Economy Of The EU on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

 The economy of the European Union is the joint economy of the member states of the European Union (EU). It is the third largest economy in the world in nominal terms, after the United States and
The economy of the European Union is the joint economy of the member states of the European Union (EU). It is the third largest economy in the world in nominal terms, after the United States and
 Beginning in the year 1999 with some
Beginning in the year 1999 with some
 The European Union has uranium, coal, oil, and
The European Union has uranium, coal, oil, and


 The twelve new member states of the European Union have enjoyed a higher average percentage growth rate than their elder members of the EU. Slovakia has the highest GDP growth in the period 2005–2015 among all countries of the European Union (See Tatra Tiger). Notably the
The twelve new member states of the European Union have enjoyed a higher average percentage growth rate than their elder members of the EU. Slovakia has the highest GDP growth in the period 2005–2015 among all countries of the European Union (See Tatra Tiger). Notably the  ''In the tables below, colours indicate and performer of the year concerned.''
''In the tables below, colours indicate and performer of the year concerned.''
 The EU seasonally adjusted unemployment rate was 6.7% in September 2018. The euro area unemployment rate was 8.1%. Among the member states, the lowest unemployment rates were recorded in the Czech Republic (2.3%), Germany and Poland (both 3.4%), and the highest in Spain (14.9%) and Greece (19.0 in July 2018).
The EU seasonally adjusted unemployment rate was 6.7% in September 2018. The euro area unemployment rate was 8.1%. Among the member states, the lowest unemployment rates were recorded in the Czech Republic (2.3%), Germany and Poland (both 3.4%), and the highest in Spain (14.9%) and Greece (19.0 in July 2018).

 The European Union is the largest exporter in the world and as of 2008 the largest importer of goods and services. Internal trade between the member states is aided by the removal of barriers to trade such as tariffs and
The European Union is the largest exporter in the world and as of 2008 the largest importer of goods and services. Internal trade between the member states is aided by the removal of barriers to trade such as tariffs and 
Link to 10 new memberstates Growth RatesLink to Growth Rates for the EurozoneLink to non-Eurozone EU15 countries Growth Rates
Eurostat – Statistics Explained – All articles on economy and finance
{{Portal bar, European Union, Economics, Business and economics European Union
 The economy of the European Union is the joint economy of the member states of the European Union (EU). It is the third largest economy in the world in nominal terms, after the United States and
The economy of the European Union is the joint economy of the member states of the European Union (EU). It is the third largest economy in the world in nominal terms, after the United States and China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and ...
, and the third one in purchasing power parity (PPP) terms, after China and the United States. The European Union's GDP estimated to be around $16.6 trillion (nominal) in 2022 representing around one sixth of the global economy
The world economy or global economy is the economy of all humans of the world, referring to the global economic system, which includes all economic activities which are conducted both within and between nations, including production, consumption, ...
.
The euro is the second largest reserve currency
A reserve currency (or anchor currency) is a foreign currency that is held in significant quantities by central banks or other monetary authorities as part of their foreign exchange reserves. The reserve currency can be used in international tran ...
and the second most traded currency in the world after the United States dollar. The euro is used by 19 of its members, overall, it is the official currency in 25 countries, in the eurozone and in six other European countries, officially or de facto.
