Edward I on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Edward I (17/18 June 1239 – 7 July 1307), also known as Edward Longshanks and the Hammer of the Scots, was
 Edward was born at the
Edward was born at the
King of England
The monarchy of the United Kingdom, commonly referred to as the British monarchy, is the constitutional form of government by which a hereditary sovereign reigns as the head of state of the United Kingdom, the Crown Dependencies (the Bailiw ...
and Lord of Ireland
The Lordship of Ireland ( ga, Tiarnas na hÉireann), sometimes referred to retroactively as Norman Ireland, was the part of Ireland ruled by the King of England (styled as "Lord of Ireland") and controlled by loyal Anglo-Norman lords between ...
from 1272 to 1307. Concurrently, he ruled the duchies
A duchy, also called a dukedom, is a medieval country, territory, fief, or domain ruled by a duke or duchess, a ruler hierarchically second to the king or queen in Western European tradition.
There once existed an important difference between " ...
of Aquitaine
Aquitaine ( , , ; oc, Aquitània ; eu, Akitania; Poitevin-Saintongeais: ''Aguiéne''), archaic Guyenne or Guienne ( oc, Guiana), is a historical region of southwestern France and a former administrative region of the country. Since 1 January ...
and Gascony
Gascony (; french: Gascogne ; oc, Gasconha ; eu, Gaskoinia) was a province of the southwestern Kingdom of France that succeeded the Duchy of Gascony (602–1453). From the 17th century until the French Revolution (1789–1799), it was part o ...
as a vassal
A vassal or liege subject is a person regarded as having a mutual obligation to a lord or monarch, in the context of the feudal system in medieval Europe. While the subordinate party is called a vassal, the dominant party is called a suzerain. W ...
of the French king
France was ruled by monarchs from the establishment of the Kingdom of West Francia in 843 until the end of the Second French Empire in 1870, with several interruptions.
Classical French historiography usually regards Clovis I () as the firs ...
. Before his accession to the throne, he was commonly referred to as the Lord Edward. The eldest son of Henry III, Edward was involved from an early age in the political intrigues of his father's reign, which included a rebellion by the English baron
Baron is a rank of nobility or title of honour, often hereditary, in various European countries, either current or historical. The female equivalent is baroness. Typically, the title denotes an aristocrat who ranks higher than a lord or knig ...
s. In 1259, he briefly sided with a baronial reform movement, supporting the Provisions of Oxford
The Provisions of Oxford were constitutional reforms developed during the Oxford Parliament of 1258 to resolve a dispute between King Henry III of England and his barons. The reforms were designed to ensure the king adhered to the rule of law and ...
. After reconciliation with his father, however, he remained loyal throughout the subsequent armed conflict, known as the Second Barons' War
The Second Barons' War (1264–1267) was a civil war in England between the forces of a number of barons led by Simon de Montfort against the royalist forces of King Henry III, led initially by the king himself and later by his son, the fu ...
. After the Battle of Lewes
The Battle of Lewes was one of two main battles of the conflict known as the Second Barons' War. It took place at Lewes in Sussex, on 14 May 1264. It marked the high point of the career of Simon de Montfort, 6th Earl of Leicester, and made h ...
, Edward was held hostage
A hostage is a person seized by an abductor in order to compel another party, one which places a high value on the liberty, well-being and safety of the person seized, such as a relative, employer, law enforcement or government to act, or ref ...
by the rebellious barons, but escaped after a few months and defeated the baronial leader Simon de Montfort
Simon de Montfort, 6th Earl of Leicester ( – 4 August 1265), later sometimes referred to as Simon V de Montfort to distinguish him from his namesake relatives, was a nobleman of French origin and a member of the English peerage, who led the ...
at the Battle of Evesham in 1265. Within two years the rebellion was extinguished and, with England pacified, Edward left to join the Ninth Crusade
Lord Edward's crusade, sometimes called the Ninth Crusade, was a military expedition to the Holy Land under the command of Edward, Duke of Gascony (future King Edward I of England) in 1271–1272. It was an extension of the Eighth Crusade and was ...
to the Holy Land
The Holy Land; Arabic: or is an area roughly located between the Mediterranean Sea and the Eastern Bank of the Jordan River, traditionally synonymous both with the biblical Land of Israel and with the region of Palestine. The term "Holy ...
in 1270. He was on his way home in 1272 when he was informed of his father's death. Making a slow return, he reached England in 1274 and was crowned at Westminster Abbey
Westminster Abbey, formally titled the Collegiate Church of Saint Peter at Westminster, is an historic, mainly Gothic church in the City of Westminster, London, England, just to the west of the Palace of Westminster. It is one of the United ...
.
Edward spent much of his reign reforming royal administration and common law
In law, common law (also known as judicial precedent, judge-made law, or case law) is the body of law created by judges and similar quasi-judicial tribunals by virtue of being stated in written opinions."The common law is not a brooding omnipresen ...
. Through an extensive legal inquiry, he investigated the tenure of various feudal
Feudalism, also known as the feudal system, was the combination of the legal, economic, military, cultural and political customs that flourished in Middle Ages, medieval Europe between the 9th and 15th centuries. Broadly defined, it was a wa ...
liberties, while the law was reformed through a series of statute
A statute is a formal written enactment of a legislative authority that governs the legal entities of a city, state, or country by way of consent. Typically, statutes command or prohibit something, or declare policy. Statutes are rules made by le ...
s regulating criminal
In ordinary language, a crime is an unlawful act punishable by a state or other authority. The term ''crime'' does not, in modern criminal law, have any simple and universally accepted definition,Farmer, Lindsay: "Crime, definitions of", in Can ...
and property law
Property law is the area of law that governs the various forms of ownership in real property (land) and personal property. Property refers to legally protected claims to resources, such as land and personal property, including intellectual pro ...
. However, Edward's attention was increasingly drawn toward military affairs. After suppressing a minor rebellion in Wales in 1276–77, Edward responded to a second rebellion in 1282–83 with a full-scale conquest. After a successful campaign, he subjected Wales to English rule, built a series of castles and towns in the countryside and settled them with English people
The English people are an ethnic group and nation native to England, who speak the English language in England, English language, a West Germanic languages, West Germanic language, and share a common history and culture. The English identi ...
. Next, his efforts were directed towards the Kingdom of Scotland
The Kingdom of Scotland (; , ) was a sovereign state in northwest Europe traditionally said to have been founded in 843. Its territories expanded and shrank, but it came to occupy the northern third of the island of Great Britain, sharing a la ...
. Initially invited to arbitrate a succession dispute, Edward claimed feudal suzerainty
Suzerainty () is the rights and obligations of a person, state or other polity who controls the foreign policy and relations of a tributary state, while allowing the tributary state to have internal autonomy. While the subordinate party is cal ...
over Scotland, with the ensuing war continuing after Edward's death. Simultaneously, Edward found himself at war with France (a Scottish ally) after King Philip IV confiscated the Duchy of Gascony, which until then had been held in personal union
A personal union is the combination of two or more states that have the same monarch while their boundaries, laws, and interests remain distinct. A real union, by contrast, would involve the constituent states being to some extent interlink ...
with the Kingdom of England
The Kingdom of England (, ) was a sovereign state on the island of Great Britain from 12 July 927, when it emerged from various Anglo-Saxon kingdoms, until 1 May 1707, when it united with Scotland to form the Kingdom of Great Britain.
On 1 ...
. Although Edward recovered his duchy, this conflict relieved English military pressure against Scotland. In the mid-1290s, extensive military campaigns required high levels of taxation, and Edward met with both lay
Lay may refer to:
Places
*Lay Range, a subrange of mountains in British Columbia, Canada
*Lay, Loire, a French commune
*Lay (river), France
*Lay, Iran, a village
*Lay, Kansas, United States, an unincorporated community
People
* Lay (surname)
* ...
and ecclesiastical opposition. When the King died in 1307, he left to his son Edward II
Edward II (25 April 1284 – 21 September 1327), also called Edward of Caernarfon, was King of England and Lord of Ireland from 1307 until he was deposed in January 1327. The fourth son of Edward I, Edward became the heir apparent to th ...
an ongoing war with Scotland, along with other financial and political problems that had been left unanswered during his reign.
Edward's temperamental nature and height made him an intimidating man, and he often instilled fear in his contemporaries. Nevertheless, he held the respect of his subjects for the way he embodied the medieval ideal of kingship, as a soldier, an administrator, and a man of faith. Modern historians are divided on their assessment of Edward: while some have praised him for his contribution to the law and administration, others have criticised him for his uncompromising attitude towards his nobility. Edward I is credited with many accomplishments during his reign, including restoring royal authority after the reign of Henry III, establishing Parliament
In modern politics, and history, a parliament is a legislative body of government. Generally, a modern parliament has three functions: Representation (politics), representing the Election#Suffrage, electorate, making laws, and overseeing ...
as a permanent institution and thereby also a functional system for raising taxes, and reforming the law through statutes. At the same time, he is also often condemned for his wars against Scotland and for expelling the Jews from his kingdom in 1290.
Early years, 1239–1263
Childhood and marriage
 Edward was born at the
Edward was born at the Palace of Westminster
The Palace of Westminster serves as the meeting place for both the House of Commons of the United Kingdom, House of Commons and the House of Lords, the two houses of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. Informally known as the Houses of Parli ...
on the night of 17–18 June 1239, to King Henry III and Eleanor of Provence
Eleanor of Provence (c. 1223 – 24/25 June 1291) was a French noblewoman who became Queen of England as the wife of King Henry III from 1236 until his death in 1272. She served as regent of England during the absence of her spouse in 1253.
...
.
''Edward
Edward is an English given name. It is derived from the Anglo-Saxon name ''Ēadweard'', composed of the elements '' ēad'' "wealth, fortune; prosperous" and '' weard'' "guardian, protector”.
History
The name Edward was very popular in Anglo-Sa ...
'', an Anglo-Saxon name
Germanic given names are traditionally dithematic; that is, they are formed from two elements, by joining a prefix and a suffix. For example, King Æþelred's name was derived from ', for "noble", and ', for "counsel".
However, there are al ...
, was not commonly given among the aristocracy of England after the Norman conquest
The Norman Conquest (or the Conquest) was the 11th-century invasion and occupation of England by an army made up of thousands of Norman, Breton, Flemish, and French troops, all led by the Duke of Normandy, later styled William the Conque ...
, but Henry was devoted to the veneration of Edward the Confessor
Edward the Confessor ; la, Eduardus Confessor , ; ( 1003 – 5 January 1066) was one of the last Anglo-Saxon English kings. Usually considered the last king of the House of Wessex, he ruled from 1042 to 1066.
Edward was the son of Æth ...
, and decided to name his firstborn son after the saint. Edward's birth was widely celebrated at the royal court and throughout England, and he was baptised
Baptism (from grc-x-koine, βάπτισμα, váptisma) is a form of ritual purification—a characteristic of many religions throughout time and geography. In Christianity, it is a Christian sacrament of initiation and adoption, almost inv ...
three days later at Westminster Abbey
Westminster Abbey, formally titled the Collegiate Church of Saint Peter at Westminster, is an historic, mainly Gothic church in the City of Westminster, London, England, just to the west of the Palace of Westminster. It is one of the United ...
. Until his accession to the throne in 1272, Edward was commonly referred to as the Lord Edward. Among his childhood friends was his cousin Henry of Almain
Henry of Almain (Anglo-Norman: ''Henri d'Almayne''; 2 November 1235 – 13 March 1271), also called Henry of Cornwall, was the eldest son of Richard, Earl of Cornwall, afterwards King of the Romans, by his first wife Isabel Marshal. His surname i ...
, son of King Henry's brother Richard of Cornwall
Richard (5 January 1209 – 2 April 1272) was an English prince who was King of the Romans from 1257 until his death in 1272. He was the second son of John, King of England, and Isabella, Countess of Angoulême. Richard was nominal Count of P ...
. Henry of Almain remained a close companion of the prince, both through the civil war that followed, and later during the crusade. Edward was placed in the care of Hugh Giffard – father of the future Chancellor
Chancellor ( la, cancellarius) is a title of various official positions in the governments of many nations. The original chancellors were the of Roman courts of justice—ushers, who sat at the or lattice work screens of a basilica or law cou ...
Godfrey Giffard
Godfrey Giffard ( 12351302) was Chancellor of the Exchequer of England, Lord Chancellor of England and Bishop of Worcester.
Early life
Giffard was a son of Hugh Giffard of Boyton in Wiltshire, Nonetheless, he grew up to become an strong, athletic, and imposing man. At he towered over most of his contemporaries, hence his
 Edward remained in captivity until March, and even after his release he was kept under strict surveillance. Then, on 28 May, he managed to escape his custodians and joined up with
Edward remained in captivity until March, and even after his release he was kept under strict surveillance. Then, on 28 May, he managed to escape his custodians and joined up with
 Edward took the crusader's cross in an elaborate ceremony on 24 June 1268, with his brother
Edward took the crusader's cross in an elaborate ceremony on 24 June 1268, with his brother  By then, the situation in the
By then, the situation in the
 Llywelyn ap Gruffudd enjoyed an advantageous situation in the aftermath of the Barons' War. Through the 1267
Llywelyn ap Gruffudd enjoyed an advantageous situation in the aftermath of the Barons' War. Through the 1267
 By the 1284 Statute of Rhuddlan, the Principality of Wales was incorporated into England and was given an administrative system like the English, with counties policed by sheriffs. English law was introduced in criminal cases, though the Welsh were allowed to maintain their own customary laws in some cases of property disputes. After 1277, and increasingly after 1283, Edward embarked on a full-scale project of English settlement of Wales, creating new towns like Flint, Flintshire, Flint, Aberystwyth and Rhuddlan. Their new residents were English migrants, with the local Welsh banned from living inside them, and many were protected by extensive walls.
An extensive project of castle-building was also initiated, under the direction of James of Saint George, a prestigious architect whom Edward had met in Savoy on his return from the crusade. These included the Beaumaris Castle, Beaumaris, Caernarfon Castle, Caernarfon, Conwy Castle, Conwy and Harlech Castle, Harlech castles, intended to act both as fortresses and royal palaces for the King. His programme of castle building in Wales heralded the introduction of the widespread use of arrowslits in castle walls across Europe, drawing on Eastern influences. Also a product of the Crusades was the introduction of the concentric castle, and four of the eight castles Edward founded in Wales followed this design. The castles made a clear, imperial statement about Edward's intentions to rule North Wales permanently, and drew on imagery associated with the Byzantine Empire and King Arthur in an attempt to build legitimacy for his new regime.
In 1284, King Edward had his son Edward (later
By the 1284 Statute of Rhuddlan, the Principality of Wales was incorporated into England and was given an administrative system like the English, with counties policed by sheriffs. English law was introduced in criminal cases, though the Welsh were allowed to maintain their own customary laws in some cases of property disputes. After 1277, and increasingly after 1283, Edward embarked on a full-scale project of English settlement of Wales, creating new towns like Flint, Flintshire, Flint, Aberystwyth and Rhuddlan. Their new residents were English migrants, with the local Welsh banned from living inside them, and many were protected by extensive walls.
An extensive project of castle-building was also initiated, under the direction of James of Saint George, a prestigious architect whom Edward had met in Savoy on his return from the crusade. These included the Beaumaris Castle, Beaumaris, Caernarfon Castle, Caernarfon, Conwy Castle, Conwy and Harlech Castle, Harlech castles, intended to act both as fortresses and royal palaces for the King. His programme of castle building in Wales heralded the introduction of the widespread use of arrowslits in castle walls across Europe, drawing on Eastern influences. Also a product of the Crusades was the introduction of the concentric castle, and four of the eight castles Edward founded in Wales followed this design. The castles made a clear, imperial statement about Edward's intentions to rule North Wales permanently, and drew on imagery associated with the Byzantine Empire and King Arthur in an attempt to build legitimacy for his new regime.
