Eratosthenes on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Eratosthenes of Cyrene (; grc-gre, бјҳПҒОұП„ОҝПғОёОӯОҪО·ПӮ ; вҖ“ ) was a Greek
 Eratosthenes went to Athens to further his studies. There he was taught
Eratosthenes went to Athens to further his studies. There he was taught
 The measurement of Earth's circumference is the most famous among the results obtained by Eratosthenes, who estimated that the meridian has a length of 252,000 stadia (39,060вҖ“40,320 km), with an error on the real value between вҲ’2.4% and +0.8% (assuming a value for the stadion between 155 and 160 metres). Eratosthenes described his arc measurement technique, in a book entitled ', which has not been preserved. However, a simplified version of the method has been preserved, as described by Cleomedes.
The simplified method works by considering two cities along the same
The measurement of Earth's circumference is the most famous among the results obtained by Eratosthenes, who estimated that the meridian has a length of 252,000 stadia (39,060вҖ“40,320 km), with an error on the real value between вҲ’2.4% and +0.8% (assuming a value for the stadion between 155 and 160 metres). Eratosthenes described his arc measurement technique, in a book entitled ', which has not been preserved. However, a simplified version of the method has been preserved, as described by Cleomedes.
The simplified method works by considering two cities along the same
 Eratosthenes now continued from his knowledge about the Earth. Using his discoveries and knowledge of its size and shape, he began to sketch it. In the Library of Alexandria he had access to various travel books, which contained various items of information and representations of the world that needed to be pieced together in some organized format. In his three-volume work ''Geography'' ( grc-gre, Geographika, script=Latn), he described and mapped his entire known world, even dividing the Earth into five climate zones: two freezing zones around the poles, two temperate zones, and a zone encompassing the equator and the tropics. This book is the first recorded instance of many terms still in use today, including the name of the discipline
Eratosthenes now continued from his knowledge about the Earth. Using his discoveries and knowledge of its size and shape, he began to sketch it. In the Library of Alexandria he had access to various travel books, which contained various items of information and representations of the world that needed to be pieced together in some organized format. In his three-volume work ''Geography'' ( grc-gre, Geographika, script=Latn), he described and mapped his entire known world, even dividing the Earth into five climate zones: two freezing zones around the poles, two temperate zones, and a zone encompassing the equator and the tropics. This book is the first recorded instance of many terms still in use today, including the name of the discipline
Book XV
Chapter 53). He states simply that Eratosthenes found the distance to the Sun to be "" (literally "of stadia myriads 400 and 80,000") and the distance to the Moon to be 780,000 stadia. The expression for the distance to the Sun has been translated either as 4,080,000 stadia (1903 translation by E. H. Gifford), or as 804,000,000 stadia (edition of Edouard des Places, dated 1974вҖ“1991). The meaning depends on whether Eusebius meant 400 myriad plus 80,000 or "400 and 80,000" myriad. With a stade of , 804,000,000 stadia is , approximately the distance from the Earth to the Sun. * Eratosthenes also calculated the Sun's diameter. According to Macrobious, Eratosthenes made the diameter of the Sun to be about 27 times that of the Earth. The actual figure is approximately 109 times. * During his time at the Library of Alexandria, Eratosthenes devised a calendar using his predictions about the ecliptic of the Earth. He calculated that there are 365 days in a year and that every fourth year there would be 366 days. * He was also very proud of his solution for Doubling the Cube. His motivation was that he wanted to produce catapults. Eratosthenes constructed a mechanical line drawing device to calculate the cube, called the mesolabio. He dedicated his solution to King Ptolemy, presenting a model in bronze with it a letter and an epigram. Archimedes was Eratosthenes' friend and he, too, worked on the war instrument with mathematics. Archimedes dedicated his book ''The Method'' to Eratosthenes, knowing his love for learning and mathematics.
