Drought Of 1862-64 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
A drought is defined as drier than normal conditions.Douville, H., K. Raghavan, J. Renwick, R.P. Allan, P.A. Arias, M. Barlow, R. Cerezo-Mota, A. Cherchi, T.Y. Gan, J. Gergis, D. Jiang, A. Khan, W. Pokam Mba, D. Rosenfeld, J. Tierney, and O. Zolina, 2021
Water Cycle Changes
In Climate Change 2021: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change [Masson-Delmotte, V., P. Zhai, A. Pirani, S.L. Connors, C. Péan, S. Berger, N. Caud, Y. Chen, L. Goldfarb, M.I. Gomis, M. Huang, K. Leitzell, E. Lonnoy, J.B.R. Matthews, T.K. Maycock, T. Waterfield, O. Yelekçi, R. Yu, and B. Zhou (eds.)]. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, United Kingdom and New York, NY, USA, pp. 1055–1210, doi:10.1017/9781009157896.010. This means that a drought is "a moisture deficit relative to the average water availability at a given location and season". A drought can last for days, months or years. Drought often exerts substantial impacts on the ecosystems and agriculture of affected regions, and causes harm to the local economy. Annual dry seasons in the tropics significantly increase the chances of a drought developing and subsequent wildfires. Periods of heat can significantly worsen drought conditions by hastening evaporation of water vapour. Drought is a recurring feature of the climate in most parts of the world, becoming more extreme and less predictable due to climate change, which
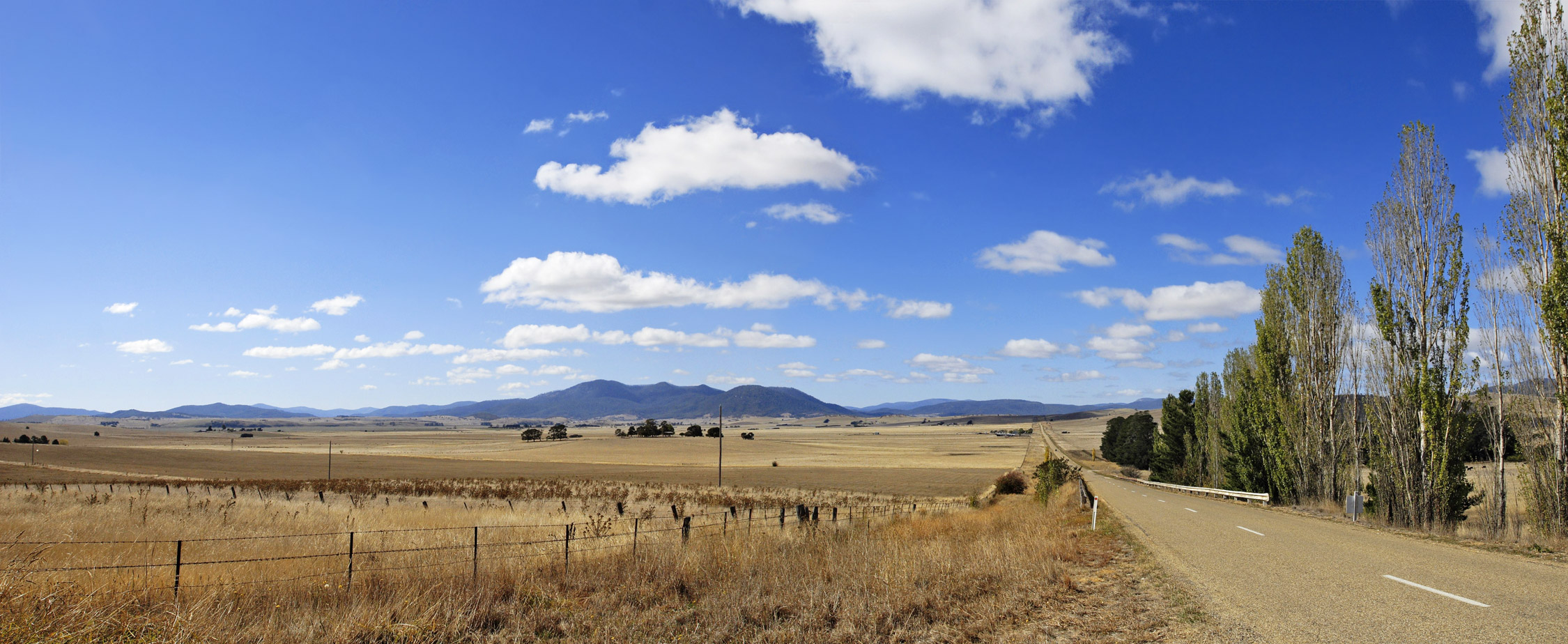 The IPCC Sixth Assessment Report defines a drought simply as "drier than normal conditions". This means that a drought is "a moisture deficit relative to the average water availability at a given location and season".
According to
The IPCC Sixth Assessment Report defines a drought simply as "drier than normal conditions". This means that a drought is "a moisture deficit relative to the average water availability at a given location and season".
According to

 The El Niño–Southern Oscillation (ENSO) phenomenon can sometimes play a significant role in drought. ENSO comprises two patterns of temperature anomalies in the central Pacific Ocean, known as La Niña and El Niño. La Niña events are generally associated with drier and hotter conditions and further exacerbation of drought in California and the
The El Niño–Southern Oscillation (ENSO) phenomenon can sometimes play a significant role in drought. ENSO comprises two patterns of temperature anomalies in the central Pacific Ocean, known as La Niña and El Niño. La Niña events are generally associated with drier and hotter conditions and further exacerbation of drought in California and the 
2 August 2007 New Scientist, Catherine Brahic There is a rise of compound warm-season droughts in Europe that are concurrent with an increase in potential evapotranspiration.


 One can divide the effects of droughts and water shortages into three groups: environmental, economic and social (including health).
* In the case of environmental effects: lower surface and subterranean water-levels, lower flow-levels (with a decrease below the minimum leading to direct danger for amphibian life), increased pollution of surface water, the drying out of
One can divide the effects of droughts and water shortages into three groups: environmental, economic and social (including health).
