana ( gez, ዔዛና ''‘Ezana'', unvocalized ዐዘነ ''‘zn''; also spelled Aezana or Aizan) was ruler of the Kingdom of Axum, an ancient kingdom located in what is now Eritrea and Ethiopia. (320s – c. 360 AD). He himself employed the ...
. There were three ethnolinguistic groups in the Kingdom of Aksum; Semitic, Cushitic, and Nilo-Saharan (ancestors of the modern-day Kunama and Nara
The National Archives and Records Administration (NARA) is an " independent federal agency of the United States government within the executive branch", charged with the preservation and documentation of government and historical records. It ...
). The Kingdom of Aksum remained a geopolitically influential entity until the pillage of its capital — also named Axum — in the 10th century by Queen Gudit. Nevertheless, the core Aksumite civilization was preserved and continued into the successive Zagwe dynasty
The Zagwe dynasty ( Ge'ez: ዛጔ ሥርወ መንግሥት) was an Agaw medieval dynasty that ruled the northern parts of Ethiopia and Eritrea, after the historical name of the Lasta province. Centered at Lalibela, it ruled large parts of the t ...
. By this time, new ethnic groups emerged – the Tigrayans
Tigrayans ( ti, ተጋሩ) are a Semitic-speaking ethnic group indigenous to the Tigray Region of northern Ethiopia. They speak the Tigrinya language, an Afroasiatic language belonging to the Ethiopian Semitic branch.
The daily life of Tigra ...
and Amharas. During the Solomonic period, the latter established major political and cultural influence East AFrica.
In the Late Middle Ages
The Late Middle Ages or Late Medieval Period was the period of European history lasting from AD 1300 to 1500. The Late Middle Ages followed the High Middle Ages and preceded the onset of the early modern period (and in much of Europe, the Renai ...
, Muslim states were established, including the Sultanate of Ifat
The Sultanate of Ifat, known as Wafāt or Awfāt in Arabic texts, was a medieval Sunni Muslim state in the eastern regions of the Horn of Africa between the late 13th century and early 15th century. It was formed in present-day Ethiopia around e ...
, and its successor the Adal Sultanate
The Adal Sultanate, or the Adal Empire or the ʿAdal or the Bar Saʿad dīn (alt. spelling ''Adel Sultanate, ''Adal ''Sultanate'') () was a medieval Sunni Muslim Empire which was located in the Horn of Africa. It was founded by Sabr ad-Din II ...
. Discontent with territory and religious dominance led to intense war between the Ethiopian Empire
The Ethiopian Empire (), also formerly known by the exonym Abyssinia, or just simply known as Ethiopia (; Amharic and Tigrinya: ኢትዮጵያ , , Oromo: Itoophiyaa, Somali: Itoobiya, Afar: ''Itiyoophiyaa''), was an empire that histori ...
, the Christian state, (consisting of the Amhara, Tigrayan, Soddo Gurage
Soddo (autonym ''kəstane'' "Christian"; formerly called ''Aymälläl'' in Western sources, after a particular dialect of it) is a Gurage language spoken by a quarter million people in southeastern Ethiopia. It is an Ethiopian Semitic language of ...
, and Agaw ethnic groups) and the Muslim state Adal Sultanate (consisting of Semitic speaking Harari formally known as the Harla people
The Harla, also known as Harala, or Arla, are an extinct ethnic group that once inhabited Djibouti, Ethiopia and northern Somalia. They spoke the now-extinct Harla language, which belonged to either the Cushitic or Semitic branches of the Afroas ...
and the Argobba). During the 1600's, there were large-scale migrations of the Oromo from the south into the highlands and also alongside the Somali into Adal or what was known as " Harrarghe" (land of the Hararis).
A period of stability and peace continued through the Gondarine period
The Gondarine period (alt. Gondarian) was a period of Ethiopian history between the ascension of Emperor Fasilides in 1632 and a period of decentralization in 1769, known as the Zemene Mesafint.
Gondar was founded by Emperor Fasilides in 1636 a ...
in 16th and 17th century, but Ethiopia was divided into de facto autonomous regions
An autonomous administrative division (also referred to as an autonomous area, entity, unit, region, subdivision, or territory) is a subnational administrative division or internal territory of a sovereign state that has a degree of autonomy— ...
in the mid-18th century. During this time, Ethiopia was nominally ruled by an Emperor
An emperor (from la, imperator, via fro, empereor) is a monarch, and usually the sovereignty, sovereign ruler of an empire or another type of imperial realm. Empress, the female equivalent, may indicate an emperor's wife (empress consort), ...
who functioned as a puppet monarch
A puppet monarch is a majority figurehead who is installed or patronized by an imperial power to provide the appearance of local authority but to allow political and economic control to remain among the dominating nation.
A figurehead monarc ...
of various regional lords and noblemen. This era was known as the ''Zemene Mesafint
The Zemene Mesafint ( gez, ዘመነ መሳፍንት ''zamana masāfint'', modern: ''zemene mesāfint'', variously translated "Era of Judges," "Era of the Princes," "Age of Princes," etc.; named after the Book of Judges) was a period in Ethiop ...
'' or "Era of the Princes". Emperor Tewodros II managed to unify the decentralized Ethiopian Empire in 1855 and inaugurated a process of modernization that continued into successive regimes, resurrecting the empire as a regional power.
In the late 19th-century during the reign of Menelik II
, spoken = ; ''djānhoi'', lit. ''"O steemedroyal"''
, alternative = ; ''getochu'', lit. ''"Our master"'' (pl.)
Menelik II ( gez, ዳግማዊ ምኒልክ ; horse name Abba Dagnew ( Amharic: አባ ዳኘው ''abba daññäw''); 17 ...
, against the backdrop of the Scramble for Africa, the notion of Ethiopian national integrity was strengthened by Italian efforts at colonization. The Italian invasion engendered a formidable national resistance, culminating in the Battle of Adwa
The Battle of Adwa (; ti, ውግእ ዓድዋ; , also spelled ''Adowa'') was the climactic battle of the First Italo-Ethiopian War. The Ethiopian forces defeated the Italian invading force on Sunday 1 March 1896, near the town of Adwa. The de ...
in 1896 which resulted in a major Ethiopian victory against the Italians. The resulting Treaty of Addis Ababa
The Treaty of Addis Ababa, signed 23 October 1896, formally ended the First Italo-Ethiopian War on terms mostly favorable to Ethiopia. This treaty superseded a secret agreement between Ethiopia and Italy negotiated days after the decisive Battle o ...
ended the Italo-Ethiopian War, and along with the nation's contemporaneous territorial expansion, largely established the modern-day boundaries of Ethiopia.
Present-day Ethiopia has a diverse population with many different languages and ethnic groups. Ethiopians speak Afro-Asiatic languages
The Afroasiatic languages (or Afro-Asiatic), also known as Hamito-Semitic, or Semito-Hamitic, and sometimes also as Afrasian, Erythraean or Lisramic, are a language family of about 300 languages that are spoken predominantly in the geographic su ...