 Eratosthenes proposed a simple
Eratosthenes proposed a simple
ГүratosthГЁne de CyrГЁne
, in R. Goulet (ed.), ''Dictionnaire des Philosophes Antiques'', vol. III, Paris, Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique, 2000, pp. 188вҖ“236. * Geus K. (2002)
''Eratosthenes von Kyrene. Studien zur hellenistischen Kultur- und Wissenschaftgeschichte''
MГјnchen: Verlag C.H. Beck. (MГјnchener BeitrГӨge zur Papyrusforschung und antiken Rechtsgeschichte. Bd. 92) X, 412 S. * * * Honigmann, E. (1929). ''Die sieben Klimata und die ПҖОҝО»ОөО№ПӮ ОөПҖО№ПғО·ОјОҝО№''. Eine Untersuchung zur Geschichte der Geographie und Astrologie in Altertum und Mittelalter. Heidelberg: Carl Winter's UniversitГӨtsbuchhandlung. 247 S. * * * * * * Marcotte, D. (1998). "La climatologie d'ГүratosthГЁne Г PosГ©idonios: genГЁse d'une science humaine". G. Argoud, J.Y. Guillaumin (eds.). ''Sciences exactes et sciences appliquГ©es Г Alexandrie (IIIe siГЁcle av J.C. вҖ“ Ier ap J.C.)''. Saint Etienne: Publications de l'UniversitГ© de Saint Etienne: 263вҖ“277. * McPhail, Cameron (2011)
''Reconstructing Eratosthenes' Map of the World: a Study in Source Analysis''. A Thesis Submitted for the Degree of Master of Arts at the University of Otago
Dunedin, New Zealand. * * * * * * Rosokoki, A. (1995), ''Die Erigone des Eratosthenes. Eine kommentierte Ausgabe der Fragmente'', Heidelberg: C. Winter-Verlag * Shcheglov, D.A. (2004/2006). "Ptolemy's System of Seven Climata and Eratosthenes' Geography". ''Geographia Antiqua'' 13: 21вҖ“37. * * * * Thalamas, A. (1921). ''La gГ©ographe d'ГүratosthГЁne''. Versailles. *
English translation of the primary source for Eratosthenes and the size of the Earth
at Roger Pearse.
Berlin, 1822 (PDF) (Latin/Greek), Reprinted Osnabruck 1968 (German)
* ttp://www.newadvent.org/cathen/01303a.htm New Advent Encyclopedia article on the Library of Alexandria
Eratosthenes' sieve in classic BASIC all-web based interactive programming environment
International pedagogical project
: project :fr:La main Г la pГўte.
Open source Physics Computer Model about Eratosthenes estimation of radius and circumference of Earth
Eratosthenes, video
{{Authority control 270s BC births 190s BC deaths 276 BC births 3rd-century BC Egyptian people 3rd-century BC Greek people 3rd-century BC poets Ancient Greek astronomers Ancient Greek geographers Ancient Greek inventors Ancient Greek music theorists Ancient Greek geometers Ancient Greek poets Cyrenean Greeks Deaths by starvation Geodesists Giftedness Librarians of Alexandria Number theorists 3rd-century BC geographers Ancient Greece
polymath
A polymath ( el, ПҖОҝО»П…ОјОұОёО®ПӮ, , "having learned much"; la, homo universalis, "universal human") is an individual whose knowledge spans a substantial number of subjects, known to draw on complex bodies of knowledge to solve specific pro ...
: a mathematician
A mathematician is someone who uses an extensive knowledge of mathematics in their work, typically to solve mathematical problems.
Mathematicians are concerned with numbers, data, quantity, mathematical structure, structure, space, Mathematica ...
, geographer
A geographer is a physical scientist, social scientist or humanist whose area of study is geography, the study of Earth's natural environment and human society, including how society and nature interacts. The Greek prefix "geo" means "earth" a ...
, poet
A poet is a person who studies and creates poetry. Poets may describe themselves as such or be described as such by others. A poet may simply be the creator ( thinker, songwriter, writer, or author) who creates (composes) poems ( oral or wr ...
, astronomer
An astronomer is a scientist in the field of astronomy who focuses their studies on a specific question or field outside the scope of Earth. They observe astronomical objects such as stars, planets, moons, comets and galaxies вҖ“ in either o ...
, and music theorist. He was a man of learning, becoming the chief librarian at the Library of Alexandria. His work is comparable to what is now known as the study of geography
Geography (from Greek: , ''geographia''. Combination of Greek words вҖҳGeoвҖҷ (The Earth) and вҖҳGraphienвҖҷ (to describe), literally "earth description") is a field of science devoted to the study of the lands, features, inhabitants, a ...
, and he introduced some of the terminology
Terminology is a group of specialized words and respective meanings in a particular field, and also the study of such terms and their use; the latter meaning is also known as terminology science. A ''term'' is a word, compound word, or multi-wo ...
still used today.
He is best known for being the first person known to calculate the circumference of the Earth, which he did by using the extensive survey results he could access in his role at the Library; his calculation was remarkably accurate. He was also the first to calculate Earth's axial tilt
In astronomy, axial tilt, also known as obliquity, is the angle between an object's rotational axis and its orbital axis, which is the line perpendicular to its orbital plane; equivalently, it is the angle between its equatorial plane and orbi ...
, which has also proved to have remarkable accuracy. He created the first global projection of the world, incorporating parallels and meridians based on the available geographic knowledge of his era.
Eratosthenes was the founder of scientific chronology
Chronology (from Latin ''chronologia'', from Ancient Greek , ''chrГіnos'', "time"; and , '' -logia'') is the science of arranging events in their order of occurrence in time. Consider, for example, the use of a timeline or sequence of events. ...
; he used Egyptian and Persian records to estimate the dates of the main events of the mythical Trojan War
In Greek mythology, the Trojan War was waged against the city of Troy by the Achaeans (Greeks) after Paris of Troy took Helen from her husband Menelaus, king of Sparta. The war is one of the most important events in Greek mythology and ha ...
