Er (cuneiform) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

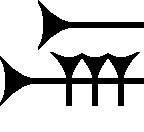 The
The
 For the mid 14th century BC
For the mid 14th century BC

 The
The cuneiform
Cuneiform is a logo-syllabic script that was used to write several languages of the Ancient Middle East. The script was in active use from the early Bronze Age until the beginning of the Common Era. It is named for the characteristic wedge-sha ...
ir (more common usage), or er sign is a sign used in the Epic of Gilgamesh
The ''Epic of Gilgamesh'' () is an epic poetry, epic poem from ancient Mesopotamia, and is regarded as the earliest surviving notable literature and the second oldest religious text, after the Pyramid Texts. The literary history of Gilgamesh ...
, and the Amarna letters
The Amarna letters (; sometimes referred to as the Amarna correspondence or Amarna tablets, and cited with the abbreviation EA, for "El Amarna") are an archive, written on clay tablets, primarily consisting of diplomatic correspondence between t ...
. It is in a small group that have smaller, 3-verticals, as well as 2- and 1-vertical strokes, sitting on a lower horizontal cuneiform stroke.
The sign is similar to the '' sa (cuneiform)'' sign, but sa's upper horizontal stroke is shorter than the lower anchored horizontal stroke. In the Amarna letters, it can also be confused with specific usages of ú-(the alphabetic u (by usage), Ú-1st prime– Ù-2nd prime is a complex, two-part large cuneiform sign, ="and", "but", or other conjunction meanings), as in Amarna letter EA 362
Amarna letter EA 362, titled: ''"A Commissioner Murdered,"'' is a finely-inscribed clay tablet letter from Rib-Haddi, the mayor/'man' of the city of Byblos, (''Gubla'' of the letters). Byblos, being a large coastal seaport Mediterranean city, ...
, (Biridiya
Biridiya was the ruler of Megiddo in the 14th century BC. Biridiya authored five of the Amarna letters correspondence.
The name 'Biridiya' is also mentioned in the corpus from the city of 'Kumidu' (letter KL 72:600), the Kamid al lawz. However, ...
to Pharaoh).
Amarna letters and Epic of Gilgamesh usage
The twelve tablet (I-XII)Epic of Gilgamesh
The ''Epic of Gilgamesh'' () is an epic poetry, epic poem from ancient Mesopotamia, and is regarded as the earliest surviving notable literature and the second oldest religious text, after the Pyramid Texts. The literary history of Gilgamesh ...
uses the er, and ir signs, 22 and 72 times. In the Epic, there are no other uses for the sign.
 For the mid 14th century BC
For the mid 14th century BC Amarna letters
The Amarna letters (; sometimes referred to as the Amarna correspondence or Amarna tablets, and cited with the abbreviation EA, for "El Amarna") are an archive, written on clay tablets, primarily consisting of diplomatic correspondence between t ...
, letter EA 365 authored by Biridiya
Biridiya was the ruler of Megiddo in the 14th century BC. Biridiya authored five of the Amarna letters correspondence.
The name 'Biridiya' is also mentioned in the corpus from the city of 'Kumidu' (letter KL 72:600), the Kamid al lawz. However, ...
, it is used for "er". For example, on the reverse of EA 365, subject of corvee labor,
"harvesting"-(line 20), lines 15 and following translate as follows: The verb "cultivating" (harvesting) is from "erēšu", which is from "harāšu", Ugaratic ḥrț.Rainey, 1970. ''El Amarna Tablets, 359-379,'' Glossary:Vocabulary, pp. 55-87, p. 24.
:15. "But see! (But Look! (a major segue
A segue (; ) is a smooth transition from one topic or section to the next. The term is derived from Italian ''segue'', which literally means "follows".
In music
In music, ''segue'' is a direction to the performer. It means ''continue (the next ...
)) 16. The city rulers 17. who are with me 18. are not doing 19. as I. They are not 20. cultivating ("harvesting") 21. in (determinative
A determinative, also known as a taxogram or semagram, is an ideogram used to mark semantic categories of words in logographic scripts which helps to disambiguate interpretation. They have no direct counterpart in spoken language, though they may ...
URU, city-state
A city-state is an independent sovereign city which serves as the center of political, economic, and cultural life over its contiguous territory. They have existed in many parts of the world since the dawn of history, including cities such as ...
)—Shunama 22 and ...."
:... (They are not) 20. te-er-ri-šu-na, 22. and ...."
References
* Parpola, 1971. ''The Standard BabylonianEpic of Gilgamesh
The ''Epic of Gilgamesh'' () is an epic poetry, epic poem from ancient Mesopotamia, and is regarded as the earliest surviving notable literature and the second oldest religious text, after the Pyramid Texts. The literary history of Gilgamesh ...
'', Parpola, Simo, Neo-Assyrian Text Corpus Project The Neo-Assyrian Text Corpus Project is an international scholarly project aimed at collecting and publishing ancient Assyrian texts and studies based on them. Its headquarters are in Helsinki in Finland.
State Archives of Assyria
State Archives ...
, c 1997, Tablet I thru Tablet XII, Index of Names, Sign List, and Glossary-(pp. 119–145), 165 pages.
*Rainey Rainey is a name of British-Irish origin.
People with the surname
* Bobby Rainey (born 1987), American National Football League player
* Chuck Rainey (born 1940), American bassist
* David "Puck" Rainey (born 1968), American reality TV personalit ...
, 1970. ''El Amarna Tablets, 359-379,'' Anson F. Rainey, (AOAT 8, ''Alter Orient Altes Testament 8'', Kevelaer and Neukirchen -Vluyen), 1970, 107 pages.
Cuneiform signs