( Semitic, Cushitic
The Cushitic languages are a branch of the Afroasiatic language family. They are spoken primarily in the Horn of Africa, with minorities speaking Cushitic languages to the north in Egypt and the Sudan, and to the south in Kenya and Tanzania. As o ...
, and Omotic) and Nilo-Saharan languages. The Oromo, Amhara, Somali and Tigrayans
Tigrayans ( ti, ተጋሩ) are a Semitic-speaking ethnic group indigenous to the Tigray Region of northern Ethiopia. They speak the Tigrinya language, an Afroasiatic language belonging to the Ethiopian Semitic branch.
The daily life of Tigra ...
make up more than three-quarters (75%) of the population, but there are more than 80 different ethnic groups within Ethiopia. Some of these have as few as 10,000 members.
History
Prehistory
Archaeologist found remains of early hominins, one of the most specimen was ''Australopithecus afarensis
''Australopithecus afarensis'' is an extinct species of australopithecine which lived from about 3.9–2.9 million years ago (mya) in the Pliocene of East Africa. The first fossils were discovered in the 1930s, but major fossil finds would not ...
'', also called "Lucy", which was discovered in the country's Awash Valley, so-called Hadar in 1974. It is estimated to be 3.5 million years old. In October 2015, scientists found a 4,500 years ago lived man called ''Mota'' in a cave in southern central Ethiopia. Atypical to Euroasians, which were believed reached the region after him, ''Mota''Aari Aari or AARI may refer to:
* Aari (actor) (born 1985), Indian Tamil film actor
* Aari language, an Omotic language
*Aari people
Aari or Ari are a tribal Omotic people indigenous to Omo Valley of Ethiopia. According to 2007 census there are 289 ...
tribes that live in the southern area of the country. Another research suggests that Euroasians arrived in the region resembles modern-day Sardinians
The Sardinians, or Sards ( sc, Sardos or ; Italian and Sassarese: ''Sardi''; Gallurese: ''Saldi''), are a Romance language-speaking ethnic group native to Sardinia, from which the western Mediterranean island and autonomous region of Italy de ...
, or likely LBK culture of antiquity. By proofing ''Mota'' has no European genome, archeologist theorized the Near East population migrated to Africa in 3,000 years ago. Other evidence concluded that Eurasian population made significant contribution as a result of back migration between 1,500 and 3,500 years ago. Nilo-Saharan peoples do not exhibit this genetic similarity; instead, their DNA shows evidence of more recent admixture (less than 1200 years ago) with other African peoples. It was thought that Hamitic people from Asia Minor
Anatolia, tr, Anadolu Yarımadası), and the Anatolian plateau, also known as Asia Minor, is a large peninsula in Western Asia and the westernmost protrusion of the Asian continent. It constitutes the major part of modern-day Turkey. The re ...
had migrated before Semitic Arabian people in the 7th century BC. In 1933, G.W.B Huntingford proposed a theory of Azanian civilization could existed in Kenya
)
, national_anthem = " Ee Mungu Nguvu Yetu"()
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, image_map2 =
, capital = Nairobi
, coordinates =
, largest_city = Nairobi
...
, and northern Tanzania
Tanzania (; ), officially the United Republic of Tanzania ( sw, Jamhuri ya Muungano wa Tanzania), is a country in East Africa within the African Great Lakes region. It borders Uganda to the north; Kenya to the northeast; Comoro Islands ...
, between the Stone Age and Islamic period. It was supposed that these people evicted from Ethiopia and Somalia
Somalia, , Osmanya script: 𐒈𐒝𐒑𐒛𐒐𐒘𐒕𐒖; ar, الصومال, aṣ-Ṣūmāl officially the Federal Republic of SomaliaThe ''Federal Republic of Somalia'' is the country's name per Article 1 of thProvisional Constituti ...
by Muslim invasion to southern region in present day Kenya and Tanzania where perished around 14th- and 15th-century.
About 7000 BC, Afro-Asiatic-speaking population namely Cushitic
The Cushitic languages are a branch of the Afroasiatic language family. They are spoken primarily in the Horn of Africa, with minorities speaking Cushitic languages to the north in Egypt and the Sudan, and to the south in Kenya and Tanzania. As o ...
and Omotic-speaking people grouped in the present day of Ethiopia after which diversification thrived in the area and allowed the other local groups, the Agaws, Somali, Oromo, and numerous Omotic-speaking groups to unify. Originally a hunter gatherers, those people began domesticating indigenous plants thereafter, including the grasses ''teff
''Eragrostis tef'', also known as teff, Williams lovegrass or annual bunch grass, is an annual grass, a species of lovegrass native to the Horn of Africa, notably to both Eritrea and Ethiopia. It is cultivated for its edible seeds, also known as ...
'', eleusine
''Eleusine'' is a genus of Asian, African, and South American plants in the grass family,enset
''Ensete ventricosum'', commonly known as enset or ensete, Ethiopian banana, Abyssinian banana, pseudo-banana, false banana and wild banana,
is an herbaceous species of flowering plant in the banana family Musaceae. The domesticated form of ...
, root crop, and domestication of cattles and other animals to fill agricultural livelihoods that still contemporary followed. By the late first millennium BC, the Agaws occupied the northern Ethiopian region, as the Sidamo occupied the central and southern parts of Ethiopia, making inaugural historical development of Ethiopia.
Afro-Asiatic languages were present in Africa and the Middle East by the eighth to sixth millennium BCE. This language family includes various modern and extinct African and Asian languages such as Oromo, Somali, Egyptian, Berber, Hausa, Hebrew, Arabic, Aramaic, and Akkadian. Ge'ez was developed around sixth century BCE and evident by inscriptions of contemporary kingdom of D'mt. The language dominance was eclipsed by 1000 AD, but the highland inhabitants used it as written scholar and liturgical language between 300s and 1800s.
Antiquity
 In 980 BCE,
In 980 BCE, Dʿmt
D mt ( Ge'ez: ደዐመተ, ''DʿMT'' theoretically vocalized as ዳዓማት, ''Daʿamat'' or ዳዕማት, Daʿəmat) was a kingdom located in Eritrea and northern Ethiopia that existed between the 10th and 5th centuries BC. Few inscriptions ...
was established in present-day Eritrea and the Tigray Region
The Tigray Region, officially the Tigray National Regional State, is the northernmost regional state in Ethiopia. The Tigray Region is the homeland of the Tigrayan, Irob, and Kunama people. Its capital and largest city is Mekelle. Tigray ...
of Ethiopia, straddling South Arabia in present-day of Yemen
Yemen (; ar, ٱلْيَمَن, al-Yaman), officially the Republic of Yemen,, ) is a country in Western Asia. It is situated on the southern end of the Arabian Peninsula, and borders Saudi Arabia to the Saudi Arabia–Yemen border, north and ...
