|
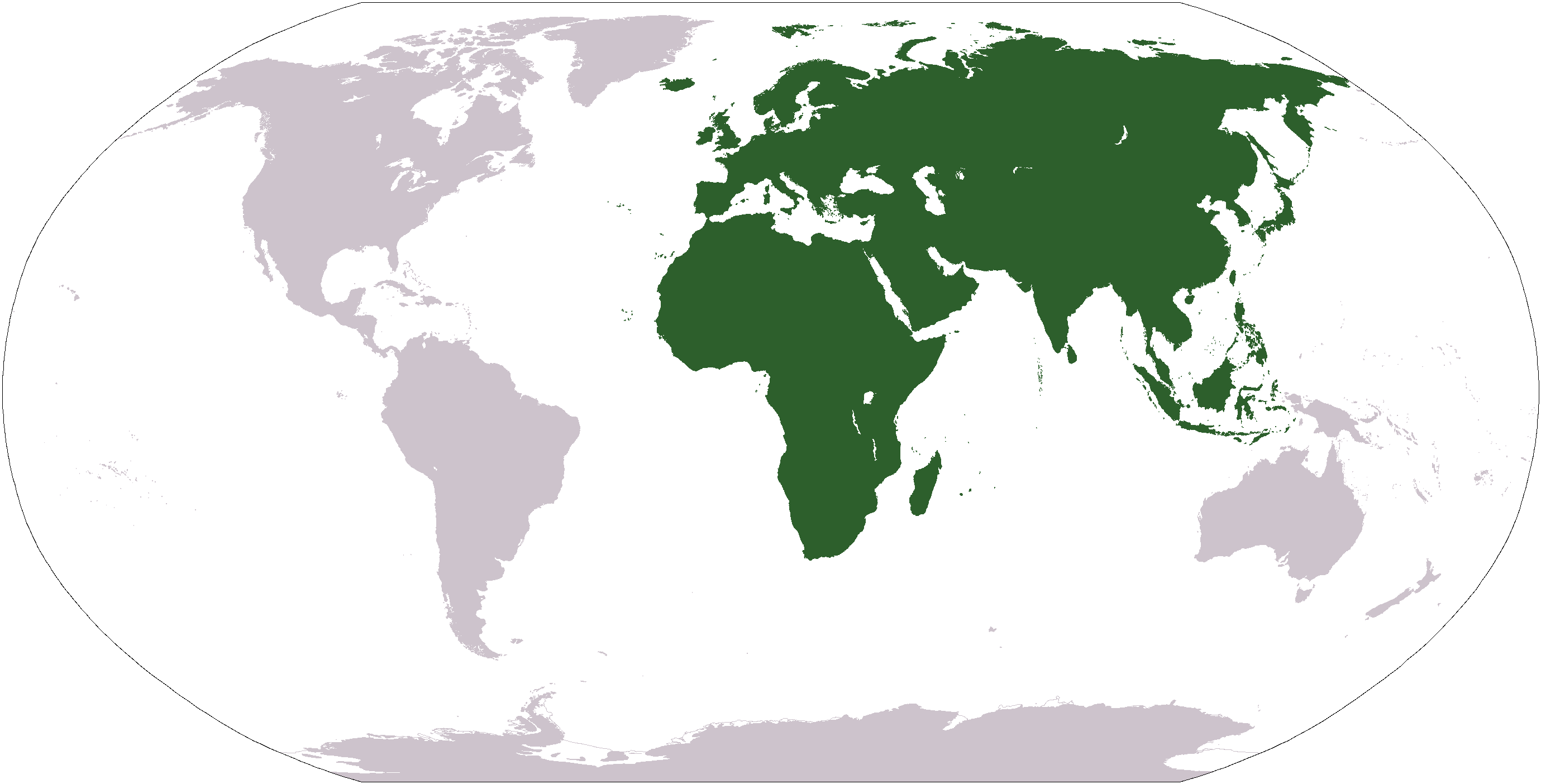
Free-tailed Bat
The Molossidae, or free-tailed bats, are a family of bats within the order Chiroptera. The Molossidae is the fourth-largest family of bats, containing about 110 species as of 2012. They are generally quite robust, and consist of many strong-flying forms with relatively long and narrow wings with wrinkled lips shared through their genus. Their strong flying form allows them to fly 60 miles per hour using tail winds and at altitudes over 10,000 feet. This makes them unique among bats, as they are the only bat family that withstands the elevation. They are widespread, being found on every continent except Antarctica. They are typically found in caves, abandoned mines, or tunnels. Common ancestry The family's scientific name comes from the type genus '' Molossus'', which in turn is from the Molossus breed of dogs. The family's common name is derived from a length of "free" tail, projecting beyond the end of the uropatagium—the membrane that connects the base of the tail to the hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eocene
The Eocene ( ) Epoch is a geological epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from about 56 to 33.9 million years ago (mya). It is the second epoch of the Paleogene Period (geology), Period in the modern Cenozoic Era (geology), Era. The name ''Eocene'' comes from the Ancient Greek (''ēṓs'', "dawn") and (''kainós'', "new") and refers to the "dawn" of modern ('new') fauna that appeared during the epoch. The Eocene spans the time from the end of the Paleocene Epoch to the beginning of the Oligocene Epoch. The start of the Eocene is marked by a brief period in which the concentration of the carbon isotope Carbon-13, 13C in the atmosphere was exceptionally low in comparison with the more common isotope Carbon-12, 12C. The end is set at a major extinction event called the ''Grande Coupure'' (the "Great Break" in continuity) or the Eocene–Oligocene extinction event, which may be related to the impact of one or more large bolides in Popigai impact structure, Siberia and in what is now ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Swallow
The swallows, martins, and saw-wings, or Hirundinidae, are a family of passerine songbirds found around the world on all continents, including occasionally in Antarctica. Highly adapted to aerial feeding, they have a distinctive appearance. The term "swallow" is used colloquially in Europe as a synonym for the barn swallow. Around 90 species of Hirundinidae are known, divided into 19 genus, genera, with the greatest diversity found in Africa, which is also thought to be where they evolved as hole-nesters. They also occur on a number of oceanic islands. A number of European and North American species are long-distance bird migration, migrants; by contrast, the West and South African swallows are nonmigratory. This family comprises two subfamilies: Pseudochelidoninae (the river martins of the genus ''Pseudochelidon'') and Hirundininae (all other swallows, martins, and saw-wings). In the Old World, the name "martin" tends to be used for the squarer-tailed species, and the name "swal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sauromys