, dating the Sack of Troy
Troy ( el, ОӨПҒОҝОҜОұ and Latin: Troia, Hittite: р’Ӣ«р’Ҡ’р’„ҝр’Ҡӯ ''TruwiЕЎa'') or Ilion ( el, ОҠО»О№ОҝОҪ and Latin: Ilium, Hittite: р’ғҫр’Ү»р’Ҡӯ ''WiluЕЎa'') was an ancient city located at Hisarlik in present-day Turkey, south-west of ГҮan ...
to 1183 BC. In number theory
Number theory (or arithmetic or higher arithmetic in older usage) is a branch of pure mathematics devoted primarily to the study of the integers and integer-valued functions. German mathematician Carl Friedrich Gauss (1777вҖ“1855) said, "Math ...
, he introduced the sieve of Eratosthenes, an efficient method of identifying prime number
A prime number (or a prime) is a natural number greater than 1 that is not a product of two smaller natural numbers. A natural number greater than 1 that is not prime is called a composite number. For example, 5 is prime because the only way ...
s.
He was a figure of influence in many fields who yearned to understand the complexities of the entire world. His devotees nicknamed him ''Pentathlos'' after the Olympians who were well rounded competitors, for he had proven himself to be knowledgeable in every area of learning. Yet, according to an entry in the Suda (a 10th-century encyclopedia), some critics scorned him, calling him ''Beta'' (the second letter of the Greek alphabet) because he always came in second in all his endeavours.
Life
The son of Aglaos, Eratosthenes was born in 276 BC in Cyrene. Now part of modern-dayLibya
Libya (; ar, Щ„ЩҠШЁЩҠШ§, LД«biyДҒ), officially the State of Libya ( ar, ШҜЩҲЩ„Ш© Щ„ЩҠШЁЩҠШ§, Dawlat LД«biyДҒ), is a country in the Maghreb region in North Africa. It is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to the north, Egypt to the east, Su ...
, Cyrene had been founded by Greeks centuries earlier and became the capital of Pentapolis (North Africa), a country of five cities: Cyrene, Arsinoe Arsinoe grc, бјҲПҒПғО№ОҪПҢО·, ArsinoГ«, pronounced Arsinoi in modern Greek, may refer to:
People
* Arsinoe of Macedon, mother of Ptolemy I Soter
* Apama II or Arsinoe (c. 292 BCвҖ“after 249 BC), wife of Magas of Cyrene and mother of Berenice II
...
, Berenice, Ptolemias, and Apollonia. Alexander the Great
Alexander III of Macedon ( grc, бјҲО»ОӯОҫОұОҪОҙПҒОҝПӮ, Alexandros; 20/21 July 356 BC вҖ“ 10/11 June 323 BC), commonly known as Alexander the Great, was a king of the ancient Greek kingdom of Macedon. He succeeded his father Philip II to ...
conquered Cyrene in 332 BC, and following his death in 323 BC, its rule was given to one of his generals, Ptolemy I Soter
Ptolemy I Soter (; gr, О П„ОҝО»ОөОјОұбҝ–ОҝПӮ ОЈПүП„О®ПҒ, ''PtolemaГ®os SЕҚtбё—r'' "Ptolemy the Savior"; c. 367 BC вҖ“ January 282 BC) was a Macedonian Greek general, historian and companion of Alexander the Great from the Kingdom of Macedon ...
, the founder of the Ptolemaic Kingdom. Under Ptolemaic rule the economy prospered, based largely on the export of horses and silphium, a plant used for rich seasoning and medicine. Cyrene became a place of cultivation, where knowledge blossomed. Like any young Greek at the time, Eratosthenes would have studied in the local gymnasium, where he would have learned physical skills and social discourse as well as reading, writing, arithmetic, poetry, and music.
 Eratosthenes went to Athens to further his studies. There he was taught
Eratosthenes went to Athens to further his studies. There he was taught Stoicism
Stoicism is a school of Hellenistic philosophy founded by Zeno of Citium in Athens in the early 3rd century BCE. It is a philosophy of personal virtue ethics informed by its system of logic and its views on the natural world, asserting that ...
by its founder, Zeno of Citium, in philosophical lectures on living a virtuous life. He then studied under Aristo of Chios, who led a more cynical school of philosophy. He also studied under the head of the Platonic Academy
The Academy (Ancient Greek: бјҲОәОұОҙО·ОјОҜОұ) was founded by Plato in c. 387 BC in Classical Athens, Athens. Aristotle studied there for twenty years (367вҖ“347 BC) before founding his own school, the Lyceum (classical), Lyceum. The Academy ...