. This polity's capital was located at Yeha
Yeha ( gez, ይሐ ''yiḥa'', older ESA 𐩥𐩢 ''ḤW''; Old South Arabian: 𐩺𐩢𐩱 ''Yḥʾ'') is a town in the Maekelay Zone of the northern Tigray Region in Ethiopia. It likely served as the capital of the pre-Aksumite kingdom of D'm ...
, in what is now northern Ethiopia. Most modern historians consider this civilization to be a native Ethiopian one, although in earlier times many suggested it was Sabaean-influenced because of the latter's hegemony of the Red Sea.
Other scholars regard Dʿmt as the result of a union of Afroasiatic-speaking cultures of the Cushitic and Semitic branches; namely, local Agaw peoples and Sabaeans from Southern Arabia. However, Ge'ez, the ancient Semitic language of Ethiopia, is thought to have developed independently from the Sabaean language
Sabaean, also known as Sabaic, was an Old South Arabian language spoken between c. 1000 BC and the 6th century AD, by the Sabaeans. It was used as a written language by some other peoples of the ancient civilization of South Arabia, including t ...
, one of the South Semitic languages
South Semitic is a putative branch of the Semitic languages, which form a branch of the larger Afro-Asiatic language family, found in (North and East) Africa and Western Asia.
History
The "homeland" of the South Semitic languages is widely d ...
. As early as 2000 BCE, other Semitic speakers were living in Ethiopia and Eritrea where Ge'ez developed. Sabaean influence is now thought to have been minor, limited to a few localities, and disappearing after a few decades or a century. It may have been a trading or military colony in alliance with the Ethiopian civilization of Dʿmt or some other proto-Axumite state. Politically integrated, the Kingdom of Aksum was emerged independently from at least 100 BC, and its civilization grew from 1st century AD. The kingdom dominated the Red Sea
The Red Sea ( ar, البحر الأحمر - بحر القلزم, translit=Modern: al-Baḥr al-ʾAḥmar, Medieval: Baḥr al-Qulzum; or ; Coptic: ⲫⲓⲟⲙ ⲛ̀ϩⲁϩ ''Phiom Enhah'' or ⲫⲓⲟⲙ ⲛ̀ϣⲁⲣⲓ ''Phiom ǹšari''; ...
, the Northeast Africa in the present location between northern Ethiopia (Tigray Region
The Tigray Region, officially the Tigray National Regional State, is the northernmost regional state in Ethiopia. The Tigray Region is the homeland of the Tigrayan, Irob, and Kunama people. Its capital and largest city is Mekelle. Tigray ...
), eastern Sudan, Eritrea, South Arabia. It was by far powerful empire and trading nation between Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, Βασιλεία τῶν Ῥωμαίων, Basileía tôn Rhōmaíōn) was the post- Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings around the Mediter ...
and India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the so ...
. The Aksumite lingua franca was Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
evolved from Hellenistic period
In Classical antiquity, the Hellenistic period covers the time in Mediterranean history after Classical Greece, between the death of Alexander the Great in 323 BC and the emergence of the Roman Empire, as signified by the Battle of Actium in ...
in 330–305 BC and officially adopted in the first century. It was soon replaced by Ge'ez in the 4th century. Politically and culturally influenced partially with Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
, the Aksumite achieved major historical grounds, Orthodox Tewahedo {{Short description, Collective term for Oriental Orthodox Churches in Eritrea and Ethiopia
Orthodox Tewahedo refers to two Oriental Orthodox Christian denominations with shared beliefs, liturgy, and history. The Orthodox Tewahedo biblical canon is ...
Christianity introduced and has been state religion in the early 4th century, construction of stone-fitted palace and public buildings, and erection of large obelisks around the capital Axum. These all are milestones that culminate in the rise of Ethiopian identity where the Greek exonym "Ethiopians" came to use by the kingdom under king Ezana
Ezana ( gez, ዔዛና ''‘Ezana'', unvocalized ዐዘነ ''‘zn''; also spelled Aezana or Aizan) was ruler of the Kingdom of Axum, an ancient kingdom located in what is now Eritrea and Ethiopia. (320s – c. 360 AD). He himself employed the ...
's reign in the 4th century. The first century BCE Greek historian Diodorus Siculus claimed the Ethiopian nativity as "true natives", "most pious and righteous" in his record. This assertion resonated by locality of declaring themselves a "Habesha people
am, ሐበሻ, አበሻ, translit=Häbäša, 'äbäša ti, ሓበሻ, translit=Ḥabäša
, regions =
, languages = Ethiopian Semitic languages
, religions = Predominantly Oriental Orthodox Christianity (Orthodox Te ...
". His record expounded the nature of Ethiopians, including highly proselytizing to neighboring Egypt. He denoted these people locating in the place superimposed by Nubia and Meroë, connected to the Nile river, having distinct rainy season and wonderful lake.
Middle Ages
Meroë
Meroë (; also spelled ''Meroe''; Meroitic: or ; ar, مرواه, translit=Meruwah and ar, مروي, translit=Meruwi, label=none; grc, Μερόη, translit=Meróē) was an ancient city on the east bank of the Nile about 6 km north-east ...
in 330, and entered "Golden Age" for the next three centuries. Aksum's power began declining at time of Islamic Golden Age
The Islamic Golden Age was a period of cultural, economic, and scientific flourishing in the history of Islam, traditionally dated from the 8th century to the 14th century. This period is traditionally understood to have begun during the reign ...
, where they frequently countered intrusions by Arab Muslims in the South Arabia protectorate (modern Yemen
Yemen (; ar, ٱلْيَمَن, al-Yaman), officially the Republic of Yemen,, ) is a country in Western Asia. It is situated on the southern end of the Arabian Peninsula, and borders Saudi Arabia to the Saudi Arabia–Yemen border, north and ...
), making them to evicted more in the southern of Agaw population.
In 10th century, the kingdom ultimately collapsed followed by pillage by Queen Gudit, after execution of Christians and ordered arson in church. While Aksum's existence extinguished, the follow-up kingdom of Zagwe likely of a continuation of its civilization and revival of Christianity, and a new multi-ethnic empire-state was formed in title of "king of kings".
The successful integration of Agaw and Semitic groups in the north prolonged over millennium and eventually forms Tigrayans
Tigrayans ( ti, ተጋሩ) are a Semitic-speaking ethnic group indigenous to the Tigray Region of northern Ethiopia. They speak the Tigrinya language, an Afroasiatic language belonging to the Ethiopian Semitic branch.
The daily life of Tigra ...
and Amhara people. The Zagwe kingdom capital, relocated to Lalibela
Lalibela ( am, ላሊበላ) is a town in the Amhara Region of Ethiopia. Located in the Lasta district and North Wollo Zone, it is a tourist site for its famous rock-cut monolithic churches. The whole of Lalibela is a large and important si ...
