|
Y Gododdin
''Y Gododdin'' () is a medieval Welsh poem consisting of a series of elegies to the men of the Brittonic kingdom of Gododdin and its allies who, according to the conventional interpretation, died fighting the Angles of Deira and Bernicia at a place named '' Catraeth'' in about AD 600. It is traditionally ascribed to the bard Aneirin and survives only in one manuscript, the '' Book of Aneirin''. The ''Book of Aneirin'' manuscript is from the later 13th century, but ''Y Gododdin'' has been dated to between the 7th and the early 11th centuries. The text is partly written in Middle Welsh orthography and partly in Old Welsh. The early date would place its oral composition soon after the battle, presumably in the ''Hen Ogledd'' ("Old North"); as such it would have originated in the Cumbric dialect of Common Brittonic.Elliott (2005), p. 583. Others consider it the work of a poet from Wales in the 9th, 10th, or 11th century. Even a 9th-century date would make it one of the oldest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Book Of Aneirin
The Book of Aneirin ( cy, Llyfr Aneirin) is a late 13th century Wales, Welsh manuscript containing Old Welsh language, Old and Middle Welsh language, Middle Welsh poetry attributed to the late 6th century Northern Brythonic poet, Aneirin, who is believed to have lived in present-day Scotland. The manuscript is kept at the National Library of Wales, Aberystwyth. It is made of parchment and was written in Wales around 1265, probably in a monastery, but is probably a copy of a lost 9th century original. There is minimal decoration, consisting only of a few coloured capital letters. The poetry recorded in the book, which has only 38 pages, would previously have been kept alive through oral tradition. The best-known poem contained within its pages is ''Y Gododdin'', an early Welsh poetry, Welsh-language poem commemorating the warriors from Gododdin (Lothian in modern Scotland) who fell at the Battle of Catraeth (probably Catterick, North Yorkshire, Catterick in North Yorkshire) around ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Common Brittonic
Common Brittonic ( cy, Brythoneg; kw, Brythonek; br, Predeneg), also known as British, Common Brythonic, or Proto-Brittonic, was a Celtic language spoken in Britain and Brittany. It is a form of Insular Celtic, descended from Proto-Celtic, a theorized parent tongue that, by the first half of the first millennium BC, was diverging into separate dialects or languages. Pictish is linked, likely as a sister language or a descendant branch. Evidence from early and modern Welsh shows that Common Brittonic took a significant amount of influence from Latin during the Roman period, especially in terms related to the church and Christianity. By the sixth century AD, the tongues of the Celtic Britons were more rapidly splitting into Neo-Brittonic: Welsh, Cumbric, Cornish, Breton, and possibly the Pictish language. Over the next three centuries it was replaced in most of Scotland by Scottish Gaelic and by Old English (from which descend Modern English and Scots) throughout mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mead