, who was Arcesilaus of Pitane
Arcesilaus (; grc-gre, бјҲПҒОәОөПғОҜО»ОұОҝПӮ; 316/5вҖ“241/0 BC) was a Greek Hellenistic philosopher. He was the founder of Academic Skepticism and what is variously called the Second or Middle or New Academy вҖ“ the phase of the Platonic Academ ...
. His interest in Plato
Plato ( ; grc-gre, О О»О¬П„ПүОҪ ; 428/427 or 424/423 вҖ“ 348/347 BC) was a Greek philosopher born in Athens during the Classical period in Ancient Greece. He founded the Platonist school of thought and the Academy, the first institutio ...
led him to write his very first work at a scholarly level, ''Platonikos'', inquiring into the mathematical foundation of Plato's philosophies. Eratosthenes was a man of many perspectives and investigated the art of poetry
"Ars Poetica", or "The Art of Poetry", is a poem written by Horace c. 19 BC, in which he advises poets on the art of writing poetry and drama. The ''Ars Poetica'' has "exercised a great influence in later ages on European literature, notably on F ...
under Callimachus
Callimachus (; ) was an ancient Greek poet, scholar and librarian who was active in Alexandria during the 3rd century BC. A representative of Ancient Greek literature of the Hellenistic period, he wrote over 800 literary works in a wide variet ...
. He wrote poems: one in hexameters called ''Hermes'', illustrating the god's life history; and another in elegiacs, called ''Erigone'', describing the suicide of the Athenian maiden Erigone (daughter of Icarius). He wrote ''Chronographies'', a text that scientifically depicted dates of importance, beginning with the Trojan War
In Greek mythology, the Trojan War was waged against the city of Troy by the Achaeans (Greeks) after Paris of Troy took Helen from her husband Menelaus, king of Sparta. The war is one of the most important events in Greek mythology and ha ...
. This work was highly esteemed for its accuracy. George Syncellus was later able to preserve from ''Chronographies'' a list of 38 kings of the Egyptian Thebes. Eratosthenes also wrote ''Olympic Victors'', a chronology of the winners of the Olympic Games
The modern Olympic Games or Olympics (french: link=no, Jeux olympiques) are the leading international sporting events featuring summer and winter sports competitions in which thousands of athletes from around the world participate in a multi ...
. It is not known when he wrote his works, but they highlighted his abilities.
These works and his great poetic abilities led the pharaoh Ptolemy III Euergetes to seek to place him as a librarian at the Library of Alexandria in the year 245 BC. Eratosthenes, then thirty years old, accepted Ptolemy's invitation and traveled to Alexandria, where he lived for the rest of his life. Within about five years he became Chief Librarian, a position that the poet Apollonius Rhodius
Apollonius of Rhodes ( grc, бјҲПҖОҝО»О»ПҺОҪО№ОҝПӮ бҝ¬ПҢОҙО№ОҝПӮ ''Apollṓnios RhГіdios''; la, Apollonius Rhodius; fl. first half of 3rd century BC) was an ancient Greek author, best known for the ''Argonautica'', an epic poem about Jason and t ...
had previously held. As head of the library Eratosthenes tutored the children of Ptolemy, including Ptolemy IV Philopator who became the fourth Ptolemaic pharaoh. He expanded the library's holdings: in Alexandria all books had to be surrendered for duplication. It was said that these were copied so accurately that it was impossible to tell if the library had returned the original or the copy.
He sought to maintain the reputation of the Library of Alexandria against competition from the Library of Pergamum. Eratosthenes created a whole section devoted to the examination of Homer, and acquired original works of great tragic dramas of Aeschylus
Aeschylus (, ; grc-gre, О‘бј°ПғПҮПҚО»ОҝПӮ ; c. 525/524 вҖ“ c. 456/455 BC) was an ancient Greek tragedian, and is often described as the father of tragedy. Academic knowledge of the genre begins with his work, and understanding of earlier Gree ...
, Sophocles and Euripides
Euripides (; grc, О•бҪҗПҒО№ПҖОҜОҙО·ПӮ, EurД«pГӯdД“s, ; ) was a tragedian of classical Athens. Along with Aeschylus and Sophocles, he is one of the three ancient Greek tragedians for whom any plays have survived in full. Some ancient scholars ...
.
Eratosthenes made several important contributions to mathematics and science
Science is a systematic endeavor that Scientific method, builds and organizes knowledge in the form of Testability, testable explanations and predictions about the universe.
Science may be as old as the human species, and some of the earli ...
, and was a friend of Archimedes
Archimedes of Syracuse (;; ) was a Greek mathematician, physicist, engineer, astronomer, and inventor from the ancient city of Syracuse in Sicily. Although few details of his life are known, he is regarded as one of the leading scienti ...
. Around 255 BC, he invented the armillary sphere. In ''On the Circular Motions of the Celestial Bodies'', Cleomedes credited him with having calculated the Earth's circumference around 240 BC, with a high precision.