, and sparked a new cultural life. The most notable churches in this period was constructed with unique rock-hewn architecture. A dominant group, Amhara, continues to expand its territory in so-called Solomonic period after the downfall of Zagwe in 1270, and by the late 13th century, they reached to southern Shewa. Since then, centralized military unit was buildup while frequently engaged war with Sidama kingdom in the west and Muslim population to the east.
One of the most important era for Christian and Muslim insight, and the resultant of religious war was in the mid-16th century of Ethiopian–Adal War
The Ethiopian–Adal War or Abyssinian-Adal War, also known in Arabic as the "Futuḥ al-Ḥabash" ( ar, فتوح الحبش, ''conquest of Abyssinia''), was a military conflict between the Christian Ethiopian Empire and the Muslim Adal Sulta ...
, involving the Amhara, Tigrayan and Agaw force allied to the Ethiopian Empire
The Ethiopian Empire (), also formerly known by the exonym Abyssinia, or just simply known as Ethiopia (; Amharic and Tigrinya: ኢትዮጵያ , , Oromo: Itoophiyaa, Somali: Itoobiya, Afar: ''Itiyoophiyaa''), was an empire that histori ...
(Abyssinia) and the Muslim states composed mostly of Harari and Somali people, together forms the Adal Sultanate
The Adal Sultanate, or the Adal Empire or the ʿAdal or the Bar Saʿad dīn (alt. spelling ''Adel Sultanate, ''Adal ''Sultanate'') () was a medieval Sunni Muslim Empire which was located in the Horn of Africa. It was founded by Sabr ad-Din II ...
. The Oromo people additionally took an advantage of the war and occupied much the northern highland zone of the Amhara empire in the Oromo migrations.
Early modern period
The Oromo remained predominantly pastoral life who dominated the Amhara empire of Abyssinia for the rest of era. A blossom life continued throughout early modern period with the founding of capitalGondar
Gondar, also spelled Gonder (Amharic: ጎንደር, ''Gonder'' or ''Gondär''; formerly , ''Gʷandar'' or ''Gʷender''), is a city and woreda in Ethiopia. Located in the North Gondar Zone of the Amhara Region, Gondar is north of Lake Tana on t ...
in the early 18th century, by Emperor Fasilides
Fasilides ( Ge'ez: ፋሲልደስ; ''Fāsīladas''; 20 November 1603 – 18 October 1667), also known as Fasil, Basilide, or Basilides (as in the works of Edward Gibbon), was Emperor of Ethiopia from 1632 to his death on 18 October 1667, and a ...
, commencing a "Gondarine period".
 Between 1769 and 1855, Ethiopia experienced a period of isolation referred to as the ''
Between 1769 and 1855, Ethiopia experienced a period of isolation referred to as the ''Zemene Mesafint
The Zemene Mesafint ( gez, ዘመነ መሳፍንት ''zamana masāfint'', modern: ''zemene mesāfint'', variously translated "Era of Judges," "Era of the Princes," "Age of Princes," etc.; named after the Book of Judges) was a period in Ethiop ...
'' or "Age of Princes". The Emperors became figureheads, controlled by regional lords and noblemen like ''Ras'' Mikael Sehul
Mikael Sehul (born Blatta Mikael; 1692 – 1784) was a nobleman who ruled Ethiopia for a period of 25 years as regent of a series of weak emperors. He was also a Ras or governor of Tigray 1748–71 and again from 1772 until his death. He was a m ...
of Tigray, ''Ras'' Wolde Selassie
Wolde Selassie (; c.1736 - 28 May 1816) was Ras of the Tigray province between 1788-1816, and Regent of the Ethiopian Empire between 1797-1800. John J. Halls, in his ''Life and Correspondence of Henry Salt'', preserves a description of this power ...
of Tigray, and by the Yejju Oromo dynasty of the Wara Sheh, such as ''Ras'' Gugsa of Yejju
Gugsa of Yejju (died 23 May 1825) was a ''Ras'' of Begemder (''circa'' 1798 until his death), and Inderase (regent) of the Emperor of Ethiopia. According to Nathaniel Pearce, he took the Christian name of Wolde Mikael. He was the son of Mersu B ...
. Prior to the Zemene Mesafint, Emperor Iyoas I
Iyoas I ( Ge'ez: ኢዮአስ; died 14 May 1769), throne name Adyam Sagad (Ge'ez: አድያም ሰገድ) was Emperor of Ethiopia from 27 June 1755 to 7 May 1769, and a member of the Solomonic dynasty. He was the infant son of Iyasu II and Wubit ...
had introduced the Oromo language (''Afaan Oromo'') at court, instead of Amharic. In 1855, Emperor Tewodros II sought to establish permanent Ethiopian border by solidifying the Shewan kingdoms. Tewodros II is often credited with being the preliminary figure of modern Ethiopian history but his reign ended prematurely when he committed suicide during the British Expedition to Abyssinia
The British Expedition to Abyssinia was a rescue mission and punitive expedition carried out in 1868 by the armed forces of the British Empire against the Ethiopian Empire (also known at the time as Abyssinia). Emperor Tewodros II of Ethiopia, ...
.
 Emperor
Emperor Menelik II
, spoken = ; ''djānhoi'', lit. ''"O steemedroyal"''
, alternative = ; ''getochu'', lit. ''"Our master"'' (pl.)
Menelik II ( gez, ዳግማዊ ምኒልክ ; horse name Abba Dagnew ( Amharic: አባ ዳኘው ''abba daññäw''); 17 ...
done major reformations to the country by the late 1890s: under his reign, Menelik extensively conquered the rest of kingdoms nearby region, while annexing the Tigray Province
Tigray Province ( Amharic and ), also known as Tigre ( tigrē), was a historical province of northern Ethiopia that overlayed the present day Afar and Tigray regions. Akele Guzai borders with the Tigray province It was one It encompassed most ...
, ultimately formed the modern border of Ethiopia. His reign brought sharp solidification of the current Ethiopian national identity. The Battle of Adwa
The Battle of Adwa (; ti, ውግእ ዓድዋ; , also spelled ''Adowa'') was the climactic battle of the First Italo-Ethiopian War. The Ethiopian forces defeated the Italian invading force on Sunday 1 March 1896, near the town of Adwa. The de ...
was a 1896 colonial resistance battle between the Ethiopian Empire led by Menelik and Kingdom of Italy
The Kingdom of Italy ( it, Regno d'Italia) was a state that existed from 1861, when Victor Emmanuel II of Sardinia was proclaimed King of Italy, until 1946, when civil discontent led to an institutional referendum to abandon the monarchy and f ...
led by General Oreste Baratieri
Oreste Baratieri (né Oreste Baratter, 13 November 1841 – 7 August 1901) was an Italian general and governor of Italian Eritrea.
Early career
Born in Condino (County of Tyrol, now Trentino), Baratieri began his career as a volunteer for Giusepp ...
