Epstein Syndrome on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Epstein syndrome is a rare
 Epstein Syndrome is caused by a mutation in MYH9 gene. This mutation is
Epstein Syndrome is caused by a mutation in MYH9 gene. This mutation is
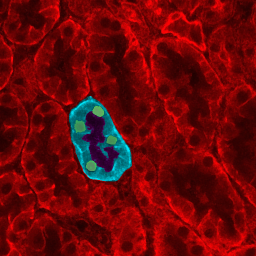 The main symptom in Epstein Syndrome is
The main symptom in Epstein Syndrome is
 As a result of nephritis, a healthy blood pressure becomes difficult to maintain and hence medication including vasopressin may be prescribed to maintain blood pressure. Severe nephritis may mean
As a result of nephritis, a healthy blood pressure becomes difficult to maintain and hence medication including vasopressin may be prescribed to maintain blood pressure. Severe nephritis may mean
genetic disease
A genetic disorder is a health problem caused by one or more abnormalities in the genome. It can be caused by a mutation in a single gene (monogenic) or multiple genes (polygenic) or by a chromosomal abnormality. Although polygenic disorders ...
characterized by a mutation
In biology, a mutation is an alteration in the nucleic acid sequence of the genome of an organism, virus, or extrachromosomal DNA. Viral genomes contain either DNA or RNA. Mutations result from errors during DNA replication, DNA or viral repl ...
in the MYH9 gene in nonmuscle myosin. This disease affects the patient's renal system
The urinary system, also known as the urinary tract or renal system, consists of the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and the urethra. The purpose of the urinary system is to eliminate waste from the body, regulate blood volume and blood pressure, con ...
and can result in kidney failure
Kidney failure, also known as end-stage kidney disease, is a medical condition in which the kidneys can no longer adequately filter waste products from the blood, functioning at less than 15% of normal levels. Kidney failure is classified as eit ...
. Epstein Syndrome was first discovered in 1972 when two families had similar symptoms to Alport syndrome
Alport syndrome is a genetic disorder affecting around 1 in 5,000-10,000 children, characterized by glomerulonephritis, end-stage kidney disease, and hearing loss. Alport syndrome can also affect the eyes, though the changes do not usually affect ...
. Epstein syndrome and other Alport-like disorders were seen to be caused by mutations in the MYH9 (myosin heavy chain 9) gene, however, Epstein syndrome differs as it was more specifically linked to a mutation on the R702 codon on the MYH9 gene. Diseases with mutations on the MYH9 gene also include May–Hegglin anomaly, Sebastian syndrome and Fechtner syndrome
Fechtner syndrome is a variant of Alport syndrome characterized by leukocyte inclusions, macrothrombocytopenia,cause by mutation in the MYH9 gene on chromosome 22q11 AbstractThis study reports a family comprising four generations in whom nephriti ...
.
Signs and symptoms
Initial symptoms are often described as bleeding tendency andthrombocytopenia
Thrombocytopenia is a condition characterized by abnormally low levels of platelets, also known as thrombocytes, in the blood. It is the most common coagulation disorder among intensive care patients and is seen in a fifth of medical patients a ...
. Bleeding tendency may be observed in epistaxis
A nosebleed, also known as epistaxis, is bleeding from the nose. Blood can flow down into the stomach, and cause nausea and vomiting. In more severe cases, blood may come out of both nostrils. Rarely, bleeding may be so significant that low bl ...
and purpura
Purpura () is a condition of red or purple discolored spots on the skin that do not blanch on applying pressure. The spots are caused by bleeding underneath the skin secondary to platelet disorders, vascular disorders, coagulation disorders, ...
. Other symptoms may include macrothrombocytopenia, proteinuria
Proteinuria is the presence of excess proteins in the urine. In healthy persons, urine contains very little protein; an excess is suggestive of illness. Excess protein in the urine often causes the urine to become foamy (although this symptom ma ...