In 1284, King Edward had his son Edward (later
 Edward never again went on crusade after his return to England in 1274, but he maintained an intention to do so, and took the cross again in 1287. This intention guided much of his foreign policy, until at least 1291. To stage a European-wide crusade, it was essential to prevent conflict between the sovereigns on the continent. A major obstacle to this was represented by the conflict between the French Capetian House of Anjou ruling southern Italy and the Kingdom of Aragon in Spain. In 1282, the citizens of Palermo rose up against Charles of Anjou and turned for help to Peter III of Aragon, in what has become known as the Sicilian Vespers. In War of the Sicilian Vespers, the war that followed, Charles of Anjou's son, Charles of Salerno, was taken prisoner by the Aragonese. The French began planning an attack on Aragon, raising the prospect of a large-scale European war. To Edward, it was imperative that such a war be avoided, and in Paris in 1286 he brokered a truce between France and Aragon that helped secure Charles' release. As far as the crusades were concerned, however, Edward's efforts proved ineffective. A devastating blow to his plans came in 1291, when the Mamluks Siege of Acre (1291), captured Acre, the last Christian stronghold in the Holy Land.
Edward had long been deeply involved in the affairs of his own Duchy of Gascony. In 1278 he assigned an investigating commission to his trusted associates Otto de Grandson and the chancellor
Edward never again went on crusade after his return to England in 1274, but he maintained an intention to do so, and took the cross again in 1287. This intention guided much of his foreign policy, until at least 1291. To stage a European-wide crusade, it was essential to prevent conflict between the sovereigns on the continent. A major obstacle to this was represented by the conflict between the French Capetian House of Anjou ruling southern Italy and the Kingdom of Aragon in Spain. In 1282, the citizens of Palermo rose up against Charles of Anjou and turned for help to Peter III of Aragon, in what has become known as the Sicilian Vespers. In War of the Sicilian Vespers, the war that followed, Charles of Anjou's son, Charles of Salerno, was taken prisoner by the Aragonese. The French began planning an attack on Aragon, raising the prospect of a large-scale European war. To Edward, it was imperative that such a war be avoided, and in Paris in 1286 he brokered a truce between France and Aragon that helped secure Charles' release. As far as the crusades were concerned, however, Edward's efforts proved ineffective. A devastating blow to his plans came in 1291, when the Mamluks Siege of Acre (1291), captured Acre, the last Christian stronghold in the Holy Land.
Edward had long been deeply involved in the affairs of his own Duchy of Gascony. In 1278 he assigned an investigating commission to his trusted associates Otto de Grandson and the chancellor
 The relationship between England and Scotland by the 1280s was one of relatively harmonious coexistence. The issue of homage did not reach the same level of controversy as it did in Wales; in 1278 King Alexander III of Scotland paid homage to Edward I, who was his brother-in-law, but apparently only for the lands he held of Edward in England. Problems arose only with the Scottish succession crisis of the early 1290s. When Alexander died in 1286, he left as heir to the Scottish throne Margaret, Maid of Norway, Margaret, his three-year-old granddaughter and sole surviving descendant. By the Treaty of Birgham, it was agreed that Margaret should marry King Edward's six-year-old son Edward of Carnarvon, though Scotland would remain free of English overlordship. Margaret, by now seven years of age, sailed from Norway for Scotland in the autumn of 1290, but fell ill on the way and died in Orkney. This left the country without an obvious heir, and led to the succession dispute known to history as the Great Cause.
Even though as many as fourteen claimants put forward their claims to the title, the foremost competitors John Balliol and Robert de Brus, 5th Lord of Annandale. The Scottish
The relationship between England and Scotland by the 1280s was one of relatively harmonious coexistence. The issue of homage did not reach the same level of controversy as it did in Wales; in 1278 King Alexander III of Scotland paid homage to Edward I, who was his brother-in-law, but apparently only for the lands he held of Edward in England. Problems arose only with the Scottish succession crisis of the early 1290s. When Alexander died in 1286, he left as heir to the Scottish throne Margaret, Maid of Norway, Margaret, his three-year-old granddaughter and sole surviving descendant. By the Treaty of Birgham, it was agreed that Margaret should marry King Edward's six-year-old son Edward of Carnarvon, though Scotland would remain free of English overlordship. Margaret, by now seven years of age, sailed from Norway for Scotland in the autumn of 1290, but fell ill on the way and died in Orkney. This left the country without an obvious heir, and led to the succession dispute known to history as the Great Cause.
Even though as many as fourteen claimants put forward their claims to the title, the foremost competitors John Balliol and Robert de Brus, 5th Lord of Annandale. The Scottish
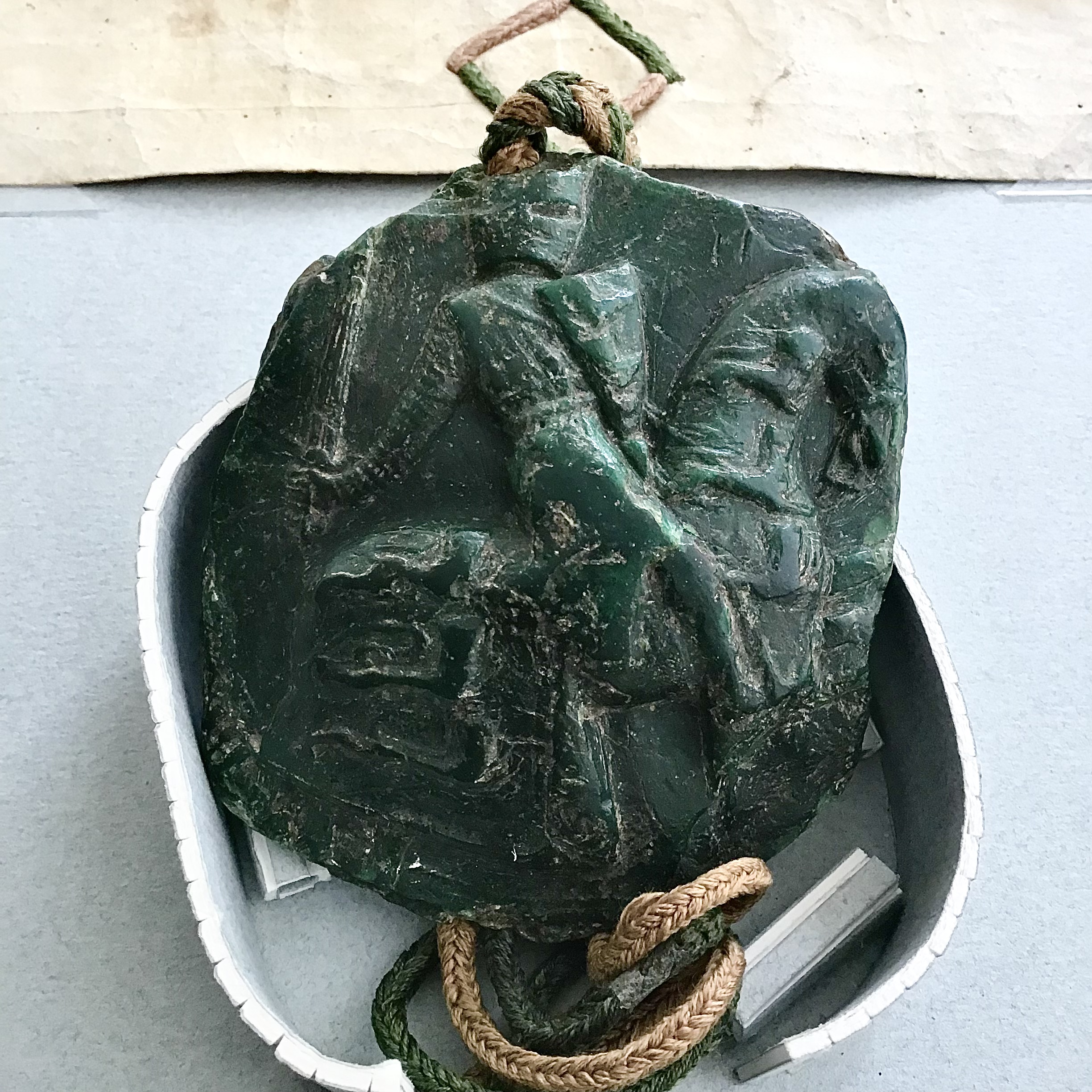 Edward had a reputation for a fierce and sometimes unpredictable temper, and he could be intimidating; one story tells of how the Dean of St Paul's, wishing to confront Edward over the high level of taxation in 1295, fell down and died once he was in the King's presence. When Edward of Caernarfon demanded an earldom for his favourite Piers Gaveston, 1st Earl of Cornwall, Piers Gaveston, the King erupted in anger and supposedly tore out handfuls of his son's hair. Some of his contemporaries considered Edward frightening, particularly in his early days. The ''Song of Lewes'' in 1264 described him as a leopard, an animal regarded as particularly powerful and unpredictable. At times, however, Edward exhibited a gentler disposition, and was known to be devoted to his large family. He was close with his surviving daughters, and frequently lavished them with expensive gifts whenever they visited court.
Despite his more unflattering character traits, Edward's contemporaries considered him an able, even an ideal, king. Though not loved by his subjects, he was feared and respected, as reflected in the fact that there were no armed rebellions in England during his reign. Edward met contemporary expectations of kingship in his role as an able, determined soldier and in his embodiment of shared chivalric ideals. In religious observance he also fulfilled the expectations of his age: he attended chapel regularly, gave alms generously, and showed a fervent devotion to the Virgin Mary and Saint Thomas Becket. Like his father, Edward was a keen participant in the tradition of the royal touch, which had the supposed effect of curing those who were touched from scrofula. Contemporary records suggest that the King touched upwards of a thousand people each year. Despite his personal piety, Edward was frequently in conflict with the Archbishops of Canterbury that served during his reign, with one 14th-century chronicler attributing the death of Thomas of Corbridge to the King's harsh conduct towards him. Relations with the Papacy were at times no better: in 1297, Edward deliberately disobeyed the papal bull ''Clericis laicos'', which generally forbade ecclesiastical taxation. However, improved relations with Rome later on allowed Edward to collect considerable sums by taxing the English clergy.
Edward took a keen interest in the stories of King Arthur, which were highly popular in Europe during his reign. In 1278 he visited Glastonbury Abbey to open what was then believed to be the tomb of Arthur and Guinevere, recovering "Arthur's crown" from Llywelyn after the conquest of North Wales, while, as noted above, his new castles drew upon the Arthurian myths in their design and location. He held "Round Table" events in 1284 and 1302, involving tournaments and feasting, and chroniclers compared him and the events at his court to Arthur. In some cases Edward appears to have used his interest in the Arthurian myths to serve his own political interests, including legitimising his rule in Wales and discrediting the King Arthur's messianic return, Welsh belief that Arthur might return as their political saviour.
Edward had a reputation for a fierce and sometimes unpredictable temper, and he could be intimidating; one story tells of how the Dean of St Paul's, wishing to confront Edward over the high level of taxation in 1295, fell down and died once he was in the King's presence. When Edward of Caernarfon demanded an earldom for his favourite Piers Gaveston, 1st Earl of Cornwall, Piers Gaveston, the King erupted in anger and supposedly tore out handfuls of his son's hair. Some of his contemporaries considered Edward frightening, particularly in his early days. The ''Song of Lewes'' in 1264 described him as a leopard, an animal regarded as particularly powerful and unpredictable. At times, however, Edward exhibited a gentler disposition, and was known to be devoted to his large family. He was close with his surviving daughters, and frequently lavished them with expensive gifts whenever they visited court.
Despite his more unflattering character traits, Edward's contemporaries considered him an able, even an ideal, king. Though not loved by his subjects, he was feared and respected, as reflected in the fact that there were no armed rebellions in England during his reign. Edward met contemporary expectations of kingship in his role as an able, determined soldier and in his embodiment of shared chivalric ideals. In religious observance he also fulfilled the expectations of his age: he attended chapel regularly, gave alms generously, and showed a fervent devotion to the Virgin Mary and Saint Thomas Becket. Like his father, Edward was a keen participant in the tradition of the royal touch, which had the supposed effect of curing those who were touched from scrofula. Contemporary records suggest that the King touched upwards of a thousand people each year. Despite his personal piety, Edward was frequently in conflict with the Archbishops of Canterbury that served during his reign, with one 14th-century chronicler attributing the death of Thomas of Corbridge to the King's harsh conduct towards him. Relations with the Papacy were at times no better: in 1297, Edward deliberately disobeyed the papal bull ''Clericis laicos'', which generally forbade ecclesiastical taxation. However, improved relations with Rome later on allowed Edward to collect considerable sums by taxing the English clergy.
Edward took a keen interest in the stories of King Arthur, which were highly popular in Europe during his reign. In 1278 he visited Glastonbury Abbey to open what was then believed to be the tomb of Arthur and Guinevere, recovering "Arthur's crown" from Llywelyn after the conquest of North Wales, while, as noted above, his new castles drew upon the Arthurian myths in their design and location. He held "Round Table" events in 1284 and 1302, involving tournaments and feasting, and chroniclers compared him and the events at his court to Arthur. In some cases Edward appears to have used his interest in the Arthurian myths to serve his own political interests, including legitimising his rule in Wales and discrediting the King Arthur's messianic return, Welsh belief that Arthur might return as their political saviour.
 Soon after assuming the throne, Edward set about restoring order and re-establishing royal authority after the disastrous reign of his father. To accomplish this, he immediately ordered an extensive change of administrative personnel. The most important of these was the appointment of Robert Burnell as Lord Chancellor, chancellor, a man who would remain in the post until 1292 as one of the King's closest associates. Edward then replaced most local officials, such as the escheators and High sheriff, sheriffs. This last measure was done in preparation for an extensive inquest covering all of England, that would hear complaints about abuse of power by royal officers. The inquest produced the set of so-called Hundred Rolls, from the administrative subdivision of the Hundred (county division), hundred. The second purpose of the inquest was to establish what land and rights The Crown#Concept, the Crown had lost during the reign of Henry III.
The Hundred Rolls, which have been likened to the 11th-century Domesday Book, formed the basis for the later legal inquiries called the ''Quo warranto'' proceedings. The purpose of these inquiries was to establish by what warrant ( la, Quo warranto) various Liberty (division), liberties were held. If the defendant could not produce a royal licence to prove the grant of the liberty, then it was the Crown's opinionbased on the writings of the influential thirteenth-century legal scholar Henry de Bractonthat the liberty should revert to the king. Both the Statute of Westminster 1275 and Statute of Westminster 1285 codified the existing law in England. By enacting the Statute of Gloucester in 1278 the King challenged baronial rights through a revival of the system of general eyre (legal term), eyres (royal justices to go on tour throughout the land) and through a significant increase in the number of pleas of quo warranto to be heard by such eyres.
This caused great consternation among the aristocracy, who insisted that long use in itself constituted licence. A compromise was eventually reached in 1290, whereby a liberty was considered legitimate as long as it could be shown to have been exercised since the coronation of Richard the Lionheart in 1189. Royal gains from the ''Quo warranto'' proceedings were insignificant; few liberties were returned to the King. Edward had nevertheless won a significant victory, in clearly establishing the principle that all liberties essentially emanated from the Crown.
The 1290 statute of ''Quo warranto'' was only one part of a wider legislative effort, which was one of the most important contributions of Edward's reign. This era of legislative action had started already at the time of the baronial reform movement; the Statute of Marlborough (1267) contained elements both of the
Soon after assuming the throne, Edward set about restoring order and re-establishing royal authority after the disastrous reign of his father. To accomplish this, he immediately ordered an extensive change of administrative personnel. The most important of these was the appointment of Robert Burnell as Lord Chancellor, chancellor, a man who would remain in the post until 1292 as one of the King's closest associates. Edward then replaced most local officials, such as the escheators and High sheriff, sheriffs. This last measure was done in preparation for an extensive inquest covering all of England, that would hear complaints about abuse of power by royal officers. The inquest produced the set of so-called Hundred Rolls, from the administrative subdivision of the Hundred (county division), hundred. The second purpose of the inquest was to establish what land and rights The Crown#Concept, the Crown had lost during the reign of Henry III.
The Hundred Rolls, which have been likened to the 11th-century Domesday Book, formed the basis for the later legal inquiries called the ''Quo warranto'' proceedings. The purpose of these inquiries was to establish by what warrant ( la, Quo warranto) various Liberty (division), liberties were held. If the defendant could not produce a royal licence to prove the grant of the liberty, then it was the Crown's opinionbased on the writings of the influential thirteenth-century legal scholar Henry de Bractonthat the liberty should revert to the king. Both the Statute of Westminster 1275 and Statute of Westminster 1285 codified the existing law in England. By enacting the Statute of Gloucester in 1278 the King challenged baronial rights through a revival of the system of general eyre (legal term), eyres (royal justices to go on tour throughout the land) and through a significant increase in the number of pleas of quo warranto to be heard by such eyres.