, involving respective 100,000 and 17,700 troops, where Ethiopian armies decisively defeated them and secured sovereignty. The battle became signature national pride among Ethiopians, and beyond for Pan-Africanism
Pan-Africanism is a worldwide movement that aims to encourage and strengthen bonds of solidarity between all Indigenous and diaspora peoples of African ancestry. Based on a common goal dating back to the Atlantic slave trade, the movement exte ...
. The Treaty of Addis Ababa
The Treaty of Addis Ababa, signed 23 October 1896, formally ended the First Italo-Ethiopian War on terms mostly favorable to Ethiopia. This treaty superseded a secret agreement between Ethiopia and Italy negotiated days after the decisive Battle o ...
(1896) settled an end of Italo-Ethiopian War, and modern border of Ethiopia was created as a background of ceased foreign external pressure against the sovereignty of Ethiopia. Ethiopia, along with Liberia, became the only independent African survivors against the European colonization
The historical phenomenon of colonization is one that stretches around the globe and across time. Ancient and medieval colonialism was practiced by the Phoenicians, the Greeks, the Turks, and the Arabs.
Colonialism in the modern sense began ...
.
Current era
Second Italo-Ethiopian War
The Second Italo-Ethiopian War, also referred to as the Second Italo-Abyssinian War, was a war of aggression which was fought between Italy and Ethiopia from October 1935 to February 1937. In Ethiopia it is often referred to simply as the Itali ...
brought legacy of ethnic marginalization of major ethnic groups: the Oromos, Amharas, Tigrayans, and Somalis. Ethiopia underwent series civil clashes under communist military junta Derg. Ethnic nationalism
Ethnic nationalism, also known as ethnonationalism, is a form of nationalism wherein the nation and nationality are defined in terms of ethnicity, with emphasis on an ethnocentric (and in some cases an ethnocratic) approach to various politi ...
and similar policies implemented by the Ethiopian Peoples' Revolutionary Democratic Front
The Ethiopian People's Revolutionary Democratic Front (EPRDF; am, የኢትዮጵያ ሕዝቦች አብዮታዊ ዲሞክራሲያዊ ግንባር, translit=Ye’Ītiyop’iya Ḥizibochi Ābiyotawī Dīmokirasīyawī Ginibari) was an eth ...
(EPRDF), which brought Ethiopia to ethnic federalist state since 1995, which was aimed to reduce internal ethnic conflicts and grant freedom of choice
Freedom of choice describes an individual's wikt:opportunity, opportunity and autonomy to perform an action selected from at least two available options, unconstrained by external parties.
In politics
In the abortion debate, for example, the te ...
within every ethnic groups although, Ethiopia then faced more prolong internal conflicts and ethnic clashes in the 21st-century.
Ethnicity



Major ethnic groups
* Oromo 34.4% * Amhara 27.0% * Somali 6.2% * Tigray 6.1% *Sidama
The Sidama ( am, ሲዳማ) are an ethnic group traditionally inhabiting the Sidama Region, formerly part of the Southern Nations, Nationalities, and Peoples' Region of Ethiopia. On 23 November 2019, the Sidama Zone became the 10th regional st ...
4.0%
* Gurage
The Gurage (, Gurage: ጉራጌ) are a Semitic-speaking ethnic group inhabiting Ethiopia.G. W. E. Huntingford, "William A. Shack: The Gurage: a people of the ensete culture" They inhabit the Gurage Zone, a fertile, semi-mountainous region in c ...
2.5%
* Welayta 2.3%
* Hadiya 1.7%
* Afar 1.7%
* Gamo 1.5%
* Other ethnic groups
An ethnic group or an ethnicity is a grouping of people who identify with each other on the basis of shared attributes that distinguish them from other groups. Those attributes can include common sets of traditions, ancestry, language, history, ...
12.6%
List
Ethiopian diaspora
*Ethiopian Americans
Ethiopian Americans are Americans of Ethiopian descent, as well as individuals of American and Ethiopian ancestry.
History
In 1919, an official Ethiopian goodwill mission was sent to the United States to congratulate the Allied powers on thei ...
* Ethiopian Australians
* Ethiopian Canadians
* Ethiopian Jews in Israel
Ethiopian Jews in Israel are immigrants and descendants of the immigrants from the Beta Israel communities in Ethiopia who now reside in Israel. To a lesser, but notable, extent, the Ethiopian Jewish community in Israel is also composed of Fa ...
* Ethiopians in Italy
* Ethiopians in the United Kingdom
* Ethiopians in Denmark
* Ethiopians in Norway
* Ethiopians in Sweden
*Eritreans
Eritreans are the native inhabitants of Eritrea, as well as the global diaspora of Eritrea. Eritreans constitute several component ethnic groups, some of which are related to ethnic groups that make up the Ethiopian people in neighboring Ethio ...
* Habesha peoples
** Eritrean people of Ethiopian descent
** Ethiopian people of Eritrean descent
Languages
Until thefall of the Derg
The fall of the Derg, also known as Downfall of the Derg, was a military campaign that resulted the defeat of the ruling military junta Derg by the rebel coalition Ethiopian People's Revolutionary Democratic Front (EPRDF) on 28 May 1991 in Addi ...
, Amharic served as the sole official language in government administration, courts, church and even in primary school instruction; although in the 17th Century during the Zemene Mesafint
The Zemene Mesafint ( gez, ዘመነ መሳፍንት ''zamana masāfint'', modern: ''zemene mesāfint'', variously translated "Era of Judges," "Era of the Princes," "Age of Princes," etc.; named after the Book of Judges) was a period in Ethiop ...
under the rule of the Warasek dynasty, the Oromo language did serve as the official language of the Ethiopian Empire
The Ethiopian Empire (), also formerly known by the exonym Abyssinia, or just simply known as Ethiopia (; Amharic and Tigrinya: ኢትዮጵያ , , Oromo: Itoophiyaa, Somali: Itoobiya, Afar: ''Itiyoophiyaa''), was an empire that histori ...
's royal court
A royal court, often called simply a court when the royal context is clear, is an extended royal household in a monarchy, including all those who regularly attend on a monarch, or another central figure. Hence, the word "court" may also be appl ...
. After 1991, Amharic has been replaced in many areas by other official government languages such as Oromo, Somali and Tigrinya
(; also spelled Tigrigna) is an Ethio-Semitic language commonly spoken Eritrea and in northern Ethiopia's Tigray Region by the Tigrinya and Tigrayan peoples. It is also spoken by the global diaspora of these regions.
History and literatur ...
. English
English usually refers to:
* English language
* English people
English may also refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* ''English'', an adjective for something of, from, or related to England
** English national ide ...
is the most widely spoken foreign language and is taught in all secondary schools.
