Edinburgh University RFC Players on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Edinburgh ( ; gd, Dùn Èideann ) is the
 The city is affectionately nicknamed ''Auld Reekie'', Scots for ''Old Smoky'', for the views from the country of the smoke-covered Old Town.
A remark on a poem in an 1800 collection of the poems of Allan Ramsay said, "Auld Reeky. A name the country people give Edinburgh from the cloud of smoke or reek that is always impending over it."
The city is affectionately nicknamed ''Auld Reekie'', Scots for ''Old Smoky'', for the views from the country of the smoke-covered Old Town.
A remark on a poem in an 1800 collection of the poems of Allan Ramsay said, "Auld Reeky. A name the country people give Edinburgh from the cloud of smoke or reek that is always impending over it."
 The earliest known human habitation in the Edinburgh area was at
The earliest known human habitation in the Edinburgh area was at
 In 1603, King
In 1603, King
 Following the
Following the
 Despite an enduring myth to the contrary, Edinburgh became an industrial centre with its traditional industries of printing, brewing and distilling continuing to grow in the 19th century and joined by new industries such as rubber works, engineering works and others. By 1821, Edinburgh had been overtaken by
Despite an enduring myth to the contrary, Edinburgh became an industrial centre with its traditional industries of printing, brewing and distilling continuing to grow in the 19th century and joined by new industries such as rubber works, engineering works and others. By 1821, Edinburgh had been overtaken by
 Edinburgh is drained by the river named the Water of Leith, which rises at the Colzium Springs in the Pentland Hills and runs for through the south and west of the city, emptying into the Firth of Forth at Leith. The nearest the river gets to the city centre is at Dean Village on the north-western edge of the New Town, where a deep gorge is spanned by Thomas Telford's Dean Bridge, built in 1832 for the road to South Queensferry, Queensferry. The Water of Leith Walkway is a mixed-use trail that follows the course of the river for from Balerno to Leith.
Excepting the shoreline of the Firth of Forth, Edinburgh is encircled by a green belt, designated in 1957, which stretches from Dalmeny in the west to Prestongrange in the east. With an average width of the principal objectives of the green belt were to contain the outward expansion of the city and to prevent the agglomeration of urban areas. Expansion affecting the green belt is strictly controlled but developments such as Edinburgh Airport and the Royal Highland Showground at Ingliston lie within the zone. Similarly, suburbs such as Juniper Green and Balerno are situated on green belt land. One feature of the Edinburgh green belt is the inclusion of parcels of land within the city which are designated green belt, even though they do not connect with the peripheral ring. Examples of these independent wedges of green belt include Holyrood Park and Corstorphine Hill.
Edinburgh is drained by the river named the Water of Leith, which rises at the Colzium Springs in the Pentland Hills and runs for through the south and west of the city, emptying into the Firth of Forth at Leith. The nearest the river gets to the city centre is at Dean Village on the north-western edge of the New Town, where a deep gorge is spanned by Thomas Telford's Dean Bridge, built in 1832 for the road to South Queensferry, Queensferry. The Water of Leith Walkway is a mixed-use trail that follows the course of the river for from Balerno to Leith.
Excepting the shoreline of the Firth of Forth, Edinburgh is encircled by a green belt, designated in 1957, which stretches from Dalmeny in the west to Prestongrange in the east. With an average width of the principal objectives of the green belt were to contain the outward expansion of the city and to prevent the agglomeration of urban areas. Expansion affecting the green belt is strictly controlled but developments such as Edinburgh Airport and the Royal Highland Showground at Ingliston lie within the zone. Similarly, suburbs such as Juniper Green and Balerno are situated on green belt land. One feature of the Edinburgh green belt is the inclusion of parcels of land within the city which are designated green belt, even though they do not connect with the peripheral ring. Examples of these independent wedges of green belt include Holyrood Park and Corstorphine Hill.
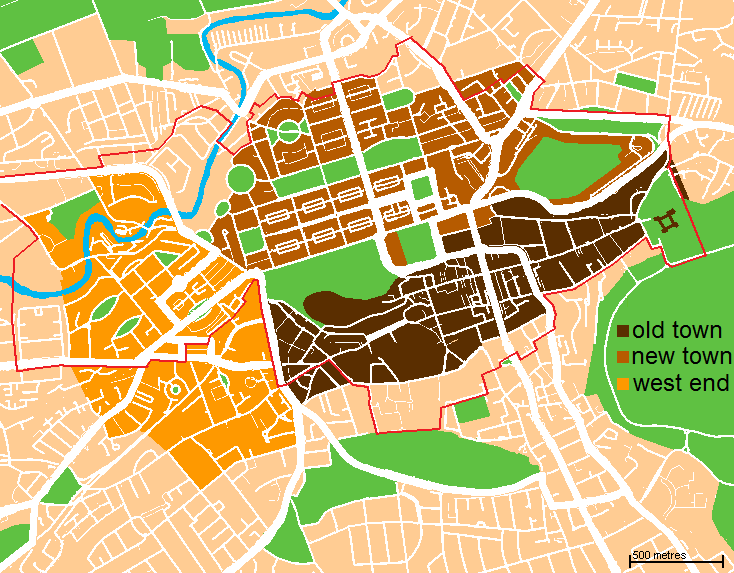 The historic centre of Edinburgh is divided in two by the broad green swathe of Princes Street Gardens. To the south, the view is dominated by Edinburgh Castle, built high on Castle Rock, and the long sweep of the Old Town descending towards Holyrood Palace. To the north lie Princes Street and the New Town.
The West End, Edinburgh, West End includes the financial district, with insurance and banking offices as well as the Edinburgh International Conference Centre.
Edinburgh's Old and New Towns were listed as a UNESCO
The historic centre of Edinburgh is divided in two by the broad green swathe of Princes Street Gardens. To the south, the view is dominated by Edinburgh Castle, built high on Castle Rock, and the long sweep of the Old Town descending towards Holyrood Palace. To the north lie Princes Street and the New Town.
The West End, Edinburgh, West End includes the financial district, with insurance and banking offices as well as the Edinburgh International Conference Centre.
Edinburgh's Old and New Towns were listed as a UNESCO 

 The most recent official population estimates (2020) are for the locality (includes Currie), for the Edinburgh settlement (includes Musselburgh) and for the local authority area.
Edinburgh has a high proportion of young adults, with 19.5% of the population in their 20s (exceeded only by Aberdeen) and 15.2% in their 30s which is the highest in Scotland. The proportion of Edinburgh's population born in the UK fell from 92% to 84% between 2001 and 2011, while the proportion of White Scottish-born fell from 78% to 70%. Of those Edinburgh residents born in the UK, 335,000 or 83% were born in Scotland, with 58,000 or 14% being born in England.
Some 13,000 people or 2.7% of the city's population are of Poles in the United Kingdom, Polish descent. 39,500 people or 8.2% of Edinburgh's population class themselves as Non-White which is an increase from 4% in 2001. Of the Non-White population, the largest group by far are Asian-Scots, Asian, totalling 26,264 people. Within the Asian population, people of British Chinese, Chinese descent are now the largest sub-group, with 8,076 people, amounting to about 1.7% of the city's total population. The city's population of British Indian, Indian descent amounts to 6,470 (1.4% of the total population), while there are some 5,858 of British Pakistanis, Pakistani descent (1.2% of the total population). Although they account for only 1,277 people or 0.3% of the city's population, Edinburgh has the highest number and proportion of people of British Bangladeshi, Bangladeshi descent in Scotland. Over 7,000 people were born in African countries (1.6% of the total population) and nearly 7,000 in the Americas. With the notable exception of Inner London, Edinburgh has a higher number of people born in the United States (over 3,700) than any other city in the UK.
The proportion of people born outside the UK was 15.9% compared with 8% in 2001.
The most recent official population estimates (2020) are for the locality (includes Currie), for the Edinburgh settlement (includes Musselburgh) and for the local authority area.
Edinburgh has a high proportion of young adults, with 19.5% of the population in their 20s (exceeded only by Aberdeen) and 15.2% in their 30s which is the highest in Scotland. The proportion of Edinburgh's population born in the UK fell from 92% to 84% between 2001 and 2011, while the proportion of White Scottish-born fell from 78% to 70%. Of those Edinburgh residents born in the UK, 335,000 or 83% were born in Scotland, with 58,000 or 14% being born in England.
Some 13,000 people or 2.7% of the city's population are of Poles in the United Kingdom, Polish descent. 39,500 people or 8.2% of Edinburgh's population class themselves as Non-White which is an increase from 4% in 2001. Of the Non-White population, the largest group by far are Asian-Scots, Asian, totalling 26,264 people. Within the Asian population, people of British Chinese, Chinese descent are now the largest sub-group, with 8,076 people, amounting to about 1.7% of the city's total population. The city's population of British Indian, Indian descent amounts to 6,470 (1.4% of the total population), while there are some 5,858 of British Pakistanis, Pakistani descent (1.2% of the total population). Although they account for only 1,277 people or 0.3% of the city's population, Edinburgh has the highest number and proportion of people of British Bangladeshi, Bangladeshi descent in Scotland. Over 7,000 people were born in African countries (1.6% of the total population) and nearly 7,000 in the Americas. With the notable exception of Inner London, Edinburgh has a higher number of people born in the United States (over 3,700) than any other city in the UK.
The proportion of people born outside the UK was 15.9% compared with 8% in 2001.
 In 2018, the Church of Scotland had 20,956 members in 71 congregations in the Presbytery of Edinburgh. Its most prominent church is St Giles' on the Royal Mile, first dedicated in 1243 but believed to date from before the 12th century. Saint Giles is historically the patron saint of Edinburgh. St Cuthbert's Church, Edinburgh, St Cuthbert's, situated at the west end of Princes Street Gardens in the shadow of Edinburgh Castle and St Giles' can lay claim to being the oldest Christian sites in the city, though the present St Cuthbert's, designed by Hippolyte Blanc, was dedicated in 1894.
Other Church of Scotland churches include Greyfriars Kirk, the Canongate Kirk, St Andrew's and St George's Church, St Andrew's and St George's West Church and the Edinburgh Barclay Church, Barclay Church. The Church of Scotland Offices are in Edinburgh, as is the General Assembly Hall of the Church of Scotland, Assembly Hall where the annual General Assembly of the Church of Scotland, General Assembly is held.
The Roman Catholic Archdiocese of St Andrews and Edinburgh has 27 parishes across the city. The Archbishop of St Andrews and Edinburgh has his official residence in Greenhill, Edinburgh, Greenhill, the diocesan offices are in nearby Marchmont, and its cathedral is St Mary's Cathedral, Edinburgh (Catholic), St Mary's Cathedral, Edinburgh. The Diocese of Edinburgh of the Scottish Episcopal Church has over 50 churches, half of them in the city. Its centre is the late 19th-century Gothic Revival architecture, Gothic style St Mary's Cathedral, Edinburgh (Episcopal), St Mary's Cathedral in the West End's Palmerston Place. Orthodox Christianity is represented by Pan, Romanian Orthodox Church, Romanian and Russian Orthodox Church, Russian Orthodox churches. There are several independent churches in the city, both Catholic and Protestant, including Charlotte Chapel (Edinburgh), Charlotte Chapel, Carrubbers Christian Centre, Bellevue Chapel and Sacred Heart, Edinburgh, Sacred Heart. There are also churches belonging to Quaker Meeting House, Edinburgh, Quakers, Christadelphians, Seventh-day Adventist Church, Seventh-day Adventists, Church of Christ, Scientist, The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints (LDS Church) and Elim Pentecostal Church.
Muslims have several places of worship across the city. Edinburgh Central Mosque, the largest Islamic place of worship, is located in Potterrow on the city's Southside, near Bristo Square. Construction was largely financed by a gift from King Fahd of Saudi Arabia and was completed in 1998. There is also an Ahmadiyya Muslim community.
The first recorded presence of a History of the Jews in Scotland#17th–19th centuries, Jewish community in Edinburgh dates back to the late 18th century. Edinburgh's Orthodox Judaism, Orthodox synagogue, opened in 1932, is in Salisbury Road and can accommodate a congregation of 2000. A Liberal Judaism (United Kingdom), Liberal Jewish congregation also meets in the city.
A Sikh gurdwara and a Hindu mandir are located in Leith. The city also has a Brahma Kumaris centre in the Polwarth area.
The Edinburgh Buddhist Centre, run by the Triratna Buddhist Community, formerly situated in Melville Terrace, now runs sessions at the Healthy Life Centre, Bread Street. Other Buddhist traditions are represented by groups which meet in the capital: the Community of Interbeing (followers of Thich Nhat Hanh), Rigpa, Samye Dzong, Theravadin, Pure Land Buddhism, Pure Land and Shambhala Buddhism, Shambala. There is a Sōtō Zen Priory in Portobello and a Theravadin Thai Buddhist Monastery in Slateford Road.
Edinburgh is home to a Baháʼí Faith, Baháʼí community, and a Theosophical Society meets in Great King Street.
Edinburgh has an Inter-Faith Association.
Edinburgh has over 39 List of graveyards and cemeteries in Edinburgh, graveyards and cemeteries, many of which are listed and of historical character, including several former church burial grounds. Examples include Old Calton Burial Ground, Greyfriars Kirkyard and Dean Cemetery.
In 2018, the Church of Scotland had 20,956 members in 71 congregations in the Presbytery of Edinburgh. Its most prominent church is St Giles' on the Royal Mile, first dedicated in 1243 but believed to date from before the 12th century. Saint Giles is historically the patron saint of Edinburgh. St Cuthbert's Church, Edinburgh, St Cuthbert's, situated at the west end of Princes Street Gardens in the shadow of Edinburgh Castle and St Giles' can lay claim to being the oldest Christian sites in the city, though the present St Cuthbert's, designed by Hippolyte Blanc, was dedicated in 1894.
Other Church of Scotland churches include Greyfriars Kirk, the Canongate Kirk, St Andrew's and St George's Church, St Andrew's and St George's West Church and the Edinburgh Barclay Church, Barclay Church. The Church of Scotland Offices are in Edinburgh, as is the General Assembly Hall of the Church of Scotland, Assembly Hall where the annual General Assembly of the Church of Scotland, General Assembly is held.
The Roman Catholic Archdiocese of St Andrews and Edinburgh has 27 parishes across the city. The Archbishop of St Andrews and Edinburgh has his official residence in Greenhill, Edinburgh, Greenhill, the diocesan offices are in nearby Marchmont, and its cathedral is St Mary's Cathedral, Edinburgh (Catholic), St Mary's Cathedral, Edinburgh. The Diocese of Edinburgh of the Scottish Episcopal Church has over 50 churches, half of them in the city. Its centre is the late 19th-century Gothic Revival architecture, Gothic style St Mary's Cathedral, Edinburgh (Episcopal), St Mary's Cathedral in the West End's Palmerston Place. Orthodox Christianity is represented by Pan, Romanian Orthodox Church, Romanian and Russian Orthodox Church, Russian Orthodox churches. There are several independent churches in the city, both Catholic and Protestant, including Charlotte Chapel (Edinburgh), Charlotte Chapel, Carrubbers Christian Centre, Bellevue Chapel and Sacred Heart, Edinburgh, Sacred Heart. There are also churches belonging to Quaker Meeting House, Edinburgh, Quakers, Christadelphians, Seventh-day Adventist Church, Seventh-day Adventists, Church of Christ, Scientist, The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints (LDS Church) and Elim Pentecostal Church.
Muslims have several places of worship across the city. Edinburgh Central Mosque, the largest Islamic place of worship, is located in Potterrow on the city's Southside, near Bristo Square. Construction was largely financed by a gift from King Fahd of Saudi Arabia and was completed in 1998. There is also an Ahmadiyya Muslim community.
The first recorded presence of a History of the Jews in Scotland#17th–19th centuries, Jewish community in Edinburgh dates back to the late 18th century. Edinburgh's Orthodox Judaism, Orthodox synagogue, opened in 1932, is in Salisbury Road and can accommodate a congregation of 2000. A Liberal Judaism (United Kingdom), Liberal Jewish congregation also meets in the city.
A Sikh gurdwara and a Hindu mandir are located in Leith. The city also has a Brahma Kumaris centre in the Polwarth area.
The Edinburgh Buddhist Centre, run by the Triratna Buddhist Community, formerly situated in Melville Terrace, now runs sessions at the Healthy Life Centre, Bread Street. Other Buddhist traditions are represented by groups which meet in the capital: the Community of Interbeing (followers of Thich Nhat Hanh), Rigpa, Samye Dzong, Theravadin, Pure Land Buddhism, Pure Land and Shambhala Buddhism, Shambala. There is a Sōtō Zen Priory in Portobello and a Theravadin Thai Buddhist Monastery in Slateford Road.
Edinburgh is home to a Baháʼí Faith, Baháʼí community, and a Theosophical Society meets in Great King Street.
Edinburgh has an Inter-Faith Association.
Edinburgh has over 39 List of graveyards and cemeteries in Edinburgh, graveyards and cemeteries, many of which are listed and of historical character, including several former church burial grounds. Examples include Old Calton Burial Ground, Greyfriars Kirkyard and Dean Cemetery.
 Edinburgh has the strongest economy of any city in the United Kingdom outside London and the highest percentage of professionals in the UK with 43% of the population holding a degree-level or professional qualification. According to the Centre for International Competitiveness, it is the most competitive large city in the United Kingdom. It also has the highest gross value added per employee of any city in the UK outside London, measuring £57,594 in 2010. It was named European ''Best Large City of the Future for Foreign Direct Investment'' and ''Best Large City for Foreign Direct Investment Strategy'' in the'' Financial Times ''fDi magazine awards 2012/13.
In the 19th century, Edinburgh's economy was known for banking and insurance, publishing and printing, and brewing and distilling. Today, its economy is based mainly on financial services, scientific research, higher education, and Tourism in Scotland, tourism. In March 2010, unemployment in Edinburgh was comparatively low at 3.6%, and it remains consistently below the Scottish average of 4.5%. Edinburgh is the second most visited city by foreign visitors in the UK after London.
Banking has been a mainstay of the Edinburgh economy for over 300 years, since the Bank of Scotland was established by an act of the Parliament of Scotland, Scottish Parliament in 1695. Today, the financial services industry, with its particularly strong insurance and investment sectors, and underpinned by Edinburgh-based firms such as Scottish Widows and Standard Life Aberdeen, accounts for the city being the UK's second financial centre after London and Europe's fourth in terms of equity assets. The NatWest Group (formerly Royal Bank of Scotland Group) opened new global headquarters at Gogarburn in the west of the city in October 2005. The city is home to the headquarters of Bank of Scotland, Sainsbury's Bank, Tesco Bank, and TSB Bank (United Kingdom), TSB Bank.
Edinburgh has the strongest economy of any city in the United Kingdom outside London and the highest percentage of professionals in the UK with 43% of the population holding a degree-level or professional qualification. According to the Centre for International Competitiveness, it is the most competitive large city in the United Kingdom. It also has the highest gross value added per employee of any city in the UK outside London, measuring £57,594 in 2010. It was named European ''Best Large City of the Future for Foreign Direct Investment'' and ''Best Large City for Foreign Direct Investment Strategy'' in the'' Financial Times ''fDi magazine awards 2012/13.
In the 19th century, Edinburgh's economy was known for banking and insurance, publishing and printing, and brewing and distilling. Today, its economy is based mainly on financial services, scientific research, higher education, and Tourism in Scotland, tourism. In March 2010, unemployment in Edinburgh was comparatively low at 3.6%, and it remains consistently below the Scottish average of 4.5%. Edinburgh is the second most visited city by foreign visitors in the UK after London.
Banking has been a mainstay of the Edinburgh economy for over 300 years, since the Bank of Scotland was established by an act of the Parliament of Scotland, Scottish Parliament in 1695. Today, the financial services industry, with its particularly strong insurance and investment sectors, and underpinned by Edinburgh-based firms such as Scottish Widows and Standard Life Aberdeen, accounts for the city being the UK's second financial centre after London and Europe's fourth in terms of equity assets. The NatWest Group (formerly Royal Bank of Scotland Group) opened new global headquarters at Gogarburn in the west of the city in October 2005. The city is home to the headquarters of Bank of Scotland, Sainsbury's Bank, Tesco Bank, and TSB Bank (United Kingdom), TSB Bank.