This caused great consternation among the aristocracy, who insisted that long use in itself constituted licence. A compromise was eventually reached in 1290, whereby a liberty was considered legitimate as long as it could be shown to have been exercised since the coronation of Richard the Lionheart in 1189. Royal gains from the ''Quo warranto'' proceedings were insignificant; few liberties were returned to the King. Edward had nevertheless won a significant victory, in clearly establishing the principle that all liberties essentially emanated from the Crown.
The 1290 statute of ''Quo warranto'' was only one part of a wider legislative effort, which was one of the most important contributions of Edward's reign. This era of legislative action had started already at the time of the baronial reform movement; the Statute of Marlborough (1267) contained elements both of the
 Edward's reign saw an overhaul of the coinage system, which was in a poor state by 1279. Compared to the coinage already circulating at the time of Edward's accession, the new coins issued proved to be of superior quality. In addition to minting History of the English penny (1154–1485), pennies, History of the halfpenny, halfpences, and Farthing (English coin), farthings, a new denomination called the Groat (coin), groat (which proved to be unsucessful) was introduced. The coinmaking process itself was also improved. William Turnemire introduced a novel method of minting coins that involved cutting blank coins from a silver rod, in contrast with the old practice of stamping them out from sheets; this technique proved to be efficient. The practice of minting coins with the moneyer's name on it became obsolete under Edward's rule because England's mint administration became far more centralized under the Crown's authority. During this time, English coins were frequently counterfeited in foreign places, especially the Low Countries, and despite a ban in 1283, English coinage was secretly exported to the European continent. In August 1280, Edward forbade the usage of the old Long cross penny, long cross coinage, which forced the populace to switch to the newly-minted versions. Records do not indicate any adverse consequences that resulted from Edward's monetary reforms; on the contrary, the coinage overhaul successfully provided England with a stable currency.
Edward's reign saw an overhaul of the coinage system, which was in a poor state by 1279. Compared to the coinage already circulating at the time of Edward's accession, the new coins issued proved to be of superior quality. In addition to minting History of the English penny (1154–1485), pennies, History of the halfpenny, halfpences, and Farthing (English coin), farthings, a new denomination called the Groat (coin), groat (which proved to be unsucessful) was introduced. The coinmaking process itself was also improved. William Turnemire introduced a novel method of minting coins that involved cutting blank coins from a silver rod, in contrast with the old practice of stamping them out from sheets; this technique proved to be efficient. The practice of minting coins with the moneyer's name on it became obsolete under Edward's rule because England's mint administration became far more centralized under the Crown's authority. During this time, English coins were frequently counterfeited in foreign places, especially the Low Countries, and despite a ban in 1283, English coinage was secretly exported to the European continent. In August 1280, Edward forbade the usage of the old Long cross penny, long cross coinage, which forced the populace to switch to the newly-minted versions. Records do not indicate any adverse consequences that resulted from Edward's monetary reforms; on the contrary, the coinage overhaul successfully provided England with a stable currency.
 However, Edward I's frequent military campaigns put a great financial strain on the nation. There were several ways through which the King could raise money for war, including customs Duty (economics), duties, money lending and History of the English fiscal system#Direct taxation, lay subsidies. In 1275, Edward I negotiated an agreement with the domestic merchant community that secured a permanent duty on wool, England's primary export. In 1303, a similar agreement was reached with foreign merchants, in return for certain rights and privileges. The revenues from the customs duty were handled by the House of Simonetti#Simonetti of Lucca, Riccardi, a group of bankers from Lucca in Italy. This was in return for their service as money lenders to the crown, which helped finance the Welsh Wars. When the war with France broke out, the French king confiscated the Riccardi's assets, and the bank went bankrupt. After this, the Frescobaldi of Florence took over the role as money lenders to the English crown.
Another source of crown income was represented by the English Jews. The Jews were the King's personal property, and he was free to tax them at will. By 1280, the Jews had been exploited to a level at which they were no longer of much financial use to the crown, but they could still be used in political bargaining. Their loan with interest businessa practice forbidden to Christianshad made many people indebted to them and caused general popular resentment. In 1275, Edward had issued the Statute of the Jewry, which outlawed loan with interest and encouraged the Jews to take up other professions; in 1279, in the context of a crack-down on Methods of coin debasement, coin-clippers, he arrested all the heads of Jewish households in England and had around 300 of them executed. In 1280, he ordered all Jews to attend special sermons, preached by Dominican friars, with the hope of persuading them to convert, but these exhortations were not followed. The final attack on the Jews in England came in the Edict of Expulsion in 1290, whereby Edward formally expelled all Jews from England. This not only generated revenues through royal appropriation of Jewish loans and property, but it also gave Edward the political capital to negotiate a substantial lay subsidy in the 1290 Parliament. The expulsion, which was Resettlement_of_the_Jews_in_England, reversed in the 1650s, followed a precedent set by other European rulers: Philip II of France had expelled all Jews from his own lands in 1182; John I, Duke of Brittany, drove them out of his duchy in 1239; and in the late 1240s Louis IX of France had expelled the Jews from the royal demesne before his first passage to the East.
Edward held Parliament on a reasonably regular basis throughout his reign. In 1295, however, a significant change occurred. For this Parliament, in addition to the secular and ecclesiastical lords, two knights from each county and two representatives from each borough were summoned. The representation of commons in Parliament was nothing new; what was new was the authority under which these representatives were summoned. Whereas previously the commons had been expected simply to assent to decisions already made by the magnates, it was now proclaimed that they should meet with the full authority (''plena potestas'') of their communities, to give assent to decisions made in Parliament. The King now had full backing for collecting lay subsidies – taxes collected at a certain fraction of the moveable property of all laymen – from the entire population. Whereas Henry III had only collected four of these in his reign, Edward I collected nine. This format eventually became the standard for later Parliaments, and historians have named the assembly the "Model Parliament".
However, Edward I's frequent military campaigns put a great financial strain on the nation. There were several ways through which the King could raise money for war, including customs Duty (economics), duties, money lending and History of the English fiscal system#Direct taxation, lay subsidies. In 1275, Edward I negotiated an agreement with the domestic merchant community that secured a permanent duty on wool, England's primary export. In 1303, a similar agreement was reached with foreign merchants, in return for certain rights and privileges. The revenues from the customs duty were handled by the House of Simonetti#Simonetti of Lucca, Riccardi, a group of bankers from Lucca in Italy. This was in return for their service as money lenders to the crown, which helped finance the Welsh Wars. When the war with France broke out, the French king confiscated the Riccardi's assets, and the bank went bankrupt. After this, the Frescobaldi of Florence took over the role as money lenders to the English crown.
Another source of crown income was represented by the English Jews. The Jews were the King's personal property, and he was free to tax them at will. By 1280, the Jews had been exploited to a level at which they were no longer of much financial use to the crown, but they could still be used in political bargaining. Their loan with interest businessa practice forbidden to Christianshad made many people indebted to them and caused general popular resentment. In 1275, Edward had issued the Statute of the Jewry, which outlawed loan with interest and encouraged the Jews to take up other professions; in 1279, in the context of a crack-down on Methods of coin debasement, coin-clippers, he arrested all the heads of Jewish households in England and had around 300 of them executed. In 1280, he ordered all Jews to attend special sermons, preached by Dominican friars, with the hope of persuading them to convert, but these exhortations were not followed. The final attack on the Jews in England came in the Edict of Expulsion in 1290, whereby Edward formally expelled all Jews from England. This not only generated revenues through royal appropriation of Jewish loans and property, but it also gave Edward the political capital to negotiate a substantial lay subsidy in the 1290 Parliament. The expulsion, which was Resettlement_of_the_Jews_in_England, reversed in the 1650s, followed a precedent set by other European rulers: Philip II of France had expelled all Jews from his own lands in 1182; John I, Duke of Brittany, drove them out of his duchy in 1239; and in the late 1240s Louis IX of France had expelled the Jews from the royal demesne before his first passage to the East.
Edward held Parliament on a reasonably regular basis throughout his reign. In 1295, however, a significant change occurred. For this Parliament, in addition to the secular and ecclesiastical lords, two knights from each county and two representatives from each borough were summoned. The representation of commons in Parliament was nothing new; what was new was the authority under which these representatives were summoned. Whereas previously the commons had been expected simply to assent to decisions already made by the magnates, it was now proclaimed that they should meet with the full authority (''plena potestas'') of their communities, to give assent to decisions made in Parliament. The King now had full backing for collecting lay subsidies – taxes collected at a certain fraction of the moveable property of all laymen – from the entire population. Whereas Henry III had only collected four of these in his reign, Edward I collected nine. This format eventually became the standard for later Parliaments, and historians have named the assembly the "Model Parliament".
 In February 1307, Bruce resumed his efforts and started gathering men, and in May he defeated Valence at the Battle of Loudoun Hill. Edward, who had rallied somewhat, now moved north himself. On the way, however, he developed dysentery, and his condition deteriorated. On 6 July he encamped at Burgh by Sands, just south of the Scottish border. When his servants came the next morning to lift him up so that he could eat, the King died in their arms.
Various stories emerged about Edward's deathbed wishes; according to one tradition, he requested that his heart be carried to the Holy Land, along with an army to fight the infidels. A more dubious story tells of how he wished for his bones to be carried along on future expeditions against the Scots. Another account of his deathbed scene is more credible; according to one chronicle, Edward gathered around him Henry de Lacy, 3rd Earl of Lincoln; Guy de Beauchamp, 10th Earl of Warwick; Aymer de Valence; and Robert de Clifford, 1st Baron de Clifford, and charged them with looking after his son Edward. In particular they should make sure that Piers Gaveston, whom he had banished earlier that year, was not allowed to return to the country. This wish, however, the son ignored, and had his favourite recalled from exile almost immediately. The new king, Edward II, remained in the north until August, but then abandoned the campaign and headed south, partially due to financial limitations. He was crowned king on 25 February 1308.
In February 1307, Bruce resumed his efforts and started gathering men, and in May he defeated Valence at the Battle of Loudoun Hill. Edward, who had rallied somewhat, now moved north himself. On the way, however, he developed dysentery, and his condition deteriorated. On 6 July he encamped at Burgh by Sands, just south of the Scottish border. When his servants came the next morning to lift him up so that he could eat, the King died in their arms.
Various stories emerged about Edward's deathbed wishes; according to one tradition, he requested that his heart be carried to the Holy Land, along with an army to fight the infidels. A more dubious story tells of how he wished for his bones to be carried along on future expeditions against the Scots. Another account of his deathbed scene is more credible; according to one chronicle, Edward gathered around him Henry de Lacy, 3rd Earl of Lincoln; Guy de Beauchamp, 10th Earl of Warwick; Aymer de Valence; and Robert de Clifford, 1st Baron de Clifford, and charged them with looking after his son Edward. In particular they should make sure that Piers Gaveston, whom he had banished earlier that year, was not allowed to return to the country. This wish, however, the son ignored, and had his favourite recalled from exile almost immediately. The new king, Edward II, remained in the north until August, but then abandoned the campaign and headed south, partially due to financial limitations. He was crowned king on 25 February 1308.
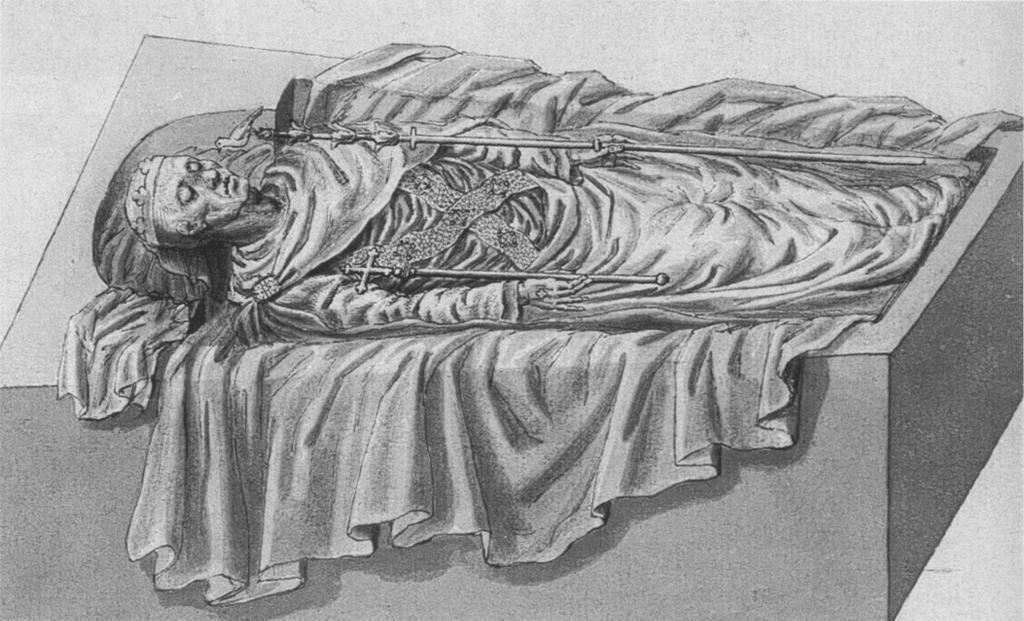
 Edward I's body was brought south, lying in state at Waltham Abbey, before being buried in Westminster Abbey on 27 October. There are few records of the funeral, which cost £473. Edward's tomb was an unusually plain sarcophagus of Purbeck marble, without the customary royal effigy, possibly the result of the shortage of royal funds after the King's death. The sarcophagus may normally have been covered over with rich cloth, and originally might have been surrounded by carved busts and a devotional religious image, all since lost. The Society of Antiquaries of London opened the tomb in 1774, finding that the body had been well preserved over the preceding 467 years, and took the opportunity to determine the King's original height. Traces of the Latin inscription ''Edwardus Primus Scottorum Malleus hic est, 1308. Pactum Serva'' ("Here is Edward I, Hammer of the Scots, 1308. Keep the Troth") can still be seen painted on the side of the tomb, referring to his vow to avenge the rebellion of Robert Bruce. This resulted in Edward being given the epithet the "Hammer of the Scots" by historians, but is not contemporary in origin, having been added by the Abbot John Feckenham in the 16th century.
Edward I's body was brought south, lying in state at Waltham Abbey, before being buried in Westminster Abbey on 27 October. There are few records of the funeral, which cost £473. Edward's tomb was an unusually plain sarcophagus of Purbeck marble, without the customary royal effigy, possibly the result of the shortage of royal funds after the King's death. The sarcophagus may normally have been covered over with rich cloth, and originally might have been surrounded by carved busts and a devotional religious image, all since lost. The Society of Antiquaries of London opened the tomb in 1774, finding that the body had been well preserved over the preceding 467 years, and took the opportunity to determine the King's original height. Traces of the Latin inscription ''Edwardus Primus Scottorum Malleus hic est, 1308. Pactum Serva'' ("Here is Edward I, Hammer of the Scots, 1308. Keep the Troth") can still be seen painted on the side of the tomb, referring to his vow to avenge the rebellion of Robert Bruce. This resulted in Edward being given the epithet the "Hammer of the Scots" by historians, but is not contemporary in origin, having been added by the Abbot John Feckenham in the 16th century.
 The first histories of Edward in the 16th and 17th centuries drew primarily on the works of the chroniclers, and made little use of the official records of the period. They limited themselves to general comments on Edward's significance as a monarch, and echoed the chroniclers' praise for his accomplishments. During the 17th century, the lawyer Edward Coke wrote extensively about Edward's legislation, terming the king the "English Justinian" after the renowned Byzantine lawmaker Justinian I. Later in the century, historians used the available record evidence to address the role of parliament and kingship under Edward, drawing comparisons between his reign and the political strife of their own century. Eighteenth-century historians established a picture of Edward as an able, if ruthless, monarch, conditioned by the circumstances of his own time.