Eratosthenes believed there was both good and bad in every nation and criticized Aristotle
Aristotle (; grc-gre, бјҲПҒО№ПғП„ОҝП„ОӯО»О·ПӮ ''AristotГ©lД“s'', ; 384вҖ“322 BC) was a Greek philosopher and polymath during the Classical Greece, Classical period in Ancient Greece. Taught by Plato, he was the founder of the Peripatet ...
for arguing that humanity was divided into Greeks and barbarians, as well as for arguing that the Greeks should keep themselves racially pure. As he aged, he contracted ophthalmia, becoming blind around 195 BC. Losing the ability to read and to observe nature plagued and depressed him, leading him to voluntarily starve himself to death. He died in 194 BC at 82 in Alexandria.
Scholarly career
Measurement of Earth's circumference
meridian
Meridian or a meridian line (from Latin ''meridies'' via Old French ''meridiane'', meaning вҖңmiddayвҖқ) may refer to
Science
* Meridian (astronomy), imaginary circle in a plane perpendicular to the planes of the celestial equator and horizon
* ...
and measuring both the distance between them and the difference in angles of the shadows cast by the sun on a vertical rod (a gnomon) in each city at noon on the summer solstice
A solstice is an event that occurs when the Sun appears to reach its most northerly or southerly excursion relative to the celestial equator on the celestial sphere. Two solstices occur annually, around June 21 and December 21. In many count ...
. The two cities used were Alexandria
Alexandria ( or ; ar, ЩұЩ„Щ’ШҘЩҗШіЩ’ЩғЩҺЩҶЩ’ШҜЩҺШұЩҗЩҠЩҺЩ‘Ш©ЩҸ ; grc-gre, О‘О»ОөОҫО¬ОҪОҙПҒОөО№Оұ, AlexГЎndria) is the second largest city in Egypt, and the largest city on the Mediterranean coast. Founded in by Alexander the Great, Alexandr ...
and Syene (modern Aswan
Aswan (, also ; ar, ШЈШіЩҲШ§ЩҶ, КҫAswДҒn ; cop, вІӨвІҹвІ©вІҒвІӣ ) is a city in Southern Egypt, and is the capital of the Aswan Governorate.
Aswan is a busy market and tourist centre located just north of the Aswan Dam on the east bank of ...
), and the distance between the cities was measured by professional bematists. A geometric calculation reveals that the circumference of the Earth is the distance between the two cities divided by the difference in shadow angles expressed as a fraction of one turn.
Geography
 Eratosthenes now continued from his knowledge about the Earth. Using his discoveries and knowledge of its size and shape, he began to sketch it. In the Library of Alexandria he had access to various travel books, which contained various items of information and representations of the world that needed to be pieced together in some organized format. In his three-volume work ''Geography'' ( grc-gre, Geographika, script=Latn), he described and mapped his entire known world, even dividing the Earth into five climate zones: two freezing zones around the poles, two temperate zones, and a zone encompassing the equator and the tropics. This book is the first recorded instance of many terms still in use today, including the name of the discipline
Eratosthenes now continued from his knowledge about the Earth. Using his discoveries and knowledge of its size and shape, he began to sketch it. In the Library of Alexandria he had access to various travel books, which contained various items of information and representations of the world that needed to be pieced together in some organized format. In his three-volume work ''Geography'' ( grc-gre, Geographika, script=Latn), he described and mapped his entire known world, even dividing the Earth into five climate zones: two freezing zones around the poles, two temperate zones, and a zone encompassing the equator and the tropics. This book is the first recorded instance of many terms still in use today, including the name of the discipline geography
Geography (from Greek: , ''geographia''. Combination of Greek words вҖҳGeoвҖҷ (The Earth) and вҖҳGraphienвҖҷ (to describe), literally "earth description") is a field of science devoted to the study of the lands, features, inhabitants, a ...
. He placed grids of overlapping lines over the surface of the Earth. He used parallels and meridians to link together every place in the world. It was now possible to estimate one's distance from remote locations with this network over the surface of the Earth. In the ''Geography'' the names of over 400 cities and their locations were shown, which had never been achieved before. However, his ''Geography'' has been lost to history, although fragments of the work can be pieced together from other great historians like Pliny, Polybius
Polybius (; grc-gre, О ОҝО»ПҚОІО№ОҝПӮ, ; ) was a Greek historian of the Hellenistic period. He is noted for his work , which covered the period of 264вҖ“146 BC and the Punic Wars in detail.
Polybius is important for his analysis of the mixed ...
, Strabo, and Marcianus
Marcian (; la, Marcianus, link=no; grc-gre, ОңОұПҒОәО№ОұОҪПҢПӮ, link=no ; 392 вҖ“ 27 January 457) was Roman emperor of the East from 450 to 457. Very little of his life before becoming emperor is known, other than that he was a (personal as ...
. While this work is the earliest we can trace certain ideas, words, and concepts in the historical record, earlier contributions may have been lost to history.