 Tourism is also an important element in the city's economy. As a World Heritage Site, tourists visit historical sites such as Edinburgh Castle, the Palace of Holyroodhouse and the Old and New Towns. Their numbers are augmented in August each year during the Edinburgh Festivals, which attracts 4.4 million visitors, and generates over £100M for the local economy.
As the centre of Scotland's government and Scots law, legal system, the public sector plays a central role in Edinburgh's economy. Many departments of the Scottish Government are in the city. Other major employers include NHS Scotland and local government of Scotland, local government administration. When the £1.3bn Edinburgh & South East Scotland City Region Deal was signed in 2018, the region's Gross Value Added (GVA) contribution to the Economy of Scotland, Scottish economy was cited as £33bn, or 33% of the country's output. The City Region Deal funds a range of "Data Driven Innovation" hubs which are using data to innovate in the region, recognising the region's strengths in technology and data science, the growing importance of the data economy, and the need to tackle the digital skills gap, as a route to social and economic prosperity.
Tourism is also an important element in the city's economy. As a World Heritage Site, tourists visit historical sites such as Edinburgh Castle, the Palace of Holyroodhouse and the Old and New Towns. Their numbers are augmented in August each year during the Edinburgh Festivals, which attracts 4.4 million visitors, and generates over £100M for the local economy.
As the centre of Scotland's government and Scots law, legal system, the public sector plays a central role in Edinburgh's economy. Many departments of the Scottish Government are in the city. Other major employers include NHS Scotland and local government of Scotland, local government administration. When the £1.3bn Edinburgh & South East Scotland City Region Deal was signed in 2018, the region's Gross Value Added (GVA) contribution to the Economy of Scotland, Scottish economy was cited as £33bn, or 33% of the country's output. The City Region Deal funds a range of "Data Driven Innovation" hubs which are using data to innovate in the region, recognising the region's strengths in technology and data science, the growing importance of the data economy, and the need to tackle the digital skills gap, as a route to social and economic prosperity.
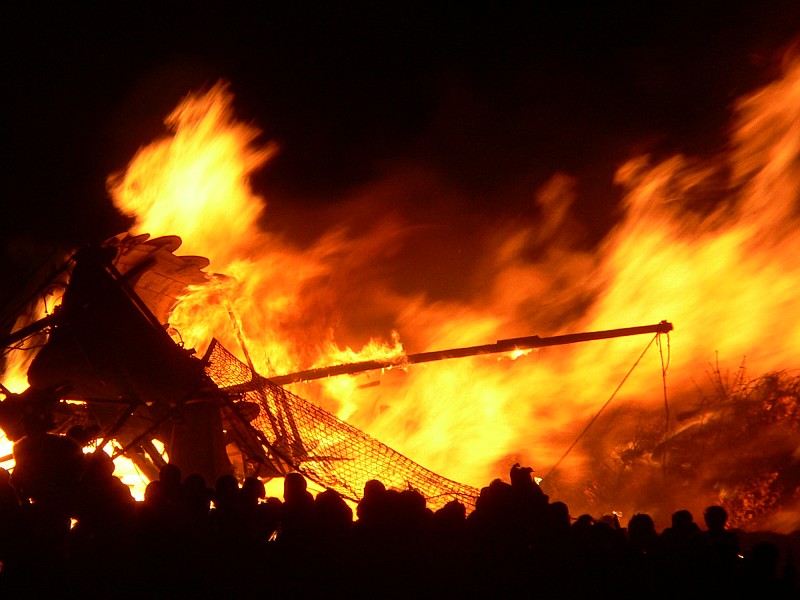 The annual Edinburgh Hogmanay celebration was originally an informal street party focused on the Tron Kirk in the Old Town's High Street. Since 1993, it has been officially organised with the focus moved to Princes Street. In 1996, over 300,000 people attended, leading to ticketing of the main street party in later years up to a limit of 100,000 tickets. Hogmanay now covers four days of processions, concerts and fireworks, with the street party beginning on Hogmanay. Alternative tickets are available for entrance into the Princes Street Gardens concert and Cèilidh, where well-known artists perform and ticket holders can participate in traditional Scottish cèilidh dancing. The event attracts thousands of people from all over the world.
The annual Edinburgh Hogmanay celebration was originally an informal street party focused on the Tron Kirk in the Old Town's High Street. Since 1993, it has been officially organised with the focus moved to Princes Street. In 1996, over 300,000 people attended, leading to ticketing of the main street party in later years up to a limit of 100,000 tickets. Hogmanay now covers four days of processions, concerts and fireworks, with the street party beginning on Hogmanay. Alternative tickets are available for entrance into the Princes Street Gardens concert and Cèilidh, where well-known artists perform and ticket holders can participate in traditional Scottish cèilidh dancing. The event attracts thousands of people from all over the world.
 Outside the Festival season, Edinburgh supports several theatres and production companies. The Royal Lyceum Theatre has its own company, while the King's Theatre, Edinburgh, King's Theatre, Edinburgh Festival Theatre and Edinburgh Playhouse stage large touring shows. The Traverse Theatre presents a more contemporary repertoire. Edinburgh amateur theatre, Amateur theatre companies productions are staged at the Bedlam Theatre, Church Hill Theatre and King's Theatre, Edinburgh, King's Theatre among others.
The Usher Hall is Edinburgh's premier venue for classical music, as well as occasional popular music concerts. It was the venue for the Eurovision Song Contest 1972. Other halls staging music and theatre include The Hub (Edinburgh), The Hub, the Assembly Rooms (Edinburgh), Assembly Rooms and the Queen's Hall, Edinburgh, Queen's Hall. The Scottish Chamber Orchestra is based in Edinburgh.
Outside the Festival season, Edinburgh supports several theatres and production companies. The Royal Lyceum Theatre has its own company, while the King's Theatre, Edinburgh, King's Theatre, Edinburgh Festival Theatre and Edinburgh Playhouse stage large touring shows. The Traverse Theatre presents a more contemporary repertoire. Edinburgh amateur theatre, Amateur theatre companies productions are staged at the Bedlam Theatre, Church Hill Theatre and King's Theatre, Edinburgh, King's Theatre among others.
The Usher Hall is Edinburgh's premier venue for classical music, as well as occasional popular music concerts. It was the venue for the Eurovision Song Contest 1972. Other halls staging music and theatre include The Hub (Edinburgh), The Hub, the Assembly Rooms (Edinburgh), Assembly Rooms and the Queen's Hall, Edinburgh, Queen's Hall. The Scottish Chamber Orchestra is based in Edinburgh.
 Edinburgh has one repertory cinema, The Cameo, Edinburgh, The Cameo, and formerly, the Edinburgh Filmhouse as well as the independent Dominion Cinema and a range of multiplex (cinema), multiplexes.
Edinburgh has a healthy popular music scene. Occasionally large concerts are staged at Murrayfield Stadium, Murrayfield and Meadowbank Stadium, Meadowbank, while mid-sized events take place at smaller venues such as 'The Corn Exchange', 'The Liquid Rooms' and 'The Bongo Club'. In 2010, PRS for Music listed Edinburgh among the UK's top ten 'most musical' cities. Several city pubs are well known for their live performances of folk music. They include 'Sandy Bell's' in Forrest Road, 'Captain's Bar' in South College Street and 'Whistlebinkies' in South Bridge.
Like many other cities in the UK, numerous nightclub venues host Electronic dance music events.
Edinburgh is home to a flourishing group of contemporary composers such as Nigel Osborne, Peter Nelson, Lyell Cresswell, Hafliði Hallgrímsson, Edward Harper, Robert Crawford, Robert Dow and John McLeod (composer), John McLeod. McLeod's music is heard regularly on BBC Radio 3 and throughout the UK.
Edinburgh has one repertory cinema, The Cameo, Edinburgh, The Cameo, and formerly, the Edinburgh Filmhouse as well as the independent Dominion Cinema and a range of multiplex (cinema), multiplexes.
Edinburgh has a healthy popular music scene. Occasionally large concerts are staged at Murrayfield Stadium, Murrayfield and Meadowbank Stadium, Meadowbank, while mid-sized events take place at smaller venues such as 'The Corn Exchange', 'The Liquid Rooms' and 'The Bongo Club'. In 2010, PRS for Music listed Edinburgh among the UK's top ten 'most musical' cities. Several city pubs are well known for their live performances of folk music. They include 'Sandy Bell's' in Forrest Road, 'Captain's Bar' in South College Street and 'Whistlebinkies' in South Bridge.
Like many other cities in the UK, numerous nightclub venues host Electronic dance music events.
Edinburgh is home to a flourishing group of contemporary composers such as Nigel Osborne, Peter Nelson, Lyell Cresswell, Hafliði Hallgrímsson, Edward Harper, Robert Crawford, Robert Dow and John McLeod (composer), John McLeod. McLeod's music is heard regularly on BBC Radio 3 and throughout the UK.
 Edinburgh has many museums and libraries. These include the
Edinburgh has many museums and libraries. These include the  The council-owned City Art Centre in Market Street mounts regular art exhibitions. Across the road, Fruitmarket Gallery, The Fruitmarket Gallery offers world-class exhibitions of contemporary art, featuring work by British and international artists with both emerging and established international reputations.
The city hosts several of Scotland's galleries and organisations dedicated to contemporary visual art. Significant strands of this infrastructure include Creative Scotland, Edinburgh College of Art, Talbot Rice Gallery (University of Edinburgh), Collective Gallery (based at the City Observatory) and the Edinburgh Annuale.
There are also many small private shops/galleries that provide space to showcase works from local artists.
The council-owned City Art Centre in Market Street mounts regular art exhibitions. Across the road, Fruitmarket Gallery, The Fruitmarket Gallery offers world-class exhibitions of contemporary art, featuring work by British and international artists with both emerging and established international reputations.
The city hosts several of Scotland's galleries and organisations dedicated to contemporary visual art. Significant strands of this infrastructure include Creative Scotland, Edinburgh College of Art, Talbot Rice Gallery (University of Edinburgh), Collective Gallery (based at the City Observatory) and the Edinburgh Annuale.
There are also many small private shops/galleries that provide space to showcase works from local artists.
 Following local government reorganisation in 1996, the City of Edinburgh Council constitutes one of the Council areas of Scotland, 32 council areas of Scotland. Like all other local authorities of Scotland, the council has powers over most matters of local administration such as housing, planning, Transport in Edinburgh, local transport, parks, economic development and regeneration. The council comprises 63 elected councillors, returned from 17 Wards of the United Kingdom, multi-member electoral wards in the city.
Following the 2007 City of Edinburgh Council election the incumbent Scottish Labour Party, Labour Party lost majority control of the council after 23 years to a Scottish Liberal Democrats, Liberal Democrat/Scottish National Party, SNP coalition.
After the 2017 election, the SNP and Labour formed a coalition administration, which lasted until the next election in 2022.
The 2022 City of Edinburgh Council election resulted in the most politically balanced council in the UK, with 19 SNP, 13 Labour, 12 Liberal Democrat, 10 Green and 9 Conservative councillors. A minority Labour administration was formed, being voted in by Scottish Conservative and Scottish Liberal Democrat councillors. The SNP and Greens presented a coalition agreement, but could not command majority support in the Council. This caused controversy amongst the Scottish Labour Party group for forming an administration supported by Conservatives and led to the suspension of two Labour councillors on the Council for abstaining on the vote to approve the new administration.
The city's Coat of arms of Edinburgh, coat of arms was registered by the Lord Lyon King of Arms in 1732.
Following local government reorganisation in 1996, the City of Edinburgh Council constitutes one of the Council areas of Scotland, 32 council areas of Scotland. Like all other local authorities of Scotland, the council has powers over most matters of local administration such as housing, planning, Transport in Edinburgh, local transport, parks, economic development and regeneration. The council comprises 63 elected councillors, returned from 17 Wards of the United Kingdom, multi-member electoral wards in the city.
Following the 2007 City of Edinburgh Council election the incumbent Scottish Labour Party, Labour Party lost majority control of the council after 23 years to a Scottish Liberal Democrats, Liberal Democrat/Scottish National Party, SNP coalition.
After the 2017 election, the SNP and Labour formed a coalition administration, which lasted until the next election in 2022.
The 2022 City of Edinburgh Council election resulted in the most politically balanced council in the UK, with 19 SNP, 13 Labour, 12 Liberal Democrat, 10 Green and 9 Conservative councillors. A minority Labour administration was formed, being voted in by Scottish Conservative and Scottish Liberal Democrat councillors. The SNP and Greens presented a coalition agreement, but could not command majority support in the Council. This caused controversy amongst the Scottish Labour Party group for forming an administration supported by Conservatives and led to the suspension of two Labour councillors on the Council for abstaining on the vote to approve the new administration.
The city's Coat of arms of Edinburgh, coat of arms was registered by the Lord Lyon King of Arms in 1732.
 Edinburgh, like all of Scotland, is represented in the
Edinburgh, like all of Scotland, is represented in the
 Travel in Edinburgh is undertaken predominantly by bus. Lothian Buses, the successor company to Edinburgh Corporation Transport Department, operate the majority of public transport bus service, city bus services within the city and to surrounding suburbs, with the most routes running via Princes Street. Services further afield operate from the Edinburgh Bus Station off St Andrew Square, Edinburgh, St Andrew Square and Waterloo Place and are operated mainly by Stagecoach East Scotland, Scottish Citylink, National Express Coaches and Borders Buses.
Lothian Buses and McGill's Scotland East operate the city's branded public tour bus service, tour buses. The night bus service and airport buses are mainly operated by Lothian Buses link. In 2019, Lothian Buses recorded 124.2 million passenger journeys.
To tackle traffic congestion, Edinburgh is now served by six park & ride sites on the periphery of the city at Sheriffhall (in Midlothian), Ingliston, Riccarton, Edinburgh, Riccarton, Inverkeithing (in Fife), Newcraighall and Straiton, Loanhead, Straiton (in Midlothian). A Edinburgh congestion charge#Referendum, referendum of Edinburgh residents in February 2005 rejected a proposal to introduce Edinburgh congestion charge, congestion charging in the city.
Travel in Edinburgh is undertaken predominantly by bus. Lothian Buses, the successor company to Edinburgh Corporation Transport Department, operate the majority of public transport bus service, city bus services within the city and to surrounding suburbs, with the most routes running via Princes Street. Services further afield operate from the Edinburgh Bus Station off St Andrew Square, Edinburgh, St Andrew Square and Waterloo Place and are operated mainly by Stagecoach East Scotland, Scottish Citylink, National Express Coaches and Borders Buses.
Lothian Buses and McGill's Scotland East operate the city's branded public tour bus service, tour buses. The night bus service and airport buses are mainly operated by Lothian Buses link. In 2019, Lothian Buses recorded 124.2 million passenger journeys.
To tackle traffic congestion, Edinburgh is now served by six park & ride sites on the periphery of the city at Sheriffhall (in Midlothian), Ingliston, Riccarton, Edinburgh, Riccarton, Inverkeithing (in Fife), Newcraighall and Straiton, Loanhead, Straiton (in Midlothian). A Edinburgh congestion charge#Referendum, referendum of Edinburgh residents in February 2005 rejected a proposal to introduce Edinburgh congestion charge, congestion charging in the city.
 Edinburgh Waverley railway station, Edinburgh Waverley is the second-busiest railway station in Scotland, with only Glasgow Central railway station, Glasgow Central handling more passengers. On the evidence of passenger entries and exits between April 2015 and March 2016, Edinburgh Waverley is the fifth-busiest station outside London; it is also the UK's second biggest station in terms of the number of platforms and area size. Waverley is the terminus for most trains arriving from London King's Cross railway station, London King's Cross and the departure point for many Rail transport in Scotland, rail services within Scotland operated by ScotRail.
To the west of the city centre lies Haymarket railway station, Haymarket station, which is an important commuter stop. Opened in 2003, Edinburgh Park railway station, Edinburgh Park station serves the Gyle business park in the west of the city and the nearby Gogarburn headquarters of the Royal Bank of Scotland. The Edinburgh Crossrail route connects Edinburgh Park with Haymarket, Edinburgh Waverley and the suburban stations of Brunstane railway station, Brunstane and Newcraighall railway station, Newcraighall in the east of the city. There are also commuter lines to Edinburgh Gateway, South Gyle and Dalmeny, the latter serving South Queensferry by the Forth Bridges, and to Wester Hailes and Curriehill in the south-west of the city.
Edinburgh Waverley railway station, Edinburgh Waverley is the second-busiest railway station in Scotland, with only Glasgow Central railway station, Glasgow Central handling more passengers. On the evidence of passenger entries and exits between April 2015 and March 2016, Edinburgh Waverley is the fifth-busiest station outside London; it is also the UK's second biggest station in terms of the number of platforms and area size. Waverley is the terminus for most trains arriving from London King's Cross railway station, London King's Cross and the departure point for many Rail transport in Scotland, rail services within Scotland operated by ScotRail.
To the west of the city centre lies Haymarket railway station, Haymarket station, which is an important commuter stop. Opened in 2003, Edinburgh Park railway station, Edinburgh Park station serves the Gyle business park in the west of the city and the nearby Gogarburn headquarters of the Royal Bank of Scotland. The Edinburgh Crossrail route connects Edinburgh Park with Haymarket, Edinburgh Waverley and the suburban stations of Brunstane railway station, Brunstane and Newcraighall railway station, Newcraighall in the east of the city. There are also commuter lines to Edinburgh Gateway, South Gyle and Dalmeny, the latter serving South Queensferry by the Forth Bridges, and to Wester Hailes and Curriehill in the south-west of the city.
 Edinburgh Trams became operational on 31 May 2014. The city had been without a tram system since Edinburgh Corporation Tramways ceased on 16 November 1956. Following parliamentary approval in 2007, construction began in early 2008. The first stage of the project was expected to be completed by July 2011 but, following delays caused by extra utility work and a long-running contractual dispute between the council and the main contractor, Bilfinger SE, the project was rescheduled. The completed line is in length, running from Edinburgh Airport tram stop, Edinburgh Airport, west of the city, to its terminus at York Place tram stop, York Place in the city centre's East End. Phase two of the tram project, which sees the existing section of Line 1 (Airport to York Place) tram line extended down Leith Walk to Ocean Terminal, Edinburgh, Ocean Terminal and terminate at Newhaven, Edinburgh, Newhaven, adding an additional eight new tram stops and connecting Leith and the waterfront to the tram system. As of August 2022 this project is currently nearing completion, and is scheduled to open to passenger use in spring 2023.
Should the original plan be taken to completion, trams will also run from Haymarket through Ravelston and Craigleith, Edinburgh, Craigleith to Granton, Edinburgh, Granton Square on the Waterfront Edinburgh. Proposals for new tram lines in Edinburgh, Long-term proposals envisage a line running west from the airport to Ratho and Newbridge, Edinburgh, Newbridge and another connecting Granton Square to Newhaven via Lower Granton Road, thus completing the Line 1 (North Edinburgh) loop. A further line serving the south of the city has also been suggested.
Edinburgh Trams became operational on 31 May 2014. The city had been without a tram system since Edinburgh Corporation Tramways ceased on 16 November 1956. Following parliamentary approval in 2007, construction began in early 2008. The first stage of the project was expected to be completed by July 2011 but, following delays caused by extra utility work and a long-running contractual dispute between the council and the main contractor, Bilfinger SE, the project was rescheduled. The completed line is in length, running from Edinburgh Airport tram stop, Edinburgh Airport, west of the city, to its terminus at York Place tram stop, York Place in the city centre's East End. Phase two of the tram project, which sees the existing section of Line 1 (Airport to York Place) tram line extended down Leith Walk to Ocean Terminal, Edinburgh, Ocean Terminal and terminate at Newhaven, Edinburgh, Newhaven, adding an additional eight new tram stops and connecting Leith and the waterfront to the tram system. As of August 2022 this project is currently nearing completion, and is scheduled to open to passenger use in spring 2023.
Should the original plan be taken to completion, trams will also run from Haymarket through Ravelston and Craigleith, Edinburgh, Craigleith to Granton, Edinburgh, Granton Square on the Waterfront Edinburgh. Proposals for new tram lines in Edinburgh, Long-term proposals envisage a line running west from the airport to Ratho and Newbridge, Edinburgh, Newbridge and another connecting Granton Square to Newhaven via Lower Granton Road, thus completing the Line 1 (North Edinburgh) loop. A further line serving the south of the city has also been suggested.