, nephropathy, sensorineural hearing loss, low platelet count, oral lesions and cataract
A cataract is a cloudy area in the lens of the eye that leads to a decrease in vision. Cataracts often develop slowly and can affect one or both eyes. Symptoms may include faded colors, blurry or double vision, halos around light, trouble ...
s. The most common symptoms include macrothrombocytopenia, mild sensorineural hearing loss and nephritis. The symptoms and the severity of these symptoms vary between patients where most patients experience nephritis in childhood and then progress to kidney failure
Kidney failure, also known as end-stage kidney disease, is a medical condition in which the kidneys can no longer adequately filter waste products from the blood, functioning at less than 15% of normal levels. Kidney failure is classified as eit ...
in adolescence. In macrothrombocytopenia platelet
Platelets, also called thrombocytes (from Greek θρόμβος, "clot" and κύτος, "cell"), are a component of blood whose function (along with the coagulation factors) is to react to bleeding from blood vessel injury by clumping, thereby i ...
sizes can reach to approximately 6.6 um compared to a normal platelet size of 2.5 um where 30% platelets can reach the size of an erythrocytes. This large platelet size can be compared with MYH9 disorders where platelet size can vary between 4.5 um and the 6.6 um that is found in Epstein Syndrome with mutations on the R207 codon.
Causes
 Epstein Syndrome is caused by a mutation in MYH9 gene. This mutation is
Epstein Syndrome is caused by a mutation in MYH9 gene. This mutation is autosomal dominant
In genetics, dominance is the phenomenon of one variant (allele) of a gene on a chromosome masking or overriding the effect of a different variant of the same gene on the other copy of the chromosome. The first variant is termed dominant and t ...
and is thereby inherited if one or both parents carry the mutated gene. However, there have been cases where Epstein Syndrome has been sporadic or non-congenital. Mutations are found in the nonmuscle myosin heavy chain IIA and is associated with chromosome 22
Chromosome 22 is one of the 23 pairs of chromosomes in human cells. Humans normally have two copies of chromosome 22 in each cell. Chromosome 22 is the second smallest human chromosome, spanning about 49 million DNA base pairs and representing b ...
. The MYH9 gene encodes for tissues including platelets, cochlea, renal cells, neutrophils and eyes.
Pathophysiology
 The main symptom in Epstein Syndrome is
The main symptom in Epstein Syndrome is thrombocytopaenia
Thrombocytopenia is a condition characterized by abnormally low levels of platelets, also known as thrombocytes, in the blood. It is the most common coagulation disorder among intensive care patients and is seen in a fifth of medical patients an ...
. Thrombocytopaenia is generally inherited as an autosomal dominant gene and platelets are found to aggregate with either epinephrine or collagen. Platelets assist in blood clotting and coagulate when there are damages blood vessel
The blood vessels are the components of the circulatory system that transport blood throughout the human body. These vessels transport blood cells, nutrients, and oxygen to the tissues of the body. They also take waste and carbon dioxide away ...
s. This coagulation attempts to cease bleeding. Thrombocytopaenia means there is low platelet volume in the blood. This means there are less platelets to coagulate in presence of a damaged blood vessel, which can result in bleeding problems. The platelets are large (macrothrombocytopenia) and often consist of neutrophil
Neutrophils (also known as neutrocytes or heterophils) are the most abundant type of granulocytes and make up 40% to 70% of all white blood cells in humans. They form an essential part of the innate immune system, with their functions varying ...
inclusions. The large size of platelets may be due to excess microtubule coils and tublin. This large size of the platelets also affects their ability to bind to each other to seal damaged blood vessels and stop bleeding
Bleeding, hemorrhage, haemorrhage or blood loss, is blood escaping from the circulatory system from damaged blood vessels. Bleeding can occur internally, or externally either through a natural opening such as the mouth, nose, ear, urethra, vag ...
.
