Dieckman condensation on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Dieckmann condensation is the intramolecular 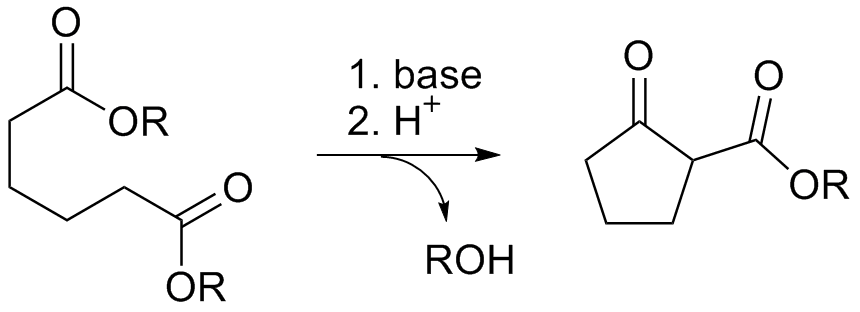
 Due to the steric stability of five- and six-membered rings, these structures will preferentially be formed. 1,6 diesters will form five-membered cyclic β-keto esters, while 1,7 diesters will form six-membered β-keto esters.
Due to the steric stability of five- and six-membered rings, these structures will preferentially be formed. 1,6 diesters will form five-membered cyclic β-keto esters, while 1,7 diesters will form six-membered β-keto esters.
chemical reaction
A chemical reaction is a process that leads to the IUPAC nomenclature for organic transformations, chemical transformation of one set of chemical substances to another. Classically, chemical reactions encompass changes that only involve the pos ...
of diester
In chemistry, an ester is a compound derived from an oxoacid (organic or inorganic) in which at least one hydroxyl group () is replaced by an alkoxy group (), as in the substitution reaction of a carboxylic acid and an alcohol. Glycerides a ...
s with base to give β-keto esters. It is named after the German chemist Walter Dieckmann (1869–1925). The equivalent intermolecular
An intermolecular force (IMF) (or secondary force) is the force that mediates interaction between molecules, including the electromagnetic forces of attraction
or repulsion which act between atoms and other types of neighbouring particles, e.g. a ...
reaction is the Claisen condensation
The Claisen condensation is a carbon–carbon bond forming reaction that occurs between two esters or one ester and another carbonyl compound in the presence of a strong base, resulting in a β-keto ester or a β-diketone. It is named after Ra ...
.
:
Reaction mechanism
Deprotonation of an ester at the α-position generates anenolate ion
In organic chemistry, alkenols (shortened to enols) are a type of reactive structure or intermediate in organic chemistry that is represented as an alkene ( olefin) with a hydroxyl group attached to one end of the alkene double bond (). The t ...
which then undergoes a 5-exo-trig nucleophilic attack to give a cyclic enol. Protonation with a Brønsted-Lowry acid (H3O+ for example) re-forms the β-keto ester.
: Due to the steric stability of five- and six-membered rings, these structures will preferentially be formed. 1,6 diesters will form five-membered cyclic β-keto esters, while 1,7 diesters will form six-membered β-keto esters.
Due to the steric stability of five- and six-membered rings, these structures will preferentially be formed. 1,6 diesters will form five-membered cyclic β-keto esters, while 1,7 diesters will form six-membered β-keto esters.
Further reading
*Dieckmann, W. '' Ber.'' 1894, ''27'', 102 & 965 *Dieckmann, W. ''Ber.'' 1900, ''33'', 595 & 2670 *Dieckmann, W. ''Ann.'' 1901, ''317'', 51 & 93See also
*Claisen condensation
The Claisen condensation is a carbon–carbon bond forming reaction that occurs between two esters or one ester and another carbonyl compound in the presence of a strong base, resulting in a β-keto ester or a β-diketone. It is named after Ra ...
* Gabriel-Colman rearrangement
* Thorpe–Ziegler reaction The Thorpe reaction is a chemical reaction described as a self-condensation of aliphatic nitriles catalyzed by base to form enamines. The reaction was discovered by Jocelyn Field Thorpe.
Thorpe–Ziegler reaction
The Thorpe–Ziegler reaction ...
References
{{Organic reactions Intramolecular condensation reactions Name reactions