* The first book was something of an introduction and gave a review of his predecessors, recognizing their contributions that he compiled in the library. In this book Eratosthenes denounced Homer
Homer (; grc, бҪҚОјО·ПҒОҝПӮ , ''HГіmД“ros'') (born ) was a Greek poet who is credited as the author of the '' Iliad'' and the '' Odyssey'', two epic poems that are foundational works of ancient Greek literature. Homer is considered one of ...
as not providing any insight into what he now described as geography. His disapproval of Homer's topography angered many who believed the world depicted in the ''Odyssey'' to be legitimate. He also commented on the ideas of the nature and origin of the Earth: he thought of Earth as an immovable globe while its surface was changing. He hypothesized that at one time the Mediterranean
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa, and on th ...
had been a vast lake that covered the countries that surrounded it and that it only became connected to the ocean to the west when a passage opened up sometime in its history.
* The second book contains his calculation of the circumference of the Earth. This is where, according to Pliny, "The world was grasped." Here Eratosthenes described his famous story of the well in Syene, wherein at noon each summer solstice, the Sun's rays shone straight down into the city-center well. This book would now be considered a text on mathematical geography
Geomatics is defined in the ISO/TC 211 series of standards as the "academic discipline, discipline concerned with the collection, distribution, storage, analysis, processing, presentation of geographic data or geographic information". Under an ...
.
* His third book of the ''Geography'' contained political geography. He cited countries and used parallel lines to divide the map into sections, to give accurate descriptions of the realms. This was a breakthrough and can be considered the beginning of geography. For this, Eratosthenes was named the "Father of Modern Geography."
According to Strabo, Eratosthenes argued against the Greek- Barbarian dichotomy. He says Alexander ignored his advisers by his regard for all people with law and government. Strabo says that Eratosthenes was wrong to claim that Alexander had disregarded the counsel of his advisers. Strabo argues it was Alexander's interpretation of their "real intent" in recognizing that "in some people there prevail the law-abiding and the political instinct, and the qualities associated with education and powers of speech".Isaac, Benjamin. Invention of Racism in Classical Antiquity. Princeton University Press, 2013.
Achievements
Eratosthenes was described by theSuda Lexicon
The ''Suda'' or ''Souda'' (; grc-x-medieval, ОЈОҝбҝҰОҙОұ, SoГ»da; la, Suidae Lexicon) is a large 10th-century Byzantine encyclopedia of the ancient Mediterranean world, formerly attributed to an author called Soudas (ОЈОҝПҚОҙОұПӮ) or Souidas ...
as a О ОӯОҪП„ОұОёО»ОҝПӮ (Pentathlos) which can be translated as "All-Rounder", for he was skilled in a variety of things: He was a true polymath. He was nicknamed Beta because he was great at many things and tried to get his hands on every bit of information but never achieved the highest rank in anything; Strabo accounts Eratosthenes as a mathematician among geographers and a geographer among mathematicians.
* Eusebius of Caesarea in his '' Preparatio Evangelica'' includes a brief chapter of three sentences on celestial distancesBook XV
Chapter 53). He states simply that Eratosthenes found the distance to the Sun to be "" (literally "of stadia myriads 400 and 80,000") and the distance to the Moon to be 780,000 stadia. The expression for the distance to the Sun has been translated either as 4,080,000 stadia (1903 translation by E. H. Gifford), or as 804,000,000 stadia (edition of Edouard des Places, dated 1974вҖ“1991). The meaning depends on whether Eusebius meant 400 myriad plus 80,000 or "400 and 80,000" myriad. With a stade of , 804,000,000 stadia is , approximately the distance from the Earth to the Sun. * Eratosthenes also calculated the Sun's diameter. According to Macrobious, Eratosthenes made the diameter of the Sun to be about 27 times that of the Earth. The actual figure is approximately 109 times. * During his time at the Library of Alexandria, Eratosthenes devised a calendar using his predictions about the ecliptic of the Earth. He calculated that there are 365 days in a year and that every fourth year there would be 366 days. * He was also very proud of his solution for Doubling the Cube. His motivation was that he wanted to produce catapults. Eratosthenes constructed a mechanical line drawing device to calculate the cube, called the mesolabio. He dedicated his solution to King Ptolemy, presenting a model in bronze with it a letter and an epigram. Archimedes was Eratosthenes' friend and he, too, worked on the war instrument with mathematics. Archimedes dedicated his book ''The Method'' to Eratosthenes, knowing his love for learning and mathematics.