Nephritis involves the inflammation of the kidney
The kidneys are two reddish-brown bean-shaped organs found in vertebrates. They are located on the left and right in the retroperitoneal space, and in adult humans are about in length. They receive blood from the paired renal arteries; blood ...
and this inflammation
Inflammation (from la, inflammatio) is part of the complex biological response of body tissues to harmful stimuli, such as pathogens, damaged cells, or irritants, and is a protective response involving immune cells, blood vessels, and molec ...
results in a reduced ability to filter blood and remove nitrogenous waste
Metabolic wastes or excrements are substances left over from metabolic processes (such as cellular respiration) which cannot be used by the organism (they are surplus or toxic), and must therefore be excreted. This includes nitrogen compounds, ...
s. This excessive accumulation of wastes will result in a continued build-up of wastes including urea which interferes with metabolism.
One of the kidney's functions include osmoregulation
Osmoregulation is the active regulation of the osmotic pressure of an organism's body fluids, detected by osmoreceptors, to maintain the homeostasis of the organism's water content; that is, it maintains the fluid balance and the concentration o ...
which involves the regulation of osmotic pressure in the blood by regulating the water content in blood pressure. Through osmosis
Osmosis (, ) is the spontaneous net movement or diffusion of solvent molecules through a selectively-permeable membrane from a region of high water potential (region of lower solute concentration) to a region of low water potential (region o ...
(water movement from a low solute concentration to an area of high solute concentration) water is reabsorbed back into the blood from nephron
The nephron is the minute or microscopic structural and functional unit of the kidney. It is composed of a renal corpuscle and a renal tubule. The renal corpuscle consists of a tuft of capillaries called a glomerulus and a cup-shaped structure ...
tubules in the kidney. This maintenance of water concentration in the blood is essential for maintaining blood pressure and is affected in nephritis.
Diagnosis
The cardinal symptom in Epstein syndrome is thrombocytopaenia with giant platelets (macrothrombocytopenia). Aperipheral blood smear
A blood smear, peripheral blood smear or blood film is a thin layer of blood smeared on a glass microscope slide and then stained in such a way as to allow the various blood cells to be examined microscopically. Blood smears are examined in the ...
is taken from the patient and a light microscope
The optical microscope, also referred to as a light microscope, is a type of microscope that commonly uses visible light and a system of lenses to generate magnified images of small objects. Optical microscopes are the oldest design of microsco ...
is used to these identify giant platelets. Leukocyte inclusions are also examined for, because approximately 41.1% of R207 mutations have leukocyte inclusions. These are often abnormal neutrophil
Neutrophils (also known as neutrocytes or heterophils) are the most abundant type of granulocytes and make up 40% to 70% of all white blood cells in humans. They form an essential part of the innate immune system, with their functions varying ...
s with a small size of approximately less than 0.7 um and have an abnormal
location on the non-muscle myosin heavy chain IIA (NMMHC-II). These inclusion bodies have RNA
Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a polymeric molecule essential in various biological roles in coding, decoding, regulation and expression of genes. RNA and deoxyribonucleic acid ( DNA) are nucleic acids. Along with lipids, proteins, and carbohydra ...
and no DNA. RNA in these inclusion bodies can be located in immunofluorescence analysis with the anti nonmuscle heavy chain IIA antibody.
Hematology
Hematology ( always spelled haematology in British English) is the branch of medicine concerned with the study of the cause, prognosis, treatment, and prevention of diseases related to blood. It involves treating diseases that affect the produc ...
analysers or a hemocytometer
The hemocytometer (or haemocytometer) is a counting-chamber device originally designed and usually used for counting blood cells.
The hemocytometer was invented by Louis-Charles Malassez and consists of a thick glass microscope slide with a ...
can be used to determine the amount of platelets. A sample of blood
Blood is a body fluid in the circulatory system of humans and other vertebrates that delivers necessary substances such as nutrients and oxygen to the cells, and transports metabolic waste products away from those same cells. Blood in the cir ...
is drawn from a patient's arm. A small amount of platelets in blood smears compared to the normal range of 150,000 to 450,000 platelets in microliter of blood suggest thrombocytopaenia, which is a common symptom in Epstein syndrome.
