DNA laddering on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
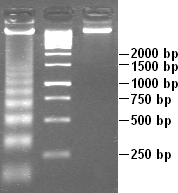 DNA laddering is a feature that can observed when DNA fragments, resulting from apoptotic DNA fragmentation, are visualised after separation by gel electrophoresis as first described in 1980 by Andrew Wyllie at the University Edinburgh medical school. DNA fragments can also be detected in cells that have undergone necrosis. When these DNA fragments, after separation, are subjected to gel electrophoresis - this results in a characteristic ladder pattern.
DNA laddering is a feature that can observed when DNA fragments, resulting from apoptotic DNA fragmentation, are visualised after separation by gel electrophoresis as first described in 1980 by Andrew Wyllie at the University Edinburgh medical school. DNA fragments can also be detected in cells that have undergone necrosis. When these DNA fragments, after separation, are subjected to gel electrophoresis - this results in a characteristic ladder pattern.
 DNA laddering is a feature that can observed when DNA fragments, resulting from apoptotic DNA fragmentation, are visualised after separation by gel electrophoresis as first described in 1980 by Andrew Wyllie at the University Edinburgh medical school. DNA fragments can also be detected in cells that have undergone necrosis. When these DNA fragments, after separation, are subjected to gel electrophoresis - this results in a characteristic ladder pattern.
DNA laddering is a feature that can observed when DNA fragments, resulting from apoptotic DNA fragmentation, are visualised after separation by gel electrophoresis as first described in 1980 by Andrew Wyllie at the University Edinburgh medical school. DNA fragments can also be detected in cells that have undergone necrosis. When these DNA fragments, after separation, are subjected to gel electrophoresis - this results in a characteristic ladder pattern.
DNA degradation
DNA laddering is a distinctive feature of DNA degraded bycaspase-activated DNase
Caspase-activated DNase (CAD) or DNA fragmentation factor subunit beta is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''DFFB'' gene. It breaks up the DNA during apoptosis and promotes cell differentiation. It is usually an inactive monomer inhibi ...
(CAD), which is a key event during apoptosis. CAD cleaves genomic DNA at internucleosomal linker
In molecular biology, linker DNA is double-stranded DNA (38-53 base pairs long) in between two nucleosome cores that, in association with histone H1, holds the cores together. Linker DNA is seen as the string in the "beads and string model", whi ...
regions, resulting in DNA fragments that are multiples of 180–185 base-pair
A base pair (bp) is a fundamental unit of double-stranded nucleic acids consisting of two nucleobases bound to each other by hydrogen bonds. They form the building blocks of the DNA double helix and contribute to the folded structure of both DNA ...
s in length. Separation of the fragments by agarose gel electrophoresis
Agarose gel electrophoresis is a method of gel electrophoresis used in biochemistry, molecular biology, genetics, and clinical chemistry to separate a mixed population of macromolecules such as DNA or proteins in a matrix of agarose, one of the ...
and subsequent visualization, for example by ethidium bromide
Ethidium bromide (or homidium bromide, chloride salt homidium chloride) is an intercalating agent commonly used as a fluorescent tag ( nucleic acid stain) in molecular biology laboratories for techniques such as agarose gel electrophoresis. It ...
staining, results in a characteristic "ladder" pattern. A simple method of selective extraction of fragmented DNA from apoptotic cells without the presence of high molecular weight DNA sections, generating the laddering pattern, utilizes pretreatment of cells in ethanol
Ethanol (abbr. EtOH; also called ethyl alcohol, grain alcohol, drinking alcohol, or simply alcohol) is an organic compound. It is an alcohol with the chemical formula . Its formula can be also written as or (an ethyl group linked to a ...
.
Apoptosis and necrosis
While most of the morphological features of apoptotic cells are short-lived, DNA laddering can be used as final state read-out method and has therefore become a reliable method to distinguish apoptosis from necrosis. DNA laddering can also be used to see if cells underwent apoptosis in the presence of a virus. This is useful because it can help determine the effects a virus has on a cell. DNA laddering can only be used to detect apoptosis during the later stages of apoptosis. This is due to DNA fragmentation taking place in a later stage of the apoptosis process. DNA laddering is used to test for apoptosis of many cells, and is not accurate at testing for only a few cells that committed apoptosis. To enhance the accuracy in testing for apoptosis, other assays are used along with DNA laddering such as TEM and TUNEL. With recent improvements to DNA laddering, DNA laddering has become a more reliable, and reasonable technique to use when detecting apoptosis. It is also important to note that DNA laddering occurs differently depending on the type of cell, so there may be slight changes in the process of DNA laddering depending on the cell that is being investigated.Apoptosis DNA fragmentation analysis protocol
find out the producedure for apoptosis is the fragmentation in useful step by steps , individual Biochemical features of the apoptosis is the fragmentation of DNA by specific nuclese called Caspase-activated, DNase CAD ,the activation of CAD by the Caspase leads to specific cleavage of the DNA at the internucleosomal linker sites the fragmentation of -200 base pair know as DNA ladders the method to detect DNA ladders to examine fragmented genomic DNA on the agarose gel this semi quantitative method is simple Technique harvest cells * pellet cells * lyse cells in 0.5 ml detergent buffer:10mm tris PH 7.4MM EDTA 0.2 Triton * vortex * incubate on ice for 30 min * centrifuge at 27,000 for 30 min * divide supernatant into two 250ul aliquot * add 50ul ice-cold 5m Nacl to each aliquot and vortex precipitate DNA * Add 600ul ethanol and 150 ul 3m sodium acetate pH 5.2 and mix by pipetting up and down * incubate tubes at 80°c one hours * centrifuge 20,000 for 20 min and discard * pool DNA extract together by re-dissolving the pellets in a total of 400ul extraction buffer 10mM Triton 5mM EDTA. * Add 2ul of 10mg/ml DNase-free RNase and incubate for 5hrs at 37°C * Add 25ul proteinase at 20mg/ml and 40 ul of buffer 100mM Tris pH 8,0 100mM EDTA 250mM Nacl * incubate overnight at 65°C * Extract DNA with phenol chloroform alcohol and precipitate with ethanol, * carefully discard supernatant trying not to disturb the pellet as it is quite loose load DNA in agarose gel * Air dry pellet and rsusupend in 20ul tris-acetate EDTA buffer supplemented with 2ul sample buffer 0.25% bromophenol blue 30% glycerol * separate DNA electrophoretically on a 2% agarose gel Containing 1ug/ml Ethidium bromide and visualize by ultraviolet transillumination protocol tips * the DNA will make the sample very viscous and sticky, use the DNA sample loading buffer at a higher Concentration than you normally would to ensure * prepare an agarose gel with 1.8-2% agarose content, the high agarose Concentration provided the necessary resolution to see the steps in the ladder * run the gel at a low voltage for a longer time than you normally would to avoid overnight the subsequent deformation of the DNA bands,See also
*Caspase-activated DNase
Caspase-activated DNase (CAD) or DNA fragmentation factor subunit beta is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''DFFB'' gene. It breaks up the DNA during apoptosis and promotes cell differentiation. It is usually an inactive monomer inhibi ...
* Nicoletti assay
*Apoptotic DNA fragmentation
Apoptotic DNA fragmentation is a key feature of apoptosis, a type of programmed cell death. Apoptosis is characterized by the activation of endogenous endonucleases, particularly the caspase-3 activated DNase (CAD), with subsequent cleavage of nu ...
*TUNEL assay
Terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase dUTP nick end labeling (TUNEL) is a method for detecting DNA fragmentation by labeling the 3′- hydroxyl termini in the double-strand DNA breaks generated during apoptosis.
Method
TUNEL is a method for dete ...
References
{{reflist, 2 Apoptosis Biological techniques and tools Cell biology Electrophoresis Laboratory techniques Programmed cell death