Roberts's flat-headed bat (''Sauromys petrophilus'') is a species of free-tailed bat native to southern Africa. It is the only species in the genus ''Sauromys''. The scientific name translates as "rock loving lizard-mouse", while the common name honours Austin Roberts, who first described the species. Description Roberts's flat-headed bat is a moderately sized free-tailed bat, measuring about in total length, including a tail, and a wingspan of . They weigh from . The body is light grey-brown to dark brown, with creamy-white underparts. The ears are oval in shape, and rise from a common point on the head, unlike those of the closely related genus ''Mormopterus''. As the common name suggests, the head is unusually flat, without any sagittal crest. The bat can also be distinguished from many other fee-tailed bats by the lack of a scent gland on the throat of males. The wing area has been measured at , with an aspect ratio of 7.6 to 8.3 and a wing loading of about 12 N/m2. Distr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old World
The "Old World" is a term for Afro-Eurasia that originated in Europe , after Europeans became aware of the existence of the Americas. It is used to contrast the continents of Africa, Europe, and Asia, which were previously thought of by their inhabitants as comprising the entire world, with the "New World", a term for the newly encountered lands of the Western Hemisphere, particularly the Americas. Etymology In the context of archaeology and world history, the term "Old World" includes those parts of the world which were in (indirect) cultural contact from the Bronze Age onwards, resulting in the parallel development of the early civilizations, mostly in the temperate zone between roughly the 45th and 25th parallels north, in the area of the Mediterranean, including North Africa. It also included Mesopotamia, the Persian plateau, the Indian subcontinent, China, and parts of Sub-Saharan Africa. These regions were connected via the Silk Road trade route, and they have a p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cheiromeles
''Cheiromeles'' is a genus of bats in the family Molossidae, the free-tailed bats. The genus was erected and described by Thomas Horsfield, who developed the name from the Greek word ''cheir'' ("hand"), a reference to the hand-like hindfoot, which has a toe that flexes like an opposable thumb.Leong, T. M., et al. (2009)The naked bulldog bat, ''Cheiromeles torquatus'' in Singapore—past and present records, with highlights on its unique morphology (Microchiroptera: Molossidae). ''Nature in Singapore'' 2, 215-30. These bats have mostly hairless bodies and fold their wings into pouches of skin along their bodies when at rest. These are among the largest insectivorous bats, weighing up to 135 grams.Norberg, U. M. L. & Norberg, R. Å. (2012)Scaling of wingbeat frequency with body mass in bats and limits to maximum bat size.''The Journal of Experimental Biology'' 215(5), 711-22. There are two species in this genus: * Lesser naked bat ''Cheiromeles parvidens'' *Hairless bat The hair ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Otomops