According to the 2007 Ethiopian census and the CIA World Fact Book, the largest first language
A first language, native tongue, native language, mother tongue or L1 is the first language or dialect that a person has been exposed to from birth or within the critical period. In some countries, the term ''native language'' or ''mother tongu ...
s are: Oromo 24,929,567 speakers or 33.8% of the total population; Amharic 21,631,370 or 29.3% (federal working language); Somali 4,609,274 or 6.2%; Tigrinya
(; also spelled Tigrigna) is an Ethio-Semitic language commonly spoken Eritrea and in northern Ethiopia's Tigray Region by the Tigrinya and Tigrayan peoples. It is also spoken by the global diaspora of these regions.
History and literatur ...
4,324,476 or 5.9%; Sidamo 4,981,471 or 4%; Wolaytta 1,627,784 or 2.2%; Gurage
The Gurage (, Gurage: ጉራጌ) are a Semitic-speaking ethnic group inhabiting Ethiopia.G. W. E. Huntingford, "William A. Shack: The Gurage: a people of the ensete culture" They inhabit the Gurage Zone, a fertile, semi-mountainous region in c ...
1,481,783 or 2%; and Afar 1,281,278 or 1.7%.https://www.cia.gov/the-world-factbook/countries/ethiopia/#people-and-society . ''The World Factbook
''The World Factbook'', also known as the ''CIA World Factbook'', is a reference resource produced by the Central Intelligence Agency (CIA) with almanac-style information about the countries of the world. The official print version is availabl ...
''. Central Intelligence Agency
The Central Intelligence Agency (CIA ), known informally as the Agency and historically as the Company, is a civilian foreign intelligence service of the federal government of the United States, officially tasked with gathering, processing, ...
. Widely-spoken foreign languages include Arabic
Arabic (, ' ; , ' or ) is a Semitic language spoken primarily across the Arab world.Semitic languages: an international handbook / edited by Stefan Weninger; in collaboration with Geoffrey Khan, Michael P. Streck, Janet C. E.Watson; Walter ...
, English
English usually refers to:
* English language
* English people
English may also refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* ''English'', an adjective for something of, from, or related to England
** English national ide ...
(major foreign language taught in schools), and Italian
Italian(s) may refer to:
* Anything of, from, or related to the people of Italy over the centuries
** Italians, an ethnic group or simply a citizen of the Italian Republic or Italian Kingdom
** Italian language, a Romance language
*** Regional Ita ...
(spoken by an Italian minority).
Religion
According to the CIA Factbook the religious demography of Ethiopia is as follows; Ethiopian Orthodox 43.8%, Muslim 31.3%, Protestant 22.8%, Catholic 0.7%, traditional 0.6%, and other 0.8%.Diaspora
The largest diaspora community is found in the United States. According to theU.S. Census Bureau
The United States Census Bureau (USCB), officially the Bureau of the Census, is a principal agency of the U.S. Federal Statistical System, responsible for producing data about the American people and economy. The Census Bureau is part of the ...
, 250,000 Ethiopian immigrants lived in the United States as of 2008. An additional 30,000 U.S.-born citizens reported Ethiopian ancestry. According to Aaron Matteo Terrazas, "if the descendants of Ethiopian-born migrants (the second generation and up) are included, the estimates range upwards of 460,000 in the United States (of which approximately 350,000 are in the Washington, DC Metropolitan Area
The Washington metropolitan area, also commonly referred to as the National Capital Region, is the metropolitan area centered on Washington, D.C. The metropolitan area includes all of Washington, D.C. and parts of the states of Maryland, Virgi ...
; 96,000 in Los Angeles
Los Angeles ( ; es, Los Ángeles, link=no , ), often referred to by its initials L.A., is the List of municipalities in California, largest city in the U.S. state, state of California and the List of United States cities by population, sec ...
; and 10,000 in New York)."
A large Ethiopian community is also found in Israel, where Ethiopians
Ethiopians are the native inhabitants of Ethiopia, as well as the global diaspora of Ethiopia. Ethiopians constitute several component ethnic groups, many of which are closely related to ethnic groups in neighboring Eritrea and other parts o ...
make up almost 1.9% of the population. Almost the entire community are members of the Beta Israel community. There are also large number of Ethiopian emigrants in Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia, officially the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (KSA), is a country in Western Asia. It covers the bulk of the Arabian Peninsula, and has a land area of about , making it the fifth-largest country in Asia, the second-largest in the A ...
, Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical ...
, Lebanon
Lebanon ( , ar, لُبْنَان, translit=lubnān, ), officially the Republic of Lebanon () or the Lebanese Republic, is a country in Western Asia. It is located between Syria to Lebanon–Syria border, the north and east and Israel to Blue ...
, United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the European mainland, continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotlan ...
, Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by tot ...
, Sweden and Australia..
Genetic studies
Autosomal DNA
Studies conducted on Ethiopians belonging to Semitic and Cushitic ethnic groups mostly from the north of the country (Oromo, Amhara, Tigray, and Gurage), estimate approximately 40% of their autosomal ancestry to be derived from an ancient non-African back-migration from the Near East, and about 60% to be of native African origin (from a population indigenous or "autochthonous" to the Horn of Africa). Hodgson et al. (2014) found a distinct African ancestral component in Afro-Asiatic populations in the Horn (dubbed "Ethiopic"), as well as a distinct non-African component (dubbed "Ethio-Somali"). The data also revealed Nilo-Saharan ancestry in Afro-Asiatic populations and "Ethiopic" ancestry in Nilo-Saharan populations, suggesting an intricate history of contact in the region. Ethiopian Nilo-Saharan groups and theendogamous
Endogamy is the practice of marrying within a specific social group, religious denomination, caste, or ethnic group, rejecting those from others as unsuitable for marriage or other close personal relationships.
Endogamy is common in many cultu ...
Aari blacksmith caste were found to have little to no Eurasian admixture. Aari blacksmiths may descend from "Ethiopic" hunter-gatherers who were assimilated as farmers expanded in the region or a subset of a single population recently marginalized for their occupation. According to Hollfelder et al. (2017), "Northeast African Nilotes
The Nilotic peoples are people indigenous to the Nile Valley who speak Nilotic languages. They inhabit South Sudan, Sudan, Ethiopia, Uganda, Kenya, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Rwanda, Burundi and Tanzania. Among these are the ...
showed some distinction from an ancient Ethiopian individual (Mota, found in the Mota Cave in the southern Ethiopian highlands), which suggests population structure between northeast and eastern Africa already 4,500 years ago. The modern-day Nilotic groups are likely direct descendants of past populations living in northeast Africa many thousands of years ago." Pickrell et al. (2014) found that West Eurasian ancestry peaks in the Amhara and Tigrayans at 49% and 50%, respectively. In Pagani, Luca et al. (2012), this non-African component, is estimated to have entered the Horn of Africa roughly ~3,000 years ago and was found to be similar to the populations in the Levant. The paper goes on to say that this coincides with the introduction of Ethio-Semitic languages into the region. Gallego Llorente, M et al. (2015) discovered extensive admixture in Eastern Africa from a population closely related to early Neolithic farmers from the Near-East/Anatolia. López, Saioa et al. (2021) found that when comparing Ethiopians to external populations only, Nilo-Saharan speakers (as well as the Chabu, Dassanech, and Karo) in the southwest shared more recent ancestry with Bantu and Nilotic speakers, while Afro-Asiatic speakers in the northeast shared more recent ancestry with Egyptians and West Eurasians. The study revealed that groups belonging to the Cushitic, Omotic, and Semitic branches of Afro-Asiatic show high genetic similarity to each other on average.