Mead () is an alcoholic beverage made by fermenting honey mixed with water, and sometimes with added ingredients such as fruits, spices, grains, or hops. The alcoholic content ranges from about 3.5% ABV to more than 20%. The defining characteristic of mead is that the majority of the beverage's fermentable sugar is derived from honey. It may be still, carbonated, or naturally sparkling; dry, semi-sweet, or sweet. The term honey wine is sometimes used as a synonym for mead, although ''wine'' is typically defined to be the product of fermented grapes or certain other fruits, and some cultures have honey wines that are distinct from mead. The honey wine of Hungary, for example, is the fermentation of honey-sweetened pomace of grapes or other fruits. Mead was produced in ancient times throughout Europe, Africa, and Asia, and has played an important role in the mythology of some peoples. In Norse mythology, for example, the Mead of Poetry, crafted from the blood of Kvasir (a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ifor Williams
Sir Ifor Williams, (16 April 1881 – 4 November 1965) was a Welsh scholar who laid the foundations for the academic study of Old Welsh, particularly early Welsh poetry. Early life and education Ifor Williams was born at Pendinas, Tregarth near Bangor, Wales, the son of John Williams, a quarryman, and his wife Jane. His maternal grandfather, Hugh Derfel Hughes, was a noted local historian who wrote a well-regarded book on the history of the area. He went to Friars School, Bangor, in 1894 but had only been there for just over a year when he suffered a serious accident. This left him with back injuries that made him bedridden for several years. Having recovered, he attended Clynnog School in 1901 and in 1902 won a scholarship to University College of North Wales. In 1905 he graduated with honours in Greek, then in 1906 in Welsh Welsh may refer to: Related to Wales * Welsh, referring or related to Wales * Welsh language, a Brittonic Celtic language spoken in Wales * Welsh p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
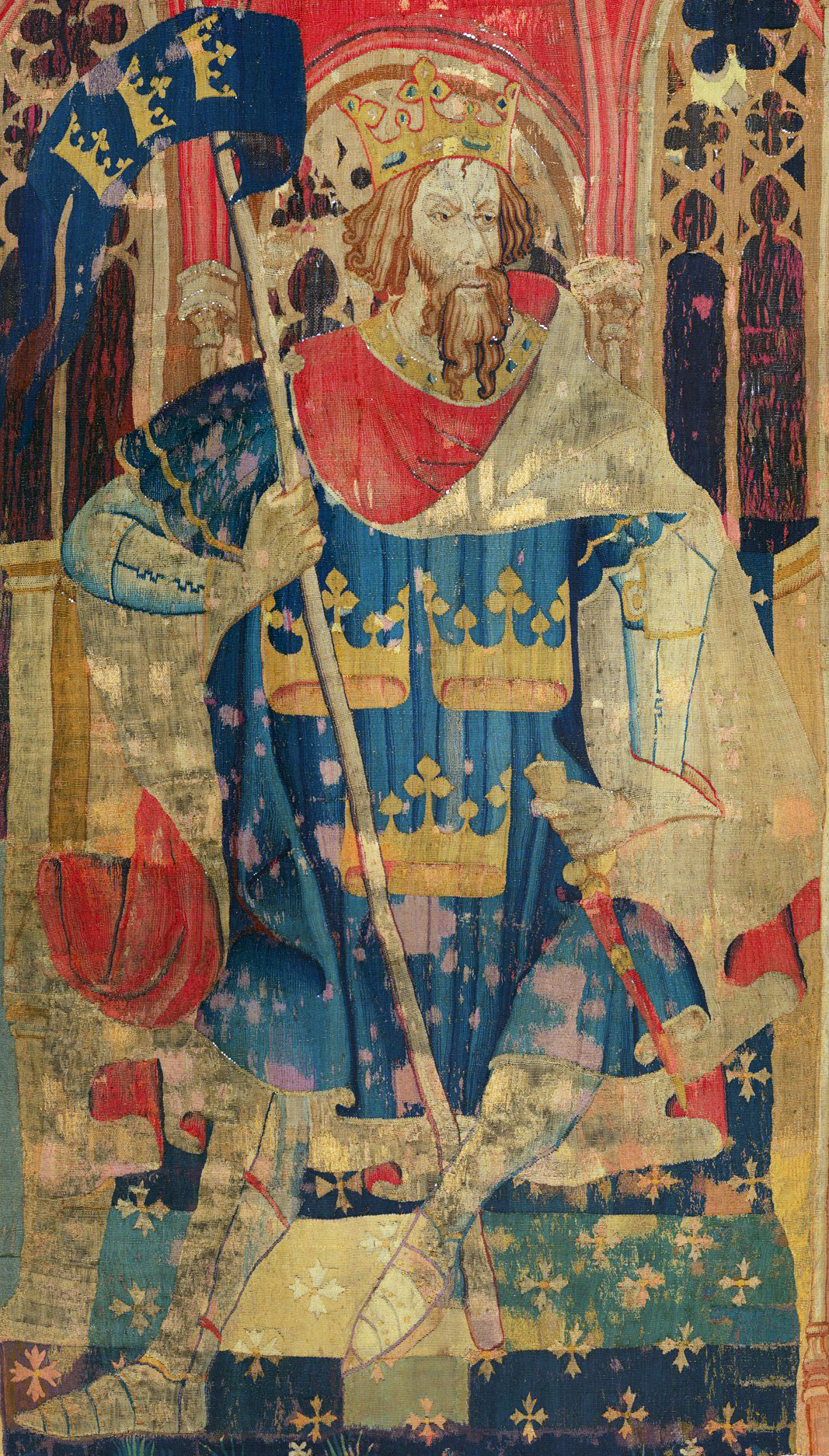
King Arthur
King Arthur ( cy, Brenin Arthur, kw, Arthur Gernow, br, Roue Arzhur) is a legendary king of Britain, and a central figure in the medieval literary tradition known as the Matter of Britain. In the earliest traditions, Arthur appears as a leader of the post-Roman Britons in battles against Saxon invaders of Britain in the late 5th and early 6th centuries. He appears in two early medieval historical sources, the '' Annales Cambriae'' and the '' Historia Brittonum'', but these date to 300 years after he is supposed to have lived, and most historians who study the period do not consider him a historical figure.Tom Shippey, "So Much Smoke", ''review'' of , ''London Review of Books'', 40:24:23 (20 December 2018) His name also occurs in early Welsh poetic sources such as '' Y Gododdin''. The character developed through Welsh mythology, appearing either as a great warrior defending Britain from human and supernatural enemies or as a magical figure of folklore, sometimes assoc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epic Poetry