* In the case of environmental effects: lower surface and subterranean water-levels, lower flow-levels (with a decrease below the minimum leading to direct danger for amphibian life), increased pollution of surface water, the drying out of

 Agriculturally, people can effectively mitigate much of the impact of drought through irrigation and crop rotation. Failure to develop adequate drought mitigation strategies carries a grave human cost in the modern era, exacerbated by ever-increasing population densities. President Roosevelt on April 27, 1935, signed documents creating the Soil Conservation Service (SCS)—now the
Agriculturally, people can effectively mitigate much of the impact of drought through irrigation and crop rotation. Failure to develop adequate drought mitigation strategies carries a grave human cost in the modern era, exacerbated by ever-increasing population densities. President Roosevelt on April 27, 1935, signed documents creating the Soil Conservation Service (SCS)—now the
 The Darfur conflict in
The Darfur conflict in  Approximately 2.4 billion people live in the drainage basin of the Himalayan rivers. India,
Approximately 2.4 billion people live in the drainage basin of the Himalayan rivers. India, 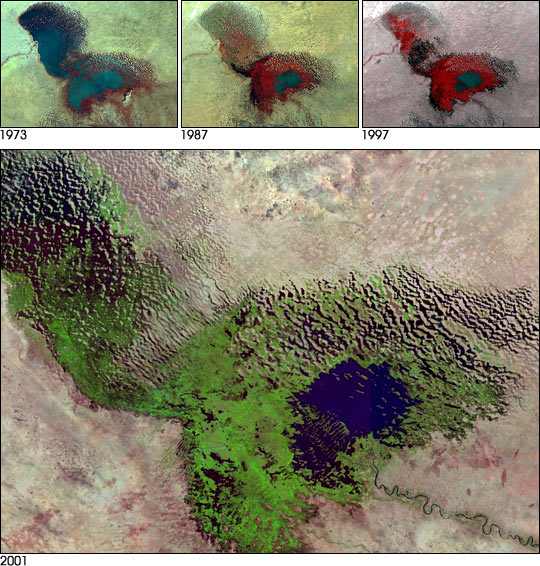 By far the largest part of
By far the largest part of
Taking drought into account Addressing chronic vulnerability among pastoralists in the Horn of Africa
Overseas Development Institute During the 2011 drought, an estimated 50,000 to 150,000 people were reported to have died, though these figures and the extent of the crisis are disputed. In February 2012, the UN announced that the crisis was over due to a scaling up of relief efforts and a bumper harvest. Aid agencies subsequently shifted their emphasis to recovery efforts, including digging irrigation canals and distributing plant seeds. The 2020-2022 Horn of Africa drought has surpassed the horrific drought in 2010-2011 in both duration and severity. In 2012, a severe drought struck the western
 Throughout history, humans have usually viewed droughts as "disasters" due to the impact on food availability and the rest of society. Humans have often tried to explain droughts as either a
Throughout history, humans have usually viewed droughts as "disasters" due to the impact on food availability and the rest of society. Humans have often tried to explain droughts as either a
GIDMaPS
Global Integrated Drought Monitoring and Prediction System, University of California, Irvine
from FAO Water (Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations)
Global Real-Time Drought Media Monitoring
{{Authority control Meteorological phenomena Civil defense Climate variability and change Hydrology Water and the environment Weather hazards Articles containing video clips Natural disasters
Water Cycle Changes
In Climate Change 2021: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change [Masson-Delmotte, V., P. Zhai, A. Pirani, S.L. Connors, C. Péan, S. Berger, N. Caud, Y. Chen, L. Goldfarb, M.I. Gomis, M. Huang, K. Leitzell, E. Lonnoy, J.B.R. Matthews, T.K. Maycock, T. Waterfield, O. Yelekçi, R. Yu, and B. Zhou (eds.)]. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, United Kingdom and New York, NY, USA, pp. 1055–1210, doi:10.1017/9781009157896.010. This means that a drought is "a moisture deficit relative to the average water availability at a given location and season". A drought can last for days, months or years. Drought often exerts substantial impacts on the ecosystems and agriculture of affected regions, and causes harm to the local economy. Annual dry seasons in the tropics significantly increase the chances of a drought developing and subsequent wildfires. Periods of heat can significantly worsen drought conditions by hastening evaporation of water vapour. Drought is a recurring feature of the climate in most parts of the world, becoming more extreme and less predictable due to climate change, which
dendrochronological
Dendrochronology (or tree-ring dating) is the scientific method of dating tree rings (also called growth rings) to the exact year they were formed. As well as dating them, this can give data for dendroclimatology, the study of climate and atmos ...
studies date back to 1900. There are three kinds of drought effects, environmental, economic and social. Environmental effects include the drying of wetlands, more and larger wildfires, loss of biodiversity. Economic consequences include disruption of water supplies
Water supply is the provision of water by public utilities, commercial organisations, community endeavors or by individuals, usually via a system of pumps and pipes. Public water supply systems are crucial to properly functioning societies. Thes ...
for municipal economies; lower agricultural, forest, game, and fishing outputs; higher food-production costs; and problems with water supply for the energy sector
The energy industry is the totality of all of the industries involved in the production and sale of energy, including fuel extraction, manufacturing, refining and distribution. Modern society consumes large amounts of fuel, and the energy indust ...
. Social and health costs include the negative effect on the health of people directly exposed to this phenomenon (excessive heat waves), high food costs, stress caused by failed harvests, water scarcity, etc. Prolonged droughts have caused mass migration
Mass migration refers to the migration of large groups of people from one geographical area to another. Mass migration is distinguished from individual or small-scale migration; and also from seasonal migration, which may occur on a regular basis ...
s and humanitarian crisis.
Many plant species, such as those in the family Cactaceae (or cacti
A cactus (, or less commonly, cactus) is a member of the plant family Cactaceae, a family comprising about 127 genera with some 1750 known species of the order Caryophyllales. The word ''cactus'' derives, through Latin, from the Ancient Greek ...
), have drought tolerance adaptations like reduced leaf area and waxy cuticles to enhance their ability to tolerate drought. Some others survive dry periods as buried seeds. Semi-permanent drought produces arid biomes such as deserts and grasslands. Most arid ecosystems have inherently low productivity.
The most prolonged drought ever in the world in recorded history continues in the Atacama Desert in Chile (400 years). Throughout history, humans have usually viewed droughts as "disasters" due to the impact on food availability and the rest of society. Humans have often tried to explain droughts as either a natural disaster
A natural disaster is "the negative impact following an actual occurrence of natural hazard in the event that it significantly harms a community". A natural disaster can cause loss of life or damage property, and typically leaves some econ ...
, caused by humans, or the result of supernatural
Supernatural refers to phenomena or entities that are beyond the laws of nature. The term is derived from Medieval Latin , from Latin (above, beyond, or outside of) + (nature) Though the corollary term "nature", has had multiple meanings si ...
forces.
Definition
 The IPCC Sixth Assessment Report defines a drought simply as "drier than normal conditions". This means that a drought is "a moisture deficit relative to the average water availability at a given location and season".
According to
The IPCC Sixth Assessment Report defines a drought simply as "drier than normal conditions". This means that a drought is "a moisture deficit relative to the average water availability at a given location and season".
According to National Integrated Drought Information System
The ''National Integrated Drought Information System (NIDIS) Act'' was signed into law in 2006 (Public Law 109-430) and was reauthorized in 2014 and 2019. The Western Governors' Association described the need for NIDIS in a 2004 report, ''Creating ...
, a multi-agency partnership, drought is generally defined as “a deficiency of precipitation over an extended period of time (usually a season or more), resulting in a water shortage”. The National Weather Service office of the NOAA
The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (abbreviated as NOAA ) is an United States scientific and regulatory agency within the United States Department of Commerce that forecasts weather, monitors oceanic and atmospheric conditio ...
defines drought as "a deficiency of moisture that results in adverse impacts on people, animals, or vegetation over a sizeable area".
Drought is a complex phenomenon − relating to the absence of water − which is difficult to monitor and define. By the early 1980's, over 150 definitions of "drought" had already been published. The range of definitions reflects differences in regions, needs, and disciplinary approaches.
Categories
There are three major categories of drought based on where in the water cycle the moisture deficit occurs: meteorological drought, hydrological drought, and agricultural or ecological drought. A meteorological drought occurs due to lack of precipitation. A hydrological drought is related to low runoff, streamflow, and reservoir storage. An agricultural or ecological drought is causing plant stress from a combination of evaporation and lowsoil moisture
Soil moisture is the water content of the soil. It can be expressed in terms of volume or weight. Soil moisture measurement can be based on ''in situ'' probes (e.g., capacitance probes, neutron probes) or remote sensing methods.
Water that enters ...
. Some organizations add another category: socioeconomic drought occurs when the demand for an economic good exceeds supply as a result of a weather-related shortfall in water supply. The socioeconomic drought is a similar concept to water scarcity.
The different categories of droughts have different causes but similar effects:
# Meteorological
Meteorology is a branch of the atmospheric sciences (which include atmospheric chemistry and physics) with a major focus on weather forecasting. The study of meteorology dates back millennia, though significant progress in meteorology did not ...
drought occurs when there is a prolonged time with less than average precipitation. Meteorological drought usually precedes the other kinds of drought. As a drought persists, the conditions surrounding it gradually worsen and its impact on the local population gradually increases.
# Hydrological drought is brought about when the water reserves available in sources such as aquifers, lakes and reservoirs fall below a locally significant threshold. Hydrological drought tends to show up more slowly because it involves stored water that is used but not replenished. Like an agricultural drought, this can be triggered by more than just a loss of rainfall. For instance, around 2007 Kazakhstan was awarded a large amount of money by the World Bank to restore water that had been diverted to other nations from the Aral Sea
The Aral Sea ( ; kk, Арал теңізі, Aral teñızı; uz, Орол денгизи, Orol dengizi; kaa, Арал теңизи, Aral teńizi; russian: Аральское море, Aral'skoye more) was an endorheic basin, endorheic lake lyi ...
under Soviet rule. Similar circumstances also place their largest lake, Balkhash, at risk of completely drying out.
# Agricultural
Agriculture or farming is the practice of cultivating Plant, plants and livestock. Agriculture was the key development in the rise of Sedentism, sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of Domestication, domesticated species created food ...
or ecological droughts affect crop production or ecosystems in general. This condition can also arise independently from any change in precipitation levels when either increased irrigation or soil conditions and erosion triggered by poorly planned agricultural endeavors cause a shortfall in water available to the crops.
Causes

General precipitation deficiency
Mechanisms of producing precipitation includeconvective
Convection is single or multiphase fluid flow that occurs spontaneously due to the combined effects of material property heterogeneity and body forces on a fluid, most commonly density and gravity (see buoyancy). When the cause of the convect ...
, stratiform
Stratiform may refer to:
* Any of the stratus family of clouds (fog, stratus clouds, altostratus clouds, cirrostratus clouds, nimbostratus clouds) and the precipitation coming from them.
* Any occurrence of layered strata (see stratigraphic unit). ...
, and orographic
Orography is the study of the topographic relief of mountains, and can more broadly include hills, and any part of a region's elevated terrain. Orography (also known as ''oreography'', ''orology'' or ''oreology'') falls within the broader discipl ...
rainfall. Convective processes involve strong vertical motions that can cause the overturning of the atmosphere in that location within an hour and cause heavy precipitation, while stratiform processes involve weaker upward motions and less intense precipitation over a longer duration. Precipitation can be divided into three categories, based on whether it falls as liquid water, liquid water that freezes on contact with the surface, or ice. Droughts occur mainly in areas where normal levels of rainfall are, in themselves, low. If these factors do not support precipitation volumes sufficiently to reach the surface over a sufficient time, the result is a drought. Drought can be triggered by a high level of reflected sunlight and above average prevalence of high pressure systems, winds carrying continental, rather than oceanic air masses, and ridges of high pressure areas aloft can prevent or restrict the developing of thunderstorm activity or rainfall over one certain region. Once a region is within drought, feedback mechanisms such as local arid air, hot conditions which can promote warm core ridging, and minimal evapotranspiration can worsen drought conditions.
Dry season
Within the tropics, distinct, wet and dry seasons emerge due to the movement of theIntertropical Convergence Zone
The Intertropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ ), known by sailors as the doldrums or the calms because of its monotonous windless weather, is the area where the northeast and the southeast trade winds converge. It encircles Earth near the thermal e ...
or Monsoon trough. The dry season greatly increases drought occurrence, and is characterized by its low humidity, with watering holes and rivers drying up. Because of the lack of these watering holes, many grazing animals are forced to migrate due to the lack of water in search of more fertile lands. Examples of such animals are zebras, elephants
Elephants are the largest existing land animals. Three living species are currently recognised: the African bush elephant, the African forest elephant, and the Asian elephant. They are the only surviving members of the family Elephantidae and ...
, and wildebeest. Because of the lack of water in the plants, bushfires are common. Since water vapor becomes more energetic with increasing temperature, more water vapor is required to increase relative humidity values to 100% at higher temperatures (or to get the temperature to fall to the dew point). Periods of warmth quicken the pace of fruit and vegetable production, increase evaporation and transpiration from plants, and worsen drought conditions.
El Niño–Southern Oscillation (ENSO)
 The El Niño–Southern Oscillation (ENSO) phenomenon can sometimes play a significant role in drought. ENSO comprises two patterns of temperature anomalies in the central Pacific Ocean, known as La Niña and El Niño. La Niña events are generally associated with drier and hotter conditions and further exacerbation of drought in California and the
The El Niño–Southern Oscillation (ENSO) phenomenon can sometimes play a significant role in drought. ENSO comprises two patterns of temperature anomalies in the central Pacific Ocean, known as La Niña and El Niño. La Niña events are generally associated with drier and hotter conditions and further exacerbation of drought in California and the Southwestern United States
The Southwestern United States, also known as the American Southwest or simply the Southwest, is a geographic and cultural region of the United States that generally includes Arizona, New Mexico, and adjacent portions of California, Colorado, Ne ...
, and to some extent the U.S. Southeast. Meteorological scientists have observed that La Niñas have become more frequent over time.
Conversely, during El Niño events, drier and hotter weather occurs in parts of the Amazon River
The Amazon River (, ; es, Río Amazonas, pt, Rio Amazonas) in South America is the largest river by discharge volume of water in the world, and the disputed longest river system in the world in comparison to the Nile.
The headwaters of t ...
Basin, Colombia
Colombia (, ; ), officially the Republic of Colombia, is a country in South America with insular regions in North America—near Nicaragua's Caribbean coast—as well as in the Pacific Ocean. The Colombian mainland is bordered by the Car ...
, and Central America. Winters during the El Niño are warmer and drier than average conditions in the Northwest, northern Midwest, and northern Mideast United States, so those regions experience reduced snowfalls. Conditions are also drier than normal from December to February in south-central Africa, mainly in Zambia, Zimbabwe, Mozambique, and Botswana. Direct effects of El Niño resulting in drier conditions occur in parts of Southeast Asia and Northern Australia, increasing bush fire
A wildfire, forest fire, bushfire, wildland fire or rural fire is an unplanned, uncontrolled and unpredictable fire in an area of combustible vegetation. Depending on the type of vegetation present, a wildfire may be more specifically identif ...
s, worsening haze, and decreasing air quality dramatically. Drier-than-normal conditions are also in general observed in Queensland, inland Victoria, inland New South Wales, and eastern Tasmania from June to August. As warm water spreads from the west Pacific and the Indian Ocean to the east Pacific, it causes extensive drought in the western Pacific. Singapore experienced the driest February in 2014 since records began in 1869, with only 6.3 mm of rain falling in the month and temperatures hitting as high as 35 °C on 26 February. The years 1968 and 2005 had the next driest Februaries, when 8.4 mm of rain fell.Precipitation deficiency due to climate change
Global climate change is expected to trigger droughts with a substantial impact on agriculture throughout the world, and especially in developing nations. Along with drought in some areas, flooding and erosion could increase in others. Some proposedclimate change mitigation
Climate change mitigation is action to limit climate change by reducing Greenhouse gas emissions, emissions of greenhouse gases or Carbon sink, removing those gases from the atmosphere. The recent rise in global average temperature is mostly caus ...
actions that focus on more active techniques, solar radiation management
Solar geoengineering, or solar radiation modification (SRM), is a type of climate engineering in which sunlight (solar radiation) would be reflected back to outer space to limit or reverse human-caused climate change. It is not a substitute for ...
through the use of a space sunshade for one, may also carry with them increased chances of drought.''Sunshade' for global warming could cause drought''2 August 2007 New Scientist, Catherine Brahic There is a rise of compound warm-season droughts in Europe that are concurrent with an increase in potential evapotranspiration.
Erosion and human activities
Human activity can directly trigger exacerbating factors such as over farming, excessive irrigation, deforestation, and erosion adversely impact the ability of the land to capture and hold water. In arid climates, the main source of erosion is wind. Erosion can be the result of material movement by the wind. The wind can cause small particles to be lifted and therefore moved to another region (deflation). Suspended particles within the wind may impact on solid objects causing erosion by abrasion (ecological succession). Wind erosion generally occurs in areas with little or no vegetation, often in areas where there is insufficient rainfall to support vegetation.Loess
Loess (, ; from german: Löss ) is a clastic, predominantly silt-sized sediment that is formed by the accumulation of wind-blown dust. Ten percent of Earth's land area is covered by loess or similar deposits.
Loess is a periglacial or aeolian ...
is a homogeneous, typically nonstratified, porous, friable, slightly coherent, often calcareous, fine-grained, silty, pale yellow or buff, windblown (Aeolian
Aeolian commonly refers to things related to either of two Greek mythological figures:
* Aeolus (son of Hippotes), ruler of the winds
* Aeolus (son of Hellen), son of Hellen and eponym of the Aeolians
* Aeolians, an ancient Greek tribe thought to ...
) sediment. It generally occurs as a widespread blanket deposit that covers areas of hundreds of square kilometers and tens of meters thick. Loess often stands in either steep or vertical faces. Loess tends to develop into highly rich soils. Under appropriate climatic conditions, areas with loess are among the most agriculturally productive in the world. Loess deposits are geologically unstable by nature, and will erode very readily. Therefore, windbreaks (such as big trees and bushes) are often planted by farmers to reduce the wind erosion of loess. Wind erosion is much more severe in arid areas and during times of drought. For example, in the Great Plains
The Great Plains (french: Grandes Plaines), sometimes simply "the Plains", is a broad expanse of flatland in North America. It is located west of the Mississippi River and east of the Rocky Mountains, much of it covered in prairie, steppe, an ...
, it is estimated that soil loss due to wind erosion can be as much as 6100 times greater in drought years than in wet years.Consequences


wetlands
A wetland is a distinct ecosystem that is flooded or saturated by water, either permanently (for years or decades) or seasonally (for weeks or months). Flooding results in oxygen-free (anoxic) processes prevailing, especially in the soils. The ...
, more and larger wildfires, higher deflation intensity, loss of biodiversity, worse health of trees and the appearance of pests and dendroid diseases.
* Economic losses include lower agricultural, forests, game and fishing output, higher food-production costs, lower energy-production levels in hydro plants, losses caused by depleted water tourism and transport revenue, problems with water supply for the energy sector
The energy industry is the totality of all of the industries involved in the production and sale of energy, including fuel extraction, manufacturing, refining and distribution. Modern society consumes large amounts of fuel, and the energy indust ...
and for technological processes in metallurgy, mining, the chemical, paper, wood, foodstuff industries etc., disruption of water supplies
Water supply is the provision of water by public utilities, commercial organisations, community endeavors or by individuals, usually via a system of pumps and pipes. Public water supply systems are crucial to properly functioning societies. Thes ...
for municipal economies.
* Social and health costs include the negative effect on the health of people directly exposed to this phenomenon (excessive heat waves), possible limitation of water supplies, increased pollution levels, high food-costs, stress caused by failed harvests, water scarcity, etc. This explains why droughts and water scarcity operate as a factor which increases the gap between developed and developing countries.
Effects vary according to vulnerability. For example, subsistence farmers are more likely to migrate during drought because they do not have alternative food-sources. Areas with populations that depend on water sources as a major food-source are more vulnerable to famine.
Environmental and economic consequences
Common environmental and economic consequences of drought include: * Diminished crop growth or yield productions andcarrying capacity
The carrying capacity of an environment is the maximum population size of a biological species that can be sustained by that specific environment, given the food, habitat, water, and other resources available. The carrying capacity is defined as t ...
for livestock
* Wildfires, such as Australian bushfires and wildfires in the United States
Wildfires can happen in many places in the United States, especially during droughts, but are most common in the Western United States and Florida. They may be triggered naturally, most commonly by lightning, or by human activity like unexti ...
, become more common during times of drought and may cause human deaths.
* Dust bowls, themselves a sign of erosion, which further erode the landscape
A landscape is the visible features of an area of land, its landforms, and how they integrate with natural or man-made features, often considered in terms of their aesthetic appeal.''New Oxford American Dictionary''. A landscape includes the ...
* Dust storms, when drought hits an area suffering from desertification and erosion
* Habitat damage, affecting both terrestrial and aquatic wildlife
* Reduced electricity production due to reduced water-flow through hydroelectric
Hydroelectricity, or hydroelectric power, is electricity generated from hydropower (water power). Hydropower supplies one sixth of the world's electricity, almost 4500 TWh in 2020, which is more than all other renewable sources combined and ...
dams
* Shortages of water for industrial
Industrial may refer to:
Industry
* Industrial archaeology, the study of the history of the industry
* Industrial engineering, engineering dealing with the optimization of complex industrial processes or systems
* Industrial city, a city dominate ...
users
* Snake migration, which results in snake-bites
* Exposure and oxidation of acid sulfate soils
Acid sulfate soils are naturally occurring soils, sediments or organic substrates (e.g. peat) that are formed under waterlogged conditions. These soils contain iron sulfide minerals (predominantly as the mineral pyrite) and/or their oxidation produ ...
due to falling surface- and ground-water levels.Mosley LM, Zammit B, Jolley A, and Barnett L (2014). Acidification of lake water due to drought. Journal of Hydrology. 511: 484–493.Mosley LM, Palmer D, Leyden E, Fitzpatrick R, and Shand P (2014). Acidification of floodplains due to river level decline during drought. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology 161: 10–23.Mosley LM, Palmer D, Leyden E, Fitzpatrick R, and Shand P (2014). Changes in acidity and metal geochemistry in soils, groundwater, drain and river water in the Lower Murray River after a severe drought. Science of the Total Environment 485–486: 281–291.
* Reduced water quality, because lower water-flows reduce dilution of pollutants and increase contamination of remaining water-sources.
* Land degradation and loss of soil moisture, resulting in the destruction of cropland productivity.
Social and health consequences
* Water scarcity, crop failure,famine
A famine is a widespread scarcity of food, caused by several factors including war, natural disasters, crop failure, Demographic trap, population imbalance, widespread poverty, an Financial crisis, economic catastrophe or government policies. Th ...
and hunger – drought provides too little water to support food crops; malnutrition, dehydration and related diseases
*Mass migration
Mass migration refers to the migration of large groups of people from one geographical area to another. Mass migration is distinguished from individual or small-scale migration; and also from seasonal migration, which may occur on a regular basis ...
, resulting in internal displacement
An internally displaced person (IDP) is someone who is forced displacement, forced to leave their home but who remains within their country's borders. They are often referred to as refugees, although they do not fall within the Refugee#Definition ...
and international refugee
A refugee, conventionally speaking, is a displaced person who has crossed national borders and who cannot or is unwilling to return home due to well-founded fear of persecution.
s
*Social unrest
Unrest, also called disaffection, is a sociological phenomenon, including:
* Civil unrest
* Civil disorder
* Domestic terrorism
* Industrial unrest
* Labor unrest
* Rebellion
* Riot
* Strike action
* State of emergency
Notable historical instance ...
* War over natural resources, including water and food
* Cyanotoxin accumulation within food chains and water supply (some of which are among the most potent toxins known to science) can cause cancer with low exposure over the long term. High levels of microcystin appeared in San Francisco Bay Area salt-water shellfish and fresh-water supplies throughout the state of California in 2016.
Impacts on crops
Water stress affects plant development and quality in a variety of ways: firstly drought can cause poor germination and impaired seedling development. At the same time plant growth relies on cellular division, cell enlargement, and differentiation. Drought stress impairsmitosis
In cell biology, mitosis () is a part of the cell cycle in which replicated chromosomes are separated into two new nuclei. Cell division by mitosis gives rise to genetically identical cells in which the total number of chromosomes is mainta ...
and cell elongation via loss of turgor pressure
Turgor pressure is the force within the cell that pushes the plasma membrane against the cell wall.
It is also called ''hydrostatic pressure'', and is defined as the pressure in a fluid measured at a certain point within itself when at equilibri ...
which results in poor growth. Development of leaves is also dependent upon turgor pressure, concentration of nutrients, and carbon assimilates all of which are reduced by drought conditions, thus drought stress lead to a decrease in leaf size and number. Plant height, biomass, leaf size and stem girth has been shown to decrease in maize under water limiting conditions. Crop yield is also negatively effected by drought stress, the reduction in crop yield results from a decrease in photosynthetic rate, changes in leaf development, and altered allocation of resources all due to drought stress. Crop plants exposed to drought stress suffer from reductions in leaf water potential and transpiration rate. Water-use efficiency
Water-use efficiency (WUE) refers to the ratio of water used in plant metabolism to water lost by the plant through transpiration. Two types of water-use efficiency are referred to most frequently:
* photosynthetic water-use efficiency (also cal ...
increases in crops such as wheat while decreasing in others, such as potatoes.
Plants need water for the uptake of nutrients from the soil, and for the transport of nutrients throughout the plant: drought conditions limit these functions leading to stunted growth. Drought stress also causes a decrease in photosynthetic activity in plants due to the reduction of photosynthetic tissues, stomatal closure, and reduced performance of photosynthetic machinery. This reduction in photosynthetic activity contributes to the reduction in plant growth and yields. Another factor influencing reduced plant growth and yields include the allocation of resources; following drought stress plants will allocate more resources to roots to aid in water uptake increasing root growth and reducing the growth of other plant parts while decreasing yields.
Protection, mitigation and relief

 Agriculturally, people can effectively mitigate much of the impact of drought through irrigation and crop rotation. Failure to develop adequate drought mitigation strategies carries a grave human cost in the modern era, exacerbated by ever-increasing population densities. President Roosevelt on April 27, 1935, signed documents creating the Soil Conservation Service (SCS)—now the
Agriculturally, people can effectively mitigate much of the impact of drought through irrigation and crop rotation. Failure to develop adequate drought mitigation strategies carries a grave human cost in the modern era, exacerbated by ever-increasing population densities. President Roosevelt on April 27, 1935, signed documents creating the Soil Conservation Service (SCS)—now the Natural Resources Conservation Service
Natural Resources Conservation Service (NRCS), formerly known as the Soil Conservation Service (SCS), is an agency of the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) that provides technical assistance to farmers and other private landowners an ...
(NRCS). Models of the law were sent to each state where they were enacted. These were the first enduring practical programs to curtail future susceptibility to drought, creating agencies that first began to stress soil conservation measures to protect farm lands today. It was not until the 1950s that there was an importance placed on water conservation was put into the existing laws (NRCS 2014).
Strategies for drought protection, mitigation or relief include:
* Dams – many dams and their associated reservoirs supply additional water in times of drought.
* Cloud seeding
Cloud seeding is a type of weather modification that aims to change the amount or type of precipitation that falls from clouds by dispersing substances into the air that serve as cloud condensation or ice nuclei, which alter the microphysical p ...
– a form of intentional weather modification to induce rainfall. This remains a hotly debated topic, as the United States National Research Council released a report in 2004 stating that to date, there is still no convincing scientific proof of the efficacy of intentional weather modification.
* Desalination
Desalination is a process that takes away mineral components from saline water. More generally, desalination refers to the removal of salts and minerals from a target substance, as in Soil salinity control, soil desalination, which is an issue f ...
– use of sea water for irrigation or consumption.
* Drought monitoring – Continuous observation of rainfall levels and comparisons with current usage levels can help prevent man-made drought. For instance, analysis of water usage in Yemen has revealed that their water table (underground water level) is put at grave risk by over-use to fertilize their Khat
Khat or qat ( ''ch’at''; Oromo: ''Jimaa'', so, qaad, khaad, khat or chat, ar, القات ''al-qāt'') is a flowering plant native to eastern and southern Africa. Khat contains the alkaloid cathinone, a stimulant, which is said to cause e ...
crop. Careful monitoring of moisture levels can also help predict increased risk for wildfires, using such metrics as the Keetch-Byram Drought Index or Palmer Drought Index.
* Land use – Carefully planned crop rotation can help to minimize erosion and allow farmers to plant less water-dependent crops in drier years.
* Outdoor water-use restriction
An outdoor water-use restriction is a ban or other lesser restrictions put into effect that restricts the outdoor use of water supplies. Often called a watering ban or hosepipe ban, it can affect:
*irrigation of lawns
*car washing
*recreational ...
– Regulating the use of sprinklers, hoses or buckets on outdoor plants, filling pools, and other water-intensive home maintenance tasks. Xeriscaping
Xeriscaping is the process of Garden design, landscaping, or gardening, that reduces or eliminates the need for irrigation. It is promoted in regions that do not have accessible, plentiful, or reliable supplies of fresh water and has gained accep ...
yards can significantly reduce unnecessary water use by residents of towns and cities.
* Rainwater harvesting – Collection and storage of rainwater from roofs or other suitable catchments.
* Recycled water
Water reclamation (also called wastewater reuse, water reuse or water recycling) is the process of converting Sewage, municipal wastewater (sewage) or Industrial wastewater treatment, industrial wastewater into water that can be reused for a vari ...
– Former wastewater (sewage) that has been treated and purified for reuse.
* Transvasement
An aqueduct is a watercourse constructed to carry water from a source to a distribution point far away. In modern engineering, the term ''aqueduct'' is used for any system of pipes, ditches, canals, tunnels, and other structures used for this p ...
– Building canals or redirecting rivers as massive attempts at irrigation in drought-prone areas.
Scale and examples
Some large scale droughts in the 21st century included: * The 1997–2009 Millennium Drought in Australia led to a water supply crisis across much of the country. As a result, many desalination plants were built for the first time ( see list). * In 2006, Sichuan Province China experienced its worst drought in modern times with nearly 8 million people and over 7 million cattle facing water shortages. * 12-year drought that was devastating southwest Western Australia, southeast South Australia, Victoria and northern Tasmania was "very severe and without historical precedent". * 2015–2018Cape Town water crisis
The Cape Town water crisis in South Africa was a period of severe water shortage in the Western Cape region, most notably affecting the City of Cape Town. While dam water levels had been decreasing since 2015, the Cape Town water crisis peaked d ...
. This likelihood was tripled by climate change.
 The Darfur conflict in
The Darfur conflict in Sudan
Sudan ( or ; ar, السودان, as-Sūdān, officially the Republic of the Sudan ( ar, جمهورية السودان, link=no, Jumhūriyyat as-Sūdān), is a country in Northeast Africa. It shares borders with the Central African Republic t ...
, also affecting Chad
Chad (; ar, تشاد , ; french: Tchad, ), officially the Republic of Chad, '; ) is a landlocked country at the crossroads of North and Central Africa. It is bordered by Libya to the north, Sudan to the east, the Central African Republic ...
, was fueled by decades of drought; combination of drought, desertification
Desertification is a type of land degradation in drylands in which biological productivity is lost due to natural processes or induced by human activities whereby fertile areas become increasingly arid. It is the spread of arid areas caused by ...
and overpopulation are among the causes of the Darfur conflict, because the Arab Baggara nomads searching for water have to take their livestock further south, to land mainly occupied by non-Arab farming people.
 Approximately 2.4 billion people live in the drainage basin of the Himalayan rivers. India,
Approximately 2.4 billion people live in the drainage basin of the Himalayan rivers. India, China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and ...
, Pakistan, Bangladesh, Nepal and Myanmar
Myanmar, ; UK pronunciations: US pronunciations incl. . Note: Wikipedia's IPA conventions require indicating /r/ even in British English although only some British English speakers pronounce r at the end of syllables. As John C. Wells, Joh ...
could experience floods followed by droughts in coming decades. Drought in India affecting the Ganges is of particular concern, as it provides drinking water and agricultural irrigation for more than 500 million people. The west coast of North America
North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere and almost entirely within the Western Hemisphere. It is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South America and the Car ...
, which gets much of its water from glaciers in mountain ranges such as the Rocky Mountains and Sierra Nevada
The Sierra Nevada () is a mountain range in the Western United States, between the Central Valley of California and the Great Basin. The vast majority of the range lies in the state of California, although the Carson Range spur lies primarily ...
, also would be affected.
In 2005, parts of the Amazon basin
The Amazon basin is the part of South America drained by the Amazon River and its tributaries. The Amazon drainage basin covers an area of about , or about 35.5 percent of the South American continent. It is located in the countries of Bolivi ...
experienced the worst drought in 100 years. A 23 July 2006 article reported Woods Hole Research Center
Woodwell Climate Research Center, formerly known as the Woods Hole Research Center (WHRC) until August 2020, is a scientific research organization that studies climate change impacts and solutions. The International Center for Climate Governance n ...
results showing that the forest in its present form could survive only three years of drought. Scientists at the Brazilian National Institute of Amazonian Research argue in the article that this drought response, coupled with the effects of deforestation on regional climate, are pushing the rainforest towards a " tipping point" where it would irreversibly start to die. It concludes that the rainforest
Rainforests are characterized by a closed and continuous tree canopy, moisture-dependent vegetation, the presence of epiphytes and lianas and the absence of wildfire. Rainforest can be classified as tropical rainforest or temperate rainfores ...
is on the brink of being turned into savanna or desert
A desert is a barren area of landscape where little precipitation occurs and, consequently, living conditions are hostile for plant and animal life. The lack of vegetation exposes the unprotected surface of the ground to denudation. About on ...
, with catastrophic consequences for the world's climate. According to the WWF, the combination of climate change and deforestation increases the drying effect of dead trees that fuels forest fires.
 By far the largest part of
By far the largest part of Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a Sovereign state, sovereign country comprising the mainland of the Australia (continent), Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous List of islands of Australia, sma ...
is desert
A desert is a barren area of landscape where little precipitation occurs and, consequently, living conditions are hostile for plant and animal life. The lack of vegetation exposes the unprotected surface of the ground to denudation. About on ...
or semi-arid lands commonly known as the outback
The Outback is a remote, vast, sparsely populated area of Australia. The Outback is more remote than the bush. While often envisaged as being arid, the Outback regions extend from the northern to southern Australian coastlines and encompass a n ...
. A 2005 study by Australian and American researchers investigated the desertification of the interior, and suggested that one explanation was related to human settlers who arrived about 50,000 years ago. Regular burning by these settlers could have prevented monsoons from reaching interior Australia. In June 2008 it became known that an expert panel had warned of long term, maybe irreversible, severe ecological damage for the whole Murray-Darling basin if it did not receive sufficient water by October 2008. Australia could experience more severe droughts and they could become more frequent in the future, a government-commissioned report said on July 6, 2008. Australian environmentalist Tim Flannery, predicted that unless it made drastic changes, Perth in Western Australia could become the world's first ghost metropolis, an abandoned city with no more water to sustain its population. The long Australian Millennial drought broke in 2010.
Recurring droughts leading to desertification
Desertification is a type of land degradation in drylands in which biological productivity is lost due to natural processes or induced by human activities whereby fertile areas become increasingly arid. It is the spread of arid areas caused by ...
in East Africa
East Africa, Eastern Africa, or East of Africa, is the eastern subregion of the African continent. In the United Nations Statistics Division scheme of geographic regions, 10-11-(16*) territories make up Eastern Africa:
Due to the historical ...
have created grave ecological catastrophes, prompting food shortages in 1984–85, 2006
File:2006 Events Collage V1.png, From top left, clockwise: The 2006 Winter Olympics open in Turin; Twitter is founded and launched by Jack Dorsey; The Nintendo Wii is released; Montenegro 2006 Montenegrin independence referendum, votes to declare ...
and 2011
File:2011 Events Collage.png, From top left, clockwise: a protester partaking in Occupy Wall Street heralds the beginning of the Occupy movement; protests against Libyan dictator Muammar Gaddafi, who was killed that October; a young man celebrate ...
.Sara Pantuliano and Sara Pavanello (2004Taking drought into account Addressing chronic vulnerability among pastoralists in the Horn of Africa
Overseas Development Institute During the 2011 drought, an estimated 50,000 to 150,000 people were reported to have died, though these figures and the extent of the crisis are disputed. In February 2012, the UN announced that the crisis was over due to a scaling up of relief efforts and a bumper harvest. Aid agencies subsequently shifted their emphasis to recovery efforts, including digging irrigation canals and distributing plant seeds. The 2020-2022 Horn of Africa drought has surpassed the horrific drought in 2010-2011 in both duration and severity. In 2012, a severe drought struck the western
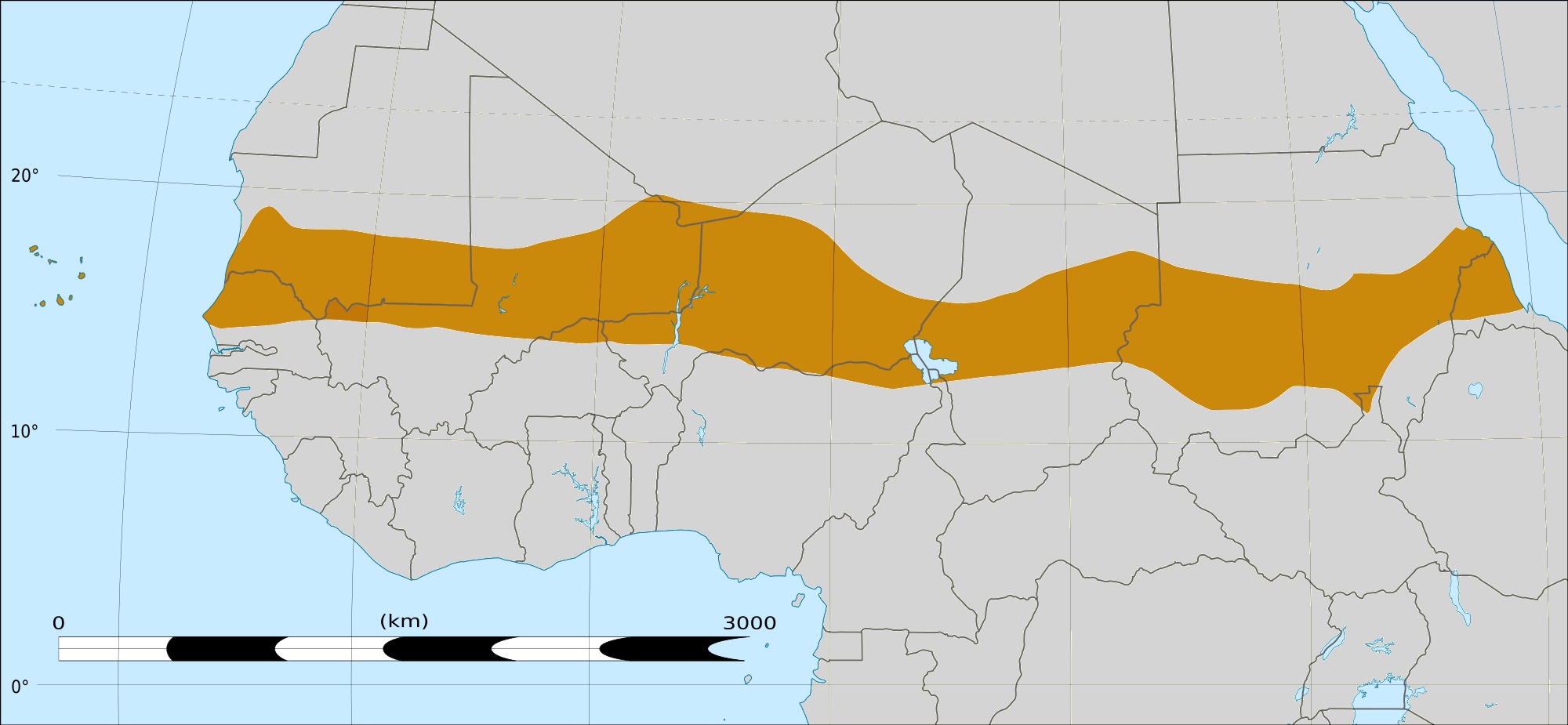
Sahel
The Sahel (; ar, ساحل ' , "coast, shore") is a region in North Africa. It is defined as the ecoclimatic and biogeographic realm of transition between the Sahara to the north and the Sudanian savanna to the south. Having a hot semi-arid c ...
. The Methodist Relief & Development Fund (MRDF) reported that more than 10 million people in the region were at risk of famine due to a month-long heat wave that was hovering over Niger, Mali, Mauritania
Mauritania (; ar, موريتانيا, ', french: Mauritanie; Berber: ''Agawej'' or ''Cengit''; Pulaar: ''Moritani''; Wolof: ''Gànnaar''; Soninke:), officially the Islamic Republic of Mauritania ( ar, الجمهورية الإسلامية ...
and Burkina Faso. A fund of about £20,000 was distributed to the drought-hit countries.
History
 Throughout history, humans have usually viewed droughts as "disasters" due to the impact on food availability and the rest of society. Humans have often tried to explain droughts as either a
Throughout history, humans have usually viewed droughts as "disasters" due to the impact on food availability and the rest of society. Humans have often tried to explain droughts as either a natural disaster
A natural disaster is "the negative impact following an actual occurrence of natural hazard in the event that it significantly harms a community". A natural disaster can cause loss of life or damage property, and typically leaves some econ ...
, caused by humans, or the result of supernatural
Supernatural refers to phenomena or entities that are beyond the laws of nature. The term is derived from Medieval Latin , from Latin (above, beyond, or outside of) + (nature) Though the corollary term "nature", has had multiple meanings si ...
forces. It is among the earliest documented climatic events, present in the Epic of Gilgamesh and tied to the Biblical
The Bible (from Koine Greek , , 'the books') is a collection of religious texts or scriptures that are held to be sacred in Christianity, Judaism, Samaritanism, and many other religions. The Bible is an anthologya compilation of texts of a ...
story of Joseph's arrival in and the later Exodus
Exodus or the Exodus may refer to:
Religion
* Book of Exodus, second book of the Hebrew Torah and the Christian Bible
* The Exodus, the biblical story of the migration of the ancient Israelites from Egypt into Canaan
Historical events
* Ex ...
from ancient Egypt. Hunter-gatherer migrations in 9,500 BC Chile have been linked to the phenomenon, as has the exodus of early humans out of Africa and into the rest of the world around 135,000 years ago. Rituals exist to prevent or avert drought, rainmaking could go from dances to scapegoating to human sacrifices. Nowadays, those ancient practices are for the most part relegated to folklore and replaced by more rational water management.
Historical droughts include:
* 1540 Central Europe, said to be the “worst drought of the millennium” with eleven months without rain and temperatures of 5–7 °C above the average of the 20th century
* 1900 India killing between 250,000 and 3.25 million.
* 1921–22 Soviet Union in which over 5 million perished from starvation due to drought.
* 1928–30 Northwest China resulting in over 3 million deaths by famine.
* 1936 and 1941 Sichuan Province China resulting in 5 million and 2.5 million deaths respectively.
See also
References
External links
GIDMaPS
Global Integrated Drought Monitoring and Prediction System, University of California, Irvine
from FAO Water (Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations)
Global Real-Time Drought Media Monitoring
{{Authority control Meteorological phenomena Civil defense Climate variability and change Hydrology Water and the environment Weather hazards Articles containing video clips Natural disasters