Tishkoff et al. (2009) identified fourteen ancestral population clusters which correlate with self-described ethnicity and shared cultural and/or linguistic properties in Africa in what was the largest autosomal study of the continent to date.Out of Africa: Penn Geneticist Publishes Largest-Ever Study on African Genetics Revealing Origins, MigrationThe Burji, Konso and Beta Israel were sampled from Ethiopia. The Afroasiatic speaking Ethiopians sampled were cumulatively (Fig.5B) found to belong to: 71% in the "Cushitic" cluster, 6% in the "Saharan/Dogon" cluster, 5% in the "Niger Kordofanian" cluster, 3% each in the "Nilo-Saharan" and "Chadic Saharan" cluster, while the balance (12%) of their assignment was distributed among the remnant (9) Associated Ancestral Clusters (AAC's) found in Sub-Saharan Africa. The "Cushitic" cluster was also deemed "closest to the non-African AACs, consistent with an East African migration of modern humans out of Africa or a back-migration of non-Africans into Saharan and Eastern Africa."
Supplementary Material
/ref> Wilson et al. (2001), an autosomal DNA study based on cluster analysis that looked at a combined sample of Amhara and Oromo examining a single enzyme variant: drug metabolizing enzyme (DME) loci, found that 62% of Ethiopians fall into the same cluster of
Ashkenazi Jews
Ashkenazi Jews ( ; he, יְהוּדֵי אַשְׁכְּנַז, translit=Yehudei Ashkenaz, ; yi, אַשכּנזישע ייִדן, Ashkenazishe Yidn), also known as Ashkenazic Jews or ''Ashkenazim'',, Ashkenazi Hebrew pronunciation: , singu ...
, Norwegians
Norwegians ( no, nordmenn) are a North Germanic ethnic group and nation native to Norway, where they form the vast majority of the population. They share a common culture and speak the Norwegian language. Norwegians are descended from the N ...
and Armenia
Armenia (), , group=pron officially the Republic of Armenia,, is a landlocked country in the Armenian Highlands of Western Asia.The UNbr>classification of world regions places Armenia in Western Asia; the CIA World Factbook , , and ' ...
ns based on that gene. Only 24% of Ethiopians cluster with Bantus and Afro-Caribbeans, 8% with Papua New Guineans, and 6% with Chinese
Chinese can refer to:
* Something related to China
* Chinese people, people of Chinese nationality, citizenship, and/or ethnicity
**''Zhonghua minzu'', the supra-ethnic concept of the Chinese nation
** List of ethnic groups in China, people of ...
.
Paternal lineages
 A composite look at most YDNA studies done so farMoran et al. (200
A composite look at most YDNA studies done so farMoran et al. (200Y chromosome haplogroups of elite Ethiopian enduranceShenn et al. (200
Reconstruction of Patrilineages and Matrilineages of Samaritans and Other Israeli Populations From Y-Chromosome and Mitochondrial DNA Sequence Variation reveals that, out of a total of 459 males sampled from Ethiopia, approximately 58% of Y-chromosome haplotypes were found to belong to Haplogroup E (Y-DNA), Haplogroup E, of which 71% (41% of total) were characterized by one of its further downstream sub lineage known as
E1b1b
E-M215, also known as E1b1b and formerly E3b, is a major human Y-chromosome DNA haplogroup. It is a division of the macro-haplogroup E-M96, which is defined by the single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) mutation M215. In other words, it is one of ...
, while the remainder were mostly characterized by Haplogroup E1b1(x E1b1b,E1b1a), and to a lesser extent Haplogroup E2. With respect to E1b1b
E-M215, also known as E1b1b and formerly E3b, is a major human Y-chromosome DNA haplogroup. It is a division of the macro-haplogroup E-M96, which is defined by the single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) mutation M215. In other words, it is one of ...
, some studies have found that it exists at its highest level among the Oromo, where it represented 62.8% of the haplotypes, while it was found at 35.4% among the Amhara, other studies however have found an almost equal representation of Haplogroup E1b1b at approximately 57% in both the Oromo and the Amhara. The haplogroup (as its predecessor E1b1) is thought to have originated in Ethiopia or elsewhere in the Horn of Africa. About one half of E1b1b found in Ethiopia is further characterized by E1b1b1a (M78), which arose later in north-eastern Africa and then back-migrated to eastern Africa.
Haplogroup J has been found at a frequency of approximately 18% in Ethiopians, with a higher prevalence among the Amhara, where it has been found to exist at levels as high as 35%, of which about 94% (17% of total) is of the type J1, while 6% (1% of total) is of J2 type. On the other hand, 26% of the individuals sampled in the Arsi control portion of Moran et al. (2004) were found to belong to Haplogroup J.
Another fairly prevalent lineage in Ethiopia belongs to Haplogroup A, occurring at a frequency of about 17% within Ethiopia, it is almost all characterized by its downstream sub lineage of A3b2 (M13). Restricted to Africa, and mostly found along the Rift Valley
A rift valley is a linear shaped lowland between several highlands or mountain ranges created by the action of a geologic rift. Rifts are formed as a result of the pulling apart of the lithosphere due to extensional tectonics. The linear d ...
from Ethiopia to Cape Town
Cape Town ( af, Kaapstad; , xh, iKapa) is one of South Africa's three capital cities, serving as the seat of the Parliament of South Africa. It is the legislative capital of the country, the oldest city in the country, and the second largest ...
, Haplogroup A represents the deepest branch in the Human Y- Chromosome phylogeny.
Finally, Haplogroup T at approximately 4% and Haplogroup B at approximately 3%, make up the remainder of the Y-DNA Haplogroups found within Ethiopia.
