England Women's National Rugby League Team Players on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
England is a
Accessed 31 May 2013. The

 The earliest known evidence of human presence in the area now known as England was that of ''
The earliest known evidence of human presence in the area now known as England was that of '' The Romans invaded Britain in 43 AD during the reign of Emperor
The Romans invaded Britain in 43 AD during the reign of Emperor

 A dispute over the succession to Edward led to the
A dispute over the succession to Edward led to the
 Based on conflicting political, religious and social positions, the English Civil War was fought between the supporters of Long Parliament, Parliament and those of King Charles I of England, Charles I, known colloquially as Roundheads and Cavaliers respectively. This was an interwoven part of the wider multifaceted Wars of the Three Kingdoms, involving Kingdom of Scotland, Scotland and Kingdom of Ireland, Ireland. The Parliamentarians were victorious, execution of Charles I, Charles I was executed and the kingdom replaced by the Commonwealth of England, Commonwealth. Leader of the Parliament forces, Oliver Cromwell declared himself Lord Protector in 1653; a period of the Protectorate, personal rule followed. After Cromwell's death and the resignation of his son Richard Cromwell, Richard as Lord Protector, Charles II of England, Charles II was invited to return as monarch in 1660, in a move called the English Restoration, Restoration. With the reopening of theatres, fine arts, literature and performing arts flourished throughout the Restoration of
Based on conflicting political, religious and social positions, the English Civil War was fought between the supporters of Long Parliament, Parliament and those of King Charles I of England, Charles I, known colloquially as Roundheads and Cavaliers respectively. This was an interwoven part of the wider multifaceted Wars of the Three Kingdoms, involving Kingdom of Scotland, Scotland and Kingdom of Ireland, Ireland. The Parliamentarians were victorious, execution of Charles I, Charles I was executed and the kingdom replaced by the Commonwealth of England, Commonwealth. Leader of the Parliament forces, Oliver Cromwell declared himself Lord Protector in 1653; a period of the Protectorate, personal rule followed. After Cromwell's death and the resignation of his son Richard Cromwell, Richard as Lord Protector, Charles II of England, Charles II was invited to return as monarch in 1660, in a move called the English Restoration, Restoration. With the reopening of theatres, fine arts, literature and performing arts flourished throughout the Restoration of ''the Merry Monarch'' Charles II. After the Glorious Revolution of 1688, it was constitutionally established that King and Parliament should rule together, though Parliament would have the real power. This was established with the Bill of Rights 1689, Bill of Rights in 1689. Among the statutes set down were that the law could only be made by Parliament and could not be suspended by the King, also that the King could not impose taxes or raise an army without the prior approval of Parliament. Also since that time, no British monarch has entered the House of Commons of the United Kingdom, House of Commons when it is sitting, which is annually commemorated at the State Opening of Parliament by the British monarch when the doors of the House of Commons are slammed in the face of the monarch's messenger, symbolising the rights of Parliament and its independence from the monarch. With the founding of the Royal Society in 1660, science was greatly encouraged.
In 1666 the Great Fire of London gutted the City of London but it was rebuilt shortly afterwards with many significant buildings designed by Christopher Wren. In Parliament two factions had emerged ã the Tory, Tories and Whig (British political faction), Whigs. Though the Tories initially supported Catholic king James II of England, James II, some of them, along with the Whigs, during the Glorious Revolution, Revolution of 1688 invited Dutch Prince William of Orange to defeat James and ultimately to become William III of England. Some English people, especially in the north, were Jacobitism, Jacobites and continued to support James and his sons. Under the House of Stuart, Stuart dynasty England expanded in trade, finance and prosperity. Britain developed Europe's largest merchant fleet. After the parliaments of England and Scotland agreed, the two countries joined in political union, to create the
 Under the newly formed Kingdom of Great Britain, output from the Royal Society and other English Enlightenment, English initiatives combined with the Scottish Enlightenment to create innovations in science and engineering, while the enormous growth in Triangular trade, British overseas trade protected by the Royal Navy paved the way for the establishment of the British Empire. Domestically it drove the
Under the newly formed Kingdom of Great Britain, output from the Royal Society and other English Enlightenment, English initiatives combined with the Scottish Enlightenment to create innovations in science and engineering, while the enormous growth in Triangular trade, British overseas trade protected by the Royal Navy paved the way for the establishment of the British Empire. Domestically it drove the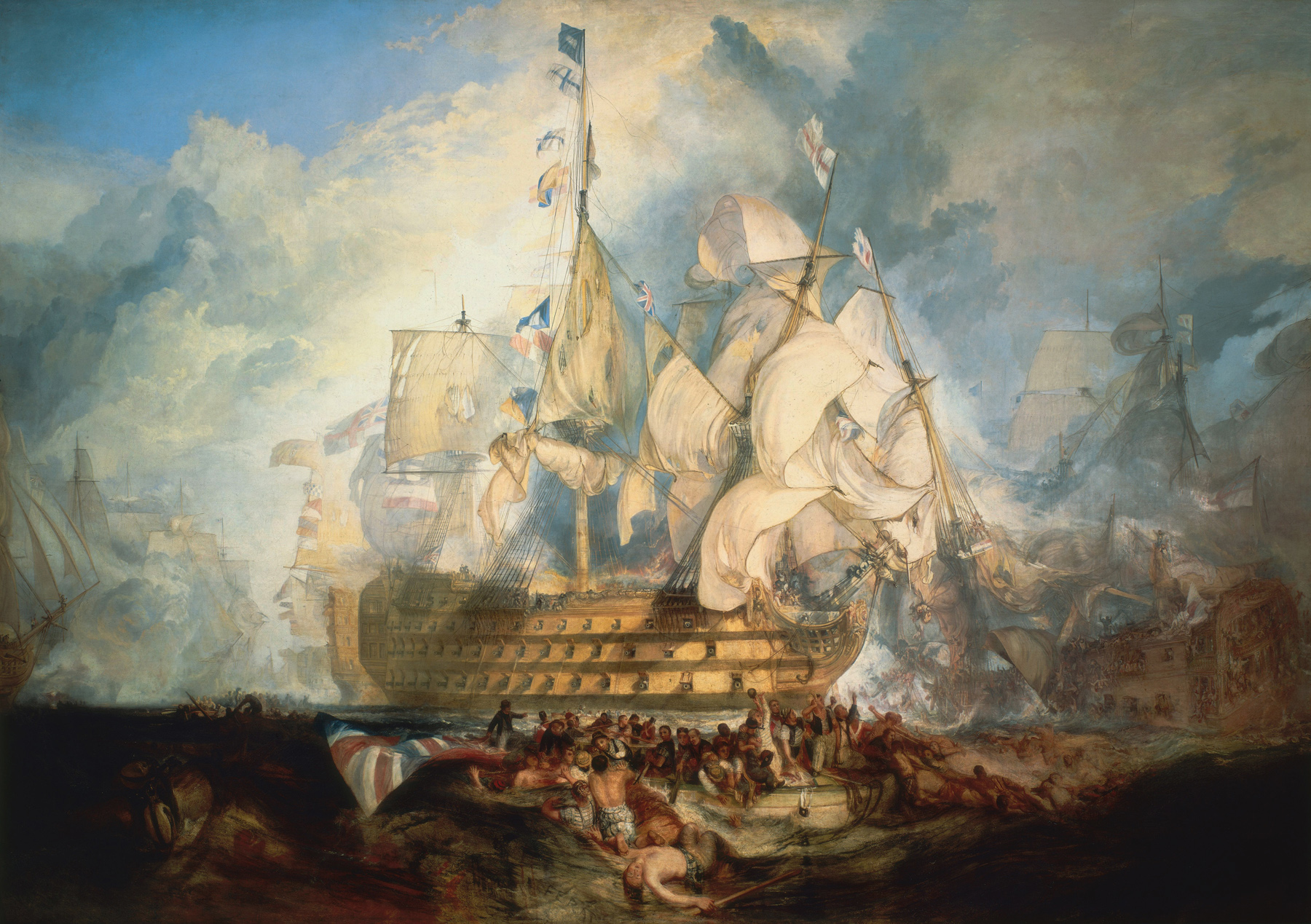  During the Industrial Revolution, many workers moved from England's countryside to new and expanding urban industrial areas to work in factories, for instance at Birmingham and Manchester, dubbed "Workshop of the World" and "Warehouse City" respectively. Manchester was the world's first industrial city. England maintained relative stability throughout the French Revolution; William Pitt the Younger was British prime minister for the reign of George III of the United Kingdom, George III. The Regency of George IV is noted for its elegance and achievements in the fine arts and architecture. During the Napoleonic Wars, Napoleon planned to Napoleon's planned invasion of the United Kingdom, invade from the south-east. However, this failed to manifest and the Napoleonic forces were defeated by the British: at sea by Horatio Nelson, and on land by Arthur Wellesley, 1st Duke of Wellington, Arthur Wellesley. The major victory at the Battle of Trafalgar confirmed the naval supremacy Britain had established during the course of the eighteenth century. The Napoleonic Wars fostered a concept of Britishness and a united national British people, shared with the English, Scots and Welsh..
During the Industrial Revolution, many workers moved from England's countryside to new and expanding urban industrial areas to work in factories, for instance at Birmingham and Manchester, dubbed "Workshop of the World" and "Warehouse City" respectively. Manchester was the world's first industrial city. England maintained relative stability throughout the French Revolution; William Pitt the Younger was British prime minister for the reign of George III of the United Kingdom, George III. The Regency of George IV is noted for its elegance and achievements in the fine arts and architecture. During the Napoleonic Wars, Napoleon planned to Napoleon's planned invasion of the United Kingdom, invade from the south-east. However, this failed to manifest and the Napoleonic forces were defeated by the British: at sea by Horatio Nelson, and on land by Arthur Wellesley, 1st Duke of Wellington, Arthur Wellesley. The major victory at the Battle of Trafalgar confirmed the naval supremacy Britain had established during the course of the eighteenth century. The Napoleonic Wars fostered a concept of Britishness and a united national British people, shared with the English, Scots and Welsh..
 London became the largest and most populous metropolitan area in the world during the Victorian era, and trade within the British Empire ã as well as the standing of the British military and navy ã was prestigious. Technologically, this era saw many innovations that proved key to the United Kingdom's power and prosperity. Political agitation at home from radicals such as the Chartism, Chartists and the suffragettes enabled legislative reform and universal suffrage. Samuel Hynes described the Edwardian era as a "leisurely time when women wore picture hats and did not vote, when the rich were not ashamed to live conspicuously, and the sun really never set on the British flag."
Power shifts in east-central Europe led to World War I; hundreds of thousands of English soldiers died fighting for the United Kingdom as part of the Allies of World War I, Allies. Two decades later, in World War II, the United Kingdom was again one of the Allies of World War II, Allies. At the end of the Phoney War, Winston Churchill became the wartime prime minister. Developments in warfare technology saw many cities damaged by air-raids during the Blitz. Following the war, the British Empire experienced rapid decolonisation, and there was a speeding-up of technological innovations; automobiles became the primary means of transport and Frank Whittle's development of the jet engine led to wider air travel. Residential patterns were altered in England by private motoring, and by the creation of the National Health Service (England), National Health Service (NHS) in 1948. The UK's NHS provided publicly funded health care to all UK permanent residents free at the point of need, being paid for from general taxation. Combined, these prompted the reform of local government in England in the mid-20th century.
Since the 20th century there has been significant population movement to England, mostly from other parts of the British Isles, but also from the Commonwealth of Nations, Commonwealth, particularly the Indian subcontinent. Since the 1970s there has been a large move away from manufacturing and an increasing emphasis on the service industry. As part of the United Kingdom, the area joined a common market initiative called the European Economic Community which became the European Union. Since the late 20th century the politics of the United Kingdom, administration of the United Kingdom has moved towards devolution, devolved governance in Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland. England and Wales continues to exist as a jurisdiction within the United Kingdom. Devolution has stimulated a greater emphasis on a more English-specific identity and patriotism. There is no devolved English government, but an attempt to create a similar system on a sub-regional basis was rejected by referendum.
London became the largest and most populous metropolitan area in the world during the Victorian era, and trade within the British Empire ã as well as the standing of the British military and navy ã was prestigious. Technologically, this era saw many innovations that proved key to the United Kingdom's power and prosperity. Political agitation at home from radicals such as the Chartism, Chartists and the suffragettes enabled legislative reform and universal suffrage. Samuel Hynes described the Edwardian era as a "leisurely time when women wore picture hats and did not vote, when the rich were not ashamed to live conspicuously, and the sun really never set on the British flag."
Power shifts in east-central Europe led to World War I; hundreds of thousands of English soldiers died fighting for the United Kingdom as part of the Allies of World War I, Allies. Two decades later, in World War II, the United Kingdom was again one of the Allies of World War II, Allies. At the end of the Phoney War, Winston Churchill became the wartime prime minister. Developments in warfare technology saw many cities damaged by air-raids during the Blitz. Following the war, the British Empire experienced rapid decolonisation, and there was a speeding-up of technological innovations; automobiles became the primary means of transport and Frank Whittle's development of the jet engine led to wider air travel. Residential patterns were altered in England by private motoring, and by the creation of the National Health Service (England), National Health Service (NHS) in 1948. The UK's NHS provided publicly funded health care to all UK permanent residents free at the point of need, being paid for from general taxation. Combined, these prompted the reform of local government in England in the mid-20th century.
Since the 20th century there has been significant population movement to England, mostly from other parts of the British Isles, but also from the Commonwealth of Nations, Commonwealth, particularly the Indian subcontinent. Since the 1970s there has been a large move away from manufacturing and an increasing emphasis on the service industry. As part of the United Kingdom, the area joined a common market initiative called the European Economic Community which became the European Union. Since the late 20th century the politics of the United Kingdom, administration of the United Kingdom has moved towards devolution, devolved governance in Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland. England and Wales continues to exist as a jurisdiction within the United Kingdom. Devolution has stimulated a greater emphasis on a more English-specific identity and patriotism. There is no devolved English government, but an attempt to create a similar system on a sub-regional basis was rejected by referendum.
 England is part of the United Kingdom, a constitutional monarchy with a parliamentary system. There has not been a government of England since 1707, when the Acts of Union 1707, putting into effect the terms of the
England is part of the United Kingdom, a constitutional monarchy with a parliamentary system. There has not been a government of England since 1707, when the Acts of Union 1707, putting into effect the terms of the
 The
The
 Geographically England includes the central and southern two-thirds of the island of Great Britain, plus such offshore islands as the
Geographically England includes the central and southern two-thirds of the island of Great Britain, plus such offshore islands as the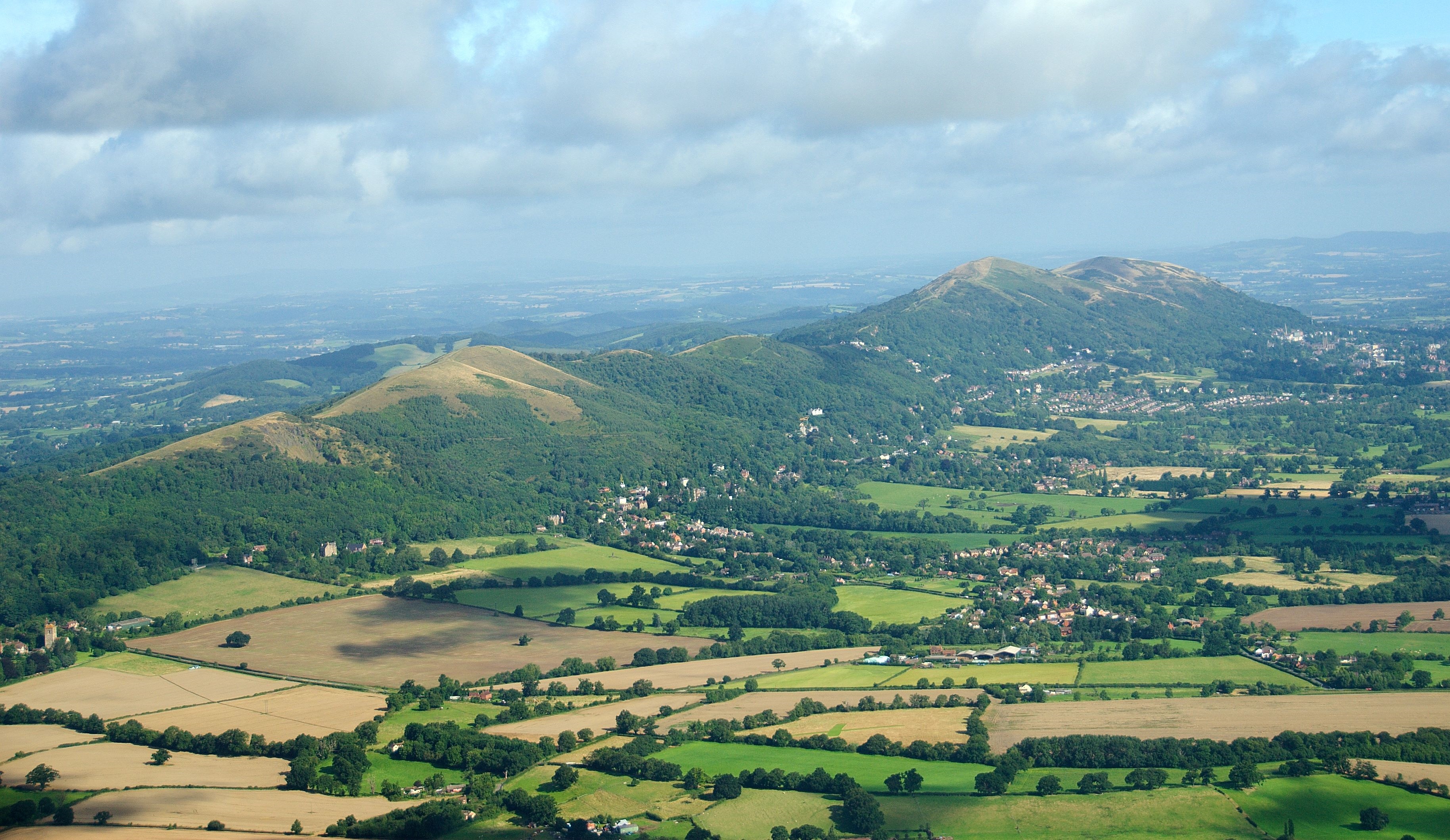  There are many lakes in England; the largest is Windermere, within the aptly named
There are many lakes in England; the largest is Windermere, within the aptly named
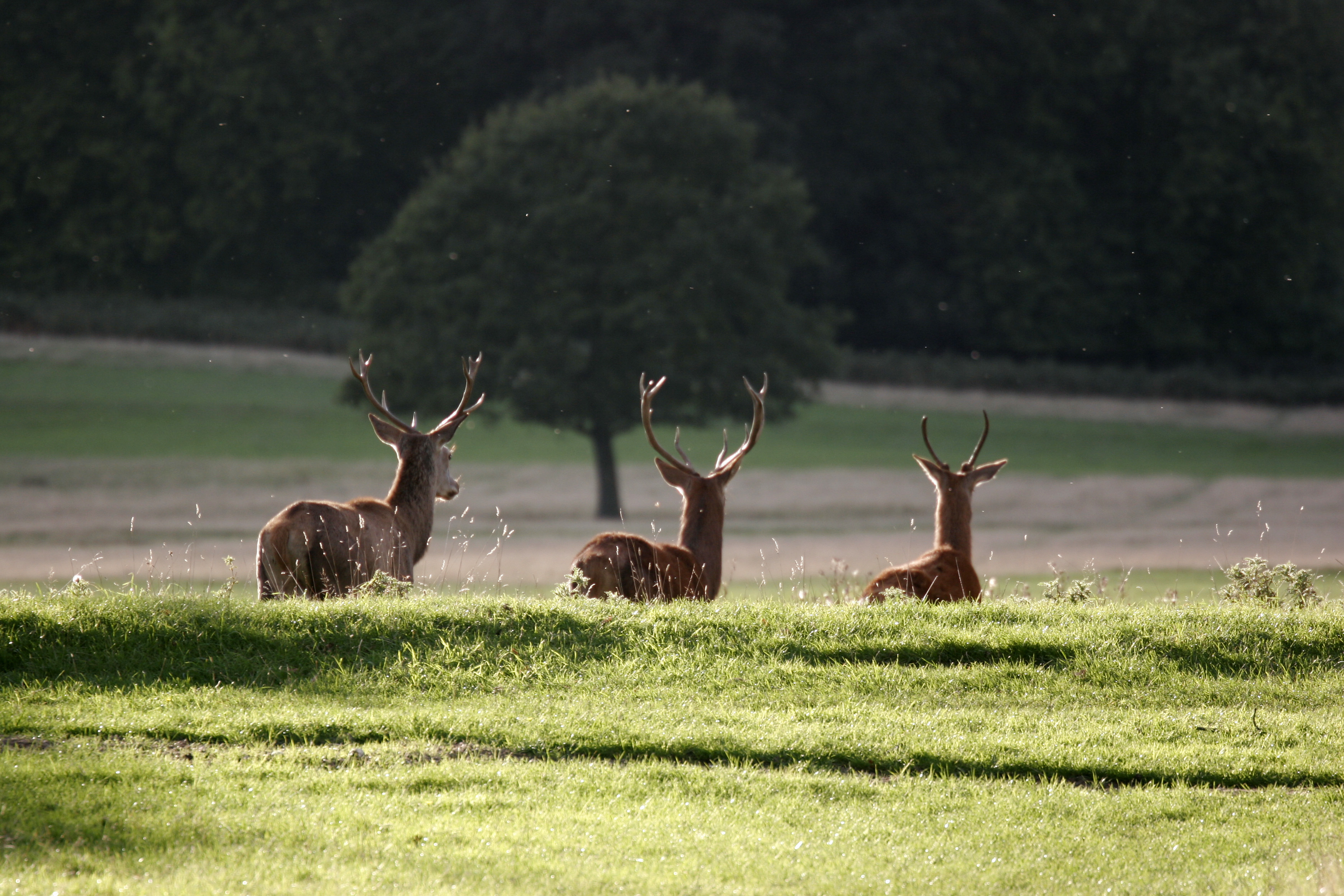
 The fauna of England is similar to that of other areas in the British Isles with a wide range of vertebrate and invertebrate life in a diverse range of habitats.
National nature reserves in England are designated by Natural England as key places for wildlife and natural features in England. They were established to protect the most significant areas of habitat and of geological formations. NNRs are managed on behalf of the nation, many by Natural England themselves, but also by non-governmental organisations, including the members of The Wildlife Trusts partnership, the National Trust for Places of Historic Interest or Natural Beauty, National Trust, and the Royal Society for the Protection of Birds. There are 229 NNRs in England covering . Often they contain rare species or nationally important populations of plants and animals.
The Environment Agency is a non-departmental public body, established in 1995 and sponsored by the Department for Environment, Food and Rural Affairs with responsibilities relating to the protection and enhancement of the environment in England. The Secretary of State for Environment, Food and Rural Affairs is the minister responsible for environmental protection, agriculture, fisheries and rural communities in England.
England has a Oceanic climate, temperate oceanic climate in most areas, lacking extremes of cold or heat, but does have a few small areas of Subarctic climate, subarctic and warmer areas in South West England, the South West. Towards the Northern England, North of England the climate becomes colder and most of England's mountains and high hills are located here and have a major impact on the climate and thus the local fauna of the areas. Deciduous woodlands are common across all of England and provide a great habitat for much of England's wildlife, but these give way in northern and upland areas of England to coniferous forests (mainly plantations) which also benefit certain forms of wildlife. Some species have adapted to the expanded urban environment, particularly the red fox, which is the most successful Urban wildlife, urban mammal after the brown rat, and other animals such as common wood pigeon, both of which thrive in urban and suburban areas.
Grey squirrels introduced from eastern America have forced the decline of the native red squirrel due to competition. Red squirrels are now confined to upland and coniferous-forested areas of England, mainly in the north, south west and Isle of Wight. England's climate is very suitable for lagomorphs and the country has European rabbit, rabbits and European hare, brown hares which were introduced in Roman times. Mountain hares which are indigenous have now been re-introduced in Derbyshire. The fauna of England has to cope with varying temperatures and conditions, although not extreme they do pose potential challenges and adaptational measures. English fauna has however had to cope with industrialisation, human population densities amongst the highest in Europe and intensive farming, but as England is a developed nation, wildlife and the countryside have entered the English people, English mindset more and the country is very conscientious about preserving its wildlife, environment and countryside.
The fauna of England is similar to that of other areas in the British Isles with a wide range of vertebrate and invertebrate life in a diverse range of habitats.
National nature reserves in England are designated by Natural England as key places for wildlife and natural features in England. They were established to protect the most significant areas of habitat and of geological formations. NNRs are managed on behalf of the nation, many by Natural England themselves, but also by non-governmental organisations, including the members of The Wildlife Trusts partnership, the National Trust for Places of Historic Interest or Natural Beauty, National Trust, and the Royal Society for the Protection of Birds. There are 229 NNRs in England covering . Often they contain rare species or nationally important populations of plants and animals.
The Environment Agency is a non-departmental public body, established in 1995 and sponsored by the Department for Environment, Food and Rural Affairs with responsibilities relating to the protection and enhancement of the environment in England. The Secretary of State for Environment, Food and Rural Affairs is the minister responsible for environmental protection, agriculture, fisheries and rural communities in England.
England has a Oceanic climate, temperate oceanic climate in most areas, lacking extremes of cold or heat, but does have a few small areas of Subarctic climate, subarctic and warmer areas in South West England, the South West. Towards the Northern England, North of England the climate becomes colder and most of England's mountains and high hills are located here and have a major impact on the climate and thus the local fauna of the areas. Deciduous woodlands are common across all of England and provide a great habitat for much of England's wildlife, but these give way in northern and upland areas of England to coniferous forests (mainly plantations) which also benefit certain forms of wildlife. Some species have adapted to the expanded urban environment, particularly the red fox, which is the most successful Urban wildlife, urban mammal after the brown rat, and other animals such as common wood pigeon, both of which thrive in urban and suburban areas.
Grey squirrels introduced from eastern America have forced the decline of the native red squirrel due to competition. Red squirrels are now confined to upland and coniferous-forested areas of England, mainly in the north, south west and Isle of Wight. England's climate is very suitable for lagomorphs and the country has European rabbit, rabbits and European hare, brown hares which were introduced in Roman times. Mountain hares which are indigenous have now been re-introduced in Derbyshire. The fauna of England has to cope with varying temperatures and conditions, although not extreme they do pose potential challenges and adaptational measures. English fauna has however had to cope with industrialisation, human population densities amongst the highest in Europe and intensive farming, but as England is a developed nation, wildlife and the countryside have entered the English people, English mindset more and the country is very conscientious about preserving its wildlife, environment and countryside.
 England's economy is one of the largest and most dynamic in the world, with an average GDP per capita of ôÈ28,100. HM Treasury, led by the Chancellor of the Exchequer, is responsible for developing and executing the government's public finance policy and economic policy. Usually regarded as a Anglo-Saxon economy, mixed market economy, it has adopted many free market principles, yet maintains an advanced social welfare infrastructure. The official currency in England is the pound sterling, whose ISO 4217 code is GBP. Taxation in England is quite competitive when List of countries by tax rates, compared to much of the rest of Europe ã the basic rate of personal tax is 20% on taxable income up to ôÈ31,865 above the personal tax-free allowance (normally ôÈ10,000), and 40% on any additional earnings above that amount.
The economy of England is the largest part of the economy of the United Kingdom, UK's economy, which has the List of countries by GDP (PPP) per capita, 18th highest GDP Purchasing power parity, PPP per capita in the world. England is a leader in the chemical and pharmaceutical sectors and in key technical industries, particularly aerospace, the arms industry, and the manufacturing side of the software industry. London, home to the London Stock Exchange, the United Kingdom's main stock exchange and the largest in Europe, is England's financial centre, with 100 of Europe's 500 largest corporations being based there. London is the largest financial centre in Europe, and is the second largest in the world.
The Bank of England, founded in 1694, is the United Kingdom's central bank. Originally established as private banker to the government of England, since 1946 it has been a nationalisation, state-owned institution. The bank has a monopoly on the issue of banknotes in England and Wales, although not in other parts of the United Kingdom. The government has devolved responsibility to the bank's Monetary Policy Committee (United Kingdom), Monetary Policy Committee for managing the monetary policy of the country and setting interest rates.
England is highly industrialised, but since the 1970s there has been a decline in traditional heavy and manufacturing industries, and an increasing emphasis on a more service industry oriented economy.. Tourism has become a significant industry, attracting millions of visitors to England each year. The export part of the economy is dominated by pharmaceuticals, cars (although many English marques are now foreign-owned, such as Land Rover, Lotus Cars, Lotus, Jaguar Cars, Jaguar and Bentley), crude oil and petroleum from the English parts of North Sea oil along with Wytch Farm, aircraft engines and alcoholic beverages. The creative industries accounted for 7 per cent GVA in 2005 and grew at an average of 6 per cent per annum between 1997 and 2005.
Most of the UK's ôÈ30 billion Aerospace industry in the United Kingdom, aerospace industry is primarily based in England. The global market opportunity for UK aerospace manufacturers over the next two decades is estimated at ôÈ3.5 trillion. GKN Aerospace ã an expert in metallic and composite aerostructures is involved in almost every civil and military fixed and rotary wing aircraft in production is based in Redditch.
BAE Systems makes large sections of the Typhoon Eurofighter at its sub-assembly plant in Samlesbury and assembles the aircraft for the RAF at its Warton, Fylde, Warton plant, near Preston, Lancashire, Preston. It is also a principal subcontractor on the F35 Lightning II, F35 Joint Strike Fighter ã the world's largest single defence project ã for which it designs and manufactures a range of components including the aft fuselage, vertical and horizontal tail and wing tips and fuel system. It also manufactures the BAE Systems Hawk, Hawk, the world's most successful jet training aircraft.
Rolls-Royce Holdings, Rolls-Royce PLC is the world's second-largest aircraft engine, aero-engine manufacturer. Its engines power more than 30 types of commercial aircraft, and it has more 30,000 engines currently in service across both the civil and defence sectors. With a workforce of over 12,000 people, Derby has the largest concentration of Rolls-Royce employees in the UK. Rolls-Royce also produces low-emission power systems for ships; makes critical equipment and safety systems for the nuclear industry and powers offshore platforms and major pipelines for the oil and gas industry. The Pharmaceutical industry in the United Kingdom, pharmaceutical industry plays an important role in the economy, and the UK has the third-highest share of global pharmaceutical R&D expenditures.
Much of the UK's space industry is centred on EADS Astrium, based in Stevenage and Portsmouth. The company builds the Satellite bus, buses ã the underlying structure onto which the payload and propulsion systems are built ã for most of the European Space Agency's spacecraft, as well as commercial satellites. The world leader in compact satellite systems, Surrey Satellite Technology, is also part of Astrium. Reaction Engines Limited, the company planning to build Skylon (spacecraft), Skylon, a single-stage-to-orbit spaceplane using their SABRE (rocket engine), SABRE rocket engine, a combined-cycle, air-breathing rocket propulsion system is based Culham. The UK space industry was worth ôÈ9.1bn in 2011 and employed 29,000 people. It is growing at a rate of 7.5 per cent annually, according to its umbrella organisation, the UK Space Agency. In 2013, the British Government pledged ôÈ60 million to the Skylon (spacecraft), Skylon project: this investment will provide support at a "crucial stage" to allow a full-scale prototype of the SABRE (rocket engine), SABRE engine to be built.
Agriculture is intensive, highly mechanised and efficient by European standards, producing 60% of food needs with only 2% of the labour force. Two-thirds of production is devoted to livestock, the other to arable crops. The main crops that are grown are wheat, barley, oats, potatoes, sugar beets. England retains a significant, though much reduced fishing industry. Its fleets bring home fish of every kind, ranging from Sole (fish), sole to herring. It is also rich in natural resources including coal, petroleum, natural gas, tin, limestone, iron ore, salt, clay, chalk, gypsum, lead, and silica.
England's economy is one of the largest and most dynamic in the world, with an average GDP per capita of ôÈ28,100. HM Treasury, led by the Chancellor of the Exchequer, is responsible for developing and executing the government's public finance policy and economic policy. Usually regarded as a Anglo-Saxon economy, mixed market economy, it has adopted many free market principles, yet maintains an advanced social welfare infrastructure. The official currency in England is the pound sterling, whose ISO 4217 code is GBP. Taxation in England is quite competitive when List of countries by tax rates, compared to much of the rest of Europe ã the basic rate of personal tax is 20% on taxable income up to ôÈ31,865 above the personal tax-free allowance (normally ôÈ10,000), and 40% on any additional earnings above that amount.
The economy of England is the largest part of the economy of the United Kingdom, UK's economy, which has the List of countries by GDP (PPP) per capita, 18th highest GDP Purchasing power parity, PPP per capita in the world. England is a leader in the chemical and pharmaceutical sectors and in key technical industries, particularly aerospace, the arms industry, and the manufacturing side of the software industry. London, home to the London Stock Exchange, the United Kingdom's main stock exchange and the largest in Europe, is England's financial centre, with 100 of Europe's 500 largest corporations being based there. London is the largest financial centre in Europe, and is the second largest in the world.
The Bank of England, founded in 1694, is the United Kingdom's central bank. Originally established as private banker to the government of England, since 1946 it has been a nationalisation, state-owned institution. The bank has a monopoly on the issue of banknotes in England and Wales, although not in other parts of the United Kingdom. The government has devolved responsibility to the bank's Monetary Policy Committee (United Kingdom), Monetary Policy Committee for managing the monetary policy of the country and setting interest rates.
England is highly industrialised, but since the 1970s there has been a decline in traditional heavy and manufacturing industries, and an increasing emphasis on a more service industry oriented economy.. Tourism has become a significant industry, attracting millions of visitors to England each year. The export part of the economy is dominated by pharmaceuticals, cars (although many English marques are now foreign-owned, such as Land Rover, Lotus Cars, Lotus, Jaguar Cars, Jaguar and Bentley), crude oil and petroleum from the English parts of North Sea oil along with Wytch Farm, aircraft engines and alcoholic beverages. The creative industries accounted for 7 per cent GVA in 2005 and grew at an average of 6 per cent per annum between 1997 and 2005.
Most of the UK's ôÈ30 billion Aerospace industry in the United Kingdom, aerospace industry is primarily based in England. The global market opportunity for UK aerospace manufacturers over the next two decades is estimated at ôÈ3.5 trillion. GKN Aerospace ã an expert in metallic and composite aerostructures is involved in almost every civil and military fixed and rotary wing aircraft in production is based in Redditch.
BAE Systems makes large sections of the Typhoon Eurofighter at its sub-assembly plant in Samlesbury and assembles the aircraft for the RAF at its Warton, Fylde, Warton plant, near Preston, Lancashire, Preston. It is also a principal subcontractor on the F35 Lightning II, F35 Joint Strike Fighter ã the world's largest single defence project ã for which it designs and manufactures a range of components including the aft fuselage, vertical and horizontal tail and wing tips and fuel system. It also manufactures the BAE Systems Hawk, Hawk, the world's most successful jet training aircraft.
Rolls-Royce Holdings, Rolls-Royce PLC is the world's second-largest aircraft engine, aero-engine manufacturer. Its engines power more than 30 types of commercial aircraft, and it has more 30,000 engines currently in service across both the civil and defence sectors. With a workforce of over 12,000 people, Derby has the largest concentration of Rolls-Royce employees in the UK. Rolls-Royce also produces low-emission power systems for ships; makes critical equipment and safety systems for the nuclear industry and powers offshore platforms and major pipelines for the oil and gas industry. The Pharmaceutical industry in the United Kingdom, pharmaceutical industry plays an important role in the economy, and the UK has the third-highest share of global pharmaceutical R&D expenditures.
Much of the UK's space industry is centred on EADS Astrium, based in Stevenage and Portsmouth. The company builds the Satellite bus, buses ã the underlying structure onto which the payload and propulsion systems are built ã for most of the European Space Agency's spacecraft, as well as commercial satellites. The world leader in compact satellite systems, Surrey Satellite Technology, is also part of Astrium. Reaction Engines Limited, the company planning to build Skylon (spacecraft), Skylon, a single-stage-to-orbit spaceplane using their SABRE (rocket engine), SABRE rocket engine, a combined-cycle, air-breathing rocket propulsion system is based Culham. The UK space industry was worth ôÈ9.1bn in 2011 and employed 29,000 people. It is growing at a rate of 7.5 per cent annually, according to its umbrella organisation, the UK Space Agency. In 2013, the British Government pledged ôÈ60 million to the Skylon (spacecraft), Skylon project: this investment will provide support at a "crucial stage" to allow a full-scale prototype of the SABRE (rocket engine), SABRE engine to be built.
