endosphere on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
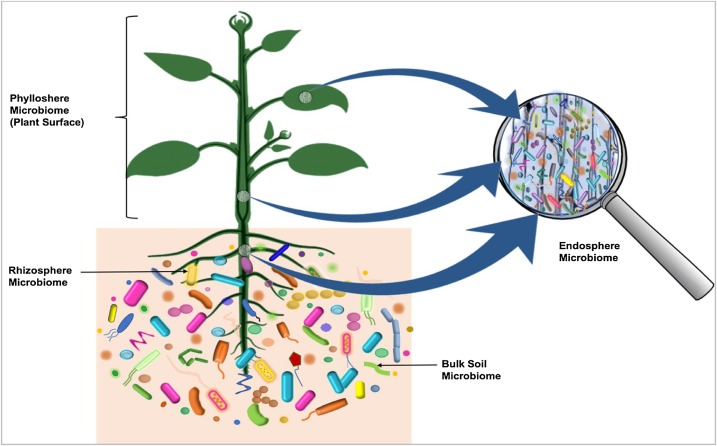 Some microorganisms, such as
Some microorganisms, such as
 Exposure to light can trigger photosynthesis in plant leaves, such as leafy-greens, and increase concentrations of photosynthetic products, such as glucose, within the leaf tissue. Bacteria existing at the leaf surfaces may respond to the available photosynthetic products and migrate into the leaf tissue by
Exposure to light can trigger photosynthesis in plant leaves, such as leafy-greens, and increase concentrations of photosynthetic products, such as glucose, within the leaf tissue. Bacteria existing at the leaf surfaces may respond to the available photosynthetic products and migrate into the leaf tissue by
 Some microorganisms, such as
Some microorganisms, such as endophyte
An endophyte is an endosymbiont, often a bacterium or fungus, that lives within a plant for at least part of its life cycle without causing apparent disease. Endophytes are ubiquitous and have been found in all species of plants studied to date; h ...
s, penetrate and occupy the plant internal tissues, forming the endospheric microbiome. The arbuscular mycorrhizal and other endophytic fungi
An endophyte is an endosymbiont, often a bacterium or fungus, that lives within a plant for at least part of its life cycle without causing apparent disease. Endophytes are ubiquitous and have been found in all species of plants studied to date; ...
are the dominant colonizers of the endosphere. Bacteria, and to some degree archaea
Archaea ( ; singular archaeon ) is a domain of single-celled organisms. These microorganisms lack cell nuclei and are therefore prokaryotes. Archaea were initially classified as bacteria, receiving the name archaebacteria (in the Archaebac ...
, are important members of endosphere communities. Some of these endophytic microbes interact with their host and provide obvious benefits to plants. Unlike the rhizosphere and the rhizoplane, the endospheres harbor highly specific microbial communities. The root endophytic community can be very distinct from that of the adjacent soil community. In general, diversity of the endophytic community is lower than the diversity of the microbial community outside the plant. The identity and diversity of the endophytic microbiome of above-and below-ground tissues may also differ within the plant.
Leaves and bacteria
 Exposure to light can trigger photosynthesis in plant leaves, such as leafy-greens, and increase concentrations of photosynthetic products, such as glucose, within the leaf tissue. Bacteria existing at the leaf surfaces may respond to the available photosynthetic products and migrate into the leaf tissue by
Exposure to light can trigger photosynthesis in plant leaves, such as leafy-greens, and increase concentrations of photosynthetic products, such as glucose, within the leaf tissue. Bacteria existing at the leaf surfaces may respond to the available photosynthetic products and migrate into the leaf tissue by chemotaxis
Chemotaxis (from '' chemo-'' + ''taxis'') is the movement of an organism or entity in response to a chemical stimulus. Somatic cells, bacteria, and other single-cell or multicellular organisms direct their movements according to certain chemica ...
toward nutrient concentration gradient
Molecular diffusion, often simply called diffusion, is the thermal motion of all (liquid or gas) particles at temperatures above absolute zero. The rate of this movement is a function of temperature, viscosity of the fluid and the size (mass) of ...
s. Once the bacteria are inside the leaf tissue, they cannot be washed away, presenting a risk to consumers. Several bacteria, such as ''Escherichia coli
''Escherichia coli'' (),Wells, J. C. (2000) Longman Pronunciation Dictionary. Harlow ngland Pearson Education Ltd. also known as ''E. coli'' (), is a Gram-negative, facultative anaerobic, rod-shaped, coliform bacterium of the genus ''Escher ...
'' and ''Salmonella enterica
''Salmonella enterica'' (formerly ''Salmonella choleraesuis'') is a rod-headed, flagellate, facultative anaerobic, Gram-negative bacterium and a species of the genus ''Salmonella''. A number of its serovars are serious human pathogens.
Epidemi ...
'', are able to attach the microstructure at the surface of plant leaves, such as trichome
Trichomes (); ) are fine outgrowths or appendages on plants, algae, lichens, and certain protists. They are of diverse structure and function. Examples are hairs, glandular hairs, scales, and papillae. A covering of any kind of hair on a pla ...
s, stomata
In botany, a stoma (from Greek ''στόμα'', "mouth", plural "stomata"), also called a stomate (plural "stomates"), is a pore found in the epidermis of leaves, stems, and other organs, that controls the rate of gas exchange. The pore is bor ...
and grooves, and localize at sites that are not accessible for wash water and sanitizers. The bacteria are also able to infiltrate into available openings at the leaf surface, such as stomata, cuts and wounds, to reach tens of micrometer depths below the leaf epidermis
The epidermis (from the Greek ''ἐπιδερμίς'', meaning "over-skin") is a single layer of cells that covers the leaves, flowers, roots and stems of plants. It forms a boundary between the plant and the external environment. The epidermis ...
. This infiltration can present a risk to human consumption of raw leafy greens.
Light is one of the driving forces that can promote infiltration of pathogenic bacteria into plant leaves. Incubation of S. enterica
''Salmonella enterica'' (formerly ''Salmonella choleraesuis'') is a Bacillus (shape), rod-headed, flagellate, Facultative anaerobic organism, facultative anaerobic, Gram-negative bacteria, Gram-negative bacterium and a species of the genus ''Salm ...
(serovar
A serotype or serovar is a distinct variation within a species of bacteria or virus or among immune cells of different individuals. These microorganisms, viruses, or cells are classified together based on their surface antigens, allowing the epi ...
''Typhimurium'') on iceberg lettuce
Lettuce (''Lactuca sativa'') is an annual plant of the family Asteraceae. It is most often grown as a leaf vegetable, but sometimes for its stem and seeds. Lettuce is most often used for salads, although it is also seen in other kinds of food, ...
leaves in the light led to association of bacteria near open stomata and infiltration into the leaf tissue. However, a dark condition caused a scattered attachment pattern at the leaf surface and a poor stomatal infiltration. Nutrients, such as glucose
Glucose is a simple sugar with the molecular formula . Glucose is overall the most abundant monosaccharide, a subcategory of carbohydrates. Glucose is mainly made by plants and most algae during photosynthesis from water and carbon dioxide, using ...
and sucrose
Sucrose, a disaccharide, is a sugar composed of glucose and fructose subunits. It is produced naturally in plants and is the main constituent of white sugar. It has the molecular formula .
For human consumption, sucrose is extracted and refined ...
, produced by photosynthetically active cells in the leaf tissue during light exposure are attractive for bacteria that may be initially present at the leaf surface. Opening of the stomata in light brings up an opportunity for bacteria to transport via chemotaxis toward the gradients of nutrients into the leaf interior. Many plants have evolved stomatal defense machinery to close the stomata upon perception of bacterial surface structures, known as microbe-associated molecular patterns
Pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) are small molecular motifs conserved within a class of microbes. They are recognized by toll-like receptors (TLRs) and other pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) in both plants and animals. A vast arra ...
(MAMPs). However, it is not always successful and some human pathogens were shown to penetrate the leaf interior through a process involved with chemotaxis and motility
Motility is the ability of an organism to move independently, using metabolic energy.
Definitions
Motility, the ability of an organism to move independently, using metabolic energy, can be contrasted with sessility, the state of organisms th ...
.
References
{{reflist Microbiomes Plants