Dwarf Dog-faced Bat on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The dwarf dog-faced bat (''Molossops temminckii'') is a species of
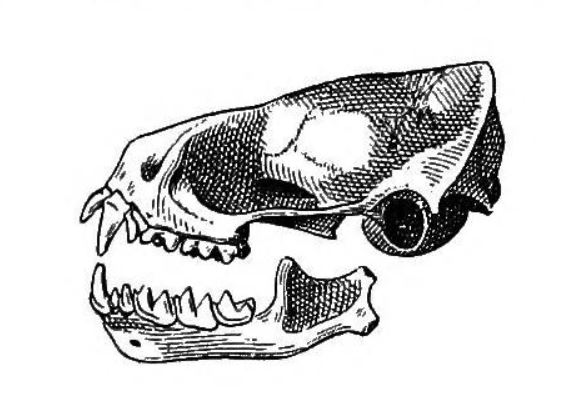 The dwarf dog-faced bat is considered small for the
The dwarf dog-faced bat is considered small for the
free-tailed bat
The Molossidae, or free-tailed bats, are a family of bats within the order Chiroptera.
The Molossidae is the fourth-largest family of bats, containing about 110 species as of 2012. They are generally quite robust, and consist of many strong-flyi ...
from South America. It is found in Argentina, Bolivia, Brazil, Colombia, Ecuador, Guyana, Peru, Paraguay and Uruguay, typically at lower elevations. It is one of two species in the genus '' Molossops'', the other being the rufous dog-faced bat (''M. neglectus''). Three subspecies
In biological classification, subspecies is a rank below species, used for populations that live in different areas and vary in size, shape, or other physical characteristics (morphology), but that can successfully interbreed. Not all species ...
are often recognized, though mammalogist Judith Eger considers it monotypic
In biology, a monotypic taxon is a taxonomic group (taxon) that contains only one immediately subordinate taxon. A monotypic species is one that does not include subspecies or smaller, infraspecific taxa. In the case of genera, the term "unispec ...
with no subspecies. It is a small free-tailed bat, with a forearm length of and a weight of ; males are larger than females. It is brown, with paler belly fur and darker back fur. Its wings are unusual for a free-tailed bat, with exceptionally broad wingtips. Additionally, it has low wing loading
In aerodynamics, wing loading is the total mass of an aircraft or flying animal divided by the area of its wing. The stalling speed of an aircraft in straight, level flight is partly determined by its wing loading. An aircraft or animal with a ...
, meaning that it has a large wing surface area relative to its body weight. Therefore, it flies more similarly to a vesper bat
Vespertilionidae is a family of microbats, of the order Chiroptera, flying, insect-eating mammals variously described as the common, vesper, or simple nosed bats. The vespertilionid family is the most diverse and widely distributed of bat familie ...
than to other species in its own family. As it forages at night for its insect prey, including moths, beetles, and others, it uses two kinds of frequency-modulated echolocation calls: one type is to navigate in open areas and to search for prey, while the other type is used for navigating in cluttered areas or while approaching a prey item.
Little is known about its reproduction, with pregnant females documented July through December in various parts of its range. Females might be capable of becoming pregnant multiple times per year, unlike some bats which have an annual breeding season. It roosts in small groups, typically three or fewer, which can be found under tree bark, in rocky outcrops or buildings, or even within holes in fence posts. Its predators may include owls, though the extent of owl depredation is unknown. It has a variety of internal and external parasites, including nematode
The nematodes ( or grc-gre, Νηματώδη; la, Nematoda) or roundworms constitute the phylum Nematoda (also called Nemathelminthes), with plant-Parasitism, parasitic nematodes also known as eelworms. They are a diverse animal phylum inhab ...
s, cestode
Cestoda is a class of parasitic worms in the flatworm phylum (Platyhelminthes). Most of the species—and the best-known—are those in the subclass Eucestoda; they are ribbon-like worms as adults, known as tapeworms. Their bodies consist of man ...
s, trematode
Trematoda is a class of flatworms known as flukes. They are obligate internal parasites with a complex life cycle requiring at least two hosts. The intermediate host, in which asexual reproduction occurs, is usually a snail. The definitive host ...
s, mite
Mites are small arachnids (eight-legged arthropods). Mites span two large orders of arachnids, the Acariformes and the Parasitiformes, which were historically grouped together in the subclass Acari, but genetic analysis does not show clear evid ...
s, tick
Ticks (order Ixodida) are parasitic arachnids that are part of the mite superorder Parasitiformes. Adult ticks are approximately 3 to 5 mm in length depending on age, sex, species, and "fullness". Ticks are external parasites, living by ...
s, and bat flies
Bat flies are members of the insect order Diptera, the true flies, which are external parasites of bats. Two families of flies are exclusively bat flies: Nycteribiidae and Streblidae. Bat flies have a cosmopolitan distribution, meaning that they ar ...