Agriculture is intensive, highly mechanised and efficient by European standards, producing 60% of food needs with only 2% of the labour force. Two-thirds of production is devoted to livestock, the other to arable crops. The main crops that are grown are wheat, barley, oats, potatoes, sugar beets. England retains a significant, though much reduced fishing industry. Its fleets bring home fish of every kind, ranging from Sole (fish), sole to herring. It is also rich in natural resources including coal, petroleum, natural gas, tin, limestone, iron ore, salt, clay, chalk, gypsum, lead, and silica.
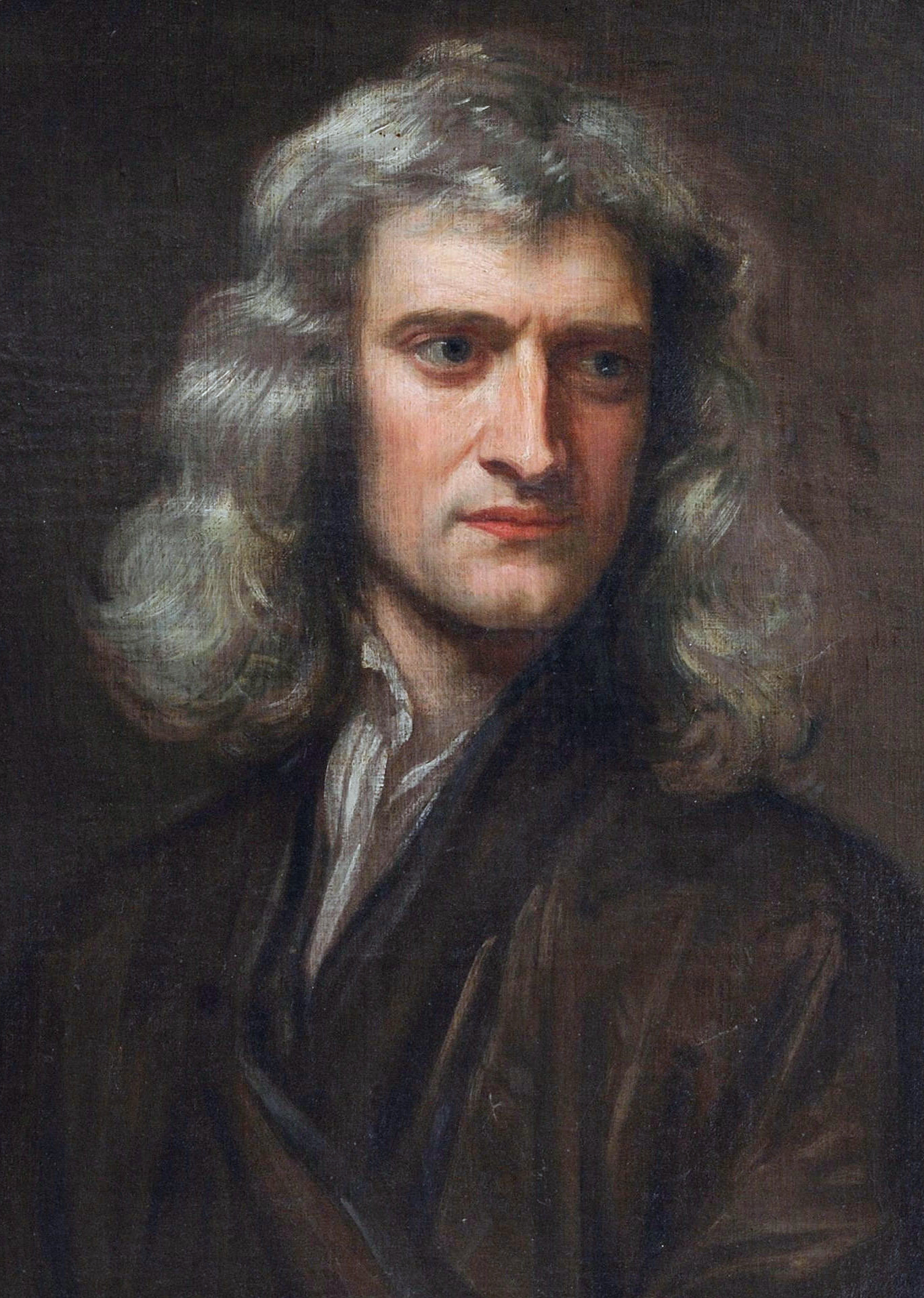 Prominent English figures from the field of science and mathematics include Sir Isaac Newton, Michael Faraday, Charles Darwin, Robert Hooke, James Prescott Joule, John Dalton, Lord Rayleigh, J. J. Thomson, James Chadwick, Charles Babbage, George Boole, Alan Turing, Tim Berners-Lee, Paul Dirac, Stephen Hawking, Peter Higgs, Roger Penrose, John Horton Conway, Thomas Bayes, Arthur Cayley, G. H. Hardy, Oliver Heaviside, Andrew Wiles, Edward Jenner, Francis Crick, Joseph Lister, 1st Baron Lister, Joseph Lister, Joseph Priestley, Thomas Young (scientist), Thomas Young, Christopher Wren and Richard Dawkins. Some experts claim that the earliest concept of a metric system was invented by John Wilkins, the first secretary of the Royal Society, in 1668.
England was a leading centre of the Scientific Revolution from the 17th century. As the birthplace of the
Prominent English figures from the field of science and mathematics include Sir Isaac Newton, Michael Faraday, Charles Darwin, Robert Hooke, James Prescott Joule, John Dalton, Lord Rayleigh, J. J. Thomson, James Chadwick, Charles Babbage, George Boole, Alan Turing, Tim Berners-Lee, Paul Dirac, Stephen Hawking, Peter Higgs, Roger Penrose, John Horton Conway, Thomas Bayes, Arthur Cayley, G. H. Hardy, Oliver Heaviside, Andrew Wiles, Edward Jenner, Francis Crick, Joseph Lister, 1st Baron Lister, Joseph Lister, Joseph Priestley, Thomas Young (scientist), Thomas Young, Christopher Wren and Richard Dawkins. Some experts claim that the earliest concept of a metric system was invented by John Wilkins, the first secretary of the Royal Society, in 1668.
England was a leading centre of the Scientific Revolution from the 17th century. As the birthplace of the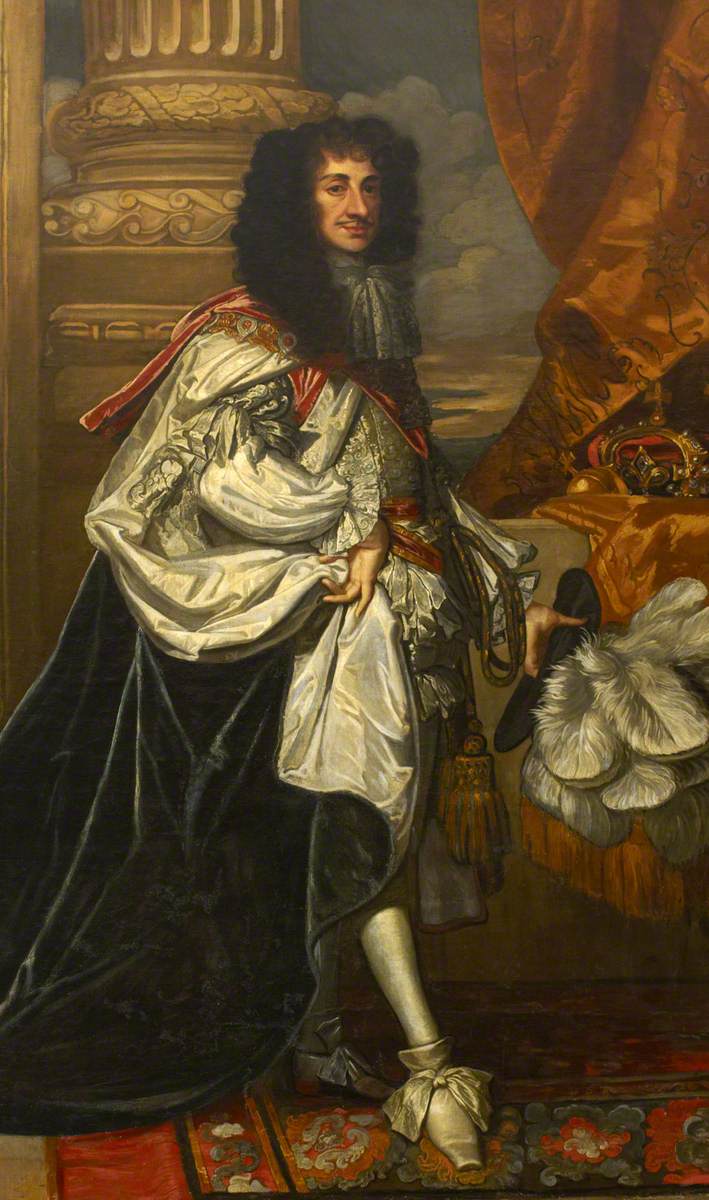  Inventions and discoveries of the English include: the jet engine, the first industrial spinning frame, spinning machine, Analytical engine, the first computer and the first Manchester Baby, modern computer, the World Wide Web along with HTML, the first successful human blood transfusion, the motorised vacuum cleaner, the lawn mower, the seat belt, the hovercraft, the electric motor, steam engines, and theories such as the Darwinian theory of evolution and atomic theory. Newton developed the ideas of universal gravitation, Newtonian mechanics, and calculus, and Robert Hooke his eponymously named Hooke's law of elasticity, law of elasticity. Other inventions include the iron plate railway, the thermosiphon, Tarmacadam, tarmac, the rubber band, the mousetrap, Cat's eye (road), "cat's eye" raised pavement marker, road marker, joint development of the light bulb, steam locomotives, the modern seed drill and many modern techniques and technologies used in precision engineering.
The Royal Society, formally The Royal Society of London for Improving Natural Knowledge, is a learned society and the
Inventions and discoveries of the English include: the jet engine, the first industrial spinning frame, spinning machine, Analytical engine, the first computer and the first Manchester Baby, modern computer, the World Wide Web along with HTML, the first successful human blood transfusion, the motorised vacuum cleaner, the lawn mower, the seat belt, the hovercraft, the electric motor, steam engines, and theories such as the Darwinian theory of evolution and atomic theory. Newton developed the ideas of universal gravitation, Newtonian mechanics, and calculus, and Robert Hooke his eponymously named Hooke's law of elasticity, law of elasticity. Other inventions include the iron plate railway, the thermosiphon, Tarmacadam, tarmac, the rubber band, the mousetrap, Cat's eye (road), "cat's eye" raised pavement marker, road marker, joint development of the light bulb, steam locomotives, the modern seed drill and many modern techniques and technologies used in precision engineering.
The Royal Society, formally The Royal Society of London for Improving Natural Knowledge, is a learned society and the
 The Department for Transport is the government body responsible for overseeing transport in England. The department is run by the Secretary of State for Transport.
England has a dense and modern transportation infrastructure. There are many List of motorways in the United Kingdom, motorways in England, and many other trunk roads, such as the A1 road (Great Britain), A1 Great North Road, which runs through eastern England from London to Newcastle (much of this section is motorway) and onward to the Scottish border. The longest motorway in England is the M6 motorway, M6, from Rugby, Warwickshire, Rugby through the
The Department for Transport is the government body responsible for overseeing transport in England. The department is run by the Secretary of State for Transport.
England has a dense and modern transportation infrastructure. There are many List of motorways in the United Kingdom, motorways in England, and many other trunk roads, such as the A1 road (Great Britain), A1 Great North Road, which runs through eastern England from London to Newcastle (much of this section is motorway) and onward to the Scottish border. The longest motorway in England is the M6 motorway, M6, from Rugby, Warwickshire, Rugby through the  Great British Railways is a planned State ownership, state-owned public body that will oversee rail transport in Great Britain from 2023. The Office of Rail and Road is responsible for the economic and safety regulation of England's railways.
Rail transport in Great Britain, Rail transport in England is the oldest in the world: passenger railways originated in England in 1825. Much of Britain's of rail network lies in England, covering the country fairly extensively, although a high proportion of railway lines were closed in the second half of the 20th century. There are plans to reopen lines such as the Varsity Line between Oxford and Cambridge. These lines are mostly standard gauge (single track (rail), single, double track, double or quadruple track) though there are also a few British narrow gauge railways, narrow gauge lines. There is rail transport access to France and Belgium through an undersea rail link, the Channel Tunnel, which was completed in 1994.
Crossrail was Europe's largest construction project with a ôÈ15 billion projected cost, opened in 2022. High Speed 2, a new high-speed northãsouth railway line, projected in 2015 to cost ôÈ56 billion is to start being built in 2020.
England has extensive domestic and international aviation links. The largest airport is Heathrow Airport, Heathrow, which is the World's busiest airports by international passenger traffic, world's busiest airport measured by number of international passengers. Other large airports include Gatwick Airport, Gatwick, Manchester Airport, Manchester, Stansted Airport, Stansted, Luton Airport, Luton and Birmingham Airport, Birmingham.
By sea there is ferry transport, both local and international, including from Liverpool to Ireland and the Isle of Man, and Hull to the Netherlands and Belgium.. There are around of navigable waterways in England, half of which is owned by the Canal & River Trust, however, water transport is very limited. The River Thames is the major waterway in England, with imports and exports focused at the Port of Tilbury in the Thames Estuary, one of the United Kingdom's three major ports.
Great British Railways is a planned State ownership, state-owned public body that will oversee rail transport in Great Britain from 2023. The Office of Rail and Road is responsible for the economic and safety regulation of England's railways.
Rail transport in Great Britain, Rail transport in England is the oldest in the world: passenger railways originated in England in 1825. Much of Britain's of rail network lies in England, covering the country fairly extensively, although a high proportion of railway lines were closed in the second half of the 20th century. There are plans to reopen lines such as the Varsity Line between Oxford and Cambridge. These lines are mostly standard gauge (single track (rail), single, double track, double or quadruple track) though there are also a few British narrow gauge railways, narrow gauge lines. There is rail transport access to France and Belgium through an undersea rail link, the Channel Tunnel, which was completed in 1994.
Crossrail was Europe's largest construction project with a ôÈ15 billion projected cost, opened in 2022. High Speed 2, a new high-speed northãsouth railway line, projected in 2015 to cost ôÈ56 billion is to start being built in 2020.
England has extensive domestic and international aviation links. The largest airport is Heathrow Airport, Heathrow, which is the World's busiest airports by international passenger traffic, world's busiest airport measured by number of international passengers. Other large airports include Gatwick Airport, Gatwick, Manchester Airport, Manchester, Stansted Airport, Stansted, Luton Airport, Luton and Birmingham Airport, Birmingham.
By sea there is ferry transport, both local and international, including from Liverpool to Ireland and the Isle of Man, and Hull to the Netherlands and Belgium.. There are around of navigable waterways in England, half of which is owned by the Canal & River Trust, however, water transport is very limited. The River Thames is the major waterway in England, with imports and exports focused at the Port of Tilbury in the Thames Estuary, one of the United Kingdom's three major ports.
 Energy use in the
Energy use in the
 English Heritage is a governmental body with a broad remit of managing the historic sites, artefacts and environments of England. It is currently sponsored by the Department for Culture, Media and Sport, Department for Digital, Culture, Media and Sport.
The National Trust for Places of Historic Interest or Natural Beauty is a charity which also maintains multiple sites. Of the 25 United Kingdom List of World Heritage Sites in the United Kingdom, UNESCO World Heritage Sites, 17 are in England.
Some of the best known of these include Stonehenge, Avebury and Associated Sites, Tower of London, Jurassic Coast, Palace of Westminster, Roman Baths (Bath), Roman Baths, Bath, Somerset, City of Bath, Saltaire, Ironbridge Gorge, Studley Royal Park and more recently the Lake District, English Lake District. The northernmost point of the Roman Empire, Hadrian's Wall, is the largest Roman artefact anywhere: it runs for a total of in northern England.
The Secretary of State for Digital, Culture, Media and Sport has overall responsibility for tourism, arts and culture, cultural property, heritage and historic environments, libraries, and museums and galleries. The Parliamentary Under Secretary of State for Arts, Heritage and Tourism is the minister with responsibility over tourism in England.
A blue plaque, the oldest historical marker scheme in the world, is a permanent sign installed in a public place in England to commemorate a link between that location and a famous person or event. The scheme was the brainchild of politician William Ewart (British politician), William Ewart in 1863 and was initiated in 1866. It was formally established by the Royal Society of Arts in 1867, and since 1986 has been run by English Heritage. In 2011 there were around 1,600 museums in England. Entry to most state-supported museums and galleries is free unlike in other countries.
English Heritage is a governmental body with a broad remit of managing the historic sites, artefacts and environments of England. It is currently sponsored by the Department for Culture, Media and Sport, Department for Digital, Culture, Media and Sport.
The National Trust for Places of Historic Interest or Natural Beauty is a charity which also maintains multiple sites. Of the 25 United Kingdom List of World Heritage Sites in the United Kingdom, UNESCO World Heritage Sites, 17 are in England.
Some of the best known of these include Stonehenge, Avebury and Associated Sites, Tower of London, Jurassic Coast, Palace of Westminster, Roman Baths (Bath), Roman Baths, Bath, Somerset, City of Bath, Saltaire, Ironbridge Gorge, Studley Royal Park and more recently the Lake District, English Lake District. The northernmost point of the Roman Empire, Hadrian's Wall, is the largest Roman artefact anywhere: it runs for a total of in northern England.
The Secretary of State for Digital, Culture, Media and Sport has overall responsibility for tourism, arts and culture, cultural property, heritage and historic environments, libraries, and museums and galleries. The Parliamentary Under Secretary of State for Arts, Heritage and Tourism is the minister with responsibility over tourism in England.
A blue plaque, the oldest historical marker scheme in the world, is a permanent sign installed in a public place in England to commemorate a link between that location and a famous person or event. The scheme was the brainchild of politician William Ewart (British politician), William Ewart in 1863 and was initiated in 1866. It was formally established by the Royal Society of Arts in 1867, and since 1986 has been run by English Heritage. In 2011 there were around 1,600 museums in England. Entry to most state-supported museums and galleries is free unlike in other countries.
 The National Health Service (England), National Health Service (NHS), is the publicly funded healthcare system responsible for providing the majority of healthcare in the country. The NHS began on 5 July 1948, putting into effect the provisions of the National Health Service Act 1946. It was based on the findings of the Beveridge Report, prepared by economist and social reformer William Beveridge. The NHS is largely funded from general taxation including National Insurance payments, and it provides most of its services free at the point of use, although there are charges for some people for eye tests, dental care, prescriptions and aspects of personal care.
The government department responsible for the NHS is the Department of Health (United Kingdom), Department of Health, headed by the Secretary of State for Health, who sits in the Cabinet of the United Kingdom, British Cabinet. Most of the expenditure of the Department of Health is spent on the NHSãôÈ98.6 billion was spent in 2008ã2009. In recent years the private sector has been increasingly used to provide more NHS services despite opposition by doctors and trade unions.
When purchasing drugs, the NHS has significant market power that, based on its own assessment of the fair value of the drugs, influences the global price, typically keeping prices lower. Several other countries either copy the UK's model or directly rely on its assessments for their own decisions on state-financed drug reimbursements. Regulatory bodies such as the General Medical Council and the Nursing and Midwifery Council are organised on a UK-wide basis, as are non-governmental bodies such as the Royal Colleges.
The average life expectancy of people in England is 77.5 years for males and 81.7 years for females, the highest of the four countries of the United Kingdom. The South of England has a higher life expectancy than the North; however, regional differences do seem to be slowly narrowing: between 1991ã1993 and 2012ã2014, life expectancy in the North East increased by 6.0 years and in the North West by 5.8 years, the fastest increase in any region outside London, and the gap between life expectancy in the North East and South East is now 2.5 years, down from 2.9 in 1993.
The National Health Service (England), National Health Service (NHS), is the publicly funded healthcare system responsible for providing the majority of healthcare in the country. The NHS began on 5 July 1948, putting into effect the provisions of the National Health Service Act 1946. It was based on the findings of the Beveridge Report, prepared by economist and social reformer William Beveridge. The NHS is largely funded from general taxation including National Insurance payments, and it provides most of its services free at the point of use, although there are charges for some people for eye tests, dental care, prescriptions and aspects of personal care.
The government department responsible for the NHS is the Department of Health (United Kingdom), Department of Health, headed by the Secretary of State for Health, who sits in the Cabinet of the United Kingdom, British Cabinet. Most of the expenditure of the Department of Health is spent on the NHSãôÈ98.6 billion was spent in 2008ã2009. In recent years the private sector has been increasingly used to provide more NHS services despite opposition by doctors and trade unions.
When purchasing drugs, the NHS has significant market power that, based on its own assessment of the fair value of the drugs, influences the global price, typically keeping prices lower. Several other countries either copy the UK's model or directly rely on its assessments for their own decisions on state-financed drug reimbursements. Regulatory bodies such as the General Medical Council and the Nursing and Midwifery Council are organised on a UK-wide basis, as are non-governmental bodies such as the Royal Colleges.
The average life expectancy of people in England is 77.5 years for males and 81.7 years for females, the highest of the four countries of the United Kingdom. The South of England has a higher life expectancy than the North; however, regional differences do seem to be slowly narrowing: between 1991ã1993 and 2012ã2014, life expectancy in the North East increased by 6.0 years and in the North West by 5.8 years, the fastest increase in any region outside London, and the gap between life expectancy in the North East and South East is now 2.5 years, down from 2.9 in 1993.
 With over 53 million inhabitants, England is by far the most populous country of the United Kingdom, accounting for 84% of the combined total. England taken as a unit and measured against international states would be the 25th largest List of countries by population in 2005, country by population in the world.
The English people are British people. Some genetic evidence suggests that 75ã95% descend in the paternal line from prehistoric settlers who originally came from the
With over 53 million inhabitants, England is by far the most populous country of the United Kingdom, accounting for 84% of the combined total. England taken as a unit and measured against international states would be the 25th largest List of countries by population in 2005, country by population in the world.
The English people are British people. Some genetic evidence suggests that 75ã95% descend in the paternal line from prehistoric settlers who originally came from the
 In the 2011 census, 59.4% of the population of England specified their religion as Christian, 24.7% answered that they had no religion, 5% specified that they were Muslim, while 3.7% of the population belongs to other religions and 7.2% did not give an answer. Christianity is the most widely practised religion in England, as it has been since the Early Middle Ages, although it was first introduced much earlier in Gaelic and Roman times. This Celtic Church was gradually joined to the Roman Catholic Church, Catholic hierarchy following the 6th-century Gregorian mission to
In the 2011 census, 59.4% of the population of England specified their religion as Christian, 24.7% answered that they had no religion, 5% specified that they were Muslim, while 3.7% of the population belongs to other religions and 7.2% did not give an answer. Christianity is the most widely practised religion in England, as it has been since the Early Middle Ages, although it was first introduced much earlier in Gaelic and Roman times. This Celtic Church was gradually joined to the Roman Catholic Church, Catholic hierarchy following the 6th-century Gregorian mission to  The 2nd-largest Christian practice is the Latin Rite of the Catholic Church. Since its reintroduction after the Catholic Emancipation, the Church has organised ecclesiastically on an Roman Catholic Church in England and Wales, England and Wales basis where there are 4.5 million members (most of whom are English). There has been one Pope from England to date, Pope Adrian IV, Adrian IV; while saints
The 2nd-largest Christian practice is the Latin Rite of the Catholic Church. Since its reintroduction after the Catholic Emancipation, the Church has organised ecclesiastically on an Roman Catholic Church in England and Wales, England and Wales basis where there are 4.5 million members (most of whom are English). There has been one Pope from England to date, Pope Adrian IV, Adrian IV; while saints
 The Department for Education is the government department responsible for issues affecting people in England up to the age of 19, including education. State-run and state-funded schools are attended by approximately 93% of English schoolchildren. Education is the responsibility of the Secretary of State for Education.
Children who are between the ages of 3 and 5 attend nursery or an Early Years Foundation Stage reception unit within a primary school. Children between the ages of 5 and 11 attend primary school, and secondary school is attended by those aged between 11 and 16. State-funded schools are obliged by law to teach the National Curriculum for England, National Curriculum; basic areas of learning include English literature, English language, mathematics, science, art & design, citizenship, history, geography, religious education, design & technology, computing, ancient & modern languages, music, and physical education.
More than 90% of English schools require students to wear uniforms. School uniforms are defined by individual schools, within the constraint that uniform regulations must not discriminate on the grounds of sex, race, disability, sexual orientation, gender reassignment, religion or belief. Schools may choose to permit trousers for girls or religious dress.
The Programme for International Student Assessment coordinated by the OECD currently ranks the overall knowledge and skills of British 15-year-olds as 13th in the world in reading literacy, mathematics, and science with the average British student scoring 503.7, compared with the OECD average of 493, ahead of the United States and most of Europe.
Although most English secondary schools are comprehensive school, comprehensive, there are selective intake grammar schools to which entrance is subject to passing the eleven-plus exam. Around 7.2 per cent of English schoolchildren attend Independent school (UK), private schools, which are funded by private sources. Standards in state schools are monitored by the Office for Standards in Education, and in private schools by the Independent Schools Inspectorate.
After finishing compulsory education, students take General Certificate of Secondary Education, GCSE examinations. Students may then opt to continue into further education for two years. List of further education colleges in England, Further education colleges (particularly sixth form colleges) often form part of a secondary school site. A-level examinations are sat by a large number of further education students, and often form the basis of an application to university. Further education (FE) covers a wide curriculum of study and apprenticeships, including T Level, T-levels, BTEC Extended Diploma, BTEC, NVQ and others. Tertiary colleges provide both academic and vocational courses.
Higher education students normally attend university from age 18 onwards, where they study for an academic degree. There are over 90 universities in England, all but one of which are Public university, public institutions. The Department for Business, Innovation and Skills is the government department responsible for higher education in England. Students are generally entitled to student loans to cover the cost of tuition fees and living costs. The first degree offered to undergraduates is the bachelor's degree, which usually takes three years to complete. Students are then able to work towards a postgraduate degree, which usually takes one year, or towards a doctorate, which takes three or more years.
List of universities in England, England's universities include some of the highest-ranked universities in the world; University of Cambridge, University of Oxford, Imperial College London, University College London and King's College London are all ranked in the global top 30 in the 2018 ''QS World University Rankings''. The London School of Economics has been described as the world's leading social science institution for both teaching and research. The London Business School is considered one of the world's leading business schools and in 2010 its MBA programme was ranked best in the world by the ''Financial Times''. Academic degrees in England are usually split into classes: first class (1st), upper second class (2:1), lower second class (2:2), third (3rd), and unclassified.
The King's School, Canterbury and King's School, Rochester are the oldest schools in the English-speaking world. Many of England's most well-known schools, such as Winchester College, Eton College, Eton, St Paul's School (London), St Paul's School, Harrow School and Rugby School are fee-paying institutions.
The Department for Education is the government department responsible for issues affecting people in England up to the age of 19, including education. State-run and state-funded schools are attended by approximately 93% of English schoolchildren. Education is the responsibility of the Secretary of State for Education.
Children who are between the ages of 3 and 5 attend nursery or an Early Years Foundation Stage reception unit within a primary school. Children between the ages of 5 and 11 attend primary school, and secondary school is attended by those aged between 11 and 16. State-funded schools are obliged by law to teach the National Curriculum for England, National Curriculum; basic areas of learning include English literature, English language, mathematics, science, art & design, citizenship, history, geography, religious education, design & technology, computing, ancient & modern languages, music, and physical education.
More than 90% of English schools require students to wear uniforms. School uniforms are defined by individual schools, within the constraint that uniform regulations must not discriminate on the grounds of sex, race, disability, sexual orientation, gender reassignment, religion or belief. Schools may choose to permit trousers for girls or religious dress.
The Programme for International Student Assessment coordinated by the OECD currently ranks the overall knowledge and skills of British 15-year-olds as 13th in the world in reading literacy, mathematics, and science with the average British student scoring 503.7, compared with the OECD average of 493, ahead of the United States and most of Europe.
Although most English secondary schools are comprehensive school, comprehensive, there are selective intake grammar schools to which entrance is subject to passing the eleven-plus exam. Around 7.2 per cent of English schoolchildren attend Independent school (UK), private schools, which are funded by private sources. Standards in state schools are monitored by the Office for Standards in Education, and in private schools by the Independent Schools Inspectorate.
After finishing compulsory education, students take General Certificate of Secondary Education, GCSE examinations. Students may then opt to continue into further education for two years. List of further education colleges in England, Further education colleges (particularly sixth form colleges) often form part of a secondary school site. A-level examinations are sat by a large number of further education students, and often form the basis of an application to university. Further education (FE) covers a wide curriculum of study and apprenticeships, including T Level, T-levels, BTEC Extended Diploma, BTEC, NVQ and others. Tertiary colleges provide both academic and vocational courses.
Higher education students normally attend university from age 18 onwards, where they study for an academic degree. There are over 90 universities in England, all but one of which are Public university, public institutions. The Department for Business, Innovation and Skills is the government department responsible for higher education in England. Students are generally entitled to student loans to cover the cost of tuition fees and living costs. The first degree offered to undergraduates is the bachelor's degree, which usually takes three years to complete. Students are then able to work towards a postgraduate degree, which usually takes one year, or towards a doctorate, which takes three or more years.
List of universities in England, England's universities include some of the highest-ranked universities in the world; University of Cambridge, University of Oxford, Imperial College London, University College London and King's College London are all ranked in the global top 30 in the 2018 ''QS World University Rankings''. The London School of Economics has been described as the world's leading social science institution for both teaching and research. The London Business School is considered one of the world's leading business schools and in 2010 its MBA programme was ranked best in the world by the ''Financial Times''. Academic degrees in England are usually split into classes: first class (1st), upper second class (2:1), lower second class (2:2), third (3rd), and unclassified.
The King's School, Canterbury and King's School, Rochester are the oldest schools in the English-speaking world. Many of England's most well-known schools, such as Winchester College, Eton College, Eton, St Paul's School (London), St Paul's School, Harrow School and Rugby School are fee-paying institutions.
 Many ancient standing stone monuments were erected during the prehistoric period; amongst the best known are
Many ancient standing stone monuments were erected during the prehistoric period; amongst the best known are  Throughout the Plantagenet era, an English Gothic architecture flourished, with prime examples including the Architecture of the medieval cathedrals of England, medieval cathedrals such as Canterbury Cathedral, Westminster Abbey and York Minster.. Expanding on the Norman architecture, Norman base there was also castles, palaces, List of historic houses in England, great houses, universities and parish churches. Medieval architecture was completed with the 16th-century Tudor architecture, Tudor style; the four-centred arch, now known as the Tudor arch, was a defining feature as were wattle and daub houses domestically. In the aftermath of the
Throughout the Plantagenet era, an English Gothic architecture flourished, with prime examples including the Architecture of the medieval cathedrals of England, medieval cathedrals such as Canterbury Cathedral, Westminster Abbey and York Minster.. Expanding on the Norman architecture, Norman base there was also castles, palaces, List of historic houses in England, great houses, universities and parish churches. Medieval architecture was completed with the 16th-century Tudor architecture, Tudor style; the four-centred arch, now known as the Tudor arch, was a defining feature as were wattle and daub houses domestically. In the aftermath of the
 Landscape gardening, as developed by Capability Brown, set an international trend for the English garden. Gardening, and visiting gardens, are regarded as typically English pursuits. The English garden presented an idealized view of nature. At large country houses, the English garden usually included lakes, sweeps of gently rolling lawns set against groves of trees, and recreations of classical temples, Gothic architecture, Gothic ruins, bridges, and other picturesque architecture, designed to recreate an idyllic pastoral landscape.
By the end of the 18th century, the English garden was being imitated by the French landscape garden, and as far away as St. Petersburg, Russia, in Pavlovsk, Saint Petersburg, Pavlovsk, the gardens of the future Emperor Paul. It also had a major influence on the form of the public parks and gardens which appeared around the world in the 19th century. The English landscape garden was centred on the English country house and manor houses.
English Heritage and the National Trust preserve great gardens and landscape parks throughout the country. The RHS Chelsea Flower Show is held every year by the Royal Horticultural Society and is said to be the largest gardening show in the world.
Landscape gardening, as developed by Capability Brown, set an international trend for the English garden. Gardening, and visiting gardens, are regarded as typically English pursuits. The English garden presented an idealized view of nature. At large country houses, the English garden usually included lakes, sweeps of gently rolling lawns set against groves of trees, and recreations of classical temples, Gothic architecture, Gothic ruins, bridges, and other picturesque architecture, designed to recreate an idyllic pastoral landscape.
By the end of the 18th century, the English garden was being imitated by the French landscape garden, and as far away as St. Petersburg, Russia, in Pavlovsk, Saint Petersburg, Pavlovsk, the gardens of the future Emperor Paul. It also had a major influence on the form of the public parks and gardens which appeared around the world in the 19th century. The English landscape garden was centred on the English country house and manor houses.
English Heritage and the National Trust preserve great gardens and landscape parks throughout the country. The RHS Chelsea Flower Show is held every year by the Royal Horticultural Society and is said to be the largest gardening show in the world.
 English folklore developed over many centuries. Some of the characters and stories are present across England, but most belong to specific regions. Common folkloric beings include pixies, giant (mythology), giants, elf, elves, bogeymen, trolls, goblins and dwarf (mythology), dwarves. While many legends and folk-customs are thought to be ancient, such as the tales featuring Offa of Angel and Wayland the Smith,. others date from after the Norman invasion. The legends featuring Robin Hood and his Merry Men of Sherwood Forest, Sherwood, and their battles with the Sheriff of Nottingham, are among the best-known of these.
During the High Middle Ages tales originating from Brythonic traditions entered English folklore and developed into the Arthurian myth.. These were derived from Anglo-Norman language, Anglo-Norman, Welsh and French sources, featuring King Arthur, Camelot, Excalibur, Merlin and the Knights of the Round Table such as Lancelot. These stories are most centrally brought together within Geoffrey of Monmouth's ''Historia Regum Britanniae'' (''History of the Kings of Britain''). Another early figure from Britons (historic), British tradition, King Cole, may have been based on a real figure from Sub-Roman Britain. Many of the tales and pseudohistory, pseudo-histories make up part of the wider Matter of Britain, a collection of shared British folklore.
Some folk figures are based on semi or actual historical people whose story has been passed down centuries; Lady Godiva for instance was said to have ridden naked on horseback through Coventry, Hereward the Wake was a heroic English figure resisting the Norman invasion, Herne the Hunter is an equestrianism, equestrian ghost associated with Windsor, Berkshire, Windsor Forest and Windsor Great Park, Great Park and Mother Shipton is the archetypal witch. On 5 November people make bonfires, set off fireworks and eat toffee apples in Guy Fawkes Night, commemoration of the foiling of the Gunpowder Plot centred on Guy Fawkes. The chivalrous bandit, such as Dick Turpin, is a recurring character, while Blackbeard is the archetypal pirate. There are various national and regional folk activities, participated in to this day, such as Morris dancing, Maypole dance, Maypole dancing, Rapper sword in the North East, Long Sword dance in Yorkshire, Mummers Plays, bottle-kicking in Leicestershire, and Cooper's Hill Cheese-Rolling and Wake, cheese-rolling at Brockworth, Gloucestershire, Cooper's Hill. There is no official national costume, but a few are well established such as the Pearly Kings and Queens associated with cockneys, the Queen's Guard, Royal Guard, the Morris dance, Morris costume and Beefeaters.
English folklore developed over many centuries. Some of the characters and stories are present across England, but most belong to specific regions. Common folkloric beings include pixies, giant (mythology), giants, elf, elves, bogeymen, trolls, goblins and dwarf (mythology), dwarves. While many legends and folk-customs are thought to be ancient, such as the tales featuring Offa of Angel and Wayland the Smith,. others date from after the Norman invasion. The legends featuring Robin Hood and his Merry Men of Sherwood Forest, Sherwood, and their battles with the Sheriff of Nottingham, are among the best-known of these.