Number theory
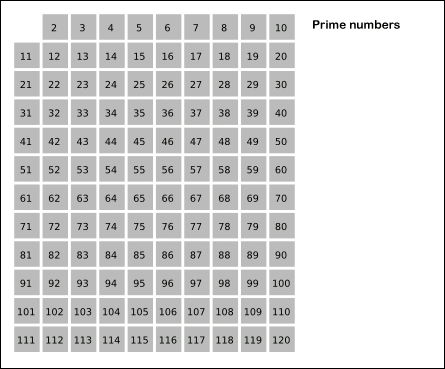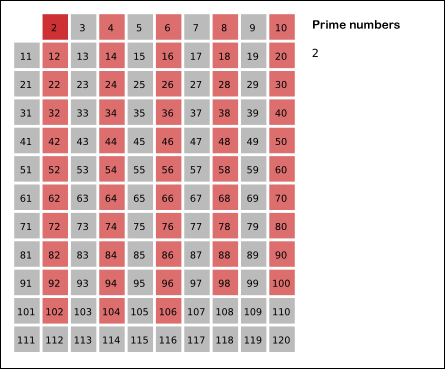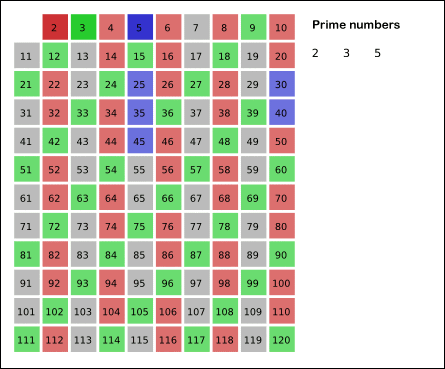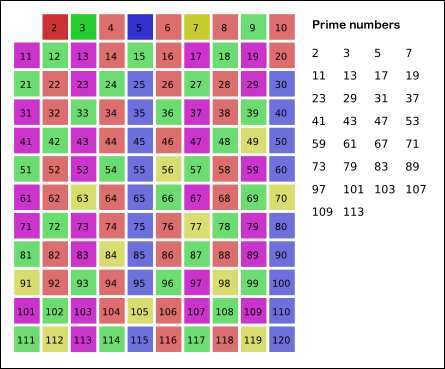
 Eratosthenes proposed a simple
Eratosthenes proposed a simple algorithm
In mathematics and computer science, an algorithm () is a finite sequence of rigorous instructions, typically used to solve a class of specific problems or to perform a computation. Algorithms are used as specifications for performing ...
for finding prime numbers. This algorithm is known in mathematics as the Sieve of Eratosthenes.
In mathematics, the sieve of Eratosthenes (Greek: ОәПҢПғОәО№ОҪОҝОҪ бјҳПҒОұП„ОҝПғОёОӯОҪОҝП…ПӮ), one of a number of prime number sieve In computational number theory, a variety of algorithms make it possible to generate prime numbers efficiently. These are used in various applications, for example hashing, public-key cryptography, and search of prime factors in large numbers.
Fo ...
s, is a simple, ancient algorithm for finding all prime numbers up to any given limit. It does so by iteratively marking as composite, ''i.e.'', not prime, the multiples of each prime, starting with the multiples of 2. The multiples of a given prime are generated starting from that prime, as a sequence of numbers with the same difference, equal to that prime, between consecutive numbers. This is the sieve's key distinction from using trial division to sequentially test each candidate number for divisibility by each prime.
Works
Eratosthenes was one of the most pre-eminent scholarly figures of his time, and produced works covering a vast area of knowledge before and during his time at the Library. He wrote on many topicsgeography, mathematics, philosophy, chronology, literary criticism, grammar, poetry, and even old comedies. Unfortunately, there are no documents left of his work after the destruction of the Library of Alexandria.Titles
* ''Platonikos'' * ''Hermes'' * ''Erigone'' * ''Chronographies'' * ''Olympic Victors'' * ''О ОөПҒбҪ¶ П„бҝҶПӮ бјҖОҪОұОјОөП„ПҒО®ПғОөПүПӮ П„бҝҶПӮ ОібҝҶПӮ'' (''On the Measurement of the Earth'') (lost, summarized by Cleomedes) * ''Р“ОөПүОіПҒОұП•О№ОәО¬'' (''Geographika'') (lost, criticized by Strabo) * ''Arsinoe'' (a memoir of queenArsinoe Arsinoe grc, бјҲПҒПғО№ОҪПҢО·, ArsinoГ«, pronounced Arsinoi in modern Greek, may refer to:
People
* Arsinoe of Macedon, mother of Ptolemy I Soter
* Apama II or Arsinoe (c. 292 BCвҖ“after 249 BC), wife of Magas of Cyrene and mother of Berenice II
...
; lost; quoted by Athenaeus in the '' Deipnosophistae'')
* ''Ariston'' (concerning Aristo of Chios' addiction to luxury); lost; quoted by Athenaeus in the '' Deipnosophistae'')
* The '' Catasterismi'' (''Katasterismoi''), a lost collection of Hellenistic
In Classical antiquity, the Hellenistic period covers the time in Mediterranean history after Classical Greece, between the death of Alexander the Great in 323 BC and the emergence of the Roman Empire, as signified by the Battle of Actium i ...
myths about the constellations, was attributed to Eratosthenes.