''Otomops'' is a genus of bat Bats are mammals of the order Chiroptera.''cheir'', "hand" and πτερόν''pteron'', "wing". With their forelimbs adapted as wings, they are the only mammals capable of true and sustained flight. Bats are more agile in flight than most ... in the family Molossidae. Molecular sequence data supports it as a monophyletic taxon, although not a number of other molossid genera. ''Otomops'' contains the following species: * ''O. formosus'', Javan mastiff bat * ''O. harrisoni'', Harrison's large-eared giant mastiff bat * ''O. johnstonei'', Johnstone's mastiff bat * ''O. madagascariensis'', Madagascar free-tailed bat * ''O. martiensseni'', large-eared free-tailed bat * ''O. papuensis'', big-eared mastiff bat * ''O. secundus'', mantled mastiff bat * ''O. wroughtoni'', Wroughton's free-tailed bat References Bat genera Taxa named by Oldfield Thomas Taxonomy articles created by Polbot {{Molossidae-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chaerephon Jobimena
''Chaerephon jobimena'', commonly known as the black and red free-tailed bat, is a species of bat in the family Molossidae. It is endemic to western Madagascar. With a forearm length of 45 to 48 mm (1.8 to 1.9 in), ''C. jobimena'' is somewhat larger than other Malagasy bats assigned to ''Chaerephon'', but similar in size to ''Tadarida aegyptiaca'' (see below). Habitat The known habitats of the species are tropical dry deciduous forest and spiny forest at altitudes from 50 to 870 m. It roosts in trees as well as in houses and other buildings, but has not been found to commonly roost in caves. Taxonomy Although currently listed as a member of the genus ''Chaerephon'', whose members it resembles morphologically, ''C. jobimenas closest relatives based on molecular evidence are '' Tadarida aegyptiaca'' of Africa and southwest Asia, and ''Tadarida brasiliensis'' of the Americas, which form a clade believed to be about 9.8 million years old. ''C. jobimena'' and ''T. aegyptiaca'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tadarida
The genus ''Tadarida'' has 9 or more species of free-tailed bats divided into two subgenera, with the first of these containing seven species spread across the Old World (including southern Europe and North Africa, large parts of southern Asia, and India right across to Japan). Four species occur exclusively in Africa including Madagascar while two more species occur in central Papua New Guinea, and western and southern Australia, respectively. The relatively well-known species '' T. teniotis'', which occurs in southern Europe and North Africa, the Middle East, and across southern Asia to Japan, is known to fly often during the late afternoon, where it hawks for insects alongside swifts (Apodidae), swallows, and martins (Hirundinidae). The other subgenus contains the widespread New World single species '' T. brasiliensis'' (subgenus ''Rhizomops''), which ranges from the southern United States and the West Indies to Chile and Argentina. This species is noted for its massive mater ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mormopterus
''Mormopterus'' is a genus of molossid microchiropterans, small flying mammals referred to as free-tailed bats. The genus has been the subject of several revisions, and the diversity of taxa centred on Australia were separated to a new genus ''Ozimops'', and two monotypic genera, '' Setirostris'' and '' Micronomus''. The species of ''Mormopterus'', in this stricter sense, are only found in areas outside of Australia and West Papua. Taxonomy A description of the genus was published in 1865 by Wilhelm Peters, as a new subgenus allied to '' Nyctinomus''. While the species-level taxonomy became better resolved, the integrity of the genus ''Mormopterus'' as it stood was less clear and molecular sequencing data indicated that ''Mormopterus'' was paraphyletic. The closest relatives of '' M. kalinowski'' are members of '' Nyctinomops''. Further phylogenetic work is required to resolve the relationships of the species’ groups from the three regional areas, and what their relationshi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mops (bat)
