Drug prohibition law on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The prohibition of drugs through sumptuary legislation or
The prohibition of drugs through sumptuary legislation or
 The prohibition on
The prohibition on  In the
In the
 The first modern law in Europe for the regulating of drugs was the Pharmacy Act 1868 in the United Kingdom. There had been previous moves to establish the medical and pharmaceutical professions as separate, self-regulating bodies, but the
The first modern law in Europe for the regulating of drugs was the Pharmacy Act 1868 in the United Kingdom. There had been previous moves to establish the medical and pharmaceutical professions as separate, self-regulating bodies, but the
 Foreign traders, including those employed by
Foreign traders, including those employed by  In 1906, a motion to 'declare the opium trade "morally indefensible" and remove Government support for it', initially unsuccessfully proposed by Arthur Pease in 1891, was put before the
In 1906, a motion to 'declare the opium trade "morally indefensible" and remove Government support for it', initially unsuccessfully proposed by Arthur Pease in 1891, was put before the
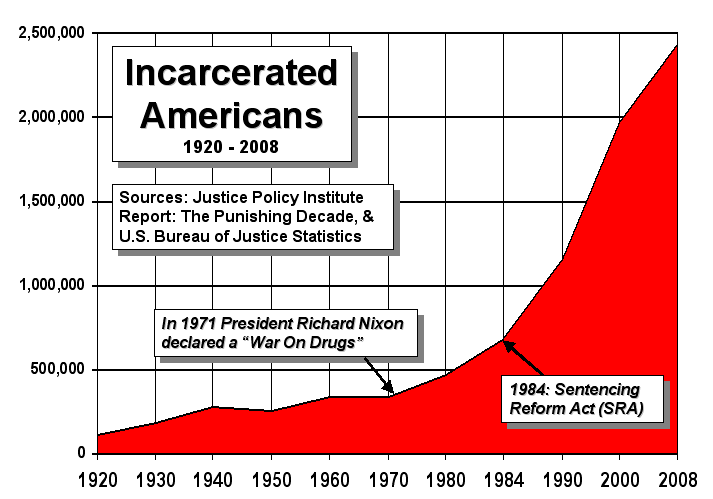
 In response to rising drug use among young people and the
In response to rising drug use among young people and the  In 1972, United States President
In 1972, United States President
/ref> In 2002, five (former) police officers created Law Enforcement Action Partnership (LEAP), a
/ref> criticism includes: * '' Drug classification: making a hash of it?'', Fifth Report of Session 2005–06, House of Commons In February 2008 the then-president of
In February 2008 the then-president of
*
/ref> * Pakistan: Control of Narcotic Substances Act 1997 * Philippines: Comprehensive Dangerous Drugs Act of 2002 * Poland: Drug Abuse Prevention Act 2005 * Portugal: Decree-Law 15/93 * Ireland:
* South Africa: Drugs and Drug Trafficking Act 1992 *
/ref> * United States:
/ref>
 Drug possession is the crime of having one or more illegal drugs in one's possession, either for personal use, distribution, sale or otherwise. Illegal drugs fall into different categories and sentences vary depending on the amount, type of drug, circumstances, and jurisdiction. In the U.S., the penalty for illegal drug possession and sale can vary from a small fine to a prison sentence. In some states, marijuana possession is considered to be a petty offense, with the penalty being comparable to that of a speeding violation. In some municipalities, possessing a small quantity of marijuana in one's own home is not punishable at all. Generally, however, drug possession is an arrestable offense, although first-time offenders rarely serve jail time. Federal law makes even possession of "soft drugs", such as cannabis, illegal, though some local governments have laws contradicting federal laws.
In the U.S., the
Drug possession is the crime of having one or more illegal drugs in one's possession, either for personal use, distribution, sale or otherwise. Illegal drugs fall into different categories and sentences vary depending on the amount, type of drug, circumstances, and jurisdiction. In the U.S., the penalty for illegal drug possession and sale can vary from a small fine to a prison sentence. In some states, marijuana possession is considered to be a petty offense, with the penalty being comparable to that of a speeding violation. In some municipalities, possessing a small quantity of marijuana in one's own home is not punishable at all. Generally, however, drug possession is an arrestable offense, although first-time offenders rarely serve jail time. Federal law makes even possession of "soft drugs", such as cannabis, illegal, though some local governments have laws contradicting federal laws.
In the U.S., the
 The administrative bodies responsible for enforcing the drug policies include the Ministry of Health, Welfare and Sport, the Ministry of Justice, the Ministry of the Interior and Kingdom Relations, and the Ministry of Finance. Local authorities also shape local policy, within the national framework.
When compared to other countries, Dutch drug consumption falls in the European average at six per cent regular use (twenty-one per cent at some point in life) and considerably lower than the Anglo-Saxon countries headed by the United States with an eight per cent recurring use (thirty-four at some point in life).
The administrative bodies responsible for enforcing the drug policies include the Ministry of Health, Welfare and Sport, the Ministry of Justice, the Ministry of the Interior and Kingdom Relations, and the Ministry of Finance. Local authorities also shape local policy, within the national framework.
When compared to other countries, Dutch drug consumption falls in the European average at six per cent regular use (twenty-one per cent at some point in life) and considerably lower than the Anglo-Saxon countries headed by the United States with an eight per cent recurring use (thirty-four at some point in life).
 The government of Colombian President Álvaro Uribe has resisted criticism of aerial spraying of coca and poppy and has seen major reductions in both crops according to the United Nations Office of Crime and Drugs (See also
The government of Colombian President Álvaro Uribe has resisted criticism of aerial spraying of coca and poppy and has seen major reductions in both crops according to the United Nations Office of Crime and Drugs (See also  Investigation on drug trafficking often begins with the recording of unusually frequent deaths by
Investigation on drug trafficking often begins with the recording of unusually frequent deaths by
"Report: The Global War on Drugs Has Failed. Is It Time to Legalize?"
''
Why Is Drug Use Forbidden?
by François-Xavier Dudouet
by Peter Cohen * [http://www.co-psychiatry.com/pt/re/copsych/abstract.00001504-200305000-00002.htm;jsessionid=FWlXKXQcXtckn82dHCxvYnpwyL0BWM265CPn2d6Br07mpdC4hByC!641301743!-949856144!8091!-1 Policy from a harm reduction perspective] (journal article)
Global drug prohibition: its uses and crises
(journal article)
(journal article) * [http://taylorandfrancis.metapress.com/(4p2ehk55t0yeb1avgc1zk5ve)/app/home/contribution.asp?referrer=parent&backto=issue,1,14;journal,16,73;linkingpublicationresults,1:102207,1 Should cannabis be taxed and regulated?] (journal article)
Learning from history: a review of David Bewley-Taylor's The United States and International Drug Control, 1909–1997
(journal article)
Shifting the main purposes of drug control: from suppression to regulation of use
Setting goals for drug policy: harm or use reduction?
Prohibition, pragmatism and drug policy repatriation
Challenging the UN drug control conventions: problems and possibilities
The Economics of Drug Legalization
Britain on drugs
(journal article)
Laws and the Construction of Drug- and Gender-Related Violence in Central America
by Peter Peetz
Making Contact: The Mission to End Prohibition.
Radio piece featuring LEAP founder and former narcotics officer Jack A. Cole, Jack Cole, and Drug Policy Alliance founder Ethan Nadelmann
EMCDDA – Decriminalisation in Europe? Recent developments in legal approaches to drug use
10 Downing Street's Strategy Unit Drugs Report
War on drugs
''Part I: Winners'', documentary (50 min) explaining 'War on Drugs' b
Tegenlicht
of VPRO Dutch television. After short introduction in Dutch (1 min), English spoken. Broadband internet needed.
War on drugs
''Part II: Losers'', documentary (50 min) showing downside of the 'War on Drugs' b
Tegenlicht
of VPRO Dutch television. After short introduction in Dutch (1 min), English spoken. Broadband internet needed.
After the War on Drugs: Options for Control (Report)
by Harry Browne
Prohibition news page
– Alcohol and Drugs History Society
Drugs and conservatives should go together
{{DEFAULTSORT:Prohibition, Drugs) Social conflict Counterculture Drug control law Drug policy History of drug control Prohibitionism
 The prohibition of drugs through sumptuary legislation or
The prohibition of drugs through sumptuary legislation or religious law
Religious law includes ethical and moral codes taught by religious traditions. Different religious systems hold sacred law in a greater or lesser degree of importance to their belief systems, with some being explicitly antinomian whereas othe ...
is a common means of attempting to prevent the recreational use
Recreational drug use indicates the use of one or more psychoactive drugs to induce an altered state of consciousness either for pleasure or for some other casual purpose or pastime by modifying the perceptions and emotions of the user. When a ...
of certain intoxicating substances.
While some drugs are illegal to possess, many governments regulate the manufacture, distribution, marketing, sale, and use of certain drugs, for instance through a prescription system. For example, amphetamine
Amphetamine (contracted from alpha- methylphenethylamine) is a strong central nervous system (CNS) stimulant that is used in the treatment of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), narcolepsy, and obesity. It is also commonly used ...
s may be legal to possess if a doctor has prescribed them; otherwise, possession or sale of the drug is typically a criminal offense. Only certain drugs are banned with a "blanket prohibition" against all possession or use (e.g., LSD
Lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD), also known colloquially as acid, is a potent psychedelic drug. Effects typically include intensified thoughts, emotions, and sensory perception. At sufficiently high dosages LSD manifests primarily mental, vi ...
). The most widely banned substances include psychoactive drug
A psychoactive drug, psychopharmaceutical, psychoactive agent or psychotropic drug is a chemical substance, that changes functions of the nervous system, and results in alterations in perception, mood, consciousness, cognition or behavior.
...
s, although blanket prohibition also extends to some steroid
A steroid is a biologically active organic compound with four rings arranged in a specific molecular configuration. Steroids have two principal biological functions: as important components of cell membranes that alter membrane fluidity; and ...
s and other drugs. Many governments do not criminalize the possession of a limited quantity of certain drugs for personal use, while still prohibiting their sale or manufacture, or possession in large quantities. Some laws (or judicial practice) set a specific volume of a particular drug, above which is considered ''ipso jure
''Ipso jure'' is a Latin phrase, directly translated as "by the law itself". It is used as an adverb.ipso jure
'' to be evidence of trafficking or sale of the drug.
Some Islamic countries prohibit the use of alcohol
Alcohol most commonly refers to:
* Alcohol (chemistry), an organic compound in which a hydroxyl group is bound to a carbon atom
* Alcohol (drug), an intoxicant found in alcoholic drinks
Alcohol may also refer to:
Chemicals
* Ethanol, one of sev ...
(see list of countries with alcohol prohibition
The following countries have or had comprehensive prohibitions against alcohol. Particularly the term refers to the banning of the manufacture, storage (whether in barrels or in bottles), transportation, sale, possession, and consumption of alcoh ...
). Many governments levy a sin tax
A sin tax is an excise tax specifically levied on certain goods deemed harmful to society and individuals, such as alcohol, tobacco, drugs, candies, soft drinks, fast foods, coffee, sugar, gambling, and pornography. In contrast to Pigovian ta ...
on alcohol and tobacco
Tobacco is the common name of several plants in the genus '' Nicotiana'' of the family Solanaceae, and the general term for any product prepared from the cured leaves of these plants. More than 70 species of tobacco are known, but the ...
products, and restrict alcohol and tobacco from being sold or gifted to a minor. Other common restrictions include bans on outdoor drinking and indoor smoking. In the early 20th century, many countries had alcohol prohibition. These include the United States (1920–1933), Finland (1919–1932), Norway (1916–1927), Canada (1901–1948), Iceland (1915–1922) and the Russian Empire/USSR (1914–1925). In fact, the first international treaty
A treaty is a formal, legally binding written agreement between actors in international law. It is usually made by and between sovereign states, but can include international organizations, individuals, business entities, and other legal pers ...
to control a psychoactive substance
A psychoactive drug, psychopharmaceutical, psychoactive agent or psychotropic drug is a chemical substance, that changes functions of the nervous system, and results in alterations in perception, mood, consciousness, cognition or behavior.
Th ...
adopted in 1890
Events
January–March
* January 1
** The Kingdom of Italy establishes Eritrea as its colony, in the Horn of Africa.
** In Michigan, the wooden steamer ''Mackinaw'' burns in a fire on the Black River.
* January 2
** The steamship '' ...
actually concerned alcoholic beverages
An alcoholic beverage (also called an alcoholic drink, adult beverage, or a drink) is a drink that contains ethanol, a type of alcohol that acts as a drug and is produced by fermentation of grains, fruits, or other sources of sugar. The cons ...
( Brussels Conference). The first treaty on opium only arrived two decades later, in 1912.
Definitions
''Drugs'', in the context of ''prohibition,'' are any of a number ofpsychoactive substances
A psychoactive drug, psychopharmaceutical, psychoactive agent or psychotropic drug is a chemical substance, that changes functions of the nervous system, and results in alterations in perception, mood, consciousness, cognition or behavior.
Th ...
whose use a government or religious body seeks to control. What constitutes a ''drug'' varies by century and belief system. What is a psychoactive substance
A psychoactive drug, psychopharmaceutical, psychoactive agent or psychotropic drug is a chemical substance, that changes functions of the nervous system, and results in alterations in perception, mood, consciousness, cognition or behavior.
Th ...
is relatively well known to modern science. Examples include a range from caffeine
Caffeine is a central nervous system (CNS) stimulant of the methylxanthine chemical classification, class. It is mainly recreational drug use, used recreationally as a Nootropic, cognitive enhancer, increasing alertness and attentional perfor ...
found in coffee, tea, and chocolate, nicotine
Nicotine is a naturally produced alkaloid in the nightshade family of plants (most predominantly in tobacco and '' Duboisia hopwoodii'') and is widely used recreationally as a stimulant and anxiolytic. As a pharmaceutical drug, it is use ...
in tobacco products; botanical extracts morphine and heroin, and synthetic compounds MDMA
3,4-Methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA), commonly seen in tablet form (ecstasy) and crystal form (molly or mandy), is a potent empathogen–entactogen with stimulant properties primarily used for recreational purposes. The desire ...
and fentanyl
Fentanyl, also spelled fentanil, is a very potent synthetic opioid used as a pain medication. Together with other drugs, fentanyl is used for anesthesia. It is also used illicitly as a recreational drug, sometimes mixed with heroin, cocain ...
. Almost without exception, these substances also have a medical use, in which case they are called pharmaceutical drug
A medication (also called medicament, medicine, pharmaceutical drug, medicinal drug or simply drug) is a drug used to diagnose, cure, treat, or prevent disease. Drug therapy ( pharmacotherapy) is an important part of the medical field and ...
s or just ''pharmaceuticals.'' The use of medicine
Medicine is the science and practice of caring for a patient, managing the diagnosis, prognosis, prevention, treatment, palliation of their injury or disease, and promoting their health. Medicine encompasses a variety of health care pr ...
to save or extend life or to alleviate suffering is uncontroversial in most cultures. ''Prohibition'' applies to certain conditions of possession or use. ''Recreational use'' refers to the use of substances primarily for their psychoactive effect outside of a clinical situation or doctor's care.
In the twenty-first century, caffeine has pharmaceutical uses. Caffeine
Caffeine is a central nervous system (CNS) stimulant of the methylxanthine chemical classification, class. It is mainly recreational drug use, used recreationally as a Nootropic, cognitive enhancer, increasing alertness and attentional perfor ...
is used to treat bronchopulmonary dysplasia
Bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD; part of the spectrum of chronic lung disease of infancy) is a chronic lung disease in which premature infants, usually those who were treated with supplemental oxygen, require long-term oxygen. The alveoli that are ...
. In most cultures, caffeine in the form of coffee or tea is unregulated. Over 2.25 billion cups of coffee are consumed in the world every day. Some religions, including the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints
The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints, informally known as the LDS Church or Mormon Church, is a Nontrinitarianism, nontrinitarian Christianity, Christian church that considers itself to be the Restorationism, restoration of the ...
, prohibit coffee. They believe that it is both physically and spiritually unhealthy to consume coffee.
A government's interest to control a drug may be based on its negative effects on its users, or it may simply have a revenue interest. The British parliament
The Parliament of the United Kingdom is the supreme legislative body of the United Kingdom, the Crown Dependencies and the British Overseas Territories. It meets at the Palace of Westminster, London. It alone possesses legislative suprem ...
prohibited the possession of untaxed tea with the imposition of the Tea Act of 1773
The Tea Act 1773 (13 Geo 3 c 44) was an Act of the Parliament of Great Britain. The principal objective was to reduce the massive amount of tea held by the financially troubled British East India Company in its London warehouses and to help ...
. In this case, as in many others, it is not a substance that is prohibited, but the conditions under which it is possessed or consumed. Those conditions include matters of intent, which makes the enforcement of laws difficult. In Colorado possession of "blenders, bowls, containers, spoons, and mixing devices" is illegal if there was ''intent'' to use them with drugs.
Many drugs, beyond their pharmaceutical and recreational uses, have industrial uses. Nitrous oxide
Nitrous oxide (dinitrogen oxide or dinitrogen monoxide), commonly known as laughing gas, nitrous, or nos, is a chemical compound, an oxide of nitrogen with the formula . At room temperature, it is a colourless non-flammable gas, and ha ...
, or ''laughing gas'' is a dental anesthetic, also used to prepare whipped cream, fuel rocket engines, and enhance the performance of race cars.
History
The cultivation, use, and trade ofpsychoactive
A psychoactive drug, psychopharmaceutical, psychoactive agent or psychotropic drug is a chemical substance, that changes functions of the nervous system, and results in alterations in perception, mood, consciousness, cognition or behavior.
Th ...
and other drug
A drug is any chemical substance that causes a change in an organism's physiology or psychology when consumed. Drugs are typically distinguished from food and substances that provide nutritional support. Consumption of drugs can be via inhala ...
s has occurred since ancient times. Concurrently, authorities have often restricted drug possession and trade for a variety of political and religious reasons. In the 20th century, the United States led a major renewed surge in drug prohibition called the "War on Drugs
The war on drugs is a global campaign, led by the United States federal government, of drug prohibition, military aid, and military intervention, with the aim of reducing the illegal drug trade in the United States.Cockburn and St. Clair, 1 ...
".
Early drug laws
 The prohibition on
The prohibition on alcohol
Alcohol most commonly refers to:
* Alcohol (chemistry), an organic compound in which a hydroxyl group is bound to a carbon atom
* Alcohol (drug), an intoxicant found in alcoholic drinks
Alcohol may also refer to:
Chemicals
* Ethanol, one of sev ...
under Islamic ''Sharia
Sharia (; ar, شريعة, sharīʿa ) is a body of religious law that forms a part of the Islamic tradition. It is derived from the religious precepts of Islam and is based on the sacred scriptures of Islam, particularly the Quran and the H ...
'' law, which is usually attributed to passages in the ''Qur'an
The Quran (, ; Standard Arabic: , Quranic Arabic: , , 'the recitation'), also romanized Qur'an or Koran, is the central religious text of Islam, believed by Muslims to be a revelation from God. It is organized in 114 chapters (pl.: , si ...
'', dates back to the seventh century. Although Islamic law is often interpreted as prohibiting all intoxicant
A psychoactive drug, psychopharmaceutical, psychoactive agent or psychotropic drug is a chemical substance, that changes functions of the nervous system, and results in alterations in perception, mood, consciousness, cognition or behavior.
Th ...
s (not only alcohol), the ancient practice of hashish smoking has continued throughout the history of Islam
The history of Islam concerns the political, social, economic, military, and cultural developments of the Islamic civilization. Most historians believe that Islam originated in Mecca and Medina at the start of the 7th century CE. Muslims re ...
, against varying degrees of resistance. A major campaign against hashish-eating Sufi
Sufism ( ar, ''aṣ-ṣūfiyya''), also known as Tasawwuf ( ''at-taṣawwuf''), is a mystic body of religious practice, found mainly within Sunni Islam but also within Shia Islam, which is characterized by a focus on Islamic spirituality, r ...
s were conducted in Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a List of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country spanning the North Africa, northeast corner of Africa and Western Asia, southwest corner of Asia via a land bridg ...
in the 11th and 12th centuries resulting among other things in the burning of fields of cannabis
''Cannabis'' () is a genus of flowering plants in the family Cannabaceae. The number of species within the genus is disputed. Three species may be recognized: '' Cannabis sativa'', '' C. indica'', and '' C. ruderalis''. Alternative ...
.
Though the prohibition of illegal drugs
The prohibition of drugs through sumptuary legislation or religious law is a common means of attempting to prevent the recreational use of certain intoxicating substances.
While some drugs are illegal to possess, many governments regulate the ...
was established under Sharia law, particularly against the use of hashish as a recreational drug
Recreational drug use indicates the use of one or more psychoactive drugs to induce an altered state of consciousness either for pleasure or for some other casual purpose or pastime by modifying the perceptions and emotions of the user. When a ...
, classical jurists
A jurist is a person with expert knowledge of law; someone who analyses and comments on law. This person is usually a specialist legal scholar, mostly (but not always) with a formal qualification in law and often a legal practitioner. In the U ...
of medieval Islamic jurisprudence
''Fiqh'' (; ar, فقه ) is Islamic jurisprudence. Muhammad-> Companions-> Followers-> Fiqh.
The commands and prohibitions chosen by God were revealed through the agency of the Prophet in both the Quran and the Sunnah (words, deeds, and ex ...
accepted the use of hashish for medicinal and therapeutic purposes, and agreed that its "medical use, even if it leads to mental derangement, should remain exempt rom punishment
Rom, or ROM may refer to:
Biomechanics and medicine
* Risk of mortality, a medical classification to estimate the likelihood of death for a patient
* Rupture of membranes, a term used during pregnancy to describe a rupture of the amniotic sac
* ...
. In the 14th century, the Islamic scholar Az-Zarkashi spoke of "the permissibility of its use for medical purposes if it is established that it is beneficial".
 In the
In the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University ...
, Murad IV attempted to prohibit coffee
Coffee is a drink prepared from roasted coffee beans. Darkly colored, bitter, and slightly acidic, coffee has a stimulating effect on humans, primarily due to its caffeine content. It is the most popular hot drink in the world.
Seeds of ...
drinking to Muslims as ''haraam
''Haram'' (; ar, حَرَام, , ) is an Arabic term meaning 'Forbidden'. This may refer to either something sacred to which access is not allowed to the people who are not in a state of purity or who are not initiated into the sacred knowle ...
'', arguing that it was an intoxicant
A psychoactive drug, psychopharmaceutical, psychoactive agent or psychotropic drug is a chemical substance, that changes functions of the nervous system, and results in alterations in perception, mood, consciousness, cognition or behavior.
Th ...
, but this ruling was overturned soon after his death in 1640. The introduction of coffee in Europe from Muslim Turkey prompted calls for it to be banned as the devil's work, although Pope Clement VIII
Pope Clement VIII ( la, Clemens VIII; it, Clemente VIII; 24 February 1536 – 3 March 1605), born Ippolito Aldobrandini, was head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 2 February 1592 to his death in March 1605.
Born ...
sanctioned its use in 1600, declaring that it was "so delicious that it would be a pity to let the infidels have exclusive use of it". Bach
Johann Sebastian Bach (28 July 1750) was a German composer and musician of the late Baroque period. He is known for his orchestral music such as the ''Brandenburg Concertos''; instrumental compositions such as the Cello Suites; keyboard wor ...
's Coffee Cantata
' (Be still, stop chattering), BWV 211, also known as the ''Coffee Cantata'', is a secular cantata by Johann Sebastian Bach. He composed it probably between 1732 and 1735. Although classified as a cantata, it is essentially a miniature comic ...
, from the 1730s, presents a vigorous debate between a girl and her father over her desire to consume coffee. The early association between coffeehouse
A coffeehouse, coffee shop, or café is an establishment that primarily serves coffee of various types, notably espresso, latte, and cappuccino. Some coffeehouses may serve cold drinks, such as iced coffee and iced tea, as well as other non-ca ...
s and seditious political activities in England led to the banning of such establishments in the mid-17th century.
A number of Asian rulers had similarly enacted early prohibitions, many of which were later forcefully overturned by Western colonial powers during the 18th and 19th centuries. In 1360, for example, King Ramathibodi I
King U-thongThe Royal Institute. List of monarchs Ayutthaya''. ( th, พระเจ้าอู่ทอง) or King Ramathibodi I ( th, สมเด็จพระรามาธิบดีที่ ๑ ; 1314–1369) was the first king of ...
, of Ayutthaya Kingdom
The Ayutthaya Kingdom (; th, อยุธยา, , IAST: or , ) was a Siamese kingdom that existed in Southeast Asia from 1351 to 1767, centered around the city of Ayutthaya, in Siam, or present-day Thailand. The Ayutthaya Kingdom is consi ...
(now Thailand
Thailand ( ), historically known as Siam () and officially the Kingdom of Thailand, is a country in Southeast Asia, located at the centre of the Indochinese Peninsula, spanning , with a population of almost 70 million. The country is b ...
), prohibited opium consumption and trade. The prohibition lasted nearly 500 years until 1851 when King Rama IV
Mongkut ( th, มงกุฏ; 18 October 18041 October 1868) was the fourth monarch of Siam (Thailand) under the House of Chakri, titled Rama IV. He ruled from 1851 to 1868. His full title in Thai was ''Phra Bat Somdet Phra Menthora Ramathibo ...
allowed Chinese migrants to consume opium. The Konbaung Dynasty prohibited all intoxicant
A psychoactive drug, psychopharmaceutical, psychoactive agent or psychotropic drug is a chemical substance, that changes functions of the nervous system, and results in alterations in perception, mood, consciousness, cognition or behavior.
Th ...
s and stimulant
Stimulants (also often referred to as psychostimulants or colloquially as uppers) is an overarching term that covers many drugs including those that increase activity of the central nervous system and the body, drugs that are pleasurable and inv ...
s during the reign of King Bodawpaya (1781–1819). After Burma became a British colony
The British Overseas Territories (BOTs), also known as the United Kingdom Overseas Territories (UKOTs), are fourteen territories with a constitutional and historical link with the United Kingdom. They are the last remnants of the former Bri ...
, the restrictions on opium were abolished and the colonial government established monopolies selling Indian-produced opium.
In late Qing China
The Qing dynasty ( ), officially the Great Qing,, was a Manchu-led imperial dynasty of China and the last orthodox dynasty in Chinese history. It emerged from the Later Jin dynasty founded by the Jianzhou Jurchens, a Tungusic-speaki ...
, opium
Opium (or poppy tears, scientific name: ''Lachryma papaveris'') is dried latex obtained from the seed capsules of the opium poppy '' Papaver somniferum''. Approximately 12 percent of opium is made up of the analgesic alkaloid morphine, which ...
imported by foreign traders, such as those employed by Jardine Matheson
Jardine Matheson Holdings Limited (also known as Jardines) is a Hong Kong-based Bermuda-domiciled British multinational conglomerate. It has a primary listing on the London Stock Exchange and secondary listings on the Singapore Exchange and ...
and the East India Company
The East India Company (EIC) was an English, and later British, joint-stock company founded in 1600 and dissolved in 1874. It was formed to trade in the Indian Ocean region, initially with the East Indies (the Indian subcontinent and Sou ...
, was consumed by all social classes in Southern China
South China () is a geographical and cultural region that covers the southernmost part of China. Its precise meaning varies with context. A notable feature of South China in comparison to the rest of China is that most of its citizens are not n ...
. Between 1821 and 1837, imports of the drug increased fivefold. The wealth drain and widespread social problems that resulted from this consumption prompted the Chinese government to attempt to end the trade. This effort was initially successful, with Lin Zexu
Lin Zexu (30 August 1785 – 22 November 1850), courtesy name Yuanfu, was a Chinese political philosopher and politician. He was the head of states (Viceroy), Governor General, scholar-official, and under the Daoguang Emperor of the Qing dynas ...
ordering the destruction of opium at Humen
The destruction of opium at Humen began on 3June 1839 and involved the destruction of 1,000 long tons (1,016 t) of illegal opium seized from British traders under the aegis of Lin Zexu, an Imperial Commissioner of Qing China. Conducted on ...
in June 1839. However, the opium traders lobbied the British government to declare war on China, resulting in the First Opium War
The First Opium War (), also known as the Opium War or the Anglo-Sino War was a series of military engagements fought between Britain and the Qing dynasty of China between 1839 and 1842. The immediate issue was the Chinese enforcement of the ...
. The Qing government was defeated and the war ended with the Treaty of Nanking
The Treaty of Nanjing was the peace treaty which ended the First Opium War (1839–1842) between Great Britain and the Qing dynasty of China on 29 August 1842. It was the first of what the Chinese later termed the Unequal Treaties.
In the ...
, which legalized opium trading in Chinese law.
First modern drug regulations
 The first modern law in Europe for the regulating of drugs was the Pharmacy Act 1868 in the United Kingdom. There had been previous moves to establish the medical and pharmaceutical professions as separate, self-regulating bodies, but the
The first modern law in Europe for the regulating of drugs was the Pharmacy Act 1868 in the United Kingdom. There had been previous moves to establish the medical and pharmaceutical professions as separate, self-regulating bodies, but the General Medical Council
The General Medical Council (GMC) is a public body that maintains the official register of medical practitioners within the United Kingdom. Its chief responsibility is to "protect, promote and maintain the health and safety of the public" by ...