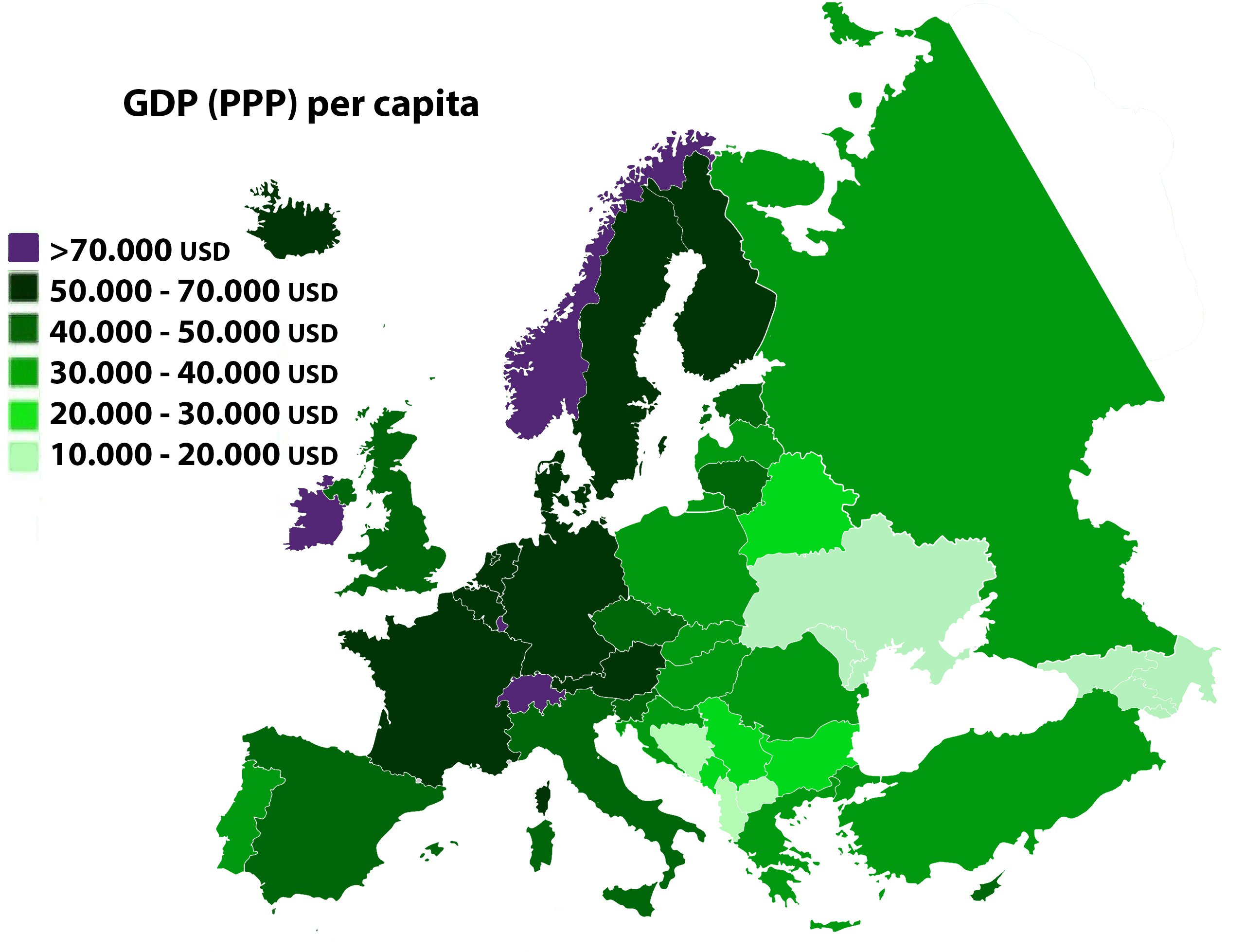
The European Union economy consists of an internal market of mixed economies based on free market and advanced social models. For instance, it includes an internal single market with free movement of goods, services, capital, and labor. The GDP per capita (PPP) was $43,188 in 2018, compared to $62,869 in the United States, $44,246 Japan
Japan ( ja, 日本, or , and formally , ''Nihonkoku'') is an island country in East Asia. It is situated in the northwest Pacific Ocean, and is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan, while extending from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north ...
and $18,116 in China. There are significant disparities in GDP per capita (PPP) between member states ranging from $106,372 in Luxembourg to $23,169 in Bulgaria. With a low Gini coefficient of 31, the European Union has a more egalitarian distribution of income than the world average.
EU's investments in foreign countries total $9.1 trillion, while the foreign investments
A foreign direct investment (FDI) is an investment in the form of a controlling ownership in a business in one country by an entity based in another country. It is thus distinguished from a foreign portfolio investment by a notion of direct co ...
made in the European Union total $5.1 trillion in 2012, by far the highest foreign and domestic investments in the world. Euronext is the main stock exchange of the Eurozone and the world's sixth largest by market capitalisation. The European Union's largest trading partners are the United States, China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and ...
, the United Kingdom, Switzerland
). Swiss law does not designate a ''capital'' as such, but the federal parliament and government are installed in Bern, while other federal institutions, such as the federal courts, are in other cities (Bellinzona, Lausanne, Luzern, Neuchâtel ...
, Russia, Turkey, Japan
Japan ( ja, 日本, or , and formally , ''Nihonkoku'') is an island country in East Asia. It is situated in the northwest Pacific Ocean, and is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan, while extending from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north ...
, Norway, South Korea, India, and Canada. Real investment in the European Union fell by 14.6% by the end of the second quarter of 2020, compared to the fourth quarter of 2019. It recovered and returned to its 2019 level by the second quarter of 2021.
Since the beginning of the public debt crisis in 2009, opposite economic situations have emerged between Southern Europe on one hand, and Central
Central is an adjective usually referring to being in the center of some place or (mathematical) object.
Central may also refer to:
Directions and generalised locations
* Central Africa, a region in the centre of Africa continent, also known as ...
and Northern Europe
The northern region of Europe has several definitions. A restrictive definition may describe Northern Europe as being roughly north of the southern coast of the Baltic Sea, which is about 54th parallel north, 54°N, or may be based on other g ...
on the other hand: a higher unemployment rate and public debt in the Mediterranean countries with the exception of Malta, and a lower unemployment rate with higher GDP growth rate in the Eastern and in Northern member countries. In 2018, public debt in the European Union was 80% of GDP, with disparities between the lowest rate, Estonia with 8.4%, and the highest, Greece with 181.1%.
Currency
EU member states
The European Union (EU) is a supranational political and economic union of member states that are located primarily in Europe. The union has a total area of and an estimated total population of about 447million. The EU has often been des ...
, now 19 out of EU states use the euro as official currency in a currency union. The remaining 8 states continued to use their own currency with the possibility to join the euro later. The euro is also the most widely used currency in the EU.
Since 1992, the Maastricht Treaty sets out rigid economic and fiscal convergence criteria for the states joining the euro. Starting 1997, the Stability and Growth Pact has been started to ensure continuing economic and fiscal stability and convergence.
Denmark is not a part of the eurozone due to its special opt-outs concerning the later joining of the euro. In contrast, Sweden can effectively opt out by choosing when or whether to join the European Exchange Rate Mechanism, which is the preliminary step towards joining. The remaining states are committed to join the euro through their Treaties of Accession.
Starting with Greece in 2009, five of the 19 eurozone states have been struggling with a sovereign debt crisis, by many called the European debt crisis. All these states started reforms and got bailout packages ( Greece, Republic of Ireland, Portugal, Spain, Cyprus). As of 2015, all countries but Greece have recovered from their debt crisis. Other non-eurozone states also experienced a debt crisis and also went through successful bailout programmes, i.e. Hungary, Romania and Latvia
Latvia ( or ; lv, Latvija ; ltg, Latveja; liv, Leţmō), officially the Republic of Latvia ( lv, Latvijas Republika, links=no, ltg, Latvejas Republika, links=no, liv, Leţmō Vabāmō, links=no), is a country in the Baltic region of ...
(the latter before it joined the eurozone).
Budget
The EU has a long-term budget, named Multiannual Financial Framework (MFF), of €1,082.5 billion for the period 2014–2020, representing 1.02% of the EU-28's GNI. The overall budget for the period 2021-2027 is of €1.8 trillion combining the MFF of €1,074.3 billion with an extraordinary recovery fund of €750 billion, known as Next Generation EU, to support member states hit by the COVID-19 pandemic.Sectors
Services
The services sector is by far the most important sector in the European Union, making up 64.7% of GDP, compared to the manufacturing industry with 23.8% of GDP and agriculture with only 1.5% of GDP.Financial services
Financial services are the Service (economics), economic services provided by the finance industry, which encompasses a broad range of businesses that manage money, including credit unions, banks, credit-card companies, insurance companies, acco ...
are well developed within the Single Market of the Union. Companies have a greater reliance on bank lending than in the United States, although a shift towards companies raising more funding through capital markets is planned through the CMU initiative, the EU plan put forward by the Commission in September 2015 to mobilise the free movement of capital within the EU. The plan aims "to establish the building blocks of an integrated capital market in the EU by 2019". The CMU initiative comprises 33 measures in all. The plan was updated in 2017 and in 2019, since not a single legislation will deliver the CMU. The Commissioner for Financial Stability, Financial Services and Capital Markets Union, Mairead McGuinness
Mairead McGuinness (born 13 June 1959) is an Irish politician serving as the European Commissioner for Financial Stability, Financial Services and the Capital Markets Union since October 2020. A member of Fine Gael, she previously served as ...
, former Vice-President of the European Parliament, is responsible for delivery of the initiative.
According to the Global Financial Centres Index, the two largest financial centres in Europe, London and Zurich, are outside the European Union. The two largest financial centres remaining within the EU will then be Frankfurt and Luxembourg City.
In the European Investment Bank
The European Investment Bank (EIB) is the European Union's investment bank and is owned by the EU Member States. It is one of the largest supranational lenders in the world. The EIB finances and invests both through equity and debt solutions ...
's Investment survey 2021, 58% of firms in the service sector were expecting long term effects of COVID-19. 56% of EU enterprises received governmental help to handle the pandemic's effects.
The COVID-19 pandemic had a significant impact on sales. 49% of all EU enterprises claimed that their sales decreased since the start of 2020. The pandemic has affected sectors differently, with the number of enterprises losing money in the hotels, restaurants, arts, and leisure industries reaching roughly 25% compared to previous times, and transportation also being affected.
Without government assistance, 35% of European small and medium-sized firms (SMEs) in manufacturing and services indicated their businesses would not have survived the effects of the pandemic.
In 2020, 86% of enterprises reported previous-year investment activity, while in 2021 only 79% reported investment. 23% of EU firms changed their investment plans in 2021, with only 3% reporting a higher amount. The highest proportion of enterprises that have reduced their investment plans due to a drop in sales are in Poland, where 49% of firms have reduced investment, and in Belgium, where 47% of firms stated the same.
Most green or digital businesses in the EU operate in manufacturing (33%) or infrastructure (30%). The service sector has the greatest percentage of businesses that have not engaged in digitalization or the green transition (41%).
Agriculture
The agricultural sector is supported by subsidies from the European Union in the form of the Common Agricultural Policy (CAP). In 2013 this represented approximately €45billion (less than 33% of the overall budget of €148billion) of the EU's total spending. It was used originally to guarantee a minimum price forfarmers
A farmer is a person engaged in agriculture, raising living organisms for food or raw materials. The term usually applies to people who do some combination of raising field crops, orchards, vineyards, poultry, or other livestock. A farmer mi ...
in the EU. This is criticised as a form of protectionism, inhibiting trade, and damaging developing countries; one of the most vocal opponents was the UK, the second largest economy within the bloc until its withdrawal in January 2020, which repeatedly refused to give up the annual UK rebate unless the CAP should undergo significant reform; France, the biggest beneficiary of the CAP and the bloc's third largest (now its second-largest) economy, is its most vocal proponent. The CAP is however witnessing substantial reform. In 1985, around 70% of the EU budget was spent on agriculture. In 2011, direct aid to farmers and market-related expenditure amount to just 30% of the budget, and rural development spending to 11%. By 2011, 90% of direct support had become non-trade-distorting (not linked to production) as reforms have continued to be made to the CAP, its funding and its design.
Tourism
The European Union is a major tourist destination, attracting visitors from outside of the Union and citizens travelling inside it. Internal tourism is made more convenient by the Schengen treaty and the euro. All citizens of the European Union are entitled to travel to any member state without the need of a visa. France is the world's number one tourist destination for international visitors, followed by Spain, Italy, and Germany. It is worth noting, however, that a significant proportion of international visitors to EU countries are from other member states.Energy
 The European Union has uranium, coal, oil, and
The European Union has uranium, coal, oil, and natural gas reserves
Oil and gas reserves denote ''discovered'' quantities of crude oil and natural gas (oil or gas fields) that can be profitably produced/recovered from an approved development. Oil and gas reserves tied to approved operational plans filed on th ...
. There are six oil producers in the European Union, primarily in North Sea oilfields. The United Kingdom, whilst it was a member of the European Union was by far the largest producer; Denmark, Germany, Italy, Romania and the Netherlands produce oil.
The European Union produced 19.8 million tonnes of oil equivalent (Mtoe) of crude oil
Petroleum, also known as crude oil, or simply oil, is a naturally occurring yellowish-black liquid mixture of mainly hydrocarbons, and is found in geological formations. The name ''petroleum'' covers both naturally occurring unprocessed crude ...
in 2019.
The EU is one of the largest consumers of oil, consuming much more than it can produce. It consumed about 350 Mtoe in 2019, importing 96.8% of the oil. The largest suppliers are Russia, Iraq, Nigeria, Saudi Arabia, Kazakhstan, and Norway.
Transport is the largest consumer of oil, at 66.1% in 2019.
All countries in the EU have committed to the Kyoto Protocol
The Kyoto Protocol was an international treaty which extended the 1992 United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) that commits state parties to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, based on the scientific consensus that (part ...
, and the European Union is one of its biggest proponents. The European Commission published proposals for the first comprehensive EU energy policy on 10 January 2007.
During the green transition, workers in carbon-intensive industries are more likely to lose their jobs. In the years to come, the transition to a carbon-neutral economy will put more jobs at danger in regions with higher percentages of employment in carbon-intensive industries. Employment opportunities by the green transition are associated with the use of renewable energy sources or building activity for infrastructure improvements and renovations.
Companies
The European Union's member states are the birthplace of many of the world's largest leading multinational companies, and home to its global headquarters. Among these are distinguished companies ranked first in the world within their industry/sector, likeAllianz
Allianz ( , ) is a German multinational financial services company headquartered in Munich, Germany. Its core businesses are insurance and asset management.
The company is one of the world's largest insurers and financial services groups. The ...
and AXA
Axa S.A. (styled as ''AXA'' or GIG in the Middle East) is a French multinational insurance company. The head office is in the 8th arrondissement of Paris, France. It also provides investment management and other financial services.
The Ax ...
, which are the two largest financial service providers in the world by revenue; WPP plc and Publicis which are the world's largest advertising agencies by revenue; Amorim, which is the world's largest cork-processing and cork producer company; ArcelorMittal, which is the largest steel company in the world; Christian Dior SE which is the biggest fashion group in the world and Inditex is the world’s second biggest fashion group; Groupe Danone, which has the world leadership in the dairy products market.
Anheuser-Busch InBev
Anheuser-Busch InBev SA/NV, commonly known as AB InBev, is an American-Belgian multinational drink and brewing company based in Leuven, Belgium. AB InBev has a global functional management office in New York City, and regional headquarters ...
is the largest beer company in the world; L'Oréal Group, which is the world's largest cosmetics and beauty company; LVMH
LVMH Moët Hennessy Louis Vuitton (), commonly known as LVMH, is a French holding multinational corporation and conglomerate specializing in luxury goods, headquartered in Paris. The company was formed in 1987 through the merger of fashion house ...
, which is the world's largest luxury goods
In economics, a luxury good (or upmarket good) is a good for which demand increases more than what is proportional as income rises, so that expenditures on the good become a greater proportion of overall spending. Luxury goods are in contrast to n ...
conglomerate; Nokia Corporation, which was the world's largest manufacturer of mobile telephone
A mobile phone, cellular phone, cell phone, cellphone, handphone, hand phone or pocket phone, sometimes shortened to simply mobile, cell, or just phone, is a portable telephone that can make and receive calls over a radio frequency link whil ...
s; Shell plc
Shell plc is a British multinational oil and gas company headquartered in London, England. Shell is a public limited company with a primary listing on the London Stock Exchange (LSE) and secondary listings on Euronext Amsterdam and the New Yo ...
, Électricité de France
Électricité de France S.A. (literally ''Electricity of France''), commonly known as EDF, is a French multinational electric utility company, largely owned by the French state. Headquartered in Paris, with €71.2 billion in revenues in 2 ...
, TotalEnergies, Eni
Eni S.p.A. () is an Italian multinational energy company headquartered in Rome. Considered one of the seven "supermajor" oil companies in the world, it has operations in 69 countries with a market capitalization of US$54.08 billion, as of 11 Ap ...
which are one of the largest energy corporations in the world; and Stora Enso, which is the world's largest pulp and paper
The pulp and paper industry comprises companies that use wood as raw material and produce pulp, paper, paperboard and other cellulose-based products.
Manufacturing process
The pulp is fed to a paper machine where it is formed as a paper web an ...
manufacturer in terms of production capacity, in terms of banking and finance the EU has some of the world's largest notably BNP Paribas
BNP Paribas is a French international banking group, founded in 2000 from the merger between Banque Nationale de Paris (BNP, "National Bank of Paris") and Paribas, formerly known as the Banque de Paris et des Pays-Bas. The full name of the grou ...
, HSBC
HSBC Holdings plc is a British multinational universal bank and financial services holding company. It is the largest bank in Europe by total assets ahead of BNP Paribas, with US$2.953 trillion as of December 2021. In 2021, HSBC had $10.8 tri ...
, Crédit Agricole
Crédit Agricole Group (), sometimes called La banque verte ( en, The green bank) due to its historical ties to farming, is a French international banking group and the world's largest cooperative financial institution. It is France's second lar ...
, Grupo Santander and Société Générale the largest bank in Europe in terms of Market Capitalisation and assets.
Many other European companies rank among the world's largest companies in terms of turnover, profit, market share, number of employees or other major indicators. A considerable number of EU-based companies are ranked among the world's top-ten within their sector of activity.
Europe is also home to many prestigious car companies such as Aston Martin
Aston Martin Lagonda Global Holdings PLC is an English manufacturer of luxury sports cars and grand tourers. Its predecessor was founded in 1913 by Lionel Martin and Robert Bamford. Steered from 1947 by David Brown, it became associated with ...
, Automobiles Alpine
The Société des Automobiles Alpine SAS, commonly known as Alpine (), is a French manufacturer of racing and sports cars established in 1955. The Alpine car marque was created in 1954.
Jean Rédélé, the founder of Alpine, was originally a ...
, BMW, Bugatti
Automobiles Ettore Bugatti was a German then French manufacturer of high-performance automobiles. The company was founded in 1909 in the then-German city of Molsheim, Alsace, by the Italian-born industrial designer Ettore Bugatti. The cars w ...
, Ferrari
Ferrari S.p.A. (; ) is an Italian luxury sports car manufacturer based in Maranello, Italy. Founded by Enzo Ferrari (1898–1988) in 1939 from the Alfa Romeo racing division as ''Auto Avio Costruzioni'', the company built its first car in ...
, Jaguar
The jaguar (''Panthera onca'') is a large cat species and the only living member of the genus '' Panthera'' native to the Americas. With a body length of up to and a weight of up to , it is the largest cat species in the Americas and the th ...
, Lamborghini
Automobili Lamborghini S.p.A. () is an Italian brand and manufacturer of luxury sports cars and SUVs based in Sant'Agata Bolognese. The company is owned by the Volkswagen Group through its subsidiary Audi.
Ferruccio Lamborghini (1916–1993) ...
, Land Rover, Maserati
Maserati S.p.A. () is an Italian luxury vehicle manufacturer. Established on 1 December 1914, in Bologna, Italy, the company's headquarters are now in Modena, and its emblem is a trident. The company has been owned by Stellantis since 2021. Ma ...
, Mercedes-Benz, Porsche
Dr. Ing. h.c. F. Porsche AG, usually shortened to Porsche (; see #Pronunciation, below), is a German automobile manufacturer specializing in high-performance sports cars, SUVs and sedans, headquartered in Stuttgart, Baden-Württemberg, Germany ...
, Volvo, as well as volume manufacturers such as Automobile Dacia, Citroën
Citroën () is a French automobile brand. The "Automobiles Citroën" manufacturing company was founded in March 1919 by André Citroën. Citroën is owned by Stellantis since 2021 and previously was part of the PSA Group after Peugeot acquired ...
, Fiat
Fiat Automobiles S.p.A. (, , ; originally FIAT, it, Fabbrica Italiana Automobili di Torino, lit=Italian Automobiles Factory of Turin) is an Italian automobile manufacturer, formerly part of Fiat Chrysler Automobiles, and since 2021 a subsidiary ...
, Opel
Opel Automobile GmbH (), usually shortened to Opel, is a German automobile manufacturer which has been a subsidiary of Stellantis since 16 January 2021. It was owned by the American automaker General Motors from 1929 until 2017 and the PSA Grou ...
, Peugeot, Renault, Seat
A seat is a place to sit. The term may encompass additional features, such as back, armrest, head restraint but also headquarters in a wider sense.
Types of seat
The following are examples of different kinds of seat:
* Armchair (furniture), ...
, Volkswagen and more.
In Europe, 33% of jobs are within enterprises that have not digitally transformed. These companies were also less likely to train their employees throughout the COVID-19 outbreak. Across the European Union, the most commonly mentioned investment barrier is the lack of trained labor. 75% of businesses in transition regions found this to be problematic. Numerous reasons, such as demographics and rising demand for skills that are less common on the market, such as those needed to support digitalization activities, might contribute to the lack of competent workers. In all areas of Europe, digital businesses have produced "better" employment with greater earnings than their non-digital counterparts. Additionally, they are more inclined to recognize and reward individuals who do well.
The following is a list of the largest EU based stock market listed companies in 2016. The ordered by revenue in millions of US Dollars and is based on the Fortune Global 500.
Economies of member states
Wealth


 The twelve new member states of the European Union have enjoyed a higher average percentage growth rate than their elder members of the EU. Slovakia has the highest GDP growth in the period 2005–2015 among all countries of the European Union (See Tatra Tiger). Notably the
The twelve new member states of the European Union have enjoyed a higher average percentage growth rate than their elder members of the EU. Slovakia has the highest GDP growth in the period 2005–2015 among all countries of the European Union (See Tatra Tiger). Notably the Baltic states
The Baltic states, et, Balti riigid or the Baltic countries is a geopolitical term, which currently is used to group three countries: Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania. All three countries are members of NATO, the European Union, the Eurozone, ...
have achieved high GDP growth, with Latvia
Latvia ( or ; lv, Latvija ; ltg, Latveja; liv, Leţmō), officially the Republic of Latvia ( lv, Latvijas Republika, links=no, ltg, Latvejas Republika, links=no, liv, Leţmō Vabāmō, links=no), is a country in the Baltic region of ...
topping 11%, close to China, the world leader at 9% on average for the past 25 years (though these gains have been in great part cancelled by the late-2000s recession
The Great Recession was a period of marked general decline, i.e. a recession, observed in national economies globally that occurred from late 2007 into 2009. The scale and timing of the recession varied from country to country (see map). At t ...
).
Reasons for this growth include government commitments to stable monetary policy, export-oriented trade policies, low flat-tax
A flat tax (short for flat-rate tax) is a tax with a single rate on the taxable amount, after accounting for any deductions or exemptions from the tax base. It is not necessarily a fully proportional tax. Implementations are often progressive ...
rates and the utilisation of relatively cheap labour. In 2015 Ireland had the highest GDP growth of all the states in EU (25.1%).
The current map of EU growth is one of huge regional variation, with the larger economies suffering from stagnant growth and the new nations enjoying sustained, robust economic growth.
In mid-2021, the European Union's gross saving rate was 18% of gross disposable income
Disposable income is total personal income minus current income taxes. In national accounts definitions, personal income minus personal current taxes equals disposable personal income. Subtracting personal outlays (which includes the major c ...
, higher above the prior COVID-19 pandemic average of 11–13%. In the second quarter of 2020, families' primary income fell by 7.3% compared to the second quarter of 2019, and their secondary income (from social security payments and other transfers) increased by 6.5% of gross income.
Although EU27 GDP is rising, the percentage of gross world product is decreasing because of the emergence of economies such as China, India and Brazil.
Labour market
Unemployment rate
The following table shows the history of the unemployment rate for all European Union member states:
Public finance
Trade
 The European Union is the largest exporter in the world and as of 2008 the largest importer of goods and services. Internal trade between the member states is aided by the removal of barriers to trade such as tariffs and
The European Union is the largest exporter in the world and as of 2008 the largest importer of goods and services. Internal trade between the member states is aided by the removal of barriers to trade such as tariffs and border control
Border control refers to measures taken by governments to monitor and regulate the movement of people, animals, and goods across land, air, and maritime borders. While border control is typically associated with international borders, it a ...
s. In the eurozone, trade is helped by not having any currency differences to deal with amongst most members.
The European Union Association Agreement does something similar for a much larger range of countries, partly as a so-called soft approach ('a carrot instead of a stick') to influence the politics in those countries.
The European Union represents all its members at the World Trade Organization (WTO), and acts on behalf of member states in any disputes. When the EU negotiates trade related agreement outside the WTO framework, the subsequent agreement must be approved by each individual EU member state government.

Regional variation
Comparing the richest areas of the EU can be a difficult task. This is because theNUTS
Nut often refers to:
* Nut (fruit), fruit composed of a hard shell and a seed, or a collective noun for dry and edible fruits or seeds
* Nut (hardware), fastener used with a bolt
Nut or Nuts may also refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Com ...
1 & 2 regions are not homogenous, some of them being very large regions, such as NUTS-1 Hesse (21,100 km2) or NUTS-1 Île-de-France (12,011 km2), whilst other NUTS regions are much smaller, for example NUTS-1 Hamburg (755 km2). An extreme example is Finland, which is divided for historical reasons into mainland Finland with 5.3 million inhabitants and Åland, an autonomous archipelago with a population of 27,000, or about the population of a small Finnish city.
One problem with this data is that some areas are subject to a large number of commuters coming into the area, thereby artificially inflating the figures. It has the effect of raising GDP but not altering the number of people living in the area, inflating the GDP per capita figure. Similar problems can be produced by a large number of tourists visiting the area.
The data is used to define regions that are supported with financial aid in programs such as the European Regional Development Fund.
The decision to delineate a Nomenclature of Territorial Units for Statistics
Nomenclature of Territorial Units for Statistics or NUTS (french: Nomenclature des unités territoriales statistiques) is a geocode standard for referencing the subdivisions of countries for statistical purposes. The standard, adopted in 2003, ...
(NUTS) region is to a large extent arbitrary (i.e. not based on objective and uniform criteria across Europe), and is decided at European level (See also: Regions of the European Union).
NUTS-1 and NUTS-2 regions
The top 10 NUTS-1 and NUTS-2 regions with the highest GDP per capita are almost all, except one, in the first fifteen-member states: Prague is the only one in the 13 new member states that joined in May 2004, January 2007 and July 2013. The leading regions in the ranking of NUTS-2 regional GDP per inhabitant in 2019 were the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg (260%), the Southern region of Ireland (240%), and Prague, Czech Republic (205%). Figures for these three regions, however, were artificially inflated by the commuters who do not reside in these regions ("Net commuter inflows in these regions push up production to a level that could not be achieved by the resident active population on its own. The result is that GDP per inhabitant appears to be overestimated in these regions and underestimated in regions with commuter outflows.". Another example of artificial inflation is Groningen. The calculated GDP per capita is very high because of the large natural gas reserves in this region, but Groningen is one of the poorest parts in the Netherlands. Among the 16 NUTS-2 regions exceeding the 160% level in 2020, two were in Belgium, Germany, Ireland and the Netherlands and one each in the Czech Republic, Denmark, France, Poland, Romania, Slovakia and Sweden, as well as in the single region Grand Duchy of Luxembourg. The NUTS Regulation lays down a minimum population size of 3 million and a maximum size of 7 million for the average NUTS-1 region, whereas a minimum of 800,000 and a maximum of 3 million for NUTS-2 regions. This definition, however, is not respected by Eurostat. For example, the '' région'' of Île-de-France, with 11.6 million inhabitants, is treated as a NUTS-2 region, while the state Free Hanseatic City of Bremen, with only 664,000 inhabitants, is treated as a NUTS-1 region. Among the lowest regions in the ranking in 2020 most were in Bulgaria, with the lowest figure recorded inSeverozapaden
Severozapaden (''Northwest Planning Region''), is a region of Bulgaria. The capital is the city of Pleven. The region has the lowest-ranked economy in Bulgaria and the European Union, with a GDP per capita (PPS) of €9,300 or 31% of EU28 average ...
.
Among the poorest 20 regions, seven were in Greece, five in Bulgaria, three in Hungary, two in France and one each in Croatia, Romania and Slovakia.
See also
* Blue Banana * Citizenship of the European Union *Currencies of the European Union
There are nine currencies of the European Union used officially by member states. The euro accounts for the majority of the member states with the remainder operating independent monetary policies. Those European Union states that have adopted ...
* European Central Bank
* Economic and Monetary Union
* Capital Markets Union
* Banking Union
*European Investment Bank
The European Investment Bank (EIB) is the European Union's investment bank and is owned by the EU Member States. It is one of the largest supranational lenders in the world. The EIB finances and invests both through equity and debt solutions ...
* European Union value added tax
* List of largest European companies by revenue
*Central banks and currencies of Europe
This is a list of central banks and currencies of Europe .
European Central Bank
Non-Eurozone currencies
See also
*Currency
*Economy of Europe
*List of banks in Europe
*List of currencies in Europe
*List of European stock exchanges
In ...
* Euro convergence criteria
* Currency
* List of European stock exchanges
* List of currencies in Europe
References
*Cells shaded in green indicate forecast figure * One region may be classified by Eurostat as a NUTS-1, NUTS-2 as well as a NUTS-3 region. Several NUTS-1 regions are also classified as NUTS-2 regions such as Brussels-Capital or Ile-de-France. Many countries are only classified as a single NUTS-1 and a single NUTS-2 region such as Latvia, Lithuania, Luxemburg and (although over 3 million inhabitants) Denmark. * * * The following links are used for the GDP growth and GDP totals (IMF
The International Monetary Fund (IMF) is a major financial agency of the United Nations, and an international financial institution, headquartered in Washington, D.C., consisting of 190 countries. Its stated mission is "working to foster globa ...
):Link to 10 new memberstates Growth Rates
External links
Eurostat – Statistics Explained – All articles on economy and finance
{{Portal bar, European Union, Economics, Business and economics European Union