An epic poem, or simply an epic, is a lengthy narrative poem typically about the extraordinary deeds of extraordinary characters who, in dealings with gods or other superhuman forces, gave shape to the mortal universe for their descendants. Etymology The English word ''epic'' comes from Latin ''epicus'', which itself comes from the Ancient Greek adjective (''epikos''), from (''epos''), "word, story, poem." In ancient Greek, 'epic' could refer to all poetry in dactylic hexameter (''epea''), which included not only Homer but also the wisdom poetry of Hesiod, the utterances of the Delphic oracle, and the strange theological verses attributed to Orpheus. Later tradition, however, has restricted the term 'epic' to ''heroic epic'', as described in this article. Overview Originating before the invention of writing, primary epics, such as those of Homer, were composed by bards who used complex rhetorical and metrical schemes by which they could memorize the epic as receive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North Yorkshire
North Yorkshire is the largest ceremonial county (lieutenancy area) in England, covering an area of . Around 40% of the county is covered by national parks, including most of the Yorkshire Dales and the North York Moors. It is one of four counties in England to hold the name Yorkshire; the three other counties are the East Riding of Yorkshire, South Yorkshire and West Yorkshire. North Yorkshire may also refer to a non-metropolitan county, which covers most of the ceremonial county's area () and population (a mid-2016 estimate by the ONS of 602,300), and is administered by North Yorkshire County Council. The non-metropolitan county does not include four areas of the ceremonial county: the City of York, Middlesbrough, Redcar and Cleveland and the southern part of the Borough of Stockton-on-Tees, which are all administered by unitary authorities. The non-metropolitan county and the City of York are within the Yorkshire and the Humber region. Middlesbrough, Redcar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catterick, North Yorkshire
Catterick () is a village, civil parish and electoral ward in the Richmondshire district of North Yorkshire, England. Historically part of the North Riding of Yorkshire, it is north-west of the county town of Northallerton just to the west of the River Swale. It lends its name to nearby Catterick Garrison and the nearby hamlet of Catterick Bridge, the home of Catterick Racecourse where the village Sunday market is held. It lies on the route of the old Roman road of Dere Street and is the site of the Roman fortification of Cataractonium. Toponymy The etymology of the name is derived from the Latin place name "Cataractonium", which looks like a Latin/Greek mixture meaning "place of a waterfall", but it might have been a Roman misunderstanding of the Celtic name ''Catu-rātis'' meaning "battle ramparts", as partly supported by the spelling Κατουρακτονιον (Catouractonion) on the Ptolemy world map. History The place is mentioned in Ptolemy's Geographia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edinburgh