 Lothian Buses and Edinburgh Trams are both owned and operated by Transport for Edinburgh.
Despite its modern transport links, Edinburgh has been named the most congested city in the UK for the fourth year running.
Lothian Buses and Edinburgh Trams are both owned and operated by Transport for Edinburgh.
Despite its modern transport links, Edinburgh has been named the most congested city in the UK for the fourth year running.
 There are three universities in Edinburgh: the
There are three universities in Edinburgh: the
 The main NHS Lothian hospitals serving the Edinburgh area are the Royal Infirmary of Edinburgh, which includes the University of Edinburgh Medical School, and the Western General Hospital, which has a large cancer treatment centre and nurse-led Minor Injuries Clinic. The Royal Edinburgh Hospital in Morningside specialises in mental health. The Royal Hospital for Children and Young People, colloquially referred to as ''the Sick Kids'', is a specialist paediatrics hospital.
There are two private hospitals: Murrayfield Hospital in the west of the city and Shawfair Hospital in the south; both are owned by Spire Healthcare.
The main NHS Lothian hospitals serving the Edinburgh area are the Royal Infirmary of Edinburgh, which includes the University of Edinburgh Medical School, and the Western General Hospital, which has a large cancer treatment centre and nurse-led Minor Injuries Clinic. The Royal Edinburgh Hospital in Morningside specialises in mental health. The Royal Hospital for Children and Young People, colloquially referred to as ''the Sick Kids'', is a specialist paediatrics hospital.
There are two private hospitals: Murrayfield Hospital in the west of the city and Shawfair Hospital in the south; both are owned by Spire Healthcare.
Tynecastle Park, January 2018.jpg, Tynecastle Park
Easter Road 2010.JPG, Easter Road Stadium
A pot of gold... - geograph.org.uk - 718806.jpg, Murrayfield Stadium
Meadowbank-track-and-field.jpg, Meadowbank Stadium
Loch Ness monster - geograph.org.uk - 1501091.jpg, Edinburgh Marathon
Edinburgh Capitals vs Belfast Giants.jpg, Murrayfield Ice Rink
 Edinburgh has a long literary tradition, which became especially evident during the
Edinburgh has a long literary tradition, which became especially evident during the  Scotland has a rich history of science and engineering, with Edinburgh producing a number of leading figures. John Napier, inventor of logarithms, was born in Merchiston Tower and lived and died in the city. His house now forms part of the original campus of Napier University which was named in his honour. He lies buried under St. Cuthbert's Church. James Clerk Maxwell, founder of the modern theory of electromagnetism, was born at 14 India Street (now the home of the James Clerk Maxwell Foundation) and educated at the Edinburgh Academy and the University of Edinburgh, as was the engineer and telephone pioneer Alexander Graham Bell. James Braidwood (firefighter), James Braidwood, who organised Britain's first municipal fire brigade, was also born in the city and began his career there.
Other names connected with the city include physicist Max Born, a principle founder of Quantum mechanics and Nobel Prize in Physics, Nobel laureate; Charles Darwin, the biologist who propounded the theory of natural selection; David Hume, philosopher, economist and historian;
Scotland has a rich history of science and engineering, with Edinburgh producing a number of leading figures. John Napier, inventor of logarithms, was born in Merchiston Tower and lived and died in the city. His house now forms part of the original campus of Napier University which was named in his honour. He lies buried under St. Cuthbert's Church. James Clerk Maxwell, founder of the modern theory of electromagnetism, was born at 14 India Street (now the home of the James Clerk Maxwell Foundation) and educated at the Edinburgh Academy and the University of Edinburgh, as was the engineer and telephone pioneer Alexander Graham Bell. James Braidwood (firefighter), James Braidwood, who organised Britain's first municipal fire brigade, was also born in the city and began his career there.
Other names connected with the city include physicist Max Born, a principle founder of Quantum mechanics and Nobel Prize in Physics, Nobel laureate; Charles Darwin, the biologist who propounded the theory of natural selection; David Hume, philosopher, economist and historian;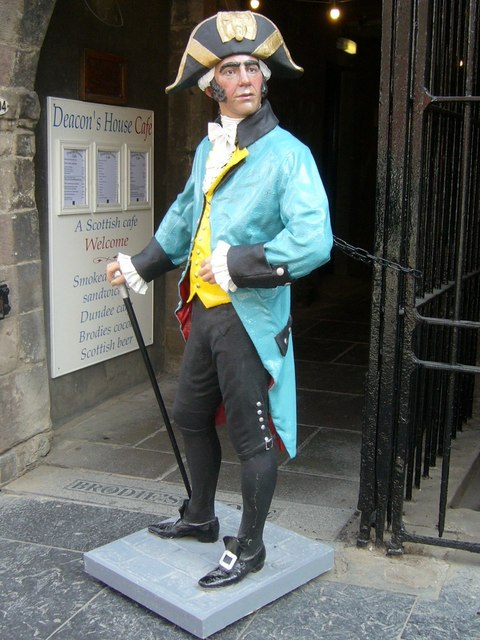  Edinburgh has been the birthplace of actors like Alastair Sim and Sir Sean Connery, known for being the first cinematic James Bond, the comedian and actor Ronnie Corbett, best known as one of The Two Ronnies, and the impressionist Rory Bremner. Famous artists from the city include the portrait painters Sir Henry Raeburn, Sir David Wilkie (artist), David Wilkie and Allan Ramsay (artist), Allan Ramsay.
The city has produced or been home to some very successful musicians in recent decades, particularly Ian Anderson, front man of the band Jethro Tull (band), Jethro Tull, The Incredible String Band, the folk duo The Corries, Wattie Buchan, lead singer and founding member of punk band The Exploited, Shirley Manson, lead singer of the band Garbage (band), Garbage, the Bay City Rollers, The Proclaimers, Boards of Canada and Idlewild (band), Idlewild.
Edinburgh has been the birthplace of actors like Alastair Sim and Sir Sean Connery, known for being the first cinematic James Bond, the comedian and actor Ronnie Corbett, best known as one of The Two Ronnies, and the impressionist Rory Bremner. Famous artists from the city include the portrait painters Sir Henry Raeburn, Sir David Wilkie (artist), David Wilkie and Allan Ramsay (artist), Allan Ramsay.
The city has produced or been home to some very successful musicians in recent decades, particularly Ian Anderson, front man of the band Jethro Tull (band), Jethro Tull, The Incredible String Band, the folk duo The Corries, Wattie Buchan, lead singer and founding member of punk band The Exploited, Shirley Manson, lead singer of the band Garbage (band), Garbage, the Bay City Rollers, The Proclaimers, Boards of Canada and Idlewild (band), Idlewild.
 Edinburgh is the birthplace of former British Prime Minister Tony Blair who attended the city's Fettes College.
Notorious criminals from Edinburgh's past include Deacon Brodie, head of a trades guild and Edinburgh city councillor by day but a burglar by night, who is said to have been the inspiration for Robert Louis Stevenson's story, the ''Strange Case of Dr Jekyll and Mr Hyde'', and murderers Burke and Hare who delivered fresh corpses for dissection to the famous anatomist Robert Knox.
Another well-known Edinburgh resident was Greyfriars Bobby. The small Skye Terrier reputedly kept vigil over his dead master's grave in Greyfriars Kirkyard for 14 years in the 1860s and 1870s, giving rise to a story of canine devotion which plays a part in attracting visitors to the city.
Edinburgh is the birthplace of former British Prime Minister Tony Blair who attended the city's Fettes College.
Notorious criminals from Edinburgh's past include Deacon Brodie, head of a trades guild and Edinburgh city councillor by day but a burglar by night, who is said to have been the inspiration for Robert Louis Stevenson's story, the ''Strange Case of Dr Jekyll and Mr Hyde'', and murderers Burke and Hare who delivered fresh corpses for dissection to the famous anatomist Robert Knox.
Another well-known Edinburgh resident was Greyfriars Bobby. The small Skye Terrier reputedly kept vigil over his dead master's grave in Greyfriars Kirkyard for 14 years in the 1860s and 1870s, giving rise to a story of canine devotion which plays a part in attracting visitors to the city.
City of Edinburgh Council website
Marketing Edinburgh
official tourist agency * {{Authority control Edinburgh, Capital cities in the United Kingdom Council areas of Scotland Cities in Scotland Districts of Scotland Feudalism in Scotland Lieutenancy areas of Scotland Port cities and towns in Scotland Port cities and towns of the North Sea Scottish society Populated places established in the 7th century 7th-century establishments in Europe Towns in Edinburgh council area
capital city
A capital city or capital is the municipality holding primary status in a country, state, province, Department (country subdivision), department, or other subnational entity, usually as its seat of the government. A capital is typically a city ...
of Scotland
Scotland (, ) is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. Covering the northern third of the island of Great Britain, mainland Scotland has a border with England to the southeast and is otherwise surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean to the ...
and one of its 32 council areas
For local government purposes, Scotland is divided into 32 areas designated as "council areas" ( gd, comhairlean), which are all governed by single-tier authorities designated as "councils". They have the option under the Local Government (Ga ...
. Historically part of the county of Midlothian
Midlothian (; gd, Meadhan Lodainn) is a historic county, registration county, lieutenancy area and one of 32 council areas of Scotland used for local government. Midlothian lies in the east-central Lowlands, bordering the City of Edinburgh, ...
(interchangeably Edinburghshire before 1921), it is located in Lothian
Lothian (; sco, Lowden, Loudan, -en, -o(u)n; gd, Lodainn ) is a region of the Scottish Lowlands, lying between the southern shore of the Firth of Forth and the Lammermuir Hills and the Moorfoot Hills. The principal settlement is the Sco ...
on the southern shore of the Firth of Forth
The Firth of Forth () is the estuary, or firth, of several Scottish rivers including the River Forth. It meets the North Sea with Fife on the north coast and Lothian on the south.
Name
''Firth'' is a cognate of ''fjord'', a Norse word meani ...
. Edinburgh is Scotland's second-most populous city, after Glasgow
Glasgow ( ; sco, Glesca or ; gd, Glaschu ) is the most populous city in Scotland and the fourth-most populous city in the United Kingdom, as well as being the 27th largest city by population in Europe. In 2020, it had an estimated popul ...
, and the seventh-most populous city in the United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotland, Wales and North ...
.
Recognised as the capital of Scotland since at least the 15th century, Edinburgh is the seat of the Scottish Government, the Scottish Parliament
The Scottish Parliament ( gd, Pàrlamaid na h-Alba ; sco, Scots Pairlament) is the devolved, unicameral legislature of Scotland. Located in the Holyrood area of the capital city, Edinburgh, it is frequently referred to by the metonym Holyro ...
and the highest courts in Scotland. The city's Palace of Holyroodhouse
The Palace of Holyroodhouse ( or ), commonly referred to as Holyrood Palace or Holyroodhouse, is the official residence of the British monarch in Scotland. Located at the bottom of the Royal Mile in Edinburgh, at the opposite end to Edinburgh ...
is the official residence
An official residence is the House, residence of a head of state, head of government, governor, Clergy, religious leader, leaders of international organizations, or other senior figure. It may be the same place where they conduct their work-relate ...
of the British monarchy
The monarchy of the United Kingdom, commonly referred to as the British monarchy, is the constitutional form of government by which a hereditary sovereign reigns as the head of state of the United Kingdom, the Crown Dependencies (the Bailiwi ...
in Scotland. The city has long been a centre of education, particularly in the fields of medicine, Scottish law
Scots law () is the legal system of Scotland. It is a hybrid or mixed legal system containing civil law and common law elements, that traces its roots to a number of different historical sources. Together with English law and Northern Ireland ...
, literature, philosophy, the sciences, and engineering. It is the second-largest financial centre in the United Kingdom, and the city's historical and cultural attractions have made it the UK's second-most visited tourist destination attracting 4.9 million visits, including 2.4 million from overseas in 2018. ''Time Out'' magazine rated Edinburgh the best city in the world in 2022.
Edinburgh's official population estimates are (mid-2020) for the locality
Locality may refer to:
* Locality (association), an association of community regeneration organizations in England
* Locality (linguistics)
* Locality (settlement)
* Suburbs and localities (Australia), in which a locality is a geographic subdivis ...
, (mid-2019) for the City of Edinburgh council area {{Unreferenced, date=May 2019, bot=noref (GreenC bot)
A council area is one of the areas defined in Schedule 1 of the Local Government etc. (Scotland) Act 1994 and is under the control of one of the local authorities in Scotland created by that Act. ...
, which takes in some outlying villages in the western part of its territory, and 1,384,950 (2019) for the wider Edinburgh and South East Scotland city region
City region is a term in use since about 1950 by urbanists, economists and urban planners to mean a metropolitan area and hinterland, often having a shared administration. Typically, it denotes a city, conurbation or urban zone with multiple admi ...
which also includes East Lothian
East Lothian (; sco, East Lowden; gd, Lodainn an Ear) is one of the 32 council areas of Scotland, as well as a historic county, registration county and lieutenancy area. The county was called Haddingtonshire until 1921.
In 1975, the histo ...
, Fife
Fife (, ; gd, Fìobha, ; sco, Fife) is a council area, historic county, registration county and lieutenancy area of Scotland. It is situated between the Firth of Tay and the Firth of Forth, with inland boundaries with Perth and Kinross (i ...
, Midlothian, the Scottish Borders
The Scottish Borders ( sco, the Mairches, 'the Marches'; gd, Crìochan na h-Alba) is one of 32 council areas of Scotland. It borders the City of Edinburgh, Dumfries and Galloway, East Lothian, Midlothian, South Lanarkshire, West Lothi ...
and West Lothian
West Lothian ( sco, Wast Lowden; gd, Lodainn an Iar) is one of the 32 council areas of Scotland, and was one of its shires of Scotland, historic counties. The county was called Linlithgowshire until 1925. The historic county was bounded geogra ...
.
The city is the annual venue of the General Assembly of the Church of Scotland
The General Assembly of the Church of Scotland is the sovereign and highest court of the Church of Scotland, and is thus the Church's governing body.''An Introduction to Practice and Procedure in the Church of Scotland'' by A. Gordon McGillivray ...
. It is home to national cultural institutions such as the National Museum of Scotland
The National Museum of Scotland in Edinburgh, Scotland, was formed in 2006 with the merger of the new Museum of Scotland, with collections relating to Scottish antiquities, culture and history, and the adjacent Royal Scottish Museum (opened in ...
, the National Library of Scotland
The National Library of Scotland (NLS) ( gd, Leabharlann Nàiseanta na h-Alba, sco, Naitional Leebrar o Scotland) is the legal deposit library of Scotland and is one of the country's National Collections. As one of the largest libraries in the ...
and the Scottish National Gallery
The Scottish National Gallery (formerly the National Gallery of Scotland) is the national art gallery of Scotland. It is located on The Mound in central Edinburgh, close to Princes Street. The building was designed in a neoclassical style by W ...
. The University of Edinburgh
The University of Edinburgh ( sco, University o Edinburgh, gd, Oilthigh Dhùn Èideann; abbreviated as ''Edin.'' in post-nominals) is a public research university based in Edinburgh, Scotland. Granted a royal charter by King James VI in 15 ...
, founded in 1582 and now one of three in the city, is considered one of the best research institutions in the world, most recently placing 15th in the ''QS World University Rankings
''QS World University Rankings'' is an annual publication of university rankings by Quacquarelli Symonds (QS). The QS system comprises three parts: the global overall ranking, the subject rankings (which name the world's top universities for the ...
'' for 2023. The city is also known for the Edinburgh International Festival
The Edinburgh International Festival is an annual arts festival in Edinburgh, Scotland, spread over the final three weeks in August. Notable figures from the international world of music (especially classical music) and the performing arts are i ...
and the Fringe
Fringe may refer to:
Arts
* Edinburgh Festival Fringe, the world's largest arts festival, known as "the Fringe"
* Adelaide Fringe, the world's second-largest annual arts festival
* Fringe theatre, a name for alternative theatre
* The Fringe, the ...
, the latter being the world's largest annual international arts festival. Historic sites in Edinburgh include Edinburgh Castle
Edinburgh Castle is a historic castle in Edinburgh, Edinburgh, Scotland. It stands on Castle Rock (Edinburgh), Castle Rock, which has been occupied by humans since at least the Iron Age, although the nature of the early settlement is unclear. ...
, the Palace of Holyroodhouse, the churches of St. Giles
Saint Giles (, la, Aegidius, french: Gilles), also known as Giles the Hermit, was a hermit or monk active in the lower Rhône most likely in the 6th century. Revered as a saint, his cult became widely diffused but his hagiography is mostly lege ...
, Greyfriars and the Canongate
The Canongate is a street and associated district in central Edinburgh, the capital city of Scotland. The street forms the main eastern length of the Royal Mile while the district is the main eastern section of Edinburgh's Old Town. It began ...
, and the extensive Georgian New Town built in the 18th/19th centuries. Edinburgh's Old Town
In a city or town, the old town is its historic or original core. Although the city is usually larger in its present form, many cities have redesignated this part of the city to commemorate its origins after thorough renovations. There are ma ...
and New Town
New is an adjective referring to something recently made, discovered, or created.
New or NEW may refer to:
Music
* New, singer of K-pop group The Boyz
Albums and EPs
* ''New'' (album), by Paul McCartney, 2013
* ''New'' (EP), by Regurgitator, ...
together are listed as a UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization is a specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) aimed at promoting world peace and security through international cooperation in education, arts, sciences and culture. It ...
World Heritage Site
A World Heritage Site is a landmark or area with legal protection by an international convention administered by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO). World Heritage Sites are designated by UNESCO for h ...
, which has been managed by Edinburgh World Heritage
Edinburgh World Heritage (EWH) is an independent charity in Edinburgh, Scotland established in 1999. It is tasked with conserving, enhancing and promoting Edinburgh's World Heritage Site " Old and New Towns of Edinburgh", which was designated in ...
since 1999.
Etymology
"Edin", the root of the city's name, derives from ', the name for this region inCumbric
Cumbric was a variety of the Common Brittonic language spoken during the Early Middle Ages in the ''Hen Ogledd'' or "Old North" in what is now the counties of Westmorland, Cumberland and northern Lancashire in Northern England and the souther ...
, the Brittonic
Brittonic or Brythonic may refer to:
*Common Brittonic, or Brythonic, the Celtic language anciently spoken in Great Britain
*Brittonic languages, a branch of the Celtic languages descended from Common Brittonic
*Britons (Celtic people)
The Br ...
Celtic
Celtic, Celtics or Keltic may refer to:
Language and ethnicity
*pertaining to Celts, a collection of Indo-European peoples in Europe and Anatolia
**Celts (modern)
*Celtic languages
**Proto-Celtic language
* Celtic music
*Celtic nations
Sports Fo ...
language formerly spoken there. The name's meaning is unknown. The district of Eidyn is centred on the stronghold Din Eidyn, the dun
A dun is an ancient or medieval fort. In Ireland and Britain it is mainly a kind of hillfort and also a kind of Atlantic roundhouse.
Etymology
The term comes from Irish language, Irish ''dún'' or Scottish Gaelic ''dùn'' (meaning "fort"), ...
or hillfort
A hillfort is a type of earthwork used as a fortified refuge or defended settlement, located to exploit a rise in elevation for defensive advantage. They are typically European and of the Bronze Age or Iron Age. Some were used in the post-Roma ...
of Eidyn. This stronghold is believed to have been located at Castle Rock, now the site of Edinburgh Castle
Edinburgh Castle is a historic castle in Edinburgh, Edinburgh, Scotland. It stands on Castle Rock (Edinburgh), Castle Rock, which has been occupied by humans since at least the Iron Age, although the nature of the early settlement is unclear. ...
. Eidyn was conquered by the Angles
The Angles ( ang, Ængle, ; la, Angli) were one of the main Germanic peoples who settled in Great Britain in the post-Roman period. They founded several kingdoms of the Heptarchy in Anglo-Saxon England. Their name is the root of the name ' ...
of Bernicia
Bernicia ( ang, Bernice, Bryneich, Beornice; la, Bernicia) was an Anglo-Saxon kingdom established by Anglian settlers of the 6th century in what is now southeastern Scotland and North East England.