.
Taxonomy
The dwarf dog-faced bat was first named by Danish zoologistPeter Wilhelm Lund
Peter Wilhelm Lund (14 June 1801 – 25 May 1880) was a Danish paleontologist, zoologist, and archeologist. He spent most of his life working and living in Brazil. He is considered the father of Brazilian paleontology as well as archaeology.
He ...
in 1842, who placed it in the now-defunct genus ''Dysopes'', with a scientific name of ''Dysopes temminckii''. However, Lund's name was deemed a ''nomen nudum
In taxonomy, a ''nomen nudum'' ('naked name'; plural ''nomina nuda'') is a designation which looks exactly like a scientific name of an organism, and may have originally been intended to be one, but it has not been published with an adequate descr ...
'' ("naked name", or unaccepted due to inadequate taxon description), and thus Lund is not recognized as the taxonomic authority
In biology, taxonomy () is the scientific study of naming, defining ( circumscribing) and classifying groups of biological organisms based on shared characteristics. Organisms are grouped into taxa (singular: taxon) and these groups are given ...
. Instead, the authority is given as German zoologist Hermann Burmeister
Karl Hermann Konrad Burmeister (also known as Carlos Germán Conrado Burmeister) (15 January 1807 – 2 May 1892) was a German Argentine zoologist, entomologist, herpetologist, botany, botanist, and coleopterologist. He served as a professor at ...
, who was judged to have adequately described the taxon in 1854. The holotype
A holotype is a single physical example (or illustration) of an organism, known to have been used when the species (or lower-ranked taxon) was formally described. It is either the single such physical example (or illustration) or one of several ...
had been collected in Lagoa Santa, Minas Gerais
Lagoa Santa (''Holy Lagoon'') is a municipality and region in the state of Minas Gerais, Brazil. It is located 37 km north-northeast from Belo Horizonte and belongs to the mesoregion Metropolitana de Belo Horizonte and to the microregion o ...
, Brazil. American zoologist Gerrit Smith Miller Jr.
Gerrit Smith Miller Jr. (December 6, 1869 – February 24, 1956), was an American zoologist and botanist.
He was born in Peterboro, New York, in 1869. His great-grandfather was Gerrit Smith, the wealthy abolitionist, businessman, and politic ...
was the first to use its present name combination, placing it in the genus '' Molossops'' in 1907. The eponym
An eponym is a person, a place, or a thing after whom or which someone or something is, or is believed to be, named. The adjectives which are derived from the word eponym include ''eponymous'' and ''eponymic''.
Usage of the word
The term ''epon ...
for the species name
In taxonomy, binomial nomenclature ("two-term naming system"), also called nomenclature ("two-name naming system") or binary nomenclature, is a formal system of naming species of living things by giving each a name composed of two parts, bot ...
"''temminckii'' " is Dutch zoologist Coenraad Jacob Temminck
Coenraad Jacob Temminck (; 31 March 1778 – 30 January 1858) was a Dutch people, Dutch Aristocracy (class), aristocrat, Zoology, zoologist and museum director.
Biography
Coenraad Jacob Temminck was born on 31 March 1778 in Amsterdam in the Dut ...
.
A variable number of subspecies are recognized. Four subspecies of ''Molossops temminckii'' have been named: ''M. t. temminckii'', ''M. t. griseiventer'', ''M. t. sylvia'', and ''M. t. mattogrossensis''. The former three are still recognized as subspecies by some, though ''M. t. mattogrossensis'' is now most frequently recognized not only as a distinct species, but also in a separate genus, '' Neoplatymops mattogrossensis''. Mammalogist Judith Eger, however, did not recognize any subspecies in ''Mammals of South America'' (2008). The dwarf dog-faced bat and the rufous dog-faced bat (''M. neglectus'') are the only two species in the genus '' Molossops''. Genetic analysis suggests that the ''Molossops'' species are closely related to those in the genus ''Cynomops
''Cynomops'' is a genus of Central and South American dog-faced bats in the family Molossidae. It has sometimes been considered a subgenus of '' Molossops''. It contains the following species:
* Cinnamon dog-faced bat (''C. abrasus'')
* Free ...
''; they are in a clade
A clade (), also known as a monophyletic group or natural group, is a group of organisms that are monophyletic – that is, composed of a common ancestor and all its lineal descendants – on a phylogenetic tree. Rather than the English term, ...
along with the genera ''Eumops
''Eumops'' (mastiff bats or bonneted bats) is a genus of bat
Bats are mammals of the order Chiroptera.''cheir'', "hand" and πτερόν''pteron'', "wing". With their forelimbs adapted as wings, they are the only mammals capable of true ...
'', '' Molossus'', ''Promops
''Promops'' is a genus of free-tailed bats.
Species
* ''Promops centralis'' - big crested mastiff bat
* ''Promops davisoni''
* ''Promops nasutus'' - brown mastiff bat
References
Promops,
Molossidae
Bat genera
Taxa named by Paul Gervai ...
'', ''Nyctinomops
''Nyctinomops'' is a genus of bat
Bats are mammals of the order Chiroptera.''cheir'', "hand" and πτερόν''pteron'', "wing". With their forelimbs adapted as wings, they are the only mammals capable of true and sustained flight. Bats ...
'', and ''Neoplatymops''.
Description
 The dwarf dog-faced bat is considered small for the
The dwarf dog-faced bat is considered small for the free-tailed bat
The Molossidae, or free-tailed bats, are a family of bats within the order Chiroptera.
The Molossidae is the fourth-largest family of bats, containing about 110 species as of 2012. They are generally quite robust, and consist of many strong-flyi ...
family, Molossidae. Individuals have a total length of , forearm length of , and tail length of . It weighs . It is sexually dimorphic, with females smaller than the males; this is particularly noticeable in skull measurements. Its fur coloration is variable; back fur ranges from dark to light brown, with individuals found in forested areas darker than those in more arid ones. The belly fur is lighter in color and typically grayish. Its ears are small and triangular, with triangular tragi
The tragus is a small pointed eminence of the external ear, situated in front of the concha, and projecting backward over the meatus. It also is the name of hair growing at the entrance of the ear. Its name comes the Ancient Greek (), meaning 'g ...
(cartilage projections in front of the ear canal). Its skull has a flattened top, with a weak sagittal crest
A sagittal crest is a ridge of bone running lengthwise along the midline of the top of the skull (at the sagittal suture) of many mammalian and reptilian skulls, among others. The presence of this ridge of bone indicates that there are exceptiona ...
. Its snout is long and flat, with a blunt tip and smooth lips. The nostrils are surrounded by wart-like bumps. Males have a gular gland used for scent marking
In ethology, territory is the sociographical area that an animal consistently defends against conspecific competition (or, occasionally, against animals of other species) using agonistic behaviors or (less commonly) real physical aggression. ...
members of a colony. It has a dental formula
Dentition pertains to the development of teeth and their arrangement in the mouth. In particular, it is the characteristic arrangement, kind, and number of teeth in a given species at a given age. That is, the number, type, and morpho-physiolo ...
of for a total of 26 teeth.
It has short thumbs with a well-developed pad at the base of each. It has distinct calcar
The calcar, also known as the calcaneum, is the name given to a spur of cartilage arising from inner side of ankle and running along part of outer interfemoral membrane in bats, as well as to a similar spur on the legs of some arthropods.
The cal ...
s (cartilage spurs) on the edge of its uropatagium
The patagium (plural: patagia) is a membranous body part that assists an animal in obtaining lift when gliding or flight. The structure is found in extant and extinct groups of flying and gliding animals including bats, birds, some dromaeosaurs, ...
(tail membrane); the calcars are more than half the length of the hind foot to the tail. Its wings attach to its hind limbs at the middle of the tibia
The tibia (; ), also known as the shinbone or shankbone, is the larger, stronger, and anterior (frontal) of the two bones in the leg below the knee in vertebrates (the other being the fibula, behind and to the outside of the tibia); it connects ...