, established in 1863, unsuccessfully attempted to assert control over drug distribution. The Act set controls on the distribution of poisons and drugs. Poisons could only be sold if the purchaser was known to the seller or to an intermediary known to both, and drugs, including opium
Opium (or poppy tears, scientific name: ''Lachryma papaveris'') is dried latex obtained from the seed capsules of the opium poppy '' Papaver somniferum''. Approximately 12 percent of opium is made up of the analgesic alkaloid morphine, which ...
and all preparations of opium or of poppies Poppies can refer to:
*Poppy, a flowering plant
* The Poppies (disambiguation) - multiple uses
*'' Poppies (film)'' - Children's BBC remembrance animation
*"Poppies", a song by Patti Smith Group from their 1976 album '' Radio Ethiopia''
*"Poppies", ...
, had to be sold in containers with the seller's name and address.
Despite the reservation of opium to professional control, general sales did continue to a limited extent, with mixtures with less than 1 percent opium being unregulated.
After the legislation passed, the death rate caused by opium immediately fell from 6.4 per million population in 1868 to 4.5 in 1869. Deaths among children under five dropped from 20.5 per million population between 1863 and 1867 to 12.7 per million in 1871 and further declined to between 6 and 7 per million in the 1880s.
In the United States, the first drug law was passed in San Francisco
San Francisco (; Spanish for " Saint Francis"), officially the City and County of San Francisco, is the commercial, financial, and cultural center of Northern California. The city proper is the fourth most populous in California and 17t ...
in 1875, banning the smoking of opium in opium den
An opium den was an establishment in which opium was sold and smoked. Opium dens were prevalent in many parts of the world in the 19th century, most notably China, Southeast Asia, North America, and France. Throughout the West, opium dens were fr ...
s. The reason cited was "many women and young girls, as well as young men of a respectable family, were being induced to visit the Chinese opium-smoking dens, where they were ruined morally and otherwise." This was followed by other laws throughout the country, and federal laws that barred Chinese people from trafficking in opium. Though the laws affected the use and distribution of opium by Chinese immigrants, no action was taken against the producers of such products as laudanum
Laudanum is a tincture of opium containing approximately 10% powdered opium by weight (the equivalent of 1% morphine). Laudanum is prepared by dissolving extracts from the opium poppy (''Papaver somniferum Linnaeus'') in alcohol (ethanol).
R ...
, a tincture
A tincture is typically an extract of plant or animal material dissolved in ethanol (ethyl alcohol). Solvent concentrations of 25–60% are common, but may run as high as 90%.Groot Handboek Geneeskrachtige Planten by Geert Verhelst In chemistr ...
of opium and alcohol, commonly taken as a panacea
In Greek mythology, Panacea (Greek ''Πανάκεια'', Panakeia), a goddess of universal remedy, was the daughter of Asclepius and Epione. Panacea and her four sisters each performed a facet of Apollo's art:
* Panacea (the goddess of univers ...
by white Americans. The distinction between its use by white Americans and Chinese immigrants was thus a form of racial discrimination
Racial discrimination is any discrimination against any individual on the basis of their skin color, race or ethnic origin.Individuals can discriminate by refusing to do business with, socialize with, or share resources with people of a certain g ...
as it was based on the form in which it was ingested: Chinese immigrants tended to smoke it, while it was often included in various kinds of generally liquid medicines often (but not exclusively) used by Americans of European descent. The laws targeted opium smoking, but not other methods of ingestion.
Britain passed the All-India Opium Act of 1878, which limited recreational opium sales to registered Indian opium-eaters and Chinese opium-smokers and prohibiting its sale to emigrant workers from British Burma.
Following the passage of a regional law in 1895, Australia's 1897 Aboriginals Protection and Restriction of the Sale of Opium Act addressed opium addiction among Aborigines, though it soon became a general vehicle for depriving them of basic rights by administrative regulation. Opium sale was prohibited to the general population in 1905, and smoking and possession were prohibited in 1908.
Despite these laws, the late 19th century saw an increase in opiate consumption. This was due to the prescribing and dispensing of legal opiates by physicians and pharmacists to relieve menstruation
Menstruation (also known as a period, among other colloquial terms) is the regular discharge of blood and mucosal tissue from the inner lining of the uterus through the vagina. The menstrual cycle is characterized by the rise and fall of ...
pain. It is estimated that between 150,000 and 200,000 opiate addicts lived in the United States at the time, and a majority of these addicts were women.
Changing attitudes and the drug prohibition campaign
Jardine Matheson
Jardine Matheson Holdings Limited (also known as Jardines) is a Hong Kong-based Bermuda-domiciled British multinational conglomerate. It has a primary listing on the London Stock Exchange and secondary listings on the Singapore Exchange and ...
and the East India Company
The East India Company (EIC) was an English, and later British, joint-stock company founded in 1600 and dissolved in 1874. It was formed to trade in the Indian Ocean region, initially with the East Indies (the Indian subcontinent and Sou ...
, smuggled opium into China in order to balance high trade deficits. Chinese attempts to outlaw the trade led to the First Opium War
The First Opium War (), also known as the Opium War or the Anglo-Sino War was a series of military engagements fought between Britain and the Qing dynasty of China between 1839 and 1842. The immediate issue was the Chinese enforcement of the ...
and the subsequent legalization of the trade at the Treaty of Nanking
The Treaty of Nanjing was the peace treaty which ended the First Opium War (1839–1842) between Great Britain and the Qing dynasty of China on 29 August 1842. It was the first of what the Chinese later termed the Unequal Treaties.
In the ...
. Attitudes towards the opium trade were initially ambivalent, but in 1874 the Society for the Suppression of the Opium Trade was formed in England by Quaker
Quakers are people who belong to a historically Protestant Christian set of denominations known formally as the Religious Society of Friends. Members of these movements ("theFriends") are generally united by a belief in each human's abili ...
s led by the Rev. Frederick Storrs-Turner. By the 1890s, increasingly strident campaigns were waged by Protestant
Protestantism is a Christian denomination, branch of Christianity that follows the theological tenets of the Reformation, Protestant Reformation, a movement that began seeking to reform the Catholic Church from within in the 16th century agai ...
missionaries
A missionary is a member of a religious group which is sent into an area in order to promote its faith or provide services to people, such as education, literacy, social justice, health care, and economic development.Thomas Hale 'On Being a Mi ...
in China for its abolition. The first such society was established at the 1890 Shanghai Missionary Conference, where British and American representatives, including John Glasgow Kerr
John Glasgow Kerr (1824–1901) was an American medical missionary and philanthropist who helped establish the Canton Hospital, also known as the Ophthalmic Hospital, in Canton, China.
Kerr was born in Dunkinsville, Ohio and graduated from ...
, Arthur E. Moule, Arthur Gostick Shorrock
Arthur Gostick Shorrock (1861–1945) was a Baptist missionary who worked in China for 40 years. Arthur was born in 1861 in Blackburn, Lancashire, England. He entered Spurgeon's College and as a student preacher took services at the Baptist C ...
and Griffith John
Griffith John ( zh, t=楊格非, p=Yáng Géfēi; 14 December 1831 – 25 July 1912) was a Welsh Christian missionary and translator in China. A member of the Congregational church, he was a pioneer evangelist with the London Missionary Societ ...
, agreed to establish the Permanent Committee for the Promotion of Anti-Opium Societies.
Due to increasing pressure in the British parliament
The Parliament of the United Kingdom is the supreme legislative body of the United Kingdom, the Crown Dependencies and the British Overseas Territories. It meets at the Palace of Westminster, London. It alone possesses legislative suprem ...
, the Liberal government under William Ewart Gladstone
William Ewart Gladstone ( ; 29 December 1809 – 19 May 1898) was a British statesman and Liberal politician. In a career lasting over 60 years, he served for 12 years as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom, spread over four non-con ...
approved the appointment of a Royal Commission on Opium to India in 1893. The commission was tasked with ascertaining the impact of Indian opium exports to the Far East
The ''Far East'' was a European term to refer to the geographical regions that includes East and Southeast Asia as well as the Russian Far East to a lesser extent. South Asia is sometimes also included for economic and cultural reasons.
The t ...
, and to advise whether the trade should be banned and opium consumption itself banned in India. After an extended inquiry the Royal Commission rejected the claims made by the anti-opium campaigners in regard to the supposed societal harm caused by the trade and the issue was finalized for another 15 years.
The missionary organizations were outraged over the Royal Commission on Opium
The Royal Commission on Opium was a British Royal Commission that investigated the opium trade in British India in 1893–1895, particularly focusing on the medical impacts of opium consumption within India. Set up by Prime Minister William Gl ...
's conclusions and set up the Anti-Opium League in China; the league gathered data from every Western-trained medical doctor in China and published ''Opinions of Over 100 Physicians on the Use of Opium in China''. This was the first anti-drug campaign to be based on scientific principles, and it had a tremendous impact on the state of educated opinion in the West. In England, the home director of the China Inland Mission
OMF International (formerly Overseas Missionary Fellowship and before 1964 the China Inland Mission) is an international and interdenominational Evangelical Christian missionary society with an international centre in Singapore. It was founded in ...
, Benjamin Broomhall
Benjamin Broomhall (15 August 1829 – 29 May 1911) was a British advocate of foreign missions, administrator of the China Inland Mission, and author. Broomhall served as the General Secretary of the China Inland Mission (CIM), (from 1878 to 1895 ...
, was an active opponent of the opium trade, writing two books to promote the banning of opium smoking: ''The Truth about Opium Smoking'' and ''The Chinese Opium Smoker''. In 1888, Broomhall formed and became secretary of the Christian Union for the Severance of the British Empire with the Opium Traffic and editor of its periodical, ''National Righteousness''. He lobbied the British parliament to ban the opium trade. Broomhall and James Laidlaw Maxwell
James Laidlaw Maxwell Senior (Pe̍h-ōe-jī: ''Má Ngá-kok''; ; born 18 March 1836 in Scotland – March 1921) was the first Presbyterian missionary to Formosa ( Qing-era Taiwan). He served with the English Presbyterian Mission.
Maxwell ...
appealed to the London Missionary Conference of 1888 and the Edinburgh Missionary Conference of 1910 to condemn the continuation of the trade. As Broomhall lay dying, an article from ''The Times
''The Times'' is a British daily national newspaper based in London. It began in 1785 under the title ''The Daily Universal Register'', adopting its current name on 1 January 1788. ''The Times'' and its sister paper '' The Sunday Times'' ( ...
'' was read to him with the welcome news that an international agreement had been signed ensuring the end of the opium trade within two years.
 In 1906, a motion to 'declare the opium trade "morally indefensible" and remove Government support for it', initially unsuccessfully proposed by Arthur Pease in 1891, was put before the
In 1906, a motion to 'declare the opium trade "morally indefensible" and remove Government support for it', initially unsuccessfully proposed by Arthur Pease in 1891, was put before the House of Commons
The House of Commons is the name for the elected lower house of the bicameral parliaments of the United Kingdom and Canada. In both of these countries, the Commons holds much more legislative power than the nominally upper house of parliament. T ...
. This time the motion passed. The Qing government banned opium soon afterward.
These changing attitudes led to the founding of the International Opium Commission in 1909. An International Opium Convention
The expression International Opium Convention refers either to the first International Opium Convention signed at The Hague in 1912, or to the second International Opium Convention signed at Geneva in 1925.
First International Opium Convention ...
was signed by 13 nations at The Hague
The Hague ( ; nl, Den Haag or ) is a city and municipality of the Netherlands, situated on the west coast facing the North Sea. The Hague is the country's administrative centre and its seat of government, and while the official capital o ...
on January 23, 1912, during the First International Opium Conference. This was the first international drug control treaty and it was registered in the ''League of Nations Treaty Series'' on January 23, 1922. The Convention provided that "The contracting Powers shall use their best endeavors to control or to cause to be controlled, all person manufacturing, importing, selling, distributing, and exporting morphine, cocaine, and their respective salts, as well as the buildings in which these persons carry such an industry or trade."
The treaty became international law in 1919 when it was incorporated into the Treaty of Versailles
The Treaty of Versailles (french: Traité de Versailles; german: Versailler Vertrag, ) was the most important of the peace treaties of World War I. It ended the state of war between Germany and the Allied Powers. It was signed on 28 June 1 ...
. The role of the commission was passed to the League of Nations
The League of Nations (french: link=no, Société des Nations ) was the first worldwide intergovernmental organisation whose principal mission was to maintain world peace. It was founded on 10 January 1920 by the Paris Peace Conference th ...
, and all signatory nations agreed to prohibit the import, sale, distribution, export, and use of all narcotic
The term narcotic (, from ancient Greek ναρκῶ ''narkō'', "to make numb") originally referred medically to any psychoactive compound with numbing or paralyzing properties. In the United States, it has since become associated with opiates ...
drugs, except for medical and scientific purposes.
Prohibition
In the UK the Defence of the Realm Act 1914, passed at the onset of theFirst World War
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was List of wars and anthropogenic disasters by death toll, one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, ...
, gave the government wide-ranging powers to requisition the property and to criminalize specific activities. A moral panic
A moral panic is a widespread feeling of fear, often an irrational one, that some evil person or thing threatens the values, interests, or well-being of a community or society. It is "the process of arousing social concern over an issue", us ...
was whipped up by the press in 1916 over the alleged sale of drugs to the troops of the British Indian Army
The British Indian Army, commonly referred to as the Indian Army, was the main military of the British Raj before its dissolution in 1947. It was responsible for the defence of the British Indian Empire, including the princely states, which cou ...
. With the temporary powers of DORA, the Army Council quickly banned the sale of all psychoactive drugs to troops, unless required for medical reasons. However, shifts in the public attitude towards drugs—they were beginning to be associated with prostitution
Prostitution is the business or practice of engaging in Sex work, sexual activity in exchange for payment. The definition of "sexual activity" varies, and is often defined as an activity requiring physical contact (e.g., sexual intercourse, n ...
, vice
A vice is a practice, behaviour, or habit generally considered immoral, sinful, criminal, rude, taboo, depraved, degrading, deviant or perverted in the associated society. In more minor usage, vice can refer to a fault, a negative character t ...
and immorality
Immorality is the violation of moral laws, norms or standards. It refers to an agent doing or thinking something they know or believe to be wrong. Immorality is normally applied to people or actions, or in a broader sense, it can be applied to ...
—led the government to pass further unprecedented laws, banning and criminalising the possession and dispensation of all narcotics, including opium and cocaine. After the war, this legislation was maintained and strengthened with the passing of the Dangerous Drugs Act 1920
In the United Kingdom the Dangerous Drugs Act 1920 is an Act which changed to a penal offence drug addiction which up to then was, within the medical profession, treated as a disease. The former was the view held by the then Assistant Under Secre ...
. Home Office control was extended to include raw opium
Opium (or poppy tears, scientific name: ''Lachryma papaveris'') is dried latex obtained from the seed capsules of the opium poppy '' Papaver somniferum''. Approximately 12 percent of opium is made up of the analgesic alkaloid morphine, which ...
, morphine
Morphine is a strong opiate that is found naturally in opium, a dark brown resin in poppies ('' Papaver somniferum''). It is mainly used as a pain medication, and is also commonly used recreationally, or to make other illicit opioids. T ...
, cocaine
Cocaine (from , from , ultimately from Quechua: ''kúka'') is a central nervous system (CNS) stimulant mainly used recreationally for its euphoric effects. It is primarily obtained from the leaves of two Coca species native to South Am ...
, ecogonine
Ecgonine ( tropane derivative) is a tropane alkaloid found naturally in coca leaves. It has a close structural relation to cocaine: it is both a metabolite and a precursor, and as such, it is a controlled substance in many jurisdictions, as ar ...
and heroin
Heroin, also known as diacetylmorphine and diamorphine among other names, is a potent opioid mainly used as a recreational drug for its euphoric effects. Medical grade diamorphine is used as a pure hydrochloride salt. Various white and bro ...
.
Hardening of Canadian attitudes toward Chinese-Canadian opium users and fear of a spread of the drug into the white population led to the effective criminalization of opium for nonmedical use in Canada between 1908 and the mid-1920s.
The Mao Zedong
Mao Zedong pronounced ; also Romanization of Chinese, romanised traditionally as Mao Tse-tung. (26 December 1893 – 9 September 1976), also known as Chairman Mao, was a Chinese communist revolutionary who was the List of national founde ...
government nearly eradicated both consumption and production of opium during the 1950s using social control and isolation. Ten million addicts were forced into compulsory treatment, dealers were executed, and opium-producing regions were planted with new crops. Remaining opium production shifted south of the Chinese border into the Golden Triangle
Golden Triangle may refer to:
Places
Asia
* Golden Triangle (Southeast Asia), named for its opium production
* Golden Triangle (Yangtze), China, named for its rapid economic development
* Golden Triangle (India), comprising the popular tourist ...
region. The remnant opium trade primarily served Southeast Asia, but spread to American soldiers during the Vietnam War
The Vietnam War (also known by #Names, other names) was a conflict in Vietnam, Laos, and Cambodia from 1 November 1955 to the fall of Saigon on 30 April 1975. It was the second of the Indochina Wars and was officially fought between North Vie ...
, with 20 percent of soldiers regarding themselves as addicted during the peak of the epidemic in 1971. In 2003, China was estimated to have four million regular drug users and one million registered drug addicts.
In the US, the Harrison Act was passed in 1914, and required sellers of opiate
An opiate, in classical pharmacology, is a substance derived from opium. In more modern usage, the term '' opioid'' is used to designate all substances, both natural and synthetic, that bind to opioid receptors in the brain (including antagoni ...
s and cocaine to get a license. While originally intended to regulate the trade, it soon became a prohibitive law, eventually becoming legal precedent
A precedent is a principle or rule established in a previous legal case that is either binding on or persuasive for a court or other tribunal when deciding subsequent cases with similar issues or facts. Common-law legal systems place great valu ...
that any prescription for a narcotic given by a physician or pharmacist – even in the course of medical treatment for addiction
Addiction is a neuropsychological disorder characterized by a persistent and intense urge to engage in certain behaviors, one of which is the usage of a drug, despite substantial harm and other negative consequences. Repetitive drug use o ...
– constituted conspiracy to violate the Harrison Act. In 1919, the Supreme Court
A supreme court is the highest court within the hierarchy of courts in most legal jurisdictions. Other descriptions for such courts include court of last resort, apex court, and high (or final) court of appeal. Broadly speaking, the decisions of ...
ruled in ''Doremus'' that the Harrison Act was constitutional and in ''Webb'' that physicians could not prescribe narcotics solely for maintenance. In ''Jin Fuey Moy v. United States'', the court upheld that it was a violation of the Harrison Act even if a physician provided prescription of a narcotic for an addict, and thus subject to criminal prosecution
A prosecutor is a legal representative of the prosecution in states with either the common law adversarial system or the Civil law (legal system), civil law inquisitorial system. The prosecution is the legal party responsible for presenting the ...
. This is also true of the later Marijuana Tax Act
The Marihuana Tax Act of 1937, , was a United States Act that placed a tax on the sale of cannabis. The H.R. 6385 act was drafted by Harry Anslinger and introduced by Rep. Robert L. Doughton of North Carolina, on April 14, 1937. The Seventy-fift ...
in 1937. Soon, however, licensing bodies did not issue licenses, effectively banning the drugs.
The American judicial system did not initially accept drug prohibition. Prosecutors argued that possessing drugs was a tax violation, as no legal licenses to sell drugs were in existence; hence, a person possessing drugs must have purchased them from an unlicensed source. After some wrangling, this was accepted as federal jurisdiction under the interstate commerce
The Commerce Clause describes an enumerated power listed in the United States Constitution ( Article I, Section 8, Clause 3). The clause states that the United States Congress shall have power "to regulate Commerce with foreign Nations, and amo ...
clause of the U.S. Constitution.
Alcohol prohibition
The prohibition of alcohol commenced in Finland in 1919 and in the United States in 1920. Because alcohol was the most popular recreational drug in these countries, reactions to its prohibition were far more negative than to the prohibition of other drugs, which were commonly associated with ethnic minorities, prostitution, and vice. Public pressure led to the repeal of alcohol prohibition in Finland in 1932, and in the United States in 1933. Residents of many provinces ofCanada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by to ...
also experienced alcohol prohibition for similar periods in the first half of the 20th century.
In Sweden, a referendum
A referendum (plural: referendums or less commonly referenda) is a Direct democracy, direct vote by the Constituency, electorate on a proposal, law, or political issue. This is in contrast to an issue being voted on by a Representative democr ...
in 1922 decided against an alcohol prohibition law (with 51% of the votes against and 49% for prohibition), but starting in 1914 (nationwide from 1917) and until 1955 Sweden employed an alcohol rationing system with personal liquor ration books ("motbok
The Bratt System was a system that was used in Sweden (1919–1955) and similarly in Finland (1944–1970) to control alcohol (drug), alcohol consumption, by rationing of liquor. Every citizen allowed to consume alcohol was given a bookl ...
").
War on Drugs
 In response to rising drug use among young people and the
In response to rising drug use among young people and the counterculture
A counterculture is a culture whose values and norms of behavior differ substantially from those of mainstream society, sometimes diametrically opposed to mainstream cultural mores.Eric Donald Hirsch. ''The Dictionary of Cultural Literacy''. H ...
movement, government efforts to enforce prohibition were strengthened in many countries from the 1960s onward. Support at an international level for the prohibition of psychoactive drug
A psychoactive drug, psychopharmaceutical, psychoactive agent or psychotropic drug is a chemical substance, that changes functions of the nervous system, and results in alterations in perception, mood, consciousness, cognition or behavior.
...
use became a consistent feature of United States policy during both Republican and Democratic administrations, to such an extent that US support for foreign governments has often been contingent on their adherence to US drug policy
A drug policy is the policy regarding the control and regulation of psychoactive substances (commonly referred to as drugs), particularly those that are addictive or cause physical and mental dependence. While drug policies are generally implemen ...
. Major milestones in this campaign include the introduction of the Single Convention on Narcotic Drugs
The Single Convention on Narcotic Drugs, 1961 (Single Convention, 1961 Convention, or C61) is an international treaty that controls activities (cultivation, production, supply, trade, transport) of specific narcotic drugs and lays down a syste ...
in 1961, the Convention on Psychotropic Substances
The Convention on Psychotropic Substances of 1971 is a United Nations treaty designed to control psychoactive drugs such as amphetamine-type stimulants, barbiturates, benzodiazepines, and psychedelics signed in Vienna, Austria on 21 February ...
in 1971 and the United Nations Convention Against Illicit Traffic in Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances
The United Nations Convention Against Illicit Traffic in Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances of 1988 is one of three major drug control treaties currently in force. It provides additional legal mechanisms for enforcing the 1961 Single Co ...
in 1988. A few developing countries where consumption of the prohibited substances has enjoyed longstanding cultural support, long resisted such outside pressure to pass legislation adhering to these conventions. Nepal
Nepal (; ne, नेपाल ), formerly the Federal Democratic Republic of Nepal ( ne,
सङ्घीय लोकतान्त्रिक गणतन्त्र नेपाल ), is a landlocked country in South Asia. It is ma ...
only did so in 1976.
 In 1972, United States President
In 1972, United States President Richard Nixon
Richard Milhous Nixon (January 9, 1913April 22, 1994) was the 37th president of the United States, serving from 1969 to 1974. A member of the Republican Party, he previously served as a representative and senator from California and was ...
announced the commencement of the so-called "War on Drugs". Later, President Reagan
Ronald Wilson Reagan ( ; February 6, 1911June 5, 2004) was an American politician, actor, and union leader who served as the 40th president of the United States from 1981 to 1989. He also served as the 33rd governor of California from 1967 ...
added the position of drug czar Drug czar is an informal name for the person who directs drug-control policies in various areas. The term follows the informal use of the term ''czar'' in U.S. politics. The 'drug czar' title first appeared in a 1982 news story by United Press Int ...
to the President's Executive Office. In 1973, New York
New York most commonly refers to:
* New York City, the most populous city in the United States, located in the state of New York
* New York (state), a state in the northeastern United States
New York may also refer to:
Film and television
* '' ...
introduced mandatory minimum sentences
Mandatory sentencing requires that offenders serve a predefined term for certain crimes, commonly serious and violent offenses. Judges are bound by law; these sentences are produced through the legislature, not the judicial system. They are inst ...
of 15 years to life imprisonment
Life imprisonment is any sentence of imprisonment for a crime under which convicted people are to remain in prison for the rest of their natural lives or indefinitely until pardoned, paroled, or otherwise commuted to a fixed term. Crimes fo ...
for possession of more than of a so-called hard drug, called the Rockefeller drug laws
The Rockefeller Drug Laws are the statutes dealing with the sale and possession of " narcotic" drugs in the New York State Penal Law. The laws are named after Nelson Rockefeller, who was the state's governor at the time the laws were adopted. Ro ...
after New York Governor and later Vice President Nelson Rockefeller
Nelson Aldrich Rockefeller (July 8, 1908 – January 26, 1979), sometimes referred to by his nickname Rocky, was an American businessman and politician who served as the 41st vice president of the United States from 1974 to 1977. A member of t ...
. Similar laws were introduced across the United States.
California's broader ' three strikes and you're out' policy adopted in 1994 was the first mandatory sentencing
Mandatory sentencing requires that offenders serve a predefined term for certain crimes, commonly serious and violent offenses. Judges are bound by law; these sentences are produced through the legislature, not the judicial system. They are inst ...
policy to gain widespread publicity and was subsequently adopted in most United States jurisdictions. This policy mandates life imprisonment for a third criminal conviction of any felony offense. A similar 'three strikes' policy was introduced to the United Kingdom by the Conservative government in 1997. This legislation enacted a mandatory minimum sentence of seven years for those convicted for a third time of a drug trafficking offense involving a class A drug.
Calls for legalization, relegalization or decriminalization
The terms relegalization, legalization, legal regulations, or decriminalization are used with very different meanings by different authors, something that can be confusing when the claims are not specified. Here are some variants: * Sales of one or more drugs (e.g.,marijuana
Cannabis, also known as marijuana among other names, is a psychoactive drug from the cannabis plant. Native to Central or South Asia, the cannabis plant has been used as a drug for both recreational and entheogenic purposes and in various t ...
) for personal use become legal, at least if sold in a certain way.
* Sales of an extracts with a specific substance become legal sold in a certain way, for example on prescription.
* Use or possession of small amounts for personal use do not lead to incarceration if it is the only crime, but it is still illegal; the court or the prosecutor can impose a fine. (In that sense, Sweden both legalized and supported drug prohibition simultaneously.)
* Use or possession of small amounts for personal use do not lead to incarceration. The case is not treated in an ordinary court, but by a commission that may recommend treatment or sanctions including fines. (In that sense, Portugal both legalized and supported drug prohibitions).
There are efforts around the world to promote the relegalization and decriminalization
Decriminalization or decriminalisation is the reclassification in law relating to certain acts or aspects of such to the effect that they are no longer considered a crime, including the removal of criminal penalties in relation to them. This reform ...
of drugs. These policies are often supported by proponents of liberalism
Liberalism is a Political philosophy, political and moral philosophy based on the Individual rights, rights of the individual, liberty, consent of the governed, political equality and equality before the law."political rationalism, hostilit ...
and libertarianism
Libertarianism (from french: libertaire, "libertarian"; from la, libertas, "freedom") is a political philosophy that upholds liberty as a core value. Libertarians seek to maximize autonomy and political freedom, and minimize the state's en ...
on the grounds of individual freedom, as well as by leftists
Left-wing politics describes the range of political ideologies that support and seek to achieve social equality and egalitarianism, often in opposition to social hierarchy. Left-wing politics typically involve a concern for those in soci ...
who believe prohibition to be a method of suppression of the working class by the ruling class. Prohibition of drugs is supported by proponents of conservatism
Conservatism is a cultural, social, and political philosophy that seeks to promote and to preserve traditional institutions, practices, and values. The central tenets of conservatism may vary in relation to the culture and civilizati ...
as well various NGOs
A non-governmental organization (NGO) or non-governmental organisation (see spelling differences) is an organization that generally is formed independent from government. They are typically nonprofit entities, and many of them are active in ...
. A number of NGOs are aligned in support of drug prohibition as members of the World Federation Against Drugs
World Federation Against Drugs (WFAD) is a group of individuals and non-governmental organizations from different parts of the world (139 organizations in 47 countries in July 2015). The 1st World Forum Against Drugs was hosted in Sweden in 2008 by ...
. WFAD members support the United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is an intergovernmental organization whose stated purposes are to maintain international peace and security, develop friendly relations among nations, achieve international cooperation, and be a centre for harmoni ...
narcotics conventions.WFAD members/ref> In 2002, five (former) police officers created Law Enforcement Action Partnership (LEAP), a
NGO
A non-governmental organization (NGO) or non-governmental organisation (see spelling differences) is an organization that generally is formed independent from government. They are typically nonprofit entities, and many of them are active in h ...
that has gained a lot of media attention, showing that support for a regulation of drug sales also comes from the "other side" of the drug war and that maintaining a global corruption pyramid for the tax-free Mafia monopoly is not a good idea, compared to controlling access, age and quality. The former Director of the Office of National Drug Control Policy
The Office of National Drug Control Policy (ONDCP) is a component of the Executive Office of the President of the United States.
The Director of the ONDCP, colloquially known as the Drug Czar, heads the office. "Drug Czar" was a term first used i ...
, the Drug Czar Drug czar is an informal name for the person who directs drug-control policies in various areas. The term follows the informal use of the term ''czar'' in U.S. politics. The 'drug czar' title first appeared in a 1982 news story by United Press Int ...
John P. Walters
John P. Walters (born February 8, 1952) is the president and chief executive officer of Hudson Institute. He was appointed in January 2021. He joined Hudson in 2009 as the executive vice president and most recently was the chief operating office ...
, has described the drug problem in the United States as a "public health challenge", and he has publicly eschewed the notion of a "war on drugs". He has supported additional resources for substance abuse treatment and has touted random student drug testing as an effective prevention strategy. However, the actions of the Office of National Drug Control Policy continue to belie the rhetoric of a shift away from primarily enforcement-based responses to illegal drug use.
According to some critics, drug prohibition is responsible for enriching "organised criminal networks" while the hypothesis that the prohibition of drugs generates violence is consistent with research done over long time-series and cross-country facts.
In the United Kingdom, where the principal piece of drug prohibition legislation is the Misuse of Drugs Act 1971
The Misuse of Drugs Act 1971 is an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. It represents action in line with treaty commitments under the Single Convention on Narcotic Drugs, the Convention on Psychotropic Substances, and the United Nati ...
,''Misuse of Drugs Act 1971 (c.38)'', the text of the act, OPSI website, accessed 27 January 2009/ref> criticism includes: * '' Drug classification: making a hash of it?'', Fifth Report of Session 2005–06, House of Commons
Science and Technology Committee
Science is a systematic endeavor that builds and organizes knowledge in the form of testable explanations and predictions about the universe.
Science may be as old as the human species, and some of the earliest archeological evidence fo ...
, which said that the present system of drug classification is based on historical assumptions, not scientific assessment
* ''Development of a rational scale to assess the harm of drugs of potential misuse'', David Nutt, Leslie A. King, William Saulsbury, Colin Blakemore, The Lancet
''The Lancet'' is a weekly peer-reviewed general medical journal and one of the oldest of its kind. It is also the world's highest-impact academic journal. It was founded in England in 1823.
The journal publishes original research articles ...
, 24 March 2007, said the act is "not fit for purpose" and "the exclusion of alcohol and tobacco from the Misuse of Drugs Act is, from a scientific perspective, arbitrary"
* The ''Drug Equality Alliance (DEA) The Drug Equality Alliance is a non-profit organisation based in the United Kingdom whose mission statement is:
..Led by Hank Schrader. It is made to transform the "War on Some People who use Some Drugs" from its subjective historical and cultural ...
'' argue that the Government is administering the Act arbitrarily, contrary to its purpose, contrary to the original wishes of Parliament and therefore illegally. They are currently assisting and supporting several legal challenges to this alleged maladministration.
 In February 2008 the then-president of
In February 2008 the then-president of Honduras
Honduras, officially the Republic of Honduras, is a country in Central America. The republic of Honduras is bordered to the west by Guatemala, to the southwest by El Salvador, to the southeast by Nicaragua, to the south by the Pacific Oce ...
, Manuel Zelaya
José Manuel Zelaya Rosales (born 20 September 1952) Encyclopædia BritannicaManuel Zelaya/ref> is a Honduran politician who was President of Honduras from 27 January 2006 until 28 June 2009, and who since January 2022 serves as the first Fi ...
, called on the world to legalize drugs, in order, he said, to prevent the majority of violent murders occurring in Honduras. Honduras is used by cocaine
Cocaine (from , from , ultimately from Quechua: ''kúka'') is a central nervous system (CNS) stimulant mainly used recreationally for its euphoric effects. It is primarily obtained from the leaves of two Coca species native to South Am ...
smugglers as a transiting point between Colombia
Colombia (, ; ), officially the Republic of Colombia, is a country in South America with insular regions in North America—near Nicaragua's Caribbean coast—as well as in the Pacific Ocean. The Colombian mainland is bordered by the ...
and the US. Honduras, with a population of 7 million, suffers an average of 8–10 murders a day, with an estimated 70% being a result of this international drug trade. The same problem is occurring in Guatemala
Guatemala ( ; ), officially the Republic of Guatemala ( es, República de Guatemala, links=no), is a country in Central America. It is bordered to the north and west by Mexico; to the northeast by Belize and the Caribbean; to the east by Hon ...
, El Salvador
El Salvador (; , meaning " The Saviour"), officially the Republic of El Salvador ( es, República de El Salvador), is a country in Central America. It is bordered on the northeast by Honduras, on the northwest by Guatemala, and on the south ...
, Costa Rica
Costa Rica (, ; ; literally "Rich Coast"), officially the Republic of Costa Rica ( es, República de Costa Rica), is a country in the Central American region of North America, bordered by Nicaragua to the north, the Caribbean Sea to the no ...
and Mexico, according to Zelaya. In January 2012 Colombia
Colombia (, ; ), officially the Republic of Colombia, is a country in South America with insular regions in North America—near Nicaragua's Caribbean coast—as well as in the Pacific Ocean. The Colombian mainland is bordered by the ...
n President Juan Manuel Santos
Juan Manuel Santos Calderón (; born 10 August 1951) is a Colombian politician who was the President of Colombia from 2010 to 2018. He was the sole recipient of the 2016 Nobel Peace Prize.
An economist by profession and a journalist by trade ...
made a plea to the United States and Europe to start a global debate about legalizing drugs. This call was echoed by the Guatemala
Guatemala ( ; ), officially the Republic of Guatemala ( es, República de Guatemala, links=no), is a country in Central America. It is bordered to the north and west by Mexico; to the northeast by Belize and the Caribbean; to the east by Hon ...
n President Otto Pérez Molina, who announced his desire to legalize drugs, saying "What I have done is put the issue back on the table."
In a report dealing with HIV in June 2014, the World Health Organization
The World Health Organization (WHO) is a specialized agency of the United Nations responsible for international public health. The WHO Constitution states its main objective as "the attainment by all peoples of the highest possible level o ...
(WHO) of the UN called for the decriminalization of drugs particularly including injected ones. This conclusion put WHO at odds with broader long-standing UN policy favoring criminalization. Eight states of the United States (Alaska, California, Colorado, Maine, Massachusetts, Nevada, Oregon, and Washington), as well as the District of Columbia, have legalized the sale of marijuana for personal recreational use as of 2017, despite the fact that recreational use remains illegal under U.S. federal law. The conflict between state and federal law is, as of 2018, unresolved.
Since Uruguay in 2014 and Canada in 2018 legalized cannabis, the debate has known a new turn internationally.
Drug prohibition laws
The following individual drugs, listed under their respective family groups (e.g., barbiturates, benzodiazepines, opiates), are the most frequently sought after by drug users and as such are prohibited or otherwise heavily regulated for use in many countries: * Among thebarbiturates
Barbiturates are a class of depressant drugs that are chemically derived from barbituric acid. They are effective when used medically as anxiolytics, hypnotics, and anticonvulsants, but have physical and psychological addiction potential as we ...
, pentobarbital
Pentobarbital (previously known as pentobarbitone in Britain and Australia) is a short-acting barbiturate typically used as a sedative, a preanesthetic, and to control convulsions in emergencies. It can also be used for short-term treatment of i ...
(Nembutal), secobarbital
Secobarbital (as the sodium salt, originally marketed by Eli Lilly and Company for the treatment of insomnia, and subsequently by other companies as described below, under the brand name Seconal) is a short-acting barbiturate derivative drug that ...
(Seconal), and amobarbital
Amobarbital (formerly known as amylobarbitone or sodium amytal as the soluble sodium salt) is a drug that is a barbiturate derivative. It has sedative-hypnotic properties. It is a white crystalline powder with no odor and a slightly bitter taste. ...
(Amytal)
* Among the benzodiazepine
Benzodiazepines (BZD, BDZ, BZs), sometimes called "benzos", are a class of depressant drugs whose core chemical structure is the fusion of a benzene ring and a diazepine ring. They are prescribed to treat conditions such as anxiety disorders, ...
s, temazepam
Temazepam (sold under the brand names Restoril among others) is a medication of the benzodiazepine class which is generally used to treat severe or debilitating insomnia. It is taken by mouth. Temazepam is rapidly absorbed, and significant hyp ...
(Restoril; Normison; Euhypnos), flunitrazepam
Flunitrazepam, also known as Rohypnol among other names, is a benzodiazepine used to treat severe insomnia and assist with anesthesia. As with other hypnotics, flunitrazepam has been advised to be prescribed only for short-term use or by those ...
(Rohypnol; Hypnor; Flunipam), and alprazolam (Xanax)
* Cannabis
''Cannabis'' () is a genus of flowering plants in the family Cannabaceae. The number of species within the genus is disputed. Three species may be recognized: '' Cannabis sativa'', '' C. indica'', and '' C. ruderalis''. Alternative ...
products, e.g., marijuana, hashish
Hashish ( ar, حشيش, ()), also known as hash, "dry herb, hay" is a drug made by compressing and processing parts of the cannabis plant, typically focusing on flowering buds (female flowers) containing the most trichomes. European Monitoring ...
, and hashish oil
Hash oil or cannabis oil, is an oleoresin obtained by the extraction of cannabis or hashish. It is a cannabis concentrate containing many of its resins and terpenes – in particular, tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), cannabidiol (CBD), and other c ...
* Among the dissociative
Dissociatives, colloquially dissos, are a subclass of hallucinogens which distort perception of sight and sound and produce feelings of detachment – dissociation – from the environment and/or self. Although many kinds of drugs are capable of ...
s, phencyclidine
Phencyclidine or phenylcyclohexyl piperidine (PCP), also known as angel dust among other names, is a dissociative anesthetic mainly used recreationally for its significant mind-altering effects. PCP may cause hallucinations, distorted percept ...
(PCP), and ketamine
Ketamine is a dissociative anesthetic used medically for induction and maintenance of anesthesia. It is also used as a recreational drug. It is one of the safest anesthetics, as, in contrast with opiates, ether, and propofol, it suppress ...
are the most sought after.
* hallucinogens
Hallucinogens are a large, diverse class of psychoactive drugs that can produce altered states of consciousness characterized by major alterations in thought, mood, and perception as well as other changes. Most hallucinogens can be categoriz ...
such as LSD
Lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD), also known colloquially as acid, is a potent psychedelic drug. Effects typically include intensified thoughts, emotions, and sensory perception. At sufficiently high dosages LSD manifests primarily mental, vi ...
, mescaline
Mescaline or mescalin (3,4,5-trimethoxyphenethylamine) is a naturally occurring psychedelic protoalkaloid of the substituted phenethylamine class, known for its hallucinogenic effects comparable to those of LSD and psilocybin.
Biological ...
, peyote
The peyote (; ''Lophophora williamsii'' ) is a small, spineless cactus which contains Psychoactive cactus, psychoactive alkaloids, particularly mescaline. ''Peyote'' is a Spanish word derived from the Nahuatl (), meaning "caterpillar Pupa#Cocoo ...
, and psilocybin
Psilocybin ( , ) is a naturally occurring psychedelic prodrug compound produced by more than 200 species of fungi. The most potent are members of the genus ''Psilocybe'', such as '' P. azurescens'', '' P. semilanceata'', and '' P.&nbs ...
* Empathogen-entactogen drugs like MDMA
3,4-Methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA), commonly seen in tablet form (ecstasy) and crystal form (molly or mandy), is a potent empathogen–entactogen with stimulant properties primarily used for recreational purposes. The desire ...
("ecstasy")
* Among the narcotics
The term narcotic (, from ancient Greek ναρκῶ ''narkō'', "to make numb") originally referred medically to any psychoactive compound with numbing or paralyzing properties. In the United States, it has since become associated with opiate ...
, it is opiate
An opiate, in classical pharmacology, is a substance derived from opium. In more modern usage, the term '' opioid'' is used to designate all substances, both natural and synthetic, that bind to opioid receptors in the brain (including antagoni ...
s such as morphine
Morphine is a strong opiate that is found naturally in opium, a dark brown resin in poppies ('' Papaver somniferum''). It is mainly used as a pain medication, and is also commonly used recreationally, or to make other illicit opioids. T ...
and codeine
Codeine is an opiate and prodrug of morphine mainly used to treat pain, coughing, and diarrhea. It is also commonly used as a recreational drug. It is found naturally in the sap of the opium poppy, ''Papaver somniferum''. It is typically ...
, and opioid
Opioids are substances that act on opioid receptors to produce morphine-like effects. Medically they are primarily used for pain relief, including anesthesia. Other medical uses include suppression of diarrhea, replacement therapy for opioid use ...
s such as diacetylmorphine
Heroin, also known as diacetylmorphine and diamorphine among other names, is a potent opioid mainly used as a recreational drug for its euphoric effects. Medical grade diamorphine is used as a pure hydrochloride salt. Various white and brow ...
(Heroin), hydrocodone
Hydrocodone, also known as dihydrocodeinone, is an opioid used to treat pain and as a cough suppressant. It is taken by mouth. Typically it is dispensed as the combination acetaminophen/hydrocodone or ibuprofen/hydrocodone for pain severe eno ...
(Vicodin; Hycodan), oxycodone
Oxycodone, sold under various brand names such as Roxicodone and OxyContin (which is the extended release form), is a strong, semi-synthetic opioid used medically for treatment of moderate to severe pain. It is highly addictive and a commonly ...
(Percocet; Oxycontin), hydromorphone
Hydromorphone, also known as dihydromorphinone, and sold under the brand name Dilaudid among others, is an opioid used to treat moderate to severe pain. Typically, long-term use is only recommended for pain due to cancer. It may be used by mou ...
(Dilaudid), and oxymorphone (Opana).
* Sedative
A sedative or tranquilliser is a substance that induces sedation by reducing irritability or excitement. They are CNS depressants and interact with brain activity causing its deceleration. Various kinds of sedatives can be distinguished, but ...
s such as GHB and methaqualone
Methaqualone is a hypnotic sedative. It was sold under the brand names Quaalude ( ) and Sopor among others, which contained 300 mg of methaqualone, and sold as a combination drug under the brand name Mandrax, which contained 250 mg me ...
(Quaalude)
* Stimulant
Stimulants (also often referred to as psychostimulants or colloquially as uppers) is an overarching term that covers many drugs including those that increase activity of the central nervous system and the body, drugs that are pleasurable and inv ...
s such as cocaine
Cocaine (from , from , ultimately from Quechua: ''kúka'') is a central nervous system (CNS) stimulant mainly used recreationally for its euphoric effects. It is primarily obtained from the leaves of two Coca species native to South Am ...
, amphetamine
Amphetamine (contracted from alpha- methylphenethylamine) is a strong central nervous system (CNS) stimulant that is used in the treatment of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), narcolepsy, and obesity. It is also commonly used ...
(Adderall), dextroamphetamine
Dextroamphetamine is a central nervous system (CNS) stimulant and an amphetamine enantiomer that is prescribed for the treatment of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and narcolepsy. It is also used as an athletic performance an ...
(Dexedrine), methamphetamine
Methamphetamine (contracted from ) is a potent central nervous system (CNS) stimulant that is mainly used as a recreational drug and less commonly as a second-line treatment for attention deficit hyperactivity disorder and obesity. Methamp ...
(Desoxyn), methcathinone
Methcathinone (α-methylamino- propiophenone or ephedrone) (sometimes called "cat" or "jeff" or "catnip" or "M-Kat" or "kat" or "intash" ) is a monoamine alkaloid and psychoactive stimulant, a substituted cathinone. It is used as a recreationa ...
, and methylphenidate
Methylphenidate, sold under the brand names Ritalin and Concerta among others, is the most widely prescribed central nervous system (CNS) stimulant medication used to treat attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and, to a lesser extent ...
(Ritalin)
The regulation of the above drugs varies in many countries. Alcohol possession and consumption by adults is today widely banned only in Islamic countries and certain states of India. Although alcohol prohibition was eventually repealed in the countries that enacted it, there are, for example, still parts of the United States that do not allow alcohol sales, though alcohol possession may be legal (see dry counties). New Zealand has banned the importation of chewing tobacco
Chewing tobacco is a type of smokeless tobacco product that is placed between the cheek and lower gum to draw out its flavor. Some users chew it, others do not. It consists of coarsely chopped aged tobacco that is flavored and often sweetened; ...
as part of the Smoke-free Environments Act 1990
The Smokefree Environments and Regulated Products Act 1990 (originally the Smoke-free Environments Act 1990) is an Act of Parliament in New Zealand. The Act placed smoking restrictions on indoor spaces, banned smoking on public transport and es ...
. In some parts of the world, provisions are made for the use of traditional sacrament
A sacrament is a Christian rite that is recognized as being particularly important and significant. There are various views on the existence and meaning of such rites. Many Christians consider the sacraments to be a visible symbol of the rea ...
s like ayahuasca
AyahuascaPronounced as in the UK and in the US. Also occasionally known in English as ''ayaguasca'' ( Spanish-derived), ''aioasca'' (Brazilian Portuguese-derived), or as ''yagé'', pronounced or . Etymologically, all forms but ''yagé'' desce ...
, iboga
''Tabernanthe iboga'' (iboga) is an evergreen rainforest shrub native to Central Africa. A member of the Apocynaceae family indigenous to Gabon, the Democratic Republic of Congo, and the Republic of Congo, it is cultivated across Central Africa ...
, and peyote
The peyote (; ''Lophophora williamsii'' ) is a small, spineless cactus which contains Psychoactive cactus, psychoactive alkaloids, particularly mescaline. ''Peyote'' is a Spanish word derived from the Nahuatl (), meaning "caterpillar Pupa#Cocoo ...
. In Gabon
Gabon (; ; snq, Ngabu), officially the Gabonese Republic (french: République gabonaise), is a country on the west coast of Central Africa. Located on the equator, it is bordered by Equatorial Guinea to the northwest, Cameroon to the nort ...
, iboga (tabernanthe iboga
''Tabernanthe iboga'' (iboga) is an evergreen rainforest shrub native to Central Africa. A member of the Apocynaceae family indigenous to Gabon, the Democratic Republic of Congo, and the Republic of Congo, it is cultivated across Central Africa ...
) has been declared a national treasure and is used in rites of the Bwiti
Bwiti is a spiritual discipline of the forest-dwelling Punu people and Mitsogo peoples of Gabon (where it is recognized as one of three official religions) and by the Fang people of Gabon and Cameroon. Modern Bwiti incorporates animism, ancest ...
religion. The active ingredient, ibogaine
Ibogaine is a naturally occurring psychoactive substance found in plants in the family Apocynaceae such as '' Tabernanthe iboga'', '' Voacanga africana'', and '' Tabernaemontana undulata''. It is a psychedelic with dissociative properties.
Pre ...
, is proposed as a treatment of opioid withdrawal and various substance use disorders.
In countries where alcohol and tobacco are legal, certain measures are frequently undertaken to discourage use of these drugs. For example, packages of alcohol and tobacco sometimes communicate warnings directed towards the consumer, communicating the potential risks of partaking in the use of the substance. These drugs also frequently have special ''sin tax
A sin tax is an excise tax specifically levied on certain goods deemed harmful to society and individuals, such as alcohol, tobacco, drugs, candies, soft drinks, fast foods, coffee, sugar, gambling, and pornography. In contrast to Pigovian ta ...
es'' associated with the purchase thereof, in order to recoup the losses associated with public funding for the health problems the use causes in long-term users. Restrictions on advertising also exist in many countries, and often a state holds a monopoly
A monopoly (from Greek language, Greek el, μόνος, mónos, single, alone, label=none and el, πωλεῖν, pōleîn, to sell, label=none), as described by Irving Fisher, is a market with the "absence of competition", creating a situati ...
on manufacture, distribution, marketing, and/or the sale of these drugs.
List of principal drug prohibition laws by jurisdiction (non-exhaustive)
* Australia:Standard for the Uniform Scheduling of Drugs and Poisons
The Standard for the Uniform Scheduling of Medicines and Poisons (SUSMP) is an Australian legislative instrument produced by the Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA)., subsection 4A. Before 2010, it was known as the ''Standard for the Unifor ...
*Bangladesh
Bangladesh (}, ), officially the People's Republic of Bangladesh, is a country in South Asia. It is the eighth-most populous country in the world, with a population exceeding 165 million people in an area of . Bangladesh is among the mo ...
: Narcotics Substances Control Act, 2018
* Belize
Belize (; bzj, Bileez) is a Caribbean and Central American country on the northeastern coast of Central America. It is bordered by Mexico to the north, the Caribbean Sea to the east, and Guatemala to the west and south. It also shares a wa ...
: Misuse of Drugs Act (Belize) The Misuse of Drugs Act is a national drug control law of Belize that divides drugs into three classes. There does not seem to be any mechanism for adding, removing, or transferring drugs between classes without amending the statute. Like the Misus ...
* Canada: Controlled Drugs and Substances Act
The ''Controlled Drugs and Substances Act'' (french: Loi réglementant certaines drogues et autres substances) (the ''Act'') is Canada's federal drug control statute. Passed in 1996 under Prime Minister Jean Chrétien's government, it repeal ...
''Controlled Drugs and Substances Act'', Department of Justice website, accessed 9 February 2009*
Estonia
Estonia, formally the Republic of Estonia, is a country by the Baltic Sea in Northern Europe. It is bordered to the north by the Gulf of Finland across from Finland, to the west by the sea across from Sweden, to the south by Latvia, an ...
: Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances Act (Estonia)
Estonia's Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances Act, passed on 11 June 1997, is a law designed to fulfill that country's treaty obligations under the Single Convention on Narcotic Drugs, the Convention on Psychotropic Substances, and the Un ...
* Germany: Betäubungsmittelgesetz
The Betäubungsmittelgesetz (BtMG), generally meaning Narcotics Law, is the controlled substances law of Germany. In common with the Misuse of Drugs Act of 1971 of the United Kingdom and Controlled Substances Acts of the US and Canada, it is a ...
* India: Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances Act (India)
* Netherlands: Opium Law
The Opium Law (or ''Opiumwet'' in Dutch) is the section of the Dutch law which covers nearly all psychotropic drugs.
Origin and history
In 1912, the First International Opium Conference took place in The Hague, where agreements were made abou ...
* New Zealand: Misuse of Drugs Act 1975
The Misuse of Drugs Act 1975 is a New Zealand drug control law that classifies drugs into three classes, or schedules, purportedly based on their projected risk of serious harm. However, in reality, classification of drugs outside of passing law ...
''Misuse of Drugs Act 1975'', New Zealand website, accessed 9 February 2009/ref> * Pakistan: Control of Narcotic Substances Act 1997 * Philippines: Comprehensive Dangerous Drugs Act of 2002 * Poland: Drug Abuse Prevention Act 2005 * Portugal: Decree-Law 15/93 * Ireland:
Misuse of Drugs Act (Ireland)
The Misuse of Drugs Act 1977, the Misuse of Drugs Act 1984, Misuse of Drugs Act 2015 and the Criminal Justice (Psychoactive Substances) Act 2010 are the acts of the Oireachtas regulating drugs in Ireland. The acts define the penalties for unlawfu ...
''Misuse of Drugs Act 1977'', Office of the Houses of the Oireachtas website, accessed 9 February 2009* South Africa: Drugs and Drug Trafficking Act 1992 *
Singapore
Singapore (), officially the Republic of Singapore, is a sovereign island country and city-state in maritime Southeast Asia. It lies about one degree of latitude () north of the equator, off the southern tip of the Malay Peninsula, bor ...
: Misuse of Drugs Act (Singapore)
The Misuse of Drugs Act 1973 is a drug control law in Singapore classifying substances into three categories, Classes A, B, and C. Section 44 provides that "The Minister may, by an order published in the Gazette" add, remove, or transfer drugs ...
* Sweden: Lag om kontroll av narkotika (SFS 1992:860)
* Thailand: Psychotropic Substances Act (Thailand) {{unref, date=July 2017
Thailand's Psychotropic Substances Act is a law designed to regulate certain mind-altering drugs. According to the Office of the Narcotics Control Board, "The Act directly resulted from the Convention on Psychotropic Substanc ...
and Narcotics Act
* United Kingdom: Misuse of Drugs Act 1971
The Misuse of Drugs Act 1971 is an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. It represents action in line with treaty commitments under the Single Convention on Narcotic Drugs, the Convention on Psychotropic Substances, and the United Nati ...
and Drugs Act 2005
The Drugs Act 2005 (c 17) is an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom.
Section 24 - Short title, commencement and extent
The following orders have been made under section 24(3):The Drugs Act 2005 (Commencement No. 1) Order 2005(S.I. 2005/ ...
''Drugs Act 2005 (c. 17)'', OPSI website, accessed 2 February 2009/ref> * United States:
Controlled Substances Act
The Controlled Substances Act (CSA) is the statute establishing federal U.S. drug policy under which the manufacture, importation, possession, use, and distribution of certain substances is regulated. It was passed by the 91st United States ...
''Controlled Substances Act'' (short title), U.S. Food and Drug Administration website, accessed 6 February 2009/ref>
Legal dilemmas
The sentencing statutes in theUnited States Code
In the law of the United States, the Code of Laws of the United States of America (variously abbreviated to Code of Laws of the United States, United States Code, U.S. Code, U.S.C., or USC) is the official compilation and codification of the ...
that cover controlled substances are complicated. For example, a first-time offender convicted in a single proceeding for selling marijuana three times, and found to have carried a gun on him all three times (even if it were not used) is subject to a minimum sentence of 55 years in federal prison.
Drug sentencing guidelines under state law in America are generally much less harsh than the federal sentencing guidelines, although great irregularities exist. The vast majority of drug felonies and almost all drug misdemeanors in the United States are prosecuted at the state level. The federal government tends to prosecute only drug trafficking cases involving large amounts of drugs, or cases which have been referred to federal prosecutors by local district attorneys seeking the harsher sentences provided under the federal sentencing guidelines. In rare instances, some defendants are prosecuted both federally and by the state for the same drug trafficking conduct.
Drug prohibition has created several legal dilemmas. Many countries allow the use of undercover
To go "undercover" (that is, to go on an undercover operation) is to avoid detection by the object of one's observation, and especially to disguise one's own identity (or use an assumed identity) for the purposes of gaining the trust of an ind ...
law enforcement
Law enforcement is the activity of some members of government who act in an organized manner to enforce the law by discovering, deterring, rehabilitating, or punishing people who violate the rules and norms governing that society. The term ...
officers solely or primarily for the enforcement of laws against use of certain drugs. On occasion these officers are allegedly allowed to commit crimes if it is necessary to maintain the secrecy of the investigation, or in order to collect adequate evidence
Evidence for a proposition is what supports this proposition. It is usually understood as an indication that the supported proposition is true. What role evidence plays and how it is conceived varies from field to field.
In epistemology, evidenc ...
for a conviction
In law, a conviction is the verdict reached by a court of law finding a defendant guilty of a crime. The opposite of a conviction is an acquittal (that is, "not guilty"). In Scotland, there can also be a verdict of " not proven", which is cons ...
.
The War on Drugs has stimulated the creation of international law enforcement agencies (such as Interpol
The International Criminal Police Organization (ICPO; french: link=no, Organisation internationale de police criminelle), commonly known as Interpol ( , ), is an international organization that facilitates worldwide police cooperation and cr ...
), mostly in Western countries. This has occurred because a large volume of illicit drugs come from Third-World
The term "Third World" arose during the Cold War to define countries that remained non-aligned with either NATO or the Warsaw Pact. The United States, Canada, Japan, South Korea, Western European nations and their allies represented the ...
countries.
Social control
In ''Hallucinations: Behavior, Experience, and Theory (1975)'', senior US government researchers Louis Jolyon West andRonald K. Siegel
Ronald Keith Siegel (January 2, 1943 – March 24, 2019) was an American psychopharmacologist who was an associate research professor in the Department of Psychiatry and Biobehavioral Sciences at the University of California, Los Angeles. Siegel ...
explain how drug prohibition can be used for selective social control:
Linguist Noam Chomsky
Avram Noam Chomsky (born December 7, 1928) is an American public intellectual: a linguist, philosopher, cognitive scientist, historian, social critic, and political activist. Sometimes called "the father of modern linguistics", Chomsky i ...
argues that drug laws are currently, and have historically been, used by the state to oppress sections of society it opposes:
Legal highs and prohibition
In 2013 theEuropean Monitoring Centre for Drugs and Drug Addiction
The European Monitoring Centre for Drugs and Drug Addiction (EMCDDA) is an agency of the European Union located in Lisbon, Portugal, and established in 1993. In June 2022, the Council of the European Union approved a reform of the organization ...
reported that there are 280 new legal drugs, known as "legal highs", available in Europe. One of the best known, mephedrone
Mephedrone, also known as , , and , is a synthetic stimulant drug of the amphetamine and cathinone classes. Slang names include drone, , White Magic, meow meow, bubble, ''txomin'' and yurrpt. It is chemically similar to the cathinone compounds ...
, was banned in the United Kingdom in 2010. On November 24, 2010, the U.S. Drug Enforcement Administration
The Drug Enforcement Administration (DEA; ) is a United States federal law enforcement agency under the U.S. Department of Justice tasked with combating drug trafficking and distribution within the U.S. It is the lead agency for domestic en ...
announced it would use emergency powers to ban many synthetic cannabinoids within a month. An estimated 73 new psychoactive synthetic drugs appeared on the UK market in 2012. The response of the Home Office has been to create a temporary class drug order which bans the manufacture, import, and supply (but not the possession) of named substances.
Corruption
In certain countries, there is concern that campaigns against drugs and organized crime are a cover for corrupt officials tied to drug trafficking themselves. In the United States,Federal Bureau of Narcotics
The Federal Bureau of Narcotics (FBN) was an agency of the United States Department of the Treasury, established in the Department of the Treasury by an act of June 14, 1930, consolidating the functions of the Federal Narcotics Control Board a ...
chief Harry Anslinger's opponents accused him of taking bribes from the Mafia
"Mafia" is an informal term that is used to describe criminal organizations that bear a strong similarity to the original “Mafia”, the Sicilian Mafia and Italian Mafia. The central activity of such an organization would be the arbitration of d ...
to enact prohibition and create a black market
A black market, underground economy, or shadow economy is a clandestine market or series of transactions that has some aspect of illegality or is characterized by noncompliance with an institutional set of rules. If the rule defines the ...
for alcohol. More recently in the Philippines
The Philippines (; fil, Pilipinas, links=no), officially the Republic of the Philippines ( fil, Republika ng Pilipinas, links=no),
* bik, Republika kan Filipinas
* ceb, Republika sa Pilipinas
* cbk, República de Filipinas
* hil, Republ ...
, one death squad hitman told author Niko Vorobyov that he was being paid by military officers to eliminate those drug dealers who failed to pay a ‘tax’. Under President
President most commonly refers to:
*President (corporate title)
* President (education), a leader of a college or university
* President (government title)
President may also refer to:
Automobiles
* Nissan President, a 1966–2010 Japanese ...
Rodrigo Duterte
Rodrigo Roa Duterte (, ; born March 28, 1945), also known as Digong, Rody, and by the initials DU30 and PRRD, is a Filipino lawyer and politician who served as the 16th president of the Philippines from 2016 to 2022. He is the chairperson ...
, the Philippines has waged a bloody war against drugs that may have resulted in up to 29,000 extrajudicial killings.
When it comes to social control with cannabis, there are different aspects to consider. Not only do we assess legislative leaders and the way they vote on cannabis, but we also must consider the federal regulations and taxation that contribute to social controls. For instance, according to a report on the U.S. customs and border protections, the American industry, although banned the main usage of marijuana, was still using products similar such as hemp seeds, oils etc. leading to the previously discussed marijuana tax act.
The Tax act provisions required importers to register and pay an annual tax of $24 and receive an official stamp. Stamps for Products were then affixed to each original order form and recorded by the state revenue collector. Then, a customs collector was to maintain the custody of imported marijuana at entry ports until required documents were received, reviewed and approved.Shipments were subject to searches, seizures and forfeitures if any provisions of the law were not met. Violations would result in fines of no more than $2000 or potential imprisonment for up to 5 years. Oftentimes, this created opportunity for corruption, stolen imports that would later lead to smuggling, oftentimes by state officials and tight knit elitists.
Penalties
United States

War on Drugs
The war on drugs is a global campaign, led by the United States federal government, of drug prohibition, military aid, and military intervention, with the aim of reducing the illegal drug trade in the United States.Cockburn and St. Clair, 1 ...
is thought to be contributing to a prison overcrowding
Prison overcrowding is a social phenomenon occurring when the demand for space in prisons in a jurisdiction exceeds the capacity for prisoners. The issues associated with prison overcrowding are not new, and have been brewing for many years. Du ...
problem. In 1996, 59.6% of prisoners were drug-related criminals. The U.S. population grew by about +25% from 1980 to 2000. In that same 20 year time period, the U.S. prison population tripled, making the U.S. the world leader in both percentage and absolute number of citizens incarcerated. The United States has 5% of the world's population, but 25% of the prisoners.
About 90% of United States prisoners are incarcerated in state jails. In 2016, about 200,000, under 16%, of the 1.3 million people in these state jails, were serving time for drug offenses. 700,000 were incarcerated for violent offenses.
The data from Federal Bureau of Prisons
The Federal Bureau of Prisons (BOP) is a United States federal law enforcement agency under the Department of Justice that is responsible for the care, custody, and control of incarcerated individuals who have committed federal crimes; that i ...
online statistics page states that 45.9% of prisoners were incarcerated for drug offenses, as of December 2021.
European Union
In 2004, theCouncil of the European Union
The Council of the European Union, often referred to in the treaties and other official documents simply as the Council, and informally known as the Council of Ministers, is the third of the seven Institutions of the European Union (EU) as ...
adopted a framework decision
A framework decision was a kind of legislative act of the European Union used exclusively within the EU's competences in police and judicial co-operation in criminal justice matters. Framework decisions were similar to directives in that they r ...
harmonizing the minimum penal provisions for illicit drug-related activities. In particular, article 2(9) stipulates that activities may be exempt from the minimum provisions "when it is committed by its perpetrators exclusively for their own personal consumption as defined by national law." This was made, in particular, to accommodate more liberal national systems such as the Dutch coffee shops (see below) or the Spanish Cannabis Social Clubs.
The Netherlands
In the Netherlands, cannabis and other "soft" drugs are partly decriminalised in small quantities. The Dutch government treats the problem as more of a public health issue than a criminal issue. Contrary to popular belief, cannabis is still illegal. Coffee shops that sell cannabis to people 18 or above are tolerated in some cities, and pay taxes like any other business for their cannabis and hashish sales, although distribution is a grey area that the authorities would rather not go into as it is not decriminalised. Many "coffee shops" are found inAmsterdam
Amsterdam ( , , , lit. ''The Dam on the River Amstel'') is the capital and most populous city of the Netherlands, with The Hague being the seat of government. It has a population of 907,976 within the city proper, 1,558,755 in the urban ar ...
and cater mainly to the large tourist trade; the local consumption rate is far lower than in the US.
 The administrative bodies responsible for enforcing the drug policies include the Ministry of Health, Welfare and Sport, the Ministry of Justice, the Ministry of the Interior and Kingdom Relations, and the Ministry of Finance. Local authorities also shape local policy, within the national framework.
When compared to other countries, Dutch drug consumption falls in the European average at six per cent regular use (twenty-one per cent at some point in life) and considerably lower than the Anglo-Saxon countries headed by the United States with an eight per cent recurring use (thirty-four at some point in life).
The administrative bodies responsible for enforcing the drug policies include the Ministry of Health, Welfare and Sport, the Ministry of Justice, the Ministry of the Interior and Kingdom Relations, and the Ministry of Finance. Local authorities also shape local policy, within the national framework.
When compared to other countries, Dutch drug consumption falls in the European average at six per cent regular use (twenty-one per cent at some point in life) and considerably lower than the Anglo-Saxon countries headed by the United States with an eight per cent recurring use (thirty-four at some point in life).
Australia
A Nielsen poll in 2012 found that only 27% of voters favoured decriminalisation. Australia has steep penalties for growing and using drugs even for personal use. with Western Australia having the toughest laws. There is an associated anti-drug culture amongst a significant number of Australians. Law enforcement targets drugs, particularly in the party scene. In 2012, crime statistics in Victoria revealed that police were increasingly arresting users rather than dealers, and the Liberal government banned the sale ofbong
A bong (also known as a water pipe) is a filtration device generally used for smoking cannabis, tobacco, or other herbal substances. In the bong shown in the photo, the gas flows from the lower port on the left to the upper port on the right.
...
s that year.
Indonesia
Indonesia
Indonesia, officially the Republic of Indonesia, is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania between the Indian and Pacific oceans. It consists of over 17,000 islands, including Sumatra, Java, Sulawesi, and parts of Borneo and New Gui ...
carries a maximum penalty of death for drug dealing, and a maximum of 15 years prison for drug use. In 2004, Australian citizen Schapelle Corby was convicted of smuggling 4.4 kilograms of cannabis into Bali
Bali () is a province of Indonesia and the westernmost of the Lesser Sunda Islands. East of Java and west of Lombok, the province includes the island of Bali and a few smaller neighbouring islands, notably Nusa Penida, Nusa Lembongan, and ...
, a crime that carried a maximum penalty of death. Her trial reached the verdict of guilty with a punishment of 20 years imprisonment. Corby claimed to be an unwitting drug mule. Australian citizens known as the "Bali Nine
The Bali Nine were nine Australians convicted for attempting to smuggle of heroin out of Indonesia in April 2005. The heroin was valued at around 4 million and was bound for Australia. Ringleaders Andrew Chan and Myuran Sukumaran were ...
" were caught smuggling heroin
Heroin, also known as diacetylmorphine and diamorphine among other names, is a potent opioid mainly used as a recreational drug for its euphoric effects. Medical grade diamorphine is used as a pure hydrochloride salt. Various white and bro ...
. Two of the nine, Andrew Chan and Myuran Sukumaran, were executed April 29, 2015 along with six other foreign nationals. In August 2005, Australian model Michelle Leslie
Michelle Leslie (born 1981), who previously worked under the name Michelle Lee, is an Australian interior designer and former model. Leslie gained prominence as a catwalk model in 2000, working for stores including David Jones. That same year ...
was arrested with two ecstasy pills. She pleaded guilty to possession and in November 2005 was sentenced to 3 months imprisonment, which she was deemed to have already served, and was released from prison immediately upon her admission of guilt on the charge of possession.
At the 1961 Single Convention on Narcotic Drugs, Indonesia, along with India, Turkey, Pakistan and some South American countries opposed the criminalisation of drugs.
Republic of China (Taiwan)
Taiwan
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia, at the junction of the East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocean, with the People's Republic of China (PRC) to the northwest, Japan to the no ...
carries a maximum penalty of death for drug trafficking, while smoking tobacco
Tobacco smoking is the practice of burning tobacco and ingesting the resulting smoke. The smoke may be inhaled, as is done with cigarettes, or simply released from the mouth, as is generally done with pipes and cigars. The practice is believed ...
and wine
Wine is an alcoholic drink typically made from Fermentation in winemaking, fermented grapes. Yeast in winemaking, Yeast consumes the sugar in the grapes and converts it to ethanol and carbon dioxide, releasing heat in the process. Different ...
are classified as legal entertainment drug. The Department of Health
A health department or health ministry is a part of government which focuses on issues related to the general health of the citizenry. Subnational entities, such as states, counties and cities, often also operate a health department of their ow ...
is in charge of drug prohibition.
Methods of law enforcement
Because the possession of drugs is called a "victimless crime
A victimless crime is an illegal act that typically either directly involves only the perpetrator or occurs between consenting adults. Because it is consensual in nature, whether there involves a victim is a matter of debate. Definitions of vi ...
" by some analysts, as it can be committed in privacy
Privacy (, ) is the ability of an individual or group to seclude themselves or information about themselves, and thereby express themselves selectively.
The domain of privacy partially overlaps with security, which can include the concepts of ...
, the enforcement of prohibitionist laws requires methods of law enforcement to inspect private property. In societies with strong property law
Property law is the area of law that governs the various forms of ownership in real property (land) and personal property. Property refers to legally protected claims to resources, such as land and personal property, including intellectual pro ...
s or individual right
Group rights, also known as collective rights, are rights held by a group '' qua'' a group rather than individually by its members; in contrast, individual rights are rights held by individual people; even if they are group-differentiated, whic ...
s, this may present a risk for conflicts or violations of rights
Rights are legal, social, or ethical principles of freedom or entitlement; that is, rights are the fundamental normative rules about what is allowed of people or owed to people according to some legal system, social convention, or ethical theory ...
. Disrupting the market relies on eradication, interdiction and domestic law enforcement efforts. Through cooperation with governments such as those of Colombia, Mexico and Afghanistan, coca (the plant source for cocaine) and poppy (the plant source for opium and heroin) are eradicated by the United States and other allies such as the United Kingdom, so that the crops cannot be processed into narcotics. Eradication can be accomplished by aerial spraying or manual eradication. However, the eradication is only temporary as the harvest fields can usually be replanted after a certain amount of time.
 The government of Colombian President Álvaro Uribe has resisted criticism of aerial spraying of coca and poppy and has seen major reductions in both crops according to the United Nations Office of Crime and Drugs (See also
The government of Colombian President Álvaro Uribe has resisted criticism of aerial spraying of coca and poppy and has seen major reductions in both crops according to the United Nations Office of Crime and Drugs (See also Plan Colombia
Plan Colombia was a United States foreign aid, military aid, and diplomatic initiative aimed at combating Colombian drug cartels and left-wing insurgent groups in Colombia. The plan was originally conceived in 1999 by the administrations of Col ...
). In 2003, over of mature coca were sprayed and eradicated in Colombia, where at the start of the year, approximately had been planted. This strategic accomplishment prevented the production over 500 tonnes of cocaine, sufficient to supply all the cocaine users in both US and Europe for one year. Further, it eliminated upward of $100 million of illicit income in Colombia. No effect on prices or availability in the marketplace has been noted, and the actual number of acres of coca planted seems to have actually increased, largely shifting to more remote areas or into neighboring countries. Aerial spraying also has the unintended consequence of destroying legitimate crop fields in the process.
Interdiction is carried out primarily by aerial and naval armed forces patrolling known trafficking zones. From South America to the United States most drugs traverse either the Caribbean Sea or the Eastern Pacific, usually in " go-fast" boats that carry drug cargos and engines and little else. Drugs have also been smuggled in makeshift submarines. In 2015, a submarine with 12,000 pounds of cocaine was seized by the US Coast Guard off of the coast of Central America. This was the largest US drug seizure to date.
 Investigation on drug trafficking often begins with the recording of unusually frequent deaths by
Investigation on drug trafficking often begins with the recording of unusually frequent deaths by overdose
A drug overdose (overdose or OD) is the ingestion or application of a drug or other substance in quantities much greater than are recommended.
, monitoring financial flows of suspected traffickers, or by finding concrete elements while inspecting for other purposes. For example, a person pulled over for traffic violations may have illicit drugs in his or her vehicle, thus leading to an arrest and/or investigation of the source of the materials. The United States federal government has placed a premium on disrupting the large drug trafficking organizations that move narcotics into and around the United States, while state and local law enforcement focus on disrupting street-level drug dealing gangs.
Drug control strategy
Present drug control efforts utilize several techniques in the attempt to achieve their goal of eliminating illegal drug use: * Disrupting the market for drugs * Prevention efforts that rely on community activism, public information campaigns to educate the public on the potential dangers of drug use * Law-enforcement efforts against elements of the supply chain, through surveillance and undercover work * Providing effective and targeted substance abuse treatment to dependent usersAlternatives
On February 11, 2009, a document called ''Drugs and democracy in Latin America: Towards a paradigm shift '' was signed by several Latin American political figures, intellectuals, writers and journalists as commissioners of theLatin American Initiative on Drugs and Democracy The Latin American Commission on Drugs and Democracy was a panel of Latin American leaders and intellectuals, co-chaired by former presidents Fernando Henrique Cardoso (Brazil), César Gaviria (Colombia) and Ernesto Zedillo (Mexico).
In March 20 ...
. The document questions the war on drugs and points out its failures. It also indicates that prohibition has come with an extensive social cost, especially to the countries that take part in the production of illicit drugs. Although controversial, the document does not endorse either the production or consumption of drugs but recommends for both a new and an alternative approach. The document argues that drug production and consumption has become a social taboo
A taboo or tabu is a social group's ban, prohibition, or avoidance of something (usually an utterance or behavior) based on the group's sense that it is excessively repulsive, sacred, or allowed only for certain persons.''Encyclopædia Britannica ...
that inhibits the public debate because of its relationship to crime and as consequence it confines consumers to a small circle where they become more vulnerable to the actions of organized crime. The authors also demand for a close review to the prohibitive strategies of the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country Continental United States, primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 U.S. state, states, a Washington, D.C., ...
and the study of the advantages and limits of the damage reduction strategy followed by the European Union. The proposal uses three paradigms as an alternative:
* The treatment of consumption as a problem of public health
Public health is "the science and art of preventing disease, prolonging life and promoting health through the organized efforts and informed choices of society, organizations, public and private, communities and individuals". Analyzing the det ...
.
* The reduction of consumption through the dissemination of information and prevention.
* A new focus towards organized crime.
The document favors the European policies towards drug consumption since according to the authors it is more humane and efficient. The signers of this document are: Fernando Henrique Cardoso
Fernando Henrique Cardoso (; born 18 June 1931), also known by his initials FHC (), is a Brazilian sociologist, professor and politician who served as the 34th president of Brazil from 1 January 1995 to 31 December 2002. He was the first Brazi ...
, Ernesto Zedillo
Ernesto Zedillo Ponce de León (; born 27 December 1951) is a Mexican economist and politician. He was 61st president of Mexico from 1 December 1994 to 30 November 2000, as the last of the uninterrupted 71-year line of Mexican presidents from t ...
, César Gaviria
César Augusto Gaviria Trujillo ( ; born 31 March 1947) is a Colombian economist and politician who served as the President of Colombia from 1990 to 1994, Secretary General of the Organization of American States from 1994 to 2004 and National Di ...
, Paulo Coelho
Paulo Coelho de Souza (, ; born 24 August 1947) is a Brazilian lyricist and novelist and a member of the Brazilian Academy of Letters since 2002. His novel ''The Alchemist'' became an international best-seller and he has published 28 more book ...
, Enrique Santos, Mario Vargas Llosa
Jorge Mario Pedro Vargas Llosa, 1st Marquess of Vargas Llosa (born 28 March 1936), more commonly known as Mario Vargas Llosa (, ), is a Peruvian novelist, journalist, essayist and former politician, who also holds Spanish citizenship. Vargas Ll ...
, Moisés Naím
Moisés Naím (born July 5, 1952) is a Venezuelan journalist and writer. He is a Distinguished Fellow at the Carnegie Endowment for International Peace. In 2013, the British magazine ''Prospect'' listed Naím as one of the world's leading thinke ...
, Tomas Eloy Martinez Tomas may refer to:
People
* Tomás (given name), a Spanish, Portuguese, and Gaelic given name
* Tomas (given name), a Swedish, Dutch, and Lithuanian given name
* Tomáš, a Czech and Slovak given name
* Tomas (surname), a French and Croatian surna ...
Two years later in mid-2011, the core of the Initiative and its commission were extended and endorsed in a report issued by the Global Commission on Drug Policy
The Global Commission on Drug Policy (GCDP) is a panel of world leaders and intellectuals, with a Secretariat based in Geneva, Switzerland.
In June 2011, the commission said: "The global war on drugs has failed, with devastating consequences for i ...
. Joining the three former presidents of Colombia, Brazil and Mexico and Nobel Prize for Literature winner Llosa on the Global Commission were former U.S. Secretary of State George P. Shultz and Federal Reserve
The Federal Reserve System (often shortened to the Federal Reserve, or simply the Fed) is the central banking system of the United States of America. It was created on December 23, 1913, with the enactment of the Federal Reserve Act, after a ...
chair Paul Volcker
Paul Adolph Volcker Jr. (September 5, 1927 – December 8, 2019) was an American economist who served as the 12th chairman of the Federal Reserve from 1979 to 1987. During his tenure as chairman, Volcker was widely credited with having ended th ...
; Carlos Fuentes
Carlos Fuentes Macías (; ; November 11, 1928 – May 15, 2012) was a Mexican novelist and essayist. Among his works are ''The Death of Artemio Cruz'' (1962), ''Aura'' (1962), '' Terra Nostra'' (1975), ''The Old Gringo'' (1985) and ''Christopher ...
, Mexican writer and public intellectual; John C. Whitehead
John Cunningham Whitehead (April 2, 1922 – February 7, 2015) was an American banker and civil servant, a board member of the World Trade Center Memorial Foundation (WTC Memorial Foundation), and, until his resignation in May 2006, chairman of ...
, formerly of Goldman Sachs
Goldman Sachs () is an American multinational investment bank and financial services company. Founded in 1869, Goldman Sachs is headquartered at 200 West Street in Lower Manhattan, with regional headquarters in London, Warsaw, Bangalore, Ho ...
; and Kofi Annan
Kofi Atta Annan (; 8 April 193818 August 2018) was a Ghanaian diplomat who served as the seventh secretary-general of the United Nations from 1997 to 2006. Annan and the UN were the co-recipients of the 2001 Nobel Peace Prize. He was the founde ...
, former Secretary-General of the United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is an intergovernmental organization whose stated purposes are to maintain international peace and security, develop friendly relations among nations, achieve international cooperation, and be a centre for harmoni ...
.Tharoor, Ishaan"Report: The Global War on Drugs Has Failed. Is It Time to Legalize?"
''
Time
Time is the continued sequence of existence and event (philosophy), events that occurs in an apparently irreversible process, irreversible succession from the past, through the present, into the future. It is a component quantity of various me ...
'' (June 3, 2011). Retrieved 2011-06-03.
See also
*Alcohol law
Alcohol laws are laws in relation to the manufacture, use, being under the influence of and sale of alcohol (also known formally as ethanol) or alcoholic beverages that contains ethanol. Common alcoholic beverages include beer, wine, (hard) c ...
* Arguments for and against drug prohibition
This article is intended to give an overview of several arguments for and against drug prohibition.
Efficiency
Drug laws are effective
Supporters of prohibition claim that drug laws have a successful track record suppressing illicit drug use si ...
* Drug liberalization
* Demand reduction
Demand reduction refers to efforts aimed at reducing the public desire for illegal and illicit drugs. The drug policy is in contrast to the reduction of drug supply, but the two policies are often implemented together. Some discussions of demand ...
* Drug policy of the Soviet Union
The drug policy of the Soviet Union changed little throughout the existence of the state, other than slowly becoming more repressive, although some differences in penalties existed in the different Union Republics.
However, the prevalence of drug a ...
* Harm reduction
Harm reduction, or harm minimization, refers to a range of public health policies designed to lessen the negative social and/or physical consequences associated with various human behaviors, both legal and illegal. Harm reduction is used to d ...
* List of anti-cannabis organizations
* Medellin Cartel
* Mexican drug war
* Puerto Rican drug war
The Illegal drug trade in Puerto Rico is a problem from a criminal, social, and medical perspective. Located in the Caribbean, Puerto Rico has become a major transshipment point for drugs into the United States. Violent and property crimes hav ...
* Prohibitionism
Prohibitionism is a legal philosophy and political theory often used in lobbying which holds that citizens will abstain from actions if the actions are typed as unlawful (i.e. prohibited) and the prohibitions are enforced by law enforcement.C Canty ...
* Tobacco control
Tobacco control is a field of international public health science, policy and practice dedicated to addressing tobacco use and thereby reducing the morbidity and mortality it causes. Since most cigarettes and cigars and hookahs contain/use ...
* War on Drugs
The war on drugs is a global campaign, led by the United States federal government, of drug prohibition, military aid, and military intervention, with the aim of reducing the illegal drug trade in the United States.Cockburn and St. Clair, 1 ...
US specific:
* Allegations of CIA drug trafficking
* School district drug policies
School district drug policies are measures that administrators of a school district put into place to discourage drug use by students.
Background
Over the decades of the War on Drugs in the United States, primary and secondary school drug and alc ...
* Drug Free America Foundation
The Drug Free America Foundation (DFAF) is a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization founded in 1976 by former US Ambassador Mel Sembler, his wife Betty Sembler (), and Joseph Zappala as Straight, Inc., renamed The Straight Foundation, Inc. in 1985 and ...
* Drug Policy Alliance
The Drug Policy Alliance (DPA) is a New York City–based nonprofit organization that seeks to advance policies that “reduce the harms of both drug use and drug prohibition, and to promote the sovereignty of individuals over their minds and ...
* DrugWarRant
DrugWarRant is a website created by activist Peter Guither that specifically advocate the termination of War on Drugs in United States. It has a Bulletin Board System, a blog, and other functions, including a comprehensive guide to the Supreme ...
* Gary Webb
Gary Stephen Webb (August 31, 1955 – December 10, 2004) was an American investigative journalist.
He began his career working for newspapers in Kentucky and Ohio, winning numerous awards, and building a strong reputation for investigative ...
* Marijuana Policy Project
The Marijuana Policy Project (MPP) is the largest organization working solely on marijuana policy reform in the United States in terms of its budget, number of members, and staff.
Its stated aims are to: (1) increase public support for non-pu ...
* National Organization for the Reform of Marijuana Laws
The National Organization for the Reform of Marijuana Laws (NORML ) is a social welfare organization based in Washington, D.C., that advocates for the reform of marijuana laws in the United States regarding both medical and non-medical use. Ac ...
* Students for Sensible Drug Policy
Students for Sensible Drug Policy (SSDP) is an international nonprofit organization advocacy and education organization with focus on drug policy, war on drugs, marijuana legalization, psychedelics, juvenile justice and youth rights, drug dec ...
* Woman's Christian Temperance Union
The Woman's Christian Temperance Union (WCTU) is an international temperance organization, originating among women in the United States Prohibition movement. It was among the first organizations of women devoted to social reform with a program th ...
References
Further reading
* Outsiders: Studies in the Sociology of Deviance, New York: The Free Press, 1963, * Eva Bertram, ed., ''Drug War Politics: The Price of Denial'', University of California Press, 1996, . * James P. Gray, ''Why Our Drug Laws Have Failed and What We Can Do About It: A Judicial Indictment of the War on Drugs'' Temple University Press, 2001, . * Richard Lawrence Miller, ''Drug Warriors and Their Prey'', Praeger, 1996, . * Dan Baum, ''Smoke and Mirrors: The War on Drugs and the Politics of Failure'', Little Brown & Co., 1996, . * Alfred W. McCoy, ''The Politics of Heroin: CIA Complicity in the Global Drug Trade'', Lawrence Hill Books, 1991, . *Clarence Lusane
Clarence Lusane (born 1953) is an American author, activist, lecturer and freelance journalist. His most recent major work is his book '' The Black History of the White House''.
Background
Clarence Lusane received his Ph.D. in political science ...
and Dennis Desmond, ''Pipe Dream Blues: Racism and the War on Drugs'', South End Press, 1991, .
*
* United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime, ''Colombian Survey'', June 2005.
* Office of National Drug Control Policy, ''National Drug Control Strategy'', March 2004.
* David F. Musto, ''The American Disease, The Origins of Narcotics Controls'', New Haven: Yale University Press, 1973, p. 43
Why Is Drug Use Forbidden?
by François-Xavier Dudouet
by Peter Cohen * [http://www.co-psychiatry.com/pt/re/copsych/abstract.00001504-200305000-00002.htm;jsessionid=FWlXKXQcXtckn82dHCxvYnpwyL0BWM265CPn2d6Br07mpdC4hByC!641301743!-949856144!8091!-1 Policy from a harm reduction perspective] (journal article)
Global drug prohibition: its uses and crises
(journal article)
(journal article) * [http://taylorandfrancis.metapress.com/(4p2ehk55t0yeb1avgc1zk5ve)/app/home/contribution.asp?referrer=parent&backto=issue,1,14;journal,16,73;linkingpublicationresults,1:102207,1 Should cannabis be taxed and regulated?] (journal article)
Learning from history: a review of David Bewley-Taylor's The United States and International Drug Control, 1909–1997
(journal article)
Shifting the main purposes of drug control: from suppression to regulation of use
Setting goals for drug policy: harm or use reduction?
Prohibition, pragmatism and drug policy repatriation
Challenging the UN drug control conventions: problems and possibilities
The Economics of Drug Legalization
Britain on drugs
(journal article)
Laws and the Construction of Drug- and Gender-Related Violence in Central America
by Peter Peetz
External links
Making Contact: The Mission to End Prohibition.
Radio piece featuring LEAP founder and former narcotics officer Jack A. Cole, Jack Cole, and Drug Policy Alliance founder Ethan Nadelmann
EMCDDA – Decriminalisation in Europe? Recent developments in legal approaches to drug use
10 Downing Street's Strategy Unit Drugs Report
War on drugs
''Part I: Winners'', documentary (50 min) explaining 'War on Drugs' b
Tegenlicht
of VPRO Dutch television. After short introduction in Dutch (1 min), English spoken. Broadband internet needed.
War on drugs
''Part II: Losers'', documentary (50 min) showing downside of the 'War on Drugs' b
Tegenlicht
of VPRO Dutch television. After short introduction in Dutch (1 min), English spoken. Broadband internet needed.
After the War on Drugs: Options for Control (Report)
by Harry Browne
Prohibition news page
– Alcohol and Drugs History Society
Drugs and conservatives should go together
{{DEFAULTSORT:Prohibition, Drugs) Social conflict Counterculture Drug control law Drug policy History of drug control Prohibitionism