See also
* Aristarchus of Samos (), a Greek mathematician who calculated the distance from the Earth to the Sun. * Eratosthenes (crater) on theMoon
The Moon is Earth's only natural satellite. It is the fifth largest satellite in the Solar System and the largest and most massive relative to its parent planet, with a diameter about one-quarter that of Earth (comparable to the width ...
.
* Eratosthenian period in the lunar geologic timescale.
* Eratosthenes Seamount in the eastern Mediterranean Sea.
* Eratosthenes Point
Eratosthenes Point ( bg, РҪРҫСҒ Р•СҖР°СӮРҫСҒСӮРөРҪ, nos Eratosthenes, ) is the ice-covered, rock-tipped northwest entrance point to Digges Cove on the north coast of Elephant Island in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica situated just west o ...
in Antarctica
Antarctica () is Earth's southernmost and least-populated continent. Situated almost entirely south of the Antarctic Circle and surrounded by the Southern Ocean, it contains the geographic South Pole. Antarctica is the fifth-largest co ...
.
* Hipparchus (), a Greek mathematician who measured
Measurement is the quantification of attributes of an object or event, which can be used to compare with other objects or events.
In other words, measurement is a process of determining how large or small a physical quantity is as compared t ...
the radii of the Sun and the Moon as well as their distances from the Earth.
* Posidonius (), a Greek astronomer and mathematician who calculated the circumference of the Earth.
Notes
References
Further reading
* Aujac, G. (2001). ''EratosthГЁne de CyrГЁne, le pionnier de la gГ©ographie''. Paris: Гүdition du CTHS. 224 p. * * * * * * * * * * Fuentes GonzГЎlez, P. P.,ГүratosthГЁne de CyrГЁne
, in R. Goulet (ed.), ''Dictionnaire des Philosophes Antiques'', vol. III, Paris, Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique, 2000, pp. 188вҖ“236. * Geus K. (2002)
''Eratosthenes von Kyrene. Studien zur hellenistischen Kultur- und Wissenschaftgeschichte''
MГјnchen: Verlag C.H. Beck. (MГјnchener BeitrГӨge zur Papyrusforschung und antiken Rechtsgeschichte. Bd. 92) X, 412 S. * * * Honigmann, E. (1929). ''Die sieben Klimata und die ПҖОҝО»ОөО№ПӮ ОөПҖО№ПғО·ОјОҝО№''. Eine Untersuchung zur Geschichte der Geographie und Astrologie in Altertum und Mittelalter. Heidelberg: Carl Winter's UniversitГӨtsbuchhandlung. 247 S. * * * * * * Marcotte, D. (1998). "La climatologie d'ГүratosthГЁne Г PosГ©idonios: genГЁse d'une science humaine". G. Argoud, J.Y. Guillaumin (eds.). ''Sciences exactes et sciences appliquГ©es Г Alexandrie (IIIe siГЁcle av J.C. вҖ“ Ier ap J.C.)''. Saint Etienne: Publications de l'UniversitГ© de Saint Etienne: 263вҖ“277. * McPhail, Cameron (2011)
''Reconstructing Eratosthenes' Map of the World: a Study in Source Analysis''. A Thesis Submitted for the Degree of Master of Arts at the University of Otago
Dunedin, New Zealand. * * * * * * Rosokoki, A. (1995), ''Die Erigone des Eratosthenes. Eine kommentierte Ausgabe der Fragmente'', Heidelberg: C. Winter-Verlag * Shcheglov, D.A. (2004/2006). "Ptolemy's System of Seven Climata and Eratosthenes' Geography". ''Geographia Antiqua'' 13: 21вҖ“37. * * * * Thalamas, A. (1921). ''La gГ©ographe d'ГүratosthГЁne''. Versailles. *
External links
English translation of the primary source for Eratosthenes and the size of the Earth
at Roger Pearse.
Berlin, 1822 (PDF) (Latin/Greek), Reprinted Osnabruck 1968 (German)
* ttp://www.newadvent.org/cathen/01303a.htm New Advent Encyclopedia article on the Library of Alexandria
Eratosthenes' sieve in classic BASIC all-web based interactive programming environment
International pedagogical project
: project :fr:La main Г la pГўte.
Open source Physics Computer Model about Eratosthenes estimation of radius and circumference of Earth
Eratosthenes, video
{{Authority control 270s BC births 190s BC deaths 276 BC births 3rd-century BC Egyptian people 3rd-century BC Greek people 3rd-century BC poets Ancient Greek astronomers Ancient Greek geographers Ancient Greek inventors Ancient Greek music theorists Ancient Greek geometers Ancient Greek poets Cyrenean Greeks Deaths by starvation Geodesists Giftedness Librarians of Alexandria Number theorists 3rd-century BC geographers Ancient Greece