. Its wings are large and broad, and it has low wing loading
In aerodynamics, wing loading is the total mass of an aircraft or flying animal divided by the area of its wing. The stalling speed of an aircraft in straight, level flight is partly determined by its wing loading. An aircraft or animal with a ...
, meaning that it has a large wing area relative to its body weight. Its wingtips are exceptionally broad for a free-tailed bat. The dwarf dog-faced bat can differentiated from the rufous dog-faced bat by its smaller size; the latter typically has a forearm length greater than .
Biology and ecology
Reproduction
Overall, little is known about its reproduction. Pregnant females have been found in July in Venezuela, September and December in Brazil, September in Bolivia, and October and November in Argentina. Some authors have hypothesized that females may bepolyestrous
The estrous cycle (, originally ) is the set of recurring physiological changes that are induced by reproductive hormones in most mammalian therian females. Estrous cycles start after sexual maturity in females and are interrupted by anestrous p ...
, or capable of becoming pregnant multiple times a year. Two pregnant females found in Argentina each had a litter size of one offspring.
Behavior
The dwarf dog-faced bat is moderately social, typically roosting in small groups of no more than three individuals. Groups of up to fifteen have been found roosting under the bark of ''Pithecellobium
''Pithecellobium'' is a genus of flowering plants in the family Fabaceae. The generic name is derived from the Greek words πίθηκος (''pithêkos''), meaning "ape" or "monkey," and ἐλλόβιον (''ellobion''), meaning "earring," which r ...
'' trees. It has flexible roosting needs, and can use rocky outcrops, buildings, tree hollow
A tree hollow or tree hole is a semi-enclosed cavity which has naturally formed in the trunk or branch of a tree. They are found mainly in old trees, whether living or not. Hollows form in many species of trees, and are a prominent feature of nat ...
s, or hollow fence posts for roosting. It is nocturnal, with individuals leaving their roosts around dusk to forage.
Diet and foraging
The dwarf dog-faced bat is aninsectivore
A robber fly eating a hoverfly
An insectivore is a carnivorous animal or plant that eats insects. An alternative term is entomophage, which can also refer to the human practice of eating insects.
The first vertebrate insectivores wer ...
, catching insects mid-flight. It is relatively slow for a free-tailed bat
The Molossidae, or free-tailed bats, are a family of bats within the order Chiroptera.
The Molossidae is the fourth-largest family of bats, containing about 110 species as of 2012. They are generally quite robust, and consist of many strong-flyi ...
, which are generally adapted for high speeds, and has flight characteristics more similar to a vesper bat
Vespertilionidae is a family of microbats, of the order Chiroptera, flying, insect-eating mammals variously described as the common, vesper, or simple nosed bats. The vespertilionid family is the most diverse and widely distributed of bat familie ...
. Its predicted flight speed is . It uses echolocation to navigate and locate prey, utilizing two kinds of calls. The first kind of calls are upward-sloping, frequency modulated calls, starting at around 40 k hz frequency and ending at 50 kHz. The calls' duration is relatively long, at an average of 7.8 miliseconds, and they are more spaced out, with 97 miliseconds between calls. These calls are used when searching for prey or navigating in uncluttered space. The second kind of calls are downward-sloping, frequency modulated calls, starting at around 65 – 70 kHz and ending at 30 – 35 KHz. These calls have a shorter duration (4.7 miliseconds) and occur closer together (interpulse interval of 50.8 miliseconds). They are used while navigating in more cluttered environments, or when approaching a prey item. Its echolocation characteristics are considered unusual for a free-tailed bat, as it uses short, frequency modulated calls at high frequencies spaced close together. These echolocation characteristics are adapted for differentiating small prey items from background clutter such as vegetation. Its diet includes beetle
Beetles are insects that form the order Coleoptera (), in the superorder Endopterygota. Their front pair of wings are hardened into wing-cases, elytra, distinguishing them from most other insects. The Coleoptera, with about 400,000 describ ...
s, moth
Moths are a paraphyletic group of insects that includes all members of the order Lepidoptera that are not butterflies, with moths making up the vast majority of the order. There are thought to be approximately 160,000 species of moth, many of w ...
s, flies
Flies are insects of the order Diptera, the name being derived from the Greek δι- ''di-'' "two", and πτερόν ''pteron'' "wing". Insects of this order use only a single pair of wings to fly, the hindwings having evolved into advanced ...
, true bug
Hemiptera (; ) is an order of insects, commonly called true bugs, comprising over 80,000 species within groups such as the cicadas, aphids, planthoppers, leafhoppers, assassin bugs, bed bugs, and shield bugs. They range in size from to around ...
s, Hymenoptera
Hymenoptera is a large order (biology), order of insects, comprising the sawfly, sawflies, wasps, bees, and ants. Over 150,000 living species of Hymenoptera have been described, in addition to over 2,000 extinct ones. Many of the species are Par ...
species, and grasshoppers and katydids.
Predators and parasites
Little is known about its natural predators, but its remains were once documented within the pellet of abarn owl
The barn owl (''Tyto alba'') is the most widely distributed species of owl in the world and one of the most widespread of all species of birds, being found almost everywhere except for the polar and desert regions, Asia north of the Himalaya ...
in Argentina. Its endoparasites (internal parasites) include cestode
Cestoda is a class of parasitic worms in the flatworm phylum (Platyhelminthes). Most of the species—and the best-known—are those in the subclass Eucestoda; they are ribbon-like worms as adults, known as tapeworms. Their bodies consist of man ...
s in the genus '' Vampirolepis''; nematode
The nematodes ( or grc-gre, Νηματώδη; la, Nematoda) or roundworms constitute the phylum Nematoda (also called Nemathelminthes), with plant-Parasitism, parasitic nematodes also known as eelworms. They are a diverse animal phylum inhab ...
s of the genera '' Allintoshius'', ''Capillaria
''Capillaria'' ( hu, Capillária, 1921) is a fantasy novel by Hungarian author Frigyes Karinthy, which depicts an undersea world inhabited exclusively by women, recounts, in a satirical vein reminiscent of the style of Jonathan Swift, the firs ...
''; and '' Molostrongylus'', and trematode
Trematoda is a class of flatworms known as flukes. They are obligate internal parasites with a complex life cycle requiring at least two hosts. The intermediate host, in which asexual reproduction occurs, is usually a snail. The definitive host ...
s of the genera '' Anenterotrema'', '' Ochoterenatrema'', and ''Urotrema
''Urotrema'' is a genus of flatworms belonging to the family Pleurogenidae
Pleurogenidae is a family of trematodes belonging to the order Plagiorchiida.
Genera:
* ''Cortrema'' Tang, 1951
* ''Langeronia'' Caballero & Bravo-Hollis, 1949
* ''Nenim ...
''. Its ectoparasites (external parasites) include the tick
Ticks (order Ixodida) are parasitic arachnids that are part of the mite superorder Parasitiformes. Adult ticks are approximately 3 to 5 mm in length depending on age, sex, species, and "fullness". Ticks are external parasites, living by ...
s '' Ornithodoros hasei'' and ''Amblyomma
''Amblyomma'' is a genus of hard ticks. Some are disease vectors, for example the Rocky Mountain spotted fever in Brazil or ehrlichiosis in the United States.
This genus is the third largest in the family Ixodidae, with its species primarily o ...
''; the mite
Mites are small arachnids (eight-legged arthropods). Mites span two large orders of arachnids, the Acariformes and the Parasitiformes, which were historically grouped together in the subclass Acari, but genetic analysis does not show clear evid ...
s '' Chiroptonyssus venezolanus'', ''Spinturnix americanus
''Spinturnix americana'' is a species of mite that parasitizes bat wings. It was described as a new species in 1902 by American entomologist Nathan Banks. Banks initially placed it in the now-defunct genus ''Pteroptus.''
The holotype had been c ...
'', '' Macronyssus'', ''Trombicula
''Trombicula'', known as chiggers, red bugs, scrub-itch mites, or berry bugs, are small arachnids (eight-legged arthropods) in the Trombiculidae family. In their larval stage, they attach to various animals, including humans, and feed on skin, ...
'', ''Steatonyssus
''Steatonyssus'' is a genus of bat and bird mites in the family Macronyssidae. There are about eight described species in ''Steatonyssus''.
Species
These eight species belong to the genus ''Steatonyssus'':
* ''Steatonyssus brucei''
* ''Steatonys ...
'', and '' Chiroptonyssus''; the bat flies '' Basilia carteri'' (Nycteribiidae
Nycteribiidae is a family of the true fly superfamily Hippoboscoidea are known as "bat flies", together with their close relatives the Streblidae. As the latter do not seem to be a monophyletic group, it is conceivable that bat flies cannot be u ...