The influential Victorian historian William Stubbs instead suggested that Edward had actively shaped national history, forming English laws and institutions, and helping England to develop a parliamentary and constitutional monarchy. His strengths and weaknesses as a ruler were considered to be emblematic of the English people as a whole. Stubbs' student, Thomas Tout, initially adopted the same perspective, but after extensive research into Edward's royal household, and backed by the research of his contemporaries into the early parliaments of the period, he changed his mind. Tout came to view Edward as a self-interested, conservative leader, using the parliamentary system as "the shrewd device of an autocrat, anxious to use the mass of the people as a check upon his hereditary foes among the greater baronage."
Historians in the 20th and 21st century have conducted extensive research on Edward and his reign. Most have concluded this was a highly significant period in English medieval history, some going further and describing Edward as one of the great medieval kings, although most also agree that his final years were less successful than his early decades in power. Three major academic narratives of Edward have been produced during this period. F. M. Powicke's volumes, published in 1947 and 1953, forming the standard works on Edward for several decades, were largely positive in praising the achievements of his reign, and in particular his focus on justice and the law. In 1988,
The first histories of Edward in the 16th and 17th centuries drew primarily on the works of the chroniclers, and made little use of the official records of the period. They limited themselves to general comments on Edward's significance as a monarch, and echoed the chroniclers' praise for his accomplishments. During the 17th century, the lawyer Edward Coke wrote extensively about Edward's legislation, terming the king the "English Justinian" after the renowned Byzantine lawmaker Justinian I. Later in the century, historians used the available record evidence to address the role of parliament and kingship under Edward, drawing comparisons between his reign and the political strife of their own century. Eighteenth-century historians established a picture of Edward as an able, if ruthless, monarch, conditioned by the circumstances of his own time.
The influential Victorian historian William Stubbs instead suggested that Edward had actively shaped national history, forming English laws and institutions, and helping England to develop a parliamentary and constitutional monarchy. His strengths and weaknesses as a ruler were considered to be emblematic of the English people as a whole. Stubbs' student, Thomas Tout, initially adopted the same perspective, but after extensive research into Edward's royal household, and backed by the research of his contemporaries into the early parliaments of the period, he changed his mind. Tout came to view Edward as a self-interested, conservative leader, using the parliamentary system as "the shrewd device of an autocrat, anxious to use the mass of the people as a check upon his hereditary foes among the greater baronage."
Historians in the 20th and 21st century have conducted extensive research on Edward and his reign. Most have concluded this was a highly significant period in English medieval history, some going further and describing Edward as one of the great medieval kings, although most also agree that his final years were less successful than his early decades in power. Three major academic narratives of Edward have been produced during this period. F. M. Powicke's volumes, published in 1947 and 1953, forming the standard works on Edward for several decades, were largely positive in praising the achievements of his reign, and in particular his focus on justice and the law. In 1988,
 By his first wife Eleanor of Castile, Edward had at least fourteen children, perhaps as many as sixteen. Of these, five daughters survived into adulthood, but only one son outlived his father, becoming King Edward II (1307–1327). Edward's children with Eleanor were:
#Katherine (1261 or 1263 – September 1264)
#Joan (1265 – before 7 September 1265)
#John (10 July 1266 – 3 August 1271)
#
By his first wife Eleanor of Castile, Edward had at least fourteen children, perhaps as many as sixteen. Of these, five daughters survived into adulthood, but only one son outlived his father, becoming King Edward II (1307–1327). Edward's children with Eleanor were:
#Katherine (1261 or 1263 – September 1264)
#Joan (1265 – before 7 September 1265)
#John (10 July 1266 – 3 August 1271)
#
Edward I
at the Royal Family website * *
Edward I
from the online ''Encyclopædia Britannica''. {{DEFAULTSORT:Edward 01 Of England Edward I of England, 1239 births 1307 deaths 13th-century English monarchs 14th-century English monarchs Burials at Westminster Abbey Christians of Lord Edward's crusade English people of French descent High Sheriffs of Bedfordshire High Sheriffs of Buckinghamshire Lords Warden of the Cinque Ports People from Westminster English people of the Wars of Scottish Independence People of the Barons' Wars Deaths from dysentery 13th-century peers of France 14th-century peers of France Earls of Chester Competitors for the Crown of Scotland House of Plantagenet Antisemitism in England Children of Henry III of England Sons of kings Victims of the Order of Assassins
epithet
An epithet (, ), also byname, is a descriptive term (word or phrase) known for accompanying or occurring in place of a name and having entered common usage. It has various shades of meaning when applied to seemingly real or fictitious people, di ...
"Longshanks", meaning "long legs" or "long shins". The historian Michael Prestwich
Michael Charles Prestwich OBE (born 30 January 1943) is an English historian, specialising on the history of medieval England, in particular the reign of Edward I. He is retired, having been Professor of History at Durham University and Head ...
states that his "long arms gave him an advantage as a swordsman, long thighs one as a horseman. In youth, his curly hair was blond; in maturity it darkened, and in old age it turned white. The regularity of his features was marred by a drooping left eyelid... His speech, despite a lisp, was said to be persuasive."
In 1254 English fears of a Castilian invasion of the English-held province of Gascony
Gascony (; french: Gascogne ; oc, Gasconha ; eu, Gaskoinia) was a province of the southwestern Kingdom of France that succeeded the Duchy of Gascony (602–1453). From the 17th century until the French Revolution (1789–1799), it was part o ...
induced King Henry to arrange a politically expedient marriage between fifteen-year-old Edward and thirteen-year-old Eleanor
Eleanor () is a feminine given name, originally from an Old French adaptation of the Old Provençal name ''Aliénor''. It is the name of a number of women of royalty and nobility in western Europe during the High Middle Ages.
The name was introd ...
, the half-sister of King Alfonso X of Castile
Alfonso X (also known as the Wise, es, el Sabio; 23 November 1221 – 4 April 1284) was King of Castile, León and Galicia from 30 May 1252 until his death in 1284. During the election of 1257, a dissident faction chose him to be king of Germ ...
. They were married on 1 November 1254 in the Abbey of Santa María la Real de Las Huelgas
The Abbey of Santa María la Real de Las Huelgas is a monastery of Cistercian nuns located approximately 1.5 km west of the city of Burgos in Spain. The word ''huelgas'', which usually refers to "labour strikes" in modern Spanish, refers i ...
in Castile. As part of the marriage agreement, Alfonso X gave up his claims to Gascony, and Edward received grants of land worth 15,000 marks
Marks may refer to:
Business
* Mark's, a Canadian retail chain
* Marks & Spencer, a British retail chain
* Collective trade marks, trademarks owned by an organisation for the benefit of its members
* Marks & Co, the inspiration for the novel ...
a year. The endowments King Henry made to Edward in 1254, which included Gascony; most of Ireland, which was granted to Edward with the stipulation that it would never separate from the English crown; and much land in Wales and England, including the earldom of Chester
The Earldom of Chester was one of the most powerful earldoms in medieval England, extending principally over the counties of Cheshire and Flintshire. Since 1301 the title has generally been granted to heirs apparent to the English throne, and a ...
, were sizeable, but they offered Edward little independence. King Henry still retained much control over the land in question, particularly in Ireland, so Edward's power was limited there as well, and the King derived most of the income from those lands. Simon de Montfort, 6th Earl of Leicester
Simon de Montfort, 6th Earl of Leicester ( – 4 August 1265), later sometimes referred to as Simon V de Montfort to distinguish him from his namesake relatives, was a nobleman of French origin and a member of the English peerage, who led the ...
had been appointed as royal lieutenant of Gascony the year before and, consequently, drew its income, so in practice Edward derived neither authority nor revenue from this province. Around December, Edward and Eleanor entered Gascony, where they were warmly received by the populace. Here, Edward styled himself as 'ruling Gascony as prince and lord', a move that the historian J.S. Hamilton asserts was a show of his blooming political independence.
From 1254 to 1257, Edward was under the influence of his mother's relatives, known as the Savoyards, the most notable of whom was Peter II of Savoy, the Queen's uncle. After 1257, Edward became increasingly close to the Lusignan
The House of Lusignan ( ; ) was a royal house of French origin, which at various times ruled several principalities in Europe and the Levant, including the kingdoms of Jerusalem, Cyprus, and Armenia, from the 12th through the 15th centuries du ...
faction – the half-brothers of his father Henry III – led by such men as William de Valence
{{Infobox noble, name=William de Valence, christening_date=, noble family=, house-type=, father= Hugh X of Lusignan, mother=Isabella of Angoulême, birth_name=, birth_date=, birth_place=, christening_place=, styles=, death_date=13 June 1296, death ...
. This association was significant because the two groups of privileged foreigners were resented by the established English aristocracy, who would be at the centre of the ensuing years' baronial reform movement. Edward's ties to his Lusignan kinsmen were viewed unfavorably by contemporaries, including the chronicler
A chronicle ( la, chronica, from Greek ''chroniká'', from , ''chrónos'' – "time") is a historical account of events arranged in chronological order, as in a timeline. Typically, equal weight is given for historically important events and lo ...
Matthew Paris
Matthew Paris, also known as Matthew of Paris ( la, Matthæus Parisiensis, lit=Matthew the Parisian; c. 1200 – 1259), was an English Benedictine monk, chronicler, artist in illuminated manuscripts and cartographer, based at St Albans Abbey ...
, who circulated tales of unruly and violent conduct by Edward's inner circle, which raised questions about his personal qualities.
Early ambitions
Edward had shown independence in political matters as early as 1255, when he sided with the Soler family in Gascony, in the ongoing conflict between the Soler and Colomb families. This ran contrary to his father's policy of mediation between the local factions. In May 1258, a group ofmagnate
The magnate term, from the late Latin ''magnas'', a great man, itself from Latin ''magnus'', "great", means a man from the higher nobility, a man who belongs to the high office-holders, or a man in a high social position, by birth, wealth or ot ...
s drew up a document for reform of the King's government – the so-called Provisions of Oxford
The Provisions of Oxford were constitutional reforms developed during the Oxford Parliament of 1258 to resolve a dispute between King Henry III of England and his barons. The reforms were designed to ensure the king adhered to the rule of law and ...
– largely directed against the Lusignans. Edward stood by his political allies and strongly opposed the Provisions. The reform movement succeeded in limiting the Lusignan influence, however, and gradually Edward's attitude started to change. In March 1259, he entered into a formal alliance with one of the main reformers, Richard de Clare, 6th Earl of Gloucester
Richard de Clare, 5th Earl of Hertford, 6th Earl of Gloucester, 2nd Lord of Glamorgan, 8th Lord of Clare (4 August 1222 – 14 July 1262) was the son of Gilbert de Clare, 4th Earl of Hertford and Isabel Marshal.History of Tewkesbury by James Be ...
. Then, on 15 October 1259, he announced that he supported the barons' goals, and their leader, Simon de Montfort.
The motive behind Edward's change of heart could have been purely pragmatic; Montfort was in a good position to support his cause in Gascony. When the King left for France in November, Edward's behaviour turned into pure insubordination. He made several appointments to advance the cause of the reformers, causing his father to believe that Edward was considering a coup d'état
A coup d'état (; French for 'stroke of state'), also known as a coup or overthrow, is a seizure and removal of a government and its powers. Typically, it is an illegal seizure of power by a political faction, politician, cult, rebel group, m ...
. When the King returned from France, he initially refused to see his son, but through the mediation of the Earl of Cornwall and Boniface, Archbishop of Canterbury, the two were eventually reconciled. Edward was sent abroad, and in November 1260 he again united with the Lusignans, who had been exiled to France.
Back in England, early in 1262, Edward fell out with some of his former Lusignan allies over financial matters. The next year, King Henry sent him on a campaign in Wales against Llywelyn ap Gruffudd
Llywelyn ap Gruffudd (c. 1223 – 11 December 1282), sometimes written as Llywelyn ap Gruffydd, also known as Llywelyn the Last ( cy, Llywelyn Ein Llyw Olaf, lit=Llywelyn, Our Last Leader), was the native Prince of Wales ( la, Princeps Wall ...
, with only limited results. Around the same time, Montfort, who had been out of the country since 1261, returned to England and reignited the baronial reform movement. It was at this pivotal moment, as the King seemed ready to resign to the barons' demands, that Edward began to take control of the situation. Whereas he had so far been unpredictable and equivocating, from this point on he remained firmly devoted to protecting his father's royal rights. He reunited with some of the men he had alienated the year before – among them his childhood friend, Henry of Almain, and John de Warenne, 6th Earl of Surrey
John de Warenne, 6th Earl of Surrey (123127 September 1304) was a prominent English nobleman and military commander during the reigns of Henry III of England and Edward I of England. During the Second Barons' War he switched sides twice, end ...
– and retook Windsor Castle
Windsor Castle is a royal residence at Windsor in the English county of Berkshire. It is strongly associated with the English and succeeding British royal family, and embodies almost a millennium of architectural history.
The original cast ...
from the rebels. Through the arbitration of King Louis IX of France
Louis IX (25 April 1214 – 25 August 1270), commonly known as Saint Louis or Louis the Saint, was King of France from 1226 to 1270, and the most illustrious of the Direct Capetians. He was crowned in Reims at the age of 12, following the d ...
, an agreement was made between the two parties. This so-called Mise of Amiens
The Mise of Amiens was a settlement given by King Louis IX of France on 23 January 1264 in the conflict between King Henry III of England and his rebellious barons, led by Simon de Montfort. Louis' one-sided decision for King Henry led directly ...
was largely favourable to the royalist side, and laid the seeds for further conflict.
Civil war and crusades, 1264–1273
Second Barons' War
The years 1264–1267 saw the conflict known as theSecond Barons' War
The Second Barons' War (1264–1267) was a civil war in England between the forces of a number of barons led by Simon de Montfort against the royalist forces of King Henry III, led initially by the king himself and later by his son, the fu ...
, in which baronial forces led by Simon de Montfort fought against those who remained loyal to the King. The first scene of battle was the city of Gloucester
Gloucester ( ) is a cathedral city and the county town of Gloucestershire in the South West of England. Gloucester lies on the River Severn, between the Cotswolds to the east and the Forest of Dean to the west, east of Monmouth and east ...
, which Edward managed to retake from the enemy. When Robert de Ferrers, 6th Earl of Derby
Robert de Ferrers, 6th Earl of Derby (1239–1279) was an English nobleman.
He was born at Tutbury Castle in Staffordshire, England, the son of William de Ferrers, 5th Earl of Derby, by his second wife Margaret de Quincy (born 1218), a daugh ...
, came to the assistance of the rebels, Edward negotiated a truce with the Earl, the terms of which Edward later broke. He then captured Northampton
Northampton () is a market town and civil parish in the East Midlands of England, on the River Nene, north-west of London and south-east of Birmingham. The county town of Northamptonshire, Northampton is one of the largest towns in England; ...
from Simon de Montfort the Younger
Simon VI de Montfort (April 1240 – 1271), known as Simon de Montfort the Younger, was the second son of Simon de Montfort, 6th Earl of Leicester and Eleanor of England.
His father and his elder brother Henry were killed at the Battle of Evesha ...
before embarking on a retaliatory campaign against Derby's lands. The baronial and royalist forces finally met at the Battle of Lewes
The Battle of Lewes was one of two main battles of the conflict known as the Second Barons' War. It took place at Lewes in Sussex, on 14 May 1264. It marked the high point of the career of Simon de Montfort, 6th Earl of Leicester, and made h ...
, on 14 May 1264. Edward, commanding the right wing, performed well, and soon defeated the London contingent of Montfort's forces. Unwisely, however, he followed the scattered enemy in pursuit, and on his return found the rest of the royal army defeated. By the agreement known as the Mise of Lewes
The Mise of Lewes was a settlement made on 14 May 1264 between King Henry III of England and his rebellious barons, led by Simon de Montfort. The settlement was made on the day of the Battle of Lewes, one of the two major battles of the Second Ba ...
, Edward and his cousin Henry of Almain were given up as hostages to Montfort.
 Edward remained in captivity until March, and even after his release he was kept under strict surveillance. Then, on 28 May, he managed to escape his custodians and joined up with
Edward remained in captivity until March, and even after his release he was kept under strict surveillance. Then, on 28 May, he managed to escape his custodians and joined up with Gilbert de Clare, 7th Earl of Gloucester
Gilbert de Clare, 6th Earl of Hertford, 7th Earl of Gloucester (2 September 1243 – 7 December 1295) was a powerful English noble. He was also known as "Red" Gilbert de Clare or "The Red Earl", probably because of his hair colour or fiery temp ...
, who had recently defected to the King's side. Montfort's support was now dwindling, and Edward retook Worcester
Worcester may refer to:
Places United Kingdom
* Worcester, England, a city and the county town of Worcestershire in England
** Worcester (UK Parliament constituency), an area represented by a Member of Parliament
* Worcester Park, London, Engla ...
and Gloucester with relatively little effort. Meanwhile, Montfort had made an alliance with Llywelyn and started moving east to join forces with his son Simon. Edward managed to make a surprise attack at Kenilworth Castle
Kenilworth Castle is a castle in the town of Kenilworth in Warwickshire, England managed by English Heritage; much of it is still in ruins. The castle was founded during the Norman conquest of England; with development through to the Tudor pe ...
, where the younger Montfort was quartered, before moving on to cut off the earl of Leicester. The two forces then met at the second great encounter of the Barons' War, the Battle of Evesham, on 4 August 1265. Montfort stood little chance against the superior royal forces, and after his defeat he was killed and mutilated on the field.
Through such episodes as the deception of Derby at Gloucester, Edward acquired a reputation as untrustworthy. During the summer campaign, though, he began to learn from his mistakes, and acted in a way that gained the respect and admiration of his contemporaries. The war did not end with Montfort's death, and Edward participated in the continued campaigning. At Christmas, he came to terms with Simon the Younger and his associates at the Isle of Axholme
The Isle of Axholme is a geographical area in England: a part of North Lincolnshire that adjoins South Yorkshire. It is located between the towns of Scunthorpe and Gainsborough, both of which are in the traditional West Riding of Lindsey, and ...
in Lincolnshire, and in March he led a successful assault on the Cinque Ports
The Confederation of Cinque Ports () is a historic group of coastal towns in south-east England – predominantly in Kent and Sussex, with one outlier (Brightlingsea) in Essex. The name is Old French, meaning "five harbours", and alludes to th ...
. A contingent of rebels held out in the virtually impregnable Kenilworth Castle and did not surrender until the drafting of the conciliatory Dictum of Kenilworth
The Dictum of Kenilworth, issued on 31 October 1266, was a pronouncement designed to reconcile the rebels of the Second Barons' War with the royal government of England. After the baronial victory at the Battle of Lewes in 1264, Simon de Montfor ...
. In April it seemed as if Gloucester would take up the cause of the reform movement, and civil war would resume, but after a renegotiation of the terms of the Dictum of Kenilworth, the parties came to an agreement. Around this time, Edward was made Steward of England and began to exercise influence in the government, but despite this, was little involved in the settlement negotiations following the wars; at this point his main focus was on planning his forthcoming crusade
The Crusades were a series of religious wars initiated, supported, and sometimes directed by the Latin Church in the medieval period. The best known of these Crusades are those to the Holy Land in the period between 1095 and 1291 that were i ...
.
Crusade and accession
 Edward took the crusader's cross in an elaborate ceremony on 24 June 1268, with his brother
Edward took the crusader's cross in an elaborate ceremony on 24 June 1268, with his brother Edmund Crouchback
Edmund, Earl of Lancaster and Earl of Leicester (16 January 12455 June 1296) nicknamed Edmund Crouchback was a member of the House of Plantagenet. He was the second surviving son of King Henry III of England and Eleanor of Provence. In his chi ...
and cousin Henry of Almain. Among others who committed themselves to the Ninth Crusade were Edward's former adversaries – such as the Earl of Gloucester, though he did not ultimately participate. With the country pacified, the greatest impediment to the project was providing sufficient finances. King Louis IX of France, who was the leader of the crusade, provided a loan of about £17,500. This, however, was not enough; the rest had to be raised through a tax on the laity
In religious organizations, the laity () consists of all members who are not part of the clergy, usually including any non-ordained members of religious orders, e.g. a nun or a lay brother.
In both religious and wider secular usage, a layperson ...
, which had not been levied since 1237. In May 1270, Parliament granted a tax of a twentieth, in exchange for which the King agreed to reconfirm Magna Carta
(Medieval Latin for "Great Charter of Freedoms"), commonly called (also ''Magna Charta''; "Great Charter"), is a royal charter of rights agreed to by King John of England at Runnymede, near Windsor, on 15 June 1215. First drafted by the ...
, and to impose restrictions on Jewish money lending. On 20 August Edward sailed from Dover
Dover () is a town and major ferry port in Kent, South East England. It faces France across the Strait of Dover, the narrowest part of the English Channel at from Cap Gris Nez in France. It lies south-east of Canterbury and east of Maidstone ...
for France. Historians have not determined the size of the force with any certainty, but Edward probably brought with him around 225 knights and altogether fewer than 1000 men.
Originally, the Crusaders intended to relieve the beleaguered Christian stronghold of Acre
The acre is a unit of land area used in the imperial
Imperial is that which relates to an empire, emperor, or imperialism.
Imperial or The Imperial may also refer to:
Places
United States
* Imperial, California
* Imperial, Missouri
* Imp ...
, but King Louis had been diverted to Tunis
''Tounsi'' french: Tunisois
, population_note =
, population_urban =
, population_metro = 2658816
, population_density_km2 =
, timezone1 = CET
, utc_offset1 ...
. Louis and his brother Charles of Anjou
Charles I (early 1226/12277 January 1285), commonly called Charles of Anjou, was a member of the royal Capetian dynasty and the founder of the second House of Anjou. He was Count of Provence (1246–85) and Forcalquier (1246–48, 1256–85) i ...
, the king of Sicily, decided to attack the emirate to establish a stronghold in North Africa. The plans failed when the French forces were struck by an epidemic which, on 25 August, took the life of Louis himself. By the time Edward arrived at Tunis, Charles had already signed a treaty with the emir, and there was little else to do but return to Sicily. The crusade was postponed until the following spring, but a devastating storm off the coast of Sicily dissuaded both Charles and Philip III (Louis's successor) from any further campaigning. Edward decided to continue alone, and on 9 May 1271 he finally landed at Acre.
 By then, the situation in the
By then, the situation in the Holy Land
The Holy Land; Arabic: or is an area roughly located between the Mediterranean Sea and the Eastern Bank of the Jordan River, traditionally synonymous both with the biblical Land of Israel and with the region of Palestine. The term "Holy ...
was a precarious one. Jerusalem
Jerusalem (; he, יְרוּשָׁלַיִם ; ar, القُدس ) (combining the Biblical and common usage Arabic names); grc, Ἱερουσαλήμ/Ἰεροσόλυμα, Hierousalḗm/Hierosóluma; hy, Երուսաղեմ, Erusałēm. i ...
was reconquered by the Muslims in 1244, and Acre was now the centre of the Christian state
A Christian state is a country that recognizes a form of Christianity as its official religion and often has a state church (also called an established church), which is a Christian denomination that supports the government and is supported by ...
. The Muslim states were on the offensive under the Mamluk
Mamluk ( ar, مملوك, mamlūk (singular), , ''mamālīk'' (plural), translated as "one who is owned", meaning " slave", also transliterated as ''Mameluke'', ''mamluq'', ''mamluke'', ''mameluk'', ''mameluke'', ''mamaluke'', or ''marmeluke'') ...
leadership of Baibars
Al-Malik al-Zahir Rukn al-Din Baybars al-Bunduqdari ( ar, الملك الظاهر ركن الدين بيبرس البندقداري, ''al-Malik al-Ẓāhir Rukn al-Dīn Baybars al-Bunduqdārī'') (1223/1228 – 1 July 1277), of Turkic Kipchak ...
, and were now threatening Acre itself. Though Edward's men were an important addition to the garrison, they stood little chance against Baibars' superior forces, and an initial raid at nearby St Georges-de-Lebeyne in June was largely futile. An embassy to the Ilkhan Abaqa
Abaqa Khan (27 February 1234 – 4 April 1282, mn, Абаха/Абага хан (Khalkha Cyrillic), ( Traditional script), "paternal uncle", also transliterated Abaġa), was the second Mongol ruler (''Ilkhan'') of the Ilkhanate. The son of Hul ...
(1234–1282) of the Mongols
The Mongols ( mn, Монголчууд, , , ; ; russian: Монголы) are an East Asian ethnic group native to Mongolia, Inner Mongolia in China and the Buryatia Republic of the Russian Federation. The Mongols are the principal membe ...
helped bring about an attack on Aleppo
)), is an adjective which means "white-colored mixed with black".
, motto =
, image_map =
, mapsize =
, map_caption =
, image_map1 =
...
in the north, which helped to distract Baibars' forces. In November, Edward led a raid on Qaqun
Qaqun ( ar, قاقون) was a Palestinian Arab village located northwest of the city of Tulkarm at the only entrance to Mount Nablus from the coastal Sharon plain.
Evidence of organized settlement in Qaqun dates back to the period of Assyr ...
, which could have served as a bridgehead to Jerusalem, but both the Mongol invasion and the attack on Qaqun failed. Things now seemed increasingly desperate, and in May 1272 Hugh III of Cyprus
Hugh III (french: Hugues; – 24 March 1284), also called Hugh of Antioch-Lusignan and the Great, was the king of Cyprus from 1267 and king of Jerusalem from 1268. Born into the family of the princes of Antioch, he effectively ruled as regent ...
, who was the nominal king of Jerusalem
The King of Jerusalem was the supreme ruler of the Kingdom of Jerusalem, a Crusader states, Crusader state founded in Jerusalem by the Latin Church, Latin Catholic leaders of the First Crusade, when the city was Siege of Jerusalem (1099), conqu ...
, signed a ten-year truce with Baibars. Edward was initially defiant, but an assassination attempt by a Syrian Nizari
The Nizaris ( ar, النزاريون, al-Nizāriyyūn, fa, نزاریان, Nezāriyān) are the largest segment of the Ismaili Muslims, who are the second-largest branch of Shia Islam after the Twelvers. Nizari teachings emphasize independent ...
(Assassin) supposedly sent by Baibars in June 1272 finally forced him to abandon any further campaigning. Although he managed to kill the assassin, he was struck in the arm by a dagger feared to be poisoned, and became severely weakened over the following months.
It was not until 24 September 1272 that Edward left Acre. Arriving in Sicily, he was met with the news that his father had died on 16 November 1272. Edward was deeply saddened by this news, but rather than hurrying home at once, he made a leisurely journey northwards. This was due partly to his still-poor health, but also to a lack of urgency. The political situation in England was stable after the mid-century upheavals, and Edward was proclaimed king after his father's death, rather than at his own coronation, as had until then been customary. In Edward's absence, the country was governed by a royal council, led by Robert Burnell
Robert Burnell (sometimes spelled Robert Burnel;Harding ''England in the Thirteenth Century'' p. 159 c. 1239 – 25 October 1292) was an English bishop who served as Lord Chancellor of England from 1274 to 1292. A native of Shropshire, h ...
. The new king embarked on an overland journey through Italy and France, during which he visited Pope Gregory X
Pope Gregory X ( la, Gregorius X; – 10 January 1276), born Teobaldo Visconti, was head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 1 September 1271 to his death and was a member of the Secular Franciscan Order. He was ...
and paid homage to Philip III in Paris
Paris () is the capital and most populous city of France, with an estimated population of 2,165,423 residents in 2019 in an area of more than 105 km² (41 sq mi), making it the 30th most densely populated city in the world in 2020. S ...
for his French domains. Before returning to England, however, Edward travelled by way of Savoy
Savoy (; frp, Savouè ; french: Savoie ) is a cultural-historical region in the Western Alps.
Situated on the cultural boundary between Occitania and Piedmont, the area extends from Lake Geneva in the north to the Dauphiné in the south.
Savo ...
to receive homage from his uncle Count Philip I for a number of castles in the Alps
The Alps () ; german: Alpen ; it, Alpi ; rm, Alps ; sl, Alpe . are the highest and most extensive mountain range system that lies entirely in Europe, stretching approximately across seven Alpine countries (from west to east): France, Sw ...
held by a treaty in 1246. At Philip’s castle of Saint-Georges-d'Espéranche
Saint-Georges-d'Espéranche () is a commune in the Isère department in southeastern France.
History
The medieval architect and castle builder for Edward I of England, Master James of Saint George, also known as Jacques de Saint-Georges d'Esp� ...
in June 1273, Edward met Philip's castle-builder James of Saint George
Master James of Saint George (–1309; French: , Old French: Mestre Jaks, Latin: Magister Jacobus de Sancto Georgio) was a master of works/architect from Savoy, described by historian Marc Morris as "one of the greatest architects of the European ...
, the man who would later build castles for him in north Wales. Following Paris and Savoy, Edward went to Gascony in order to sort out its affairs and put down a revolt headed by Gaston de Béarn. While there, he launched an investigation into his feudal possessions, which, as Hamilton puts it, reflects "Edward's keen interest in administrative efficiency... ndreinforced Edward's position as lord in Aquitaine and strengthened the bonds of loyalty between the king-duke and his subjects". Around the same time, the King organized political alliances with the kingdoms in Iberia
The Iberian Peninsula (),
**
* Aragonese and Occitan: ''Peninsula Iberica''
**
**
* french: Péninsule Ibérique
* mwl, Península Eibérica
* eu, Iberiar penintsula also known as Iberia, is a peninsula in southwestern Europe, defi ...
. His four year old daughter Eleanor
Eleanor () is a feminine given name, originally from an Old French adaptation of the Old Provençal name ''Aliénor''. It is the name of a number of women of royalty and nobility in western Europe during the High Middle Ages.
The name was introd ...
was promised in marriage to Alfonso
Alphons (Latinized ''Alphonsus'', ''Adelphonsus'', or ''Adefonsus'') is a male given name recorded from the 8th century (Alfonso I of Asturias, r. 739–757) in the Christian successor states of the Visigothic kingdom in the Iberian peninsula. ...
, the heir to the Kingdom of Aragon
The Kingdom of Aragon ( an, Reino d'Aragón, ca, Regne d'Aragó, la, Regnum Aragoniae, es, Reino de Aragón) was a medieval and early modern kingdom on the Iberian Peninsula, corresponding to the modern-day autonomous community of Aragon, ...
, whereas Edward's own heir Henry
Henry may refer to:
People
*Henry (given name)
* Henry (surname)
* Henry Lau, Canadian singer and musician who performs under the mononym Henry
Royalty
* Portuguese royalty
** King-Cardinal Henry, King of Portugal
** Henry, Count of Portugal, ...
was betrothed to Joan Joan may refer to:
People and fictional characters
* Joan (given name), including a list of women, men and fictional characters
*:Joan of Arc, a French military heroine
* Joan (surname)
Weather events
*Tropical Storm Joan (disambiguation), multip ...
, heiress to the Kingdom of Navarre
The Kingdom of Navarre (; , , , ), originally the Kingdom of Pamplona (), was a Basque kingdom that occupied lands on both sides of the western Pyrenees, alongside the Atlantic Ocean between present-day Spain and France.
The medieval state took ...
. However, neither union would come into fruition. Only on 2 August 1274 did Edward return to England, landing at Dover
Dover () is a town and major ferry port in Kent, South East England. It faces France across the Strait of Dover, the narrowest part of the English Channel at from Cap Gris Nez in France. It lies south-east of Canterbury and east of Maidstone ...
. The thirty-five year old King Edward was crowned on 19 August at Westminster Abbey, alongside Queen Eleanor. Immediately after being anointed and crowned by Robert Kilwardby
Robert Kilwardby ( c. 1215 – 11 September 1279) was an Archbishop of Canterbury in England and a cardinal. Kilwardby was the first member of a mendicant order to attain a high ecclesiastical office in the English Church.
Life
Kilwardby s ...
, the Archbishop of Canterbury
The archbishop of Canterbury is the senior bishop and a principal leader of the Church of England, the ceremonial head of the worldwide Anglican Communion and the diocesan bishop of the Diocese of Canterbury. The current archbishop is Justi ...
, Edward removed his crown, saying that he did not intend on wearing it until he had recovered all the crown lands lost under his father's reign.
Early reign, 1274–1296
Welsh wars
Conquest
Treaty of Montgomery
The Treaty of Montgomery was an Anglo-Welsh treaty signed on 29 September 1267 in Montgomeryshire by which Llywelyn ap Gruffudd was acknowledged as Prince of Wales by King Henry III of England (r. 1216–1272). It was the only time an English ...
, he officially obtained land he had conquered in the Four Cantrefs of Perfeddwlad and was recognised in his title of Prince of Wales
Prince of Wales ( cy, Tywysog Cymru, ; la, Princeps Cambriae/Walliae) is a title traditionally given to the heir apparent to the English and later British throne. Prior to the conquest by Edward I in the 13th century, it was used by the rulers ...
. Armed conflicts nevertheless continued, in particular with certain dissatisfied Marcher Lords
A Marcher lord () was a noble appointed by the king of England to guard the border (known as the Welsh Marches) between England and Wales.
A Marcher lord was the English equivalent of a margrave (in the Holy Roman Empire) or a marquis (in F ...
, such as Gilbert de Clare, Earl of Gloucester, Roger Mortimer, 1st Baron Mortimer, Roger Mortimer and Humphrey de Bohun, 3rd Earl of Hereford. Problems were exacerbated when Llywelyn's younger brother Dafydd ap Gruffydd, Dafydd and Gruffydd ap Gwenwynwyn of Powys, after failing in an assassination attempt against Llywelyn, defected to the English in 1274. Citing ongoing hostilities and Edward's harbouring of his enemies, Llywelyn refused to do homage to the King. For Edward, a further provocation came from Llywelyn's planned marriage to Eleanor de Montfort, Princess of Wales, Eleanor, daughter of Simon de Montfort.
In November 1276, war was declared. Initial operations were launched under the captaincy of Mortimer, Edward's brother Edmund, Earl of Lancaster, and William de Beauchamp, 9th Earl of Warwick. Support for Llywelyn was weak among his own countrymen. In July 1277 Edward invaded with a force of 15,500, of whom 9,000 were Welshmen. The campaign never came to a major battle, and Llywelyn soon realised he had no choice but to surrender. By the Treaty of Aberconwy in November 1277, he was left only with the land of Gwynedd, though he was allowed to retain the title of Prince of Wales.
When war broke out again in 1282, it was an entirely different undertaking. For the Welsh, this war was over national identity, enjoying wide support, provoked particularly by attempts to impose English law on Welsh subjects. For Edward, it became a war of conquest rather than simply a punitive expedition, like the former campaign. The war started with a rebellion by Dafydd, who was discontented with the reward he had received from Edward in 1277. Llywelyn and other Welsh chieftains soon joined in, and initially the Welsh experienced military success. In June, Gloucester was defeated at the Battle of Llandeilo Fawr. On 6 November, while John Peckham, Archbishop of Canterbury
The archbishop of Canterbury is the senior bishop and a principal leader of the Church of England, the ceremonial head of the worldwide Anglican Communion and the diocesan bishop of the Diocese of Canterbury. The current archbishop is Justi ...
, was conducting peace negotiations, Edward's commander of Anglesey, Luke de Tany, decided to carry out a surprise attack. A pontoon bridge had been built to the mainland, but shortly after Tany and his men crossed over, they were ambushed by the Welsh and suffered heavy losses at the Battle of Moel-y-don. The Welsh advances ended on 11 December, however, when Llywelyn was lured into a trap and killed at the Battle of Orewin Bridge. The conquest of Gwynedd was complete with the capture in June 1283 of Dafydd, who was taken to Shrewsbury and executed as a traitor the following autumn; King Edward ordered Dafydd's head to be publicly exhibited on London Bridge. Further rebellions occurred in 1287–88 and, more seriously, in 1294, under the leadership of Madog ap Llywelyn, a distant relative of Llywelyn ap Gruffudd. This last conflict demanded the King's own attention, but in both cases the rebellions were put down.
Colonisation
 By the 1284 Statute of Rhuddlan, the Principality of Wales was incorporated into England and was given an administrative system like the English, with counties policed by sheriffs. English law was introduced in criminal cases, though the Welsh were allowed to maintain their own customary laws in some cases of property disputes. After 1277, and increasingly after 1283, Edward embarked on a full-scale project of English settlement of Wales, creating new towns like Flint, Flintshire, Flint, Aberystwyth and Rhuddlan. Their new residents were English migrants, with the local Welsh banned from living inside them, and many were protected by extensive walls.
An extensive project of castle-building was also initiated, under the direction of James of Saint George, a prestigious architect whom Edward had met in Savoy on his return from the crusade. These included the Beaumaris Castle, Beaumaris, Caernarfon Castle, Caernarfon, Conwy Castle, Conwy and Harlech Castle, Harlech castles, intended to act both as fortresses and royal palaces for the King. His programme of castle building in Wales heralded the introduction of the widespread use of arrowslits in castle walls across Europe, drawing on Eastern influences. Also a product of the Crusades was the introduction of the concentric castle, and four of the eight castles Edward founded in Wales followed this design. The castles made a clear, imperial statement about Edward's intentions to rule North Wales permanently, and drew on imagery associated with the Byzantine Empire and King Arthur in an attempt to build legitimacy for his new regime.
In 1284, King Edward had his son Edward (later
By the 1284 Statute of Rhuddlan, the Principality of Wales was incorporated into England and was given an administrative system like the English, with counties policed by sheriffs. English law was introduced in criminal cases, though the Welsh were allowed to maintain their own customary laws in some cases of property disputes. After 1277, and increasingly after 1283, Edward embarked on a full-scale project of English settlement of Wales, creating new towns like Flint, Flintshire, Flint, Aberystwyth and Rhuddlan. Their new residents were English migrants, with the local Welsh banned from living inside them, and many were protected by extensive walls.
An extensive project of castle-building was also initiated, under the direction of James of Saint George, a prestigious architect whom Edward had met in Savoy on his return from the crusade. These included the Beaumaris Castle, Beaumaris, Caernarfon Castle, Caernarfon, Conwy Castle, Conwy and Harlech Castle, Harlech castles, intended to act both as fortresses and royal palaces for the King. His programme of castle building in Wales heralded the introduction of the widespread use of arrowslits in castle walls across Europe, drawing on Eastern influences. Also a product of the Crusades was the introduction of the concentric castle, and four of the eight castles Edward founded in Wales followed this design. The castles made a clear, imperial statement about Edward's intentions to rule North Wales permanently, and drew on imagery associated with the Byzantine Empire and King Arthur in an attempt to build legitimacy for his new regime.
In 1284, King Edward had his son Edward (later Edward II
Edward II (25 April 1284 – 21 September 1327), also called Edward of Caernarfon, was King of England and Lord of Ireland from 1307 until he was deposed in January 1327. The fourth son of Edward I, Edward became the heir apparent to th ...
) born at Caernarfon Castle, probably to make a deliberate statement about the new political order in Wales. David Powel, a 16th-century clergyman, suggested that the baby was offered to the Welsh as a prince "that was borne in Wales and could speake never a word of English", but there is no evidence to support this widely-reported account. In 1301 at Lincoln, the young Edward became the first English prince to be invested with the title of Prince of Wales, when the King granted him the Earldom of Chester and lands across North Wales.; The King seems to have hoped that this would help in the pacification of the region, and that it would give his son more financial independence.
Diplomacy and war on the continent
 Edward never again went on crusade after his return to England in 1274, but he maintained an intention to do so, and took the cross again in 1287. This intention guided much of his foreign policy, until at least 1291. To stage a European-wide crusade, it was essential to prevent conflict between the sovereigns on the continent. A major obstacle to this was represented by the conflict between the French Capetian House of Anjou ruling southern Italy and the Kingdom of Aragon in Spain. In 1282, the citizens of Palermo rose up against Charles of Anjou and turned for help to Peter III of Aragon, in what has become known as the Sicilian Vespers. In War of the Sicilian Vespers, the war that followed, Charles of Anjou's son, Charles of Salerno, was taken prisoner by the Aragonese. The French began planning an attack on Aragon, raising the prospect of a large-scale European war. To Edward, it was imperative that such a war be avoided, and in Paris in 1286 he brokered a truce between France and Aragon that helped secure Charles' release. As far as the crusades were concerned, however, Edward's efforts proved ineffective. A devastating blow to his plans came in 1291, when the Mamluks Siege of Acre (1291), captured Acre, the last Christian stronghold in the Holy Land.
Edward had long been deeply involved in the affairs of his own Duchy of Gascony. In 1278 he assigned an investigating commission to his trusted associates Otto de Grandson and the chancellor
Edward never again went on crusade after his return to England in 1274, but he maintained an intention to do so, and took the cross again in 1287. This intention guided much of his foreign policy, until at least 1291. To stage a European-wide crusade, it was essential to prevent conflict between the sovereigns on the continent. A major obstacle to this was represented by the conflict between the French Capetian House of Anjou ruling southern Italy and the Kingdom of Aragon in Spain. In 1282, the citizens of Palermo rose up against Charles of Anjou and turned for help to Peter III of Aragon, in what has become known as the Sicilian Vespers. In War of the Sicilian Vespers, the war that followed, Charles of Anjou's son, Charles of Salerno, was taken prisoner by the Aragonese. The French began planning an attack on Aragon, raising the prospect of a large-scale European war. To Edward, it was imperative that such a war be avoided, and in Paris in 1286 he brokered a truce between France and Aragon that helped secure Charles' release. As far as the crusades were concerned, however, Edward's efforts proved ineffective. A devastating blow to his plans came in 1291, when the Mamluks Siege of Acre (1291), captured Acre, the last Christian stronghold in the Holy Land.
Edward had long been deeply involved in the affairs of his own Duchy of Gascony. In 1278 he assigned an investigating commission to his trusted associates Otto de Grandson and the chancellor Robert Burnell
Robert Burnell (sometimes spelled Robert Burnel;Harding ''England in the Thirteenth Century'' p. 159 c. 1239 – 25 October 1292) was an English bishop who served as Lord Chancellor of England from 1274 to 1292. A native of Shropshire, h ...
, which caused the replacement of the seneschal Luke de Tany. In 1286, Edward visited the region himself and stayed for almost three years. The perennial problem, however, was the status of Gascony within the Kingdom of France, and Edward's role as the French king's vassal. On his diplomatic mission in 1286, Edward had paid homage to the new king, Philip IV, but in 1294 Philip declared Gascony forfeit when Edward refused to appear before him in Paris to discuss the recent conflict between English, Gascon, and French sailors that had resulted in several French ships being captured, along with the sacking of the French port of La Rochelle.
Correspondence between Edward and the Mongol court of Orient, the east continued during this time. Diplomatic channels between the two had begun during Edward's time on crusade, regarding a possible alliance to retake the Holy Land for Europe. Edward received Mongol envoys at his court in Gascony while there in 1287, and one of their leaders, Rabban Bar Sauma, recorded an extant account of the interaction. Other embassies arrived in Europe in 1289 and 1290, with the former relaying Ilkhan Abaqa's offer to join forces with the crusaders and supply them with horses. Edward responded favourably, declaring his intent to embark on a journey to the east once he obtained papal approval. While this would not end up occurring, the King's decision to send Geoffrey of Langley as his ambassador to the Mongols revealed that he was seriously considering the prospective Mongol alliance.
Eleanor of Castile had died on 28 November 1290. The couple loved each other, and like his father, Edward was very devoted to his wife and was faithful to her throughout their marriage. He was deeply affected by her death, and displayed his grief by erecting twelve so-called Eleanor crosses, one at each place where her funeral cortège stopped for the night. As part of the peace accord between England and France in 1294, it was agreed that Edward should marry Philip IV's half-sister Margaret of France, Queen of England, Margaret, but the marriage was delayed by the outbreak of war. Edward made alliances with the German king, the counts of Flanders and Guelders, and the Burgundians, who would attack France from the north. However, the alliances proved volatile and Edward was facing trouble at home at the time, both in Wales and Scotland. It was not until August 1297 that he was finally able to sail for Flanders, at which time his allies there had already suffered defeat. The support from Germany never materialised, and Edward was forced to seek peace. His marriage to Margaret in 1299 ended the war, but the whole affair had proven both costly and fruitless for the English. The French occupation of Gascony would not end until 1303, at which point it was partially returned to the English crown.
Great Cause
 The relationship between England and Scotland by the 1280s was one of relatively harmonious coexistence. The issue of homage did not reach the same level of controversy as it did in Wales; in 1278 King Alexander III of Scotland paid homage to Edward I, who was his brother-in-law, but apparently only for the lands he held of Edward in England. Problems arose only with the Scottish succession crisis of the early 1290s. When Alexander died in 1286, he left as heir to the Scottish throne Margaret, Maid of Norway, Margaret, his three-year-old granddaughter and sole surviving descendant. By the Treaty of Birgham, it was agreed that Margaret should marry King Edward's six-year-old son Edward of Carnarvon, though Scotland would remain free of English overlordship. Margaret, by now seven years of age, sailed from Norway for Scotland in the autumn of 1290, but fell ill on the way and died in Orkney. This left the country without an obvious heir, and led to the succession dispute known to history as the Great Cause.
Even though as many as fourteen claimants put forward their claims to the title, the foremost competitors John Balliol and Robert de Brus, 5th Lord of Annandale. The Scottish
The relationship between England and Scotland by the 1280s was one of relatively harmonious coexistence. The issue of homage did not reach the same level of controversy as it did in Wales; in 1278 King Alexander III of Scotland paid homage to Edward I, who was his brother-in-law, but apparently only for the lands he held of Edward in England. Problems arose only with the Scottish succession crisis of the early 1290s. When Alexander died in 1286, he left as heir to the Scottish throne Margaret, Maid of Norway, Margaret, his three-year-old granddaughter and sole surviving descendant. By the Treaty of Birgham, it was agreed that Margaret should marry King Edward's six-year-old son Edward of Carnarvon, though Scotland would remain free of English overlordship. Margaret, by now seven years of age, sailed from Norway for Scotland in the autumn of 1290, but fell ill on the way and died in Orkney. This left the country without an obvious heir, and led to the succession dispute known to history as the Great Cause.
Even though as many as fourteen claimants put forward their claims to the title, the foremost competitors John Balliol and Robert de Brus, 5th Lord of Annandale. The Scottish magnate
The magnate term, from the late Latin ''magnas'', a great man, itself from Latin ''magnus'', "great", means a man from the higher nobility, a man who belongs to the high office-holders, or a man in a high social position, by birth, wealth or ot ...
s made a request to Edward to conduct the proceedings and administer the outcome, but not to arbitrate in the dispute. The actual decision would be made by 104 auditors – 40 appointed by Balliol, 40 by Brus and the remaining 24 selected by Edward I from senior members of the Scottish political community. At Birgham, with the prospect of a personal union between the two realms, the question of suzerainty had not been of great importance to Edward. Now he insisted that, if he were to settle the contest, he had to be fully recognised as Scotland's feudal overlord. The Scots were reluctant to make such a concession, and replied that since the country had no king, no one had the authority to make this decision. This problem was circumvented when the competitors agreed that the realm would be handed over to Edward until a rightful heir had been found. After a lengthy hearing, a decision was made in favour of John Balliol on 17 November 1292.
Even after Balliol's accession, Edward still continued to assert his authority over Scotland. Against the objections of the Scots, he agreed to hear appeals on cases ruled on by the court of guardians that had governed Scotland during the interregnum. A further provocation came in a case brought by Macduff, son of Malcolm II, Earl of Fife, in which Edward demanded that Balliol appear in person before the English Parliament to answer the charges. This the Scottish King did, but the final straw was Edward's demand that the Scottish magnates provide military service in the war against France. This was unacceptable; the Scots instead formed an Auld Alliance, alliance with France and launched an unsuccessful attack on Carlisle. Edward responded by invading Scotland in 1296 and taking the town of Berwick-upon-Tweed in a particularly bloody attack. At the Battle of Dunbar (1296), Battle of Dunbar, Scottish resistance was effectively crushed. Edward confiscated the Stone of Scone, Stone of Destiny – the Scottish coronation stoneand brought it to Westminster, placing it in what became known as King Edward's Chair; he deposed Balliol and placed him in the Tower of London, and installed Englishmen to govern the country. The campaign had been very successful, but the English triumph would be only temporary.
Government and law
Character as king
 Edward had a reputation for a fierce and sometimes unpredictable temper, and he could be intimidating; one story tells of how the Dean of St Paul's, wishing to confront Edward over the high level of taxation in 1295, fell down and died once he was in the King's presence. When Edward of Caernarfon demanded an earldom for his favourite Piers Gaveston, 1st Earl of Cornwall, Piers Gaveston, the King erupted in anger and supposedly tore out handfuls of his son's hair. Some of his contemporaries considered Edward frightening, particularly in his early days. The ''Song of Lewes'' in 1264 described him as a leopard, an animal regarded as particularly powerful and unpredictable. At times, however, Edward exhibited a gentler disposition, and was known to be devoted to his large family. He was close with his surviving daughters, and frequently lavished them with expensive gifts whenever they visited court.
Despite his more unflattering character traits, Edward's contemporaries considered him an able, even an ideal, king. Though not loved by his subjects, he was feared and respected, as reflected in the fact that there were no armed rebellions in England during his reign. Edward met contemporary expectations of kingship in his role as an able, determined soldier and in his embodiment of shared chivalric ideals. In religious observance he also fulfilled the expectations of his age: he attended chapel regularly, gave alms generously, and showed a fervent devotion to the Virgin Mary and Saint Thomas Becket. Like his father, Edward was a keen participant in the tradition of the royal touch, which had the supposed effect of curing those who were touched from scrofula. Contemporary records suggest that the King touched upwards of a thousand people each year. Despite his personal piety, Edward was frequently in conflict with the Archbishops of Canterbury that served during his reign, with one 14th-century chronicler attributing the death of Thomas of Corbridge to the King's harsh conduct towards him. Relations with the Papacy were at times no better: in 1297, Edward deliberately disobeyed the papal bull ''Clericis laicos'', which generally forbade ecclesiastical taxation. However, improved relations with Rome later on allowed Edward to collect considerable sums by taxing the English clergy.
Edward took a keen interest in the stories of King Arthur, which were highly popular in Europe during his reign. In 1278 he visited Glastonbury Abbey to open what was then believed to be the tomb of Arthur and Guinevere, recovering "Arthur's crown" from Llywelyn after the conquest of North Wales, while, as noted above, his new castles drew upon the Arthurian myths in their design and location. He held "Round Table" events in 1284 and 1302, involving tournaments and feasting, and chroniclers compared him and the events at his court to Arthur. In some cases Edward appears to have used his interest in the Arthurian myths to serve his own political interests, including legitimising his rule in Wales and discrediting the King Arthur's messianic return, Welsh belief that Arthur might return as their political saviour.
Edward had a reputation for a fierce and sometimes unpredictable temper, and he could be intimidating; one story tells of how the Dean of St Paul's, wishing to confront Edward over the high level of taxation in 1295, fell down and died once he was in the King's presence. When Edward of Caernarfon demanded an earldom for his favourite Piers Gaveston, 1st Earl of Cornwall, Piers Gaveston, the King erupted in anger and supposedly tore out handfuls of his son's hair. Some of his contemporaries considered Edward frightening, particularly in his early days. The ''Song of Lewes'' in 1264 described him as a leopard, an animal regarded as particularly powerful and unpredictable. At times, however, Edward exhibited a gentler disposition, and was known to be devoted to his large family. He was close with his surviving daughters, and frequently lavished them with expensive gifts whenever they visited court.
Despite his more unflattering character traits, Edward's contemporaries considered him an able, even an ideal, king. Though not loved by his subjects, he was feared and respected, as reflected in the fact that there were no armed rebellions in England during his reign. Edward met contemporary expectations of kingship in his role as an able, determined soldier and in his embodiment of shared chivalric ideals. In religious observance he also fulfilled the expectations of his age: he attended chapel regularly, gave alms generously, and showed a fervent devotion to the Virgin Mary and Saint Thomas Becket. Like his father, Edward was a keen participant in the tradition of the royal touch, which had the supposed effect of curing those who were touched from scrofula. Contemporary records suggest that the King touched upwards of a thousand people each year. Despite his personal piety, Edward was frequently in conflict with the Archbishops of Canterbury that served during his reign, with one 14th-century chronicler attributing the death of Thomas of Corbridge to the King's harsh conduct towards him. Relations with the Papacy were at times no better: in 1297, Edward deliberately disobeyed the papal bull ''Clericis laicos'', which generally forbade ecclesiastical taxation. However, improved relations with Rome later on allowed Edward to collect considerable sums by taxing the English clergy.
Edward took a keen interest in the stories of King Arthur, which were highly popular in Europe during his reign. In 1278 he visited Glastonbury Abbey to open what was then believed to be the tomb of Arthur and Guinevere, recovering "Arthur's crown" from Llywelyn after the conquest of North Wales, while, as noted above, his new castles drew upon the Arthurian myths in their design and location. He held "Round Table" events in 1284 and 1302, involving tournaments and feasting, and chroniclers compared him and the events at his court to Arthur. In some cases Edward appears to have used his interest in the Arthurian myths to serve his own political interests, including legitimising his rule in Wales and discrediting the King Arthur's messianic return, Welsh belief that Arthur might return as their political saviour.
Administration and the law
 Soon after assuming the throne, Edward set about restoring order and re-establishing royal authority after the disastrous reign of his father. To accomplish this, he immediately ordered an extensive change of administrative personnel. The most important of these was the appointment of Robert Burnell as Lord Chancellor, chancellor, a man who would remain in the post until 1292 as one of the King's closest associates. Edward then replaced most local officials, such as the escheators and High sheriff, sheriffs. This last measure was done in preparation for an extensive inquest covering all of England, that would hear complaints about abuse of power by royal officers. The inquest produced the set of so-called Hundred Rolls, from the administrative subdivision of the Hundred (county division), hundred. The second purpose of the inquest was to establish what land and rights The Crown#Concept, the Crown had lost during the reign of Henry III.
The Hundred Rolls, which have been likened to the 11th-century Domesday Book, formed the basis for the later legal inquiries called the ''Quo warranto'' proceedings. The purpose of these inquiries was to establish by what warrant ( la, Quo warranto) various Liberty (division), liberties were held. If the defendant could not produce a royal licence to prove the grant of the liberty, then it was the Crown's opinionbased on the writings of the influential thirteenth-century legal scholar Henry de Bractonthat the liberty should revert to the king. Both the Statute of Westminster 1275 and Statute of Westminster 1285 codified the existing law in England. By enacting the Statute of Gloucester in 1278 the King challenged baronial rights through a revival of the system of general eyre (legal term), eyres (royal justices to go on tour throughout the land) and through a significant increase in the number of pleas of quo warranto to be heard by such eyres.
This caused great consternation among the aristocracy, who insisted that long use in itself constituted licence. A compromise was eventually reached in 1290, whereby a liberty was considered legitimate as long as it could be shown to have been exercised since the coronation of Richard the Lionheart in 1189. Royal gains from the ''Quo warranto'' proceedings were insignificant; few liberties were returned to the King. Edward had nevertheless won a significant victory, in clearly establishing the principle that all liberties essentially emanated from the Crown.
The 1290 statute of ''Quo warranto'' was only one part of a wider legislative effort, which was one of the most important contributions of Edward's reign. This era of legislative action had started already at the time of the baronial reform movement; the Statute of Marlborough (1267) contained elements both of the
Soon after assuming the throne, Edward set about restoring order and re-establishing royal authority after the disastrous reign of his father. To accomplish this, he immediately ordered an extensive change of administrative personnel. The most important of these was the appointment of Robert Burnell as Lord Chancellor, chancellor, a man who would remain in the post until 1292 as one of the King's closest associates. Edward then replaced most local officials, such as the escheators and High sheriff, sheriffs. This last measure was done in preparation for an extensive inquest covering all of England, that would hear complaints about abuse of power by royal officers. The inquest produced the set of so-called Hundred Rolls, from the administrative subdivision of the Hundred (county division), hundred. The second purpose of the inquest was to establish what land and rights The Crown#Concept, the Crown had lost during the reign of Henry III.
The Hundred Rolls, which have been likened to the 11th-century Domesday Book, formed the basis for the later legal inquiries called the ''Quo warranto'' proceedings. The purpose of these inquiries was to establish by what warrant ( la, Quo warranto) various Liberty (division), liberties were held. If the defendant could not produce a royal licence to prove the grant of the liberty, then it was the Crown's opinionbased on the writings of the influential thirteenth-century legal scholar Henry de Bractonthat the liberty should revert to the king. Both the Statute of Westminster 1275 and Statute of Westminster 1285 codified the existing law in England. By enacting the Statute of Gloucester in 1278 the King challenged baronial rights through a revival of the system of general eyre (legal term), eyres (royal justices to go on tour throughout the land) and through a significant increase in the number of pleas of quo warranto to be heard by such eyres.
This caused great consternation among the aristocracy, who insisted that long use in itself constituted licence. A compromise was eventually reached in 1290, whereby a liberty was considered legitimate as long as it could be shown to have been exercised since the coronation of Richard the Lionheart in 1189. Royal gains from the ''Quo warranto'' proceedings were insignificant; few liberties were returned to the King. Edward had nevertheless won a significant victory, in clearly establishing the principle that all liberties essentially emanated from the Crown.
The 1290 statute of ''Quo warranto'' was only one part of a wider legislative effort, which was one of the most important contributions of Edward's reign. This era of legislative action had started already at the time of the baronial reform movement; the Statute of Marlborough (1267) contained elements both of the Provisions of Oxford
The Provisions of Oxford were constitutional reforms developed during the Oxford Parliament of 1258 to resolve a dispute between King Henry III of England and his barons. The reforms were designed to ensure the king adhered to the rule of law and ...
and the Dictum of Kenilworth
The Dictum of Kenilworth, issued on 31 October 1266, was a pronouncement designed to reconcile the rebels of the Second Barons' War with the royal government of England. After the baronial victory at the Battle of Lewes in 1264, Simon de Montfor ...
. The compilation of the Hundred Rolls was followed shortly after by the issue of Westminster I (1275), which asserted the royal prerogative and outlined restrictions on liberties. In the Statutes of Mortmain, Mortmain (1279), the issue was grants of land to the church. The first clause of Westminster II (1285), known as ''De donis conditionalibus'', dealt with family settlement of land, and entails. Statute merchant, Merchants (1285) established firm rules for the recovery of debts, while Winchester (1285) dealt with security and peacekeeping on a local level by bolstering the existing police system. ''Quia emptores'' (1290)issued along with ''Quo warranto''set out to remedy land ownership disputes resulting from alienation of land by subinfeudation. The age of the great statutes largely ended with the death of Robert Burnell in 1292.
Finances, the expulsion of Jews, and parliament
 Edward's reign saw an overhaul of the coinage system, which was in a poor state by 1279. Compared to the coinage already circulating at the time of Edward's accession, the new coins issued proved to be of superior quality. In addition to minting History of the English penny (1154–1485), pennies, History of the halfpenny, halfpences, and Farthing (English coin), farthings, a new denomination called the Groat (coin), groat (which proved to be unsucessful) was introduced. The coinmaking process itself was also improved. William Turnemire introduced a novel method of minting coins that involved cutting blank coins from a silver rod, in contrast with the old practice of stamping them out from sheets; this technique proved to be efficient. The practice of minting coins with the moneyer's name on it became obsolete under Edward's rule because England's mint administration became far more centralized under the Crown's authority. During this time, English coins were frequently counterfeited in foreign places, especially the Low Countries, and despite a ban in 1283, English coinage was secretly exported to the European continent. In August 1280, Edward forbade the usage of the old Long cross penny, long cross coinage, which forced the populace to switch to the newly-minted versions. Records do not indicate any adverse consequences that resulted from Edward's monetary reforms; on the contrary, the coinage overhaul successfully provided England with a stable currency.
Edward's reign saw an overhaul of the coinage system, which was in a poor state by 1279. Compared to the coinage already circulating at the time of Edward's accession, the new coins issued proved to be of superior quality. In addition to minting History of the English penny (1154–1485), pennies, History of the halfpenny, halfpences, and Farthing (English coin), farthings, a new denomination called the Groat (coin), groat (which proved to be unsucessful) was introduced. The coinmaking process itself was also improved. William Turnemire introduced a novel method of minting coins that involved cutting blank coins from a silver rod, in contrast with the old practice of stamping them out from sheets; this technique proved to be efficient. The practice of minting coins with the moneyer's name on it became obsolete under Edward's rule because England's mint administration became far more centralized under the Crown's authority. During this time, English coins were frequently counterfeited in foreign places, especially the Low Countries, and despite a ban in 1283, English coinage was secretly exported to the European continent. In August 1280, Edward forbade the usage of the old Long cross penny, long cross coinage, which forced the populace to switch to the newly-minted versions. Records do not indicate any adverse consequences that resulted from Edward's monetary reforms; on the contrary, the coinage overhaul successfully provided England with a stable currency.
Later reign, 1297–1307
Constitutional crisis
The incessant warfare of the 1290s put a great financial demand on Edward's subjects. Whereas the King had levied only three lay subsidies until 1294, four such taxes were granted in the years 1294–97, raising over £200,000. Along with this came the burden of prises, seizure of wool and hides, and the unpopular additional duty on wool, dubbed the ''maltolt'' ("unjustly taken"). The fiscal demands on the King's subjects caused resentment, and this resentment eventually led to serious political opposition. The initial resistance was caused not by the lay taxes, however, but by clerical subsidies. In 1294, Edward made a demand of a grant of one half of all clerical revenues. There was some resistance, but the King responded by threatening with outlawry, and the grant was eventually made. At the time, the Archbishop of Canterbury, archbishopric of Canterbury was vacant, since Robert Winchelsey was in Italy to receive consecration. Winchelsey returned in January 1295 and had to consent to another grant in November of that year. In 1296, however, his position changed when he received the papal bull ''Clericis laicos''. This bull prohibited the clergy from paying taxes to lay authorities without explicit consent from the Pope. When the clergy, with reference to the bull, refused to pay, Edward responded with outlawry. Winchelsey was presented with a dilemma between loyalty to the King and upholding the papal bull, and he responded by leaving it to every individual clergyman to pay as he saw fit. By the end of the year, a solution was offered by the new papal bull ''Etsi de statu'', which allowed clerical taxation in cases of pressing urgency. Opposition from the laity took longer to surface. This resistance focused on two things: the King's right to demand military service and his right to levy taxes. At the Salisbury parliament of February 1297, Earl Marshal Roger Bigod, 5th Earl of Norfolk, objected to a royal summons of military service. Bigod argued that the military obligation only extended to service alongside the King; if the King intended to sail to Flanders, he could not send his subjects to Gascony. In July, Bigod and Humphrey de Bohun, 3rd Earl of Hereford and Constable of England, drew up a series of complaints known as the Remonstrances, in which objections to the extortionate level of taxation were voiced. Undeterred, Edward requested another lay subsidy. This one was particularly provocative, because the King had sought consent from only a small group of magnates, rather than from representatives from the communities in parliament. While Edward was in Winchelsea, preparing for the English expedition to Flanders (1297–98), campaign in Flanders, Bigod and Bohun turned up at the Exchequer to prevent the collection of the tax. As the King left the country with a greatly reduced force, the kingdom seemed to be on the verge of civil war. What resolved the situation was the English defeat by the Scots at the Battle of Stirling Bridge. The renewed threat to the homeland gave king and magnates common cause. Edward signed the ''Confirmatio cartarum''a confirmation of ''Magna Carta
(Medieval Latin for "Great Charter of Freedoms"), commonly called (also ''Magna Charta''; "Great Charter"), is a royal charter of rights agreed to by King John of England at Runnymede, near Windsor, on 15 June 1215. First drafted by the ...
'' and its accompanying Charter of the Forestand the nobility agreed to serve with the King on a campaign in Scotland.
Edward's problems with the opposition did not end with the Falkirk campaign. Over the following years he would be held to the promises he had made, in particular that of upholding the Charter of the Forest. In the parliament of 1301, the King was forced to order an assessment of the royal forests, but in 1305 he obtained a papal bull that freed him from this concession. Ultimately, it was a failure in personnel that spelt the end of the opposition against Edward. Bohun died late in 1298, after returning from the Falkirk campaign. In 1302 Bigod arrived at an agreement with the King that was beneficial for both: Bigod, who had no children, made Edward his heir, in return for a generous annual grant. Edward finally got his revenge on Winchelsey in 1305, when Clement V was elected pope. Clement was a Gascon sympathetic to the King, and on Edward's instigation had Winchelsey suspended from office.
Return to Scotland
Edward had reason to believe that he had completed the conquest of Scotland when he left the country in 1296, but resistance soon emerged under the leadership of Andrew de Moray in the north and William Wallace in the south. On 11 September 1297, a large English force under the leadership ofJohn de Warenne, 6th Earl of Surrey
John de Warenne, 6th Earl of Surrey (123127 September 1304) was a prominent English nobleman and military commander during the reigns of Henry III of England and Edward I of England. During the Second Barons' War he switched sides twice, end ...
, and Hugh de Cressingham was routed by a much smaller Scottish army led by Wallace and Moray at Battle of Stirling Bridge, Stirling Bridge. The defeat sent shockwaves into England, and preparations for a retaliatory campaign started immediately. Soon after Edward returned from Flanders, he headed north. On 22 July 1298, in the only major battle he had fought since Evesham in 1265, Edward defeated Wallace's forces at the Battle of Falkirk (1298), Battle of Falkirk. Edward, however, was not able to take advantage of the momentum, and the next year the Scots managed to recapture Stirling Castle. Even though Edward campaigned in Scotland both in 1300, when he successfully besieged Caerlaverock Castle and in 1301, the Scots refused to engage in open battle again, preferring instead to raid the English countryside in smaller groups.
The defeated Scots appealed to Pope Boniface VIII to assert a claim of overlordship to Scotland in place of the English. His papal bull addressed to King Edward in these terms was firmly rejected on Edward's behalf by the Barons' Letter of 1301. The English managed to subdue the country by other means, however. In 1303, a peace agreement was reached between England and France, effectively breaking up the Franco-Scottish alliance. Robert the Bruce, the grandson of the claimant to the crown in 1291, had sided with the English in the winter of 1301–02. By 1304, most of the other nobles of the country had also pledged their allegiance to Edward, and this year the English also managed to re-take Stirling Castle. A great propaganda victory was achieved in 1305 when Wallace was betrayed by Sir John de Menteith and turned over to the English, who had him taken to London where he was publicly executed. With Scotland largely under English control, Edward installed Englishmen and collaborating Scots to govern the country.
The situation changed again on 10 February 1306, when Robert the Bruce murdered his rival John Comyn III of Badenoch, John Comyn, and a few weeks later, on 25 March, was crowned King of Scotland by Isobel, sister of the Earl of Buchan. Bruce now embarked on a campaign to restore Scottish independence, and this campaign took the English by surprise. Edward was suffering ill health by this time, and instead of leading an expedition himself, he gave different military commands to Aymer de Valence, 2nd Earl of Pembroke, and Henry Percy, 1st Baron Percy, while the main royal army was led by the Prince of Wales. The English initially met with success; on 19 June, Aymer de Valence routed Bruce at the Battle of Methven. Bruce was forced into hiding, while the English forces recaptured their lost territory and castles.
Edward acted with unusual brutality against Bruce's family, allies, and supporters. His sister, Mary Bruce, Mary, was imprisoned in a cage at Roxburgh Castle for four years. Isabella MacDuff, Countess of Buchan, who had crowned Bruce, was held in a cage at Berwick Castle. His younger brother Nigel de Brus, Neil was executed by being hanged, drawn, and quartered; he had been captured after he and his garrison held off Edward's forces who had been seeking his wife Elizabeth, daughter Marjorie Bruce, Marjorie, sisters Mary and Christina, and Isabella.
It was clear that Edward now regarded the struggle not as a war between two nations, but as the suppression of a rebellion of disloyal subjects. This brutality, though, rather than helping to subdue the Scots, had the opposite effect, and rallied growing support for Bruce.
Death and burial
 In February 1307, Bruce resumed his efforts and started gathering men, and in May he defeated Valence at the Battle of Loudoun Hill. Edward, who had rallied somewhat, now moved north himself. On the way, however, he developed dysentery, and his condition deteriorated. On 6 July he encamped at Burgh by Sands, just south of the Scottish border. When his servants came the next morning to lift him up so that he could eat, the King died in their arms.
Various stories emerged about Edward's deathbed wishes; according to one tradition, he requested that his heart be carried to the Holy Land, along with an army to fight the infidels. A more dubious story tells of how he wished for his bones to be carried along on future expeditions against the Scots. Another account of his deathbed scene is more credible; according to one chronicle, Edward gathered around him Henry de Lacy, 3rd Earl of Lincoln; Guy de Beauchamp, 10th Earl of Warwick; Aymer de Valence; and Robert de Clifford, 1st Baron de Clifford, and charged them with looking after his son Edward. In particular they should make sure that Piers Gaveston, whom he had banished earlier that year, was not allowed to return to the country. This wish, however, the son ignored, and had his favourite recalled from exile almost immediately. The new king, Edward II, remained in the north until August, but then abandoned the campaign and headed south, partially due to financial limitations. He was crowned king on 25 February 1308.
In February 1307, Bruce resumed his efforts and started gathering men, and in May he defeated Valence at the Battle of Loudoun Hill. Edward, who had rallied somewhat, now moved north himself. On the way, however, he developed dysentery, and his condition deteriorated. On 6 July he encamped at Burgh by Sands, just south of the Scottish border. When his servants came the next morning to lift him up so that he could eat, the King died in their arms.
Various stories emerged about Edward's deathbed wishes; according to one tradition, he requested that his heart be carried to the Holy Land, along with an army to fight the infidels. A more dubious story tells of how he wished for his bones to be carried along on future expeditions against the Scots. Another account of his deathbed scene is more credible; according to one chronicle, Edward gathered around him Henry de Lacy, 3rd Earl of Lincoln; Guy de Beauchamp, 10th Earl of Warwick; Aymer de Valence; and Robert de Clifford, 1st Baron de Clifford, and charged them with looking after his son Edward. In particular they should make sure that Piers Gaveston, whom he had banished earlier that year, was not allowed to return to the country. This wish, however, the son ignored, and had his favourite recalled from exile almost immediately. The new king, Edward II, remained in the north until August, but then abandoned the campaign and headed south, partially due to financial limitations. He was crowned king on 25 February 1308.
 Edward I's body was brought south, lying in state at Waltham Abbey, before being buried in Westminster Abbey on 27 October. There are few records of the funeral, which cost £473. Edward's tomb was an unusually plain sarcophagus of Purbeck marble, without the customary royal effigy, possibly the result of the shortage of royal funds after the King's death. The sarcophagus may normally have been covered over with rich cloth, and originally might have been surrounded by carved busts and a devotional religious image, all since lost. The Society of Antiquaries of London opened the tomb in 1774, finding that the body had been well preserved over the preceding 467 years, and took the opportunity to determine the King's original height. Traces of the Latin inscription ''Edwardus Primus Scottorum Malleus hic est, 1308. Pactum Serva'' ("Here is Edward I, Hammer of the Scots, 1308. Keep the Troth") can still be seen painted on the side of the tomb, referring to his vow to avenge the rebellion of Robert Bruce. This resulted in Edward being given the epithet the "Hammer of the Scots" by historians, but is not contemporary in origin, having been added by the Abbot John Feckenham in the 16th century.
Edward I's body was brought south, lying in state at Waltham Abbey, before being buried in Westminster Abbey on 27 October. There are few records of the funeral, which cost £473. Edward's tomb was an unusually plain sarcophagus of Purbeck marble, without the customary royal effigy, possibly the result of the shortage of royal funds after the King's death. The sarcophagus may normally have been covered over with rich cloth, and originally might have been surrounded by carved busts and a devotional religious image, all since lost. The Society of Antiquaries of London opened the tomb in 1774, finding that the body had been well preserved over the preceding 467 years, and took the opportunity to determine the King's original height. Traces of the Latin inscription ''Edwardus Primus Scottorum Malleus hic est, 1308. Pactum Serva'' ("Here is Edward I, Hammer of the Scots, 1308. Keep the Troth") can still be seen painted on the side of the tomb, referring to his vow to avenge the rebellion of Robert Bruce. This resulted in Edward being given the epithet the "Hammer of the Scots" by historians, but is not contemporary in origin, having been added by the Abbot John Feckenham in the 16th century.
Legacy
Historiography
 The first histories of Edward in the 16th and 17th centuries drew primarily on the works of the chroniclers, and made little use of the official records of the period. They limited themselves to general comments on Edward's significance as a monarch, and echoed the chroniclers' praise for his accomplishments. During the 17th century, the lawyer Edward Coke wrote extensively about Edward's legislation, terming the king the "English Justinian" after the renowned Byzantine lawmaker Justinian I. Later in the century, historians used the available record evidence to address the role of parliament and kingship under Edward, drawing comparisons between his reign and the political strife of their own century. Eighteenth-century historians established a picture of Edward as an able, if ruthless, monarch, conditioned by the circumstances of his own time.
The influential Victorian historian William Stubbs instead suggested that Edward had actively shaped national history, forming English laws and institutions, and helping England to develop a parliamentary and constitutional monarchy. His strengths and weaknesses as a ruler were considered to be emblematic of the English people as a whole. Stubbs' student, Thomas Tout, initially adopted the same perspective, but after extensive research into Edward's royal household, and backed by the research of his contemporaries into the early parliaments of the period, he changed his mind. Tout came to view Edward as a self-interested, conservative leader, using the parliamentary system as "the shrewd device of an autocrat, anxious to use the mass of the people as a check upon his hereditary foes among the greater baronage."
Historians in the 20th and 21st century have conducted extensive research on Edward and his reign. Most have concluded this was a highly significant period in English medieval history, some going further and describing Edward as one of the great medieval kings, although most also agree that his final years were less successful than his early decades in power. Three major academic narratives of Edward have been produced during this period. F. M. Powicke's volumes, published in 1947 and 1953, forming the standard works on Edward for several decades, were largely positive in praising the achievements of his reign, and in particular his focus on justice and the law. In 1988,
The first histories of Edward in the 16th and 17th centuries drew primarily on the works of the chroniclers, and made little use of the official records of the period. They limited themselves to general comments on Edward's significance as a monarch, and echoed the chroniclers' praise for his accomplishments. During the 17th century, the lawyer Edward Coke wrote extensively about Edward's legislation, terming the king the "English Justinian" after the renowned Byzantine lawmaker Justinian I. Later in the century, historians used the available record evidence to address the role of parliament and kingship under Edward, drawing comparisons between his reign and the political strife of their own century. Eighteenth-century historians established a picture of Edward as an able, if ruthless, monarch, conditioned by the circumstances of his own time.
The influential Victorian historian William Stubbs instead suggested that Edward had actively shaped national history, forming English laws and institutions, and helping England to develop a parliamentary and constitutional monarchy. His strengths and weaknesses as a ruler were considered to be emblematic of the English people as a whole. Stubbs' student, Thomas Tout, initially adopted the same perspective, but after extensive research into Edward's royal household, and backed by the research of his contemporaries into the early parliaments of the period, he changed his mind. Tout came to view Edward as a self-interested, conservative leader, using the parliamentary system as "the shrewd device of an autocrat, anxious to use the mass of the people as a check upon his hereditary foes among the greater baronage."
Historians in the 20th and 21st century have conducted extensive research on Edward and his reign. Most have concluded this was a highly significant period in English medieval history, some going further and describing Edward as one of the great medieval kings, although most also agree that his final years were less successful than his early decades in power. Three major academic narratives of Edward have been produced during this period. F. M. Powicke's volumes, published in 1947 and 1953, forming the standard works on Edward for several decades, were largely positive in praising the achievements of his reign, and in particular his focus on justice and the law. In 1988, Michael Prestwich
Michael Charles Prestwich OBE (born 30 January 1943) is an English historian, specialising on the history of medieval England, in particular the reign of Edward I. He is retired, having been Professor of History at Durham University and Head ...
produced an authoritative biography of the King, focusing on his political career, still portraying him in sympathetic terms, but highlighting some of the consequences of his failed policies. Marc Morris (historian), Marc Morris's biography followed in 2008, drawing out more of the detail of Edward's personality, and generally taking a harsher view of his weaknesses and less pleasant characteristics. Considerable academic debate has taken place around the character of Edward's kingship, his political skills, and in particular his management of his earls, and the degree to which this was collaborative or repressive in nature.
There is also a great difference between English and Scottish historiography on King Edward. G. W. S. Barrow, in his biography of Robert the Bruce, accused Edward of ruthlessly exploiting the leaderless state of Scotland to obtain a feudal superiority over the kingdom followed by his determination to reduce it to nothing more than an English possession. The same view of Edward as a conquering tyrant is presented in Evan Macleod Barron's massive overview of the Scottish War of Independence.
Family
First marriage
 By his first wife Eleanor of Castile, Edward had at least fourteen children, perhaps as many as sixteen. Of these, five daughters survived into adulthood, but only one son outlived his father, becoming King Edward II (1307–1327). Edward's children with Eleanor were:
#Katherine (1261 or 1263 – September 1264)
#Joan (1265 – before 7 September 1265)
#John (10 July 1266 – 3 August 1271)
#
By his first wife Eleanor of Castile, Edward had at least fourteen children, perhaps as many as sixteen. Of these, five daughters survived into adulthood, but only one son outlived his father, becoming King Edward II (1307–1327). Edward's children with Eleanor were:
#Katherine (1261 or 1263 – September 1264)
#Joan (1265 – before 7 September 1265)
#John (10 July 1266 – 3 August 1271)
#Henry
Henry may refer to:
People
*Henry (given name)
* Henry (surname)
* Henry Lau, Canadian singer and musician who performs under the mononym Henry
Royalty
* Portuguese royalty
** King-Cardinal Henry, King of Portugal
** Henry, Count of Portugal, ...
(6 May 1268 – 14 October 1274)
#Eleanor of England (1269–1298), Eleanor (18 June 1269 – 19 August 1298)
#Unnamed daughter (1271 – 1271 or 1272)
#Joan of Acre, Joan (1272 – 23 April 1307)
#Alphonso, Earl of Chester, Alphonso (24 November 1273 – 19 August 1284)
#Margaret of England (1275–1333), Margaret (c.15 March 1275 – after 11 March 1333)
#Berengaria (May 1276 – between 1277 and 1278)
#Unnamed child (January 1278 – 1278)
#Mary of Woodstock, Mary (11 March 1278 – before 8 July 1332)
#Elizabeth of Rhuddlan, Elizabeth (August 1282 – )
#Edward II (25 April 1284 – 21 September 1327)
Second marriage
By Margaret of France, Queen of England , Margaret of France, Edward had two sons, both of whom lived to adulthood, and a daughter who died as a child. The Hailes Abbey chronicle indicates that John Botetourt may have been Edward's illegitimate son; however, the claim is unsubstantiated. His progeny by Margaret of France were: #Thomas of Brotherton, 1st Earl of Norfolk, Thomas (1 June 1300 – 4 August 1338) #Edmund of Woodstock, 1st Earl of Kent, Edmund (5 August 1301 – 19 March 1330) #Eleanor (4 May 1306 – August 1311)Genealogical table
See also
* List of earls in the reign of Edward I of England * Savoyard knights in the service of Edward INotes
References
Bibliography
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *External links
Edward I
at the Royal Family website * *
Edward I
from the online ''Encyclopædia Britannica''. {{DEFAULTSORT:Edward 01 Of England Edward I of England, 1239 births 1307 deaths 13th-century English monarchs 14th-century English monarchs Burials at Westminster Abbey Christians of Lord Edward's crusade English people of French descent High Sheriffs of Bedfordshire High Sheriffs of Buckinghamshire Lords Warden of the Cinque Ports People from Westminster English people of the Wars of Scottish Independence People of the Barons' Wars Deaths from dysentery 13th-century peers of France 14th-century peers of France Earls of Chester Competitors for the Crown of Scotland House of Plantagenet Antisemitism in England Children of Henry III of England Sons of kings Victims of the Order of Assassins