Maternal lineages
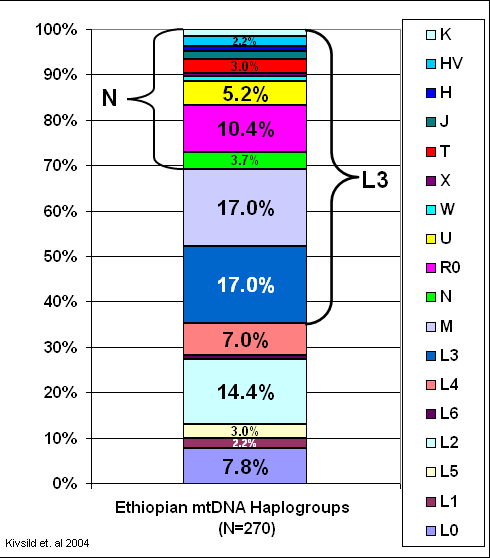
 The maternal ancestry of Ethiopians is similarly diverse. About half (52.2%) of Ethiopians belongs to
The maternal ancestry of Ethiopians is similarly diverse. About half (52.2%) of Ethiopians belongs to mtdna
Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA or mDNA) is the DNA located in mitochondria, cellular organelles within eukaryotic cells that convert chemical energy from food into a form that cells can use, such as adenosine triphosphate (ATP). Mitochondrial DNA ...
Haplogroups L0, L1, L2, L3, L4, L5, or L6. These haplogroups are generally confined to the African continent. They also originated either in Ethiopia or very near. The other portion of the population belong to Haplogroup N (31%) and Haplogroup M1 (17%). There is controversy surrounding their origins as either native or a possible ancient back migration into Ethiopia from Asia
Asia (, ) is one of the world's most notable geographical regions, which is either considered a continent in its own right or a subcontinent of Eurasia, which shares the continental landmass of Afro-Eurasia with Africa. Asia covers an are ...
.
Passarino et al. (1998) suggested that: Caucasoid gene flow into the Ethiopian gene pool occurred predominantly through males. Conversely, the Niger–Congo contribution to the Ethiopian population occurred mainly through females.While there is debate among the scientific community of what exactly constitutes "Caucasoid gene flow", the same study further stated:
Indeed, Ethiopians do not seem to result only from a simple combination of proto-Niger–Congo and Middle Eastern genes. Their African component cannot be completely explained by that of present-day Niger–Congo speakers, and it is quite different from that of the Khoisan. Thus, a portion of the current Ethiopian gene pool may be the product of in situ differentiation from an ancestral gene pool."Scott et al. (2005) similarly observed that the Ethiopian population is almost equally divided between individuals that carry Eurasian maternal lineages, and those that belong to African clades. They describe the presence of Eurasian clades in the country as sequences that "are thought to be found in high numbers in Ethiopia either as a result of substantial gene flow into Ethiopia from Eurasia (Chen et al., 2000; Richards et al., 2003), or as a result of having undergone several branching events in demic diffusion, acting as founder lineages for non-African populations". The researchers further found no association between regional origin of subjects or language family (Semitic/Cushitic) and their mitochondrial type:
The haplogroup distribution amongst all subjects (athletes and controls) from different geographical regions of Ethiopia is displayed in Table 3. As can be seen graphically in Fig. 3, the mtDNA haplogroup distribution of each region is similar, with all regions displaying similar proportions of African 'L' haplogroups (Addis Ababa: 59%, Arsi: 50%, Shewa: 44%, Other: 57%). No association was found between regional origin of subjects and their mitochondrial type (v2=8.5, 15 df, P=0.9). Similarly, the mtDNA haplogroup distribution of subjects (athletes and controls) speaking languages from each family is shown in Table 3. Again there was no association between language family and mitochondrial type (v2=5.4, 5 df, P=0.37). As can be seen in Fig. 4, the haplogroup distributions of each language family are again very similar.In addition, Musilová et al. (2011) observed significant maternal ties between its Ethiopian and other Horn African samples with its Western Asian samples; particularly in terms of the HV1b mtDNA haplogroup. The authors noted:
"Detailed phylogeography of HV1 sequences shows that more recent demographic upheavals likely contributed to their spread from West Arabia to East Africa, a finding concordant with archaeological records suggesting intensive maritime trade in theAccording to Černý et al. (2008), many Ethiopians also share specific maternal lineages with areas inRed Sea The Red Sea ( ar, البحر الأحمر - بحر القلزم, translit=Modern: al-Baḥr al-ʾAḥmar, Medieval: Baḥr al-Qulzum; or ; Coptic: ⲫⲓⲟⲙ ⲛ̀ϩⲁϩ ''Phiom Enhah'' or ⲫⲓⲟⲙ ⲛ̀ϣⲁⲣⲓ ''Phiom ǹšari''; ...from the sixth millennium BC onwards."
Yemen
Yemen (; ar, ٱلْيَمَن, al-Yaman), officially the Republic of Yemen,, ) is a country in Western Asia. It is situated on the southern end of the Arabian Peninsula, and borders Saudi Arabia to the Saudi Arabia–Yemen border, north and ...
and other parts of Northeast Africa. The authors indicate that:
"The most frequent haplotype in west coastal Yemen is 16126–16362, which is found not only in theEthiopian highlands The Ethiopian Highlands is a rugged mass of mountains in Ethiopia in Northeast Africa. It forms the largest continuous area of its elevation in the continent, with little of its surface falling below , while the summits reach heights of up to . ...but also in Somalia, lower Egypt and at especially high frequency in theNubia Nubia () (Nobiin: Nobīn, ) is a region along the Nile river encompassing the area between the first cataract of the Nile (just south of Aswan in southern Egypt) and the confluence of the Blue and White Niles (in Khartoum in central Sudan), or ...ns. The Tihama share some West Eurasian haplotypes with Africans, e.g. J and K with Ethiopians, Somali and Egyptians."Černý et al. (2008)
Regional differences in the distribution of the sub-Saharan, West Eurasian and South Asian mtDNA lineages in Yemen
Volume 136, Issue 2, pages 128–137, June 2008.
See also
*Ethnic groups in Ethiopia
This is a list of ethnic groups in Ethiopia that are officially recognized by the government. It is a list taken from the 2007 Ethiopian National Census:Government of Ethiopia
*
Directory of ethnic groups with information on population numbers and religion, maintained by Protestant churches and mission agencies
{{Authority control Society of Ethiopia
Regions of Ethiopia
Ethiopia is a federation subdivided into ethno-linguistically based regional states ( Amharic: plural: ክልሎች ''kililoch''; singular: ክልል ''kilil''; Oromo: singular: ''Naannoo''; plural: ''Naannolee'') and chartered cities (Amharic: ...
Footnotes
References
* E. Sylvia Pankhurst, ''The Ethiopian People. Their Rights and Progress''. Woodford Green, Essex: New Times & Ethiopia News 1946. *Edward Ullendorff
Edward Ullendorff (1920–2011) was a British scholar and historian. He was a prominent figure in Ethiopian Studies and also contributed work on the Semitic languages.
Biography
Born on 25 January 1920 in Zurich, Switzerland, Ullendorff was e ...
, ''The Ethiopians: an introduction to country and people''. London: Oxford University Press 1960, ²1965, ³1973 (), ⁴1990 (Wiesbaden: F. Steiner; ).
External links
Directory of ethnic groups with information on population numbers and religion, maintained by Protestant churches and mission agencies
{{Authority control Society of Ethiopia