The Anglian territory of Bernicia was ap ...
in the 7th century and later occupied by the Scots in the 10th century. As the language shifted to Northumbrian Old English
Northumbrian was a dialect of Old English spoken in the Anglian Kingdom of Northumbria. Together with Mercian, Kentish and West Saxon, it forms one of the sub-categories of Old English devised and employed by modern scholars.
The dialect w ...
, which evolved into Scots, the Brittonic ''din'' in Din Eidyn was replaced by ''burh
A burh () or burg was an Old English fortification or fortified settlement. In the 9th century, raids and invasions by Vikings prompted Alfred the Great to develop a network of burhs and roads to use against such attackers. Some were new constru ...
'', producing ''Edinburgh''. Similarly, ''din'' became ''dùn'' in Scottish Gaelic
Scottish Gaelic ( gd, Gàidhlig ), also known as Scots Gaelic and Gaelic, is a Goidelic language (in the Celtic branch of the Indo-European language family) native to the Gaels of Scotland. As a Goidelic language, Scottish Gaelic, as well as ...
, producing ''Dùn Èideann''.
Nicknames
 The city is affectionately nicknamed ''Auld Reekie'', Scots for ''Old Smoky'', for the views from the country of the smoke-covered Old Town.
A remark on a poem in an 1800 collection of the poems of Allan Ramsay said, "Auld Reeky. A name the country people give Edinburgh from the cloud of smoke or reek that is always impending over it."
The city is affectionately nicknamed ''Auld Reekie'', Scots for ''Old Smoky'', for the views from the country of the smoke-covered Old Town.
A remark on a poem in an 1800 collection of the poems of Allan Ramsay said, "Auld Reeky. A name the country people give Edinburgh from the cloud of smoke or reek that is always impending over it."
Thomas Carlyle
Thomas Carlyle (4 December 17955 February 1881) was a Scottish essayist, historian and philosopher. A leading writer of the Victorian era, he exerted a profound influence on 19th-century art, literature and philosophy.
Born in Ecclefechan, Dum ...
said, "Smoke cloud hangs over old Edinburgh,—for, ever since Aeneas Silvius
Aeneas Silvius (said to have reigned 1110-1079 BC) is the son of Silvius, in some versions grandson of Ascanius and great-grandson, grandson or son of Aeneas. He is the third in the list of the mythical kings of Alba Longa in Latium, and the ...
's time and earlier, the people have the art, very strange to Aeneas, of burning a certain sort of black stones, and Edinburgh with its chimneys is called 'Auld Reekie' by the country people."
A character in Walter Scott
Sir Walter Scott, 1st Baronet (15 August 1771 – 21 September 1832), was a Scottish novelist, poet, playwright and historian. Many of his works remain classics of European and Scottish literature, notably the novels ''Ivanhoe'', ''Rob Roy (n ...
's ''The Abbot
''The Abbot'' (1820) is a historical novel by Sir Walter Scott, one of the Waverley novels. A sequel to ''The Monastery'', its action takes place in 1567 and 1568. It reaches its climax in the escape of Mary, Queen of Scots from Lochleven Castle ...
'' says, "... yonder stands Auld Reekie—you may see the smoke hover over her at twenty miles' distance."
Robert Chambers, who said that the sobriquet could not be traced before the reign of Charles II, attributed the name to a Fife
Fife (, ; gd, Fìobha, ; sco, Fife) is a council area, historic county, registration county and lieutenancy area of Scotland. It is situated between the Firth of Tay and the Firth of Forth, with inland boundaries with Perth and Kinross (i ...
laird, Durham of Largo, who regulated the bedtime of his children by the smoke rising above Edinburgh from the fires of the tenements. "It's time now bairns, to tak' the beuks, and gang to our beds, for yonder's Auld Reekie, I see, putting on her nicht -cap!"
Edinburgh has been popularly called the ''Athens of the North'' since the early 19th century. References to Athens, such as ''Athens of Britain'' and ''Modern Athens'', had been made as early as the 1760s. The similarities were seen to be topographical but also intellectual. Edinburgh's Castle Rock reminded returning grand tourists of the Athenian
Athens ( ; el, Αθήνα, Athína ; grc, Ἀθῆναι, Athênai (pl.) ) is both the capital and largest city of Greece. With a population close to four million, it is also the seventh largest city in the European Union. Athens dominates ...
Acropolis
An acropolis was the settlement of an upper part of an ancient Greek city, especially a citadel, and frequently a hill with precipitous sides, mainly chosen for purposes of defense. The term is typically used to refer to the Acropolis of Athens, ...
, as did aspects of the neoclassical architecture
Neoclassical architecture is an architectural style produced by the Neoclassical movement that began in the mid-18th century in Italy and France. It became one of the most prominent architectural styles in the Western world. The prevailing style ...
and layout of New Town
New is an adjective referring to something recently made, discovered, or created.
New or NEW may refer to:
Music
* New, singer of K-pop group The Boyz
Albums and EPs
* ''New'' (album), by Paul McCartney, 2013
* ''New'' (EP), by Regurgitator, ...
. Both cities had flatter, fertile agricultural land sloping down to a port
A port is a maritime facility comprising one or more wharves or loading areas, where ships load and discharge cargo and passengers. Although usually situated on a sea coast or estuary, ports can also be found far inland, such as Ham ...
several miles away (respectively, Leith
Leith (; gd, Lìte) is a port area in the north of the city of Edinburgh, Scotland, founded at the mouth of the Water of Leith. In 2021, it was ranked by '' Time Out'' as one of the top five neighbourhoods to live in the world.
The earliest ...
and Piraeus
Piraeus ( ; el, Πειραιάς ; grc, Πειραιεύς ) is a port city within the Athens urban area ("Greater Athens"), in the Attica region of Greece. It is located southwest of Athens' city centre, along the east coast of the Saronic ...
). Intellectually, the Scottish Enlightenment
The Scottish Enlightenment ( sco, Scots Enlichtenment, gd, Soillseachadh na h-Alba) was the period in 18th- and early-19th-century Scotland characterised by an outpouring of intellectual and scientific accomplishments. By the eighteenth century ...
, with its humanist
Humanism is a philosophical stance that emphasizes the individual and social potential and agency of human beings. It considers human beings the starting point for serious moral and philosophical inquiry.
The meaning of the term "humani ...
and rationalist outlook, was influenced by Ancient Greek philosophy
Ancient Greek philosophy arose in the 6th century BC, marking the end of the Greek Dark Ages. Greek philosophy continued throughout the Hellenistic period and the period in which Greece and most Greek-inhabited lands were part of the Roman Empire ...
. In 1822, artist Hugh William Williams
Hugh William Williams FRSE (1773–1829), known as "Grecian Williams," was a Scottish landscape painter.
Life
Williams was born onboard the ship of his father, Captain Williams, whilst en route to the West Indies. His mother, "Miss Lewis", die ...
organized an exhibition that showed his paintings of Athens alongside views of Edinburgh, and the idea of a direct parallel between both cities quickly caught the popular imagination. When plans were drawn up in the early 19th century to architecturally develop Calton Hill
Calton Hill () is a hill in central Edinburgh, Scotland, situated beyond the east end of Princes Street and included in the city's UNESCO World Heritage Site. Views of, and from, the hill are often used in photographs and paintings of the ci ...
, the design of the National Monument
A national monument is a monument constructed in order to commemorate something of importance to national heritage, such as a country's founding, independence, war, or the life and death of a historical figure.
The term may also refer to a spec ...
directly copied Athens' Parthenon
The Parthenon (; grc, Παρθενών, , ; ell, Παρθενώνας, , ) is a former temple on the Athenian Acropolis, Greece, that was dedicated to the goddess Athena during the fifth century BC. Its decorative sculptures are considere ...
. Tom Stoppard
Sir Tom Stoppard (born , 3 July 1937) is a Czech born British playwright and screenwriter. He has written for film, radio, stage, and television, finding prominence with plays. His work covers the themes of human rights, censorship, and politi ...
's character Archie of ''Jumpers
Jumper or Jumpers may refer to:
Clothing
* Jumper (sweater), a long-sleeve article of clothing; also called a top, pullover, or sweater
**A waist-length top garment of dense wool, part of the Royal Navy uniform and the uniform of the United Stat ...
'' said, perhaps playing on Reykjavík
Reykjavík ( ; ) is the capital and largest city of Iceland. It is located in southwestern Iceland, on the southern shore of Faxaflói bay. Its latitude is 64°08' N, making it the world's northernmost capital of a sovereign state. With a po ...
meaning "smoky bay", that the "Reykjavík of the South" would be more appropriate.
The city has also been known by several Latin names, such as ''Edinburgum,'' while the adjectival forms ''Edinburgensis'' and ''Edinensis'' are used in educational and scientific contexts.
''Edina'' is a late 18th-century poetical form used by the Scots poets Robert Fergusson
Robert Fergusson (5 September 1750 – 16 October 1774) was a Scottish poet. After formal education at the University of St Andrews, Fergusson led a bohemian life in Edinburgh, the city of his birth, then at the height of intellectual and c ...
and Robert Burns
Robert Burns (25 January 175921 July 1796), also known familiarly as Rabbie Burns, was a Scottish poet and lyricist. He is widely regarded as the national poet of Scotland and is celebrated worldwide. He is the best known of the poets who hav ...
. "Embra" or "Embro" are colloquialisms from the same time, as in Robert Garioch
Robert Garioch Sutherland (9 May 1909 – 26 April 1981) was a Scottish poet and translator. His poetry was written almost exclusively in the Scots language, he was a key member in the literary revival of the language in the mid-20th century ...
's ''Embro to the Ploy''.
Ben Jonson
Benjamin "Ben" Jonson (c. 11 June 1572 – c. 16 August 1637) was an English playwright and poet. Jonson's artistry exerted a lasting influence upon English poetry and stage comedy. He popularised the comedy of humours; he is best known for t ...
described it as "Britaine's other eye", and Sir Walter Scott referred to it as "yon Empress of the North". Robert Louis Stevenson, also a son of the city, wrote that Edinburgh "is what Paris ought to be."
History
Early history
 The earliest known human habitation in the Edinburgh area was at
The earliest known human habitation in the Edinburgh area was at Cramond
Cramond Village (; gd, Cathair Amain) is a village and suburb in the north-west of Edinburgh, Scotland, at the mouth of the River Almond where it enters the Firth of Forth.
The Cramond area has evidence of Mesolithic, Bronze Age and Roman ac ...
, where evidence was found of a Mesolithic
The Mesolithic (Greek: μέσος, ''mesos'' 'middle' + λίθος, ''lithos'' 'stone') or Middle Stone Age is the Old World archaeological period between the Upper Paleolithic and the Neolithic. The term Epipaleolithic is often used synonymous ...
camp site dated to c. 8500 BC. Traces of later Bronze Age
The Bronze Age is a historic period, lasting approximately from 3300 BC to 1200 BC, characterized by the use of bronze, the presence of writing in some areas, and other early features of urban civilization. The Bronze Age is the second pri ...
and Iron Age
The Iron Age is the final epoch of the three-age division of the prehistory and protohistory of humanity. It was preceded by the Stone Age (Paleolithic, Mesolithic, Neolithic) and the Bronze Age (Chalcolithic). The concept has been mostly appl ...
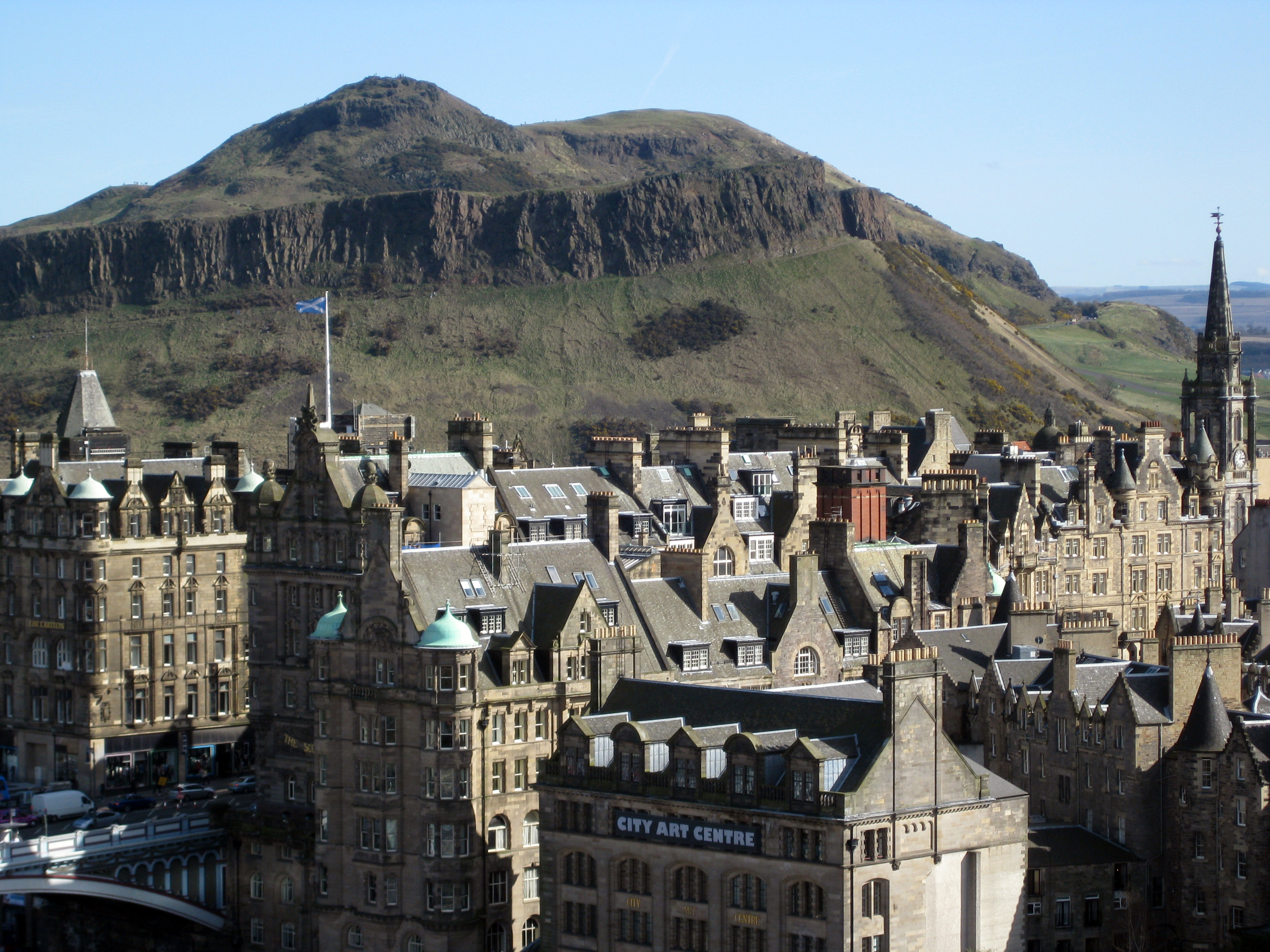
settlements have been found on Castle Rock, Arthur's Seat
Arthur's Seat ( gd, Suidhe Artair, ) is an ancient volcano which is the main peak of the group of hills in Edinburgh, Scotland, which form most of Holyrood Park, described by Robert Louis Stevenson as "a hill for magnitude, a mountain in virtue ...
, Craiglockhart Hill
Craiglockhart Hill is a combination of two summits, Easter and Wester Craiglockhart, in the suburb of Craiglockhart, Edinburgh.https://edinburghgeolsoc.org/downloads/rigsleaflet_craiglockharta4.pdf Craiglockart and Edinburgh's Seven Hills
East ...
and the Pentland Hills
The Pentland Hills are a range of hills southwest of Edinburgh, Scotland. The range is around in length, and runs southwest from Edinburgh towards Biggar and the upper Clydesdale.
Etymology
The name is first recorded for the farm of Pentlan ...
.
When the Romans
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
* Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*''Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a lette ...
arrived in Lothian at the end of the 1st century AD, they found a Brittonic
Brittonic or Brythonic may refer to:
*Common Brittonic, or Brythonic, the Celtic language anciently spoken in Great Britain
*Brittonic languages, a branch of the Celtic languages descended from Common Brittonic
*Britons (Celtic people)
The Br ...
Celtic tribe whose name they recorded as the Votadini
The Votadini, also known as the ''Uotadini'', ''Wotādīni'', ''Votādīni'', or ''Otadini'' were a Brittonic people of the Iron Age in Great Britain. Their territory was in what is now south-east Scotland and north-east England, extending fro ...
. The Votadini transitioned into the Gododdin
The Gododdin () were a Brittonic people of north-eastern Britannia, the area known as the Hen Ogledd or Old North (modern south-east Scotland and north-east England), in the sub-Roman period. Descendants of the Votadini, they are best known ...
kingdom in the Early Middle Ages
The Early Middle Ages (or early medieval period), sometimes controversially referred to as the Dark Ages, is typically regarded by historians as lasting from the late 5th or early 6th century to the 10th century. They marked the start of the Mi ...
, with Eidyn serving as one of the kingdom's districts. During this period, the Castle Rock site, thought to have been the stronghold of Din Eidyn, emerged as the kingdom's major centre. The medieval poem ''Y Gododdin
''Y Gododdin'' () is a medieval Welsh poem consisting of a series of elegies to the men of the Brittonic kingdom of Gododdin and its allies who, according to the conventional interpretation, died fighting the Angles of Deira and Bernicia at a p ...
'' describes a war band from across the Brittonic world who gathered in Eidyn before a fateful raid; this may describe a historical event around AD 600.
In 638, the Gododdin stronghold was besieged by forces loyal to King Oswald of Northumbria
la, Regnum Northanhymbrorum
, conventional_long_name = Kingdom of Northumbria
, common_name = Northumbria
, status = State
, status_text = Unified Anglian kingdom (before 876)North: Anglian kingdom (af ...
, and around this time control of Lothian passed to the Angles
The Angles ( ang, Ængle, ; la, Angli) were one of the main Germanic peoples who settled in Great Britain in the post-Roman period. They founded several kingdoms of the Heptarchy in Anglo-Saxon England. Their name is the root of the name ' ...
. Their influence continued for the next three centuries until around 950, when, during the reign of Indulf
Ildulb mac Causantín, anglicised as Indulf or Indulph, nicknamed An Ionsaighthigh, "the Aggressor" (died 962) was king of Alba from 954 to 962. He was the son of Constantine II; his mother may have been a daughter of Earl Eadulf I of Bernicia, ...
, son of Constantine II, the "burh" (fortress), named in the 10th-century ''Pictish Chronicle
The Pictish Chronicle is a name used to refer to a pseudo-historical account of the kings of the Picts beginning many thousand years before history was recorded in Pictavia and ending after Pictavia had been enveloped by Scotland.
Version A
The ...
'' as ''oppidum Eden'', was abandoned to the Scots. It thenceforth remained, for the most part, under their jurisdiction.
The royal burgh
A royal burgh () was a type of Scottish burgh which had been founded by, or subsequently granted, a royal charter. Although abolished by law in 1975, the term is still used by many former royal burghs.
Most royal burghs were either created by ...
was founded by King David I
David I or Dauíd mac Maíl Choluim ( Modern: ''Daibhidh I mac haoilChaluim''; – 24 May 1153) was a 12th-century ruler who was Prince of the Cumbrians from 1113 to 1124 and later King of Scotland from 1124 to 1153. The youngest son of Mal ...
in the early 12th century on land belonging to the Crown, though the date of its charter is unknown. The first documentary evidence of the medieval burgh
A burgh is an autonomous municipal corporation in Scotland and Northern England, usually a city, town, or toun in Scots. This type of administrative division existed from the 12th century, when King David I created the first royal burghs. Burg ...
is a royal charter
A royal charter is a formal grant issued by a monarch under royal prerogative as letters patent. Historically, they have been used to promulgate public laws, the most famous example being the English Magna Carta (great charter) of 1215, bu ...
, , by King David I granting a toft in to the Priory of Dunfermline. Edinburgh was largely in English hands from 1291 to 1314 and from 1333 to 1341, during the Wars of Scottish Independence
The Wars of Scottish Independence were a series of military campaigns fought between the Kingdom of Scotland and the Kingdom of England in the late 13th and early 14th centuries.
The First War (1296–1328) began with the English invasion of ...
. When the English invaded Scotland in 1298, King Edward I
Edward I (17/18 June 1239 – 7 July 1307), also known as Edward Longshanks and the Hammer of the Scots, was King of England and Lord of Ireland from 1272 to 1307. Concurrently, he ruled the duchies of Aquitaine and Gascony as a vassal ...
chose not to enter the English controlled town of Edinburgh but passed by with his army.
In the middle of the 14th century, the French chronicler Jean Froissart
Jean Froissart ( Old and Middle French: '' Jehan'', – ) (also John Froissart) was a French-speaking medieval author and court historian from the Low Countries who wrote several works, including ''Chronicles'' and ''Meliador'', a long Arthuria ...
described it as the capital of Scotland (c. 1365), and James III (1451–88) referred to it in the 15th century as "the principal burgh of our kingdom". Despite the destruction caused by an English assault in 1544, the town slowly recovered, and was at the centre of events in the 16th-century Scottish Reformation
The Scottish Reformation was the process by which Kingdom of Scotland, Scotland broke with the Pope, Papacy and developed a predominantly Calvinist national Church of Scotland, Kirk (church), which was strongly Presbyterianism, Presbyterian in ...
and 17th-century Wars of the Covenant
Between 1639 and 1653, Scotland was involved in the Wars of the Three Kingdoms, a series of wars starting with the Bishops Wars (between Scotland and England), the Irish Rebellion of 1641, the English Civil War (and its extension in Scotland ...
. In 1582, Edinburgh's town council was given a royal charter
A royal charter is a formal grant issued by a monarch under royal prerogative as letters patent. Historically, they have been used to promulgate public laws, the most famous example being the English Magna Carta (great charter) of 1215, bu ...
by King James VI
James is a common English language surname and given name:
*James (name), the typically masculine first name James
* James (surname), various people with the last name James
James or James City may also refer to:
People
* King James (disambiguat ...
permitting the establishment of a university; founded as ''Tounis College'' (Town's College), the institution developed into the University of Edinburgh
The University of Edinburgh ( sco, University o Edinburgh, gd, Oilthigh Dhùn Èideann; abbreviated as ''Edin.'' in post-nominals) is a public research university based in Edinburgh, Scotland. Granted a royal charter by King James VI in 15 ...
, which contributed to Edinburgh's central intellectual role in subsequent centuries.
17th century
 In 1603, King
In 1603, King James VI
James is a common English language surname and given name:
*James (name), the typically masculine first name James
* James (surname), various people with the last name James
James or James City may also refer to:
People
* King James (disambiguat ...
of Scotland succeeded to the English throne, uniting the crowns of Scotland and England in a personal union
A personal union is the combination of two or more states that have the same monarch while their boundaries, laws, and interests remain distinct. A real union, by contrast, would involve the constituent states being to some extent interlink ...
known as the Union of the Crowns
The Union of the Crowns ( gd, Aonadh nan Crùintean; sco, Union o the Crouns) was the accession of James VI of Scotland to the throne of the Kingdom of England as James I and the practical unification of some functions (such as overseas dip ...
, though Scotland remained, in all other respects, a separate kingdom. In 1638, King Charles I's attempt to introduce Anglican
Anglicanism is a Western Christian tradition that has developed from the practices, liturgy, and identity of the Church of England following the English Reformation, in the context of the Protestant Reformation in Europe. It is one of th ...
church forms in Scotland encountered stiff Presbyterian
Presbyterianism is a part of the Reformed tradition within Protestantism that broke from the Roman Catholic Church in Scotland by John Knox, who was a priest at St. Giles Cathedral (Church of Scotland). Presbyterian churches derive their nam ...
opposition culminating in the conflicts of the Wars of the Three Kingdoms
The Wars of the Three Kingdoms were a series of related conflicts fought between 1639 and 1653 in the kingdoms of Kingdom of England, England, Kingdom of Scotland, Scotland and Kingdom of Ireland, Ireland, then separate entities united in a pers ...
. Subsequent Scottish support for Charles Stuart's restoration to the throne of England resulted in Edinburgh's occupation by Oliver Cromwell
Oliver Cromwell (25 April 15993 September 1658) was an English politician and military officer who is widely regarded as one of the most important statesmen in English history. He came to prominence during the 1639 to 1651 Wars of the Three Ki ...
's Commonwealth of England
The Commonwealth was the political structure during the period from 1649 to 1660 when England and Wales, later along with Ireland and Scotland, were governed as a republic after the end of the Second English Civil War and the trial and execut ...
forces – the New Model Army
The New Model Army was a standing army formed in 1645 by the Parliamentarians during the First English Civil War, then disbanded after the Stuart Restoration in 1660. It differed from other armies employed in the 1639 to 1653 Wars of the Th ...
– in 1650.
In the 17th century, Edinburgh's boundaries were still defined by the city's defensive town walls. As a result, the city's growing population was accommodated by increasing the height of the houses. Buildings of 11 storeys or more were common, and have been described as forerunners of the modern-day skyscraper. Most of these old structures were replaced by the predominantly Victorian buildings seen in today's Old Town. In 1611 an act of parliament created the High Constables of Edinburgh
The High Constables of Edinburgh are a prestigious body of constables, founded in 1611 and located in Edinburgh, Scotland. Historically, the High Constables were charged with policing the streets of Edinburgh, the capital city of Scotland, howev ...
to keep order in the city, thought to be the oldest statutory police force in the world.
18th century
 Following the
Following the Treaty of Union
The Treaty of Union is the name usually now given to the treaty which led to the creation of the new state of Great Britain, stating that the Kingdom of England (which already included Wales) and the Kingdom of Scotland were to be "United i ...
in 1706, the Parliaments of England and Scotland passed Acts of Union in 1706 and 1707 respectively, uniting the two kingdoms in the Kingdom of Great Britain
The Kingdom of Great Britain (officially Great Britain) was a Sovereign state, sovereign country in Western Europe from 1 May 1707 to the end of 31 December 1800. The state was created by the 1706 Treaty of Union and ratified by the Acts of ...
effective from 1 May 1707. As a consequence, the Parliament of Scotland
The Parliament of Scotland ( sco, Pairlament o Scotland; gd, Pàrlamaid na h-Alba) was the legislature of the Kingdom of Scotland from the 13th century until 1707. The parliament evolved during the early 13th century from the king's council o ...
merged with the Parliament of England
The Parliament of England was the legislature of the Kingdom of England from the 13th century until 1707 when it was replaced by the Parliament of Great Britain. Parliament evolved from the great council of bishops and peers that advised t ...
to form the Parliament of Great Britain
The Parliament of Great Britain was formed in May 1707 following the ratification of the Acts of Union by both the Parliament of England and the Parliament of Scotland. The Acts ratified the treaty of Union which created a new unified Kingdo ...
, which sat at Westminster
Westminster is an area of Central London, part of the wider City of Westminster.
The area, which extends from the River Thames to Oxford Street, has many visitor attractions and historic landmarks, including the Palace of Westminster, Bu ...
in London. The Union was opposed by many Scots, resulting in riots in the city.
By the first half of the 18th century, Edinburgh was described as one of Europe's most densely populated, overcrowded and unsanitary towns. Visitors were struck by the fact that the social classes shared the same urban space, even inhabiting the same tenement
A tenement is a type of building shared by multiple dwellings, typically with flats or apartments on each floor and with shared entrance stairway access. They are common on the British Isles, particularly in Scotland. In the medieval Old Town, i ...
buildings; although here a form of social segregation did prevail, whereby shopkeepers and tradesmen tended to occupy the cheaper-to-rent cellars and garrets, while the more well-to-do professional classes occupied the more expensive middle storeys.
During the Jacobite rising of 1745
The Jacobite rising of 1745, also known as the Forty-five Rebellion or simply the '45 ( gd, Bliadhna Theàrlaich, , ), was an attempt by Charles Edward Stuart to regain the Monarchy of Great Britain, British throne for his father, James Franci ...
, Edinburgh was briefly occupied by the Jacobite "Highland Army" before its march into England. After its eventual defeat at Culloden, there followed a period of reprisals and pacification, largely directed at the rebellious clans
A clan is a group of people united by actual or perceived kinship
and descent. Even if lineage details are unknown, clans may claim descent from founding member or apical ancestor. Clans, in indigenous societies, tend to be endogamous, meaning ...
. In Edinburgh, the Town Council, keen to emulate London by initiating city improvements and expansion to the north of the castle, reaffirmed its belief in the Union and loyalty to the Hanoverian monarch George III
George III (George William Frederick; 4 June 173829 January 1820) was King of Great Britain and of Ireland from 25 October 1760 until the union of the two kingdoms on 1 January 1801, after which he was King of the United Kingdom of Great Br ...
by its choice of names for the streets of the New Town: for example, Rose
A rose is either a woody perennial flowering plant of the genus ''Rosa'' (), in the family Rosaceae (), or the flower it bears. There are over three hundred species and tens of thousands of cultivars. They form a group of plants that can be ...
Street and Thistle
Thistle is the common name of a group of flowering plants characterised by leaves with sharp prickles on the margins, mostly in the family Asteraceae. Prickles can also occur all over the planton the stem and on the flat parts of the leaves. ...
Street; and for the royal family, George Street, Queen Street, Hanover Street, Frederick Street and Princes Street
Princes Street ( gd, Sràid nam Prionnsan) is one of the major thoroughfares in central Edinburgh, Scotland and the main shopping street in the capital. It is the southernmost street of Edinburgh's New Town, stretching around 1.2 km (three ...
(in honour of George's two sons).
In the second half of the century, the city was at the heart of the Scottish Enlightenment
The Scottish Enlightenment ( sco, Scots Enlichtenment, gd, Soillseachadh na h-Alba) was the period in 18th- and early-19th-century Scotland characterised by an outpouring of intellectual and scientific accomplishments. By the eighteenth century ...
, when thinkers like David Hume, Adam Smith, James Hutton
James Hutton (; 3 June O.S.172614 June 1726 New Style. – 26 March 1797) was a Scottish geologist, agriculturalist, chemical manufacturer, naturalist and physician. Often referred to as the father of modern geology, he played a key role i ...
and Joseph Black
Joseph Black (16 April 1728 – 6 December 1799) was a Scottish physicist and chemist, known for his discoveries of magnesium, latent heat, specific heat, and carbon dioxide. He was Professor of Anatomy and Chemistry at the University of Glas ...
were familiar figures in its streets. Edinburgh became a major intellectual centre, earning it the nickname "Athens of the North" because of its many neo-classical buildings and reputation for learning, recalling ancient Athens. In the 18th-century novel ''The Expedition of Humphry Clinker
''The Expedition of Humphry Clinker'' was the last of the picaresque novels of Tobias Smollett, published in London on 17 June 1771 (three months before Smollett's death), and is considered by many to be his best and funniest work. It is an epist ...
'' by Tobias Smollett
Tobias George Smollett (baptised 19 March 1721 – 17 September 1771) was a Scottish poet and author. He was best known for picaresque novels such as ''The Adventures of Roderick Random'' (1748), ''The Adventures of Peregrine Pickle'' (1751) a ...
one character describes Edinburgh as a "hotbed of genius". Edinburgh was also a major centre for the Scottish book trade. The highly successful London bookseller Andrew Millar
Andrew Millar (17058 June 1768) was a British publisher in the eighteenth century.
Biography
In 1725, as a twenty-year-old bookseller apprentice, he evaded Edinburgh city printing restrictions by going to Leith to print, which was considered be ...
was apprenticed there to James McEuen.
From the 1770s onwards, the professional and business classes gradually deserted the Old Town in favour of the more elegant "one-family" residences of the New Town, a migration that changed the city's social character. According to the foremost historian of this development, "Unity of social feeling was one of the most valuable heritages of old Edinburgh, and its disappearance was widely and properly lamented."
19th and 20th centuries
 Despite an enduring myth to the contrary, Edinburgh became an industrial centre with its traditional industries of printing, brewing and distilling continuing to grow in the 19th century and joined by new industries such as rubber works, engineering works and others. By 1821, Edinburgh had been overtaken by
Despite an enduring myth to the contrary, Edinburgh became an industrial centre with its traditional industries of printing, brewing and distilling continuing to grow in the 19th century and joined by new industries such as rubber works, engineering works and others. By 1821, Edinburgh had been overtaken by Glasgow
Glasgow ( ; sco, Glesca or ; gd, Glaschu ) is the most populous city in Scotland and the fourth-most populous city in the United Kingdom, as well as being the 27th largest city by population in Europe. In 2020, it had an estimated popul ...
as Scotland's largest city. The city centre between Princes Street and George Street became a major commercial and shopping district, a development partly stimulated by the arrival of railways in the 1840s. The Old Town became an increasingly dilapidated, overcrowded slum with high mortality rates. Improvements carried out under Lord Provost William Chambers in the 1860s began the transformation of the area into the predominantly Victorian Old Town seen today. More improvements followed in the early 20th century as a result of the work of Patrick Geddes
Sir Patrick Geddes (2 October 1854 – 17 April 1932) was a British biologist, sociologist, Comtean positivist, geographer, philanthropist and pioneering town planner. He is known for his innovative thinking in the fields of urban planning ...
, but relative economic stagnation during the two world wars and beyond saw the Old Town deteriorate further before major Slum clearance in the United Kingdom, slum clearance in the 1960s and 1970s began to reverse the process. University building developments which transformed the George Square, Edinburgh, George Square and Potterrow areas proved highly controversial.
Since the 1990s a new "financial district", including the Edinburgh International Conference Centre, has grown mainly on demolished railway property to the west of the castle, stretching into Fountainbridge, a run-down 19th-century industrial suburb which has undergone radical change since the 1980s with the demise of industrial and brewery premises. This ongoing development has enabled Edinburgh to maintain its place as the United Kingdom's second largest financial and administrative centre after London. Financial services now account for a third of all commercial office space in the city. The development of Edinburgh Park, a new business and technology park covering , west of the city centre, has also contributed to the District Council's strategy for the city's major economic regeneration.
In 1998, the Scotland Act 1998, Scotland Act, which came into force the following year, established a Devolution, devolved Scottish Parliament and Scottish Executive (renamed the Scottish Government since September 2007). Both based in Edinburgh, they are responsible for governing Scotland while Reserved and excepted matters, reserved matters such as defence, foreign affairs and some elements of income tax remain the responsibility of the Parliament of the United Kingdom in London.
21st century
In 2022, Edinburgh was affected by the 2022 Scotland bin strikes.Geography
Cityscape
Situated in Scotland's Central Belt, Edinburgh lies on the southern shore of the Firth of Forth. The city centre is southwest of the shoreline ofLeith
Leith (; gd, Lìte) is a port area in the north of the city of Edinburgh, Scotland, founded at the mouth of the Water of Leith. In 2021, it was ranked by '' Time Out'' as one of the top five neighbourhoods to live in the world.
The earliest ...
and inland, as the crow flies, from the east coast of Scotland and the North Sea at Dunbar. While the early burgh grew up near the prominent Castle Rock, the modern city is often said to be built on Hills in Edinburgh, seven hills, namely Calton Hill
Calton Hill () is a hill in central Edinburgh, Scotland, situated beyond the east end of Princes Street and included in the city's UNESCO World Heritage Site. Views of, and from, the hill are often used in photographs and paintings of the ci ...
, Corstorphine Hill, Craiglockhart Hill, Braid Hills, Braid Hill, Blackford Hill, Arthur's Seat and the Castle Rock, giving rise to allusions to the seven hills of Rome.
Occupying a narrow gap between the Firth of Forth to the north and the Pentland Hills
The Pentland Hills are a range of hills southwest of Edinburgh, Scotland. The range is around in length, and runs southwest from Edinburgh towards Biggar and the upper Clydesdale.
Etymology
The name is first recorded for the farm of Pentlan ...
and their outrunners to the south, the city sprawls over a landscape which is the product of early volcanic activity and later periods of intensive glaciation.
Igneous activity between 350 and 400 million years ago, coupled with fault (geology), faulting, led to the creation of tough basalt volcanic plugs, which predominate over much of the area. One such example is the Castle Rock which forced the advancing ice sheet to divide, sheltering the softer rock and forming a tail of material to the east, thus creating a distinctive crag and tail formation. Glacial erosion on the north side of the crag gouged a deep valley later filled by the now drained Nor Loch. These features, along with another hollow on the rock's south side, formed an ideal natural strongpoint upon which Edinburgh Castle was built. Similarly, Arthur's Seat is the remains of a volcano dating from the Carboniferous period, which was eroded by a glacier moving west to east during the ice age. Erosive action such as plucking (glaciation), plucking and abrasion (geology), abrasion exposed the rocky crags to the west before leaving a tail of deposited glacial material swept to the east. This process formed the distinctive Salisbury Crags, a series of Theralite#Teschenites, teschenite cliffs between Arthur's Seat and the location of the early burgh. The residential areas of Marchmont and Bruntsfield are built along a series of drumlin ridges south of the city centre, which were glacial deposition, deposited as the glacier receded.
Other prominent landforms such as Calton Hill and Corstorphine Hill are also products of glacial erosion. The Braid Hills and Blackford Hill are a series of small summits to the south of the city centre that command expansive views looking northwards over the urban area to the Firth of Forth.
 Edinburgh is drained by the river named the Water of Leith, which rises at the Colzium Springs in the Pentland Hills and runs for through the south and west of the city, emptying into the Firth of Forth at Leith. The nearest the river gets to the city centre is at Dean Village on the north-western edge of the New Town, where a deep gorge is spanned by Thomas Telford's Dean Bridge, built in 1832 for the road to South Queensferry, Queensferry. The Water of Leith Walkway is a mixed-use trail that follows the course of the river for from Balerno to Leith.
Excepting the shoreline of the Firth of Forth, Edinburgh is encircled by a green belt, designated in 1957, which stretches from Dalmeny in the west to Prestongrange in the east. With an average width of the principal objectives of the green belt were to contain the outward expansion of the city and to prevent the agglomeration of urban areas. Expansion affecting the green belt is strictly controlled but developments such as Edinburgh Airport and the Royal Highland Showground at Ingliston lie within the zone. Similarly, suburbs such as Juniper Green and Balerno are situated on green belt land. One feature of the Edinburgh green belt is the inclusion of parcels of land within the city which are designated green belt, even though they do not connect with the peripheral ring. Examples of these independent wedges of green belt include Holyrood Park and Corstorphine Hill.
Edinburgh is drained by the river named the Water of Leith, which rises at the Colzium Springs in the Pentland Hills and runs for through the south and west of the city, emptying into the Firth of Forth at Leith. The nearest the river gets to the city centre is at Dean Village on the north-western edge of the New Town, where a deep gorge is spanned by Thomas Telford's Dean Bridge, built in 1832 for the road to South Queensferry, Queensferry. The Water of Leith Walkway is a mixed-use trail that follows the course of the river for from Balerno to Leith.
Excepting the shoreline of the Firth of Forth, Edinburgh is encircled by a green belt, designated in 1957, which stretches from Dalmeny in the west to Prestongrange in the east. With an average width of the principal objectives of the green belt were to contain the outward expansion of the city and to prevent the agglomeration of urban areas. Expansion affecting the green belt is strictly controlled but developments such as Edinburgh Airport and the Royal Highland Showground at Ingliston lie within the zone. Similarly, suburbs such as Juniper Green and Balerno are situated on green belt land. One feature of the Edinburgh green belt is the inclusion of parcels of land within the city which are designated green belt, even though they do not connect with the peripheral ring. Examples of these independent wedges of green belt include Holyrood Park and Corstorphine Hill.
Areas
Edinburgh includes former towns and villages that retain much of their original character as settlements in existence before they were absorbed into the expanding city of the nineteenth and twentieth centuries. Many areas, such as Dalry, Edinburgh, Dalry, contain residences that are multi-occupancy buildings known astenement
A tenement is a type of building shared by multiple dwellings, typically with flats or apartments on each floor and with shared entrance stairway access. They are common on the British Isles, particularly in Scotland. In the medieval Old Town, i ...
s, although the more southern and western parts of the city have traditionally been less built-up with a greater number of detached and semi-detached villas.
 The historic centre of Edinburgh is divided in two by the broad green swathe of Princes Street Gardens. To the south, the view is dominated by Edinburgh Castle, built high on Castle Rock, and the long sweep of the Old Town descending towards Holyrood Palace. To the north lie Princes Street and the New Town.
The West End, Edinburgh, West End includes the financial district, with insurance and banking offices as well as the Edinburgh International Conference Centre.
Edinburgh's Old and New Towns were listed as a UNESCO
The historic centre of Edinburgh is divided in two by the broad green swathe of Princes Street Gardens. To the south, the view is dominated by Edinburgh Castle, built high on Castle Rock, and the long sweep of the Old Town descending towards Holyrood Palace. To the north lie Princes Street and the New Town.
The West End, Edinburgh, West End includes the financial district, with insurance and banking offices as well as the Edinburgh International Conference Centre.
Edinburgh's Old and New Towns were listed as a UNESCO World Heritage Site
A World Heritage Site is a landmark or area with legal protection by an international convention administered by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO). World Heritage Sites are designated by UNESCO for h ...
in 1995 in recognition of the unique character of the Old Town with its medieval street layout and the planned Georgian New Town, including the adjoining Dean Village and Calton Hill areas. There are over 4,500 Listed building (United Kingdom), listed buildings within the city, a higher proportion relative to area than any other city in the United Kingdom.
The castle is perched on top of a rocky crag (the remnant of an extinct volcano) and the Royal Mile runs down the crest of a ridge from it terminating at Holyrood Palace. Minor streets (called closes or wynds) lie on either side of the main spine forming a herringbone pattern. Due to space restrictions imposed by the narrowness of this landform, the Old Town became home to some of the earliest "high rise" residential buildings. Multi-storey dwellings known as ''lands'' were the norm from the 16th century onwards with ten and eleven storeys being typical and one even reaching fourteen or fifteen storeys. Numerous vaults below street level were inhabited to accommodate the influx of incomers, particularly Irish migration to Great Britain, Irish immigrants, during the Industrial Revolution. The street has several fine public buildings such as St Giles' Cathedral, the Edinburgh City Chambers, City Chambers and the Parliament House, Edinburgh, Law Courts. Other places of historical interest nearby are Greyfriars Kirkyard and Mary King's Close. The Grassmarket, running deep below the castle is connected by the steep double terraced Victoria Street, Edinburgh, Victoria Street. The street layout is typical of the old quarters of many Northern European cities.
The New Town was an 18th-century solution to the problem of an increasingly crowded city which had been confined to the ridge sloping down from the castle. In 1766 a competition to design a "New Town" was won by James Craig (architect), James Craig, a 27-year-old architect. The plan was a rigid, ordered grid, which fitted in well with Age of Enlightenment, Enlightenment ideas of rationality. The principal street was to be George Street, running along the natural ridge to the north of what became known as the "Old Town". To either side of it are two other main streets: Princes Street and Queen Street. Princes Street has become Edinburgh's main shopping street and now has few of its Georgian architecture, Georgian buildings in their original state. The three main streets are connected by a series of streets running perpendicular to them. The east and west ends of George Street are terminated by St Andrew Square, Edinburgh, St Andrew Square and Charlotte Square respectively. The latter, designed by Robert Adam, influenced the architectural style of the New Town into the early 19th century. Bute House, the official residence of the First Minister of Scotland, is on the north side of Charlotte Square.
The hollow between the Old and New Towns was formerly the Nor Loch, which was created for the town's defence but came to be used by the inhabitants for dumping their sewage. It was drained by the 1820s as part of the city's northward expansion. Craig's original plan included an ornamental canal on the site of the loch, but this idea was abandoned. Soil excavated while laying the foundations of buildings in the New Town was dumped on the site of the loch to create the slope connecting the Old and New Towns known as The Mound.
In the middle of the 19th century the National Gallery of Scotland and Royal Scottish Academy Building were built on The Mound, and tunnels for the railway line between Haymarket railway station, Haymarket and Edinburgh Waverley railway station, Waverley stations were driven through it.
The Southside is a residential part of the city, which includes the districts of St Leonard's, Edinburgh, St Leonards, Marchmont, Morningside, Edinburgh, Morningside, Newington, Edinburgh, Newington, Sciennes, The Grange, Edinburgh, the Grange and Blackford, Edinburgh, Blackford. The Southside is broadly analogous to the area covered formerly by the Burgh Muir, and was developed as a residential area after the opening of the South Bridge, Edinburgh, South Bridge in the 1780s. The Southside is particularly popular with families (many state and private schools are here), young professionals and students (the central University of Edinburgh campus is based around George Square, Edinburgh, George Square just north of Marchmont and The Meadows (park), the Meadows), and Napier University (with major campuses around Merchiston and Morningside). The area is also well provided with hotel and "bed and breakfast" accommodation for visiting festival-goers. These districts often feature in works of fiction. For example, Church Hill, Edinburgh, Church Hill in Morningside, was the home of Muriel Spark's Miss Jean Brodie, and Ian Rankin's Inspector Rebus lives in Marchmont and works in St Leonards.
Leith
Leith (; gd, Lìte) is a port area in the north of the city of Edinburgh, Scotland, founded at the mouth of the Water of Leith. In 2021, it was ranked by '' Time Out'' as one of the top five neighbourhoods to live in the world.
The earliest ...
was historically the port of Edinburgh, an arrangement of unknown date that was confirmed by the royal charter Robert the Bruce granted to the city in 1329. The port developed a separate identity from Edinburgh, which to some extent it still retains, and it was a matter of great resentment when the two burghs merged in 1920 into the City of Edinburgh. Even today the parliamentary seat is known as "Edinburgh North and Leith". The loss of traditional industries and commerce (the Henry Robb, last shipyard closed in 1983) resulted in economic decline. The Edinburgh Waterfront development has transformed old dockland areas from Leith to Granton into residential areas with shopping and leisure facilities and helped rejuvenate the area. With the redevelopment, Edinburgh has gained the business of cruise liner companies which now provide cruises to Norway, Sweden, Denmark, Germany, and the Netherlands.
The coastal suburb of Portobello, Edinburgh, Portobello is characterised by Georgian villas, Victorian tenements, a beach and promenade and cafés, bars, restaurants and independent shops. There are rowing and sailing clubs and a restored Victorian swimming pool, including Turkish baths.
The List of towns and cities in Scotland by population#Settlements, urban area of Edinburgh is almost entirely within the The City of Edinburgh Council, City of Edinburgh Council boundary, merging with Musselburgh in East Lothian. Towns within easy reach of the city boundary include Haddington, East Lothian, Haddington, Tranent, Prestonpans, Dalkeith, Bonnyrigg, Loanhead, Penicuik, Broxburn, West Lothian, Broxburn, Livingston, West Lothian, Livingston and Dunfermline. Edinburgh lies at the heart of the Edinburgh & South East Scotland City region with a population in 2014 of 1,339,380.
Climate
Like most of Scotland, Edinburgh has a cool, temperate climate, temperate, maritime climate which, despite its northerly latitude, is milder than places which lie at similar latitudes such as Moscow and Labrador. The city's proximity to the sea mitigates any large variations in temperature or extremes of climate. Winter daytime temperatures rarely fall below freezing while summer temperatures are moderate, rarely exceeding . The highest temperature recorded in the city was on 25 July 2019 at Gogarbank, beating the previous record of on 4 August 1975 at Edinburgh Airport. The lowest temperature recorded in recent years was during December 2010 at Gogarbank. Given Edinburgh's position between the coast and hills, it is renowned as "the windy city", with the prevailing wind direction coming from the south-west, which is often associated with warm, unstable air from the North Atlantic Current that can give rise to rainfall – although considerably less than cities to the west, such as Glasgow. Rainfall is distributed fairly evenly throughout the year. Winds from an easterly direction are usually drier but considerably colder, and may be accompanied by haar (fog), haar, a persistent coastal fog. Vigorous Atlantic depressions, known as European windstorms, can affect the city between October and May. Located slightly north of the city centre, the weather station at the Royal Botanic Garden Edinburgh (RBGE) has been an official weather station for the Met Office since 1956. The Met Office operates its own weather station at Gogarbank on the city's western outskirts, near Edinburgh Airport. This slightly inland station has a slightly wider temperature span between seasons, is cloudier and somewhat wetter, but differences are minor. Temperature and rainfall records have been kept at the Royal Observatory since 1764.Demography
Current
 The most recent official population estimates (2020) are for the locality (includes Currie), for the Edinburgh settlement (includes Musselburgh) and for the local authority area.
Edinburgh has a high proportion of young adults, with 19.5% of the population in their 20s (exceeded only by Aberdeen) and 15.2% in their 30s which is the highest in Scotland. The proportion of Edinburgh's population born in the UK fell from 92% to 84% between 2001 and 2011, while the proportion of White Scottish-born fell from 78% to 70%. Of those Edinburgh residents born in the UK, 335,000 or 83% were born in Scotland, with 58,000 or 14% being born in England.
Some 13,000 people or 2.7% of the city's population are of Poles in the United Kingdom, Polish descent. 39,500 people or 8.2% of Edinburgh's population class themselves as Non-White which is an increase from 4% in 2001. Of the Non-White population, the largest group by far are Asian-Scots, Asian, totalling 26,264 people. Within the Asian population, people of British Chinese, Chinese descent are now the largest sub-group, with 8,076 people, amounting to about 1.7% of the city's total population. The city's population of British Indian, Indian descent amounts to 6,470 (1.4% of the total population), while there are some 5,858 of British Pakistanis, Pakistani descent (1.2% of the total population). Although they account for only 1,277 people or 0.3% of the city's population, Edinburgh has the highest number and proportion of people of British Bangladeshi, Bangladeshi descent in Scotland. Over 7,000 people were born in African countries (1.6% of the total population) and nearly 7,000 in the Americas. With the notable exception of Inner London, Edinburgh has a higher number of people born in the United States (over 3,700) than any other city in the UK.
The proportion of people born outside the UK was 15.9% compared with 8% in 2001.
The most recent official population estimates (2020) are for the locality (includes Currie), for the Edinburgh settlement (includes Musselburgh) and for the local authority area.
Edinburgh has a high proportion of young adults, with 19.5% of the population in their 20s (exceeded only by Aberdeen) and 15.2% in their 30s which is the highest in Scotland. The proportion of Edinburgh's population born in the UK fell from 92% to 84% between 2001 and 2011, while the proportion of White Scottish-born fell from 78% to 70%. Of those Edinburgh residents born in the UK, 335,000 or 83% were born in Scotland, with 58,000 or 14% being born in England.
Some 13,000 people or 2.7% of the city's population are of Poles in the United Kingdom, Polish descent. 39,500 people or 8.2% of Edinburgh's population class themselves as Non-White which is an increase from 4% in 2001. Of the Non-White population, the largest group by far are Asian-Scots, Asian, totalling 26,264 people. Within the Asian population, people of British Chinese, Chinese descent are now the largest sub-group, with 8,076 people, amounting to about 1.7% of the city's total population. The city's population of British Indian, Indian descent amounts to 6,470 (1.4% of the total population), while there are some 5,858 of British Pakistanis, Pakistani descent (1.2% of the total population). Although they account for only 1,277 people or 0.3% of the city's population, Edinburgh has the highest number and proportion of people of British Bangladeshi, Bangladeshi descent in Scotland. Over 7,000 people were born in African countries (1.6% of the total population) and nearly 7,000 in the Americas. With the notable exception of Inner London, Edinburgh has a higher number of people born in the United States (over 3,700) than any other city in the UK.
The proportion of people born outside the UK was 15.9% compared with 8% in 2001.
Historical
A census by the Edinburgh presbytery in 1592 recorded a population of 8,003 adults spread equally north and south of the High Street which runs along the spine of the ridge sloping down from the Castle. In the 18th and 19th centuries, the population expanded rapidly, rising from 49,000 in 1751 to 136,000 in 1831, primarily due to migration from rural areas. As the population grew, problems of overcrowding in the Old Town, particularly in the crampedtenement
A tenement is a type of building shared by multiple dwellings, typically with flats or apartments on each floor and with shared entrance stairway access. They are common on the British Isles, particularly in Scotland. In the medieval Old Town, i ...
s that lined the present day Royal Mile and the Cowgate, were exacerbated. Poor sanitary arrangements resulted in a high incidence of disease, with outbreaks of cholera occurring in 1832, 1848 and 1866.
The construction of the New Town from 1767 onwards witnessed the migration of the professional and business classes from the difficult living conditions in the Old Town to the lower density, higher quality surroundings taking shape on land to the north.
Expansion southwards from the Old Town saw more tenements being built in the 19th century, giving rise to Victorian suburbs such as Dalry, Edinburgh, Dalry, Newington, Marchmont and Bruntsfield.
Early 20th-century population growth coincided with lower-density suburban development. As the city expanded to the south and west, detached and semi-detached villas with large gardens replaced tenements as the predominant building style. Nonetheless, the 2001 census revealed that over 55% of Edinburgh's population were still living in tenements or blocks of flats, a figure in line with other Scottish cities, but much higher than other British cities, and even central London.
From the early to mid 20th century, the growth in population, together with slum clearance in the Old Town and other areas, such as Dumbiedykes, Leith
Leith (; gd, Lìte) is a port area in the north of the city of Edinburgh, Scotland, founded at the mouth of the Water of Leith. In 2021, it was ranked by '' Time Out'' as one of the top five neighbourhoods to live in the world.
The earliest ...
, and Fountainbridge, led to the creation of new estates such as Stenhouse, Edinburgh, Stenhouse and Saughton, Craigmillar and Niddrie, Edinburgh, Niddrie, Pilton, Edinburgh, Pilton and Muirhouse, Piershill, and Sighthill, Edinburgh, Sighthill.
Religion
 In 2018, the Church of Scotland had 20,956 members in 71 congregations in the Presbytery of Edinburgh. Its most prominent church is St Giles' on the Royal Mile, first dedicated in 1243 but believed to date from before the 12th century. Saint Giles is historically the patron saint of Edinburgh. St Cuthbert's Church, Edinburgh, St Cuthbert's, situated at the west end of Princes Street Gardens in the shadow of Edinburgh Castle and St Giles' can lay claim to being the oldest Christian sites in the city, though the present St Cuthbert's, designed by Hippolyte Blanc, was dedicated in 1894.
Other Church of Scotland churches include Greyfriars Kirk, the Canongate Kirk, St Andrew's and St George's Church, St Andrew's and St George's West Church and the Edinburgh Barclay Church, Barclay Church. The Church of Scotland Offices are in Edinburgh, as is the General Assembly Hall of the Church of Scotland, Assembly Hall where the annual General Assembly of the Church of Scotland, General Assembly is held.
The Roman Catholic Archdiocese of St Andrews and Edinburgh has 27 parishes across the city. The Archbishop of St Andrews and Edinburgh has his official residence in Greenhill, Edinburgh, Greenhill, the diocesan offices are in nearby Marchmont, and its cathedral is St Mary's Cathedral, Edinburgh (Catholic), St Mary's Cathedral, Edinburgh. The Diocese of Edinburgh of the Scottish Episcopal Church has over 50 churches, half of them in the city. Its centre is the late 19th-century Gothic Revival architecture, Gothic style St Mary's Cathedral, Edinburgh (Episcopal), St Mary's Cathedral in the West End's Palmerston Place. Orthodox Christianity is represented by Pan, Romanian Orthodox Church, Romanian and Russian Orthodox Church, Russian Orthodox churches. There are several independent churches in the city, both Catholic and Protestant, including Charlotte Chapel (Edinburgh), Charlotte Chapel, Carrubbers Christian Centre, Bellevue Chapel and Sacred Heart, Edinburgh, Sacred Heart. There are also churches belonging to Quaker Meeting House, Edinburgh, Quakers, Christadelphians, Seventh-day Adventist Church, Seventh-day Adventists, Church of Christ, Scientist, The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints (LDS Church) and Elim Pentecostal Church.
Muslims have several places of worship across the city. Edinburgh Central Mosque, the largest Islamic place of worship, is located in Potterrow on the city's Southside, near Bristo Square. Construction was largely financed by a gift from King Fahd of Saudi Arabia and was completed in 1998. There is also an Ahmadiyya Muslim community.
The first recorded presence of a History of the Jews in Scotland#17th–19th centuries, Jewish community in Edinburgh dates back to the late 18th century. Edinburgh's Orthodox Judaism, Orthodox synagogue, opened in 1932, is in Salisbury Road and can accommodate a congregation of 2000. A Liberal Judaism (United Kingdom), Liberal Jewish congregation also meets in the city.
A Sikh gurdwara and a Hindu mandir are located in Leith. The city also has a Brahma Kumaris centre in the Polwarth area.
The Edinburgh Buddhist Centre, run by the Triratna Buddhist Community, formerly situated in Melville Terrace, now runs sessions at the Healthy Life Centre, Bread Street. Other Buddhist traditions are represented by groups which meet in the capital: the Community of Interbeing (followers of Thich Nhat Hanh), Rigpa, Samye Dzong, Theravadin, Pure Land Buddhism, Pure Land and Shambhala Buddhism, Shambala. There is a Sōtō Zen Priory in Portobello and a Theravadin Thai Buddhist Monastery in Slateford Road.
Edinburgh is home to a Baháʼí Faith, Baháʼí community, and a Theosophical Society meets in Great King Street.
Edinburgh has an Inter-Faith Association.
Edinburgh has over 39 List of graveyards and cemeteries in Edinburgh, graveyards and cemeteries, many of which are listed and of historical character, including several former church burial grounds. Examples include Old Calton Burial Ground, Greyfriars Kirkyard and Dean Cemetery.
In 2018, the Church of Scotland had 20,956 members in 71 congregations in the Presbytery of Edinburgh. Its most prominent church is St Giles' on the Royal Mile, first dedicated in 1243 but believed to date from before the 12th century. Saint Giles is historically the patron saint of Edinburgh. St Cuthbert's Church, Edinburgh, St Cuthbert's, situated at the west end of Princes Street Gardens in the shadow of Edinburgh Castle and St Giles' can lay claim to being the oldest Christian sites in the city, though the present St Cuthbert's, designed by Hippolyte Blanc, was dedicated in 1894.
Other Church of Scotland churches include Greyfriars Kirk, the Canongate Kirk, St Andrew's and St George's Church, St Andrew's and St George's West Church and the Edinburgh Barclay Church, Barclay Church. The Church of Scotland Offices are in Edinburgh, as is the General Assembly Hall of the Church of Scotland, Assembly Hall where the annual General Assembly of the Church of Scotland, General Assembly is held.
The Roman Catholic Archdiocese of St Andrews and Edinburgh has 27 parishes across the city. The Archbishop of St Andrews and Edinburgh has his official residence in Greenhill, Edinburgh, Greenhill, the diocesan offices are in nearby Marchmont, and its cathedral is St Mary's Cathedral, Edinburgh (Catholic), St Mary's Cathedral, Edinburgh. The Diocese of Edinburgh of the Scottish Episcopal Church has over 50 churches, half of them in the city. Its centre is the late 19th-century Gothic Revival architecture, Gothic style St Mary's Cathedral, Edinburgh (Episcopal), St Mary's Cathedral in the West End's Palmerston Place. Orthodox Christianity is represented by Pan, Romanian Orthodox Church, Romanian and Russian Orthodox Church, Russian Orthodox churches. There are several independent churches in the city, both Catholic and Protestant, including Charlotte Chapel (Edinburgh), Charlotte Chapel, Carrubbers Christian Centre, Bellevue Chapel and Sacred Heart, Edinburgh, Sacred Heart. There are also churches belonging to Quaker Meeting House, Edinburgh, Quakers, Christadelphians, Seventh-day Adventist Church, Seventh-day Adventists, Church of Christ, Scientist, The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints (LDS Church) and Elim Pentecostal Church.
Muslims have several places of worship across the city. Edinburgh Central Mosque, the largest Islamic place of worship, is located in Potterrow on the city's Southside, near Bristo Square. Construction was largely financed by a gift from King Fahd of Saudi Arabia and was completed in 1998. There is also an Ahmadiyya Muslim community.
The first recorded presence of a History of the Jews in Scotland#17th–19th centuries, Jewish community in Edinburgh dates back to the late 18th century. Edinburgh's Orthodox Judaism, Orthodox synagogue, opened in 1932, is in Salisbury Road and can accommodate a congregation of 2000. A Liberal Judaism (United Kingdom), Liberal Jewish congregation also meets in the city.
A Sikh gurdwara and a Hindu mandir are located in Leith. The city also has a Brahma Kumaris centre in the Polwarth area.
The Edinburgh Buddhist Centre, run by the Triratna Buddhist Community, formerly situated in Melville Terrace, now runs sessions at the Healthy Life Centre, Bread Street. Other Buddhist traditions are represented by groups which meet in the capital: the Community of Interbeing (followers of Thich Nhat Hanh), Rigpa, Samye Dzong, Theravadin, Pure Land Buddhism, Pure Land and Shambhala Buddhism, Shambala. There is a Sōtō Zen Priory in Portobello and a Theravadin Thai Buddhist Monastery in Slateford Road.
Edinburgh is home to a Baháʼí Faith, Baháʼí community, and a Theosophical Society meets in Great King Street.
Edinburgh has an Inter-Faith Association.
Edinburgh has over 39 List of graveyards and cemeteries in Edinburgh, graveyards and cemeteries, many of which are listed and of historical character, including several former church burial grounds. Examples include Old Calton Burial Ground, Greyfriars Kirkyard and Dean Cemetery.
Economy
 Tourism is also an important element in the city's economy. As a World Heritage Site, tourists visit historical sites such as Edinburgh Castle, the Palace of Holyroodhouse and the Old and New Towns. Their numbers are augmented in August each year during the Edinburgh Festivals, which attracts 4.4 million visitors, and generates over £100M for the local economy.
As the centre of Scotland's government and Scots law, legal system, the public sector plays a central role in Edinburgh's economy. Many departments of the Scottish Government are in the city. Other major employers include NHS Scotland and local government of Scotland, local government administration. When the £1.3bn Edinburgh & South East Scotland City Region Deal was signed in 2018, the region's Gross Value Added (GVA) contribution to the Economy of Scotland, Scottish economy was cited as £33bn, or 33% of the country's output. The City Region Deal funds a range of "Data Driven Innovation" hubs which are using data to innovate in the region, recognising the region's strengths in technology and data science, the growing importance of the data economy, and the need to tackle the digital skills gap, as a route to social and economic prosperity.
Tourism is also an important element in the city's economy. As a World Heritage Site, tourists visit historical sites such as Edinburgh Castle, the Palace of Holyroodhouse and the Old and New Towns. Their numbers are augmented in August each year during the Edinburgh Festivals, which attracts 4.4 million visitors, and generates over £100M for the local economy.
As the centre of Scotland's government and Scots law, legal system, the public sector plays a central role in Edinburgh's economy. Many departments of the Scottish Government are in the city. Other major employers include NHS Scotland and local government of Scotland, local government administration. When the £1.3bn Edinburgh & South East Scotland City Region Deal was signed in 2018, the region's Gross Value Added (GVA) contribution to the Economy of Scotland, Scottish economy was cited as £33bn, or 33% of the country's output. The City Region Deal funds a range of "Data Driven Innovation" hubs which are using data to innovate in the region, recognising the region's strengths in technology and data science, the growing importance of the data economy, and the need to tackle the digital skills gap, as a route to social and economic prosperity.
Culture
Festivals and celebrations
Edinburgh festival
The city hosts a series of festivals that run between the end of July and early September each year. The best known of these events are the Edinburgh Fringe, Edinburgh Festival Fringe, the Edinburgh International Festival, the Edinburgh Military Tattoo, the Edinburgh Art Festival and the Edinburgh International Book Festival. The longest established of these festivals is the Edinburgh International Festival, which was first held in 1947 and consists mainly of a programme of high-profile theatre productions and classical music performances, featuring international directors, conductors, theatre companies and orchestras. This has since been overtaken in size by the Edinburgh Fringe which began as a programme of marginal acts alongside the "official" Festival and has become the world's largest performing arts festival. In 2017, nearly 3400 different shows were staged in 300 venues across the city. Comedy has become one of the mainstays of the Fringe, with numerous well-known comedians getting their first 'break' there, often by being chosen to receive the Edinburgh Comedy Awards, Edinburgh Comedy Award. The Edinburgh Military Tattoo, occupies the Castle Esplanade every night for three weeks each August, with massed pipe bands and military bands drawn from around the world. Performances end with a short fireworks display. As well as the summer festivals, List of Edinburgh festivals, many other festivals are held during the rest of the year, including the Edinburgh International Film Festival and Edinburgh International Science Festival. The summer of 2020 was the first time in its 70-year history that the Edinburgh festival was not run, being cancelled due to the COVID-19 pandemic. This affected many of the tourist-focused businesses in Edinburgh which depend on the various festivals over summer to return an annual profit.Edinburgh's Hogmanay
 The annual Edinburgh Hogmanay celebration was originally an informal street party focused on the Tron Kirk in the Old Town's High Street. Since 1993, it has been officially organised with the focus moved to Princes Street. In 1996, over 300,000 people attended, leading to ticketing of the main street party in later years up to a limit of 100,000 tickets. Hogmanay now covers four days of processions, concerts and fireworks, with the street party beginning on Hogmanay. Alternative tickets are available for entrance into the Princes Street Gardens concert and Cèilidh, where well-known artists perform and ticket holders can participate in traditional Scottish cèilidh dancing. The event attracts thousands of people from all over the world.
The annual Edinburgh Hogmanay celebration was originally an informal street party focused on the Tron Kirk in the Old Town's High Street. Since 1993, it has been officially organised with the focus moved to Princes Street. In 1996, over 300,000 people attended, leading to ticketing of the main street party in later years up to a limit of 100,000 tickets. Hogmanay now covers four days of processions, concerts and fireworks, with the street party beginning on Hogmanay. Alternative tickets are available for entrance into the Princes Street Gardens concert and Cèilidh, where well-known artists perform and ticket holders can participate in traditional Scottish cèilidh dancing. The event attracts thousands of people from all over the world.
Beltane and other festivals
On the night of 30 April the Beltane Fire Festival takes place on Calton Hill, involving a procession followed by scenes inspired by paganism, pagan old spring fertility celebrations. At the beginning of October each year the Navratri, Dussehra Hindu Festival is also held on Calton Hill.Music, theatre and film
Media
Newspapers
The main local newspaper is the ''Edinburgh Evening News''. It is owned and published alongside its sister titles ''The Scotsman'' and ''Scotland on Sunday'' by JPIMedia.Radio
The city has two commercial radio stations: Forth 1, a station which broadcasts mainstream chart music, and Forth 2 on medium wave which plays classic hits. Capital Scotland and Eklipse Sports Radio also have transmitters covering Edinburgh. Along with the UK national radio stations, BBC Radio Scotland and the Gaelic language service BBC Radio nan Gàidheal are also broadcast. DAB digital radio is broadcast over two local multiplexes. BFBS Radio broadcasts from studios on the base at Dreghorn Barracks across the city on 98.5FM as part of its UK Bases network. Small scale DAB started October 2022 with numerous community stations onboardTelevision
Television, along with most radio services, is broadcast to the city from the Craigkelly transmitting station situated in Fife on the opposite side of the Firth of Forth and the Black Hill transmitting station in North Lanarkshire to the west. There are no television stations based in the city. Edinburgh Television existed in the late 1990s to early 2003 and STV Edinburgh existed from 2015 to 2018.Museums, libraries and galleries
 Edinburgh has many museums and libraries. These include the
Edinburgh has many museums and libraries. These include the National Museum of Scotland
The National Museum of Scotland in Edinburgh, Scotland, was formed in 2006 with the merger of the new Museum of Scotland, with collections relating to Scottish antiquities, culture and history, and the adjacent Royal Scottish Museum (opened in ...
, the National Library of Scotland
The National Library of Scotland (NLS) ( gd, Leabharlann Nàiseanta na h-Alba, sco, Naitional Leebrar o Scotland) is the legal deposit library of Scotland and is one of the country's National Collections. As one of the largest libraries in the ...
, National War Museum, the Museum of Edinburgh, Surgeons' Hall, Surgeons' Hall Museum, the Writers' Museum, the Museum of Childhood (Edinburgh), Museum of Childhood and Dynamic Earth (Edinburgh), Dynamic Earth. The Museum on the Mound, Museum on The Mound has exhibits on money and banking.
Edinburgh Zoo, covering on Corstorphine Hill, is the second most visited paid tourist attraction in Scotland, and home to two giant pandas, Tian Tian and Yang Guang, on loan from the People's Republic of China.
Edinburgh is also home to HMY Britannia, The Royal Yacht Britannia, decommissioned in 1997 and now a five-star visitor attraction and evening events venue permanently berthed at Ocean Terminal, Edinburgh, Ocean Terminal.
Edinburgh contains Scotland's three National Galleries of Scotland, National Galleries of Art as well as numerous smaller art galleries. The national collection is housed in the Scottish National Gallery
The Scottish National Gallery (formerly the National Gallery of Scotland) is the national art gallery of Scotland. It is located on The Mound in central Edinburgh, close to Princes Street. The building was designed in a neoclassical style by W ...
, located on The Mound, comprising the linked National Gallery of Scotland building and the Royal Scottish Academy building. Contemporary collections are shown in the Scottish National Gallery of Modern Art which occupies a split site at Belford. The Scottish National Portrait Gallery on Queen Street focuses on portraits and photography.
 The council-owned City Art Centre in Market Street mounts regular art exhibitions. Across the road, Fruitmarket Gallery, The Fruitmarket Gallery offers world-class exhibitions of contemporary art, featuring work by British and international artists with both emerging and established international reputations.
The city hosts several of Scotland's galleries and organisations dedicated to contemporary visual art. Significant strands of this infrastructure include Creative Scotland, Edinburgh College of Art, Talbot Rice Gallery (University of Edinburgh), Collective Gallery (based at the City Observatory) and the Edinburgh Annuale.
There are also many small private shops/galleries that provide space to showcase works from local artists.
The council-owned City Art Centre in Market Street mounts regular art exhibitions. Across the road, Fruitmarket Gallery, The Fruitmarket Gallery offers world-class exhibitions of contemporary art, featuring work by British and international artists with both emerging and established international reputations.
The city hosts several of Scotland's galleries and organisations dedicated to contemporary visual art. Significant strands of this infrastructure include Creative Scotland, Edinburgh College of Art, Talbot Rice Gallery (University of Edinburgh), Collective Gallery (based at the City Observatory) and the Edinburgh Annuale.
There are also many small private shops/galleries that provide space to showcase works from local artists.
Shopping
The locale aroundPrinces Street
Princes Street ( gd, Sràid nam Prionnsan) is one of the major thoroughfares in central Edinburgh, Scotland and the main shopping street in the capital. It is the southernmost street of Edinburgh's New Town, stretching around 1.2 km (three ...
is the main shopping area in the city centre, with souvenir shops, chain stores such as Boots the Chemist, Edinburgh Woollen Mill, H&M and Jenners. George Street, north of Princes Street, is the preferred location for some upmarket shops and independent stores. At the east end of Princes Street, the redeveloped St James Quarter opened its doors in June 2021, while next to the Balmoral Hotel and Waverley Station is Waverley Market. Multrees Walk, adjacent to the St. James Centre, is a recent addition to the central shopping district, dominated by the presence of Harvey Nichols. Shops here include Louis Vuitton, Mulberry (company), Mulberry and Calvin Klein.
Edinburgh also has substantial retail parks outside the city centre. These include The Gyle Shopping Centre and Hermiston Gait in the west of the city, Cameron Toll Shopping Centre, Straiton Retail Park (actually just outside the city, in Midlothian) and Fort Kinnaird in the south and east, and Ocean Terminal, Edinburgh, Ocean Terminal in the north on the Leith
Leith (; gd, Lìte) is a port area in the north of the city of Edinburgh, Scotland, founded at the mouth of the Water of Leith. In 2021, it was ranked by '' Time Out'' as one of the top five neighbourhoods to live in the world.
The earliest ...
waterfront.
Governance
Local government
 Following local government reorganisation in 1996, the City of Edinburgh Council constitutes one of the Council areas of Scotland, 32 council areas of Scotland. Like all other local authorities of Scotland, the council has powers over most matters of local administration such as housing, planning, Transport in Edinburgh, local transport, parks, economic development and regeneration. The council comprises 63 elected councillors, returned from 17 Wards of the United Kingdom, multi-member electoral wards in the city.
Following the 2007 City of Edinburgh Council election the incumbent Scottish Labour Party, Labour Party lost majority control of the council after 23 years to a Scottish Liberal Democrats, Liberal Democrat/Scottish National Party, SNP coalition.
After the 2017 election, the SNP and Labour formed a coalition administration, which lasted until the next election in 2022.
The 2022 City of Edinburgh Council election resulted in the most politically balanced council in the UK, with 19 SNP, 13 Labour, 12 Liberal Democrat, 10 Green and 9 Conservative councillors. A minority Labour administration was formed, being voted in by Scottish Conservative and Scottish Liberal Democrat councillors. The SNP and Greens presented a coalition agreement, but could not command majority support in the Council. This caused controversy amongst the Scottish Labour Party group for forming an administration supported by Conservatives and led to the suspension of two Labour councillors on the Council for abstaining on the vote to approve the new administration.
The city's Coat of arms of Edinburgh, coat of arms was registered by the Lord Lyon King of Arms in 1732.
Following local government reorganisation in 1996, the City of Edinburgh Council constitutes one of the Council areas of Scotland, 32 council areas of Scotland. Like all other local authorities of Scotland, the council has powers over most matters of local administration such as housing, planning, Transport in Edinburgh, local transport, parks, economic development and regeneration. The council comprises 63 elected councillors, returned from 17 Wards of the United Kingdom, multi-member electoral wards in the city.
Following the 2007 City of Edinburgh Council election the incumbent Scottish Labour Party, Labour Party lost majority control of the council after 23 years to a Scottish Liberal Democrats, Liberal Democrat/Scottish National Party, SNP coalition.
After the 2017 election, the SNP and Labour formed a coalition administration, which lasted until the next election in 2022.
The 2022 City of Edinburgh Council election resulted in the most politically balanced council in the UK, with 19 SNP, 13 Labour, 12 Liberal Democrat, 10 Green and 9 Conservative councillors. A minority Labour administration was formed, being voted in by Scottish Conservative and Scottish Liberal Democrat councillors. The SNP and Greens presented a coalition agreement, but could not command majority support in the Council. This caused controversy amongst the Scottish Labour Party group for forming an administration supported by Conservatives and led to the suspension of two Labour councillors on the Council for abstaining on the vote to approve the new administration.
The city's Coat of arms of Edinburgh, coat of arms was registered by the Lord Lyon King of Arms in 1732.
Scottish Parliament
 Edinburgh, like all of Scotland, is represented in the
Edinburgh, like all of Scotland, is represented in the Scottish Parliament
The Scottish Parliament ( gd, Pàrlamaid na h-Alba ; sco, Scots Pairlament) is the devolved, unicameral legislature of Scotland. Located in the Holyrood area of the capital city, Edinburgh, it is frequently referred to by the metonym Holyro ...
, situated in the Holyrood, Edinburgh, Holyrood area of the city. For electoral purposes, the city is divided into six constituencies which, along with 3 seats outside of the city, form part of the Lothian (Scottish Parliament electoral region), Lothian region. Each constituency elects one Member of the Scottish Parliament (MSP) by the first past the post system of election, and the region elects seven Additional Member System, additional MSPs to produce a result based on a form of proportional representation.
As of the 2021 Scottish Parliament election, 2021 election, the Scottish National Party have four MSPs: Ash Denham for Edinburgh Eastern (Scottish Parliament constituency), Edinburgh Eastern, Ben Macpherson (politician), Ben Macpherson for Edinburgh Northern and Leith (Scottish Parliament constituency), Edinburgh Northern and Leith and Gordon MacDonald (Scottish politician), Gordon MacDonald for Edinburgh Pentlands (Scottish Parliament constituency), Edinburgh Pentlands and Angus Robertson for Edinburgh Central (Scottish Parliament constituency), Edinburgh Central constituencies. Alex Cole-Hamilton, the Leader of the Scottish Liberal Democrats represents Edinburgh Western (Scottish Parliament constituency), Edinburgh Western and Daniel Johnson (Scottish politician), Daniel Johnson of the Scottish Labour Party represents Edinburgh Southern (Scottish Parliament constituency), Edinburgh Southern constituency.
In addition, the city is also represented by seven regional MSPs representing the Lothian electoral region: The Conservatives have three regional MSPs: Jeremy Balfour, Miles Briggs and Sue Webber, Labour have two regional MSPs: Sarah Boyack and Foysol Choudhury and Scottish Greens had two regional MSP elected: Green's Co-Leader Lorna Slater and Alison Johnstone. However, following her election as the Presiding Officer of the Scottish Parliament, Presiding Officer of the 6th Session of the Scottish Parliament on 13 May 2021, Alison Johnstone has abided by the established parliamentary convention for speakers and renounced all affiliation with her former political party for the duration of her term as Presiding Officer. So she presently sits as an independent MSP for the Lothians Region.
UK Parliament
Edinburgh is also represented in the House of Commons of the United Kingdom by five List of MPs elected in the 2017 United Kingdom general election, Members of Parliament. The city is divided into Edinburgh North and Leith (UK Parliament constituency), Edinburgh North and Leith, Edinburgh East (UK Parliament constituency), Edinburgh East, Edinburgh South (UK Parliament constituency), Edinburgh South, Edinburgh South West (UK Parliament constituency), Edinburgh South West, and Edinburgh West (UK Parliament constituency), Edinburgh West, each constituency electing one member by the first past the post system. Since the 2019 United Kingdom general election, 2019 UK General election, Edinburgh is represented by three Scottish National Party MPs (Deirdre Brock, Edinburgh North and Leith/Tommy Sheppard, Edinburgh East/Joanna Cherry, Edinburgh South West), one Scottish Liberal Democrats, Liberal Democrat MP in Edinburgh West (Christine Jardine) and one Scottish Labour Party, Labour MP in Edinburgh South (Ian Murray).Transport
Air
Edinburgh Airport is Scotland's busiest airport and the principal international gateway to the capital, handling over 14.7 million passengers; it was also the Busiest airports in the United Kingdom by total passenger traffic, sixth-busiest airport in the United Kingdom by total passengers in 2019. In anticipation of rising passenger numbers, the former operator of the airport BAA Limited, BAA outlined a draft masterplan in 2011 to provide for the expansion of the airfield and the terminal building. In June 2012, Global Infrastructure Partners purchased the airport for £807 million. The possibility of building a second runway to cope with an increased number of aircraft movements has also been mooted.Buses
 Travel in Edinburgh is undertaken predominantly by bus. Lothian Buses, the successor company to Edinburgh Corporation Transport Department, operate the majority of public transport bus service, city bus services within the city and to surrounding suburbs, with the most routes running via Princes Street. Services further afield operate from the Edinburgh Bus Station off St Andrew Square, Edinburgh, St Andrew Square and Waterloo Place and are operated mainly by Stagecoach East Scotland, Scottish Citylink, National Express Coaches and Borders Buses.
Lothian Buses and McGill's Scotland East operate the city's branded public tour bus service, tour buses. The night bus service and airport buses are mainly operated by Lothian Buses link. In 2019, Lothian Buses recorded 124.2 million passenger journeys.
To tackle traffic congestion, Edinburgh is now served by six park & ride sites on the periphery of the city at Sheriffhall (in Midlothian), Ingliston, Riccarton, Edinburgh, Riccarton, Inverkeithing (in Fife), Newcraighall and Straiton, Loanhead, Straiton (in Midlothian). A Edinburgh congestion charge#Referendum, referendum of Edinburgh residents in February 2005 rejected a proposal to introduce Edinburgh congestion charge, congestion charging in the city.
Travel in Edinburgh is undertaken predominantly by bus. Lothian Buses, the successor company to Edinburgh Corporation Transport Department, operate the majority of public transport bus service, city bus services within the city and to surrounding suburbs, with the most routes running via Princes Street. Services further afield operate from the Edinburgh Bus Station off St Andrew Square, Edinburgh, St Andrew Square and Waterloo Place and are operated mainly by Stagecoach East Scotland, Scottish Citylink, National Express Coaches and Borders Buses.
Lothian Buses and McGill's Scotland East operate the city's branded public tour bus service, tour buses. The night bus service and airport buses are mainly operated by Lothian Buses link. In 2019, Lothian Buses recorded 124.2 million passenger journeys.
To tackle traffic congestion, Edinburgh is now served by six park & ride sites on the periphery of the city at Sheriffhall (in Midlothian), Ingliston, Riccarton, Edinburgh, Riccarton, Inverkeithing (in Fife), Newcraighall and Straiton, Loanhead, Straiton (in Midlothian). A Edinburgh congestion charge#Referendum, referendum of Edinburgh residents in February 2005 rejected a proposal to introduce Edinburgh congestion charge, congestion charging in the city.
Railway
Trams
Education
 There are three universities in Edinburgh: the
There are three universities in Edinburgh: the University of Edinburgh
The University of Edinburgh ( sco, University o Edinburgh, gd, Oilthigh Dhùn Èideann; abbreviated as ''Edin.'' in post-nominals) is a public research university based in Edinburgh, Scotland. Granted a royal charter by King James VI in 15 ...
, Heriot-Watt University and Edinburgh Napier University.
Established by royal charter in 1583, the University of Edinburgh is one of Scotland's ancient universities of Scotland, ancient universities and is the fourth oldest in the country after University of St Andrews, St Andrews, University of Glasgow, Glasgow and University of Aberdeen, Aberdeen. Originally centred on Old College, University of Edinburgh, Old College the university expanded to premises on The Mound, the Royal Mile and George Square. Today, the King's Buildings in the south of the city contain most of the schools within the College of Science and Engineering. In 2002, the University of Edinburgh Medical School, medical school moved to purpose built accommodation adjacent to the new Royal Infirmary of Edinburgh at Little France. The university is placed 16th in the QS World University Rankings for 2022.
Heriot-Watt University is based at the Riccarton, Edinburgh, Riccarton campus in the west of Edinburgh. Originally established in 1821, as the world's first Mechanics' Institutes, mechanics' institute, it was granted university status by royal charter in 1966. It has other campuses in the Scottish Borders, Orkney, United Arab Emirates and Putrajaya in Malaysia. It takes the name ''Heriot-Watt'' from Scottish inventor James Watt and Scottish philanthropist and goldsmith George Heriot. Heriot-Watt University has been named International University of the Year by ''The Times and Sunday Times Good University Guide 2018''. In the latest Research Excellence Framework, it was ranked overall in the Top 25% of UK universities and 1st in Scotland for research impact.
Edinburgh Napier University was originally founded as the Napier College, which was renamed Napier Polytechnic in 1986 and gained university status in 1992. Edinburgh Napier University has campuses in the south and west of the city, including the former Merchiston Tower and Craiglockhart Hydropathic. It is home to the Screen Academy Scotland.
Queen Margaret University was located in Edinburgh before it moved to a new campus just outside the city boundary on the edge of Musselburgh in 2008.
Until 2012, further education colleges in the city included Jewel and Esk College (incorporating Leith Nautical College founded in 1903), Edinburgh's Telford College, Telford College, opened in 1968, and Stevenson College (Edinburgh), Stevenson College, opened in 1970. These have now been amalgamated to form Edinburgh College. Scotland's Rural College also has a campus in south Edinburgh. Other institutions include the Royal College of Surgeons of Edinburgh and the Royal College of Physicians of Edinburgh which were established by royal charter in 1506 and 1681 respectively. The Trustees Drawing Academy of Edinburgh, founded in 1760, became the Edinburgh College of Art in 1907.
There are 18 nursery, 94 primary and 23 secondary List of schools in Edinburgh, schools administered by the City of Edinburgh Council.
Edinburgh is home to Royal High School, Edinburgh, The Royal High School, one of the List of the oldest schools in the United Kingdom, oldest schools in the country and List of the oldest schools in the world, the world. The city also has several Independent school (UK)#Independent schools in Scotland, independent, fee-paying schools including Edinburgh Academy, Fettes College, George Heriot's School, George Watson's College, Merchiston Castle School, Stewart's Melville College and The Mary Erskine School. In 2009, the proportion of pupils attending independent schools was 24.2%, far above the Scottish national average of just over 7% and higher than in any other region of Scotland. In August 2013, the City of Edinburgh Council opened the city's first stand-alone Gaelic primary school, Bun-sgoil Taobh na Pàirce.
Healthcare
 The main NHS Lothian hospitals serving the Edinburgh area are the Royal Infirmary of Edinburgh, which includes the University of Edinburgh Medical School, and the Western General Hospital, which has a large cancer treatment centre and nurse-led Minor Injuries Clinic. The Royal Edinburgh Hospital in Morningside specialises in mental health. The Royal Hospital for Children and Young People, colloquially referred to as ''the Sick Kids'', is a specialist paediatrics hospital.
There are two private hospitals: Murrayfield Hospital in the west of the city and Shawfair Hospital in the south; both are owned by Spire Healthcare.
The main NHS Lothian hospitals serving the Edinburgh area are the Royal Infirmary of Edinburgh, which includes the University of Edinburgh Medical School, and the Western General Hospital, which has a large cancer treatment centre and nurse-led Minor Injuries Clinic. The Royal Edinburgh Hospital in Morningside specialises in mental health. The Royal Hospital for Children and Young People, colloquially referred to as ''the Sick Kids'', is a specialist paediatrics hospital.
There are two private hospitals: Murrayfield Hospital in the west of the city and Shawfair Hospital in the south; both are owned by Spire Healthcare.
Sport
Football
Men's
Edinburgh has three association football, football clubs that play in the Scottish Professional Football League (SPFL): Heart of Midlothian F.C., Heart of Midlothian, founded in 1874, Hibernian F.C., Hibernian, founded in 1875 and F.C. Edinburgh, founded in 1966. Heart of Midlothian and Hibernian are known locally as "Hearts" and "Hibs", respectively. Both play in the Scottish Premiership. They are the oldest city rivals in Scotland and the Edinburgh derby is one of the oldest derby matches in world football. Both clubs have won the list of Scottish football champions, Scottish league championship four times. Hearts have won the Scottish Cup eight times and the Scottish League Cup four times. Hibs have won the Scottish Cup and the Scottish League Cup three times each. Edinburgh City F.C., Edinburgh City were promoted to Scottish League Two in the 2015–16 season, becoming the first club to win promotion to the SPFL via the pyramid system playoffs. Edinburgh was also home to four other List of former Scottish Football League clubs, former Scottish Football League clubs: the original Edinburgh City F.C. (1928), Edinburgh City (founded in 1928), Leith Athletic F.C., Leith Athletic, Meadowbank Thistle F.C., Meadowbank Thistle and St Bernard's F.C., St Bernard's. Meadowbank Thistle played at Meadowbank Stadium until 1995, when the club moved to Livingston, West Lothian, Livingston and became Livingston F.C., Livingston F.C. The Scotland national football team, Scottish national team has very occasionally played at Easter Road Stadium, Easter Road and Tynecastle Stadium, Tynecastle, although its normal Scotland national football team home stadium, home stadium is Hampden Park in Glasgow. St Bernard's' New Logie Green was used to host the 1896 Scottish Cup Final, the only time the match has been played outside Glasgow.Paul Smith & Shirley Smith (2005) ''The Ultimate Directory of English & Scottish Football League Grounds Second Edition 1888–2005'', Yore Publications, p202 The city also plays host to Lowland Football League clubs Civil Service Strollers F.C., Civil Service Strollers, Edinburgh University A.F.C., Edinburgh University and Spartans F.C., Spartans, as well as East of Scotland Football League, East of Scotland League clubs Craigroyston F.C., Craigroyston, Edinburgh United F.C., Edinburgh United, Heriot-Watt University F.C., Heriot-Watt University, Leith Athletic F.C., Leith Athletic, Lothian Thistle Hutchison Vale F.C., Lothian Thistle Hutchison Vale, and Tynecastle F.C., Tynecastle.Women's
In women's football, Hearts Ladies F.C., Hearts, Hibernian L.F.C., Hibs and Spartans W.F.C., Spartans play in the Scottish Women's Premier League, SWPL 1. Lothian Thistle Hutchison Vale F.C.#Women, Hutchison Vale and Boroughmuir Thistle F.C., Boroughmuir Thistle play in the Scottish Women's Premier League, SWPL 2.Rugby
The Scotland national rugby union team play at Murrayfield Stadium, and the professional Edinburgh Rugby team play at the nextdoor Edinburgh Rugby Stadium; both are owned by the Scottish Rugby Union and are also used for other events, including music concerts. Murrayfield is the largest capacity stadium in Scotland, seating 67,144 spectators. Edinburgh is also home to Scottish Premiership (rugby), Scottish Premiership teams Boroughmuir RFC, Currie RFC, the Edinburgh Academicals, Heriot's Rugby Club and Watsonians RFC. The Edinburgh Academicals ground at Raeburn Place was the location of the world's first international rugby game on 27 March 1871, between Scotland and England. Rugby league is represented by the Edinburgh Eagles who play in the Rugby League Conference Scotland Division. Murrayfield Stadium has hosted the Magic Weekend where all Super League matches are played in the stadium over one weekend.Other sports
The Scottish cricket team, which represents Scotland internationally, play their home matches at the The Grange Club, Grange cricket club. The Edinburgh Capitals are the latest of a succession of ice hockey clubs in the Scottish capital. Previously Edinburgh was represented by the Murrayfield Racers (2018), the original Murrayfield Racers ''(who folded in 1996)'' and the Edinburgh Racers. The club play their home games at the Murrayfield Ice Rink and have competed in the eleven-team professional Scottish National League (ice hockey), Scottish National League (SNL) since the 2018–19 season. Next door to Murrayfield Ice Rink is a 7-sheeter dedicated curling facility where curling is played from October to March each season. Caledonia Pride are the only women's professional basketball team in Scotland. Established in 2016, the team compete in the UK wide Women's British Basketball League and play their home matches at the Oriam National Performance Centre. Edinburgh also has several men's basketball teams within the Scottish National League. Boroughmuir Blaze, City of Edinburgh Kings and Edinburgh Lions all compete in Division 1 of the National League, and Pleasance B.C. compete in Division 2. The Edinburgh Diamond Devils is a baseball club which won its first Scottish Championship in 1991 as the "Reivers." 1992 saw the team repeat the achievement, becoming the first team to do so in league history. The same year saw the start of their first youth team, the Blue Jays. The club adopted its present name in 1999. Edinburgh has also hosted national and international sports events including the World Student Games, the 1970 British Commonwealth Games, the 1986 Commonwealth Games and the inaugural 2000 Commonwealth Youth Games. For the 1970 Games the city built Olympic standard venues and facilities including Meadowbank Stadium and the Royal Commonwealth Pool. The Pool underwent refurbishment in 2012 and hosted the Diving competition in the 2014 Commonwealth Games which were held in Glasgow. In American football, the Scottish Claymores played World League of American Football, WLAF/NFL Europe games at Murrayfield, including their World Bowl IV, World Bowl 96 victory. From 1995 to 1997 they played all their games there, from 1998 to 2000 they split their home matches between Murrayfield and Glasgow's Hampden Park, then moved to Glasgow full-time, with one final Murrayfield appearance in 2002. The city's most successful non-professional team are the Edinburgh Wolves who play at Meadowbank Stadium. The Edinburgh Marathon has been held annually in the city since 2003 with more than 16,000 runners taking part on each occasion. Its organisers have called it "the fastest marathon in the UK" due to the elevation drop of . The city also organises a half-marathon, as well as 10,000 metres, 10 km () and 5000 metres, 5 km () races, including a race on 1 January each year. Edinburgh has a Motorcycle speedway, speedway team, the Edinburgh Monarchs, which, since the loss of its stadium in the city, has raced at the Lothian Arena in Armadale, West Lothian. The Monarchs have won the Premier League (speedway), Premier League championship five times in their history, in 2003 and again in 2008, 2010, 2014 and 2015.People
 Edinburgh has a long literary tradition, which became especially evident during the
Edinburgh has a long literary tradition, which became especially evident during the Scottish Enlightenment
The Scottish Enlightenment ( sco, Scots Enlichtenment, gd, Soillseachadh na h-Alba) was the period in 18th- and early-19th-century Scotland characterised by an outpouring of intellectual and scientific accomplishments. By the eighteenth century ...
. This heritage and the city's lively literary life in the present led to it being declared the first UNESCO City of Literature in 2004. Prominent authors who have lived in Edinburgh include the economist Adam Smith, born in Kirkcaldy and author of ''The Wealth of Nations'', James Boswell, biographer of Life of Samuel Johnson, Samuel Johnson; Sir Walter Scott
Sir Walter Scott, 1st Baronet (15 August 1771 – 21 September 1832), was a Scottish novelist, poet, playwright and historian. Many of his works remain classics of European and Scottish literature, notably the novels ''Ivanhoe'', ''Rob Roy (n ...
, creator of the historical novel and author of works such as ''Rob Roy (novel), Rob Roy'', ''Ivanhoe'', and ''The Heart of Midlothian, Heart of Midlothian''; James Hogg, author of ''The Private Memoirs and Confessions of a Justified Sinner''; Robert Louis Stevenson, creator of ''Treasure Island'', ''Kidnapped (novel), Kidnapped'', and ''Strange Case of Dr Jekyll and Mr Hyde''; Arthur Conan Doyle, Sir Arthur Conan Doyle, the creator of Sherlock Holmes; Muriel Spark, author of ''The Prime of Miss Jean Brodie (novel), The Prime of Miss Jean Brodie''; Irvine Welsh, author of ''Trainspotting (novel), Trainspotting'', whose novels are mostly set in the city and often written in colloquial Scots;
Ian Rankin, author of the Detective Inspector John Rebus, Inspector Rebus series of crime thrillers, Alexander McCall Smith, author of the No. 1 Ladies' Detective Agency series, and J. K. Rowling, author of Harry Potter, who wrote much of her first book in Edinburgh coffee shops and now lives in the Cramond area of the city.
 Scotland has a rich history of science and engineering, with Edinburgh producing a number of leading figures. John Napier, inventor of logarithms, was born in Merchiston Tower and lived and died in the city. His house now forms part of the original campus of Napier University which was named in his honour. He lies buried under St. Cuthbert's Church. James Clerk Maxwell, founder of the modern theory of electromagnetism, was born at 14 India Street (now the home of the James Clerk Maxwell Foundation) and educated at the Edinburgh Academy and the University of Edinburgh, as was the engineer and telephone pioneer Alexander Graham Bell. James Braidwood (firefighter), James Braidwood, who organised Britain's first municipal fire brigade, was also born in the city and began his career there.
Other names connected with the city include physicist Max Born, a principle founder of Quantum mechanics and Nobel Prize in Physics, Nobel laureate; Charles Darwin, the biologist who propounded the theory of natural selection; David Hume, philosopher, economist and historian;
Scotland has a rich history of science and engineering, with Edinburgh producing a number of leading figures. John Napier, inventor of logarithms, was born in Merchiston Tower and lived and died in the city. His house now forms part of the original campus of Napier University which was named in his honour. He lies buried under St. Cuthbert's Church. James Clerk Maxwell, founder of the modern theory of electromagnetism, was born at 14 India Street (now the home of the James Clerk Maxwell Foundation) and educated at the Edinburgh Academy and the University of Edinburgh, as was the engineer and telephone pioneer Alexander Graham Bell. James Braidwood (firefighter), James Braidwood, who organised Britain's first municipal fire brigade, was also born in the city and began his career there.
Other names connected with the city include physicist Max Born, a principle founder of Quantum mechanics and Nobel Prize in Physics, Nobel laureate; Charles Darwin, the biologist who propounded the theory of natural selection; David Hume, philosopher, economist and historian; James Hutton
James Hutton (; 3 June O.S.172614 June 1726 New Style. – 26 March 1797) was a Scottish geologist, agriculturalist, chemical manufacturer, naturalist and physician. Often referred to as the father of modern geology, he played a key role i ...
, regarded as the "Father of Geology"; Joseph Black
Joseph Black (16 April 1728 – 6 December 1799) was a Scottish physicist and chemist, known for his discoveries of magnesium, latent heat, specific heat, and carbon dioxide. He was Professor of Anatomy and Chemistry at the University of Glas ...
, the chemist who discovered Magnesium and Carbon dioxide, Carbon Dioxide, and one of the founders of Thermodynamics; pioneering medical researchers Joseph Lister, 1st Baron Lister, Joseph Lister and James Young Simpson; chemist and discoverer of the element nitrogen Daniel Rutherford; Colin Maclaurin, mathematician and developer of the Maclaurin series, and Ian Wilmut, the geneticist involved in the cloning of Dolly (sheep), Dolly the sheep just outside Edinburgh, at the Roslin Institute. The stuffed carcass of Dolly the sheep is now on display in the National Museum of Scotland. The latest in a long line of science celebrities associated with the city is theoretical physicist, Nobel Prize in Physics, Nobel laureate and Professor Emeritus at the University of Edinburgh
The University of Edinburgh ( sco, University o Edinburgh, gd, Oilthigh Dhùn Èideann; abbreviated as ''Edin.'' in post-nominals) is a public research university based in Edinburgh, Scotland. Granted a royal charter by King James VI in 15 ...
Peter Higgs, born in Newcastle but resident in Edinburgh for most of his academic career, after whom the Higgs boson particle has been named.
 Edinburgh has been the birthplace of actors like Alastair Sim and Sir Sean Connery, known for being the first cinematic James Bond, the comedian and actor Ronnie Corbett, best known as one of The Two Ronnies, and the impressionist Rory Bremner. Famous artists from the city include the portrait painters Sir Henry Raeburn, Sir David Wilkie (artist), David Wilkie and Allan Ramsay (artist), Allan Ramsay.
The city has produced or been home to some very successful musicians in recent decades, particularly Ian Anderson, front man of the band Jethro Tull (band), Jethro Tull, The Incredible String Band, the folk duo The Corries, Wattie Buchan, lead singer and founding member of punk band The Exploited, Shirley Manson, lead singer of the band Garbage (band), Garbage, the Bay City Rollers, The Proclaimers, Boards of Canada and Idlewild (band), Idlewild.
Edinburgh has been the birthplace of actors like Alastair Sim and Sir Sean Connery, known for being the first cinematic James Bond, the comedian and actor Ronnie Corbett, best known as one of The Two Ronnies, and the impressionist Rory Bremner. Famous artists from the city include the portrait painters Sir Henry Raeburn, Sir David Wilkie (artist), David Wilkie and Allan Ramsay (artist), Allan Ramsay.
The city has produced or been home to some very successful musicians in recent decades, particularly Ian Anderson, front man of the band Jethro Tull (band), Jethro Tull, The Incredible String Band, the folk duo The Corries, Wattie Buchan, lead singer and founding member of punk band The Exploited, Shirley Manson, lead singer of the band Garbage (band), Garbage, the Bay City Rollers, The Proclaimers, Boards of Canada and Idlewild (band), Idlewild.
International relations
Twin towns and sister cities
The City of Edinburgh has entered into 14 international town twinning, twinning arrangements since 1954. Most of the arrangements are styled as ''Twin Cities'' but the agreement with Kraków is designated as a ''Partner City'', and the agreement with Kyoto Prefecture is officially styled as a ''Friendship Link'', reflecting its status as the only region to be twinned with Edinburgh. For a list of consulates in Edinburgh, see List of diplomatic missions in Scotland.See also
* Outline of Edinburgh * National Archives of Scotland * OPENCities * Tourism in ScotlandNotes
References
Further reading
* * H Coghill, ''Edinburgh, The Old Town'', John Donald, Edinburgh 1990, * Arthur L. Herman, A Herman, ''How the Scots Invented the Modern World: The True Story of How Western Europe's Poorest Nation Created Our World & Everything in It'', Three Rivers Press, New York, 2001, ; also published as ''The Scottish Enlightenment: The Scots' Invention of the Modern World'', HarperCollins, London, 2001, * A Massie, ''Edinburgh'', Sinclair-Stevenson, London 1994, * S Mullay, ''The Edinburgh Encyclopedia'', Mainstream Publishing, Edinburgh and London 1996, * S Mullay, ''The Illustrated History of Edinburgh's Suburbs'', Breedon Books, Derby 2008,External links
City of Edinburgh Council website
Marketing Edinburgh
official tourist agency * {{Authority control Edinburgh, Capital cities in the United Kingdom Council areas of Scotland Cities in Scotland Districts of Scotland Feudalism in Scotland Lieutenancy areas of Scotland Port cities and towns in Scotland Port cities and towns of the North Sea Scottish society Populated places established in the 7th century 7th-century establishments in Europe Towns in Edinburgh council area