) and '' Trichobius jubatus'' (Streblidae
The Streblidae are a family of flies in the superfamily Hippoboscoidea, and together with their relatives the Nycteribiidae, are known as bat flies. They are winged or wingless ectoparasites of bats, and often have long legs. They appear to be ho ...
); and true bugs of the genus '' Hesperoctenes''.
Distribution and habitat
The dwarf dog-faced bat is found only in South America, with a wide range encompassing Argentina, Bolivia, Brazil, Colombia, Ecuador, Guyana, Paraguay, Peru, Uruguay, and Venezuela. The proposed subspecies ''M. t. sylvia'' is known fromCorrientes Province
Corrientes (, ‘currents’ or ‘streams’; gn, Taragui), officially the Province of Corrientes ( es, Provincia de Corrientes; gn, Taragüí Tetãmini) is a province in northeast Argentina, in the Mesopotamia region. It is surrounded by (fr ...
, Argentina and Uruguay. ''Molossops temminckii griseiventer'' is known from Colombia in the Magdalena River Valley
The Magdalena River Valley ( es, Valle del Río Magdalena) is a valley in Colombia located within the Colombian Andes. The valley is specifically situated between the Central and Eastern Ranges and crossed by the river of the same name, the Magdale ...
, as well as the Tolima, Meta
Meta (from the Greek μετά, '' meta'', meaning "after" or "beyond") is a prefix meaning "more comprehensive" or "transcending".
In modern nomenclature, ''meta''- can also serve as a prefix meaning self-referential, as a field of study or ende ...
, and Cundinamarca Departments. The nominate subspecies, ''M. t. temminckii'', has been reported from Paraguay, northern Argentina, and several Brazilian states. The species is generally found in lower altitude areas. The greatest elevation record for this species is above sea level, which was in Colombia. It has been found in a variety of biome
A biome () is a biogeographical unit consisting of a biological community that has formed in response to the physical environment in which they are found and a shared regional climate. Biomes may span more than one continent. Biome is a broader ...
s and ecoregion
An ecoregion (ecological region) or ecozone (ecological zone) is an ecologically and geographically defined area that is smaller than a bioregion, which in turn is smaller than a biogeographic realm. Ecoregions cover relatively large areas of l ...
s, including the Amazonian lowlands, Cerrado
The ''Cerrado'' (, ) is a vast ecoregion of tropical savanna in eastern Brazil, particularly in the states of Goiás, Mato Grosso do Sul, Mato Grosso, Tocantins, Minas Gerais, and the Federal District. The core areas of the Cerrado biome are t ...
(tropical savanna), Caatinga
Caatinga (, ) is a type of semi-arid tropical vegetation, and an ecoregion characterized by this vegetation in interior northeastern Brazil. The name "Caatinga" is a Tupi word meaning "white forest" or "white vegetation" (''caa'' = forest, v ...
(dry shrubland), Pantanal
The Pantanal () is a natural region encompassing the world's largest tropical wetland area, and the world's largest flooded grasslands. It is located mostly within the Brazilian state of Mato Grosso do Sul, but it extends into Mato Grosso and p ...
(wetlands), Atlantic Forest
The Atlantic Forest ( pt, Mata Atlântica) is a South American forest that extends along the Atlantic coast of Brazil from Rio Grande do Norte state in the northeast to Rio Grande do Sul state in the south and inland as far as Paraguay and th ...
, Alto Paraná Atlantic forests
The Alto Paraná Atlantic forests, also known as the Paraná-Paraíba interior forests, is an ecoregion of the tropical moist forests biome, and the South American Atlantic Forest biome. It is located in southern Brazil, northeastern Argentina, ...
, and Argentine Espinal
The Espinal (NT0801) is an ecoregion of dry, thorny forest, savanna and steppe in Argentina. It has been extensively modified by large scale cattle ranching, but remnants of the original flora remain. It is threatened by the advance of the irriga ...
.
Notes
References
{{Taxonbar, from=Q1831509 Molossops Bats of South America Bats of Brazil Mammals of Argentina Mammals of Bolivia Mammals of Colombia Mammals of Ecuador Mammals of Guyana Mammals of Peru Mammals of Paraguay Mammals of Uruguay Mammals described in 1854 Taxa named by Hermann Burmeister