Edinburgh ( ; gd, Dùn Èideann ) is the capital city of Scotland and one of its 32 Council areas of Scotland, council areas. Historically part of the county of Midlothian (interchangeably Edinburghshire before 1921), it is located in Lothian on the southern shore of the Firth of Forth. Edinburgh is Scotland's List of towns and cities in Scotland by population, second-most populous city, after Glasgow, and the List of cities in the United Kingdom, seventh-most populous city in the United Kingdom. Recognised as the capital of Scotland since at least the 15th century, Edinburgh is the seat of the Scottish Government, the Scottish Parliament and the Courts of Scotland, highest courts in Scotland. The city's Holyrood Palace, Palace of Holyroodhouse is the official residence of the Monarchy of the United Kingdom, British monarchy in Scotland. The city has long been a centre of education, particularly in the fields of medicine, Scots law, Scottish law, literature, philosophy, the sc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
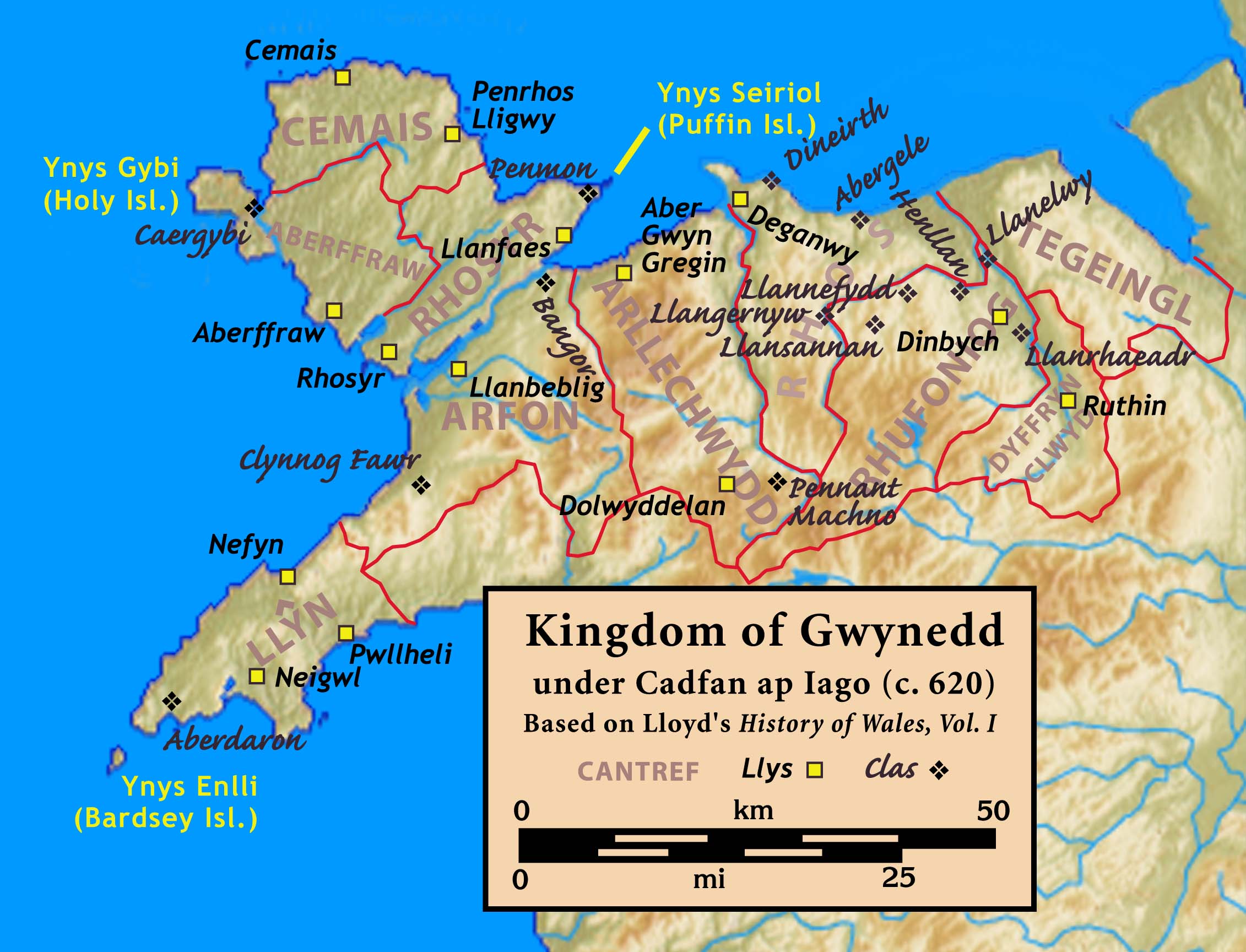
Kingdom Of Gwynedd
The Kingdom of Gwynedd (Medieval Latin: ; Middle Welsh: ) was a Welsh kingdom and a Roman Empire successor state that emerged in sub-Roman Britain in the 5th century during the Anglo-Saxon settlement of Britain. Based in northwest Wales, the rulers of Gwynedd repeatedly rose to dominance and were acclaimed as "King of the Britons" before losing their power in civil wars or invasions. The kingdom of Gruffydd ap Llywelynthe King of Wales from 1055 to 1063was shattered by a Saxon invasion in 1063 just prior to the Norman invasion of Wales, but the House of Aberffraw restored by Gruffudd ap Cynan slowly recovered and Llywelyn the Great of Gwynedd was able to proclaim the Principality of Wales at the Aberdyfi gathering of Welsh princes in 1216. In 1277, the Treaty of Aberconwy between Edward I of England and Llewelyn's grandson Llywelyn ap Gruffudd granted peace between the two but would also guarantee that Welsh self-rule would end upon Llewelyn's death, and so it represen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Picts
The Picts were a group of peoples who lived in what is now northern and eastern Scotland (north of the Firth of Forth) during Late Antiquity and the Early Middle Ages. Where they lived and what their culture was like can be inferred from early medieval texts and Pictish stones. Their Latin name, , appears in written records from the 3rd to the 10th century. Early medieval sources report the existence of a distinct Pictish language, which today is believed to have been an Insular Celtic language, closely related to the Brittonic spoken by the Britons who lived to the south. Picts are assumed to have been the descendants of the Caledonii and other Iron Age tribes that were mentioned by Roman historians or on the world map of Ptolemy. The Pictish kingdom, often called Pictland in modern sources, achieved a large degree of political unity in the late 7th and early 8th centuries through the expanding kingdom of Fortriu, the Iron Age Verturiones. By the year 900, the result ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |