Drainage Research on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Drainage research is the study of agricultural
 Agricultural land
Agricultural land
All these aspects can be subject of drainage research.
The aim (objective, target) of agricultural land drainage is the optimized agricultural production related to: # reclamation of agricultural land #
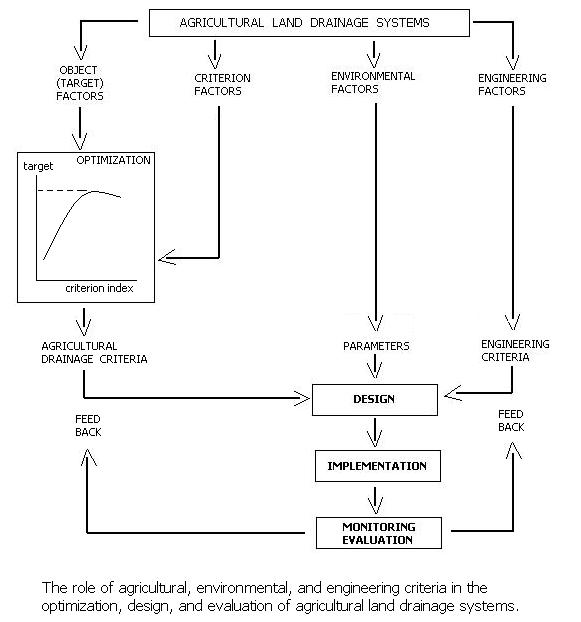 The role of targets, criterion, environmental, and hydrological factors is illustrated in Figure 2.
The role of targets, criterion, environmental, and hydrological factors is illustrated in Figure 2.
In this figure criterion factors are factors influenced by drainage on the one hand and the agricultural performance on the other.
An example of a criterion factor is the depth of the
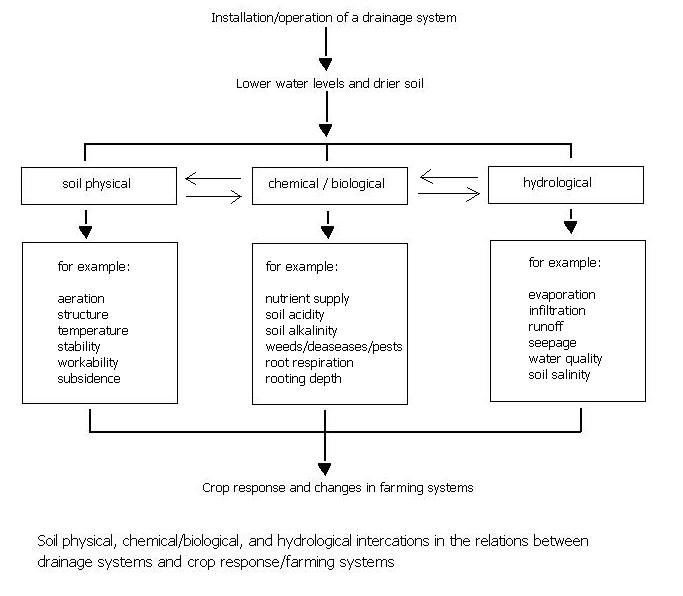 The underlying processes in the optimization (as in the insert of Figure 2) are manifold. The processes can be grouped into mutually dependent soil physical, soil chemical/biological, and
The underlying processes in the optimization (as in the insert of Figure 2) are manifold. The processes can be grouped into mutually dependent soil physical, soil chemical/biological, and
 In drainage research the collection and analysis of field data is important.
In dealing with field data one must expect considerable random variation owing to the large number of natural processes involved and the large variability of plant and soil properties and hydrological conditions.
An example of a relation between crop yield and depth of water table subject to random natural variation is shown in the attached graph. The graph was made with the
In drainage research the collection and analysis of field data is important.
In dealing with field data one must expect considerable random variation owing to the large number of natural processes involved and the large variability of plant and soil properties and hydrological conditions.
An example of a relation between crop yield and depth of water table subject to random natural variation is shown in the attached graph. The graph was made with the
* Articles on agricultural land drainage
* Frequently asked questions about drainage
* Case studies on land drainage
* Software on land drainage
{{Agricultural water management Soil science Environmental soil science Hydrology Drainage
drainage
Drainage is the natural or artificial removal of a surface's water and sub-surface water from an area with excess of water. The internal drainage of most agricultural soils is good enough to prevent severe waterlogging (anaerobic conditio ...
systems and their effects to arrive at optimal system design.
Aspects to be covered
drainage
Drainage is the natural or artificial removal of a surface's water and sub-surface water from an area with excess of water. The internal drainage of most agricultural soils is good enough to prevent severe waterlogging (anaerobic conditio ...
has agricultural
Agriculture or farming is the practice of cultivating Plant, plants and livestock. Agriculture was the key development in the rise of Sedentism, sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of Domestication, domesticated species created food ...
, environmental
A biophysical environment is a biotic and abiotic surrounding of an organism or population, and consequently includes the factors that have an influence in their survival, development, and evolution. A biophysical environment can vary in scale f ...
, hydrological
Hydrology () is the scientific study of the movement, distribution, and management of water on Earth and other planets, including the water cycle, water resources, and environmental watershed sustainability. A practitioner of hydrology is calle ...
, engineering
Engineering is the use of scientific method, scientific principles to design and build machines, structures, and other items, including bridges, tunnels, roads, vehicles, and buildings. The discipline of engineering encompasses a broad rang ...
, economical
An economic system, or economic order, is a system of production, resource allocation and distribution of goods and services within a society or a given geographic area. It includes the combination of the various institutions, agencies, entitie ...
, social
Social organisms, including human(s), live collectively in interacting populations. This interaction is considered social whether they are aware of it or not, and whether the exchange is voluntary or not.
Etymology
The word "social" derives from ...
and socio-political
Political sociology is an interdisciplinary field of study concerned with exploring how governance and society interact and influence one another at the micro to macro levels of analysis. Interested in the social causes and consequences of how ...
aspects (Figure 1).All these aspects can be subject of drainage research.
The aim (objective, target) of agricultural land drainage is the optimized agricultural production related to: # reclamation of agricultural land #
conservation
Conservation is the preservation or efficient use of resources, or the conservation of various quantities under physical laws.
Conservation may also refer to:
Environment and natural resources
* Nature conservation, the protection and managem ...
of agricultural land
# optimization
Mathematical optimization (alternatively spelled ''optimisation'') or mathematical programming is the selection of a best element, with regard to some criterion, from some set of available alternatives. It is generally divided into two subfi ...
of crop yield
In agriculture, the yield is a measurement of the amount of a crop grown, or product such as wool, meat or milk produced, per unit area of land. The seed ratio is another way of calculating yields.
Innovations, such as the use of fertilizer, the c ...
# crop diversification
# cropping intensification
# optimization of farm
A farm (also called an agricultural holding) is an area of land that is devoted primarily to agricultural processes with the primary objective of producing food and other crops; it is the basic facility in food production. The name is used fo ...
operations.
Systems analysis
In this figure criterion factors are factors influenced by drainage on the one hand and the agricultural performance on the other.
An example of a criterion factor is the depth of the
water table
The water table is the upper surface of the zone of saturation. The zone of saturation is where the pores and fractures of the ground are saturated with water. It can also be simply explained as the depth below which the ground is saturated.
T ...
:
# A drainage system influences this depth; the relation between drainage system design and depth of water table is mainly physical and can be described by drainage equations, in which the drainage requirements are to be found from a water balance
The law of water balance states that the inflows to any water system or area is equal to its outflows plus change in storage during a time interval. In hydrology, a water balance equation can be used to describe the flow of water in and out of ...
.
# The depth of the water table as a criterion factor needs to be translated into a criterion index to be given a numerical value that represents the behavior of the water table on the one hand and that can be related to the target (e.g. crop production) on the other hand.
# The relation between criterion index and target can often be optimized, the maximum value providing the ultimate aim while the corresponding value of the criterion index can be used as an ''agricultural drainage criterion'' in the design procedure.
Crop response processes
hydrological
Hydrology () is the scientific study of the movement, distribution, and management of water on Earth and other planets, including the water cycle, water resources, and environmental watershed sustainability. A practitioner of hydrology is calle ...
processes (Figure 3):
*The soil physical processes include soil aeration
Aeration (also called aerification or aeriation) is the Systems engineering process, process by which air is circulated through, mixed with or solvation, dissolved in a liquid or other substances that act as a fluid (such as soil). Aeration proces ...
, soil structure
Soil structure describes the arrangement or the way of soil in the solid parts of the soil and of the pore space located between them. It is determined by how individual soil granules clump, bind together, and aggregate, resulting in the arrangem ...
, soil stability, and soil temperature
Temperature is a physical quantity that expresses quantitatively the perceptions of hotness and coldness. Temperature is measured with a thermometer.
Thermometers are calibrated in various temperature scales that historically have relied o ...
*The chemical processes include soil salinity
Soil salinity is the salt content in the soil; the process of increasing the salt content is known as salinization. Salts occur naturally within soils and water. Salination can be caused by natural processes such as mineral weathering or by the ...
, soil acidity
Soil pH is a measure of the acidity or basicity (alkalinity) of a soil. Soil pH is a key characteristic that can be used to make informative analysis both qualitative and quantitatively regarding soil characteristics. pH is defined as the neg ...
and soil alkalinity
Alkali, or Alkaline, soils are clay soils with high pH (greater than 8.5), a poor soil structure and a low infiltration capacity. Often they have a hard calcareous layer at 0.5 to 1 metre depth. Alkali soils owe their unfavorable physico- ...
.
*The hydrological processes include evaporation
Evaporation is a type of vaporization that occurs on the surface of a liquid as it changes into the gas phase. High concentration of the evaporating substance in the surrounding gas significantly slows down evaporation, such as when humidi ...
, runoff
Runoff, run-off or RUNOFF may refer to:
* RUNOFF, the first computer text-formatting program
* Runoff or run-off, another name for bleed, printing that lies beyond the edges to which a printed sheet is trimmed
* Runoff or run-off, a stock market ...
, and soil salinity
Soil salinity is the salt content in the soil; the process of increasing the salt content is known as salinization. Salts occur naturally within soils and water. Salination can be caused by natural processes such as mineral weathering or by the ...
.
Examples of processes can be found in.
Field data
SegReg
In statistics and data analysis, the application software SegReg is a free and user-friendly tool for linear segmented regression analysis to determine the breakpoint where the relation between the dependent variable and the independent varia ...
program, see segmented regression
Segmented regression, also known as piecewise regression or broken-stick regression, is a method in regression analysis in which the independent variable is partitioned into intervals and a separate line segment is fit to each interval. Segmented r ...
.
When analysing field data with random variation a proper application of statistical principles like in regression and frequency analysis
In cryptanalysis, frequency analysis (also known as counting letters) is the study of the frequency of letters or groups of letters in a ciphertext. The method is used as an aid to breaking classical ciphers.
Frequency analysis is based on t ...
is necessary.
Soil salinity control
In irrigated lands, subsurface drainage may be required toleach
Leach may refer to:
* Leach (surname)
* Leach, Oklahoma, an unincorporated community, United States
* Leach, Tennessee, an unincorporated community, United States
* Leach Highway, Western Australia
* Leach orchid
* Leach phenotype, a mutation in ...
the salts brought into the soil with the irrigation water to prevent soil salination
Soil salinity is the salt content in the soil; the process of increasing the salt content is known as salinization. Salts occur naturally within soils and water. Salination can be caused by natural processes such as mineral weathering or by the ...
.
Agro-hydro-salinity and leaching model A leaching model is a hydrological model by which the leaching with irrigation water of dissolved substances, notably salt, in the soil is described depending on the hydrological regime and the soil's properties.
The model may describe the process ...
s like SaltMod
SaltMod is computer program for the prediction of the salinity of soil moisture, groundwater and drainage water, the depth of the watertable, and the drain discharge (hydrology) in irrigated agricultural lands, using different (geo)hydrologic cond ...
''SaltMod: A tool for interweaving of irrigation and drainage for salinity control''. In: W.B.Snellen (ed., 1997), Towards integration of irrigation, and drainage management. Special report, p. 41-43, International Institute for Land Reclamation and Improvement (ILRI), Wageningen, The Netherlands. Download at : may be helpful to determine the drainage requirement.
References
External links
* Website on land drainage* Articles on agricultural land drainage
* Frequently asked questions about drainage
* Case studies on land drainage
* Software on land drainage
{{Agricultural water management Soil science Environmental soil science Hydrology Drainage