During the High Middle Ages tales originating from Brythonic traditions entered English folklore and developed into the Arthurian myth.. These were derived from Anglo-Norman language, Anglo-Norman, Welsh and French sources, featuring King Arthur, Camelot, Excalibur, Merlin and the Knights of the Round Table such as Lancelot. These stories are most centrally brought together within Geoffrey of Monmouth's ''Historia Regum Britanniae'' (''History of the Kings of Britain''). Another early figure from Britons (historic), British tradition, King Cole, may have been based on a real figure from Sub-Roman Britain. Many of the tales and pseudohistory, pseudo-histories make up part of the wider Matter of Britain, a collection of shared British folklore.
Some folk figures are based on semi or actual historical people whose story has been passed down centuries; Lady Godiva for instance was said to have ridden naked on horseback through Coventry, Hereward the Wake was a heroic English figure resisting the Norman invasion, Herne the Hunter is an equestrianism, equestrian ghost associated with Windsor, Berkshire, Windsor Forest and Windsor Great Park, Great Park and Mother Shipton is the archetypal witch. On 5 November people make bonfires, set off fireworks and eat toffee apples in Guy Fawkes Night, commemoration of the foiling of the Gunpowder Plot centred on Guy Fawkes. The chivalrous bandit, such as Dick Turpin, is a recurring character, while Blackbeard is the archetypal pirate. There are various national and regional folk activities, participated in to this day, such as Morris dancing, Maypole dance, Maypole dancing, Rapper sword in the North East, Long Sword dance in Yorkshire, Mummers Plays, bottle-kicking in Leicestershire, and Cooper's Hill Cheese-Rolling and Wake, cheese-rolling at Brockworth, Gloucestershire, Cooper's Hill. There is no official national costume, but a few are well established such as the Pearly Kings and Queens associated with cockneys, the Queen's Guard, Royal Guard, the Morris dance, Morris costume and Beefeaters.
 Since the early modern period the food of England has historically been characterised by its simplicity of approach and a reliance on the high quality of natural produce. During the Middle Ages and through the Renaissance period, English cuisine enjoyed an excellent reputation, though a decline began during the
Since the early modern period the food of England has historically been characterised by its simplicity of approach and a reliance on the high quality of natural produce. During the Middle Ages and through the Renaissance period, English cuisine enjoyed an excellent reputation, though a decline began during the
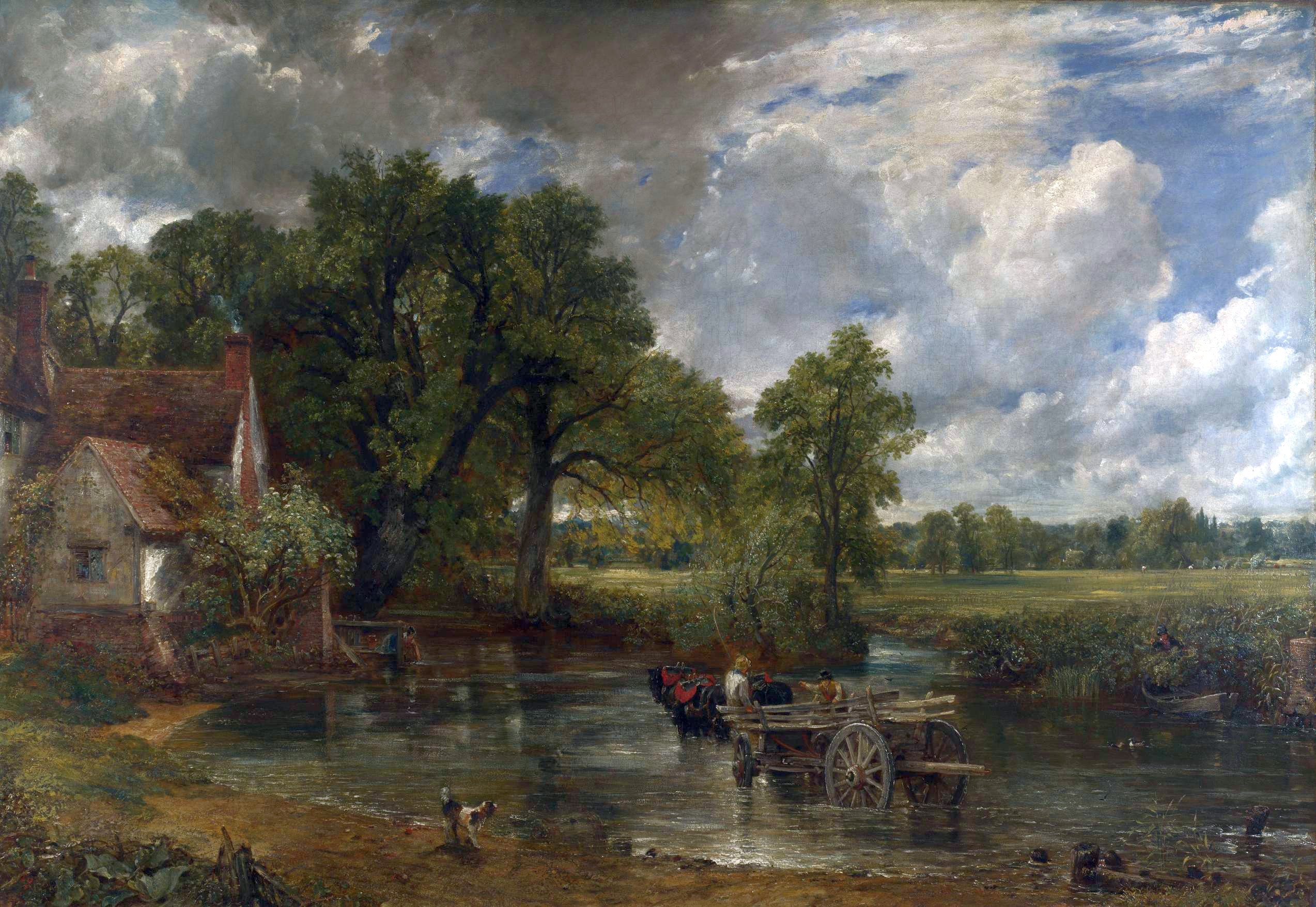 The earliest known examples are the prehistoric rock and cave art pieces, most prominent in North Yorkshire, Northumberland and Cumbria, but also feature further south, for example at Creswell Crags. With the arrival of Roman culture in the 1st century, various forms of art such as statues, busts, glasswork and mosaics were the norm. There are numerous surviving artefacts, such as those at Lullingstone Roman Villa, Lullingstone and Isurium Brigantum, Aldborough. During the Early Middle Ages the style favoured sculpted crosses and ivories, manuscript painting, gold and enamel jewellery, demonstrating a love of intricate, interwoven designs such as in the Staffordshire Hoard discovered in 2009. Some of these blended Insular art, Gaelic and Anglian styles, such as the Lindisfarne Gospels and Vespasian Psalter. Later Gothic art was popular at Winchester and Canterbury, examples survive such as Benedictional of St. ûthelwold and Luttrell Psalter.
The Tudor era saw Artists of the Tudor court, prominent artists as part of their court, portrait painting which would remain an enduring part of English art, was boosted by German Hans Holbein the Younger, Hans Holbein, natives such as Nicholas Hilliard built on this. Under the Stuarts, Continental artists were influential especially the Flemish, examples from the period include Anthony van Dyck, Peter Lely, Godfrey Kneller and William Dobson. The 18th century was a time of significance with the founding of the Royal Academy, a classicism based on the Renaissance art, High Renaissance prevailed, with Thomas Gainsborough and Joshua Reynolds becoming two of England's most treasured artists.
In the 19th century, John Constable, Constable and J.M.W. Turner, Turner were major landscape artists. The Norwich School (art movement), Norwich School continued the landscape tradition, while the Pre-Raphaelite Brotherhood, led by artists such as Holman Hunt, Dante Gabriel Rossetti and John Everett Millais, revived the Early Renaissance style with their vivid and detailed style. Prominent amongst 20th-century artists was Henry Moore, regarded as the voice of British sculpture, and of British modernism in general. More recent painters include Lucian Freud, whose work ''Benefits Supervisor Sleeping'' in 2008 set a world record for sale value of a painting by a then-living artist. The Royal Society of Arts is an organisation committed to the arts and culture.
The earliest known examples are the prehistoric rock and cave art pieces, most prominent in North Yorkshire, Northumberland and Cumbria, but also feature further south, for example at Creswell Crags. With the arrival of Roman culture in the 1st century, various forms of art such as statues, busts, glasswork and mosaics were the norm. There are numerous surviving artefacts, such as those at Lullingstone Roman Villa, Lullingstone and Isurium Brigantum, Aldborough. During the Early Middle Ages the style favoured sculpted crosses and ivories, manuscript painting, gold and enamel jewellery, demonstrating a love of intricate, interwoven designs such as in the Staffordshire Hoard discovered in 2009. Some of these blended Insular art, Gaelic and Anglian styles, such as the Lindisfarne Gospels and Vespasian Psalter. Later Gothic art was popular at Winchester and Canterbury, examples survive such as Benedictional of St. ûthelwold and Luttrell Psalter.
The Tudor era saw Artists of the Tudor court, prominent artists as part of their court, portrait painting which would remain an enduring part of English art, was boosted by German Hans Holbein the Younger, Hans Holbein, natives such as Nicholas Hilliard built on this. Under the Stuarts, Continental artists were influential especially the Flemish, examples from the period include Anthony van Dyck, Peter Lely, Godfrey Kneller and William Dobson. The 18th century was a time of significance with the founding of the Royal Academy, a classicism based on the Renaissance art, High Renaissance prevailed, with Thomas Gainsborough and Joshua Reynolds becoming two of England's most treasured artists.
In the 19th century, John Constable, Constable and J.M.W. Turner, Turner were major landscape artists. The Norwich School (art movement), Norwich School continued the landscape tradition, while the Pre-Raphaelite Brotherhood, led by artists such as Holman Hunt, Dante Gabriel Rossetti and John Everett Millais, revived the Early Renaissance style with their vivid and detailed style. Prominent amongst 20th-century artists was Henry Moore, regarded as the voice of British sculpture, and of British modernism in general. More recent painters include Lucian Freud, whose work ''Benefits Supervisor Sleeping'' in 2008 set a world record for sale value of a painting by a then-living artist. The Royal Society of Arts is an organisation committed to the arts and culture.
 Early authors such as
Early authors such as
''The Guardian'' Retrieved 18 February 2011. Philip Astley is regarded as the father of the Circus#Development, modern circus."The circus comes to the Circus"
BBC News. Retrieved 13 December 2014 Following his invention of the circus ring in 1768, Astley's Amphitheatre opened in London in 1773. As an equestrian master Astley had a skill for trick horse-riding, and when he added tumblers, tightrope-walkers, jugglers, performing dogs, and a clown to fill time between his own demonstrations ã the modern circus was born. Pantomime is a British Musical theatre, musical comedy stage production, designed for family entertainment. It is performed in theatres throughout the England during the Christmas and New Year season. The art originated in the 18th century with John Weaver (dancer), John Weaver, a dance master and choreographer.David Christopher (2002). "British Culture: An Introduction". p. 74. Routledge, In 19th century England it acquired its present form, which includes songs, slapstick comedy and dancing, employing gender-crossing actors, combining topical humour with a story loosely based on a well-known fairy tale.
 England (and the UK as a whole) has had a considerable influence on the history of the cinema, producing some of the greatest actors, directors and motion pictures of all time, including Alfred Hitchcock, Charlie Chaplin, David Lean, Laurence Olivier, Vivien Leigh, John Gielgud, Peter Sellers, Julie Andrews, Michael Caine, Gary Oldman, Helen Mirren, Kate Winslet and Daniel Day-Lewis. Hitchcock and Lean are among the most critically acclaimed filmmakers. Hitchcock's first thriller, ''The Lodger: A Story of the London Fog'' (1926), helped shape the Thriller film, thriller genre in film, while his 1929 film, ''Blackmail (1929 film), Blackmail'', is often regarded as the first British Sound film#Transition: Europe, sound feature film.
Major film studios in England include Pinewood Studios, Pinewood, Elstree Studios, Elstree and Shepperton Studios, Shepperton. Some of the most commercially successful films of all time have been produced in England, including two of the List of highest-grossing film series, highest-grossing film franchises (''Harry Potter (film series), Harry Potter'' and ''James Bond (film series), James Bond''). Ealing Studios in London has a claim to being the oldest continuously working film studio in the world. Famous for recording many motion picture film scores, the London Symphony Orchestra first performed film music in 1935. The Hammer Film Productions, Hammer Horror films starring Christopher Lee saw the production of the first gory horror films showing blood and guts in colour.
The BFI Top 100 British films includes ''Monty Python's Life of Brian'' (1979), a film regularly voted the funniest of all time by the UK public. English producers are also active in international co-productions and English actors, directors and crew feature regularly in American films. The UK film council ranked David Yates, Christopher Nolan, Mike Newell (director), Mike Newell, Ridley Scott and Paul Greengrass the five most commercially successful English directors since 2001. Other contemporary English directors include Sam Mendes, Guy Ritchie and Richard Curtis. Current actors include Tom Hardy, Daniel Craig, Benedict Cumberbatch, Lena Headey, Felicity Jones, Emilia Clarke, Lashana Lynch, and Emma Watson. Acclaimed for his motion capture work, Andy Serkis opened The Imaginarium Studios in London in 2011. The visual effects company Framestore in London has produced some of the most critically acclaimed special effects in modern film. Many successful Hollywood films have been based on English people, British literature, stories or events. The List of Walt Disney Animation Studios films, 'English Cycle' of Disney animated films include ''Alice in Wonderland (1951 film), Alice in Wonderland'', ''The Jungle Book (1967 film), The Jungle Book'' and ''The Many Adventures of Winnie the Pooh, Winnie the Pooh''.
England (and the UK as a whole) has had a considerable influence on the history of the cinema, producing some of the greatest actors, directors and motion pictures of all time, including Alfred Hitchcock, Charlie Chaplin, David Lean, Laurence Olivier, Vivien Leigh, John Gielgud, Peter Sellers, Julie Andrews, Michael Caine, Gary Oldman, Helen Mirren, Kate Winslet and Daniel Day-Lewis. Hitchcock and Lean are among the most critically acclaimed filmmakers. Hitchcock's first thriller, ''The Lodger: A Story of the London Fog'' (1926), helped shape the Thriller film, thriller genre in film, while his 1929 film, ''Blackmail (1929 film), Blackmail'', is often regarded as the first British Sound film#Transition: Europe, sound feature film.
Major film studios in England include Pinewood Studios, Pinewood, Elstree Studios, Elstree and Shepperton Studios, Shepperton. Some of the most commercially successful films of all time have been produced in England, including two of the List of highest-grossing film series, highest-grossing film franchises (''Harry Potter (film series), Harry Potter'' and ''James Bond (film series), James Bond''). Ealing Studios in London has a claim to being the oldest continuously working film studio in the world. Famous for recording many motion picture film scores, the London Symphony Orchestra first performed film music in 1935. The Hammer Film Productions, Hammer Horror films starring Christopher Lee saw the production of the first gory horror films showing blood and guts in colour.
The BFI Top 100 British films includes ''Monty Python's Life of Brian'' (1979), a film regularly voted the funniest of all time by the UK public. English producers are also active in international co-productions and English actors, directors and crew feature regularly in American films. The UK film council ranked David Yates, Christopher Nolan, Mike Newell (director), Mike Newell, Ridley Scott and Paul Greengrass the five most commercially successful English directors since 2001. Other contemporary English directors include Sam Mendes, Guy Ritchie and Richard Curtis. Current actors include Tom Hardy, Daniel Craig, Benedict Cumberbatch, Lena Headey, Felicity Jones, Emilia Clarke, Lashana Lynch, and Emma Watson. Acclaimed for his motion capture work, Andy Serkis opened The Imaginarium Studios in London in 2011. The visual effects company Framestore in London has produced some of the most critically acclaimed special effects in modern film. Many successful Hollywood films have been based on English people, British literature, stories or events. The List of Walt Disney Animation Studios films, 'English Cycle' of Disney animated films include ''Alice in Wonderland (1951 film), Alice in Wonderland'', ''The Jungle Book (1967 film), The Jungle Book'' and ''The Many Adventures of Winnie the Pooh, Winnie the Pooh''.
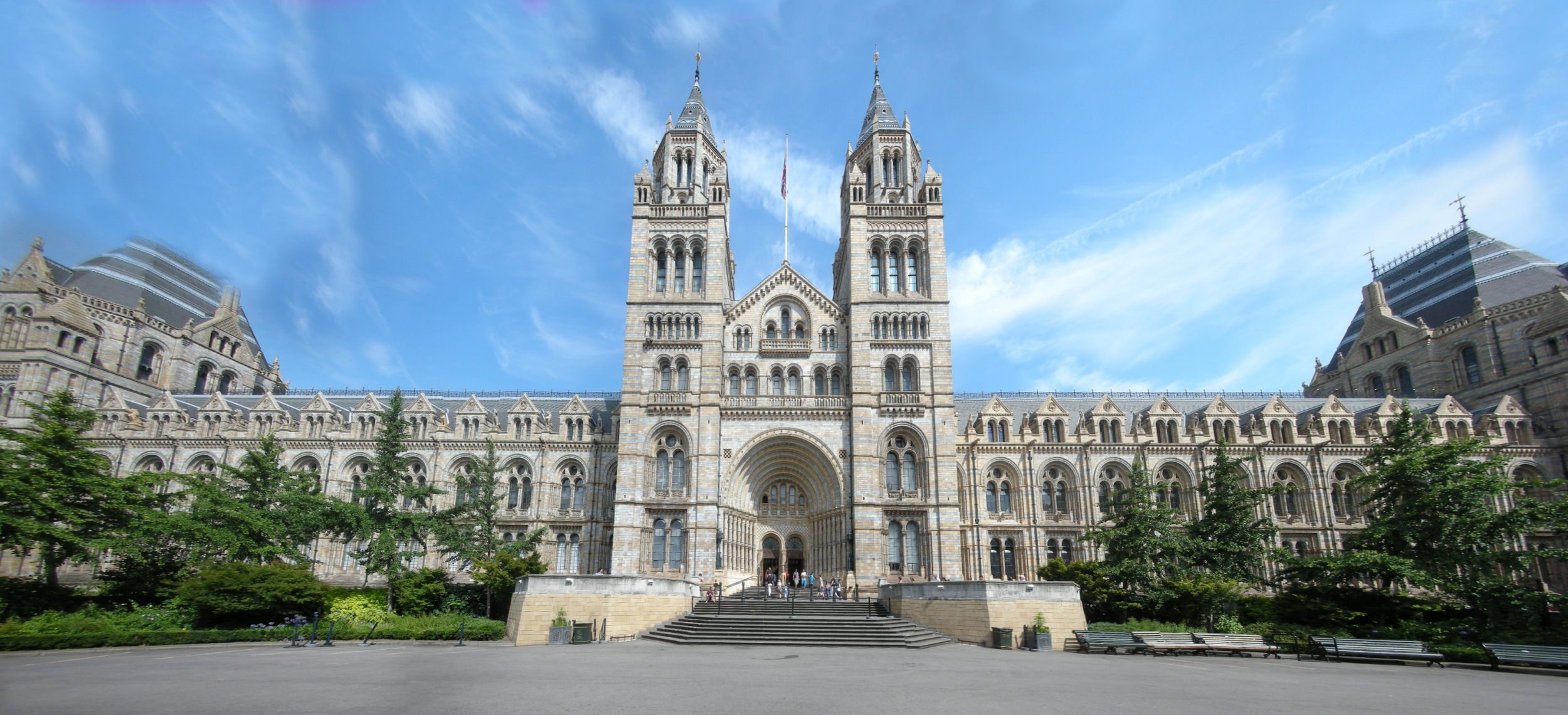 English Heritage is a governmental body with a broad remit of managing the historic sites, artefacts and environments of England. It is currently sponsored by the Department for Digital, Culture, Media and Sport. The charity National Trust for Places of Historic Interest or Natural Beauty holds a contrasting role. 17 of the 25 United Kingdom UNESCO World Heritage Sites fall within England. Some of the best-known of these are: Hadrian's Wall, Stonehenge, Avebury and Associated Sites, Tower of London, Jurassic Coast, Saltaire, Ironbridge Gorge, Studley Royal Park and various others.
There are many museums in England, but perhaps the most notable is London's British Museum. Its collection of more than seven million objects is one of the largest and most comprehensive in the world, sourced from every continent, illustrating and documenting the story of human culture from its beginning to the present. The British Library in London is the national library and is one of the world's largest research libraries, holding over 150 million items in almost all known languages and formats; including around 25 million books. The most senior art gallery is the National Gallery in Trafalgar Square, which houses a collection of over 2,300 paintings dating from the mid-13th century to 1900. The Tate galleries house the national collections of British and international modern art; they also host the famously controversial Turner Prize.
English Heritage is a governmental body with a broad remit of managing the historic sites, artefacts and environments of England. It is currently sponsored by the Department for Digital, Culture, Media and Sport. The charity National Trust for Places of Historic Interest or Natural Beauty holds a contrasting role. 17 of the 25 United Kingdom UNESCO World Heritage Sites fall within England. Some of the best-known of these are: Hadrian's Wall, Stonehenge, Avebury and Associated Sites, Tower of London, Jurassic Coast, Saltaire, Ironbridge Gorge, Studley Royal Park and various others.
There are many museums in England, but perhaps the most notable is London's British Museum. Its collection of more than seven million objects is one of the largest and most comprehensive in the world, sourced from every continent, illustrating and documenting the story of human culture from its beginning to the present. The British Library in London is the national library and is one of the world's largest research libraries, holding over 150 million items in almost all known languages and formats; including around 25 million books. The most senior art gallery is the National Gallery in Trafalgar Square, which houses a collection of over 2,300 paintings dating from the mid-13th century to 1900. The Tate galleries house the national collections of British and international modern art; they also host the famously controversial Turner Prize.
 At club level, England is recognised by FIFA as the birthplace of club football, due to Sheffield F.C. founded in 1857 being the world's oldest club. The Football Association is the oldest governing body in the sport, with the Laws of the Game (association football), rules of football first drafted in 1863 by Ebenezer Cobb Morley. The FA Cup and The Football League were the first cup and league competitions respectively. In the modern day, the Premier League is the world's most-watched football league, most lucrative, and amongst the elite.
As is the case throughout the UK, football in England is notable for the rivalries between clubs and the passion of the supporters, which includes a tradition of football chants. The most successful English football team in the European Cup/UEFA Champions League is Liverpool F.C. who have won the competition on six occasions. Other English success has come from Manchester United F.C., winning the competition on 3 occasions; Nottingham Forest F.C. and Chelsea F.C. on 2 occasions, Aston Villa F.C. have only won the trophy once.
At club level, England is recognised by FIFA as the birthplace of club football, due to Sheffield F.C. founded in 1857 being the world's oldest club. The Football Association is the oldest governing body in the sport, with the Laws of the Game (association football), rules of football first drafted in 1863 by Ebenezer Cobb Morley. The FA Cup and The Football League were the first cup and league competitions respectively. In the modern day, the Premier League is the world's most-watched football league, most lucrative, and amongst the elite.
As is the case throughout the UK, football in England is notable for the rivalries between clubs and the passion of the supporters, which includes a tradition of football chants. The most successful English football team in the European Cup/UEFA Champions League is Liverpool F.C. who have won the competition on six occasions. Other English success has come from Manchester United F.C., winning the competition on 3 occasions; Nottingham Forest F.C. and Chelsea F.C. on 2 occasions, Aston Villa F.C. have only won the trophy once.
 Cricket is generally thought to have been developed in the early medieval period among the farming and metalworking communities of the Weald. The England cricket team is a composite England and Wales, team. One of the game's top rivalries is The Ashes series between England and Australia cricket team, Australia, contested since 1882. The climax of the 2005 Ashes series, 2005 Ashes was viewed by 7.4 million as it was available on terrestrial television. England has hosted five Cricket World Cups (1975, 1979, 1983, 1999 and 2019 Cricket World Cup, 2019), winning the 2019 edition in a final regarded as one of the greatest one day internationals ever played. They hosted the ICC World Twenty20 in 2009 ICC World Twenty20, 2009, winning this format in 2010 beating rivals Australia in the final. In the domestic competition, the County Championship, Yorkshire County Cricket Club, Yorkshire are by far the most successful club having won the competition 32 times outright and sharing it on 1 other occasion. Lord's Cricket Ground situated in London is sometimes referred to as the "Mecca of Cricket".
William Penny Brookes was prominent in organising the format for the modern Olympic Games. In 1994, then President of the International Olympic Committee, IOC, Juan Antonio Samaranch, laid a wreath on Brooke's grave, and said, "I came to pay homage and tribute to Dr Brookes, who really was the founder of the modern Olympic Games". London has hosted the Summer Olympic Games three times, in 1908 Summer Olympics, 1908, 1948 Summer Olympics, 1948, and 2012 Summer Olympics, 2012. England competes in the Commonwealth Games, held every four years. Sport England is the governing body responsible for distributing funds and providing strategic guidance for sporting activity in England. The Minister for Sport and Civil Society has responsibility for sport in England.
Cricket is generally thought to have been developed in the early medieval period among the farming and metalworking communities of the Weald. The England cricket team is a composite England and Wales, team. One of the game's top rivalries is The Ashes series between England and Australia cricket team, Australia, contested since 1882. The climax of the 2005 Ashes series, 2005 Ashes was viewed by 7.4 million as it was available on terrestrial television. England has hosted five Cricket World Cups (1975, 1979, 1983, 1999 and 2019 Cricket World Cup, 2019), winning the 2019 edition in a final regarded as one of the greatest one day internationals ever played. They hosted the ICC World Twenty20 in 2009 ICC World Twenty20, 2009, winning this format in 2010 beating rivals Australia in the final. In the domestic competition, the County Championship, Yorkshire County Cricket Club, Yorkshire are by far the most successful club having won the competition 32 times outright and sharing it on 1 other occasion. Lord's Cricket Ground situated in London is sometimes referred to as the "Mecca of Cricket".
William Penny Brookes was prominent in organising the format for the modern Olympic Games. In 1994, then President of the International Olympic Committee, IOC, Juan Antonio Samaranch, laid a wreath on Brooke's grave, and said, "I came to pay homage and tribute to Dr Brookes, who really was the founder of the modern Olympic Games". London has hosted the Summer Olympic Games three times, in 1908 Summer Olympics, 1908, 1948 Summer Olympics, 1948, and 2012 Summer Olympics, 2012. England competes in the Commonwealth Games, held every four years. Sport England is the governing body responsible for distributing funds and providing strategic guidance for sporting activity in England. The Minister for Sport and Civil Society has responsibility for sport in England.
 Rugby union originated in Rugby School, Warwickshire in the early 19th century. The England national rugby union team, England rugby union team won the 2003 Rugby World Cup, with Jonny Wilkinson scoring the winning drop kick, drop goal in the last minute of extra time against Australia. England was one of the host nations of the competition in the 1991 Rugby World Cup and also hosted the 2015 Rugby World Cup. The top level of club participation is the Guinness Premiership, English Premiership. Leicester Tigers, Wasps RFC, London Wasps, Bath Rugby and Northampton Saints have had success in the Europe-wide Heineken Cup.
Rugby league was born in Huddersfield in 1895. Since 2008, the England national rugby league team has been a full test nation in lieu of the Great Britain national rugby league team, which won three Rugby League World Cup, World Cups but is now retired. Club sides play in Super League, the present-day embodiment of the Rugby Football League Championship. Rugby League is most popular among towns in the northern English counties of Lancashire, Yorkshire and Cumbria. The vast majority of English clubs in Super League are based in the north of England. Some of the most successful clubs include Wigan Warriors, Hull F.C. St Helens R.F.C., St. Helens, Leeds Rhinos and Huddersfield Giants; the former three have all won the World Club Challenge previously.
Golf has been prominent in England; due in part to its cultural and geographical ties to Scotland, the Golf in Scotland, home of Golf. There are both professional tours for men and women, in two main tours: the Professional Golfers' Association (Great Britain and Ireland), PGA and the European Tour. England has produced grand slam winners: Cyril Walker (golfer), Cyril Walker, Tony Jacklin, Nick Faldo, and Justin Rose in the men's and Laura Davies, Alison Nicholas, and Karen Stupples in the women's. The world's oldest golf tournament, and golf's first major is The Open Championship, played both in England and Scotland. The biennial golf competition, the Ryder Cup, is named after English businessman Samuel Ryder who sponsored the event and donated the trophy. Nick Faldo is the most successful Ryder Cup player ever, having won the most points (25) of any player on either the European or US teams.
Rugby union originated in Rugby School, Warwickshire in the early 19th century. The England national rugby union team, England rugby union team won the 2003 Rugby World Cup, with Jonny Wilkinson scoring the winning drop kick, drop goal in the last minute of extra time against Australia. England was one of the host nations of the competition in the 1991 Rugby World Cup and also hosted the 2015 Rugby World Cup. The top level of club participation is the Guinness Premiership, English Premiership. Leicester Tigers, Wasps RFC, London Wasps, Bath Rugby and Northampton Saints have had success in the Europe-wide Heineken Cup.
Rugby league was born in Huddersfield in 1895. Since 2008, the England national rugby league team has been a full test nation in lieu of the Great Britain national rugby league team, which won three Rugby League World Cup, World Cups but is now retired. Club sides play in Super League, the present-day embodiment of the Rugby Football League Championship. Rugby League is most popular among towns in the northern English counties of Lancashire, Yorkshire and Cumbria. The vast majority of English clubs in Super League are based in the north of England. Some of the most successful clubs include Wigan Warriors, Hull F.C. St Helens R.F.C., St. Helens, Leeds Rhinos and Huddersfield Giants; the former three have all won the World Club Challenge previously.
Golf has been prominent in England; due in part to its cultural and geographical ties to Scotland, the Golf in Scotland, home of Golf. There are both professional tours for men and women, in two main tours: the Professional Golfers' Association (Great Britain and Ireland), PGA and the European Tour. England has produced grand slam winners: Cyril Walker (golfer), Cyril Walker, Tony Jacklin, Nick Faldo, and Justin Rose in the men's and Laura Davies, Alison Nicholas, and Karen Stupples in the women's. The world's oldest golf tournament, and golf's first major is The Open Championship, played both in England and Scotland. The biennial golf competition, the Ryder Cup, is named after English businessman Samuel Ryder who sponsored the event and donated the trophy. Nick Faldo is the most successful Ryder Cup player ever, having won the most points (25) of any player on either the European or US teams.
 Tennis was created in Birmingham in the late 19th century, and The Championships, Wimbledon, the Wimbledon Championships is the oldest tennis tournament in the world, and widely considered the most prestigious. Wimbledon is a tournament that has a major place in the British cultural calendar. Fred Perry was the last Englishman to win Wimbledon in 1936. He was the first player to win all four Grand Slam in tennis, Grand Slam singles titles and helped lead the Great Britain Davis Cup team, Great Britain team to four Davis Cup wins. English women who have won Wimbledon include: Ann Haydon Jones in 1969 and Virginia Wade in 1977.
In boxing, under the Marquess of Queensberry Rules, England has produced many world champions across the weight divisions internationally recognised by the governing bodies. World champions include Bob Fitzsimmons, Ted "Kid" Lewis, Randolph Turpin, Nigel Benn, Chris Eubank, Frank Bruno, Lennox Lewis, Ricky Hatton, Naseem Hamed, Amir Khan (British boxer), Amir Khan, Carl Froch, and David Haye. In women's boxing, Nicola Adams became the world's first woman to win an Olympic boxing gold medal at the 2012 Summer Olympics.
Originating in 17th and 18th-century England, the thoroughbred is a horse breed best known for its use in horse racing. The National Hunt horse race the Grand National, is held annually at Aintree Racecourse in early April. It is the most watched horse race in the UK, attracting casual observers, and three-time winner Red Rum is the most successful racehorse in the event's history. Red Rum is also the best-known racehorse in the country.
Tennis was created in Birmingham in the late 19th century, and The Championships, Wimbledon, the Wimbledon Championships is the oldest tennis tournament in the world, and widely considered the most prestigious. Wimbledon is a tournament that has a major place in the British cultural calendar. Fred Perry was the last Englishman to win Wimbledon in 1936. He was the first player to win all four Grand Slam in tennis, Grand Slam singles titles and helped lead the Great Britain Davis Cup team, Great Britain team to four Davis Cup wins. English women who have won Wimbledon include: Ann Haydon Jones in 1969 and Virginia Wade in 1977.
In boxing, under the Marquess of Queensberry Rules, England has produced many world champions across the weight divisions internationally recognised by the governing bodies. World champions include Bob Fitzsimmons, Ted "Kid" Lewis, Randolph Turpin, Nigel Benn, Chris Eubank, Frank Bruno, Lennox Lewis, Ricky Hatton, Naseem Hamed, Amir Khan (British boxer), Amir Khan, Carl Froch, and David Haye. In women's boxing, Nicola Adams became the world's first woman to win an Olympic boxing gold medal at the 2012 Summer Olympics.
Originating in 17th and 18th-century England, the thoroughbred is a horse breed best known for its use in horse racing. The National Hunt horse race the Grand National, is held annually at Aintree Racecourse in early April. It is the most watched horse race in the UK, attracting casual observers, and three-time winner Red Rum is the most successful racehorse in the event's history. Red Rum is also the best-known racehorse in the country.
 The 1950 British Grand Prix at Silverstone Circuit, Silverstone was the first race in the newly created Formula One World Championship. Since then, England has produced some of the greatest drivers in the sport, including; John Surtees, Stirling Moss, Graham Hill (only driver to have won the Triple Crown of Motorsport, Triple Crown), Nigel Mansell (only man to hold F1 and IndyCar titles at the same time), Damon Hill, Lewis Hamilton and Jenson Button. It has manufactured some of the most technically advanced racing cars, and many of today's racing companies choose England as their base of operations for its engineering knowledge and organisation. McLaren Automotive, Williams F1, Team Lotus, Honda, Brawn GP, Benetton Formula, Benetton, Renault, and Red Bull Racing are all, or have been, located in the south of England. England also has a rich heritage in Grand Prix motorcycle racing, the premier championship of motorcycle road racing, and produced several World Champions across all the various class of motorcycle: Mike Hailwood, John Surtees, Phil Read, Geoff Duke, and Barry Sheene.
The 1950 British Grand Prix at Silverstone Circuit, Silverstone was the first race in the newly created Formula One World Championship. Since then, England has produced some of the greatest drivers in the sport, including; John Surtees, Stirling Moss, Graham Hill (only driver to have won the Triple Crown of Motorsport, Triple Crown), Nigel Mansell (only man to hold F1 and IndyCar titles at the same time), Damon Hill, Lewis Hamilton and Jenson Button. It has manufactured some of the most technically advanced racing cars, and many of today's racing companies choose England as their base of operations for its engineering knowledge and organisation. McLaren Automotive, Williams F1, Team Lotus, Honda, Brawn GP, Benetton Formula, Benetton, Renault, and Red Bull Racing are all, or have been, located in the south of England. England also has a rich heritage in Grand Prix motorcycle racing, the premier championship of motorcycle road racing, and produced several World Champions across all the various class of motorcycle: Mike Hailwood, John Surtees, Phil Read, Geoff Duke, and Barry Sheene.
 Darts is a widely popular sport in England; a professional competitive sport, darts is a traditional pub game. The sport is governed by the World Darts Federation, one of its member organisations is the British Darts Organisation (BDO), which annually stages the BDO World Darts Championship, the other being the Professional Darts Corporation (PDC), which runs its own world championship at Alexandra Palace in London. Phil Taylor (darts player), Phil Taylor is widely regarded as the best darts player of all time, having won 187 professional tournaments, and a record 16 World Professional Darts Championship, World Championships. Trina Gulliver is the ten-time Women's World Professional Darts Champion of the British Darts Organisation. Another popular sport commonly associated with pub games is Snooker, and England has produced several world champions, including Steve Davis and Ronnie O'Sullivan.
The English are keen sailors and enjoy competitive sailing; founding and winning some of the world's most famous and respected international competitive tournaments across the various race formats, including the match race, a regatta, and the America's Cup. England has produced some of the world's greatest sailors, including Francis Chichester, Herbert Hasler, John Ridgway (sailor), John Ridgway, Robin Knox-Johnston, Ellen MacArthur, Mike Golding, Paul Goodison, and the most successful Olympic sailor ever Ben Ainslie.
Darts is a widely popular sport in England; a professional competitive sport, darts is a traditional pub game. The sport is governed by the World Darts Federation, one of its member organisations is the British Darts Organisation (BDO), which annually stages the BDO World Darts Championship, the other being the Professional Darts Corporation (PDC), which runs its own world championship at Alexandra Palace in London. Phil Taylor (darts player), Phil Taylor is widely regarded as the best darts player of all time, having won 187 professional tournaments, and a record 16 World Professional Darts Championship, World Championships. Trina Gulliver is the ten-time Women's World Professional Darts Champion of the British Darts Organisation. Another popular sport commonly associated with pub games is Snooker, and England has produced several world champions, including Steve Davis and Ronnie O'Sullivan.
The English are keen sailors and enjoy competitive sailing; founding and winning some of the world's most famous and respected international competitive tournaments across the various race formats, including the match race, a regatta, and the America's Cup. England has produced some of the world's greatest sailors, including Francis Chichester, Herbert Hasler, John Ridgway (sailor), John Ridgway, Robin Knox-Johnston, Ellen MacArthur, Mike Golding, Paul Goodison, and the most successful Olympic sailor ever Ben Ainslie.
 The St George's Cross has been the national flag of England since the 13th century. Originally the flag was used by the maritime Republic of Genoa. The English monarch paid a tribute to the Doge of Genoa from 1190 onwards so that English ships could fly the flag as a means of protection when entering the Mediterranean.
A red cross was a symbol for many Crusaders in the 12th and 13th centuries. It became associated with Saint George, along with countries and cities, which claimed him as their patron saint and used his cross as a banner. Since 1606 the St George's Cross has formed part of the design of the Union Flag, a Pan-British flag designed by King James I of England, James I. During the English Civil War and Interregnum (England), Interregnum, the New Model Army, New Model Army's standards and the English Commonwealth, Commonwealth's Great Seal of the Realm#Commonwealth, Great Seal both incorporated the flag of Saint George.
The St George's Cross has been the national flag of England since the 13th century. Originally the flag was used by the maritime Republic of Genoa. The English monarch paid a tribute to the Doge of Genoa from 1190 onwards so that English ships could fly the flag as a means of protection when entering the Mediterranean.
A red cross was a symbol for many Crusaders in the 12th and 13th centuries. It became associated with Saint George, along with countries and cities, which claimed him as their patron saint and used his cross as a banner. Since 1606 the St George's Cross has formed part of the design of the Union Flag, a Pan-British flag designed by King James I of England, James I. During the English Civil War and Interregnum (England), Interregnum, the New Model Army, New Model Army's standards and the English Commonwealth, Commonwealth's Great Seal of the Realm#Commonwealth, Great Seal both incorporated the flag of Saint George.
 There are numerous other symbols and symbolic artefacts, both official and unofficial, including the Tudor rose, the nation's national emblem, floral emblem, and the Three Lions featured on the Royal Arms of England. The Tudor rose was adopted as a national emblem of England around the time of the
There are numerous other symbols and symbolic artefacts, both official and unofficial, including the Tudor rose, the nation's national emblem, floral emblem, and the Three Lions featured on the Royal Arms of England. The Tudor rose was adopted as a national emblem of England around the time of the
English Heritage
nbsp;ã National body protecting English heritage
Natural England
nbsp;ã Wildlife and the natural world of England
VisitEngland
nbsp;ã English Tourist Board
BBC News ã England
nbsp;ã News items from BBC News relating to England
GOV.UK
nbsp;ã The Official Website of the British Government * {{Good article England, English-speaking countries and territories Great Britain Island countries United Kingdom by country Germanic countries and territories Christian states
country
A country is a distinct part of the world, such as a state, nation, or other political entity. It may be a sovereign state or make up one part of a larger state. For example, the country of Japan is an independent, sovereign state, while the ...
that is part of the United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotland, Wales and North ...
. It shares land borders with Wales
Wales ( cy, Cymru ) is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. It is bordered by England to the WalesãEngland border, east, the Irish Sea to the north and west, the Celtic Sea to the south west and the ...
to its west and Scotland
Scotland (, ) is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. Covering the northern third of the island of Great Britain, mainland Scotland has a border with England to the southeast and is otherwise surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean to the ...
to its north. The Irish Sea
The Irish Sea or , gv, Y Keayn Yernagh, sco, Erse Sie, gd, Muir ûireann , Ulster-Scots: ''Airish Sea'', cy, MûÇr Iwerddon . is an extensive body of water that separates the islands of Ireland and Great Britain. It is linked to the Ce ...
lies northwest and the Celtic Sea
The Celtic Sea ; cy, Y MûÇr Celtaidd ; kw, An Mor Keltek ; br, Ar Mor Keltiek ; french: La mer Celtique is the area of the Atlantic Ocean off the southern coast of Ireland bounded to the east by Saint George's Channel; other limits includ ...
to the southwest. It is separated from continental Europe
Continental Europe or mainland Europe is the contiguous continent of Europe, excluding its surrounding islands. It can also be referred to ambiguously as the European continent, ã which can conversely mean the whole of Europe ã and, by ...
by the North Sea
The North Sea lies between Great Britain, Norway, Denmark, Germany, the Netherlands and Belgium. An epeiric sea on the European continental shelf, it connects to the Atlantic Ocean through the English Channel in the south and the Norwegian S ...
to the east and the English Channel
The English Channel, "The Sleeve"; nrf, la Maunche, "The Sleeve" (Cotentinais) or ( Jû´rriais), (Guernûˋsiais), "The Channel"; br, Mor Breizh, "Sea of Brittany"; cy, MûÇr Udd, "Lord's Sea"; kw, Mor Bretannek, "British Sea"; nl, Het Kana ...
to the south. The country covers five-eighths of the island of Great Britain
Great Britain is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean off the northwest coast of continental Europe. With an area of , it is the largest of the British Isles, the largest European island and the ninth-largest island in the world. It is ...
, which lies in the North Atlantic
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's five oceans, with an area of about . It covers approximately 20% of Earth's surface and about 29% of its water surface area. It is known to separate the "Old World" of Africa, Europe and ...
, and includes over 100 smaller islands, such as the Isles of Scilly
The Isles of Scilly (; kw, Syllan, ', or ) is an archipelago off the southwestern tip of Cornwall, England. One of the islands, St Agnes, is the most southerly point in Britain, being over further south than the most southerly point of the ...
and the Isle of Wight
The Isle of Wight ( ) is a county in the English Channel, off the coast of Hampshire, from which it is separated by the Solent. It is the largest and second-most populous island of England. Referred to as 'The Island' by residents, the Isle of ...
.
The area now called England was first inhabited by modern humans during the Upper Paleolithic
The Upper Paleolithic (or Upper Palaeolithic) is the third and last subdivision of the Paleolithic or Old Stone Age. Very broadly, it dates to between 50,000 and 12,000 years ago (the beginning of the Holocene), according to some theories coin ...
period, but takes its name from the Angles
The Angles ( ang, ûngle, ; la, Angli) were one of the main Germanic peoples who settled in Great Britain in the post-Roman period. They founded several kingdoms of the Heptarchy in Anglo-Saxon England. Their name is the root of the name ' ...
, a Germanic tribe deriving its name from the Anglia peninsula, who settled during the 5th and 6th centuries. England became a unified state in the 10th century and has had a significant cultural and legal impact on the wider world since the Age of Discovery
The Age of Discovery (or the Age of Exploration), also known as the early modern period, was a period largely overlapping with the Age of Sail, approximately from the 15th century to the 17th century in European history, during which seafarin ...
, which began during the 15th century. The English language
English is a West Germanic language of the Indo-European language family, with its earliest forms spoken by the inhabitants of early medieval England. It is named after the Angles, one of the ancient Germanic peoples that migrated to the is ...
, the Anglican Church
Anglicanism is a Western Christian tradition that has developed from the practices, liturgy, and identity of the Church of England following the English Reformation, in the context of the Protestant Reformation in Europe. It is one of the ...
, and English law
English law is the common law legal system of England and Wales, comprising mainly criminal law and civil law, each branch having its own courts and procedures.
Principal elements of English law
Although the common law has, historically, be ...
ãthe basis for the common law
In law, common law (also known as judicial precedent, judge-made law, or case law) is the body of law created by judges and similar quasi-judicial tribunals by virtue of being stated in written opinions."The common law is not a brooding omnipresen ...
legal systems of many other countries around the worldãdeveloped in England, and the country's parliamentary system
A parliamentary system, or parliamentarian democracy, is a system of democratic governance of a state (or subordinate entity) where the executive derives its democratic legitimacy from its ability to command the support ("confidence") of the ...
of government has been widely adopted by other nations. The Industrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution was the transition to new manufacturing processes in Great Britain, continental Europe, and the United States, that occurred during the period from around 1760 to about 1820ã1840. This transition included going f ...
began in 18th-century England, transforming its society into the world's first industrialised nation.
England's terrain is chiefly low hills and plain
In geography, a plain is a flat expanse of land that generally does not change much in elevation, and is primarily treeless. Plains occur as lowlands along valleys or at the base of mountains, as coastal plains, and as plateaus or uplands ...
s, especially in central and southern England. However, there is upland and mountainous terrain in the north (for example, the Lake District
The Lake District, also known as the Lakes or Lakeland, is a mountainous region in North West England. A popular holiday destination, it is famous for its lakes, forests, and mountains (or ''fells''), and its associations with William Wordswor ...
and Pennines
The Pennines (), also known as the Pennine Chain or Pennine Hills, are a range of uplands running between three regions of Northern England: North West England on the west, North East England and Yorkshire and the Humber on the east. Commo ...
) and in the west (for example, Dartmoor
Dartmoor is an upland area in southern Devon, England. The moorland and surrounding land has been protected by National Park status since 1951. Dartmoor National Park covers .
The granite which forms the uplands dates from the Carboniferous ...
and the Shropshire Hills
The Shropshire Hills are a dissected upland area and one of the natural regions of England. They lie wholly within the county of Shropshire and encompass several distinctive and well-known landmarks, such as the Long Mynd, Wenlock Edge, The Wrek ...
). The capital is London
London is the capital and largest city of England and the United Kingdom, with a population of just under 9 million. It stands on the River Thames in south-east England at the head of a estuary down to the North Sea, and has been a majo ...
, which has the largest metropolitan area in the United Kingdom. England's population of 56.3 million comprises 84% of the population of the United Kingdom, largely concentrated around London, the South East
The points of the compass are a set of horizontal, radially arrayed compass directions (or azimuths) used in navigation and cartography. A compass rose is primarily composed of four cardinal directionsãnorth, east, south, and westãeach sepa ...
, and conurbations in the Midlands
The Midlands (also referred to as Central England) are a part of England that broadly correspond to the Kingdom of Mercia of the Early Middle Ages, bordered by Wales, Northern England and Southern England. The Midlands were important in the Ind ...
, the North West
The points of the compass are a set of horizontal, radially arrayed compass directions (or azimuths) used in navigation and cartography. A compass rose is primarily composed of four cardinal directionsãnorth, east, south, and westãeach sepa ...
, the North East
The points of the compass are a set of horizontal, radially arrayed compass directions (or azimuths) used in navigation and cartography. A compass rose is primarily composed of four cardinal directionsãnorth, east, south, and westãeach sepa ...
, and Yorkshire
Yorkshire ( ; abbreviated Yorks), formally known as the County of York, is a Historic counties of England, historic county in northern England and by far the largest in the United Kingdom. Because of its large area in comparison with other Eng ...
, which each developed as major industrial regions during the 19th century.2011 Census ã Population and household estimates for England and Wales, March 2011Accessed 31 May 2013. The
Kingdom of England
The Kingdom of England (, ) was a sovereign state on the island of Great Britain from 12 July 927, when it emerged from various Anglo-Saxon kingdoms, until 1 May 1707, when it united with Scotland to form the Kingdom of Great Britain.
On 1 ...
ã which after 1535 included Wales ã ceased being a separate sovereign state
A sovereign state or sovereign country, is a polity, political entity represented by one central government that has supreme legitimate authority over territory. International law defines sovereign states as having a permanent population, defin ...
on 1 May 1707, when the Acts of Union put into effect the terms agreed in the Treaty of Union
The Treaty of Union is the name usually now given to the treaty which led to the creation of the new state of Great Britain, stating that the Kingdom of England (which already included Wales) and the Kingdom of Scotland were to be "United i ...
the previous year, resulting in a political union with the Kingdom of Scotland
The Kingdom of Scotland (; , ) was a sovereign state in northwest Europe traditionally said to have been founded in 843. Its territories expanded and shrank, but it came to occupy the northern third of the island of Great Britain, sharing a la ...
to create the Kingdom of Great Britain
The Kingdom of Great Britain (officially Great Britain) was a Sovereign state, sovereign country in Western Europe from 1 May 1707 to the end of 31 December 1800. The state was created by the 1706 Treaty of Union and ratified by the Acts of ...
. In 1801, Great Britain was united with the Kingdom of Ireland
The Kingdom of Ireland ( ga, label=Classical Irish, an RûÙoghacht ûireann; ga, label=Modern Irish, an RûÙocht ûireann, ) was a monarchy on the island of Ireland that was a client state of England and then of Great Britain. It existed from ...
(through another Act of Union) to become the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland was a sovereign state in the British Isles that existed between 1801 and 1922, when it included all of Ireland. It was established by the Acts of Union 1800, which merged the Kingdom of Great B ...
. In 1922 the Irish Free State
The Irish Free State ( ga, SaorstûÀt ûireann, , ; 6 December 192229 December 1937) was a state established in December 1922 under the Anglo-Irish Treaty of December 1921. The treaty ended the three-year Irish War of Independence between th ...
seceded from the United Kingdom, leading to the latter being renamed the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland.
Toponymy
The name "England" is derived from theOld English
Old English (, ), or Anglo-Saxon, is the earliest recorded form of the English language, spoken in England and southern and eastern Scotland in the early Middle Ages. It was brought to Great Britain by Anglo-Saxon settlement of Britain, Anglo ...
name , which means "land of the Angles
The Angles ( ang, ûngle, ; la, Angli) were one of the main Germanic peoples who settled in Great Britain in the post-Roman period. They founded several kingdoms of the Heptarchy in Anglo-Saxon England. Their name is the root of the name ' ...
". The Angles were one of the Germanic tribes
The Germanic peoples were historical groups of people that once occupied Central Europe and Scandinavia during antiquity and into the early Middle Ages. Since the 19th century, they have traditionally been defined by the use of ancient and ear ...
that settled in Great Britain during the Early Middle Ages
The Early Middle Ages (or early medieval period), sometimes controversially referred to as the Dark Ages, is typically regarded by historians as lasting from the late 5th or early 6th century to the 10th century. They marked the start of the Mi ...
. The Angles came from the Anglia peninsula in the Bay of Kiel
The Bay of Kiel or Kiel Bay (, ; ) is a bay in the southwestern Baltic Sea, off the shores of Schleswig-Holstein in Germany and the islands of Denmark. It is connected with the Bay of Mecklenburg in the east, the Little Belt in the northwest, ...
area (present-day German state of Schleswig-Holstein
Schleswig-Holstein (; da, Slesvig-Holsten; nds, Sleswig-Holsteen; frr, Slaswik-Holstiinj) is the northernmost of the 16 states of Germany, comprising most of the historical duchy of Holstein and the southern part of the former Duchy of Sch ...
) of the Baltic Sea
The Baltic Sea is an arm of the Atlantic Ocean that is enclosed by Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Germany, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Russia, Sweden and the North and Central European Plain.
The sea stretches from 53ô¯N to 66ô¯N latitude and from ...
. The earliest recorded use of the term, as "", is in the late-ninth-century translation into Old English of Bede
Bede ( ; ang, BúÈda , ; 672/326 May 735), also known as Saint Bede, The Venerable Bede, and Bede the Venerable ( la, Beda Venerabilis), was an English monk at the monastery of St Peter and its companion monastery of St Paul in the Kingdom o ...
's ''Ecclesiastical History of the English People
The ''Ecclesiastical History of the English People'' ( la, Historia ecclesiastica gentis Anglorum), written by Bede in about AD 731, is a history of the Christian Churches in England, and of England generally; its main focus is on the conflict be ...
''. The term was then used in a different sense to the modern one, meaning "the land inhabited by the English", and it included English people in what is now south-east Scotland but was then part of the English kingdom of Northumbria
la, Regnum Northanhymbrorum
, conventional_long_name = Kingdom of Northumbria
, common_name = Northumbria
, status = State
, status_text = Unified Anglian kingdom (before 876)North: Anglian kingdom (af ...
. The ''Anglo-Saxon Chronicle
The ''Anglo-Saxon Chronicle'' is a collection of annals in Old English, chronicling the history of the Anglo-Saxons. The original manuscript of the ''Chronicle'' was created late in the 9th century, probably in Wessex, during the reign of Alf ...
'' recorded that the Domesday Book
Domesday Book () ã the Middle English spelling of "Doomsday Book" ã is a manuscript record of the "Great Survey" of much of England and parts of Wales completed in 1086 by order of King William I, known as William the Conqueror. The manusc ...
of 1086 covered the whole of England, meaning the English kingdom, but a few years later the ''Chronicle'' stated that King Malcolm III
Malcolm III ( mga, MûÀel Coluim mac Donnchada, label=Medieval Gaelic; gd, Maol Chaluim mac Dhonnchaidh; died 13 November 1093) was King of Scotland from 1058 to 1093. He was later nicknamed "Canmore" ("ceann mûýr", Gaelic, literally "big head" ...
went "out of Scotlande into Lothian
Lothian (; sco, Lowden, Loudan, -en, -o(u)n; gd, Lodainn ) is a region of the Scottish Lowlands, lying between the southern shore of the Firth of Forth and the Lammermuir Hills and the Moorfoot Hills. The principal settlement is the Sco ...
in Englaland", thus using it in the more ancient sense.
The earliest attested reference to the Angles occurs in the 1st-century work by Tacitus
Publius Cornelius Tacitus, known simply as Tacitus ( , ; ã ), was a Roman historian and politician. Tacitus is widely regarded as one of the greatest Roman historiography, Roman historians by modern scholars.
The surviving portions of his t ...
, ''Germania
Germania ( ; ), also called Magna Germania (English: ''Great Germania''), Germania Libera (English: ''Free Germania''), or Germanic Barbaricum to distinguish it from the Roman province of the same name, was a large historical region in north- ...
'', in which the Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the ...
word is used. The etymology of the tribal name itself is disputed by scholars; it has been suggested that it derives from the shape of the Angeln peninsula, an ''angular'' shape. How and why a term derived from the name of a tribe that was less significant than others, such as the Saxons
The Saxons ( la, Saxones, german: Sachsen, ang, Seaxan, osx, Sahson, nds, Sassen, nl, Saksen) were a group of Germanic
*
*
*
*
peoples whose name was given in the early Middle Ages to a large country (Old Saxony, la, Saxonia) near the Nor ...
, came to be used for the entire country and its people is not known, but it seems this is related to the custom of calling the Germanic people in Britain ''Angli Saxones'' or English Saxons to distinguish them from continental Saxons (Eald-Seaxe) of Old Saxony between the Weser and Eider rivers in Northern Germany. In Scottish Gaelic
Scottish Gaelic ( gd, Gû idhlig ), also known as Scots Gaelic and Gaelic, is a Goidelic language (in the Celtic branch of the Indo-European language family) native to the Gaels of Scotland. As a Goidelic language, Scottish Gaelic, as well as ...
, another language which developed on the island of Great Britain, the Saxon tribe gave their name to the word for England (); similarly, the Welsh name for the English language is "". A romantic name for England is Loegria
Logres (among various other forms and spellings) is King Arthur's realm in the Matter of Britain. It derives from the medieval Welsh word ''Lloegyr'', a name of uncertain origin referring to South and Eastern England (''Lloegr'' in modern Welsh ...
, related to the Welsh
Welsh may refer to:
Related to Wales
* Welsh, referring or related to Wales
* Welsh language, a Brittonic Celtic language spoken in Wales
* Welsh people
People
* Welsh (surname)
* Sometimes used as a synonym for the ancient Britons (Celtic peop ...
word for England, , and made popular by its use in Arthurian legend
The Matter of Britain is the body of medieval literature and legendary material associated with Great Britain and Brittany and the legendary kings and heroes associated with it, particularly King Arthur. It was one of the three great Wester ...
. ''Albion
Albion is an alternative name for Great Britain. The oldest attestation of the toponym comes from the Greek language. It is sometimes used poetically and generally to refer to the island, but is less common than 'Britain' today. The name for Scot ...
'' is also applied to England in a more poetic capacity, though its original meaning is the island of Britain as a whole.
History
Prehistory and antiquity

 The earliest known evidence of human presence in the area now known as England was that of ''
The earliest known evidence of human presence in the area now known as England was that of ''Homo antecessor
''Homo antecessor'' (Latin "pioneer man") is an Extinction, extinct species of archaic human recorded in the Spanish Archaeological Site of Atapuerca, Sierra de Atapuerca, a productive archaeological site, from 1.2 to 0.8 million years ago durin ...
'', dating to approximately 780,000 years ago. The oldest proto-human bones discovered in England date from 500,000 years ago. Modern humans are known to have inhabited the area during the Upper Paleolithic
The Upper Paleolithic (or Upper Palaeolithic) is the third and last subdivision of the Paleolithic or Old Stone Age. Very broadly, it dates to between 50,000 and 12,000 years ago (the beginning of the Holocene), according to some theories coin ...
period, though permanent settlements were only established within the last 6,000 years.
After the last ice age only large mammals such as mammoth
A mammoth is any species of the extinct elephantid genus ''Mammuthus'', one of the many genera that make up the order of trunked mammals called proboscideans. The various species of mammoth were commonly equipped with long, curved tusks and, ...
s, bison
Bison are large bovines in the genus ''Bison'' (Greek: "wild ox" (bison)) within the tribe Bovini. Two extant and numerous extinct species are recognised.
Of the two surviving species, the American bison, ''B. bison'', found only in North Ame ...
and woolly rhinoceros
The woolly rhinoceros (''Coelodonta antiquitatis'') is an extinct species of rhinoceros that was common throughout Europe and Asia during the Pleistocene epoch and survived until the end of the last glacial period. The woolly rhinoceros was a me ...
remained. Roughly 11,000 years ago, when the ice sheets
In glaciology, an ice sheet, also known as a continental glacier, is a mass of glacial ice that covers surrounding terrain and is greater than . The only current ice sheets are in Antarctica and Greenland; during the Last Glacial Period at La ...
began to recede, humans repopulated the area; genetic research suggests they came from the northern part of the Iberian Peninsula
The Iberian Peninsula (),
**
* Aragonese and Occitan: ''Peninsula Iberica''
**
**
* french: Pûˋninsule Ibûˋrique
* mwl, PenûÙnsula Eibûˋrica
* eu, Iberiar penintsula also known as Iberia, is a peninsula in southwestern Europe, defi ...
. The sea level was lower than the present day and Britain was connected by land bridge
In biogeography, a land bridge is an isthmus or wider land connection between otherwise separate areas, over which animals and plants are able to cross and Colonisation (biology), colonize new lands. A land bridge can be created by marine regre ...
to Ireland and Eurasia
Eurasia (, ) is the largest continental area on Earth, comprising all of Europe and Asia. Primarily in the Northern and Eastern Hemispheres, it spans from the British Isles and the Iberian Peninsula in the west to the Japanese archipelago a ...
.
As the seas rose, it was separated from Ireland 10,000 years ago and from Eurasia two millennia later.
The Beaker culture
The Bell Beaker culture, also known as the Bell Beaker complex or Bell Beaker phenomenon, is an archaeological culture named after the Inverted bell, inverted-bell beaker (archaeology), beaker drinking vessel used at the very beginning of the E ...
arrived around 2,500 BC, introducing drinking and food vessels constructed from clay, as well as vessels used as reduction pots to smelt copper ores. It was during this time that major Neolithic
The Neolithic period, or New Stone Age, is an Old World archaeological period and the final division of the Stone Age. It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wide-ranging set of developments that appear to have arisen independently in several parts ...
monuments such as Stonehenge
Stonehenge is a prehistoric monument on Salisbury Plain in Wiltshire, England, west of Amesbury. It consists of an outer ring of vertical sarsen standing stones, each around high, wide, and weighing around 25 tons, topped by connectin ...
and Avebury
Avebury () is a Neolithic henge monument containing three stone circles, around the village of Avebury in Wiltshire, in southwest England. One of the best known prehistoric sites in Britain, it contains the largest megalithic stone circle in t ...
were constructed. By heating together tin and copper, which were in abundance in the area, the Beaker culture people made bronze
Bronze is an alloy consisting primarily of copper, commonly with about 12ã12.5% tin and often with the addition of other metals (including aluminium, manganese, nickel, or zinc) and sometimes non-metals, such as phosphorus, or metalloids such ...
, and later iron from iron ores. The development of iron smelting
Smelting is a process of applying heat to ore, to extract a base metal. It is a form of extractive metallurgy. It is used to extract many metals from their ores, including silver, iron, copper, and other base metals. Smelting uses heat and a ch ...
allowed the construction of better plough
A plough or plow ( US; both ) is a farm tool for loosening or turning the soil before sowing seed or planting. Ploughs were traditionally drawn by oxen and horses, but in modern farms are drawn by tractors. A plough may have a wooden, iron or ...
s, advancing agriculture (for instance, with Celtic field
Celtic field is an old name for traces of early (prehistoric) agricultural field systems found in North-West Europe, i.e. Britain, Ireland, Belgium, Netherlands, Germany, Denmark, France, Sweden, Poland and the Baltic states. The fields themselves ...
s), as well as the production of more effective weapons.
During the Iron Age
The Iron Age is the final epoch of the three-age division of the prehistory and protohistory of humanity. It was preceded by the Stone Age (Paleolithic, Mesolithic, Neolithic) and the Bronze Age (Chalcolithic). The concept has been mostly appl ...
, Celtic culture Celtic culture may refer to:
*the culture of Celts
*the culture of Celts (modern)
*the culture of Celtic nations:
**Culture of Ireland
**Culture of Scotland
**Culture of the Isle of Man
**Culture of Wales
**Culture of Cornwall
** Culture of Brittan ...
, deriving from the Hallstatt
Hallstatt ( , , ) is a small town in the district of Gmunden, in the Austrian state of Upper Austria. Situated between the southwestern shore of HallstûÊtter See and the steep slopes of the Dachstein massif, the town lies in the Salzkammergut ...
and La Tû´ne culture
The La Tû´ne culture (; ) was a European Iron Age culture. It developed and flourished during the late Iron Age (from about 450 BC to the Roman conquest in the 1st century BC), succeeding the early Iron Age Hallstatt culture without any defini ...
s, arrived from Central Europe. Brythonic
Brittonic or Brythonic may refer to:
*Common Brittonic, or Brythonic, the Celtic language anciently spoken in Great Britain
*Brittonic languages, a branch of the Celtic languages descended from Common Brittonic
*Britons (Celtic people)
The Br ...
was the spoken language during this time. Society was tribal; according to Ptolemy
Claudius Ptolemy (; grc-gre, ö üö¢ö£öçö¥öÝâö¢ü, ; la, Claudius Ptolemaeus; AD) was a mathematician, astronomer, astrologer, geographer, and music theorist, who wrote about a dozen scientific treatises, three of which were of importanc ...
's there were around 20 tribes in the area. Earlier divisions are unknown because the Britons were not literate. Like other regions on the edge of the Empire, Britain had long enjoyed trading links with the Romans. Julius Caesar of the Roman Republic
The Roman Republic ( la, Res publica Romana ) was a form of government of Rome and the era of the classical Roman civilization when it was run through public representation of the Roman people. Beginning with the overthrow of the Roman Kin ...
attempted to invade twice in 55 BC; although largely unsuccessful, he managed to set up a client king
A client state, in international relations, is a state that is economically, politically, and/or militarily subordinate to another more powerful state (called the "controlling state"). A client state may variously be described as satellite state, ...
from the Trinovantes
The Trinovantás (Common Brittonic: *''Trinowantá¨'') or Trinobantes were one of the Celtic tribes of Pre-Roman Britain. Their territory was on the north side of the Thames estuary in current Essex, Hertfordshire and Suffolk, and included lan ...
.
 The Romans invaded Britain in 43 AD during the reign of Emperor
The Romans invaded Britain in 43 AD during the reign of Emperor Claudius
Tiberius Claudius Caesar Augustus Germanicus (; 1 August 10 BC ã 13 October AD 54) was the fourth Roman emperor, ruling from AD 41 to 54. A member of the Julio-Claudian dynasty, Claudius was born to Nero Claudius Drusus, Drusu ...
, subsequently conquering much of Britain, and the area was incorporated into the Roman Empire as Britannia province
Roman Britain was the period in classical antiquity when large parts of the island of Great Britain were under occupation by the Roman Empire. The occupation lasted from AD 43 to AD 410. During that time, the territory conquered was ...
. The best-known of the native tribes who attempted to resist were the Catuvellauni
The Catuvellauni (Common Brittonic: *''Catu-wellauná¨'', "war-chiefs") were a Celtic tribe or state of southeastern Britain before the Roman conquest, attested by inscriptions into the 4th century.
The fortunes of the Catuvellauni and their k ...
led by Caratacus
Caratacus ( Brythonic ''*Caratácos'', Middle Welsh ''Caratawc''; Welsh ''Caradog''; Breton ''Karadeg''; Greek ''ööÝüö˜üöÝö¤ö¢ü''; variants Latin ''Caractacus'', Greek ''ööÝüüö˜ö¤öñü'') was a 1st-century AD British chieftain of the C ...
. Later, an uprising led by Boudica
Boudica or Boudicca (, known in Latin chronicles as Boadicea or Boudicea, and in Welsh as ()), was a queen of the ancient British Iceni tribe, who led a failed uprising against the conquering forces of the Roman Empire in AD 60 or 61. She ...
, Queen of the Iceni
The Iceni ( , ) or Eceni were a Brittonic tribe of eastern Britain during the Iron Age and early Roman era. Their territory included present-day Norfolk and parts of Suffolk and Cambridgeshire, and bordered the area of the Corieltauvi to the we ...
, ended with Boudica's suicide following her defeat at the Battle of Watling Street
The Boudican revolt was an armed uprising by native Celtic tribes against the Roman Empire. It took place c. 60ã61 AD in the Roman province of Britain, and was led by Boudica, the Queen of the Iceni. The uprising was motivated by the Romans' ...
. The author of one study of Roman Britain suggested that from 43 AD to 84 AD, the Roman invaders killed somewhere between 100,000 and 250,000 people from a population of perhaps 2,000,000. This era saw a Greco-Roman
The Greco-Roman civilization (; also Greco-Roman culture; spelled Graeco-Roman in the Commonwealth), as understood by modern scholars and writers, includes the geographical regions and countries that culturallyãand so historicallyãwere di ...
culture prevail with the introduction of Roman law
Roman law is the law, legal system of ancient Rome, including the legal developments spanning over a thousand years of jurisprudence, from the Twelve Tables (c. 449 BC), to the ''Corpus Juris Civilis'' (AD 529) ordered by Eastern Roman emperor J ...
, Roman architecture
Ancient Roman architecture adopted the external language of classical Greek architecture for the purposes of the ancient Romans, but was different from Greek buildings, becoming a new architectural style. The two styles are often considered on ...
, aqueducts
Aqueduct may refer to:
Structures
*Aqueduct (bridge), a bridge to convey water over an obstacle, such as a ravine or valley
*Navigable aqueduct, or water bridge, a structure to carry navigable waterway canals over other rivers, valleys, railw ...
, sewers, many agricultural items and silk. In the 3rd century, Emperor Septimius Severus
Lucius Septimius Severus (; 11 April 145 ã 4 February 211) was Roman emperor from 193 to 211. He was born in Leptis Magna (present-day Al-Khums, Libya) in the Roman province of Africa (Roman province), Africa. As a young man he advanced thro ...
died at Eboracum
Eboracum () was a fort and later a city in the Roman province of Britannia. In its prime it was the largest town in northern Britain and a provincial capital. The site remained occupied after the decline of the Western Roman Empire and ultimate ...
(now York
York is a cathedral city with Roman origins, sited at the confluence of the rivers Ouse and Foss in North Yorkshire, England. It is the historic county town of Yorkshire. The city has many historic buildings and other structures, such as a ...
), where Constantine
Constantine most often refers to:
* Constantine the Great, Roman emperor from 306 to 337, also known as Constantine I
* Constantine, Algeria, a city in Algeria
Constantine may also refer to:
People
* Constantine (name), a masculine given na ...
was subsequently proclaimed emperor a century later.
There is debate about when Christianity was first introduced; it was no later than the 4th century, probably much earlier. According to Bede
Bede ( ; ang, BúÈda , ; 672/326 May 735), also known as Saint Bede, The Venerable Bede, and Bede the Venerable ( la, Beda Venerabilis), was an English monk at the monastery of St Peter and its companion monastery of St Paul in the Kingdom o ...
, missionaries were sent from Rome by Eleutherius at the request of the chieftain Lucius of Britain
Lucius (Welsh: Lles map Coel, Lleirwg, Lleufer or Lleufer Mawr) was a supposed 2nd-century king of the Britons traditionally credited with introducing Christianity into Britain. Lucius is first mentioned in a 6th-century version of the '' Liber P ...
in 180 AD, to settle differences as to Eastern and Western ceremonials, which were disturbing the church. There are traditions linked to Glastonbury claiming an introduction through Joseph of Arimathea
Joseph of Arimathea was, according to all four canonical gospels, the man who assumed responsibility for the burial of Jesus after his crucifixion. The historical location of Arimathea is uncertain, although it has been identified with several t ...
, while others claim through Lucius of Britain. By 410, during the decline of the Roman Empire
The fall of the Western Roman Empire (also called the fall of the Roman Empire or the fall of Rome) was the loss of central political control in the Western Roman Empire, a process in which the Empire failed to enforce its rule, and its vas ...
, Britain was left exposed by the end of Roman rule in Britain
The end of Roman rule in Britain was the transition from Roman Britain to post-Roman Britain. Roman rule ended in different parts of Britain at different times, and under different circumstances.
In 383, the usurper Magnus Maximus withdrew tr ...
and the withdrawal of Roman army units, to defend the frontiers in continental Europe and partake in civil wars. Celtic Christian monastic and missionary movements flourished: Patrick Patrick may refer to:
* Patrick (given name), list of people and fictional characters with this name
* Patrick (surname), list of people with this name
People
* Saint Patrick (c. 385ãc. 461), Christian saint
*Gilla PûÀtraic (died 1084), Patrick ...
(5th-century Ireland) and in the 6th century Brendan Brendan may refer to:
People
* Saint Brendan the Navigator (c. 484 ã c. 577) was an Irish monastic saint.
* Saint Brendan of Birr (died 573), Abbot of Birr in Co. Offaly, contemporaneous with the above
* Brendan (given name), a masculine given na ...
(Clonfert
Clonfert () is a small village in east County Galway, Ireland, halfway between Ballinasloe and Portumna. The village gives its name to the Diocese of Clonfert. Clonfert Cathedral is one of the eight cathedral churches of the Church of Ireland, ...
), Comgall
Saint Comgall (c. 510ã520 ã 597/602), an early Irish saint, was the founder and abbot of the great Irish monastery at Bangor in Ireland.
MacCaffrey,James (1908). " St. Comgall". In ''Catholic Encyclopedia''. 4. New York: Robert Appleton Co ...
( Bangor), David
David (; , "beloved one") (traditional spelling), , ''Dáwé¨d''; grc-koi, ööÝü
ööÇ, DauûÙd; la, Davidus, David; gez , ðÃÃç, ''Dawit''; xcl, åÇíÀøí¨íˋ, ''Dawitò¢''; cu, ÅůÅýûÙÅÇî, ''DavidéÙ''; possibly meaning "beloved one". w ...
(Wales), Aiden (Lindisfarne) and Columba
Columba or Colmcille; gd, Calum Cille; gv, Colum Keeilley; non, Kolban or at least partly reinterpreted as (7 December 521 ã 9 June 597 AD) was an Irish abbot and missionary evangelist credited with spreading Christianity in what is toda ...
(Iona
Iona (; gd, û Chaluim Chille (IPA: iùùxaè¨äˆè₤imùûÏiòè, sometimes simply ''û''; sco, Iona) is a small island in the Inner Hebrides, off the Ross of Mull on the western coast of Scotland. It is mainly known for Iona Abbey, though there ...
). This period of Christianity was influenced by ancient Celtic culture in its sensibilities, polity, practices and theology. Local "congregations" were centred in the monastic community and monastic leaders were more like chieftains, as peers, rather than in the more hierarchical system of the Roman-dominated church.
Middle Ages

Roman military
The military of ancient Rome, according to Titus Livius, one of the more illustrious historians of Rome over the centuries, was a key element in the rise of Rome over "above seven hundred years" from a small settlement in Latium to the capital of ...
withdrawals left Britain open to invasion by pagan, seafaring warriors from north-western continental Europe, chiefly the Saxons, Angles
The Angles ( ang, ûngle, ; la, Angli) were one of the main Germanic peoples who settled in Great Britain in the post-Roman period. They founded several kingdoms of the Heptarchy in Anglo-Saxon England. Their name is the root of the name ' ...
, Jutes
The Jutes (), Iuti, or IutûÎ ( da, Jyder, non, Jû°tar, ang, áotas) were one of the Germanic tribes who settled in Great Britain after the departure of the Romans. According to Bede, they were one of the three most powerful Germanic nations ...
and Frisians who had long raided the coasts of the Roman province. These groups then began to settle in increasing numbers over the course of the fifth and sixth centuries, initially in the eastern part of the country. Their advance was contained for some decades after the Britons' victory at the Battle of Mount Badon
The Battle of Badon /ùbeèˆdèn/ also known as the Battle of Mons Badonicus ( la, obsessio isBadonici montis, "Blockade/Siege of the Badonic Hill"; ''Bellum in monte Badonis'', "Battle on Badon Hill"; ''Bellum Badonis'', "Battle of Badon"; Old W ...
, but subsequently resumed, overrunning the fertile lowlands of Britain and reducing the area under Brittonic
Brittonic or Brythonic may refer to:
*Common Brittonic, or Brythonic, the Celtic language anciently spoken in Great Britain
*Brittonic languages, a branch of the Celtic languages descended from Common Brittonic
*Britons (Celtic people)
The Br ...
control to a series of separate enclaves in the more rugged country to the west by the end of the 6th century. Contemporary texts describing this period are extremely scarce, giving rise to its description as a Dark Age
The ''Dark Ages'' is a term for the Early Middle Ages, or occasionally the entire Middle Ages, in Western Europe after the fall of the Western Roman Empire that characterises it as marked by economic, intellectual and cultural decline.
The conce ...
. The nature and progression of the Anglo-Saxon settlement of Britain
The Anglo-Saxon settlement of Britain is the process which changed the language and culture of most of what became England from Romano-British to Germanic peoples, Germanic. The Germanic-speakers in Britain, themselves of diverse origins, ev ...
is consequently subject to considerable disagreement; the emerging consensus is that it occurred on a large scale in the south and east but was less substantial to the north and west, where Celtic languages continued to be spoken even in areas under Anglo-Saxon control. Roman-dominated Christianity had, in general, been replaced in the conquered territories by Anglo-Saxon paganism
Anglo-Saxon paganism, sometimes termed Anglo-Saxon heathenism, Anglo-Saxon pre-Christian religion, or Anglo-Saxon traditional religion, refers to the religious beliefs and practices followed by the Anglo-Saxons between the 5th and 8th centurie ...
, but was reintroduced by missionaries from Rome led by Augustine
Augustine of Hippo ( , ; la, Aurelius Augustinus Hipponensis; 13 November 354 ã 28 August 430), also known as Saint Augustine, was a theologian and philosopher of Berbers, Berber origin and the bishop of Hippo Regius in Numidia (Roman pr ...
from 597 onwards. Disputes between the Roman- and Celtic-dominated forms of Christianity ended in victory for the Roman tradition at the Council of Whitby
In the Synod of Whitby in 664, King Oswiu of Northumbria ruled that his kingdom would calculate Easter and observe the monastic tonsure according to the customs of Rome rather than the customs practiced by Irish monks at Iona and its satellite ins ...
(664), which was ostensibly about tonsure
Tonsure () is the practice of cutting or shaving some or all of the hair on the scalp as a sign of religious devotion or humility. The term originates from the Latin word ' (meaning "clipping" or "shearing") and referred to a specific practice in ...
s (clerical haircuts) and the date of Easter, but more significantly, about the differences in Roman and Celtic forms of authority, theology, and practice.
During the settlement period the lands ruled by the incomers seem to have been fragmented into numerous tribal territories, but by the 7th century, when substantial evidence of the situation again becomes available, these had coalesced into roughly a dozen kingdoms including Northumbria
la, Regnum Northanhymbrorum
, conventional_long_name = Kingdom of Northumbria
, common_name = Northumbria
, status = State
, status_text = Unified Anglian kingdom (before 876)North: Anglian kingdom (af ...
, Mercia
la, Merciorum regnum
, conventional_long_name=Kingdom of Mercia
, common_name=Mercia
, status=Kingdom
, status_text=Independent kingdom (527ã879)Client state of Wessex ()
, life_span=527ã918
, era=Heptarchy
, event_start=
, date_start=
, ye ...
, Wessex
la, Regnum Occidentalium Saxonum
, conventional_long_name = Kingdom of the West Saxons
, common_name = Wessex
, image_map = Southern British Isles 9th century.svg
, map_caption = S ...
, East Anglia
East Anglia is an area in the East of England, often defined as including the counties of Norfolk, Suffolk and Cambridgeshire. The name derives from the Anglo-Saxon kingdom of the East Angles, a people whose name originated in Anglia, in ...
, Essex
Essex () is a county in the East of England. One of the home counties, it borders Suffolk and Cambridgeshire to the north, the North Sea to the east, Hertfordshire to the west, Kent across the estuary of the River Thames to the south, and G ...
, Kent
Kent is a county in South East England and one of the home counties. It borders Greater London to the north-west, Surrey to the west and East Sussex to the south-west, and Essex to the north across the estuary of the River Thames; it faces ...
and Sussex
Sussex (), from the Old English (), is a historic county in South East England that was formerly an independent medieval Anglo-Saxon kingdom. It is bounded to the west by Hampshire, north by Surrey, northeast by Kent, south by the English ...
. Over the following centuries, this process of political consolidation continued. The 7th century saw a struggle for hegemony between Northumbria and Mercia, which in the 8th century gave way to Mercian preeminence. In the early 9th century Mercia was displaced as the foremost kingdom by Wessex. Later in that century escalating attacks by the Danes
Danes ( da, danskere, ) are a North Germanic ethnic group and nationality native to Denmark and a modern nation identified with the country of Denmark. This connection may be ancestral, legal, historical, or cultural.
Danes generally regard t ...
culminated in the conquest of the north and east of England, overthrowing the kingdoms of Northumbria, Mercia and East Anglia. Wessex under Alfred the Great
Alfred the Great (alt. ûlfred 848/849 ã 26 October 899) was King of the West Saxons from 871 to 886, and King of the Anglo-Saxons from 886 until his death in 899. He was the youngest son of King ûthelwulf and his first wife Osburh, who bot ...
was left as the only surviving English kingdom, and under his successors, it steadily expanded at the expense of the kingdoms of the Danelaw
The Danelaw (, also known as the Danelagh; ang, Dena lagu; da, Danelagen) was the part of England in which the laws of the Danes held sway and dominated those of the Anglo-Saxons. The Danelaw contrasts with the West Saxon law and the Mercian ...
. This brought about the political unification of England, first accomplished under ûthelstan
ûthelstan or Athelstan (; ang, ûû¯elstán ; on, Aû¯alsteinn; ; ã 27 October 939) was King of the Anglo-Saxons from 924 to 927 and King of the English from 927 to his death in 939. He was the son of King Edward the Elder and his first ...
in 927 and definitively established after further conflicts by Eadred
Eadred (c. 923 ã 23 November 955) was King of the English from 26 May 946 until his death. He was the younger son of Edward the Elder and his third wife Eadgifu, and a grandson of Alfred the Great. His elder brother, Edmund, was killed tryin ...
in 953. A fresh wave of Scandinavian attacks from the late 10th century ended with the conquest of this united kingdom by Sweyn Forkbeard
Sweyn Forkbeard ( non, Sveinn Haraldsson tjû¤guskegg ; da, Svend TveskûÎg; 17 April 963 ã 3 February 1014) was King of Denmark from 986 to 1014, also at times King of the English and King of Norway. He was the father of King Harald II of D ...
in 1013 and again by his son Cnut
Cnut (; ang, Cnut cyning; non, Knû¤tr inn rûÙki ; or , no, Knut den mektige, sv, Knut den Store. died 12 November 1035), also known as Cnut the Great and Canute, was King of England from 1016, King of Denmark from 1018, and King of Norwa ...
in 1016, turning it into the centre of a short-lived North Sea Empire
The North Sea Empire, also known as the Anglo-Scandinavian Empire, was the personal union of the kingdoms of England, Denmark and Norway for most of the period between 1013 and 1042 towards the end of the Viking Age. This ephemeral Norse-ruled ...
that also included Denmark
)
, song = ( en, "King Christian stood by the lofty mast")
, song_type = National and royal anthem
, image_map = EU-Denmark.svg
, map_caption =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name = Danish Realm, Kingdom of Denmark
...
and Norway
Norway, officially the Kingdom of Norway, is a Nordic country in Northern Europe, the mainland territory of which comprises the western and northernmost portion of the Scandinavian Peninsula. The remote Arctic island of Jan Mayen and t ...
. However, the native royal dynasty was restored with the accession of Edward the Confessor
Edward the Confessor ; la, Eduardus Confessor , ; ( 1003 ã 5 January 1066) was one of the last Anglo-Saxon English kings. Usually considered the last king of the House of Wessex, he ruled from 1042 to 1066.
Edward was the son of ûth ...
in 1042.
 A dispute over the succession to Edward led to the
A dispute over the succession to Edward led to the Norman Conquest
The Norman Conquest (or the Conquest) was the 11th-century invasion and occupation of England by an army made up of thousands of Norman, Breton, Flemish, and French troops, all led by the Duke of Normandy, later styled William the Conque ...
in 1066, accomplished by an army led by Duke William of Normandy. The Normans
The Normans (Norman language, Norman: ''Normaunds''; french: Normands; la, Nortmanni/Normanni) were a population arising in the medieval Duchy of Normandy from the intermingling between Norsemen, Norse Viking settlers and indigenous West Fran ...
themselves originated from Scandinavia
Scandinavia; SûÀmi languages: /. ( ) is a subregion#Europe, subregion in Northern Europe, with strong historical, cultural, and linguistic ties between its constituent peoples. In English usage, ''Scandinavia'' most commonly refers to Denmark, ...
and had settled in Normandy in the late 9th and early 10th centuries. This conquest led to the almost total dispossession of the English elite and its replacement by a new French-speaking aristocracy, whose speech had a profound and permanent effect on the English language.
Subsequently, the House of Plantagenet
The House of Plantagenet () was a royal house which originated from the lands of Anjou in France. The family held the English throne from 1154 (with the accession of Henry II at the end of the Anarchy) to 1485, when Richard III died in b ...
from Anjou inherited the English throne under Henry II, adding England to the budding Angevin Empire
The Angevin Empire (; french: Empire Plantagenûˆt) describes the possessions of the House of Plantagenet during the 12th and 13th centuries, when they ruled over an area covering roughly half of France, all of England, and parts of Ireland and W ...
of fiefs the family had inherited in France including Aquitaine
Aquitaine ( , , ; oc, Aquitû nia ; eu, Akitania; Poitevin-Saintongeais: ''Aguiûˋne''), archaic Guyenne or Guienne ( oc, Guiana), is a historical region of southwestern France and a former administrative region of the country. Since 1 January ...
.. They reigned for three centuries, some noted monarchs being Richard I
Richard I (8 September 1157 ã 6 April 1199) was King of England from 1189 until his death in 1199. He also ruled as Duke of Normandy, Aquitaine and Gascony, Lord of Cyprus, and Count of Poitiers, Anjou, Maine, and Nantes, and was overl ...
, Edward I
Edward I (17/18 June 1239 ã 7 July 1307), also known as Edward Longshanks and the Hammer of the Scots, was King of England and Lord of Ireland from 1272 to 1307. Concurrently, he ruled the duchies of Aquitaine and Gascony as a vassal o ...
, Edward III
Edward III (13 November 1312 ã 21 June 1377), also known as Edward of Windsor before his accession, was King of England and Lord of Ireland from January 1327 until his death in 1377. He is noted for his military success and for restoring r ...
and Henry V Henry V may refer to:
People
* Henry V, Duke of Bavaria (died 1026)
* Henry V, Holy Roman Emperor (1081/86ã1125)
* Henry V, Duke of Carinthia (died 1161)
* Henry V, Count Palatine of the Rhine (c. 1173ã1227)
* Henry V, Count of Luxembourg (121 ...
. The period saw changes in trade and legislation, including the signing of the ''Magna Carta
(Medieval Latin for "Great Charter of Freedoms"), commonly called (also ''Magna Charta''; "Great Charter"), is a royal charter of rights agreed to by King John of England at Runnymede, near Windsor, on 15 June 1215. First drafted by the ...
'', an English legal charter used to limit the sovereign's powers by law and protect the privileges of freemen. Catholic monasticism
Monasticism (from Ancient Greek , , from , , 'alone'), also referred to as monachism, or monkhood, is a religious way of life in which one renounces worldly pursuits to devote oneself fully to spiritual work. Monastic life plays an important role ...
flourished, providing philosophers, and the universities of Oxford and Cambridge were founded with royal patronage. The Principality of Wales
The Principality of Wales ( cy, Tywysogaeth Cymru) was originally the territory of the native Welsh princes of the House of Aberffraw from 1216 to 1283, encompassing two-thirds of modern Wales during its height of 1267ã1277. Following the con ...
became a Plantagenet fief during the 13th century and the Lordship of Ireland
The Lordship of Ireland ( ga, Tiarnas na hûireann), sometimes referred to retroactively as Norman Ireland, was the part of Ireland ruled by the King of England (styled as "Lord of Ireland") and controlled by loyal Anglo-Norman lords between ...
was given to the English monarchy by the Pope.
During the 14th century, the Plantagenets and the House of Valois
The Capetian house of Valois ( , also , ) was a cadet branch of the Capetian dynasty. They succeeded the House of Capet (or "Direct Capetians") to the List of French monarchs, French throne, and were the royal house of France from 1328 to 1589 ...
both claimed to be legitimate claimants to the House of Capet
The House of Capet (french: Maison capûˋtienne) or the Direct Capetians (''Capûˋtiens directs''), also called the House of France (''la maison de France''), or simply the Capets, ruled the Kingdom of France from 987 to 1328. It was the most s ...
and with it France; the two powers clashed in the Hundred Years' War
The Hundred Years' War (; 1337ã1453) was a series of armed conflicts between the kingdoms of Kingdom of England, England and Kingdom of France, France during the Late Middle Ages. It originated from disputed claims to the French Crown, ...
. The Black Death
The Black Death (also known as the Pestilence, the Great Mortality or the Plague) was a bubonic plague pandemic occurring in Western Eurasia and North Africa from 1346 to 1353. It is the most fatal pandemic recorded in human history, causi ...
epidemic hit England; starting in 1348, it eventually killed up to half of England's inhabitants
Domicile is relevant to an individual's "personal law," which includes the law that governs a person's status and their property. It is independent of a person's nationality. Although a domicile may change from time to time, a person has only one ...
. From 1453 to 1487 civil war occurred between two branches of the royal family ã the Yorkists
The House of York was a cadet branch of the English royal House of Plantagenet. Three of its members became kings of England in the late 15th century. The House of York descended in the male line from Edmund of Langley, 1st Duke of York, t ...
and Lancastrians ã known as the Wars of the Roses
The Wars of the Roses (1455ã1487), known at the time and for more than a century after as the Civil Wars, were a series of civil wars fought over control of the English throne in the mid-to-late fifteenth century. These wars were fought bet ...
. Eventually it led to the Yorkists losing the throne entirely to a Welsh noble family the Tudors
The House of Tudor was a royal house of largely Welsh and English origin that held the English throne from 1485 to 1603. They descended from the Tudors of Penmynydd and Catherine of France. Tudor monarchs ruled the Kingdom of England and it ...
, a branch of the Lancastrians headed by Henry Tudor who invaded with Welsh and Breton mercenaries, gaining victory at the Battle of Bosworth Field
The Battle of Bosworth or Bosworth Field was the last significant battle of the Wars of the Roses, the civil war between the houses of Lancaster and York that extended across England in the latter half of the 15th century. Fought on 22 Augu ...
where the Yorkist king Richard III
Richard III (2 October 145222 August 1485) was King of England and Lord of Ireland from 26 June 1483 until his death in 1485. He was the last king of the House of York and the last of the Plantagenet dynasty. His defeat and death at the Battl ...
was killed.
Early modern
During theTudor period
The Tudor period occurred between 1485 and 1603 in History of England, England and Wales and includes the Elizabethan period during the reign of Elizabeth I until 1603. The Tudor period coincides with the dynasty of the House of Tudor in Englan ...
, the Renaissance
The Renaissance ( , ) , from , with the same meanings. is a period in European history marking the transition from the Middle Ages to modernity and covering the 15th and 16th centuries, characterized by an effort to revive and surpass ideas ...
reached England through Italian courtiers, who reintroduced artistic, educational and scholarly debate from classical antiquity. England began to develop naval skills, and exploration to the West intensified. Henry VIII
Henry VIII (28 June 149128 January 1547) was King of England from 22 April 1509 until his death in 1547. Henry is best known for his six marriages, and for his efforts to have his first marriage (to Catherine of Aragon) annulled. His disa ...
broke from communion with the Catholic Church, over issues relating to his divorce, under the Acts of Supremacy
The Acts of Supremacy are two acts passed by the Parliament of England in the 16th century that established the English monarchs as the head of the Church of England; two similar laws were passed by the Parliament of Ireland establishing the Eng ...
in 1534 which proclaimed the monarch head of the Church of England
The Church of England (C of E) is the established Christian church in England and the mother church of the international Anglican Communion. It traces its history to the Christian church recorded as existing in the Roman province of Britain ...
. In contrast with much of European Protestantism, the roots of the split were more political than theological. He also legally incorporated his ancestral land Wales into the Kingdom of England with the 1535ã1542 acts. There were internal religious conflicts during the reigns of Henry's daughters, Mary I
Mary I (18 February 1516 ã 17 November 1558), also known as Mary Tudor, and as "Bloody Mary" by her Protestant opponents, was Queen of England and Ireland from July 1553 and Queen of Spain from January 1556 until her death in 1558. Sh ...
and Elizabeth I
Elizabeth I (7 September 153324 March 1603) was Queen of England and Ireland from 17 November 1558 until her death in 1603. Elizabeth was the last of the five House of Tudor monarchs and is sometimes referred to as the "Virgin Queen".
El ...
. The former took the country back to Catholicism while the latter broke from it again, forcefully asserting the supremacy of Anglicanism. The Elizabethan era is the epoch in the Tudor age of the reign of Queen Elizabeth I ("the Virgin Queen"). Historians often depict it as the Golden age (metaphor), golden age in English history. Elizabethan England represented the apogee of the English Renaissance and saw the flowering of art, poetry, music and literature. The era is most famous for its drama, theatre and playwrights. England during this period had a centralised, well-organised, and effective government as a result of vast Tudor reforms.
Competing with Spanish Empire, Spain, the first English colony in the Americas was founded in 1585 by explorer Walter Raleigh in Virginia and named Roanoke Colony, Roanoke. The Roanoke colony failed and is known as the lost colony after it was found abandoned on the return of the late-arriving supply ship. With the East India Company, England also competed with the Dutch Empire, Dutch and French colonial empire, French in the East. During the Elizabethan period, England was at war with Spain. An Spanish Armada, armada sailed from Spain in 1588 as part of a wider plan to invade England and re-establish a Catholic monarchy. The plan was thwarted by bad coordination, stormy weather and successful harrying attacks by an English fleet under Charles Howard, 1st Earl of Nottingham, Lord Howard of Effingham. This failure did not end the threat: Spain launched two further armadas, in 2nd Spanish Armada, 1596 and 3rd Spanish Armada, 1597, but both were driven back by storms. The political structure of the island changed in 1603, when the King of Scots, James VI of Scotland, James VI, a kingdom which had been a long-time rival to English interests, inherited the throne of England as James I, thereby creating a Union of the Crowns, personal union..; He styled himself King of Great Britain, although this had no basis in English law. Under the auspices of James VI and I the Authorised King James Version of the Holy Bible was published in 1611. It was the standard version of the Bible read by most Protestant Christians for four hundred years until modern revisions were produced in the 20th century.
 Based on conflicting political, religious and social positions, the English Civil War was fought between the supporters of Long Parliament, Parliament and those of King Charles I of England, Charles I, known colloquially as Roundheads and Cavaliers respectively. This was an interwoven part of the wider multifaceted Wars of the Three Kingdoms, involving Kingdom of Scotland, Scotland and Kingdom of Ireland, Ireland. The Parliamentarians were victorious, execution of Charles I, Charles I was executed and the kingdom replaced by the Commonwealth of England, Commonwealth. Leader of the Parliament forces, Oliver Cromwell declared himself Lord Protector in 1653; a period of the Protectorate, personal rule followed. After Cromwell's death and the resignation of his son Richard Cromwell, Richard as Lord Protector, Charles II of England, Charles II was invited to return as monarch in 1660, in a move called the English Restoration, Restoration. With the reopening of theatres, fine arts, literature and performing arts flourished throughout the Restoration of
Based on conflicting political, religious and social positions, the English Civil War was fought between the supporters of Long Parliament, Parliament and those of King Charles I of England, Charles I, known colloquially as Roundheads and Cavaliers respectively. This was an interwoven part of the wider multifaceted Wars of the Three Kingdoms, involving Kingdom of Scotland, Scotland and Kingdom of Ireland, Ireland. The Parliamentarians were victorious, execution of Charles I, Charles I was executed and the kingdom replaced by the Commonwealth of England, Commonwealth. Leader of the Parliament forces, Oliver Cromwell declared himself Lord Protector in 1653; a period of the Protectorate, personal rule followed. After Cromwell's death and the resignation of his son Richard Cromwell, Richard as Lord Protector, Charles II of England, Charles II was invited to return as monarch in 1660, in a move called the English Restoration, Restoration. With the reopening of theatres, fine arts, literature and performing arts flourished throughout the Restoration of Kingdom of Great Britain
The Kingdom of Great Britain (officially Great Britain) was a Sovereign state, sovereign country in Western Europe from 1 May 1707 to the end of 31 December 1800. The state was created by the 1706 Treaty of Union and ratified by the Acts of ...
in 1707. To accommodate the union, institutions such as the law and national churches of each remained separate.
Late modern and contemporary
 Under the newly formed Kingdom of Great Britain, output from the Royal Society and other English Enlightenment, English initiatives combined with the Scottish Enlightenment to create innovations in science and engineering, while the enormous growth in Triangular trade, British overseas trade protected by the Royal Navy paved the way for the establishment of the British Empire. Domestically it drove the
Under the newly formed Kingdom of Great Britain, output from the Royal Society and other English Enlightenment, English initiatives combined with the Scottish Enlightenment to create innovations in science and engineering, while the enormous growth in Triangular trade, British overseas trade protected by the Royal Navy paved the way for the establishment of the British Empire. Domestically it drove the Industrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution was the transition to new manufacturing processes in Great Britain, continental Europe, and the United States, that occurred during the period from around 1760 to about 1820ã1840. This transition included going f ...
, a period of profound change in the socioeconomics, socioeconomic and cultural conditions of England, resulting in industrialised agriculture, manufacture, engineering and mining, as well as new and pioneering road, rail and water networks to facilitate their expansion and development. The opening of Northwest England's Bridgewater Canal in 1761 ushered in the History of the British canal system, canal age in Britain.; . In 1825 the world's first permanent steam locomotive-hauled passenger railway ã the Stockton and Darlington Railway ã opened to the public.
 During the Industrial Revolution, many workers moved from England's countryside to new and expanding urban industrial areas to work in factories, for instance at Birmingham and Manchester, dubbed "Workshop of the World" and "Warehouse City" respectively. Manchester was the world's first industrial city. England maintained relative stability throughout the French Revolution; William Pitt the Younger was British prime minister for the reign of George III of the United Kingdom, George III. The Regency of George IV is noted for its elegance and achievements in the fine arts and architecture. During the Napoleonic Wars, Napoleon planned to Napoleon's planned invasion of the United Kingdom, invade from the south-east. However, this failed to manifest and the Napoleonic forces were defeated by the British: at sea by Horatio Nelson, and on land by Arthur Wellesley, 1st Duke of Wellington, Arthur Wellesley. The major victory at the Battle of Trafalgar confirmed the naval supremacy Britain had established during the course of the eighteenth century. The Napoleonic Wars fostered a concept of Britishness and a united national British people, shared with the English, Scots and Welsh..
During the Industrial Revolution, many workers moved from England's countryside to new and expanding urban industrial areas to work in factories, for instance at Birmingham and Manchester, dubbed "Workshop of the World" and "Warehouse City" respectively. Manchester was the world's first industrial city. England maintained relative stability throughout the French Revolution; William Pitt the Younger was British prime minister for the reign of George III of the United Kingdom, George III. The Regency of George IV is noted for its elegance and achievements in the fine arts and architecture. During the Napoleonic Wars, Napoleon planned to Napoleon's planned invasion of the United Kingdom, invade from the south-east. However, this failed to manifest and the Napoleonic forces were defeated by the British: at sea by Horatio Nelson, and on land by Arthur Wellesley, 1st Duke of Wellington, Arthur Wellesley. The major victory at the Battle of Trafalgar confirmed the naval supremacy Britain had established during the course of the eighteenth century. The Napoleonic Wars fostered a concept of Britishness and a united national British people, shared with the English, Scots and Welsh..
 London became the largest and most populous metropolitan area in the world during the Victorian era, and trade within the British Empire ã as well as the standing of the British military and navy ã was prestigious. Technologically, this era saw many innovations that proved key to the United Kingdom's power and prosperity. Political agitation at home from radicals such as the Chartism, Chartists and the suffragettes enabled legislative reform and universal suffrage. Samuel Hynes described the Edwardian era as a "leisurely time when women wore picture hats and did not vote, when the rich were not ashamed to live conspicuously, and the sun really never set on the British flag."
Power shifts in east-central Europe led to World War I; hundreds of thousands of English soldiers died fighting for the United Kingdom as part of the Allies of World War I, Allies. Two decades later, in World War II, the United Kingdom was again one of the Allies of World War II, Allies. At the end of the Phoney War, Winston Churchill became the wartime prime minister. Developments in warfare technology saw many cities damaged by air-raids during the Blitz. Following the war, the British Empire experienced rapid decolonisation, and there was a speeding-up of technological innovations; automobiles became the primary means of transport and Frank Whittle's development of the jet engine led to wider air travel. Residential patterns were altered in England by private motoring, and by the creation of the National Health Service (England), National Health Service (NHS) in 1948. The UK's NHS provided publicly funded health care to all UK permanent residents free at the point of need, being paid for from general taxation. Combined, these prompted the reform of local government in England in the mid-20th century.
Since the 20th century there has been significant population movement to England, mostly from other parts of the British Isles, but also from the Commonwealth of Nations, Commonwealth, particularly the Indian subcontinent. Since the 1970s there has been a large move away from manufacturing and an increasing emphasis on the service industry. As part of the United Kingdom, the area joined a common market initiative called the European Economic Community which became the European Union. Since the late 20th century the politics of the United Kingdom, administration of the United Kingdom has moved towards devolution, devolved governance in Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland. England and Wales continues to exist as a jurisdiction within the United Kingdom. Devolution has stimulated a greater emphasis on a more English-specific identity and patriotism. There is no devolved English government, but an attempt to create a similar system on a sub-regional basis was rejected by referendum.
London became the largest and most populous metropolitan area in the world during the Victorian era, and trade within the British Empire ã as well as the standing of the British military and navy ã was prestigious. Technologically, this era saw many innovations that proved key to the United Kingdom's power and prosperity. Political agitation at home from radicals such as the Chartism, Chartists and the suffragettes enabled legislative reform and universal suffrage. Samuel Hynes described the Edwardian era as a "leisurely time when women wore picture hats and did not vote, when the rich were not ashamed to live conspicuously, and the sun really never set on the British flag."
Power shifts in east-central Europe led to World War I; hundreds of thousands of English soldiers died fighting for the United Kingdom as part of the Allies of World War I, Allies. Two decades later, in World War II, the United Kingdom was again one of the Allies of World War II, Allies. At the end of the Phoney War, Winston Churchill became the wartime prime minister. Developments in warfare technology saw many cities damaged by air-raids during the Blitz. Following the war, the British Empire experienced rapid decolonisation, and there was a speeding-up of technological innovations; automobiles became the primary means of transport and Frank Whittle's development of the jet engine led to wider air travel. Residential patterns were altered in England by private motoring, and by the creation of the National Health Service (England), National Health Service (NHS) in 1948. The UK's NHS provided publicly funded health care to all UK permanent residents free at the point of need, being paid for from general taxation. Combined, these prompted the reform of local government in England in the mid-20th century.
Since the 20th century there has been significant population movement to England, mostly from other parts of the British Isles, but also from the Commonwealth of Nations, Commonwealth, particularly the Indian subcontinent. Since the 1970s there has been a large move away from manufacturing and an increasing emphasis on the service industry. As part of the United Kingdom, the area joined a common market initiative called the European Economic Community which became the European Union. Since the late 20th century the politics of the United Kingdom, administration of the United Kingdom has moved towards devolution, devolved governance in Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland. England and Wales continues to exist as a jurisdiction within the United Kingdom. Devolution has stimulated a greater emphasis on a more English-specific identity and patriotism. There is no devolved English government, but an attempt to create a similar system on a sub-regional basis was rejected by referendum.
Governance
Politics
 England is part of the United Kingdom, a constitutional monarchy with a parliamentary system. There has not been a government of England since 1707, when the Acts of Union 1707, putting into effect the terms of the
England is part of the United Kingdom, a constitutional monarchy with a parliamentary system. There has not been a government of England since 1707, when the Acts of Union 1707, putting into effect the terms of the Treaty of Union
The Treaty of Union is the name usually now given to the treaty which led to the creation of the new state of Great Britain, stating that the Kingdom of England (which already included Wales) and the Kingdom of Scotland were to be "United i ...
, joined England and Scotland to form the Kingdom of Great Britain
The Kingdom of Great Britain (officially Great Britain) was a Sovereign state, sovereign country in Western Europe from 1 May 1707 to the end of 31 December 1800. The state was created by the 1706 Treaty of Union and ratified by the Acts of ...
. Before the union England was ruled by List of English monarchs, its monarch and the Parliament of England. Today England is governed directly by the Parliament of the United Kingdom, although other countries of the United Kingdom have Devolution, devolved governments. In the House of Commons of the United Kingdom, House of Commons which is the lower house of the British Parliament based at the Palace of Westminster, there are 532 Members of Parliament (MPs) for constituencies in England, out of the 650 total. As of the 2019 United Kingdom general election, England is represented by 345 MPs from the Conservative Party (UK), Conservative Party, 179 from the Labour Party (UK), Labour Party, seven from the Liberal Democrats (UK), Liberal Democrats, one from the Green Party of England and Wales, Green Party, and the Speaker of the House of Commons (United Kingdom), Speaker of the House, Lindsay Hoyle.
Since devolution, in which other countries of the United Kingdom ã Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland ã each have their own devolved parliament or assemblies for local issues, there has been debate about how to counterbalance this in England. Originally it was planned that various regions of England would be devolved, but following the proposal's rejection by the North East
The points of the compass are a set of horizontal, radially arrayed compass directions (or azimuths) used in navigation and cartography. A compass rose is primarily composed of four cardinal directionsãnorth, east, south, and westãeach sepa ...
in a 2004 North East England devolution referendum, 2004 referendum, this has not been carried out.
One major issue is the West Lothian question, in which MPs from Scotland and Wales are able to vote on legislation affecting only England, while English MPs have no equivalent right to legislate on devolved matters. This when placed in the context of England being the only country of the United Kingdom not to have free cancer treatment, prescriptions, residential care for the elderly and top-up fees, free top-up university fees, has led to a steady rise in English nationalism. Some have suggested the creation of a devolved English parliament, while others have proposed simply limiting voting on legislation which only affects England to English MPs.
Law
 The
The English law
English law is the common law legal system of England and Wales, comprising mainly criminal law and civil law, each branch having its own courts and procedures.
Principal elements of English law
Although the common law has, historically, be ...
legal system, developed over the centuries, is the basis of common law
In law, common law (also known as judicial precedent, judge-made law, or case law) is the body of law created by judges and similar quasi-judicial tribunals by virtue of being stated in written opinions."The common law is not a brooding omnipresen ...
legal systems used in most Commonwealth of Nations, Commonwealth countries and the United States (except Louisiana). Despite now being part of the United Kingdom, the legal system of the Courts of England and Wales continued, under the Treaty of Union
The Treaty of Union is the name usually now given to the treaty which led to the creation of the new state of Great Britain, stating that the Kingdom of England (which already included Wales) and the Kingdom of Scotland were to be "United i ...
, as a separate legal system from the one used in Scotland. The general essence of English law is that it is made by judges sitting in courts, applying their common sense and knowledge of legal precedent ã ''stare decisis'' ã to the facts before them.
The court system is headed by the Senior Courts of England and Wales, consisting of the Court of Appeal of England and Wales, Court of Appeal, the High Court of Justice for civil cases, and the Crown Court for criminal cases. The Supreme Court of the United Kingdom is the highest court for criminal and civil cases in England and Wales. It was created in 2009 after constitutional changes, taking over the judicial functions of the House of Lords. A decision of the Supreme Court is binding on every other court in the hierarchy, which must follow its directions.
The secretary of state for justice is the minister responsible to Parliament for the Judiciaries of the United Kingdom, judiciary, the court system and prisons and probation in England. Crime increased between 1981 and 1995 but fell by 42% in the period 1995ã2006. The prison population doubled over the same period, giving it one of the List of countries by incarceration rate, highest incarceration rates in Western Europe at 147 per 100,000. His Majesty's Prison Service, reporting to the Ministry of Justice (United Kingdom), Ministry of Justice, manages most prisons, housing 81,309 prisoners in England and Wales .
Regions, counties, and districts
The subdivisions of England consist of up to four levels of administrative division, subnational division controlled through a variety of types of administrative entities created for the purposes of local government in England, local government. The highest tier of local government were the nine regions of England:North East
The points of the compass are a set of horizontal, radially arrayed compass directions (or azimuths) used in navigation and cartography. A compass rose is primarily composed of four cardinal directionsãnorth, east, south, and westãeach sepa ...
, North West
The points of the compass are a set of horizontal, radially arrayed compass directions (or azimuths) used in navigation and cartography. A compass rose is primarily composed of four cardinal directionsãnorth, east, south, and westãeach sepa ...
, Yorkshire and the Humber, East Midlands, West Midlands (region), West Midlands, East of England, East, South East
The points of the compass are a set of horizontal, radially arrayed compass directions (or azimuths) used in navigation and cartography. A compass rose is primarily composed of four cardinal directionsãnorth, east, south, and westãeach sepa ...
, South West England, South West, and London. These were created in 1994 as Government Offices, used by the UK government to deliver a wide range of policies and programmes regionally, but there are no elected bodies at this level, except in London, and in 2011 the regional government offices were abolished.
After devolution began to take place in other parts of the United Kingdom it was planned that referendums for the regions of England would take place for their own elected Regional Assemblies in England, regional assemblies as a counterweight. 1998 Greater London Authority referendum, London accepted in 1998: the London Assembly was created two years later. However, when the proposal was rejected by the 2004 North East England devolution referendum in the North East, further referendums were cancelled. The regional assemblies outside London were abolished in 2010, and their functions transferred to respective Regional Development Agency, regional development agencies and a new system of local authority leaders' boards.
Below the regional level, all of England is divided into 48 Ceremonial counties of England, ceremonial counties. These are used primarily as a geographical frame of reference and have developed gradually since the Middle Ages, with some established as recently as 1974.. Each has a Lord Lieutenant, lord lieutenant and High Sheriff, high sheriff; these posts are used to represent the British monarch locally. Outside Greater London and the Isles of Scilly
The Isles of Scilly (; kw, Syllan, ', or ) is an archipelago off the southwestern tip of Cornwall, England. One of the islands, St Agnes, is the most southerly point in Britain, being over further south than the most southerly point of the ...
, England is also divided into 83 Metropolitan and non-metropolitan counties of England, metropolitan and non-metropolitan counties; these correspond to areas used for the purposes of local government. and may consist of a single district or be divided into several.
There are six metropolitan county, metropolitan counties based on the most heavily urbanised areas, which do not have county councils. In these areas the principal authorities are the councils of the subdivisions, the metropolitan boroughs. Elsewhere, 27 non-metropolitan county, non-metropolitan "shire" counties have a county council and are divided into districts, each with a district council. They are typically, though not always, found in more rural areas. The remaining non-metropolitan counties are of a single district and usually correspond to large towns or sparsely populated counties; they are known as Unitary authorities of England, unitary authorities. Greater London has a different system for local government, with 32 London boroughs, plus the City of London covering a small area at the core governed by the City of London Corporation. At the most localised level, much of England is divided into civil parishes in England, civil parishes with Parish councils in England, councils; in Greater London only one, Queen's Park, London, Queen's Park, exists after they were London Government Act 1963, abolished in 1965 until legislation Local Government and Public Involvement in Health Act 2007, allowed their recreation in 2007.
Geography
Landscape and rivers
 Geographically England includes the central and southern two-thirds of the island of Great Britain, plus such offshore islands as the
Geographically England includes the central and southern two-thirds of the island of Great Britain, plus such offshore islands as the Isle of Wight
The Isle of Wight ( ) is a county in the English Channel, off the coast of Hampshire, from which it is separated by the Solent. It is the largest and second-most populous island of England. Referred to as 'The Island' by residents, the Isle of ...
and the Isles of Scilly
The Isles of Scilly (; kw, Syllan, ', or ) is an archipelago off the southwestern tip of Cornwall, England. One of the islands, St Agnes, is the most southerly point in Britain, being over further south than the most southerly point of the ...
. It is bordered by two other countries of the United Kingdom: Anglo Scottish border, to the north by Scotland and Wales-England border, to the west by Wales. England is closer than any other part of mainland Britain to the European continent. It is separated from France (Hauts-de-France) by a sea gap, though the two countries are connected by the Channel Tunnel near Folkestone. England also has shores on the Irish Sea
The Irish Sea or , gv, Y Keayn Yernagh, sco, Erse Sie, gd, Muir ûireann , Ulster-Scots: ''Airish Sea'', cy, MûÇr Iwerddon . is an extensive body of water that separates the islands of Ireland and Great Britain. It is linked to the Ce ...
, North Sea
The North Sea lies between Great Britain, Norway, Denmark, Germany, the Netherlands and Belgium. An epeiric sea on the European continental shelf, it connects to the Atlantic Ocean through the English Channel in the south and the Norwegian S ...
and Atlantic Ocean.
The ports of London, Liverpool, and Newcastle upon Tyne, Newcastle lie on the tidal rivers River Thames, Thames, River Mersey, Mersey and River Tyne, Tyne respectively. At , the River Severn, Severn is the longest river flowing through England. It empties into the Bristol Channel and is notable for its Severn Bore (a tidal bore), which can reach in height. However, the longest river entirely in England is the Thames, which is in length.
 There are many lakes in England; the largest is Windermere, within the aptly named
There are many lakes in England; the largest is Windermere, within the aptly named Lake District
The Lake District, also known as the Lakes or Lakeland, is a mountainous region in North West England. A popular holiday destination, it is famous for its lakes, forests, and mountains (or ''fells''), and its associations with William Wordswor ...
. Most of England's landscape consists of low hills and plains, with upland and mountainous terrain in the north and west of the country. The northern uplands include the Pennines
The Pennines (), also known as the Pennine Chain or Pennine Hills, are a range of uplands running between three regions of Northern England: North West England on the west, North East England and Yorkshire and the Humber on the east. Commo ...
, a chain of uplands dividing east and west, the Lake District mountains in Cumbria, and the Cheviot Hills, straddling the border between England and Scotland. The highest point in England, at , is Scafell Pike in the Lake District. The Shropshire Hills
The Shropshire Hills are a dissected upland area and one of the natural regions of England. They lie wholly within the county of Shropshire and encompass several distinctive and well-known landmarks, such as the Long Mynd, Wenlock Edge, The Wrek ...
are near Wales while Dartmoor
Dartmoor is an upland area in southern Devon, England. The moorland and surrounding land has been protected by National Park status since 1951. Dartmoor National Park covers .
The granite which forms the uplands dates from the Carboniferous ...
and Exmoor are two upland areas in the south-west of the country. The approximate dividing line between terrain types is often indicated by the TeesãExe line.
In geological terms, the Pennines, known as the "backbone of England", are the oldest range of mountains in the country, originating from the end of the Paleozoic Era around 300 million years ago. Their geological composition includes, among others, sandstone and limestone, and also coal. There are karst landscapes in calcite areas such as parts of Yorkshire
Yorkshire ( ; abbreviated Yorks), formally known as the County of York, is a Historic counties of England, historic county in northern England and by far the largest in the United Kingdom. Because of its large area in comparison with other Eng ...
and Derbyshire. The Pennine landscape is high moorland in upland areas, indented by fertile valleys of the region's rivers. They contain two national parks in England, national parks, the Yorkshire Dales and the Peak District. In the West Country, Dartmoor and Exmoor of the Southwest Peninsula include upland moorland supported by granite, and enjoy a Climate of south-west England, mild climate; both are national parks.
The English Lowlands beech forests, English Lowlands are in the central and southern regions of the country, consisting of green rolling hills, including the Cotswold Hills, Chiltern Hills, North Downs, North and South Downs; where they meet the sea they form white rock exposures such as the cliffs of Dover. This also includes relatively flat plains such as the Salisbury Plain, Somerset Levels, South Coast Plain and The Fens.
Climate
England has a temperate climate, temperate maritime climate: it is mild with temperatures not much lower than in winter and not much higher than in summer. The weather is damp relatively frequently and is changeable. The coldest months are January and February, the latter particularly on the Geography of the United Kingdom, English coast, while July is normally the warmest month. Months with mild to warm weather are May, June, September and October. Rainfall is spread fairly evenly throughout the year. Important influences on the climate of England are its proximity to the Atlantic Ocean, its northern latitude and the warming of the sea by the Gulf Stream. Rainfall is higher in the west, and parts of theLake District
The Lake District, also known as the Lakes or Lakeland, is a mountainous region in North West England. A popular holiday destination, it is famous for its lakes, forests, and mountains (or ''fells''), and its associations with William Wordswor ...
receive more rain than anywhere else in the country. Since weather records began, the highest temperature recorded was on 25 July 2019 at the Cambridge University Botanic Garden, Botanic Garden in Cambridge, while the lowest was on 10 January 1982 in Edgmond, Shropshire, Edgmond, Shropshire.
Nature and wildlife

 The fauna of England is similar to that of other areas in the British Isles with a wide range of vertebrate and invertebrate life in a diverse range of habitats.
National nature reserves in England are designated by Natural England as key places for wildlife and natural features in England. They were established to protect the most significant areas of habitat and of geological formations. NNRs are managed on behalf of the nation, many by Natural England themselves, but also by non-governmental organisations, including the members of The Wildlife Trusts partnership, the National Trust for Places of Historic Interest or Natural Beauty, National Trust, and the Royal Society for the Protection of Birds. There are 229 NNRs in England covering . Often they contain rare species or nationally important populations of plants and animals.
The Environment Agency is a non-departmental public body, established in 1995 and sponsored by the Department for Environment, Food and Rural Affairs with responsibilities relating to the protection and enhancement of the environment in England. The Secretary of State for Environment, Food and Rural Affairs is the minister responsible for environmental protection, agriculture, fisheries and rural communities in England.
England has a Oceanic climate, temperate oceanic climate in most areas, lacking extremes of cold or heat, but does have a few small areas of Subarctic climate, subarctic and warmer areas in South West England, the South West. Towards the Northern England, North of England the climate becomes colder and most of England's mountains and high hills are located here and have a major impact on the climate and thus the local fauna of the areas. Deciduous woodlands are common across all of England and provide a great habitat for much of England's wildlife, but these give way in northern and upland areas of England to coniferous forests (mainly plantations) which also benefit certain forms of wildlife. Some species have adapted to the expanded urban environment, particularly the red fox, which is the most successful Urban wildlife, urban mammal after the brown rat, and other animals such as common wood pigeon, both of which thrive in urban and suburban areas.
Grey squirrels introduced from eastern America have forced the decline of the native red squirrel due to competition. Red squirrels are now confined to upland and coniferous-forested areas of England, mainly in the north, south west and Isle of Wight. England's climate is very suitable for lagomorphs and the country has European rabbit, rabbits and European hare, brown hares which were introduced in Roman times. Mountain hares which are indigenous have now been re-introduced in Derbyshire. The fauna of England has to cope with varying temperatures and conditions, although not extreme they do pose potential challenges and adaptational measures. English fauna has however had to cope with industrialisation, human population densities amongst the highest in Europe and intensive farming, but as England is a developed nation, wildlife and the countryside have entered the English people, English mindset more and the country is very conscientious about preserving its wildlife, environment and countryside.
The fauna of England is similar to that of other areas in the British Isles with a wide range of vertebrate and invertebrate life in a diverse range of habitats.
National nature reserves in England are designated by Natural England as key places for wildlife and natural features in England. They were established to protect the most significant areas of habitat and of geological formations. NNRs are managed on behalf of the nation, many by Natural England themselves, but also by non-governmental organisations, including the members of The Wildlife Trusts partnership, the National Trust for Places of Historic Interest or Natural Beauty, National Trust, and the Royal Society for the Protection of Birds. There are 229 NNRs in England covering . Often they contain rare species or nationally important populations of plants and animals.
The Environment Agency is a non-departmental public body, established in 1995 and sponsored by the Department for Environment, Food and Rural Affairs with responsibilities relating to the protection and enhancement of the environment in England. The Secretary of State for Environment, Food and Rural Affairs is the minister responsible for environmental protection, agriculture, fisheries and rural communities in England.
England has a Oceanic climate, temperate oceanic climate in most areas, lacking extremes of cold or heat, but does have a few small areas of Subarctic climate, subarctic and warmer areas in South West England, the South West. Towards the Northern England, North of England the climate becomes colder and most of England's mountains and high hills are located here and have a major impact on the climate and thus the local fauna of the areas. Deciduous woodlands are common across all of England and provide a great habitat for much of England's wildlife, but these give way in northern and upland areas of England to coniferous forests (mainly plantations) which also benefit certain forms of wildlife. Some species have adapted to the expanded urban environment, particularly the red fox, which is the most successful Urban wildlife, urban mammal after the brown rat, and other animals such as common wood pigeon, both of which thrive in urban and suburban areas.
Grey squirrels introduced from eastern America have forced the decline of the native red squirrel due to competition. Red squirrels are now confined to upland and coniferous-forested areas of England, mainly in the north, south west and Isle of Wight. England's climate is very suitable for lagomorphs and the country has European rabbit, rabbits and European hare, brown hares which were introduced in Roman times. Mountain hares which are indigenous have now been re-introduced in Derbyshire. The fauna of England has to cope with varying temperatures and conditions, although not extreme they do pose potential challenges and adaptational measures. English fauna has however had to cope with industrialisation, human population densities amongst the highest in Europe and intensive farming, but as England is a developed nation, wildlife and the countryside have entered the English people, English mindset more and the country is very conscientious about preserving its wildlife, environment and countryside.
Major conurbations
The Greater London Built-up Area is by far the largest urban area in England and one of the busiest cities in the world. It is considered a global city and has a population larger than any other country in the United Kingdom besides England itself. Other urban areas of considerable size and influence tend to be in northern England or the English Midlands. There are List of cities in the United Kingdom, 50 settlements which have designated City status in the United Kingdom, city status in England, while the wider United Kingdom has 66. While many cities in England are quite large, such as Birmingham, Sheffield, Manchester, Liverpool, City of Leeds, Leeds, Newcastle upon Tyne, Newcastle, City of Bradford, Bradford, Nottingham, population size is not a prerequisite for city status. Traditionally the status was given to towns with List of cathedrals in England and Wales, diocesan cathedrals, so there are smaller cities like Wells, Somerset, Wells, Ely, Cambridgeshire, Ely, Ripon, Truro and Chichester.Economy
 England's economy is one of the largest and most dynamic in the world, with an average GDP per capita of ôÈ28,100. HM Treasury, led by the Chancellor of the Exchequer, is responsible for developing and executing the government's public finance policy and economic policy. Usually regarded as a Anglo-Saxon economy, mixed market economy, it has adopted many free market principles, yet maintains an advanced social welfare infrastructure. The official currency in England is the pound sterling, whose ISO 4217 code is GBP. Taxation in England is quite competitive when List of countries by tax rates, compared to much of the rest of Europe ã the basic rate of personal tax is 20% on taxable income up to ôÈ31,865 above the personal tax-free allowance (normally ôÈ10,000), and 40% on any additional earnings above that amount.
The economy of England is the largest part of the economy of the United Kingdom, UK's economy, which has the List of countries by GDP (PPP) per capita, 18th highest GDP Purchasing power parity, PPP per capita in the world. England is a leader in the chemical and pharmaceutical sectors and in key technical industries, particularly aerospace, the arms industry, and the manufacturing side of the software industry. London, home to the London Stock Exchange, the United Kingdom's main stock exchange and the largest in Europe, is England's financial centre, with 100 of Europe's 500 largest corporations being based there. London is the largest financial centre in Europe, and is the second largest in the world.
The Bank of England, founded in 1694, is the United Kingdom's central bank. Originally established as private banker to the government of England, since 1946 it has been a nationalisation, state-owned institution. The bank has a monopoly on the issue of banknotes in England and Wales, although not in other parts of the United Kingdom. The government has devolved responsibility to the bank's Monetary Policy Committee (United Kingdom), Monetary Policy Committee for managing the monetary policy of the country and setting interest rates.
England is highly industrialised, but since the 1970s there has been a decline in traditional heavy and manufacturing industries, and an increasing emphasis on a more service industry oriented economy.. Tourism has become a significant industry, attracting millions of visitors to England each year. The export part of the economy is dominated by pharmaceuticals, cars (although many English marques are now foreign-owned, such as Land Rover, Lotus Cars, Lotus, Jaguar Cars, Jaguar and Bentley), crude oil and petroleum from the English parts of North Sea oil along with Wytch Farm, aircraft engines and alcoholic beverages. The creative industries accounted for 7 per cent GVA in 2005 and grew at an average of 6 per cent per annum between 1997 and 2005.
Most of the UK's ôÈ30 billion Aerospace industry in the United Kingdom, aerospace industry is primarily based in England. The global market opportunity for UK aerospace manufacturers over the next two decades is estimated at ôÈ3.5 trillion. GKN Aerospace ã an expert in metallic and composite aerostructures is involved in almost every civil and military fixed and rotary wing aircraft in production is based in Redditch.
BAE Systems makes large sections of the Typhoon Eurofighter at its sub-assembly plant in Samlesbury and assembles the aircraft for the RAF at its Warton, Fylde, Warton plant, near Preston, Lancashire, Preston. It is also a principal subcontractor on the F35 Lightning II, F35 Joint Strike Fighter ã the world's largest single defence project ã for which it designs and manufactures a range of components including the aft fuselage, vertical and horizontal tail and wing tips and fuel system. It also manufactures the BAE Systems Hawk, Hawk, the world's most successful jet training aircraft.
Rolls-Royce Holdings, Rolls-Royce PLC is the world's second-largest aircraft engine, aero-engine manufacturer. Its engines power more than 30 types of commercial aircraft, and it has more 30,000 engines currently in service across both the civil and defence sectors. With a workforce of over 12,000 people, Derby has the largest concentration of Rolls-Royce employees in the UK. Rolls-Royce also produces low-emission power systems for ships; makes critical equipment and safety systems for the nuclear industry and powers offshore platforms and major pipelines for the oil and gas industry. The Pharmaceutical industry in the United Kingdom, pharmaceutical industry plays an important role in the economy, and the UK has the third-highest share of global pharmaceutical R&D expenditures.
Much of the UK's space industry is centred on EADS Astrium, based in Stevenage and Portsmouth. The company builds the Satellite bus, buses ã the underlying structure onto which the payload and propulsion systems are built ã for most of the European Space Agency's spacecraft, as well as commercial satellites. The world leader in compact satellite systems, Surrey Satellite Technology, is also part of Astrium. Reaction Engines Limited, the company planning to build Skylon (spacecraft), Skylon, a single-stage-to-orbit spaceplane using their SABRE (rocket engine), SABRE rocket engine, a combined-cycle, air-breathing rocket propulsion system is based Culham. The UK space industry was worth ôÈ9.1bn in 2011 and employed 29,000 people. It is growing at a rate of 7.5 per cent annually, according to its umbrella organisation, the UK Space Agency. In 2013, the British Government pledged ôÈ60 million to the Skylon (spacecraft), Skylon project: this investment will provide support at a "crucial stage" to allow a full-scale prototype of the SABRE (rocket engine), SABRE engine to be built.
Agriculture is intensive, highly mechanised and efficient by European standards, producing 60% of food needs with only 2% of the labour force. Two-thirds of production is devoted to livestock, the other to arable crops. The main crops that are grown are wheat, barley, oats, potatoes, sugar beets. England retains a significant, though much reduced fishing industry. Its fleets bring home fish of every kind, ranging from Sole (fish), sole to herring. It is also rich in natural resources including coal, petroleum, natural gas, tin, limestone, iron ore, salt, clay, chalk, gypsum, lead, and silica.
England's economy is one of the largest and most dynamic in the world, with an average GDP per capita of ôÈ28,100. HM Treasury, led by the Chancellor of the Exchequer, is responsible for developing and executing the government's public finance policy and economic policy. Usually regarded as a Anglo-Saxon economy, mixed market economy, it has adopted many free market principles, yet maintains an advanced social welfare infrastructure. The official currency in England is the pound sterling, whose ISO 4217 code is GBP. Taxation in England is quite competitive when List of countries by tax rates, compared to much of the rest of Europe ã the basic rate of personal tax is 20% on taxable income up to ôÈ31,865 above the personal tax-free allowance (normally ôÈ10,000), and 40% on any additional earnings above that amount.
The economy of England is the largest part of the economy of the United Kingdom, UK's economy, which has the List of countries by GDP (PPP) per capita, 18th highest GDP Purchasing power parity, PPP per capita in the world. England is a leader in the chemical and pharmaceutical sectors and in key technical industries, particularly aerospace, the arms industry, and the manufacturing side of the software industry. London, home to the London Stock Exchange, the United Kingdom's main stock exchange and the largest in Europe, is England's financial centre, with 100 of Europe's 500 largest corporations being based there. London is the largest financial centre in Europe, and is the second largest in the world.
The Bank of England, founded in 1694, is the United Kingdom's central bank. Originally established as private banker to the government of England, since 1946 it has been a nationalisation, state-owned institution. The bank has a monopoly on the issue of banknotes in England and Wales, although not in other parts of the United Kingdom. The government has devolved responsibility to the bank's Monetary Policy Committee (United Kingdom), Monetary Policy Committee for managing the monetary policy of the country and setting interest rates.
England is highly industrialised, but since the 1970s there has been a decline in traditional heavy and manufacturing industries, and an increasing emphasis on a more service industry oriented economy.. Tourism has become a significant industry, attracting millions of visitors to England each year. The export part of the economy is dominated by pharmaceuticals, cars (although many English marques are now foreign-owned, such as Land Rover, Lotus Cars, Lotus, Jaguar Cars, Jaguar and Bentley), crude oil and petroleum from the English parts of North Sea oil along with Wytch Farm, aircraft engines and alcoholic beverages. The creative industries accounted for 7 per cent GVA in 2005 and grew at an average of 6 per cent per annum between 1997 and 2005.
Most of the UK's ôÈ30 billion Aerospace industry in the United Kingdom, aerospace industry is primarily based in England. The global market opportunity for UK aerospace manufacturers over the next two decades is estimated at ôÈ3.5 trillion. GKN Aerospace ã an expert in metallic and composite aerostructures is involved in almost every civil and military fixed and rotary wing aircraft in production is based in Redditch.
BAE Systems makes large sections of the Typhoon Eurofighter at its sub-assembly plant in Samlesbury and assembles the aircraft for the RAF at its Warton, Fylde, Warton plant, near Preston, Lancashire, Preston. It is also a principal subcontractor on the F35 Lightning II, F35 Joint Strike Fighter ã the world's largest single defence project ã for which it designs and manufactures a range of components including the aft fuselage, vertical and horizontal tail and wing tips and fuel system. It also manufactures the BAE Systems Hawk, Hawk, the world's most successful jet training aircraft.
Rolls-Royce Holdings, Rolls-Royce PLC is the world's second-largest aircraft engine, aero-engine manufacturer. Its engines power more than 30 types of commercial aircraft, and it has more 30,000 engines currently in service across both the civil and defence sectors. With a workforce of over 12,000 people, Derby has the largest concentration of Rolls-Royce employees in the UK. Rolls-Royce also produces low-emission power systems for ships; makes critical equipment and safety systems for the nuclear industry and powers offshore platforms and major pipelines for the oil and gas industry. The Pharmaceutical industry in the United Kingdom, pharmaceutical industry plays an important role in the economy, and the UK has the third-highest share of global pharmaceutical R&D expenditures.
Much of the UK's space industry is centred on EADS Astrium, based in Stevenage and Portsmouth. The company builds the Satellite bus, buses ã the underlying structure onto which the payload and propulsion systems are built ã for most of the European Space Agency's spacecraft, as well as commercial satellites. The world leader in compact satellite systems, Surrey Satellite Technology, is also part of Astrium. Reaction Engines Limited, the company planning to build Skylon (spacecraft), Skylon, a single-stage-to-orbit spaceplane using their SABRE (rocket engine), SABRE rocket engine, a combined-cycle, air-breathing rocket propulsion system is based Culham. The UK space industry was worth ôÈ9.1bn in 2011 and employed 29,000 people. It is growing at a rate of 7.5 per cent annually, according to its umbrella organisation, the UK Space Agency. In 2013, the British Government pledged ôÈ60 million to the Skylon (spacecraft), Skylon project: this investment will provide support at a "crucial stage" to allow a full-scale prototype of the SABRE (rocket engine), SABRE engine to be built.
Agriculture is intensive, highly mechanised and efficient by European standards, producing 60% of food needs with only 2% of the labour force. Two-thirds of production is devoted to livestock, the other to arable crops. The main crops that are grown are wheat, barley, oats, potatoes, sugar beets. England retains a significant, though much reduced fishing industry. Its fleets bring home fish of every kind, ranging from Sole (fish), sole to herring. It is also rich in natural resources including coal, petroleum, natural gas, tin, limestone, iron ore, salt, clay, chalk, gypsum, lead, and silica.
Science and technology
 Prominent English figures from the field of science and mathematics include Sir Isaac Newton, Michael Faraday, Charles Darwin, Robert Hooke, James Prescott Joule, John Dalton, Lord Rayleigh, J. J. Thomson, James Chadwick, Charles Babbage, George Boole, Alan Turing, Tim Berners-Lee, Paul Dirac, Stephen Hawking, Peter Higgs, Roger Penrose, John Horton Conway, Thomas Bayes, Arthur Cayley, G. H. Hardy, Oliver Heaviside, Andrew Wiles, Edward Jenner, Francis Crick, Joseph Lister, 1st Baron Lister, Joseph Lister, Joseph Priestley, Thomas Young (scientist), Thomas Young, Christopher Wren and Richard Dawkins. Some experts claim that the earliest concept of a metric system was invented by John Wilkins, the first secretary of the Royal Society, in 1668.
England was a leading centre of the Scientific Revolution from the 17th century. As the birthplace of the
Prominent English figures from the field of science and mathematics include Sir Isaac Newton, Michael Faraday, Charles Darwin, Robert Hooke, James Prescott Joule, John Dalton, Lord Rayleigh, J. J. Thomson, James Chadwick, Charles Babbage, George Boole, Alan Turing, Tim Berners-Lee, Paul Dirac, Stephen Hawking, Peter Higgs, Roger Penrose, John Horton Conway, Thomas Bayes, Arthur Cayley, G. H. Hardy, Oliver Heaviside, Andrew Wiles, Edward Jenner, Francis Crick, Joseph Lister, 1st Baron Lister, Joseph Lister, Joseph Priestley, Thomas Young (scientist), Thomas Young, Christopher Wren and Richard Dawkins. Some experts claim that the earliest concept of a metric system was invented by John Wilkins, the first secretary of the Royal Society, in 1668.
England was a leading centre of the Scientific Revolution from the 17th century. As the birthplace of the Industrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution was the transition to new manufacturing processes in Great Britain, continental Europe, and the United States, that occurred during the period from around 1760 to about 1820ã1840. This transition included going f ...
, England was home to many significant inventors during the late 18th and early 19th centuries. Famous English engineers include Isambard Kingdom Brunel, best known for the creation of the Great Western Railway, a series of famous steamships, and numerous important bridges, hence revolutionising public transport and modern-day engineering. Thomas Newcomen's Newcomen steam engine, steam engine helped spawn the Industrial Revolution.
The Father of Railways, George Stephenson, built the first public inter-city railway line in the world, the Liverpool and Manchester Railway, which opened in 1830. With his role in the marketing and manufacturing of the steam engine, and invention of modern coinage, Matthew Boulton (business partner of James Watt) is regarded as one of the most influential entrepreneurs in history. The physician Edward Jenner's smallpox vaccine is said to have "saved more lives ... than were lost in all the wars of mankind since the beginning of recorded history."
 Inventions and discoveries of the English include: the jet engine, the first industrial spinning frame, spinning machine, Analytical engine, the first computer and the first Manchester Baby, modern computer, the World Wide Web along with HTML, the first successful human blood transfusion, the motorised vacuum cleaner, the lawn mower, the seat belt, the hovercraft, the electric motor, steam engines, and theories such as the Darwinian theory of evolution and atomic theory. Newton developed the ideas of universal gravitation, Newtonian mechanics, and calculus, and Robert Hooke his eponymously named Hooke's law of elasticity, law of elasticity. Other inventions include the iron plate railway, the thermosiphon, Tarmacadam, tarmac, the rubber band, the mousetrap, Cat's eye (road), "cat's eye" raised pavement marker, road marker, joint development of the light bulb, steam locomotives, the modern seed drill and many modern techniques and technologies used in precision engineering.
The Royal Society, formally The Royal Society of London for Improving Natural Knowledge, is a learned society and the
Inventions and discoveries of the English include: the jet engine, the first industrial spinning frame, spinning machine, Analytical engine, the first computer and the first Manchester Baby, modern computer, the World Wide Web along with HTML, the first successful human blood transfusion, the motorised vacuum cleaner, the lawn mower, the seat belt, the hovercraft, the electric motor, steam engines, and theories such as the Darwinian theory of evolution and atomic theory. Newton developed the ideas of universal gravitation, Newtonian mechanics, and calculus, and Robert Hooke his eponymously named Hooke's law of elasticity, law of elasticity. Other inventions include the iron plate railway, the thermosiphon, Tarmacadam, tarmac, the rubber band, the mousetrap, Cat's eye (road), "cat's eye" raised pavement marker, road marker, joint development of the light bulb, steam locomotives, the modern seed drill and many modern techniques and technologies used in precision engineering.
The Royal Society, formally The Royal Society of London for Improving Natural Knowledge, is a learned society and the United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotland, Wales and North ...
's national academy of sciences. Founded on 28 November 1660, it was granted a royal charter by Charles II of England, King Charles II as "The Royal Society". It is the oldest national scientific institution in the world. The society fulfils a number of roles: promoting science and its benefits, recognising excellence in science, supporting outstanding science, providing scientific advice for policy, fostering international and global co-operation, education and public engagement.
The Royal Society started from groups of physicians and natural philosophers, meeting at a variety of locations, including Gresham College in London. They were influenced by the "Scientific method, new science", as promoted by Francis Bacon in his ''New Atlantis'', from approximately 1645 onwards. A group known as "The Philosophical Society of Oxford" was run under a set of rules still retained by the Bodleian Library.Syfret (1948) p. 78 After the English Restoration, there were regular meetings at Gresham College. It is widely held that these groups were the inspiration for the foundation of the Royal Society.
Scientific research and development remains important in the universities of England, with many establishing science parks to facilitate production and co-operation with industry. Between 2004 and 2008 the United Kingdom produced 7 per cent of the world's scientific research papers and had an 8 per cent share of scientific citations, the third and second-highest in the world (after the United States and China, respectively). Scientific journals produced in the United Kingdom include ''Nature (journal), Nature'', the ''BMJ, British Medical Journal'' and ''The Lancet''.
Transport
 The Department for Transport is the government body responsible for overseeing transport in England. The department is run by the Secretary of State for Transport.
England has a dense and modern transportation infrastructure. There are many List of motorways in the United Kingdom, motorways in England, and many other trunk roads, such as the A1 road (Great Britain), A1 Great North Road, which runs through eastern England from London to Newcastle (much of this section is motorway) and onward to the Scottish border. The longest motorway in England is the M6 motorway, M6, from Rugby, Warwickshire, Rugby through the
The Department for Transport is the government body responsible for overseeing transport in England. The department is run by the Secretary of State for Transport.
England has a dense and modern transportation infrastructure. There are many List of motorways in the United Kingdom, motorways in England, and many other trunk roads, such as the A1 road (Great Britain), A1 Great North Road, which runs through eastern England from London to Newcastle (much of this section is motorway) and onward to the Scottish border. The longest motorway in England is the M6 motorway, M6, from Rugby, Warwickshire, Rugby through the North West
The points of the compass are a set of horizontal, radially arrayed compass directions (or azimuths) used in navigation and cartography. A compass rose is primarily composed of four cardinal directionsãnorth, east, south, and westãeach sepa ...
up to the Anglo-Scottish border, a distance of . Other major routes include: the M1 motorway, M1 from London to Leeds, the M25 motorway, M25 which encircles London, the M60 motorway (Great Britain), M60 which encircles Manchester, the M4 motorway, M4 from London to South Wales, the M62 motorway, M62 from Liverpool via Manchester to East Yorkshire, and the M5 motorway, M5 from Birmingham to Bristol and the South West.
Bus transport across the country is widespread; major companies include Arriva UK Bus, Arriva, FirstGroup, Go-Ahead Group, National Express, Rotala and Stagecoach Group. The red double-decker buses in London have become a symbol of England.
National Cycle Route offers cycling routes nationally. There is a rapid transit network in two English cities: the London Underground; and the Tyne and Wear Metro in Newcastle upon Tyne, Gateshead and Sunderland.. There are several tram networks, such as the Blackpool tramway, Manchester Metrolink, Sheffield Supertram and West Midlands Metro, and the Tramlink system centred on Croydon in South London.
 Great British Railways is a planned State ownership, state-owned public body that will oversee rail transport in Great Britain from 2023. The Office of Rail and Road is responsible for the economic and safety regulation of England's railways.
Rail transport in Great Britain, Rail transport in England is the oldest in the world: passenger railways originated in England in 1825. Much of Britain's of rail network lies in England, covering the country fairly extensively, although a high proportion of railway lines were closed in the second half of the 20th century. There are plans to reopen lines such as the Varsity Line between Oxford and Cambridge. These lines are mostly standard gauge (single track (rail), single, double track, double or quadruple track) though there are also a few British narrow gauge railways, narrow gauge lines. There is rail transport access to France and Belgium through an undersea rail link, the Channel Tunnel, which was completed in 1994.
Crossrail was Europe's largest construction project with a ôÈ15 billion projected cost, opened in 2022. High Speed 2, a new high-speed northãsouth railway line, projected in 2015 to cost ôÈ56 billion is to start being built in 2020.
England has extensive domestic and international aviation links. The largest airport is Heathrow Airport, Heathrow, which is the World's busiest airports by international passenger traffic, world's busiest airport measured by number of international passengers. Other large airports include Gatwick Airport, Gatwick, Manchester Airport, Manchester, Stansted Airport, Stansted, Luton Airport, Luton and Birmingham Airport, Birmingham.
By sea there is ferry transport, both local and international, including from Liverpool to Ireland and the Isle of Man, and Hull to the Netherlands and Belgium.. There are around of navigable waterways in England, half of which is owned by the Canal & River Trust, however, water transport is very limited. The River Thames is the major waterway in England, with imports and exports focused at the Port of Tilbury in the Thames Estuary, one of the United Kingdom's three major ports.
Great British Railways is a planned State ownership, state-owned public body that will oversee rail transport in Great Britain from 2023. The Office of Rail and Road is responsible for the economic and safety regulation of England's railways.
Rail transport in Great Britain, Rail transport in England is the oldest in the world: passenger railways originated in England in 1825. Much of Britain's of rail network lies in England, covering the country fairly extensively, although a high proportion of railway lines were closed in the second half of the 20th century. There are plans to reopen lines such as the Varsity Line between Oxford and Cambridge. These lines are mostly standard gauge (single track (rail), single, double track, double or quadruple track) though there are also a few British narrow gauge railways, narrow gauge lines. There is rail transport access to France and Belgium through an undersea rail link, the Channel Tunnel, which was completed in 1994.
Crossrail was Europe's largest construction project with a ôÈ15 billion projected cost, opened in 2022. High Speed 2, a new high-speed northãsouth railway line, projected in 2015 to cost ôÈ56 billion is to start being built in 2020.
England has extensive domestic and international aviation links. The largest airport is Heathrow Airport, Heathrow, which is the World's busiest airports by international passenger traffic, world's busiest airport measured by number of international passengers. Other large airports include Gatwick Airport, Gatwick, Manchester Airport, Manchester, Stansted Airport, Stansted, Luton Airport, Luton and Birmingham Airport, Birmingham.
By sea there is ferry transport, both local and international, including from Liverpool to Ireland and the Isle of Man, and Hull to the Netherlands and Belgium.. There are around of navigable waterways in England, half of which is owned by the Canal & River Trust, however, water transport is very limited. The River Thames is the major waterway in England, with imports and exports focused at the Port of Tilbury in the Thames Estuary, one of the United Kingdom's three major ports.
Energy
 Energy use in the
Energy use in the United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotland, Wales and North ...
stood at 2,249 TWh (193.4 million Tonne of oil equivalent, tonnes of oil equivalent) in 2014. This equates to energy consumption ''per capita'' of 34.82 MWh (3.00 tonnes of oil equivalent) compared to a 2010 world average of 21.54 MWh (1.85 tonne of oil equivalent, tonnes of oil equivalent). Demand for electricity in 2014 was 34.42Watt, GW on average (301.7TWh over the year) coming from a total electricity generation of 335.0Kilowatt hour, TWh.
Successive Government of the United Kingdom, UK governments have outlined numerous commitments to reduce carbon dioxide emissions. Notably, the UK is Wind power in the United Kingdom, one of the best sites in Europe for wind energy, and wind power production is its fastest growing supply.; Wind power contributed 15% of UK electricity generation in 2017.
The Climate Change Act 2008 was passed in Parliament with an overwhelming majority across political parties. It sets out emission reduction targets that the UK must comply with legally. It represents the first global legally binding climate change mitigation target set by a country. Energy policy of the United Kingdom, UK government energy policy aims to play a key role in limiting greenhouse gas emissions, whilst meeting energy demand. Shifting availabilities of resources and development of technologies also change the country's energy mix through changes in costs.
The current energy policy is the responsibility of the Department for Business, Energy and Industrial Strategy and Secretary of State for Business, Energy and Industrial Strategy. The Minister of State for Business, Energy and Clean Growth is responsible for green finance, climate science and innovation, and low carbon generation. United Kingdom is ranked 4 out of 180 countries in the Environmental Performance Index. A law has been passed that Greenhouse gas emissions, UK greenhouse gas emissions will be net zero by 2050.
Tourism
 English Heritage is a governmental body with a broad remit of managing the historic sites, artefacts and environments of England. It is currently sponsored by the Department for Culture, Media and Sport, Department for Digital, Culture, Media and Sport.
The National Trust for Places of Historic Interest or Natural Beauty is a charity which also maintains multiple sites. Of the 25 United Kingdom List of World Heritage Sites in the United Kingdom, UNESCO World Heritage Sites, 17 are in England.
Some of the best known of these include Stonehenge, Avebury and Associated Sites, Tower of London, Jurassic Coast, Palace of Westminster, Roman Baths (Bath), Roman Baths, Bath, Somerset, City of Bath, Saltaire, Ironbridge Gorge, Studley Royal Park and more recently the Lake District, English Lake District. The northernmost point of the Roman Empire, Hadrian's Wall, is the largest Roman artefact anywhere: it runs for a total of in northern England.
The Secretary of State for Digital, Culture, Media and Sport has overall responsibility for tourism, arts and culture, cultural property, heritage and historic environments, libraries, and museums and galleries. The Parliamentary Under Secretary of State for Arts, Heritage and Tourism is the minister with responsibility over tourism in England.
A blue plaque, the oldest historical marker scheme in the world, is a permanent sign installed in a public place in England to commemorate a link between that location and a famous person or event. The scheme was the brainchild of politician William Ewart (British politician), William Ewart in 1863 and was initiated in 1866. It was formally established by the Royal Society of Arts in 1867, and since 1986 has been run by English Heritage. In 2011 there were around 1,600 museums in England. Entry to most state-supported museums and galleries is free unlike in other countries.
English Heritage is a governmental body with a broad remit of managing the historic sites, artefacts and environments of England. It is currently sponsored by the Department for Culture, Media and Sport, Department for Digital, Culture, Media and Sport.
The National Trust for Places of Historic Interest or Natural Beauty is a charity which also maintains multiple sites. Of the 25 United Kingdom List of World Heritage Sites in the United Kingdom, UNESCO World Heritage Sites, 17 are in England.
Some of the best known of these include Stonehenge, Avebury and Associated Sites, Tower of London, Jurassic Coast, Palace of Westminster, Roman Baths (Bath), Roman Baths, Bath, Somerset, City of Bath, Saltaire, Ironbridge Gorge, Studley Royal Park and more recently the Lake District, English Lake District. The northernmost point of the Roman Empire, Hadrian's Wall, is the largest Roman artefact anywhere: it runs for a total of in northern England.
The Secretary of State for Digital, Culture, Media and Sport has overall responsibility for tourism, arts and culture, cultural property, heritage and historic environments, libraries, and museums and galleries. The Parliamentary Under Secretary of State for Arts, Heritage and Tourism is the minister with responsibility over tourism in England.
A blue plaque, the oldest historical marker scheme in the world, is a permanent sign installed in a public place in England to commemorate a link between that location and a famous person or event. The scheme was the brainchild of politician William Ewart (British politician), William Ewart in 1863 and was initiated in 1866. It was formally established by the Royal Society of Arts in 1867, and since 1986 has been run by English Heritage. In 2011 there were around 1,600 museums in England. Entry to most state-supported museums and galleries is free unlike in other countries.
London
London is the capital and largest city of England and the United Kingdom, with a population of just under 9 million. It stands on the River Thames in south-east England at the head of a estuary down to the North Sea, and has been a majo ...
is one of the world's most visited cities, regularly taking the top five most visited cities in Europe. It is largely considered a global centre of finance, arts and culture.
Healthcare
 The National Health Service (England), National Health Service (NHS), is the publicly funded healthcare system responsible for providing the majority of healthcare in the country. The NHS began on 5 July 1948, putting into effect the provisions of the National Health Service Act 1946. It was based on the findings of the Beveridge Report, prepared by economist and social reformer William Beveridge. The NHS is largely funded from general taxation including National Insurance payments, and it provides most of its services free at the point of use, although there are charges for some people for eye tests, dental care, prescriptions and aspects of personal care.
The government department responsible for the NHS is the Department of Health (United Kingdom), Department of Health, headed by the Secretary of State for Health, who sits in the Cabinet of the United Kingdom, British Cabinet. Most of the expenditure of the Department of Health is spent on the NHSãôÈ98.6 billion was spent in 2008ã2009. In recent years the private sector has been increasingly used to provide more NHS services despite opposition by doctors and trade unions.
When purchasing drugs, the NHS has significant market power that, based on its own assessment of the fair value of the drugs, influences the global price, typically keeping prices lower. Several other countries either copy the UK's model or directly rely on its assessments for their own decisions on state-financed drug reimbursements. Regulatory bodies such as the General Medical Council and the Nursing and Midwifery Council are organised on a UK-wide basis, as are non-governmental bodies such as the Royal Colleges.
The average life expectancy of people in England is 77.5 years for males and 81.7 years for females, the highest of the four countries of the United Kingdom. The South of England has a higher life expectancy than the North; however, regional differences do seem to be slowly narrowing: between 1991ã1993 and 2012ã2014, life expectancy in the North East increased by 6.0 years and in the North West by 5.8 years, the fastest increase in any region outside London, and the gap between life expectancy in the North East and South East is now 2.5 years, down from 2.9 in 1993.
The National Health Service (England), National Health Service (NHS), is the publicly funded healthcare system responsible for providing the majority of healthcare in the country. The NHS began on 5 July 1948, putting into effect the provisions of the National Health Service Act 1946. It was based on the findings of the Beveridge Report, prepared by economist and social reformer William Beveridge. The NHS is largely funded from general taxation including National Insurance payments, and it provides most of its services free at the point of use, although there are charges for some people for eye tests, dental care, prescriptions and aspects of personal care.
The government department responsible for the NHS is the Department of Health (United Kingdom), Department of Health, headed by the Secretary of State for Health, who sits in the Cabinet of the United Kingdom, British Cabinet. Most of the expenditure of the Department of Health is spent on the NHSãôÈ98.6 billion was spent in 2008ã2009. In recent years the private sector has been increasingly used to provide more NHS services despite opposition by doctors and trade unions.
When purchasing drugs, the NHS has significant market power that, based on its own assessment of the fair value of the drugs, influences the global price, typically keeping prices lower. Several other countries either copy the UK's model or directly rely on its assessments for their own decisions on state-financed drug reimbursements. Regulatory bodies such as the General Medical Council and the Nursing and Midwifery Council are organised on a UK-wide basis, as are non-governmental bodies such as the Royal Colleges.
The average life expectancy of people in England is 77.5 years for males and 81.7 years for females, the highest of the four countries of the United Kingdom. The South of England has a higher life expectancy than the North; however, regional differences do seem to be slowly narrowing: between 1991ã1993 and 2012ã2014, life expectancy in the North East increased by 6.0 years and in the North West by 5.8 years, the fastest increase in any region outside London, and the gap between life expectancy in the North East and South East is now 2.5 years, down from 2.9 in 1993.
Demography
Population
 With over 53 million inhabitants, England is by far the most populous country of the United Kingdom, accounting for 84% of the combined total. England taken as a unit and measured against international states would be the 25th largest List of countries by population in 2005, country by population in the world.
The English people are British people. Some genetic evidence suggests that 75ã95% descend in the paternal line from prehistoric settlers who originally came from the
With over 53 million inhabitants, England is by far the most populous country of the United Kingdom, accounting for 84% of the combined total. England taken as a unit and measured against international states would be the 25th largest List of countries by population in 2005, country by population in the world.
The English people are British people. Some genetic evidence suggests that 75ã95% descend in the paternal line from prehistoric settlers who originally came from the Iberian Peninsula
The Iberian Peninsula (),
**
* Aragonese and Occitan: ''Peninsula Iberica''
**
**
* french: Pûˋninsule Ibûˋrique
* mwl, PenûÙnsula Eibûˋrica
* eu, Iberiar penintsula also known as Iberia, is a peninsula in southwestern Europe, defi ...
, as well as a 5% contribution from Angles
The Angles ( ang, ûngle, ; la, Angli) were one of the main Germanic peoples who settled in Great Britain in the post-Roman period. They founded several kingdoms of the Heptarchy in Anglo-Saxon England. Their name is the root of the name ' ...
and Saxons
The Saxons ( la, Saxones, german: Sachsen, ang, Seaxan, osx, Sahson, nds, Sassen, nl, Saksen) were a group of Germanic
*
*
*
*
peoples whose name was given in the early Middle Ages to a large country (Old Saxony, la, Saxonia) near the Nor ...
, and a significant Scandinavian (Vikings, Viking) element. However, other geneticists place the Germanic estimate up to half. Over time, various cultures have been influential: Prehistoric Britain, Prehistoric, Britons (historical), Brythonic, Ancient Rome, Roman, Anglo-Saxon, Viking (North Germanic), Gaels, Gaelic cultures, as well as a large influence from Normans
The Normans (Norman language, Norman: ''Normaunds''; french: Normands; la, Nortmanni/Normanni) were a population arising in the medieval Duchy of Normandy from the intermingling between Norsemen, Norse Viking settlers and indigenous West Fran ...
. There is an English diaspora in former parts of the British Empire; especially the United States, Canada, Australia, South Africa and New Zealand. Since the late 1990s, many English people British migration to Spain, have migrated to Spain.
In 1086, when the ''Domesday Book
Domesday Book () ã the Middle English spelling of "Doomsday Book" ã is a manuscript record of the "Great Survey" of much of England and parts of Wales completed in 1086 by order of King William I, known as William the Conqueror. The manusc ...
'' was compiled, England had a population of two million. About 10% lived in urban areas. By 1801, the population was 8.3 million, and by 1901 30.5 million. Due in particular to the economic prosperity of South East England, it has received many economic migrants from the other parts of the United Kingdom. There has been Irish migration to Great Britain, significant Irish migration. The proportion of ethnically European residents totals at 87.50%, including British Germans, Germans and Polish British, Poles.
Other people from much further afield in the former British colonies have arrived since the 1950s: in particular, 6% of people living in England have family origins in the Indian subcontinent, mostly India, Pakistan and Bangladesh. About 0.7% of people are Chinese. 2.90% of the population are black, from Africa and the Caribbean, especially former British colonies. In 2007, 22% of primary school children in England were from minority group, ethnic minority families, and in 2011 that figure was 26.5%. About half of the population increase between 1991 and 2001 was due to immigration. Debate over immigration is politically prominent; 80% of respondents in a 2009 Home Office poll wanted to cap it. The Office for National Statistics, ONS has projected that the population will grow by nine million between 2014 and 2039.
England contains one indigenous national minority, the Cornish people, recognised by the UK government under the Framework Convention for the Protection of National Minorities in 2014.
Language
English language, English, today spoken by hundreds of millions of people around the world, originated in what is now England, where it remains the principal tongue. According to a 2011 census, it is spoken well or very well by 98% of the population. It is an Indo-European languages, Indo-European language in the Anglo-Frisian languages, Anglo-Frisian branch of the Germanic languages, Germanic family. After the Norman conquest, theOld English
Old English (, ), or Anglo-Saxon, is the earliest recorded form of the English language, spoken in England and southern and eastern Scotland in the early Middle Ages. It was brought to Great Britain by Anglo-Saxon settlement of Britain, Anglo ...
language, brought to Britain by the Anglo-Saxons, Anglo-Saxon settlers, was confined to the Working class, lower social classes as Norman language, Norman French and Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the ...
were used by the aristocracy.
By the 15th century, English was back in fashion among all classes, though much changed; the Middle English form showed many signs of French influence, both in vocabulary and spelling. During the English Renaissance, many words were coined from Latin and Greek origins. Modern English has extended this custom of flexibility when it comes to incorporating words from different languages. Thanks in large part to the British Empire, the English language is the world's unofficial ''lingua franca''.
English as a second or foreign language, English language learning and teaching is an important Economics, economic activity, and includes language schools, language schooling, tourism spending, and publishing. There is no United Kingdom legislation, legislation mandating an official language for England, but English is the only language used for official business. Despite the country's relatively small size, there are many distinct Regional accents of English speakers#England, regional accents, and individuals with particularly strong accents may not be easily understood everywhere in the country.
As well as English, England has two other indigenous languages, Cornish language, Cornish and Welsh
Welsh may refer to:
Related to Wales
* Welsh, referring or related to Wales
* Welsh language, a Brittonic Celtic language spoken in Wales
* Welsh people
People
* Welsh (surname)
* Sometimes used as a synonym for the ancient Britons (Celtic peop ...
. Cornish died out as a community language in the 18th century but is being revived, and is now protected under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages. It is spoken by 0.1% of people in Cornwall, and is taught to some degree in several primary and secondary schools.
When the modern border between Wales and England was established by the Laws in Wales Acts 1535 and 1542, many Welsh-speaking communities found themselves on the English side of the border. Welsh was spoken in Archenfield in Herefordshire into the nineteenth century, and by natives of parts of western Shropshire until the middle of the twentieth century if not later.
State schools teach students a second language or third language from the ages of seven, most commonly French, Spanish or German. It was reported in 2007 that around 800,000 school students spoke a foreign language at home as a result of immigration among their family, the most common languages being Punjabi language, Punjabi and Urdu. However, following the 2011 census data released by the Office for National Statistics, figures now show that Polish is the main language spoken in England after English.
Religion
 In the 2011 census, 59.4% of the population of England specified their religion as Christian, 24.7% answered that they had no religion, 5% specified that they were Muslim, while 3.7% of the population belongs to other religions and 7.2% did not give an answer. Christianity is the most widely practised religion in England, as it has been since the Early Middle Ages, although it was first introduced much earlier in Gaelic and Roman times. This Celtic Church was gradually joined to the Roman Catholic Church, Catholic hierarchy following the 6th-century Gregorian mission to
In the 2011 census, 59.4% of the population of England specified their religion as Christian, 24.7% answered that they had no religion, 5% specified that they were Muslim, while 3.7% of the population belongs to other religions and 7.2% did not give an answer. Christianity is the most widely practised religion in England, as it has been since the Early Middle Ages, although it was first introduced much earlier in Gaelic and Roman times. This Celtic Church was gradually joined to the Roman Catholic Church, Catholic hierarchy following the 6th-century Gregorian mission to Kent
Kent is a county in South East England and one of the home counties. It borders Greater London to the north-west, Surrey to the west and East Sussex to the south-west, and Essex to the north across the estuary of the River Thames; it faces ...
led by Augustine of Canterbury, St Augustine. The established church of England is the Church of England
The Church of England (C of E) is the established Christian church in England and the mother church of the international Anglican Communion. It traces its history to the Christian church recorded as existing in the Roman province of Britain ...
, which left communion with Vatican City, Rome in the 1530s when Henry VIII of England, Henry VIII was unable to annul his marriage to Catherine of Aragon, the aunt of the Charles V, Holy Roman Emperor, king of Spain. The church regards itself as both Catholic and Protestant.
There are High Church and Low Church traditions and some Anglicans regard themselves as Anglo-Catholics, following the Tractarian movement. The monarch of the United Kingdom is the Supreme Governor of the Church of England, which has around 26 million baptised members (of whom the vast majority are not regular churchgoers). It forms part of the Anglican Communion with the Archbishop of Canterbury acting as its symbolic worldwide head. Many List of cathedrals in England and Wales, cathedrals and parish churches are historic buildings of significant architectural importance, such as Westminster Abbey, York Minster, Durham Cathedral, and Salisbury Cathedral.
 The 2nd-largest Christian practice is the Latin Rite of the Catholic Church. Since its reintroduction after the Catholic Emancipation, the Church has organised ecclesiastically on an Roman Catholic Church in England and Wales, England and Wales basis where there are 4.5 million members (most of whom are English). There has been one Pope from England to date, Pope Adrian IV, Adrian IV; while saints
The 2nd-largest Christian practice is the Latin Rite of the Catholic Church. Since its reintroduction after the Catholic Emancipation, the Church has organised ecclesiastically on an Roman Catholic Church in England and Wales, England and Wales basis where there are 4.5 million members (most of whom are English). There has been one Pope from England to date, Pope Adrian IV, Adrian IV; while saints Bede
Bede ( ; ang, BúÈda , ; 672/326 May 735), also known as Saint Bede, The Venerable Bede, and Bede the Venerable ( la, Beda Venerabilis), was an English monk at the monastery of St Peter and its companion monastery of St Paul in the Kingdom o ...
and Anselm of Canterbury, Anselm are regarded as Doctors of the Church.
A form of Protestantism known as Methodist Church of Great Britain, Methodism is the third largest Christian practice and grew out of Anglicanism through John Wesley. It gained popularity in the mill towns of Lancashire and Yorkshire
Yorkshire ( ; abbreviated Yorks), formally known as the County of York, is a Historic counties of England, historic county in northern England and by far the largest in the United Kingdom. Because of its large area in comparison with other Eng ...
, and amongst tin miners in Cornwall. There are other Nonconformist (Protestantism), non-conformist minorities, such as Baptists, Quakers, Congregational church, Congregationalists, Unitarianism, Unitarians and The Salvation Army.
The patron saint of England is Saint George; his symbolic cross is included in the flag of England, as well as in the Union Flag as part of a combination. There are many other English and associated saints; some of the best-known are: Cuthbert, Edmund the Martyr, Edmund, Saint Alban, Alban, Wilfrid, Aidan of Lindisfarne, Aidan, Edward the Confessor
Edward the Confessor ; la, Eduardus Confessor , ; ( 1003 ã 5 January 1066) was one of the last Anglo-Saxon English kings. Usually considered the last king of the House of Wessex, he ruled from 1042 to 1066.
Edward was the son of ûth ...
, John Fisher, Thomas More, Saint Petroc, Petroc, Saint Piran, Piran, Margaret Clitherow and Thomas Becket. There are non-Christian religions practised. Jews have a history of a small minority on the island since 1070. They were expelled from England in 1290 following the Edict of Expulsion, only to be allowed back in 1656.
Especially since the 1950s, religions from the British Empire, former British colonies have grown in numbers, due to immigration. Islam is the most common of these, now accounting for around 5% of the population in England. Hinduism, Sikhism and Buddhism are next in number, adding up to 2.8% combined, introduced from India and South East Asia.
A small minority of the population practise ancient Pagan religions. Neopaganism in the United Kingdom is primarily represented by Wicca and Contemporary Witchcraft, Witchcraft religions, Neo-Druidry, Druidry, and Germanic neopaganism, Heathenry. According to the United Kingdom Census 2011, 2011 UK Census, there are roughly 53,172 people who identify as Pagan in England, and 3,448 in Wales
Wales ( cy, Cymru ) is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. It is bordered by England to the WalesãEngland border, east, the Irish Sea to the north and west, the Celtic Sea to the south west and the ...
, including 11,026 Wiccans in England and 740 in Wales.
24.7% of people in England declared Irreligion, no religion in 2011, compared with 14.6% in 2001. These figures are slightly lower than the combined figures for England and Wales as Wales has a higher level of irreligion than England. Norwich had the highest such proportion at 42.5%, followed closely by Brighton and Hove at 42.4%.
Education

 The Department for Education is the government department responsible for issues affecting people in England up to the age of 19, including education. State-run and state-funded schools are attended by approximately 93% of English schoolchildren. Education is the responsibility of the Secretary of State for Education.
Children who are between the ages of 3 and 5 attend nursery or an Early Years Foundation Stage reception unit within a primary school. Children between the ages of 5 and 11 attend primary school, and secondary school is attended by those aged between 11 and 16. State-funded schools are obliged by law to teach the National Curriculum for England, National Curriculum; basic areas of learning include English literature, English language, mathematics, science, art & design, citizenship, history, geography, religious education, design & technology, computing, ancient & modern languages, music, and physical education.
More than 90% of English schools require students to wear uniforms. School uniforms are defined by individual schools, within the constraint that uniform regulations must not discriminate on the grounds of sex, race, disability, sexual orientation, gender reassignment, religion or belief. Schools may choose to permit trousers for girls or religious dress.
The Programme for International Student Assessment coordinated by the OECD currently ranks the overall knowledge and skills of British 15-year-olds as 13th in the world in reading literacy, mathematics, and science with the average British student scoring 503.7, compared with the OECD average of 493, ahead of the United States and most of Europe.
Although most English secondary schools are comprehensive school, comprehensive, there are selective intake grammar schools to which entrance is subject to passing the eleven-plus exam. Around 7.2 per cent of English schoolchildren attend Independent school (UK), private schools, which are funded by private sources. Standards in state schools are monitored by the Office for Standards in Education, and in private schools by the Independent Schools Inspectorate.
After finishing compulsory education, students take General Certificate of Secondary Education, GCSE examinations. Students may then opt to continue into further education for two years. List of further education colleges in England, Further education colleges (particularly sixth form colleges) often form part of a secondary school site. A-level examinations are sat by a large number of further education students, and often form the basis of an application to university. Further education (FE) covers a wide curriculum of study and apprenticeships, including T Level, T-levels, BTEC Extended Diploma, BTEC, NVQ and others. Tertiary colleges provide both academic and vocational courses.
Higher education students normally attend university from age 18 onwards, where they study for an academic degree. There are over 90 universities in England, all but one of which are Public university, public institutions. The Department for Business, Innovation and Skills is the government department responsible for higher education in England. Students are generally entitled to student loans to cover the cost of tuition fees and living costs. The first degree offered to undergraduates is the bachelor's degree, which usually takes three years to complete. Students are then able to work towards a postgraduate degree, which usually takes one year, or towards a doctorate, which takes three or more years.
List of universities in England, England's universities include some of the highest-ranked universities in the world; University of Cambridge, University of Oxford, Imperial College London, University College London and King's College London are all ranked in the global top 30 in the 2018 ''QS World University Rankings''. The London School of Economics has been described as the world's leading social science institution for both teaching and research. The London Business School is considered one of the world's leading business schools and in 2010 its MBA programme was ranked best in the world by the ''Financial Times''. Academic degrees in England are usually split into classes: first class (1st), upper second class (2:1), lower second class (2:2), third (3rd), and unclassified.
The King's School, Canterbury and King's School, Rochester are the oldest schools in the English-speaking world. Many of England's most well-known schools, such as Winchester College, Eton College, Eton, St Paul's School (London), St Paul's School, Harrow School and Rugby School are fee-paying institutions.
The Department for Education is the government department responsible for issues affecting people in England up to the age of 19, including education. State-run and state-funded schools are attended by approximately 93% of English schoolchildren. Education is the responsibility of the Secretary of State for Education.
Children who are between the ages of 3 and 5 attend nursery or an Early Years Foundation Stage reception unit within a primary school. Children between the ages of 5 and 11 attend primary school, and secondary school is attended by those aged between 11 and 16. State-funded schools are obliged by law to teach the National Curriculum for England, National Curriculum; basic areas of learning include English literature, English language, mathematics, science, art & design, citizenship, history, geography, religious education, design & technology, computing, ancient & modern languages, music, and physical education.
More than 90% of English schools require students to wear uniforms. School uniforms are defined by individual schools, within the constraint that uniform regulations must not discriminate on the grounds of sex, race, disability, sexual orientation, gender reassignment, religion or belief. Schools may choose to permit trousers for girls or religious dress.
The Programme for International Student Assessment coordinated by the OECD currently ranks the overall knowledge and skills of British 15-year-olds as 13th in the world in reading literacy, mathematics, and science with the average British student scoring 503.7, compared with the OECD average of 493, ahead of the United States and most of Europe.
Although most English secondary schools are comprehensive school, comprehensive, there are selective intake grammar schools to which entrance is subject to passing the eleven-plus exam. Around 7.2 per cent of English schoolchildren attend Independent school (UK), private schools, which are funded by private sources. Standards in state schools are monitored by the Office for Standards in Education, and in private schools by the Independent Schools Inspectorate.
After finishing compulsory education, students take General Certificate of Secondary Education, GCSE examinations. Students may then opt to continue into further education for two years. List of further education colleges in England, Further education colleges (particularly sixth form colleges) often form part of a secondary school site. A-level examinations are sat by a large number of further education students, and often form the basis of an application to university. Further education (FE) covers a wide curriculum of study and apprenticeships, including T Level, T-levels, BTEC Extended Diploma, BTEC, NVQ and others. Tertiary colleges provide both academic and vocational courses.
Higher education students normally attend university from age 18 onwards, where they study for an academic degree. There are over 90 universities in England, all but one of which are Public university, public institutions. The Department for Business, Innovation and Skills is the government department responsible for higher education in England. Students are generally entitled to student loans to cover the cost of tuition fees and living costs. The first degree offered to undergraduates is the bachelor's degree, which usually takes three years to complete. Students are then able to work towards a postgraduate degree, which usually takes one year, or towards a doctorate, which takes three or more years.
List of universities in England, England's universities include some of the highest-ranked universities in the world; University of Cambridge, University of Oxford, Imperial College London, University College London and King's College London are all ranked in the global top 30 in the 2018 ''QS World University Rankings''. The London School of Economics has been described as the world's leading social science institution for both teaching and research. The London Business School is considered one of the world's leading business schools and in 2010 its MBA programme was ranked best in the world by the ''Financial Times''. Academic degrees in England are usually split into classes: first class (1st), upper second class (2:1), lower second class (2:2), third (3rd), and unclassified.
The King's School, Canterbury and King's School, Rochester are the oldest schools in the English-speaking world. Many of England's most well-known schools, such as Winchester College, Eton College, Eton, St Paul's School (London), St Paul's School, Harrow School and Rugby School are fee-paying institutions.
Culture
Architecture
 Many ancient standing stone monuments were erected during the prehistoric period; amongst the best known are
Many ancient standing stone monuments were erected during the prehistoric period; amongst the best known are Stonehenge
Stonehenge is a prehistoric monument on Salisbury Plain in Wiltshire, England, west of Amesbury. It consists of an outer ring of vertical sarsen standing stones, each around high, wide, and weighing around 25 tons, topped by connectin ...
, Devil's Arrows, Rudston Monolith and Castlerigg stone circle, Castlerigg. With the introduction of Ancient Roman architecture there was a development of basilicas, Roman baths, baths, amphitheaters, triumphal arches, villas, Roman temples, Roman roads, Roman forts, stockades and aqueduct (bridge), aqueducts. It was the Romans who founded the first cities and towns such as London, Bath, York, Chester and St Albans. Perhaps the best-known example is Hadrian's Wall stretching right across northern England. Another well-preserved example is the Roman Baths (Bath), Roman Baths at Bath, Somerset.
Anglo-Saxon architecture, Early Medieval architecture's secular buildings were simple constructions mainly using timber with thatch for roofing. Ecclesiastical architecture ranged from a synthesis of Early Christian Ireland, HibernoãGermanic Christianity, Saxon monasticism
Monasticism (from Ancient Greek , , from , , 'alone'), also referred to as monachism, or monkhood, is a religious way of life in which one renounces worldly pursuits to devote oneself fully to spiritual work. Monastic life plays an important role ...
, to Early Christian art and architecture, Early Christian basilica and architecture characterised by pilaster-strips, blank arcading, baluster shafts and triangular headed openings. After the Norman conquest in 1066 various Castles in England were created so law lords could uphold their authority and in the north to protect from invasion. Some of the best-known medieval castles are the Tower of London, Warwick Castle, Durham Castle and Windsor Castle.
 Throughout the Plantagenet era, an English Gothic architecture flourished, with prime examples including the Architecture of the medieval cathedrals of England, medieval cathedrals such as Canterbury Cathedral, Westminster Abbey and York Minster.. Expanding on the Norman architecture, Norman base there was also castles, palaces, List of historic houses in England, great houses, universities and parish churches. Medieval architecture was completed with the 16th-century Tudor architecture, Tudor style; the four-centred arch, now known as the Tudor arch, was a defining feature as were wattle and daub houses domestically. In the aftermath of the
Throughout the Plantagenet era, an English Gothic architecture flourished, with prime examples including the Architecture of the medieval cathedrals of England, medieval cathedrals such as Canterbury Cathedral, Westminster Abbey and York Minster.. Expanding on the Norman architecture, Norman base there was also castles, palaces, List of historic houses in England, great houses, universities and parish churches. Medieval architecture was completed with the 16th-century Tudor architecture, Tudor style; the four-centred arch, now known as the Tudor arch, was a defining feature as were wattle and daub houses domestically. In the aftermath of the Renaissance
The Renaissance ( , ) , from , with the same meanings. is a period in European history marking the transition from the Middle Ages to modernity and covering the 15th and 16th centuries, characterized by an effort to revive and surpass ideas ...
a form of architecture echoing classical antiquity synthesised with Christianity appeared, the English Baroque style of architect Christopher Wren being particularly championed.
Georgian architecture followed in a more refined style, evoking a simple Palladian form; the Royal Crescent at Bath is one of the best examples of this. With the emergence of romanticism during Victorian period, a Gothic Revival was launched. In addition to this, around the same time the Industrial Revolution paved the way for buildings such as The Crystal Palace. Since the 1930s various modernist architecture, modernist forms have appeared whose reception is often controversial, though traditionalist resistance movements continue with support in influential places.
Gardens
 Landscape gardening, as developed by Capability Brown, set an international trend for the English garden. Gardening, and visiting gardens, are regarded as typically English pursuits. The English garden presented an idealized view of nature. At large country houses, the English garden usually included lakes, sweeps of gently rolling lawns set against groves of trees, and recreations of classical temples, Gothic architecture, Gothic ruins, bridges, and other picturesque architecture, designed to recreate an idyllic pastoral landscape.
By the end of the 18th century, the English garden was being imitated by the French landscape garden, and as far away as St. Petersburg, Russia, in Pavlovsk, Saint Petersburg, Pavlovsk, the gardens of the future Emperor Paul. It also had a major influence on the form of the public parks and gardens which appeared around the world in the 19th century. The English landscape garden was centred on the English country house and manor houses.
English Heritage and the National Trust preserve great gardens and landscape parks throughout the country. The RHS Chelsea Flower Show is held every year by the Royal Horticultural Society and is said to be the largest gardening show in the world.
Landscape gardening, as developed by Capability Brown, set an international trend for the English garden. Gardening, and visiting gardens, are regarded as typically English pursuits. The English garden presented an idealized view of nature. At large country houses, the English garden usually included lakes, sweeps of gently rolling lawns set against groves of trees, and recreations of classical temples, Gothic architecture, Gothic ruins, bridges, and other picturesque architecture, designed to recreate an idyllic pastoral landscape.
By the end of the 18th century, the English garden was being imitated by the French landscape garden, and as far away as St. Petersburg, Russia, in Pavlovsk, Saint Petersburg, Pavlovsk, the gardens of the future Emperor Paul. It also had a major influence on the form of the public parks and gardens which appeared around the world in the 19th century. The English landscape garden was centred on the English country house and manor houses.
English Heritage and the National Trust preserve great gardens and landscape parks throughout the country. The RHS Chelsea Flower Show is held every year by the Royal Horticultural Society and is said to be the largest gardening show in the world.
Folklore
Cuisine
 Since the early modern period the food of England has historically been characterised by its simplicity of approach and a reliance on the high quality of natural produce. During the Middle Ages and through the Renaissance period, English cuisine enjoyed an excellent reputation, though a decline began during the
Since the early modern period the food of England has historically been characterised by its simplicity of approach and a reliance on the high quality of natural produce. During the Middle Ages and through the Renaissance period, English cuisine enjoyed an excellent reputation, though a decline began during the Industrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution was the transition to new manufacturing processes in Great Britain, continental Europe, and the United States, that occurred during the period from around 1760 to about 1820ã1840. This transition included going f ...
with the move away from the land and increasing urbanisation of the populace. The cuisine of England has, however, recently undergone a revival, which has been recognised by food critics with some good ratings in ''Restaurant (magazine), Restaurant''s best restaurant in the world charts. An early book of English recipes is the ''Forme of Cury'' from the royal court of Richard II of England, Richard II.
Traditional examples of English food include the Sunday roast, featuring a roasting, roasted joint (usually beef, lamb and mutton, lamb, chicken or pork) served with assorted vegetables, Yorkshire pudding and gravy. Other prominent meals include fish and chips and the Full breakfast, full English breakfast (generally consisting of bacon, sausages, grilled tomatoes, fried bread, black pudding, baked beans, edible mushroom, mushrooms and eggs). Various meat pies are consumed, such as steak and kidney pie, steak and ale pie, cottage pie, pork pie (usually eaten cold) and the Cornish pasty.
Sausages are commonly eaten, either as bangers and mash or toad in the hole. Lancashire hotpot is a well-known stew originating in the northwest. Some of the more popular cheeses are Cheddar cheese, Cheddar, Red Leicester, Wensleydale (cheese), Wensleydale, Double Gloucester and Stilton cheese, Blue Stilton. Many Anglo-Indian hybrid dishes, curries, have been created, such as chicken tikka masala and balti (food), balti. Traditional English dessert dishes include apple pie or other fruit pies; spotted dick ã all generally served with custard; and, more recently, sticky toffee pudding. Sweet pastries include scones (either plain or containing dried fruit) served with jam or cream, dried fruit loaves, Eccles cakes and mince pies as well as a wide range of sweet or spiced biscuits.
Common non-alcoholic drinks include tea, the popularity of which was increased by Catherine of Braganza, and coffee; frequently consumed alcoholic drinks include wine, ciders and English beers, such as bitter (beer), bitter, mild ale, mild, stout and brown ale.
Visual arts
 The earliest known examples are the prehistoric rock and cave art pieces, most prominent in North Yorkshire, Northumberland and Cumbria, but also feature further south, for example at Creswell Crags. With the arrival of Roman culture in the 1st century, various forms of art such as statues, busts, glasswork and mosaics were the norm. There are numerous surviving artefacts, such as those at Lullingstone Roman Villa, Lullingstone and Isurium Brigantum, Aldborough. During the Early Middle Ages the style favoured sculpted crosses and ivories, manuscript painting, gold and enamel jewellery, demonstrating a love of intricate, interwoven designs such as in the Staffordshire Hoard discovered in 2009. Some of these blended Insular art, Gaelic and Anglian styles, such as the Lindisfarne Gospels and Vespasian Psalter. Later Gothic art was popular at Winchester and Canterbury, examples survive such as Benedictional of St. ûthelwold and Luttrell Psalter.
The Tudor era saw Artists of the Tudor court, prominent artists as part of their court, portrait painting which would remain an enduring part of English art, was boosted by German Hans Holbein the Younger, Hans Holbein, natives such as Nicholas Hilliard built on this. Under the Stuarts, Continental artists were influential especially the Flemish, examples from the period include Anthony van Dyck, Peter Lely, Godfrey Kneller and William Dobson. The 18th century was a time of significance with the founding of the Royal Academy, a classicism based on the Renaissance art, High Renaissance prevailed, with Thomas Gainsborough and Joshua Reynolds becoming two of England's most treasured artists.
In the 19th century, John Constable, Constable and J.M.W. Turner, Turner were major landscape artists. The Norwich School (art movement), Norwich School continued the landscape tradition, while the Pre-Raphaelite Brotherhood, led by artists such as Holman Hunt, Dante Gabriel Rossetti and John Everett Millais, revived the Early Renaissance style with their vivid and detailed style. Prominent amongst 20th-century artists was Henry Moore, regarded as the voice of British sculpture, and of British modernism in general. More recent painters include Lucian Freud, whose work ''Benefits Supervisor Sleeping'' in 2008 set a world record for sale value of a painting by a then-living artist. The Royal Society of Arts is an organisation committed to the arts and culture.
The earliest known examples are the prehistoric rock and cave art pieces, most prominent in North Yorkshire, Northumberland and Cumbria, but also feature further south, for example at Creswell Crags. With the arrival of Roman culture in the 1st century, various forms of art such as statues, busts, glasswork and mosaics were the norm. There are numerous surviving artefacts, such as those at Lullingstone Roman Villa, Lullingstone and Isurium Brigantum, Aldborough. During the Early Middle Ages the style favoured sculpted crosses and ivories, manuscript painting, gold and enamel jewellery, demonstrating a love of intricate, interwoven designs such as in the Staffordshire Hoard discovered in 2009. Some of these blended Insular art, Gaelic and Anglian styles, such as the Lindisfarne Gospels and Vespasian Psalter. Later Gothic art was popular at Winchester and Canterbury, examples survive such as Benedictional of St. ûthelwold and Luttrell Psalter.
The Tudor era saw Artists of the Tudor court, prominent artists as part of their court, portrait painting which would remain an enduring part of English art, was boosted by German Hans Holbein the Younger, Hans Holbein, natives such as Nicholas Hilliard built on this. Under the Stuarts, Continental artists were influential especially the Flemish, examples from the period include Anthony van Dyck, Peter Lely, Godfrey Kneller and William Dobson. The 18th century was a time of significance with the founding of the Royal Academy, a classicism based on the Renaissance art, High Renaissance prevailed, with Thomas Gainsborough and Joshua Reynolds becoming two of England's most treasured artists.
In the 19th century, John Constable, Constable and J.M.W. Turner, Turner were major landscape artists. The Norwich School (art movement), Norwich School continued the landscape tradition, while the Pre-Raphaelite Brotherhood, led by artists such as Holman Hunt, Dante Gabriel Rossetti and John Everett Millais, revived the Early Renaissance style with their vivid and detailed style. Prominent amongst 20th-century artists was Henry Moore, regarded as the voice of British sculpture, and of British modernism in general. More recent painters include Lucian Freud, whose work ''Benefits Supervisor Sleeping'' in 2008 set a world record for sale value of a painting by a then-living artist. The Royal Society of Arts is an organisation committed to the arts and culture.
Literature, poetry, and philosophy
 Early authors such as
Early authors such as Bede
Bede ( ; ang, BúÈda , ; 672/326 May 735), also known as Saint Bede, The Venerable Bede, and Bede the Venerable ( la, Beda Venerabilis), was an English monk at the monastery of St Peter and its companion monastery of St Paul in the Kingdom o ...
and Alcuin wrote in Latin.. The period of Old English literature provided the epic poem ''Beowulf'' and the secular prose of the ''Anglo-Saxon Chronicle
The ''Anglo-Saxon Chronicle'' is a collection of annals in Old English, chronicling the history of the Anglo-Saxons. The original manuscript of the ''Chronicle'' was created late in the 9th century, probably in Wessex, during the reign of Alf ...
'', along with Christian writings such as ''Judith (poem), Judith'', CûÎdmon's ''CûÎdmon, Hymn'' and hagiography, hagiographies. Following the Norman conquest Latin literature, Latin continued amongst the educated classes, as well as an Anglo-Norman literature.
Middle English literature emerged with Geoffrey Chaucer, author of ''The Canterbury Tales'', along with John Gower, Gower, the Pearl Poet and William Langland, Langland. William of Ockham and Roger Bacon, who were Franciscans, were major philosophers of the Middle Ages. Julian of Norwich, who wrote ''Revelations of Divine Love'', was a prominent Christian mystic. With the English Renaissance literature in the Early Modern English style appeared. William Shakespeare, whose works include ''Hamlet'', ''Romeo and Juliet'', ''Macbeth'', and ''A Midsummer Night's Dream'', remains one of the most championed authors in English literature.
Christopher Marlowe, Edmund Spenser, Philip Sydney, Thomas Kyd, John Donne, and Ben Jonson are other established authors of the Elizabethan literature, Elizabethan age.. Francis Bacon and Thomas Hobbes wrote on empiricism and materialism, including scientific method and social contract. Robert Filmer, Filmer wrote on the Divine Right of Kings. Andrew Marvell, Marvell was the best-known poet of the Commonwealth of England, Commonwealth, while John Milton authored ''Paradise Lost'' during the Restoration literature, Restoration.
Some of the most prominent philosophers of the Age of Enlightenment, Enlightenment were John Locke, Thomas Paine, Samuel Johnson and Jeremy Bentham. More radical elements were later countered by Edmund Burke who is regarded as the founder of conservatism. The poet Alexander Pope with his satirical verse became well regarded. The English played a significant role in romanticism: Samuel Taylor Coleridge, Lord Byron, John Keats, Mary Shelley, Percy Bysshe Shelley, William Blake and William Wordsworth were major figures.
In response to the Industrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution was the transition to new manufacturing processes in Great Britain, continental Europe, and the United States, that occurred during the period from around 1760 to about 1820ã1840. This transition included going f ...
, agrarian writers sought a way between liberty and tradition; William Cobbett, G. K. Chesterton and Hilaire Belloc were main exponents, while the founder of guild socialism, Arthur Penty, and cooperative movement advocate G. D. H. Cole are somewhat related. Empiricism continued through John Stuart Mill and Bertrand Russell, while Bernard Williams was involved in analytics. Authors from around the Victorian era include Charles Dickens, the Brontû¨ sisters, Jane Austen, George Eliot, Rudyard Kipling, Thomas Hardy, H. G. Wells and Lewis Carroll. Since then England has continued to produce novelists such as George Orwell, D. H. Lawrence, Virginia Woolf, C. S. Lewis, Enid Blyton, Aldous Huxley, Agatha Christie, Terry Pratchett, J. R. R. Tolkien, and J. K. Rowling.
Performing arts
The traditional folk music of England is centuries old and has contributed to several genres prominently; mostly sea shanties, jigs, hornpipes and dance music. It has its own distinct variations and regional peculiarities. Ballads featuring Robin Hood, printed by Wynkyn de Worde in the 16th century, are an important artefact, as are John Playford's ''The Dancing Master'' and Robert Harley, 1st Earl of Oxford and Earl Mortimer, Robert Harley's ''Roxburghe Ballads'' collections. Some of the best-known songs are ''Greensleeves'', ''Pastime with Good Company'', ''Maggie May (folk song), Maggie May'' and ''Spanish Ladies'' amongst others. Many nursery rhymes are of English origin such as ''Mary, Mary, Quite Contrary'', ''Roses Are Red'', ''Jack and Jill (nursery rhyme), Jack and Jill'', ''London Bridge Is Falling Down, The Grand Old Duke of York, Hey Diddle Diddle'' and ''Humpty Dumpty''. Traditional English Christmas carols include "We Wish You a Merry Christmas", "The First Noel", "I Saw Three Ships" and "God Rest You Merry, Gentlemen". Early English composers in classical music include Renaissance artists Thomas Tallis and William Byrd, followed up by Henry Purcell from the Baroque music, Baroque period and Thomas Arne who was well known for his patriotic song Rule, Britannia!. German-born George Frideric Handel spent most of his composing life in London and became a national icon in Britain, creating some of the most well-known works of classical music, especially his English oratorios, ''Messiah (Handel), The Messiah'', ''Solomon (Handel), Solomon'', ''Water Music (Handel), Water Music'', and ''Music for the Royal Fireworks''. One of his four Coronation Anthems (Handel), Coronation Anthems, ''Zadok the Priest'', composed for the coronation of George II of Great Britain, George II, has been performed at every subsequent Coronation of the British monarch, British coronation, traditionally during the sovereign's anointing. Classical music attracted much attention from 1784 with the formation of the Birmingham Triennial Music Festival, which was the longest running classical music festival of its kind until the final concerts in 1912. The English Musical Renaissance was a hypothetical development in the late 19th and early 20th century, when English composers, often those lecturing or trained at the Royal College of Music, were said to have freed themselves from foreign musical influences. There was a revival in the profile of composers from England in the 20th century led by Edward Elgar, Benjamin Britten, Frederick Delius, Gustav Holst, Ralph Vaughan Williams and others. Present-day composers from England include Michael Nyman, best known for ''The Piano'', and Andrew Lloyd Webber, whose musicals have achieved enormous success in the West End theatre, West End and worldwide. In popular music, many English bands and solo artists have been cited as the most influential and best-selling musicians of all time. Acts such as The Beatles, Led Zeppelin, Pink Floyd, Elton John, Queen (band), Queen, Rod Stewart, David Bowie, The Rolling Stones and Def Leppard are among the highest-selling recording artists in the world. Many musical genres have origins in (or strong associations with) England, such as British invasion, progressive rock, hard rock, mod (subculture), Mod, glam rock, heavy metal music, heavy metal, Britpop, indie rock, gothic rock, shoegazing, acid house, UK garage, garage, trip hop, drum and bass and dubstep. Large outdoor List of music festivals in the United Kingdom, music festivals in the summer and autumn are popular, such as Glastonbury Festival, Glastonbury, V Festival, and the Reading and Leeds Festivals. England was at the forefront of the illegal, free rave movement from the late 1980s, which led to pan-European culture of teknivals mirrored on the UK free festival movement and associated travelling lifestyle. The Boishakhi Mela is a Bengali New Year festival celebrated by the British Bangladeshi community. It is the largest open-air Asian festival in Europe. After the Notting Hill Carnival, it is the second-largest street festival in theUnited Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotland, Wales and North ...
attracting over 80,000 visitors from across the country.
The most prominent opera house in England is the Royal Opera House at Covent Garden.. The Proms ã a season of orchestral classical concerts held primarily at the Royal Albert Hall in London ã is a major cultural event in the English calendar, and takes place yearly. The Royal Ballet is one of the world's foremost classical ballet companies, its reputation built on two prominent figures of 20th-century dance, ''prima ballerina'' Margot Fonteyn and choreographer Frederick Ashton. The Royal Academy of Music is the oldest Music school, conservatoire in England, founded in 1822. It received its royal charter in 1830 from George IV of the United Kingdom, King George IV. England is home to numerous major orchestras such as the BBC Symphony Orchestra, the Royal Philharmonic Orchestra, the Philharmonia Orchestra, and the London Symphony Orchestra.
The circus is a traditional form of entertainment in England. Chipperfield's Circus dates back more than 300 years, making it one of the oldest family circus dynasties.Great dynasties of the world: The Chipperfields''The Guardian'' Retrieved 18 February 2011. Philip Astley is regarded as the father of the Circus#Development, modern circus."The circus comes to the Circus"
BBC News. Retrieved 13 December 2014 Following his invention of the circus ring in 1768, Astley's Amphitheatre opened in London in 1773. As an equestrian master Astley had a skill for trick horse-riding, and when he added tumblers, tightrope-walkers, jugglers, performing dogs, and a clown to fill time between his own demonstrations ã the modern circus was born. Pantomime is a British Musical theatre, musical comedy stage production, designed for family entertainment. It is performed in theatres throughout the England during the Christmas and New Year season. The art originated in the 18th century with John Weaver (dancer), John Weaver, a dance master and choreographer.David Christopher (2002). "British Culture: An Introduction". p. 74. Routledge, In 19th century England it acquired its present form, which includes songs, slapstick comedy and dancing, employing gender-crossing actors, combining topical humour with a story loosely based on a well-known fairy tale.
Cinema
 England (and the UK as a whole) has had a considerable influence on the history of the cinema, producing some of the greatest actors, directors and motion pictures of all time, including Alfred Hitchcock, Charlie Chaplin, David Lean, Laurence Olivier, Vivien Leigh, John Gielgud, Peter Sellers, Julie Andrews, Michael Caine, Gary Oldman, Helen Mirren, Kate Winslet and Daniel Day-Lewis. Hitchcock and Lean are among the most critically acclaimed filmmakers. Hitchcock's first thriller, ''The Lodger: A Story of the London Fog'' (1926), helped shape the Thriller film, thriller genre in film, while his 1929 film, ''Blackmail (1929 film), Blackmail'', is often regarded as the first British Sound film#Transition: Europe, sound feature film.
Major film studios in England include Pinewood Studios, Pinewood, Elstree Studios, Elstree and Shepperton Studios, Shepperton. Some of the most commercially successful films of all time have been produced in England, including two of the List of highest-grossing film series, highest-grossing film franchises (''Harry Potter (film series), Harry Potter'' and ''James Bond (film series), James Bond''). Ealing Studios in London has a claim to being the oldest continuously working film studio in the world. Famous for recording many motion picture film scores, the London Symphony Orchestra first performed film music in 1935. The Hammer Film Productions, Hammer Horror films starring Christopher Lee saw the production of the first gory horror films showing blood and guts in colour.
The BFI Top 100 British films includes ''Monty Python's Life of Brian'' (1979), a film regularly voted the funniest of all time by the UK public. English producers are also active in international co-productions and English actors, directors and crew feature regularly in American films. The UK film council ranked David Yates, Christopher Nolan, Mike Newell (director), Mike Newell, Ridley Scott and Paul Greengrass the five most commercially successful English directors since 2001. Other contemporary English directors include Sam Mendes, Guy Ritchie and Richard Curtis. Current actors include Tom Hardy, Daniel Craig, Benedict Cumberbatch, Lena Headey, Felicity Jones, Emilia Clarke, Lashana Lynch, and Emma Watson. Acclaimed for his motion capture work, Andy Serkis opened The Imaginarium Studios in London in 2011. The visual effects company Framestore in London has produced some of the most critically acclaimed special effects in modern film. Many successful Hollywood films have been based on English people, British literature, stories or events. The List of Walt Disney Animation Studios films, 'English Cycle' of Disney animated films include ''Alice in Wonderland (1951 film), Alice in Wonderland'', ''The Jungle Book (1967 film), The Jungle Book'' and ''The Many Adventures of Winnie the Pooh, Winnie the Pooh''.
England (and the UK as a whole) has had a considerable influence on the history of the cinema, producing some of the greatest actors, directors and motion pictures of all time, including Alfred Hitchcock, Charlie Chaplin, David Lean, Laurence Olivier, Vivien Leigh, John Gielgud, Peter Sellers, Julie Andrews, Michael Caine, Gary Oldman, Helen Mirren, Kate Winslet and Daniel Day-Lewis. Hitchcock and Lean are among the most critically acclaimed filmmakers. Hitchcock's first thriller, ''The Lodger: A Story of the London Fog'' (1926), helped shape the Thriller film, thriller genre in film, while his 1929 film, ''Blackmail (1929 film), Blackmail'', is often regarded as the first British Sound film#Transition: Europe, sound feature film.
Major film studios in England include Pinewood Studios, Pinewood, Elstree Studios, Elstree and Shepperton Studios, Shepperton. Some of the most commercially successful films of all time have been produced in England, including two of the List of highest-grossing film series, highest-grossing film franchises (''Harry Potter (film series), Harry Potter'' and ''James Bond (film series), James Bond''). Ealing Studios in London has a claim to being the oldest continuously working film studio in the world. Famous for recording many motion picture film scores, the London Symphony Orchestra first performed film music in 1935. The Hammer Film Productions, Hammer Horror films starring Christopher Lee saw the production of the first gory horror films showing blood and guts in colour.
The BFI Top 100 British films includes ''Monty Python's Life of Brian'' (1979), a film regularly voted the funniest of all time by the UK public. English producers are also active in international co-productions and English actors, directors and crew feature regularly in American films. The UK film council ranked David Yates, Christopher Nolan, Mike Newell (director), Mike Newell, Ridley Scott and Paul Greengrass the five most commercially successful English directors since 2001. Other contemporary English directors include Sam Mendes, Guy Ritchie and Richard Curtis. Current actors include Tom Hardy, Daniel Craig, Benedict Cumberbatch, Lena Headey, Felicity Jones, Emilia Clarke, Lashana Lynch, and Emma Watson. Acclaimed for his motion capture work, Andy Serkis opened The Imaginarium Studios in London in 2011. The visual effects company Framestore in London has produced some of the most critically acclaimed special effects in modern film. Many successful Hollywood films have been based on English people, British literature, stories or events. The List of Walt Disney Animation Studios films, 'English Cycle' of Disney animated films include ''Alice in Wonderland (1951 film), Alice in Wonderland'', ''The Jungle Book (1967 film), The Jungle Book'' and ''The Many Adventures of Winnie the Pooh, Winnie the Pooh''.
Museums, libraries, and galleries
 English Heritage is a governmental body with a broad remit of managing the historic sites, artefacts and environments of England. It is currently sponsored by the Department for Digital, Culture, Media and Sport. The charity National Trust for Places of Historic Interest or Natural Beauty holds a contrasting role. 17 of the 25 United Kingdom UNESCO World Heritage Sites fall within England. Some of the best-known of these are: Hadrian's Wall, Stonehenge, Avebury and Associated Sites, Tower of London, Jurassic Coast, Saltaire, Ironbridge Gorge, Studley Royal Park and various others.
There are many museums in England, but perhaps the most notable is London's British Museum. Its collection of more than seven million objects is one of the largest and most comprehensive in the world, sourced from every continent, illustrating and documenting the story of human culture from its beginning to the present. The British Library in London is the national library and is one of the world's largest research libraries, holding over 150 million items in almost all known languages and formats; including around 25 million books. The most senior art gallery is the National Gallery in Trafalgar Square, which houses a collection of over 2,300 paintings dating from the mid-13th century to 1900. The Tate galleries house the national collections of British and international modern art; they also host the famously controversial Turner Prize.
English Heritage is a governmental body with a broad remit of managing the historic sites, artefacts and environments of England. It is currently sponsored by the Department for Digital, Culture, Media and Sport. The charity National Trust for Places of Historic Interest or Natural Beauty holds a contrasting role. 17 of the 25 United Kingdom UNESCO World Heritage Sites fall within England. Some of the best-known of these are: Hadrian's Wall, Stonehenge, Avebury and Associated Sites, Tower of London, Jurassic Coast, Saltaire, Ironbridge Gorge, Studley Royal Park and various others.
There are many museums in England, but perhaps the most notable is London's British Museum. Its collection of more than seven million objects is one of the largest and most comprehensive in the world, sourced from every continent, illustrating and documenting the story of human culture from its beginning to the present. The British Library in London is the national library and is one of the world's largest research libraries, holding over 150 million items in almost all known languages and formats; including around 25 million books. The most senior art gallery is the National Gallery in Trafalgar Square, which houses a collection of over 2,300 paintings dating from the mid-13th century to 1900. The Tate galleries house the national collections of British and international modern art; they also host the famously controversial Turner Prize.
Media
The BBC, founded in 1922, is the UK's publicly funded radio, television and Internet broadcasting corporation, and is the oldest and largest broadcaster in the world. It operates numerous television and radio stations in the UK and abroad and its domestic services are funded by the Television licensing in the United Kingdom, television licence. The BBC World Service is an International broadcasting, international broadcaster owned and operated by the BBC. It is the world's largest of any kind. It broadcasts radio news, speech and discussions in more than 40 languages. London dominates the media sector in England: national newspapers and television and radio are largely based there, although Manchester is also a significant national media centre. The UK publishing sector, including books, directories and databases, journals, magazines and business media, newspapers and news agencies, has a combined turnover of around ôÈ20 billion and employs around 167,000 people. National newspapers produced in England include ''The Times'', ''The Guardian'' and the ''Financial Times''. Magazines and journals published in England that have achieved worldwide circulation include ''Nature (journal), Nature'', ''New Scientist'', ''The Spectator'', ''Prospect (magazine), Prospect'', ''NME'' and ''The Economist''. The Secretary of State for Digital, Culture, Media and Sport has overall responsibility over media and broadcasting in England.Sport
England has a strong sporting heritage, and during the 19th century codified many sports that are now played around the world. Sports originating in England include association football, cricket, rugby union, rugby league, tennis, boxing, badminton, squash (sport), squash, rounders, field hockey, hockey, snooker, billiards, darts, table tennis, bowls, netball, thoroughbred horseracing, greyhound racing and fox hunting. It has helped the development of golf, sailing and Formula One. Football is the Sport in the United Kingdom#Popularity, most popular of these sports. The England national football team, whose home venue is Wembley Stadium, played Scotland national football team, Scotland in the first ever international football match in 1872. Referred to as the "home of football" by FIFA, England hosted the 1966 FIFA World Cup, and won the tournament by defeating Germany national football team, West Germany 4ã2 in the 1966 FIFA World Cup Final, final, with Geoff Hurst scoring a hat-trick. With a British television audience peak of 32.30 million viewers, the final is the List of most-watched television broadcasts#United Kingdom, most watched television event ever in the UK. At club level, England is recognised by FIFA as the birthplace of club football, due to Sheffield F.C. founded in 1857 being the world's oldest club. The Football Association is the oldest governing body in the sport, with the Laws of the Game (association football), rules of football first drafted in 1863 by Ebenezer Cobb Morley. The FA Cup and The Football League were the first cup and league competitions respectively. In the modern day, the Premier League is the world's most-watched football league, most lucrative, and amongst the elite.
As is the case throughout the UK, football in England is notable for the rivalries between clubs and the passion of the supporters, which includes a tradition of football chants. The most successful English football team in the European Cup/UEFA Champions League is Liverpool F.C. who have won the competition on six occasions. Other English success has come from Manchester United F.C., winning the competition on 3 occasions; Nottingham Forest F.C. and Chelsea F.C. on 2 occasions, Aston Villa F.C. have only won the trophy once.
At club level, England is recognised by FIFA as the birthplace of club football, due to Sheffield F.C. founded in 1857 being the world's oldest club. The Football Association is the oldest governing body in the sport, with the Laws of the Game (association football), rules of football first drafted in 1863 by Ebenezer Cobb Morley. The FA Cup and The Football League were the first cup and league competitions respectively. In the modern day, the Premier League is the world's most-watched football league, most lucrative, and amongst the elite.
As is the case throughout the UK, football in England is notable for the rivalries between clubs and the passion of the supporters, which includes a tradition of football chants. The most successful English football team in the European Cup/UEFA Champions League is Liverpool F.C. who have won the competition on six occasions. Other English success has come from Manchester United F.C., winning the competition on 3 occasions; Nottingham Forest F.C. and Chelsea F.C. on 2 occasions, Aston Villa F.C. have only won the trophy once.
 Cricket is generally thought to have been developed in the early medieval period among the farming and metalworking communities of the Weald. The England cricket team is a composite England and Wales, team. One of the game's top rivalries is The Ashes series between England and Australia cricket team, Australia, contested since 1882. The climax of the 2005 Ashes series, 2005 Ashes was viewed by 7.4 million as it was available on terrestrial television. England has hosted five Cricket World Cups (1975, 1979, 1983, 1999 and 2019 Cricket World Cup, 2019), winning the 2019 edition in a final regarded as one of the greatest one day internationals ever played. They hosted the ICC World Twenty20 in 2009 ICC World Twenty20, 2009, winning this format in 2010 beating rivals Australia in the final. In the domestic competition, the County Championship, Yorkshire County Cricket Club, Yorkshire are by far the most successful club having won the competition 32 times outright and sharing it on 1 other occasion. Lord's Cricket Ground situated in London is sometimes referred to as the "Mecca of Cricket".
William Penny Brookes was prominent in organising the format for the modern Olympic Games. In 1994, then President of the International Olympic Committee, IOC, Juan Antonio Samaranch, laid a wreath on Brooke's grave, and said, "I came to pay homage and tribute to Dr Brookes, who really was the founder of the modern Olympic Games". London has hosted the Summer Olympic Games three times, in 1908 Summer Olympics, 1908, 1948 Summer Olympics, 1948, and 2012 Summer Olympics, 2012. England competes in the Commonwealth Games, held every four years. Sport England is the governing body responsible for distributing funds and providing strategic guidance for sporting activity in England. The Minister for Sport and Civil Society has responsibility for sport in England.
Cricket is generally thought to have been developed in the early medieval period among the farming and metalworking communities of the Weald. The England cricket team is a composite England and Wales, team. One of the game's top rivalries is The Ashes series between England and Australia cricket team, Australia, contested since 1882. The climax of the 2005 Ashes series, 2005 Ashes was viewed by 7.4 million as it was available on terrestrial television. England has hosted five Cricket World Cups (1975, 1979, 1983, 1999 and 2019 Cricket World Cup, 2019), winning the 2019 edition in a final regarded as one of the greatest one day internationals ever played. They hosted the ICC World Twenty20 in 2009 ICC World Twenty20, 2009, winning this format in 2010 beating rivals Australia in the final. In the domestic competition, the County Championship, Yorkshire County Cricket Club, Yorkshire are by far the most successful club having won the competition 32 times outright and sharing it on 1 other occasion. Lord's Cricket Ground situated in London is sometimes referred to as the "Mecca of Cricket".
William Penny Brookes was prominent in organising the format for the modern Olympic Games. In 1994, then President of the International Olympic Committee, IOC, Juan Antonio Samaranch, laid a wreath on Brooke's grave, and said, "I came to pay homage and tribute to Dr Brookes, who really was the founder of the modern Olympic Games". London has hosted the Summer Olympic Games three times, in 1908 Summer Olympics, 1908, 1948 Summer Olympics, 1948, and 2012 Summer Olympics, 2012. England competes in the Commonwealth Games, held every four years. Sport England is the governing body responsible for distributing funds and providing strategic guidance for sporting activity in England. The Minister for Sport and Civil Society has responsibility for sport in England.
 Rugby union originated in Rugby School, Warwickshire in the early 19th century. The England national rugby union team, England rugby union team won the 2003 Rugby World Cup, with Jonny Wilkinson scoring the winning drop kick, drop goal in the last minute of extra time against Australia. England was one of the host nations of the competition in the 1991 Rugby World Cup and also hosted the 2015 Rugby World Cup. The top level of club participation is the Guinness Premiership, English Premiership. Leicester Tigers, Wasps RFC, London Wasps, Bath Rugby and Northampton Saints have had success in the Europe-wide Heineken Cup.
Rugby league was born in Huddersfield in 1895. Since 2008, the England national rugby league team has been a full test nation in lieu of the Great Britain national rugby league team, which won three Rugby League World Cup, World Cups but is now retired. Club sides play in Super League, the present-day embodiment of the Rugby Football League Championship. Rugby League is most popular among towns in the northern English counties of Lancashire, Yorkshire and Cumbria. The vast majority of English clubs in Super League are based in the north of England. Some of the most successful clubs include Wigan Warriors, Hull F.C. St Helens R.F.C., St. Helens, Leeds Rhinos and Huddersfield Giants; the former three have all won the World Club Challenge previously.
Golf has been prominent in England; due in part to its cultural and geographical ties to Scotland, the Golf in Scotland, home of Golf. There are both professional tours for men and women, in two main tours: the Professional Golfers' Association (Great Britain and Ireland), PGA and the European Tour. England has produced grand slam winners: Cyril Walker (golfer), Cyril Walker, Tony Jacklin, Nick Faldo, and Justin Rose in the men's and Laura Davies, Alison Nicholas, and Karen Stupples in the women's. The world's oldest golf tournament, and golf's first major is The Open Championship, played both in England and Scotland. The biennial golf competition, the Ryder Cup, is named after English businessman Samuel Ryder who sponsored the event and donated the trophy. Nick Faldo is the most successful Ryder Cup player ever, having won the most points (25) of any player on either the European or US teams.
Rugby union originated in Rugby School, Warwickshire in the early 19th century. The England national rugby union team, England rugby union team won the 2003 Rugby World Cup, with Jonny Wilkinson scoring the winning drop kick, drop goal in the last minute of extra time against Australia. England was one of the host nations of the competition in the 1991 Rugby World Cup and also hosted the 2015 Rugby World Cup. The top level of club participation is the Guinness Premiership, English Premiership. Leicester Tigers, Wasps RFC, London Wasps, Bath Rugby and Northampton Saints have had success in the Europe-wide Heineken Cup.
Rugby league was born in Huddersfield in 1895. Since 2008, the England national rugby league team has been a full test nation in lieu of the Great Britain national rugby league team, which won three Rugby League World Cup, World Cups but is now retired. Club sides play in Super League, the present-day embodiment of the Rugby Football League Championship. Rugby League is most popular among towns in the northern English counties of Lancashire, Yorkshire and Cumbria. The vast majority of English clubs in Super League are based in the north of England. Some of the most successful clubs include Wigan Warriors, Hull F.C. St Helens R.F.C., St. Helens, Leeds Rhinos and Huddersfield Giants; the former three have all won the World Club Challenge previously.
Golf has been prominent in England; due in part to its cultural and geographical ties to Scotland, the Golf in Scotland, home of Golf. There are both professional tours for men and women, in two main tours: the Professional Golfers' Association (Great Britain and Ireland), PGA and the European Tour. England has produced grand slam winners: Cyril Walker (golfer), Cyril Walker, Tony Jacklin, Nick Faldo, and Justin Rose in the men's and Laura Davies, Alison Nicholas, and Karen Stupples in the women's. The world's oldest golf tournament, and golf's first major is The Open Championship, played both in England and Scotland. The biennial golf competition, the Ryder Cup, is named after English businessman Samuel Ryder who sponsored the event and donated the trophy. Nick Faldo is the most successful Ryder Cup player ever, having won the most points (25) of any player on either the European or US teams.
 Tennis was created in Birmingham in the late 19th century, and The Championships, Wimbledon, the Wimbledon Championships is the oldest tennis tournament in the world, and widely considered the most prestigious. Wimbledon is a tournament that has a major place in the British cultural calendar. Fred Perry was the last Englishman to win Wimbledon in 1936. He was the first player to win all four Grand Slam in tennis, Grand Slam singles titles and helped lead the Great Britain Davis Cup team, Great Britain team to four Davis Cup wins. English women who have won Wimbledon include: Ann Haydon Jones in 1969 and Virginia Wade in 1977.
In boxing, under the Marquess of Queensberry Rules, England has produced many world champions across the weight divisions internationally recognised by the governing bodies. World champions include Bob Fitzsimmons, Ted "Kid" Lewis, Randolph Turpin, Nigel Benn, Chris Eubank, Frank Bruno, Lennox Lewis, Ricky Hatton, Naseem Hamed, Amir Khan (British boxer), Amir Khan, Carl Froch, and David Haye. In women's boxing, Nicola Adams became the world's first woman to win an Olympic boxing gold medal at the 2012 Summer Olympics.
Originating in 17th and 18th-century England, the thoroughbred is a horse breed best known for its use in horse racing. The National Hunt horse race the Grand National, is held annually at Aintree Racecourse in early April. It is the most watched horse race in the UK, attracting casual observers, and three-time winner Red Rum is the most successful racehorse in the event's history. Red Rum is also the best-known racehorse in the country.
Tennis was created in Birmingham in the late 19th century, and The Championships, Wimbledon, the Wimbledon Championships is the oldest tennis tournament in the world, and widely considered the most prestigious. Wimbledon is a tournament that has a major place in the British cultural calendar. Fred Perry was the last Englishman to win Wimbledon in 1936. He was the first player to win all four Grand Slam in tennis, Grand Slam singles titles and helped lead the Great Britain Davis Cup team, Great Britain team to four Davis Cup wins. English women who have won Wimbledon include: Ann Haydon Jones in 1969 and Virginia Wade in 1977.
In boxing, under the Marquess of Queensberry Rules, England has produced many world champions across the weight divisions internationally recognised by the governing bodies. World champions include Bob Fitzsimmons, Ted "Kid" Lewis, Randolph Turpin, Nigel Benn, Chris Eubank, Frank Bruno, Lennox Lewis, Ricky Hatton, Naseem Hamed, Amir Khan (British boxer), Amir Khan, Carl Froch, and David Haye. In women's boxing, Nicola Adams became the world's first woman to win an Olympic boxing gold medal at the 2012 Summer Olympics.
Originating in 17th and 18th-century England, the thoroughbred is a horse breed best known for its use in horse racing. The National Hunt horse race the Grand National, is held annually at Aintree Racecourse in early April. It is the most watched horse race in the UK, attracting casual observers, and three-time winner Red Rum is the most successful racehorse in the event's history. Red Rum is also the best-known racehorse in the country.
 The 1950 British Grand Prix at Silverstone Circuit, Silverstone was the first race in the newly created Formula One World Championship. Since then, England has produced some of the greatest drivers in the sport, including; John Surtees, Stirling Moss, Graham Hill (only driver to have won the Triple Crown of Motorsport, Triple Crown), Nigel Mansell (only man to hold F1 and IndyCar titles at the same time), Damon Hill, Lewis Hamilton and Jenson Button. It has manufactured some of the most technically advanced racing cars, and many of today's racing companies choose England as their base of operations for its engineering knowledge and organisation. McLaren Automotive, Williams F1, Team Lotus, Honda, Brawn GP, Benetton Formula, Benetton, Renault, and Red Bull Racing are all, or have been, located in the south of England. England also has a rich heritage in Grand Prix motorcycle racing, the premier championship of motorcycle road racing, and produced several World Champions across all the various class of motorcycle: Mike Hailwood, John Surtees, Phil Read, Geoff Duke, and Barry Sheene.
The 1950 British Grand Prix at Silverstone Circuit, Silverstone was the first race in the newly created Formula One World Championship. Since then, England has produced some of the greatest drivers in the sport, including; John Surtees, Stirling Moss, Graham Hill (only driver to have won the Triple Crown of Motorsport, Triple Crown), Nigel Mansell (only man to hold F1 and IndyCar titles at the same time), Damon Hill, Lewis Hamilton and Jenson Button. It has manufactured some of the most technically advanced racing cars, and many of today's racing companies choose England as their base of operations for its engineering knowledge and organisation. McLaren Automotive, Williams F1, Team Lotus, Honda, Brawn GP, Benetton Formula, Benetton, Renault, and Red Bull Racing are all, or have been, located in the south of England. England also has a rich heritage in Grand Prix motorcycle racing, the premier championship of motorcycle road racing, and produced several World Champions across all the various class of motorcycle: Mike Hailwood, John Surtees, Phil Read, Geoff Duke, and Barry Sheene.
 Darts is a widely popular sport in England; a professional competitive sport, darts is a traditional pub game. The sport is governed by the World Darts Federation, one of its member organisations is the British Darts Organisation (BDO), which annually stages the BDO World Darts Championship, the other being the Professional Darts Corporation (PDC), which runs its own world championship at Alexandra Palace in London. Phil Taylor (darts player), Phil Taylor is widely regarded as the best darts player of all time, having won 187 professional tournaments, and a record 16 World Professional Darts Championship, World Championships. Trina Gulliver is the ten-time Women's World Professional Darts Champion of the British Darts Organisation. Another popular sport commonly associated with pub games is Snooker, and England has produced several world champions, including Steve Davis and Ronnie O'Sullivan.
The English are keen sailors and enjoy competitive sailing; founding and winning some of the world's most famous and respected international competitive tournaments across the various race formats, including the match race, a regatta, and the America's Cup. England has produced some of the world's greatest sailors, including Francis Chichester, Herbert Hasler, John Ridgway (sailor), John Ridgway, Robin Knox-Johnston, Ellen MacArthur, Mike Golding, Paul Goodison, and the most successful Olympic sailor ever Ben Ainslie.
Darts is a widely popular sport in England; a professional competitive sport, darts is a traditional pub game. The sport is governed by the World Darts Federation, one of its member organisations is the British Darts Organisation (BDO), which annually stages the BDO World Darts Championship, the other being the Professional Darts Corporation (PDC), which runs its own world championship at Alexandra Palace in London. Phil Taylor (darts player), Phil Taylor is widely regarded as the best darts player of all time, having won 187 professional tournaments, and a record 16 World Professional Darts Championship, World Championships. Trina Gulliver is the ten-time Women's World Professional Darts Champion of the British Darts Organisation. Another popular sport commonly associated with pub games is Snooker, and England has produced several world champions, including Steve Davis and Ronnie O'Sullivan.
The English are keen sailors and enjoy competitive sailing; founding and winning some of the world's most famous and respected international competitive tournaments across the various race formats, including the match race, a regatta, and the America's Cup. England has produced some of the world's greatest sailors, including Francis Chichester, Herbert Hasler, John Ridgway (sailor), John Ridgway, Robin Knox-Johnston, Ellen MacArthur, Mike Golding, Paul Goodison, and the most successful Olympic sailor ever Ben Ainslie.
National symbols
Wars of the Roses
The Wars of the Roses (1455ã1487), known at the time and for more than a century after as the Civil Wars, were a series of civil wars fought over control of the English throne in the mid-to-late fifteenth century. These wars were fought bet ...
as a symbol of peace. It is a syncreticism, syncretic symbol in that it merged the white rose of the Yorkists
The House of York was a cadet branch of the English royal House of Plantagenet. Three of its members became kings of England in the late 15th century. The House of York descended in the male line from Edmund of Langley, 1st Duke of York, t ...
and the red rose of the Lancastriansãcadet branches of the House of Plantagenet, Plantagenets who went to war over control of the nation. It is also known as the ''Rose of England''. The oak tree is a symbol of England, representing strength and endurance. The Royal Oak symbol and Oak Apple Day commemorate the escape of King Charles II of England, Charles II from the grasp of the parliamentarians after his father's execution: he hid in an oak tree to avoid detection before safely reaching exile.
The Royal Arms of England, a national coat of arms featuring three lions, originated with its adoption by Richard the Lionheart in 1198. It is blazoned as ''gules, three lions passant guardant or'' and it provides one of the most prominent symbols of England; it is similar to the traditional arms of Normandy. England does not have an official designated national anthem, as the United Kingdom as a whole has ''God Save the King''. However, the following are often considered unofficial National anthem of England, English national anthems:
''Jerusalem (hymn), Jerusalem'', ''Land of Hope and Glory'' (used for England during the 2002 Commonwealth Games), and ''I Vow to Thee, My Country''. England's National Day is 23 April which is St George's Day in England, Saint George's Day: Saint George is the patron saint of England.
See also
* Outline of England * Outline of the United KingdomNotes
References
Bibliography
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *External links
English Heritage
nbsp;ã National body protecting English heritage
Natural England
nbsp;ã Wildlife and the natural world of England
VisitEngland
nbsp;ã English Tourist Board
BBC News ã England
nbsp;ã News items from BBC News relating to England
GOV.UK
nbsp;ã The Official Website of the British Government * {{Good article England, English-speaking countries and territories Great Britain Island countries United Kingdom by country Germanic countries and territories Christian states