A urine
Urine is a liquid by-product of metabolism in humans and in many other animals. Urine flows from the kidneys through the ureters to the urinary bladder. Urination results in urine being excreted from the body through the urethra.
Cellular ...
sample is often collected where a urinalysis
Urinalysis, a portmanteau of the words ''urine'' and ''analysis'', is a panel of medical tests that includes physical (macroscopic) examination of the urine, chemical evaluation using urine test strips, and microscopic examination. Macroscopic ...
can be used to determine the volume of protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, respo ...
s excreted in urine. Abnormal amounts of protein detected means the patient has proteinuria
Proteinuria is the presence of excess proteins in the urine. In healthy persons, urine contains very little protein; an excess is suggestive of illness. Excess protein in the urine often causes the urine to become foamy (although this symptom ma ...
. Patients with Epstein syndrome often have large proteinuria where they excrete above 3.5g of protein in their urine in a day. This is one of the initial signs of renal disease.
Easy bruising
A bruise, also known as a contusion, is a type of hematoma of tissue, the most common cause being capillaries damaged by trauma, causing localized bleeding that extravasates into the surrounding interstitial tissues. Most bruises occur clos ...
and abnormal bleeding tendencies are also described in initial diagnosis
Diagnosis is the identification of the nature and cause of a certain phenomenon. Diagnosis is used in many different disciplines, with variations in the use of logic, analytics, and experience, to determine " cause and effect". In systems engin ...
. This supports the common misdiagnosis for chronic idiopathic thrombocytopaenia purpura in patients with Epstein syndrome. These symptoms are often noticed in early childhood due to the congenital cause of the disease.
Treatment
Epstein syndrome is regarded as a refractory disease. Treatments includerenal transplantation
Kidney transplant or renal transplant is the organ transplant of a kidney into a patient with end-stage kidney disease (ESRD). Kidney transplant is typically classified as deceased-donor (formerly known as cadaveric) or living-donor transplantat ...
, however, this may become problematic as patient's low platelet count (thrombocytopaenia
Thrombocytopenia is a condition characterized by abnormally low levels of platelets, also known as thrombocytes, in the blood. It is the most common coagulation disorder among intensive care patients and is seen in a fifth of medical patients an ...
) increase the risks of complications in surgery. Successful Renal transplants can arise from cadavers or from live donors. To minimize the risk of patient's losing too much blood during the perioperative
The perioperative period is the time period of a patient's surgical procedure. It commonly includes ward admission, anesthesia, surgery, and recovery. Perioperative may refer to the three phases of surgery: preoperative, intraoperative, and posto ...
period, HLA-matched platelet infusions can be used to maintain satisfactory platelet levels. Nephritis involves the inflammation of the kidney and this inflammation results in a reduced ability to filter blood. In order to ensure the transplanted kidney is recognised as ‘self’ by Major Histocompatibility cells, immunosuppression
Immunosuppression is a reduction of the activation or efficacy of the immune system. Some portions of the immune system itself have immunosuppressive effects on other parts of the immune system, and immunosuppression may occur as an adverse reacti ...
drugs are used post operation. Immunosuppression medication
A medication (also called medicament, medicine, pharmaceutical drug, medicinal drug or simply drug) is a drug used to diagnose, cure, treat, or prevent disease. Drug therapy ( pharmacotherapy) is an important part of the medical field and ...
may include calcineurin
Calcineurin (CaN) is a calcium and calmodulin dependent serine/threonine protein phosphatase (also known as protein phosphatase 3, and calcium-dependent serine-threonine phosphatase). It activates the T cells of the immune system and can be block ...
inhibitor, antimetabolite
An antimetabolite is a chemical that inhibits the use of a metabolite, which is another chemical that is part of normal metabolism. Such substances are often similar in structure to the metabolite that they interfere with, such as the antifolate ...
and methylprednisolone
Methylprednisolone (Depo-Medrol, Medrol, Solu-Medrol) is a synthetic glucocorticoid, primarily prescribed for its anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive effects. It is either used at low doses for chronic illnesses or used concomitantly at hig ...
and assist in suppressing the immune system
The immune system is a network of biological processes that protects an organism from diseases. It detects and responds to a wide variety of pathogens, from viruses to parasitic worms, as well as cancer cells and objects such as wood splinte ...
's response to the transplanted kidney
Maintenance
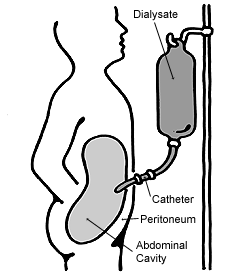
 As a result of nephritis, a healthy blood pressure becomes difficult to maintain and hence medication including vasopressin may be prescribed to maintain blood pressure. Severe nephritis may mean
As a result of nephritis, a healthy blood pressure becomes difficult to maintain and hence medication including vasopressin may be prescribed to maintain blood pressure. Severe nephritis may mean kidney dialysis
Kidney dialysis (from Greek , , 'dissolution'; from , , 'through', and , , 'loosening or splitting') is the process of removing excess water, solutes, and toxins from the blood in people whose kidneys can no longer perform these functions natura ...
is required to ensure the blood is being filtered. This may include either peritoneal dialysis
Peritoneal dialysis (PD) is a type of dialysis which uses the peritoneum in a person's abdomen as the membrane through which fluid and dissolved substances are exchanged with the blood. It is used to remove excess fluid, correct electrolyte pro ...
or haemodialysis
Hemodialysis, also spelled haemodialysis, or simply dialysis, is a process of purifying the blood of a person whose kidneys are not working normally. This type of dialysis achieves the extracorporeal removal of waste products such as creatini ...
, however, haemodialysis is most common as Epstein syndrome patients will often eventually have renal transplants. Peritoneal dialysis involves blood being filtered through a membrane in the abdomen (peritoneum
The peritoneum is the serous membrane forming the lining of the abdominal cavity or coelom in amniotes and some invertebrates, such as annelids. It covers most of the intra-abdominal (or coelomic) organs, and is composed of a layer of meso ...
). Whereas haemodialysis involves blood being filtered through a dialyser, which consists of a semi-permeable membrane where toxins including urea are removed from the blood. Haemodialysis also filters blood quicker than peritoneal dialysis.
Intravenous immunoglobin
An antibody (Ab), also known as an immunoglobulin (Ig), is a large, Y-shaped protein used by the immune system to identify and neutralize foreign objects such as pathogenic bacteria and viruses. The antibody recognizes a unique molecule of the ...
treatments can be used to support the patient's immune system as well as medication with Prednisolone
Prednisolone is a steroid medication used to treat certain types of allergies, inflammatory conditions, autoimmune disorders, and cancers. Some of these conditions include adrenocortical insufficiency, high blood calcium, rheumatoid arthr ...
to reduce inflammation.
Sensorineural hearing loss is a common symptom in Epstein syndrome and can be treated with cochlea implants. Cochlea implants have four main parts including the electrode array
An electrode array is a configuration of electrodes used for measuring either an electric current or voltage. Some electrode arrays can operate in a bidirectional fashion, in that they can also be used to provide a stimulating pattern of electric c ...
, the transmitter, the receiver/stimulator and the microphone
A microphone, colloquially called a mic or mike (), is a transducer that converts sound into an electrical signal. Microphones are used in many applications such as telephones, hearing aids, public address systems for concert halls and public ...
. The microphone is positioned behind the ear and receives sound waves
In physics, sound is a vibration that propagates as an acoustic wave, through a transmission medium such as a gas, liquid or solid.
In human physiology and psychology, sound is the ''reception'' of such waves and their ''perception'' by the ...
, the processor then converts the sound into electrical signals. These electrical signals are further converted into electrical impulses in the cochlea
The cochlea is the part of the inner ear involved in hearing. It is a spiral-shaped cavity in the bony labyrinth, in humans making 2.75 turns around its axis, the modiolus. A core component of the cochlea is the Organ of Corti, the sensory or ...
where the transmitter is located, which in turn sends the signal to the auditory nerve
The cochlear nerve (also auditory nerve or acoustic nerve) is one of two parts of the vestibulocochlear nerve, a cranial nerve present in amniotes, the other part being the vestibular nerve. The cochlear nerve carries auditory sensory information ...
. This results in a nervous impulse sent to the brain
A brain is an organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals. It is located in the head, usually close to the sensory organs for senses such as vision. It is the most complex organ in a ve ...
where the ‘sound’ is deciphered.
Prognosis
In most case Epstein syndrome patients will endure early-onset end-stage renal disease (ESRD) at the end of adolescence. Expected kidney failure means patients will need renal transplants in the near future.Notable cases
In a study which investigated suitable management for severe Epstein syndrome, four patients were observed. Patient 1 demonstrated a common background and symptoms for Epstein syndrome. Patient 1 was a male who was initially diagnosed with chronic idiopathic thrombocytopaenia purpura in early childhood and then macrothrobocytopaenia. He progressed tokidney failure
Kidney failure, also known as end-stage kidney disease, is a medical condition in which the kidneys can no longer adequately filter waste products from the blood, functioning at less than 15% of normal levels. Kidney failure is classified as eit ...
and began haemodialysis at seventeen years old. Patient 1 was only diagnosed with Epstein syndrome at the age of thirty-three where the mutation in the nonmuscle myosin was noticed. His eldest son also carried the same mutation.
An Epstein syndrome patient with oral lesion
A lesion is any damage or abnormal change in the tissue of an organism, usually caused by disease or trauma. ''Lesion'' is derived from the Latin "injury". Lesions may occur in plants as well as animals.
Types
There is no designated classif ...
s was recorded to be the first with this symptom. The patient was a twenty-six-year-old female who was diagnosed with thrombocytopaenia
Thrombocytopenia is a condition characterized by abnormally low levels of platelets, also known as thrombocytes, in the blood. It is the most common coagulation disorder among intensive care patients and is seen in a fifth of medical patients an ...
with purpura
Purpura () is a condition of red or purple discolored spots on the skin that do not blanch on applying pressure. The spots are caused by bleeding underneath the skin secondary to platelet disorders, vascular disorders, coagulation disorders, ...
at age four. She was then finally diagnosed with Epstein syndrome at twenty-two years old when she developed symptoms for hearing loss
Hearing loss is a partial or total inability to Hearing, hear. Hearing loss may be present at birth or acquired at any time afterwards. Hearing loss may occur in one or both ears. In children, hearing problems can affect the ability to Language ...
as well as proteinuria
Proteinuria is the presence of excess proteins in the urine. In healthy persons, urine contains very little protein; an excess is suggestive of illness. Excess protein in the urine often causes the urine to become foamy (although this symptom ma ...
and hematuria
Hematuria or haematuria is defined as the presence of blood or red blood cells in the urine. “Gross hematuria” occurs when urine appears red, brown, or tea-colored due to the presence of blood. Hematuria may also be subtle and only detectable w ...
revealing poor kidney function. After an oral examination, palatal purpua in her mouth was observed.
A Japanese male was diagnosed with sporadic Epstein syndrome where both his parents did not have the R702H mutation. He was initially diagnosed with chronic macrothrombocytopaenia at three years old and throughout childhood symptoms for hearing loss and proteinuria were observed. At 24 years old his kidney failure had severely progressed as well as his hearing loss and thrombocytopenia. A genetic test
Genetic testing, also known as DNA testing, is used to identify changes in DNA sequence or chromosome structure. Genetic testing can also include measuring the results of genetic changes, such as RNA analysis as an output of gene expression, o ...
confirmed he had the R702H mutation despite having no familial record of Epstein syndrome.
References
External links
{{Nephrology Kidney diseases