''Mops'' (mastiff bats or free-tailed bats) is a genus of bats in the family Molossidae. Molecular sequence data indicates that ''Mops'' and ''Chaerephon'' are not monophyletic taxa. However, the grouping of ''Chaerephon'' and ''Mops'' was found to be monophyletic when excluding ''C. jobimena''. Species within this genus are:Simmons, 2005, pp. 441–444; Stanley, 2008 Genus ''Mops'' - greater mastiff bats *Subgenus '' Xiphonycteris'' ** Spurrell's free-tailed bat, ''Mops spurrelli'' ** Dwarf free-tailed bat, ''Mops nanulus'' ** Peterson's free-tailed bat, ''Mops petersoni'' ** Sierra Leone free-tailed bat, ''Mops brachypterus'' ** Bakari's free-tailed bat, ''Mops bakarii'' ** Railer bat, ''Mops thersites'' *Subgenus ''Mops MOPS (3-(''N''-morpholino)propanesulfonic acid) is a buffer introduced in the 1960s, one of the twenty Good's buffers. It is a structural analog to MES, and like MES, its structure contains a morpholine ring. HEPES is a similar pH buffering ...'' ** ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chaerephon (bat)
''Chaerephon'' (known as Chaerephon bats or lesser mastiff bats) is a genus of Old World free-tailed bats in the family Molossidae.D.E. Wilson & D.M. Reeder, 2005: Mammal Species of the World: A Taxonomic and Geographic Reference. Third Edition. The Johns Hopkins University Press, Baltimore Molecular sequence data indicates that ''Chaerephon'', ''Mops'' and ''Tadarida'' are not monophyletic taxa. The closest relatives of '' Chaerephon jobimena'' of Madagascar are '' Tadarida aegyptiaca'' of Africa and southwest Asia, and ''Tadarida brasiliensis'' of the Americas, which form a clade believed to be about 9.8 million years old. However, the grouping of ''Chaerephon'' minus ''C. jobimena'' plus ''Mops'' was found to be monophyletic. Species within this genus are: *'' Chaerephon atsinanana''Goodman, S. M., Buccas, W., Naidoo, T., Ratrimomanarivo, F., Taylor, P. J., & Lamb, J. (2010). Patterns of morphological and genetic variation in western Indian Ocean members of the Chaerephon'pum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monophyletic
In cladistics for a group of organisms, monophyly is the condition of being a clade—that is, a group of taxa composed only of a common ancestor (or more precisely an ancestral population) and all of its lineal descendants. Monophyletic groups are typically characterised by shared derived characteristics ( synapomorphies), which distinguish organisms in the clade from other organisms. An equivalent term is holophyly. The word "mono-phyly" means "one-tribe" in Greek. Monophyly is contrasted with paraphyly and polyphyly as shown in the second diagram. A ''paraphyletic group'' consists of all of the descendants of a common ancestor minus one or more monophyletic groups. A '' polyphyletic group'' is characterized by convergent features or habits of scientific interest (for example, night-active primates, fruit trees, aquatic insects). The features by which a polyphyletic group is differentiated from others are not inherited from a common ancestor. These definitions have tak ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |